lcd screen burn fix supplier

Screen burn-inhappens when you leave something displaying on your screen for an extended period of time. The screen retains the image and you see a “ghost” image of what used to be there. Screen burn can be hard to see at first, but usually is visible when a single color is on the screen.
A stuck pixel is usually a single bright color dot on the screen that has failed to change colors. Stuck pixels are generally most noticeable when the entire screen is black.
Sometimes nothing that can be done to fix these, outside of replacing the screen. But before seeking costly hardware repair, it’s best to try and fix it with software or videos. ScreenBurnFixerwas made just for this purpose! We’ve made many videos on YouTubewhich fit different screen sizes, and this site organizes them and helps you find the right video for your device.

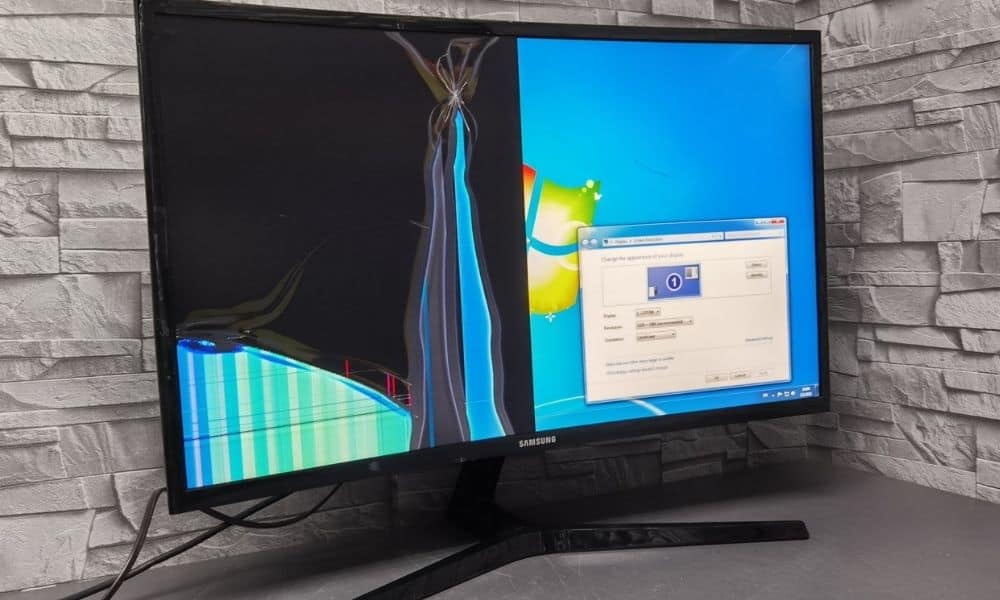
Have you ever left your TV or monitor on for days, stuck on the same image? You return to your screen, only to find an image burned into the display. No matter what you do, it won"t go away. It is a permanent image burn.
Why do monitors and TVs get image burn? Why can"t manufacturers prevent LCDs and plasma screens from a burnt image imprint? Moreover, what can you do to fix an image burn?
In some cases, you can minimize the image burn effect. In others, you can remove the image burn completely, so long as it hasn"t been burning too long.
Before flat-screens and crystal displays, most TVs and monitors featured CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) technology. In CRTs, individual pixels comprise a red, blue, and green phosphor component. Depending on the intensity of each phosphor component, the pixel appears to the human eye as a unique color.
When a particular still image remains for too long, the intensity of each phosphor component diminishes at an uneven rate. The result is a ghost image on the screen, which is known as image burning.
This is a very simplified version of how a plasma screen works. However, the main thing to understand is that plasma screens use phosphor material (like CRTs) to turn those photons into images.
LCD and LED do not work in the same way as CRTs, either. LCD and LED screens use backlit liquid crystals to display colors. Although manufacturers market screens using LED and LCD, an LED screen is still a type of LCD. The white backlight filters through the liquid crystals, which extract particular colors per pixel.
LCD and LED displays don"t suffer from the same type of image burn as CRTs and plasma screens. They"re not completely clear, though. LCD and LED screens suffer from image persistence. Read on to find out more about image persistence.
Before you can fix screen burn-in, take a second to understand why these images burn in the first place. LCDs and LEDs don"t suffer from burn-in as seriously as plasma screens. But static images can leave an imprint on both display types if left alone for too long. So, why does image burn happen?
First, let"s tackle plasma screen burn-in. Remember why CRTs experience image burn? When a still image remains on the screen for too long, the phosphor components in each pixel wear out at different rates. The uneven burn rates leave behind a ghost image, forever etched into the screen.
Plasma screens also suffer from phosphor deterioration. Plasma burning occurs when pixels on the screen are damaged through long exposure. The phosphor loses its intensity and only shows the light it was fed repeatedly. In this case, the still image, which causes the burn.
LCD and LED screens can also experience image burn, though the image burn process can take longer to develop into a permanent issue. In addition, LCD and LED screens suffer from another issue, known as image retention (also known as image persistence or an LCD shadow).
Image retention is a temporary issue that you are more likely to notice before it becomes a permanent issue. However, proper image burn can still affect LCD, LED, and OLED screens.
Image retention is a different issue from image burn (although it is a precursor to image burn). For example, you"re using an image of a steam train as a reference point for a drawing. You have the steam train image on your screen for a few hours before you decide to play a video game instead.
When you load up the video game on the screen, you can still see the faint outline of the steam train on the screen. The steam train image will remain for a short while, but the movement and color changes of the video game (or film, TV show, or other media type) should erase the retained image.
The other thing to consider is that LED and OLED image burn-in, when it happens, is irreversible. That"s because of how LED and OLED screens work. Individual pixels within an LED display decay when they emit light.
Under normal use, an LED, OLED, or QLED screen won"t suffer image burn. However, if you leave your screen on a single channel for hours every day, then burn-in can become an issue, as it would with almost any screen.
Issues arise when a screen shows a single news channel 24 hours a day, every day, causing channel logos to burn-in, along with the outline of the scrolling news ticker and so on. News channels are a well-known source of television burn-in, no matter the screen type.
Image burn-in fixes exist for LCD and plasma screens. How effective an image burn-in fix is depends on the screen damage. Depending on the length and severity of the image burn, some displays may have permanent damage.
The best fix for screen burn is to prevent it in the first place. Okay, that isn"t super useful if your screen is already experiencing image burn. However, you should always try not to leave your screen on a still image for too long. The time it takes for an image to burn-in varies from screen to screen, between manufacturers, sizes, and panel type.
