lcd displays with arduino free sample
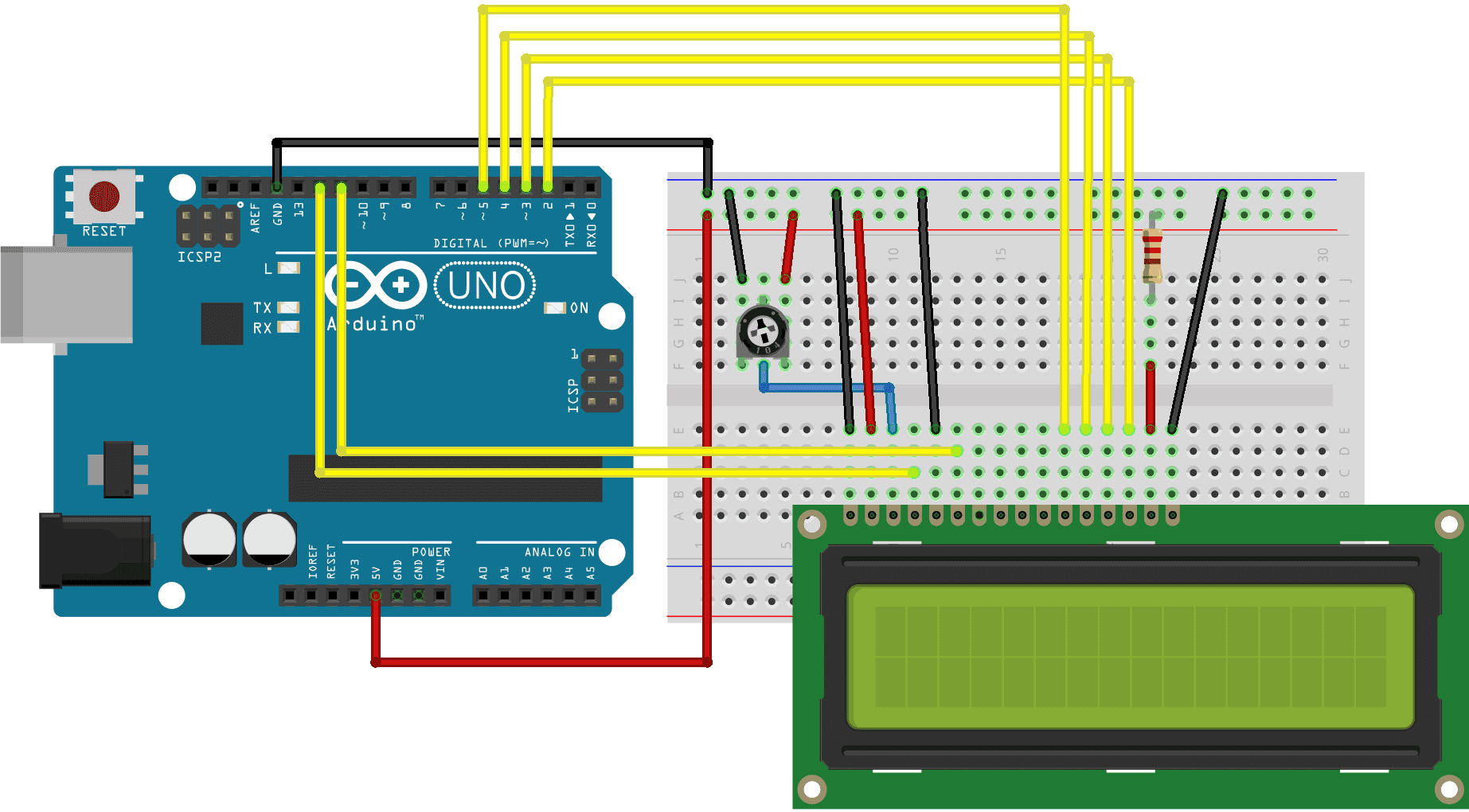
Follow the sketch below to connect the part together. Make sure the connections are right before powering up the project. A bad connection can easily damage the LCD.