Another prevention method is to reduce screen contrast as much as you can. Unfortunately, most screens aren"t calibrated correctly, often pushing the contrast and brightness settings too high.
Lower contrast means the lighting across your screen is more even. This means less strain on specific areas of the screen, which helps protect against image burning.
If your plasma or LCD screen already has image burn-in, you can try turning on white static for 12 to 24 hours. The constant moving of white-and-black across your screen in random patterns can help remove the ghost image from your screen.
Unfortunately, this won"t work for extreme cases. Some TVs will have a built-in pattern swiping option that basically accomplishes the same thing (filling your screen with random patterns).
Pixel-shift constantly slightly adjusts the image on your screen, which varies the pixel usage to counteract image burn. You might have to enable a pixel or screen shift option in your screen settings. Pixel-shift is a handy feature for LED and OLED screens that cannot recover from image burn and should help counteract an LCD shadow.
Other modern screens feature built-in screen refresh functions that the manufacturer will advise using to remove image retention and image burn issues.
The best tool for fixing ghost images is JScreenFix. The original program helps fix monitors with dead pixels, but the same company also released an "advanced" version of the tool, known as JScreenFix Deluxe.
While the Deluxe version uses advanced algorithms to repair burned screens and prolong plasma and LCD longevity, the official site is no longer up and running, and there is no way to download the full version officially.
Another option is to set a completely white desktop background and leaving to run for a few hours. The solid color might reset the image burn. A solid color background is more likely to help with image persistence than image burn, but it is still worth trying.
If you have television burn-in, you can attach a laptop to your TV using an HDMI cable, extend your desktop to the television, and share the white screensaver. Hopefully, that will shift your television burn-in.
The team over at ScreenBurnFixer offers a few different ways you can attempt to fix screen burn on your TV or monitor. As with any other screen burn-in fixes, their chance of working depends on the scale of the issue.
You can head to the ScreenBurnFixer Video page and find a video that matches your screen type, then let the video play for as long as possible (we"re talking multiple hours, not a quick half an hour blast). Alternatively, head to the Chart page and find your device or a device that matches your specifications.
There are several ways you can attempt to fix screen burn-in. The results will vary between the screen type and the level of burn-in. A screen with extensive image burn may not clear entirely, although you might see an improvement.
Some screen degradation over time is understandable. However, if you follow the steps in this guide, you"ll protect your screen from image burn before it becomes a permanent issue.

Screen burn-in isn’t as common on modern display technologies as it was in the past, but few screens are immune to its ability to ruin a perfectly good display. If you run into this irritating problem, here are some tips and tricks that might help fix it.
Screen burn-in is a noticeable discoloration or ghosting of a previous image on a digital display. It’s caused by the regular use of certain pixels more than others, leaving them to display colors slightly differently. The end result is a noticeable and often permanent impression on the display.
Time, screen brightness, and other factors can cause burn-in, but the circumstances are different for each display technology, as different screens and their pixels operate differently at the hardware level. For LCD panels, like those used in many TVs and computer monitors, burn-in can develop because pixels eventually become unable to return to their unlit state and retain a colored profile.
Colloquially “burn-in” is used as a catchall term for any kind of ghosted image on a screen. The most common form of such “burn-in” though, is technically known as image retention. While that might seem like a case of pedantic semantics, it’s an important distinction to make. Screen burn-in refers to permanent degradation of a display which is almost impossible to fix; image retention is typically fixable.
As described above, screen burn-in on a technical level is hard to fix. However, the much more common image retention is not. Here’s how to sort out your image retention problems on whatever device you have.
Enable Pixel-Shift. Many modern TVs have a built-in pixel-shift, or screen shift, which constantly moves the image slightly to vary pixel usage. If not enabled automatically, you should be able to turn it on in the settings menu. Other settings offer “Refresh” functions that can be manually run to try and clean out any image retention problems.
Use a White Screensaver. Try setting your screensaver to a pure white image and leaving it to run for a few hours. That may not remove image retention entirely, but it should dampen how noticeable it is.
Try JScreenFix. Some have also found success using JScreenFix. Although designed to fix stuck pixels rather than burn-in, it may help clear up any issues you’re experiencing.
Try a burn-in fixer. There are a number of great burn-in fixer apps on the Google Play Store and Apple App Store. Some, like OLED tools, will try to fix image retention and check for more permanent burn-in.
Replace the screen. If none of the above works, your best bet is to either replace the screen yourself or talk to your mobile carrier about a replacement device. Manufacturers like Apple have extended the warranties on certain devices that are prone to image retention and burn-in, so if your device is fairly new, you should still be covered by the warranty.
To prevent screen burn-in on a TV, reduce the brightness to the 45-50 range, use the sleep timer and screen savers, and turn the TV off when not in use. If you have an OLED TV, turn on pixel shift and play a color-changing video that"s designed to help lower the risk of burn-in.
On Androids and iPhones, reduce the brightness to 50 percent or lower, use a screen-timeout length of about 30 seconds, and turn off your phone when not in use. You can also operate in dark mode, use swipes and taps instead of button navigation, and download a screen-burn fixer app.
On a smartphone, screen burn presents as a discolored display with pink or gray tones. On monitors and TVs, it looks like a "ghosting" of previous images remaining on the screen. Screen burn happens so gradually that you may not notice it until using a white background.
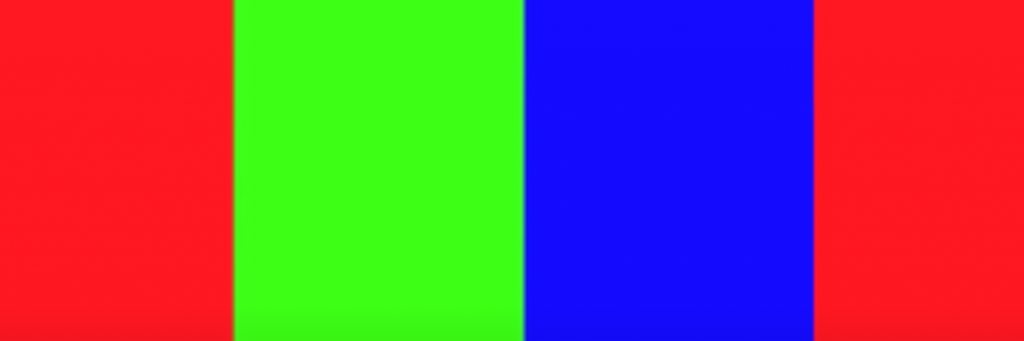
Image burn-in, also referenced as screen burn-in or ghost image, is a permanent discoloration of sections on an electronic display caused by increasing, non-uniform use of the screen.
The term burn-in dates back to when old monitors using phosphor compounds that emit light to produce images lost their luminance due to severe usage in specific display areas.
Chances are you"ve encountered image burn-in and image retention before, but you didn"t know which one you were seeing. They both have the same visual effects, so it"s easy to mistake them for each other, but there"s one key difference:
Most of the time, these guides explain how image retention works and how you can speed up its recovery process. We want to clear up any confusion you might have about image burn-in and image retention on LCD and OLED displays.
Image retention, also known as ghosting or image persistence, is the temporary effect of images remaining visible on LCDs or OLEDs for a short period, usually a few seconds.
If the images fade away after a short time, you are dealing with temporary image retention. If the images stay permanently, you are dealing with image burn-in.
Image retention doesn"t require any intervention from the user to make it go away – it"ll do that by itself. Retention will often occur before burn-in does on newer display technology like our
using a screen saver, cycling various graphics on the screen to exercise the pixels, and powering off the display whenever possible will help clear the image retention on your display.
These are the same tricks you"ll see advertised as a "cure" for image burn-in, but don"t be fooled. There"s no fix for burn-in, only ways to prolong it from happening.
Before you assume your screen has burn-in damage, try these tips and wait to see if it"s just image retention. Image retention is a harmless and common occurrence on many screens.
Image burn-in is caused by screen pixels that stay activated in a static position for long periods of time.Think of a TV in a lobby or waiting area that"s always playing the same news channel. The news channel footer and logo get burned into the screen permanently, even when you change the channel.
When LCD or OLED pixels stay activated in a static position, they"ll eventually become "stuck" in that position. When this happens, you"ll notice a faded, stubborn image that persists on the screen.
When pixels fail to activate or deactivate entirely, it results in faded images that won"t clear from the screen. This is common in applications using character LCDs where the alphanumeric characters are updated less frequently.
Remember: There"s no way to remove or reduce burn-in after it occurs. If a stubborn image persists for extended periods or after restarting your display, you"re likely dealing with image burn-in.
Even the most advanced displays will experience burn-in at some point, but there are some simple actions you can take to extend your screen"s lifespan before burn-in occurs. With the proper practices, you can get years of outstanding performance from your display without any burn-in effects.
A screensaver is a good alternative if you can"t turn your display off. For displays that don"t need to be ON at all times, it"s helpful to let the screen rest when not in use.
Get those pixels moving! The longer a pixel stays activated in a static position, the closer it gets to being burned in. You can exercise your screen"s pixels with scrolling text, moving images, or changing colors.
For an OLED display, decreasing the contrast will lower the brightness and reduce the rate of image burn. More illumination (brightness) requires more current, which reduces OLED pixel lifespans.
For a LCD display, lowering the contrast will put less stress on the liquid crystals and will help to reduce the rate of pixels becoming weak, or sticking.
Remember that image burn-in is not reversible and can not be fixed once it happens. Whether it is a scrolling effect, rotating pixels, using a screensaver, or turning off the screen when not in use, it"s essential to establish image burn-in preventive measures to help extend the lifespan of your display.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/screenburnin01-5bdc37e9c9e77c00269c4545.jpg)
The display is a major factor that affects our decision to purchase a particular smartphone. The difficult part is choosing between AMOLED (or OLED) and LCD. Although in recent times most of the flagship brands have made the shift to AMOLED, it does not mean that it is flawless. One point of concern with AMOLED display is that of screen burn-in or ghost images. AMOLED displays are much more likely to face the problem of screen burn-in, image retention, or ghost images when compared to LCD. Thus, in the debate between LCD and AMOLED, the latter has a clear disadvantage in this field.
Now, you may not have experienced screen burn-in first hand, but a lot of Android users have. Instead of being puzzled and confused by this new term and before allowing it to affect your final decision, it is better if you get to know the complete story. In this article we are going to discuss what screen burn-in actually is and whether or not you can fix it. So, without any further ado let’s get started.
Screen burn-in is the condition where the display suffers from permanent discoloration due to irregular pixel usage. It is also known as a ghost image as in this condition a blurred image lingers on the screen and overlaps with the present item being displayed. When a static image is used on a screen for a long time then the pixels struggle to switch to a new image. Some pixels still emit the same color and thus a faint outline of the previous image can be seen. It is similar to a human leg feeling dead and unable to move after a prolonged period of sitting down. This phenomenon is also known as image retention and is a common problem in OLED or AMOLED screens. To better understand this phenomenon, we need to know what causes it.
A smartphone’s display is made up of numerous pixels. These pixels illuminate to form a part of the picture. Now the various colors that you see are formed by mixing colors from three subpixels of green, red, and blue. Any color that you see on your screen is produced by a combination of these three subpixels. Now, these subpixels decay over time, and each sub-pixel has a different life span. Red is most durable followed by green and then blue which is the weakest. Burn-in occurs due to the weakening of the blue sub-pixel.
Apart from that pixels that are more extensively used take for example the ones responsible to create the navigation panel or navigation buttons decay faster. When a burn-in starts it usually starts from the navigation region of the screen. These worn-out pixels aren’t able to produce colors of an image as good as others. They are still stuck on the previous image and this leaves behind a trace of the image on the screen. Areas of the screen that are usually stuck with a static image for a long time tend to wear out as the sub-pixels are in a state of constant illumination and do not get an opportunity to change or switch off. These areas are no longer as responsive as others. The worn-out pixels are also responsible for variation in color reproduction among different parts of the screen.
As mentioned earlier, the blue light subpixels wear out faster than red and green. This is because in order to produce light of a particular intensity, blue light needs to glow brighter than red or green and this requires extra power. Due to the continuous intake of excess power, blue lights wear out faster. Over the course of time OLED display begins to acquire a reddish or greenish tint. This is another aspect of burn-in.