There are 4 pins of the LCD we are not using, those pins are used to read data coming from the LCD which is not needed for this project. We are only using the LCD to write on, nothing more.
The Potentiometer is used to control the contrast of the LCD. In some case, you might need to rotate the potentiometer handle to see anything appearing on the LCD.
When you are done connecting everything, you can upload the following code to the Arduino. But before doing that you need to add the Adafruit_LiquidCrystal.h to your code. To do so, simply navigate to the library manager, search for LCD and it will be right there. Click on it to add it.

In this Arduino tutorial we will learn how to connect and use an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)with Arduino. LCD displays like these are very popular and broadly used in many electronics projects because they are great for displaying simple information, like sensors data, while being very affordable.
You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below. It includes everything you need to know about using an LCD character display with Arduino, such as, LCD pinout, wiring diagram and several example codes.
An LCD character display is a unique type of display that can only output individual ASCII characters with fixed size. Using these individual characters then we can form a text.
If we take a closer look at the display we can notice that there are small rectangular areas composed of 5×8 pixels grid. Each pixel can light up individually, and so we can generate characters within each grid.
The number of the rectangular areas define the size of the LCD. The most popular LCD is the 16×2 LCD, which has two rows with 16 rectangular areas or characters. Of course, there are other sizes like 16×1, 16×4, 20×4 and so on, but they all work on the same principle. Also, these LCDs can have different background and text color.
It has 16 pins and the first one from left to right is the Groundpin. The second pin is the VCCwhich we connect the 5 volts pin on the Arduino Board. Next is the Vo pin on which we can attach a potentiometer for controlling the contrast of the display.
Next, The RSpin or register select pin is used for selecting whether we will send commands or data to the LCD. For example if the RS pin is set on low state or zero volts, then we are sending commands to the LCD like: set the cursor to a specific location, clear the display, turn off the display and so on. And when RS pin is set on High state or 5 volts we are sending data or characters to the LCD.
Next comes the R/W pin which selects the mode whether we will read or write to the LCD. Here the write mode is obvious and it is used for writing or sending commands and data to the LCD. The read mode is used by the LCD itself when executing the program which we don’t have a need to discuss about it in this tutorial.
After all we don’t have to worry much about how the LCD works, as the Liquid Crystal Library takes care for almost everything. From the Arduino’s official website you can find and see the functions of the library which enable easy use of the LCD. We can use the Library in 4 or 8 bit mode. In this tutorial we will use it in 4 bit mode, or we will just use 4 of the 8 data pins.
We will use just 6 digital input pins from the Arduino Board. The LCD’s registers from D4 to D7 will be connected to Arduino’s digital pins from 4 to 7. The Enable pin will be connected to pin number 2 and the RS pin will be connected to pin number 1. The R/W pin will be connected to Ground and theVo pin will be connected to the potentiometer middle pin.
We can adjust the contrast of the LCD by adjusting the voltage input at the Vo pin. We are using a potentiometer because in that way we can easily fine tune the contrast, by adjusting input voltage from 0 to 5V.
Yes, in case we don’t have a potentiometer, we can still adjust the LCD contrast by using a voltage divider made out of two resistors. Using the voltage divider we need to set the voltage value between 0 and 5V in order to get a good contrast on the display. I found that voltage of around 1V worked worked great for my LCD. I used 1K and 220 ohm resistor to get a good contrast.
There’s also another way of adjusting the LCD contrast, and that’s by supplying a PWM signal from the Arduino to the Vo pin of the LCD. We can connect the Vo pin to any Arduino PWM capable pin, and in the setup section, we can use the following line of code:
It will generate PWM signal at pin D11, with value of 100 out of 255, which translated into voltage from 0 to 5V, it will be around 2V input at the Vo LCD pin.
First thing we need to do is it insert the Liquid Crystal Library. We can do that like this: Sketch > Include Library > Liquid Crystal. Then we have to create an LC object. The parameters of this object should be the numbers of the Digital Input pins of the Arduino Board respectively to the LCD’s pins as follow: (RS, Enable, D4, D5, D6, D7). In the setup we have to initialize the interface to the LCD and specify the dimensions of the display using the begin()function.