The problem of burn-in has been acknowledged by all smartphone manufacturers that use OLED or AMOLED display. They know that the problem is caused because of the faster decay of the blue sub-pixel. They have thus tried various innovative solutions to avoid this problem. Samsung for example started using pentile subpixel arrangement in all their AMOLED display phones. In this arrangement, the blue sub-pixel is made bigger in size as compared to red and green. This means that it would be able to produce higher intensity with less power. This in turn will increase the life span of blue sub-pixel. High-end phones also use better-quality long-lasting LEDs that ensure that burn-in does not occur any time soon.
Apart from that, there are in-built software features that prevent burn-in. Android Wear products come with a “burn protection” option that can be enabled to prevent burn-in. This system shifts the image displayed on the screen by a few pixels from time to time to make sure there isn’t too much pressure on any one particular pixel. Smartphones that come with Always-on feature also use the same technique to increase the life-span of the device. There are also certain preventive measures that you can take on your end to avoid screen burn-in from happening. We are going to discuss this in the next section.
Screen Burn-in takes place in stages. It starts with a few pixels here and there and then gradually more and more areas of the screen get damaged. It is nearly impossible to detect burn-in in the early stages unless you are viewing a solid color on the screen with maximum brightness. The easiest way to detect screen burn-in is by using a simple screen-testing app.
One of the best apps available on Google Play Store is Screen Test by Hajime Namura. Once you download and install the app you can start the test right away. Your screen will be completely filled with a solid color that changes when you touch the screen. There are also a couple of patterns and gradients in the mix. These screens allow you to check if there is any lingering effect when the color changes or if there is any section of the screen that is less bright than the rest. Color variations, dead pixels, botched screen are some of the other things to look out for while the test is taking place. If you do not notice any of these things then your device does not have burn-in. However, if it does show signs of burn-in then there are certain fixes that can help you prevent further damage.
Although there are multiple apps that claim to reverse the effects of screen burn-in, they rarely work. Some of them even burn the rest of the pixels to create a balance, but that is not good at all. This is because screen burn-in is permanent damage and there isn’t a lot that you can do. If certain pixels are damaged then they can’t be repaired. However, there are certain preventive measures that you can take to prevent further damage and restrict screen burn-in from claiming more sections of the screen. Given below is a list of measures that you can take to increase the life-span of your display.
It is simple math that higher the brightness, the higher is the energy supplied to the pixels. Lowering your device’s brightness will reduce energy flow to the pixels and prevent them from wearing out soon. You can also decrease the screen timeout so that the phone’s screen turns off when not in use saving not only power but also boosting the longevity of pixels.
One of the regions where burn-in occurs first is the navigation panel or region allocated for navigation buttons. This is because the pixels in that region constantly display the same thing. The only way to avoid screen burn-in is to get rid of the persistent navigation panel. This is possible only in Immersive mode or Full-screen display. As the name suggests, in this mode the entire screen is occupied by whichever app is currently running and the navigation panel is hidden. You need to swipe up from the bottom to access the navigation panel. Enabling a Full-screen display for apps allows the pixels in the top and bottom regions to experience change as some other color replaces the fixed static image of the navigation buttons.
If your device does not have the setting in-built, then you can use a third-party app to enable a full-screen display. Download and install GMD Immersive. It is a free app and will allow you to remove the navigation and notification panels when using an app.
The color black is the least harmful to your display. It requires minimum illumination and thus increases the lifespan of the pixels of an AMOLED screen. Using a black screen as your wallpaper greatly reduces the chances of burn-in on AMOLED or LCD display. Check your wallpaper gallery, if the solid color black is available as an option then set it as your wallpaper. If you are using Android 8.0 or higher then you will probably be able to do this.
However, if that is not possible, then you can simply download an image of a black screen and set it as your wallpaper. You can also download a third-party app called Colors developed by Tim Clark that allows you to set solid colors as your wallpaper. It is a free app and extremely simple to use. Simply select the black color from the list of colors and set it as your wallpaper.
Download and install the free app called Minima Icon Pack that allows you to convert your icons to dark and minimalistic ones which are ideal for AMOLED screens. These icons are smaller in size and have a darker theme. This means that a smaller number of pixels are now being used and this reduces the chances of screen burn-in. The app is compatible with most Android launchers so feel free to give it a try.
A lot of apps on the Play Store claim to be able to reverse the effects of screen burn-in. They are supposedly capable of fixing the damage that is already done. Although we did state the fact most of these apps are useless there are a few that might be of some help. You can download an app called OLED Tools from the Play Store. This app has a dedicated tool called Burn-in reduce that you can use. It re-trains the pixels on your screen to try and restore the balance. The process includes cycling the pixels on your screen through different primary colors at peak brightness to reset them. Sometimes doing so actually fixes the error.
For iOS devices, you can download Dr.OLED X. It pretty much does the same thing as its Android counterpart. However, if you do not wish to download any app then you can also visit the official site of ScreenBurnFixer and use the colored slides and checkered pattern provided on the site to re-train your pixels.
As mentioned above it is unlikely that screen burn-in will take place on an LCD screen but it is not impossible. Also, if a screen burn-in does happen on an LCD screen then the damage is mostly permanent. However, there is an app called LCD Burn-in Wiper that you can download and install on your device. The app only works for devices having an LCD screen. It cycles the LCD pixels through various colors at different intensities to reset the effect of burn-in. If it does not work then you need to visit a service center and consider changing the LCD display panel.
I hope the above tutorial was helpful and you were able to fix screen burn-in on the AMOLED or LCD display of your Android phone. But if you still have any queries then feel free to ask them in the comment section.
Screen burn, a term derived from old CRT (cathode-ray tube) technology — and the reason for a vast industry of decorative screen savers — describes the phenomenon of image retention, otherwise known as persistence, ghost images, blurred images, artifacts, or after-images that linger on your smartphone screen after the original image is long gone. These can mar screen readability and coloration over time and can diminish your smartphone experience.
On mobile devices, screen burn is identified most often on AMOLED or OLED screens, and even then, it’s pretty rare on newer smartphones. It happens when users leave an image on their screen for too long, causing the pixels to struggle when switching to a different color. This may happen more easily with blue colors, but can occur with any image that’s left on screen too long, especially in the brightest setting. Screen burn also may be permanent and considered a display hardware defect as opposed to a software graphics or display driver issue. For screen burn on your mobile devices, there are a few things you can do to fix the issue and, even better, prevent it from happening. Here are a few simple steps you can take.