The cursor() function is used for displaying underscore cursor and the noCursor() function for turning off. Using the clear() function we can clear the LCD screen.
In case we have a text with length greater than 16 characters, we can scroll the text using the scrollDisplayLeft() orscrollDisplayRight() function from the LiquidCrystal library.
We can choose whether the text will scroll left or right, using the scrollDisplayLeft() orscrollDisplayRight() functions. With the delay() function we can set the scrolling speed.
So, we have covered pretty much everything we need to know about using an LCD with Arduino. These LCD Character displays are really handy for displaying information for many electronics project. In the examples above I used 16×2 LCD, but the same working principle applies for any other size of these character displays.
I hope you enjoyed this tutorial and learned something new. Feel free to ask any question in the comments section below and don’t forget to check out my full collection of 30+ Arduino Projects.

Adding a display to your Arduino can serve many purposes. Since a common use for microcontrollers is reading data from sensors, a display allows you to see this data in real-time without needing to use the serial monitor within the Arduino IDE. It also allows you to give your projects a personal touch with text, images, or even interactivity through a touch screen.
Transparent Organic Light Emitting Diode (TOLED) is a type of LED that, as you can guess, has a transparent screen. It builds on the now common OLED screens found in smartphones and TVs, but with a transparent display, offers up some new possibilities for Arduino screens.
Take for example this brilliant project that makes use of TOLED displays. By stacking 10 transparent OLED screens in parallel, creator Sean Hodgins has converted a handful of 2D screens into a solid-state volumetric display. This kind of display creates an image that has 3-dimensional depth, taking us one step closer to the neon, holographic screens we imagine in the future.
Crystalfontz has a tiny monochrome (light blue) 1.51" TOLED that has 128x56 pixels. As the technology is more recent than the following displays in this list, the cost is higher too. One of these screens can be purchased for around $26, but for certain applications, it might just be worth it.
The liquid crystal display (LCD) is the most common display to find in DIY projects and home appliances alike. This is no surprise as they are simple to operate, low-powered, and incredibly cheap.
This type of display can vary in design. Some are larger, with more character spaces and rows; some come with a backlight. Most attach directly to the board through 8 or 12 connections to the Arduino pins, making them incompatible with boards with fewer pins available. In this instance, buy a screen with an I2C adapter, allowing control using only four pins.
Available for only a few dollars (or as little as a couple of dollars on AliExpress with included I2C adapter), these simple displays can be used to give real-time feedback to any project.
The screens are capable of a large variety of preset characters which cover most use cases in a variety of languages. You can control your LCD using the Liquid Crystal Library provided by Arduino. The display() and noDisplay() methods write to the LCD, as shown in the official tutorial on the Arduino website.
Are you looking for something simple to display numbers and a few basic characters? Maybe you are looking for something with that old-school arcade feel? A seven-segment display might suit your needs.
These simple boards are made up of 7 LEDs (8 if you include the dot), and work much like normal LEDs with a common Anode or Cathode connection. This allows them to take one connection to V+ (or GND for common cathode) and be controlled from the pins of your Arduino. By combining these pins in code, you can create numbers and several letters, along with more abstract designs—anything you can dream up using the segments available!
These tiny LCD screens are monochrome and have a screen size of 84 x 48 pixels, but don"t let that fool you. Coming in at around $2 on AliExpress, these displays are incredibly cheap and usually come with a backlight as standard.
For a step up in resolution and functionality, an OLED display might be what you are looking for. At first glance, these screens look similar to the 5110 screens, but they are a significant upgrade. The standard 0.96" screens are 128 x 64 monochrome, and come with a backlight as standard.
They connect to your Arduino using I2C, meaning that alongside the V+ and GND pins, only two further pins are required to communicate with the screen. With various sizes and full color options available, these displays are incredibly versatile.
For a project to get you started with OLED displays, our Electronic D20 build will teach you everything you need to know -- and you"ll end up with the ultimate geeky digital dice for your gaming sessions!