This is the simplest solution and is frequently effective, especially when you catch image retention early on and want to fix it fast. Turn your phone off entirely, powering it down fully, and let it rest for a couple of hours. If the screen burn issue is minor, this gives the pixels enough time to recover, diminishing after-images, so your phone screen will look fresh when you power back on. This is one advantage of the versatile organic pixel layer used in OLED-based screens, which can correct itself more easily than pixels of the past.
If turning your mobile device off for a while doesn’t fully resolve your issue, a good next option to try is re-training the pixels on your screen to get them back into balance. The good news is, there are apps for that. For Android devices, the Google Play Store has a robustcollection of screen correctors and testersincludingOLED Saver. If you have an iOS device, then you can use an app likeDoctor OLED X instead. This app cycles your pixels through multiple colors and brightness levels, working towards resetting them.
If you don’t want to download an app, you can try checking out theScreenBurnFixerwebsite. It features a collection of videos with color slides and checkered patterns designed to help get your pixels back on track. Run a few of these and see if they fix your pixel problem.
You can be proactive about avoiding or mitigating screen burns on your mobile hardware by modifying various settings you might not have realized could help you. Make sure you are following guidelines like these:
Lower brightness settings:The higher the brightness setting, the harder your OLED pixels have to work, which can cause screen burn. If your mobile device is permanently set on a higher brightness, switch it to auto-brightness or a lower brightness level to prevent problems. For iOS 14, go toSettings > Display & Brightnessand toggle on theAutomaticsetting. TheOptions, True Tone,andNight Shiftsettings also help to modulate excessive brightness and prevent burn-in. On Android, go toSettings > Display > Brightness slideror toggle onAutoto automatically adjust brightness.
Set lock screen and sleep timers:Smartphones come equipped with automatic timers for locking and going into sleep mode, both of which turn off the screen after it hasn’t been used in a while. Make sure these settings are turned on and set to a minute or so. If you haven’t looked at your phone in one minute, it’s probably fine for it to shut off the screen and lock. This essentially prevents image retention because the screen won’t stay on long enough for it to happen. For iOS 14, go toSettings > Display & Brightness >Auto-Lockand choose which time interval you want. On Android 10, go toSettings > Display > Screen timeoutand choose the interval you want.
Get rid of menu, status, and navigation bars:Image retention can happen when you are actively using an app that has a permanent bar for tools or notifications, like when you’re playing a game or watching a movie, for example. When these bars don’t disappear, they cause screen burn after long sessions. Look for options to hide these icons and tools after a moment so they aren’t always present. Immersive modes for your mobile OS will also do this.
Screen burn can also become a problem on LCD mobile screens. While this may be a rare occurrence, it’s not impossible either. When it does, fixing it is a lot more of a challenge, since LCD pixels work differently from OLED screens. Therefore, you might have to accept that screen burns on your LCD screen are most likely there to stay. But before you give upall hope, you should still tryusing LCD Burn-In Wiper, whichcycles colors similar to its OLED counterpart to try to repair pixels.
Your last resort after failing to rectify screen burns with the previously mentioned methods would be to see if your device is under warranty so that you can switch out your screen or have it repaired by a professional.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Emerson-McDonalds_CNN_Burn-In-5692ad0d3df78cafda81df58-5c619daec9e77c0001d92fc1.jpg)
LCD and OLED monitors are most vulnerable to screen burn when new, so you may want to avoid leaving the same image up for too long during the first 100 hours of use
Image retention on a phone display or computer monitor is mostly an issue for devices that display static content or are used for video gameplay with a heads-up display. Unlike with old CRT devices where the phosphor compounds would degrade over time, the “permanent” stationary object or remnant of a picture on an LCD monitor is usually a form of transient image persistence. Here’s how you can fix it and get your high-performing computer monitor back up and running.
Alternatively, if you’re trying to get your second monitor working, check out our resource article about how to fix a second monitor not detected error.
While screen burn and image retention are often used interchangeably they’re not quite the same thing. Image retention is a temporary “ghost image” that you can usually get rid of, while “screen burn” means some of the screen’s pixels are “burned out” and it is more difficult to fix, typically requiring hardware repairs, as it’s a more complicated monitor display problem to repair. Obviously it’s not the most convenient problem to have, especially if it’s happening on your best 32-inch gaming monitor, but there are ways to test it, mitigate it, and potentially resolve it
OLED screens are the favored choice for new smartphones and high-resolution TVs, but this type of screen is more susceptible to image retention than LCD screens. Irregular pixel usage can cause noticeable discoloration over a long period of time, typically of static elements like navigation buttons or news station logos. That said, screen burn-in is preventable and for most users should not deter the purchase of a new OLED monitor.
The reason for OLED screens’ being more vulnerable to screen burn-in has to do with the different lifespans and energy demands of different colored pixels. Blue pixels use more energy and tend to wear out faster, which contributes to the ghosting effect of burned-in images. Still, ghost images are generally only an issue for use cases involving static image elements displayed at full brightness for a long time. Also, double-check your warranty and/or computer insurance if you can get professional help for fixing image retention. You might even have coverage through your property insurance, and we have guides on explaining if, for example, your homeowners insurance can cover a computer.
If you’re not sure whether you have screen burn on your device, you can run a screen burn test. Several apps for Android and iOS devices help test for screen burn. Typically this involves displaying one primary color at a time at varying brightness on the device’s LCD screen.
These tips should help get rid of ghost images caused by image retention on modern LCD screens and OLED devices like smartphones, tablets, TVs, and laptops. Image persistence on LCD displays is generally more fixable than “burn-in” on a CRT monitor or AMOLED screen.
Sometimes you can fix a seemingly permanent ghost-like image on an LCD by turning the device off and then turning it back on again after several hours. Try colorful video content or fast-paced videos, or any varied content.
Setting the display brightness to a lower level or enabling auto-brightness if so equipped may reduce the appearance of screen burn or image retention.
Depending on the display technology, you can sometimes fix stuck pixels on a monitor by changing display & brightness settings, choosing dynamic screensavers or adjusting preset picture displays, and turning on auto-brightness. Some software fixes are also available. These typically involve displaying one solid color at a time, which may help get rid of image retention. You may also want to check for “dirty screen effect” and make appropriate adjustments.
On some devices, you can download apps that aim to fix image retention and help reduce the risk of burn-in. To address image persistence on an Android Phone, you can find apps on the Google Play Store that adjust display timeout, play dynamic, all black or moving screensaver images, and even test for burn-in using a white image.
Likewise, for an iPhone, you can visit the App Store for apps that help check your phone for burn-in problems and protect your phone from developing annoying image burn.
On most smart TVs there are some settings you can utilize to reduce the appearance of image retention. LG offers an option called Screen Shift for its OLED TV models, similar to Sony’s Pixel Shift technology, which shifts the image very slightly so as to minimize wear on individual pixels.
In extreme cases where you have dead blocks of pixels or significant degradation of image quality, you may want to opt for display device replacement to remedy screen burn.
There are some easy techniques you can use to help prevent screen burn-in from happening in the first place. The following tips should work on most OLED and LCD screen devices including Android smartphones and tablets, iOS devices, and laptop computers.
Manufacturers recommend keeping brightness at 50% or lower on screens that will be used to display a non-moving picture for more than a few hours at a time.

If you are looking for a screen burn-in fix for your smartphone, let us inform you at the outset that severe cases of screen burn-in are difficult to fix, and the solution almost always involves replacing the display.
Screen replacements, however, are an expensive proposition—especially if your phone is out of warranty. And in cases where the screen burn-in issue isn"t that prominent, it is best that you look for other fixes. And that is what this article aims to explore.
At the outset, it is important to know what this problem actually is. A screen burn-in is the phenomenon observed on displays where a part of the display suffers from permanent discoloration—often caused by prolonged use of a static image. It is also important to note that OLED displays are much more susceptible to screen burn-in than their LCD counterparts. In fact, what people think of as screen burn-in on an LCD panel might usually another issue.
Also important to note is the fact that screen burn-in is a hardware issue and affects OLED-based panels across a wide spectrum of products. For the same reason, any product that uses an AMOLED panel—ranging from Apple iPhones to Samsung Galaxy devices and OLED TVs could be prospective victims.
In a desperate attempt to find a fix for the screen burn-in problem on your phone, you search on Google, and it turns out there are several apps that claim to address the problem. But how effective are these apps, really?
First things first, you need to know that a screen-burn-in is a hardware problem. Attempting to fix it using software is almost always an exercise in futility. It is no surprise, therefore, that the reviews of most of these apps are mixed. But then what exactly do these apps do? And what about users who claim that their issue was fixed after they installed and used the app?
For LCD screens, there"s a dedicated app, LCD Burn-in Wiper that could possibly fix minor cases. However, this tool is not suitable for OLED or AMOLED displays, such as those found on most modern flagship smartphones. For that, you"ll need a different app.
For Android smartphones with OLED/AMOLED screens, it is a good idea to try an app called Ghost Screen Fix - Burn-In. iPhone" users can try out an app called Doctor OLED X from the App Store for $0.99.
In most of these apps, the "fix" is to display a sequence of primary colors in an attempt to restore the "burnt" pixels. Interestingly, this was the original function of computer screen-savers: one dynamic image that appears when the screen is idle to make the pixels "exercise" and ensure that the same area of the display doesn’t remain constantly illuminated.
A workaround that has been suggested by one of our users involves an app called "Negative Image" from the Google Play Store. This is what NextPit user Chai Bula did to fix the screen burn-in issue on his smartphone.Take a screenshot of your screen when the screen burn-in issue is the most visible.
Open the negative image, which matches pixel to pixel with the original screenshot, and for the same reason, it will precisely overlay the affected pixels.
As already mentioned in the introduction, screen burn-in is an issue with the actual hardware. As such, a proper fix to the problem usually involves replacing the display. However, do note that modern displays are much more resistant to screen burn-in compared to their older counterparts, and the devices they are attached to also boast of several screen burn-in protection mechanisms.
For the same reason, chances are high you will rarely see a screen burn-in issue on newer devices that are so severe, a screen replacement becomes necessary.
Even so, in the rare instance the problem is awful, the best bet is to contact your manufacturer directly. If your smartphone is under warranty, they will offer you a fix. Bear in mind, however, that an out-of-warranty screen replacement might be quite an expensive affair. In fact, in some cases, it is cheaper to simply buy a new phone instead.
As you might have understood by now, screen burn-in can be an annoying problem. That being said, there are quite a few simple steps you can take so that your smartphone never encounters this issue at all. Note that the steps below are applicable for both Android smartphones and iPhones.Keep the brightness levels of your phone display to low or moderate. Never keep it at full brightness for extended periods of time.
If you still use on-screen navigation buttons, it is a good idea to learn to use gesture-based navigation. By doing this, you prevent the screen from displaying the permanent on-screen navigation keys.
If you are not a huge wallpaper buff, the best solution is to use a black screen as your wallpaper. On AMOLED displays, this effectively turns the pixels off – and therefore, no fear of burn-in!
Screen burn, also called screen burn-in, ghost image, or display burns are images or icons that are displayed on a screen when they should not be there. Screen burn comes on gradually and gets worse over time and is most common on OLED screens. The navigation bar, the top status bar, or home screen apps are frequent images that get “burned” into the display.
1. You aren’t looking at your phone screen with a white display. Screen burn is easiest to notice on an all-white or blank screen with no icons on it. And it is rare that your phone will display an all-white screen. This is why SmartphonesPLUS uses industry-leading phone diagnosis software and other tools that allow us to see phone screens on an all-white screen, along with other tests, to examine each phone we receive thoroughly.
2. You do not change your home screen layout or background image. You look at the same phone, with the same background every day, and can’t notice the screen burn because the icons and apps on the phone are always in the same position. It is much easier to notice screen burn when you shift the layout of icons and apps on your home screen.
Here’s an example we think relates to screen burn to help explain why it’s not as noticeable: when you see a person every day that is losing weight you don’t notice how much weight they lost, but if you saw a person you haven’t seen in over a year that lost 50 pounds you would notice right away. In the same way, your eyes and mind adjust to the screen burn as it gradually burns into the display over months or years.
Screen burn is caused by pixels displaying the same image or icon for an extended period of time. Static images such as apps, navigation bars, and keyboards can deteriorate pixels in the display from overuse. This causes these over-used pixels to look darker in color than others around them. Certain areas of the screen like status bars are more susceptible to screen burn as they are constantly displaying the same image.
As you can tell from the photos, screen burn can make the display look discolored with darker pink or gray hues. Because of its gradual onset, many users don’t even realize their display has screen burn. If you would like to check for screen burn on your phone, put your phone on a white screen. A white screen will provide contrast making the discolored pixels more noticeable.