These displays can be used in the same way as the others we have mentioned so far, but their refresh rate allows for much more ambitious projects. The basic monochrome screen is available on Amazon.
Thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal displays (TFT LCDs) are in many ways another step up in quality when it comes to options for adding a screen to your Arduino. Available with or without touchscreen functionality, they also add the ability to load bitmap files from an on-board microSD card slot.
Arduino have an official guide for setting up their non-touchscreen TFT LCD screen. For a video tutorial teaching you the basics of setting up the touchscreen version, YouTuber educ8s.tv has you covered:
With the touchscreen editions of these screens costing less than $10 on AliExpress, these displays are another great choice for when you need a nice-looking display for your project.
The reason these displays look so good is down to the way they function. Each "pixel" contains charged particles between two electrodes. By switching the charge of each electrode, you can influence the negatively charged black particles to swap places with the positively charged white particles.
This is what gives e-paper such a natural feel. As a bonus, once the ink is moved to its location, it uses no power to keep it there. This makes these displays naturally low-power to operate.
This article has covered most options available for Arduino displays, though there are definitely more weird and wonderful ways to add feedback to your DIY devices.
Now that you have an idea of what is out there, why not incorporate a screen into your DIY smart home setup? If retro gaming is more your thing, why not create some retro games on Arduino?

Liquid Crystal displays or LCDs have been used in electronics equipment since the late 1970s. LCD displays have the advantage of consuming very little current And they are ideal for your Arduino projects.
In this article and in the accompanying video I’ll show you how easy it is to add an LCD display to your next Arduino design. I’ll also show you a very popular Arduino Shield that has a keypad which you can use in your projects as well.
Today LCD displays are used in a variety of items from test equipment to televisions. They’re inexpensive and versatile, this makes them ideal for all sorts of designs.
LCD displays do not emit light. Instead they block the passage of light, like little windows which open and shut the let light through. The liquid crystals used inside LCD displays are sandwiched between two layers of polarized material. By changing the orientation of the liquid crystals they allow light to pass or they block the light entirely.
Because transmissive LCD displays (the type we will be using) work by blocking light they require a backlight. Several methods have been used to create back lights including electroluminescent panels and fluorescent tubes. these days the most common form of backlight is an LED, in fact so-called LED televisions are usually just LCD screens with an LED backlight system.
Another type of LCD display, the passive-matrix display, does not require a backlight, it works using reflected light. This type of display is often found in digital watches.
The principles of liquid crystals were discovered in the late 1880s but work on Modern LCD displays did not begin until the mid-1960s. a number of patents were filed in the early 1970s and in 1973 the Sharp Corporation introduced LCD displays for calculators.
The first color LCD displays were developed in the early 1980s but production units were not commonly available until the mid-1990s. By the late 1990s LCD displays were quite common.
A number of LCD displays are available for experimenters. These low-cost monochrome displays are ideal for use with microcontrollers like the Arduino and micro computers like the Raspberry Pi.
These displays are available in a number of different configurations. The part number for the display generally relates to the number of rows and columns in the display.
Common display configurations include 16 x 2, 16 x 4 and 20 x 4. All of these displays are used in a virtually identical fashion the only difference being the number of columns and rows they have.
The LCD1602 display module is a very popular and inexpensive LCD display. It is available in a number of different colors such as blue yellow and green and can easily be connected to an Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
Because the LCD module uses a parallel data input it requires 8 connections to the host microcontroller for the data alone. Add that to the other control pins and it consumes a lot of connections. On an Arduino Uno half of the I/O pins would be taken up by the display, which can be problematic if you want to use the I/O pins for other input or output devices.
We will begin our experiments by hooking up the LCD1602 to an Arduino Uno and running a few of the example sketches included with the Arduino IDE. This will allow you to get familiar with the display without needing to write any code.
We need to hookup our LCD display to our Arduino. The display can use any of the Arduino digital I/O pins as it has no special requirements, but if you hook it up as I’ve illustrated here you can run the example sketches without needing to make any modifications.
In addition to the LCD1602 display ands the Arduino Uno you will need a 10K trimpot ot potentiometer, this is used a s a brightness control for the display. You