Lowering the brightness will lengthen the life of the pixels in your display. Keeping the brightness as low as possible will ensure that screen burn won’t happen as quickly.
Avoid screen savers when your screen times out as they are generally static images that are displayed for a long period of time. Screen savers will cause the pixels of your display to be overworked when you are not even using your device. If you have a phone that uses always on display, make sure to turn this off to prolong the life of your screen’s pixels.
There are some apps and videos out there that claim they can fix screen burn, however, the results tend to be insignificant as it is a hardware issue of the display. The only way to truly fix screen burn is to replace the entire display of the phone. If you’d like to speak with a technician to see the cost of replacing a screen you can make an appointment or contact us.

But these devices do have one drawback: OLED burn-in, sometimes called OLED screen burn. That"s what happens when the outline of an image stays on the screen, leading to discoloration. Fortunately, there are some quick and easy ways to fix it, or at least reduce its effects.
At Asurion, our experts help millions of customers get the most out of their tech, diagnose device problems, and resolve them every day. Here they"ll break down what screen burn is and tell you how to prevent or correct it.
Burn-in is the appearance of a “ghost image" on your TV or phone that won"t go away. It"s caused by the display"s technology. Each individual pixel produces its own light, which gradually dims over time. If an image remains on the screen for many hours, certain pixels get overused and degrade faster, creating discoloration in particular areas. Your screen will still function, but the dark spots can be distracting or annoying.
Some common causes of TV screen burn-in include:Keeping your TV on news or sports network channels that display a static logo or a ticker for a long time - parts of the logo or ticker may burn in
While screen burn-in and image retention appear similar at first, they"re actually very different. Screen burn-in is permanent and will remain whether you change the channel, scroll to a different menu, or turn off your device. With image retention, the discoloration is temporary and will eventually disappear once you switch to a different image or power off.
QLED® TVs use a different technology than OLED TVs and are unlikely to experience burn-in. Samsung® will repair or replace its QLED models if they experience this issue within the first 10 years.
Think your television or smartphone may have burn-in? You can easily check by running a burn-in test, which will play a video that helps you spot discoloration in your screen.
Samsung has a TV burn-in test video on YouTube™ that will work with any brand of TV or phone. It displays a solid red screen; if you notice any other colors, you may have burn-in. There are also videos that cycle through a range of colors to help diagnose the problem.
Tips to prevent OLED screen burn on TV:Reduce the brightness. Keeping your brightness level in the 45–50 range will lower the stress on your TV"s pixels and help prolong their life.
Use the sleep timer. If you doze off in front of the TV, a channel logo or streaming menu could be on your screen for hours, creating a risk for burn-in. This feature will turn off your TV after a set amount of time.
Change the channel periodically. If you"re an avid sports watcher or news viewer, the ticker at the bottom of the screen may cause burn-in without you realizing it. Switching the channel will give those pixels a rest.
Enable screen savers for gaming and streaming devices. If pausing is something you can"t avoid, turning on screen savers will keep the colors on your TV changing and help prevent burn-in.
Burn-in is permanent on your television, but there are a few ways you can try to improve it.Adjust the brightness. Lowering your brightness setting to below 50 could reduce any burn-in. This should also cause any image retention to disappear.
Enable pixel shift. OLED TVs from brands like LG® and Sony® include pixel-shift technology that automatically moves images on the screen to protect pixels from overuse. You can manually turn this on in your settings.
Replace your TV. Unlike phones, you can"t just swap in a new screen on your television. But before buying a new one, check your manufacturer"s warranty to see if it covers burn-in.
If your smartphone has an OLED screen—like the iPhone® 12, Samsung Galaxy® S21, or Google Pixel™ 5—it"s at risk of developing burn-in. However, there are simple steps you can take to protect your device.
Tips to prevent Android and iPhone screen burn-in:Lower the brightness. The brighter your display, the faster the pixels will decay. Go into your settings and reduce the brightness to 50% or lower.
Enable immersive mode on Android™. Turning this on will hide the status and navigation bars, which often cause screen burn-in. Some apps default to this mode, but you may need to configure it for others.
Unfortunately, there"s no such thing as a quick screen burn fix. OLED phone screen burn-in is permanent, but there are a few steps you can try to reduce it.
Ways to reduce Android and iPhone screen burn:Power it off. Leaving your phone off for a few hours could help lessen the impact of burn-in. If your issue goes away completely, you probably just had image retention.
Download a fixer app. These test to see if your phone has burn-in. They"ll then run a pixel refresh or adjust your settings so the discoloration isn"t as visible.
Replace the screen. If nothing has worked to reduce burn-in, you may need to purchase a new screen. But first, check your device"s warranty to see if screen replacement is covered.
From sudden breaks to software bugs, Asurion has all of your devices covered. Schedule a repair at the nearest uBreakiFix® by Asurion or Asurion Tech Repair & Solutions™ store and our certified experts can get your devices back up and running as soon as the same day.

I just replaced the Burnt-in OLED screen on this iPhone X with a brand new LCD display. All seemed fine until today, I pick the phone up and it"s showing the same Burn-in pattern from before. Did I receive a used display under the guise of new or is something deeper the issue? This LCD was obtained from iFixit

If you spend long enough debating the merits of LCD vs. OLED display technologies, eventually, someone will touch upon the subject of the dreaded OLED screen burn in. The point made is that OLED displays will inevitably suffer from horrible-looking artifacts over time, while LCD and new technologies like Mini-LED won’t. But like most of these debates, you’ll probably hear as many overblown anecdotes as you will actual facts about the issue.
You may never have experienced it for yourself, but many consumers are wary about the possibility of burn in when pondering their next smartphone purchase. Particularly as expensive flagship smartphones have universally adopted OLED display technology. Apple, Google, and other manufacturers acknowledge that burn in can be a problem in rare cases. OLED technology has made its way to much more affordable price points in recent years, putting the issue on the radar for even more consumers.
The word “burn in” is a little misleading, as no actual burning or heat problems are involved. Instead, this term describes a display suffering from permanent discoloration across any part of the panel. This may take the form of a text or image outline, fading of colors, or other noticeable patches and patterns on display. The display still works as expected, but a somewhat noticeable ghost image or discoloration persists when the screen is on. To be considered screen burn in, these artifacts have to be permanent and are a defect caused on the display hardware side. Rather than a graphical glitch that may be caused by software, temporary image retention, or a problem with the display driver circuitry.
The term dates back to old CRT monitors, where phosphor compounds that emit light to produce images lost their luminance with time. LCD panels can exhibit similar problems, but these are much rarer due to the nature of LCD’s backlight and color matrix design.
Although not as bad or noticeable as old CRT issues, today’s OLED smartphone displays can eventually suffer from a similar problem. That being said, it’s pretty difficult and rare to notice unless you know what you’re looking for, and it takes hundreds, if not thousands, of hours of screen-on time before any such errors appear. In smartphones, pattern burn in is typically associated with always-on displays, navigation buttons, and the notification bar. The example below demonstrates a textbook case:
Although most smartphones now support gesture navigation controls in the place of the old button design. So this type of burn-in is much less of a problem than it used to be.
The cause of all screen burn in is the varying lifecycle of a display’s light-producing components. As these parts age, their brightness changes, and therefore the panel’s color reproduction gradually shifts with time. Although this can be mitigated somewhat with clever software, all displays experience some color shift as they age. But with burn in, some parts of the screen age faster than others. This can gradually shift the perceivable colors of the screen in one area more than in another, leaving what looks like a ghost image behind.
With modern smartphone and smartwatch technology, screen burn in can manifest due to the different life spans between the red, green, and blue LED subpixels used in OLED panels. As we mentioned before, areas of the display that seldom change, are bright white, or are often black and switched off, such as navigation buttons or the notification bar, are the most likely areas to notice this issue. You may also notice the effect in darkened status bars designed to hide display notches.
So, if one part of the panel spends a lot of time displaying a blue or white image, the blue pixels in this area will degrade faster than in other areas. That’s essentially what burn in is. However, display manufacturers do account for this in their panel designs.
If OLED screens have a problem with burn in, why do we continue using them? Burn in is a true downside to OLED displays, but there are plenty of reasons consumers and manufacturers like them. For starters, image quality is much better than in LCDs. OLED panels can reproduce more vibrant colors, more contrast, wider viewing angles, and faster refresh rates. Colors tend to be much more saturated, and blacks are much darker.
Additionally, burn in problems are only common after prolonged periods of use. As you may already know, smartphone manufacturers don’t expect you to keep a smartphone for more than 2-3 years. Recent statistics show that consumers currently keep their phones for an average of 2.75 years.
At this stage, manufacturers are very aware of the potential issues and have already taken some intelligent steps to help avoid burn in. For starters, Samsung has been using its pentile subpixel arrangement in its AMOLED displays since the Galaxy S3. By making the blue subpixel larger, it requires less current to drive in order to provide the necessary light. Driving the LED with less current increases its lifespan, so it takes longer for any noticeable color shift to occur.
This doesn’t directly address the issue of different parts of the screen aging at different rates, but it does mean that it will take significantly longer to notice than with older or cheaper OLED panels. More expensive and modern OLED panels are built with longer-lasting LEDs and well-designed layouts, meaning flagship smartphone displays age slower. These days, it’s cheaper phones packing cheaper displays that are marginally more likely to see issues after heavy use.
There are software solutions too. Android Wear product manufacturers can enable the OS’s “burn protection” option. This mode periodically shifts the screen’s contents by a few pixels, so they spend equal time displaying different colors. Smartphones equipped with Always-On display technology employ a similar tactic. Google also suggests a selection of design guidelines tailored to avoid screen burn-in problems when designing OLED watches. The move towards gesture rather than on-screen navigation controls is also helping to alleviate one of the more noticeable burn in areas.
If your screen is already burnt in, there’s not much that can be done to undo the damage. Some apps on the Play Store claim to reverse the problem. These will end up “burning” the rest of the screen to match the colors, which isn’t a real solution.
Try to make it so that the screen isn’t displaying the same thing all the time, in the same areas of the screen. For example, if you have a widget that almost always looks the same, chances are it will eventually burn into the image. Move things around now and then, and try to keep the view of your phone dynamic.
All that said, screen burn in isn’t something that should concern many users if they’re looking to buy a new OLED smartphone. Modern panels have much longer lifespans than early OLED smartphones, and even then, burn in was rare. Just don’t leave a static image on the screen 24/7 with the brightness set at max.
The bottom line is that you should be looking at several years’ worth of use out of a modern smartphone display before any screen burn in will be noticeable. But it doesn’t hurt to be aware of what can happen to aging handsets and how to maximize their lifespan.

Manufacturers of plasma and LCD flat panel televisions are continuously introducing technology to help reduce the likelihood of this problem, but there are simple steps you can take to help reduce the chances of experiencing image "burn-in.
For new plasma TVs in particular, be wary of leaving images on the screen for long periods. When phosphors are fresh, they burn more intensely as they are ignited. This means that relatively new plasma TVs are prone to "ghosting", which occurs when on-screen images appear on the screen for an extended time.
If you are using your TV to display a video game from a computer, make sure to utilize screen saver features or power management settings that can change or turn off the display after a period of time.
"Stuck" images can be removed by "exercising" the LCD pixels to bleed off the residual capacitive charge. This can most easily be accomplished by using a random pattern screen saver that changes the screen image repeatedly. You should be able to connect your LCD TV to a computer with TV-out capability. The time required to clear the stuck image can vary widely (minutes, hours, days) depending on the panel technology and the severity of the stuck image.
Turning the LCD monitor off for an extended period of time does not clear the image. The charge must be bled off by charging/discharging the pixels with random images.

There were several issues with the Google Pixel 2 XL when it arrived on the market in 2017. One of those issues was screen burn in. Users noticed “ghost images” on their screens after using the phones for just a short time.
The first question you might ask is, “What is screen burn?” It’s a problem for most phones and devices with AMOLED or OLED technology. It can happen to LCD displays as well, but it’s rarer.
Unfortunately, screen burn in is a natural part of the aging process for OLED displays. The more you use your phone, the more likely damage is to occur. Since the average person checks their phone 52 times a day, these screens age a lot faster than we’d like.
Irregular pixel usage causes screen discoloration. When an image appears on the screen for a long time, it “burns” the image into the screen. A phantom copy of the image is etched on the screen afterward.
Most manufacturers claim it takes a good deal of time for screen discoloration to happen. Some independent tests say it could happen sooner than you think.
Organic Light Emitting Diode technology uses pixels that emit light. Over time, the individual pixels decay. The rate of decay varies between pixels, resulting in burn in.
Usage affects which pixels wear out first. In cases of phone




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey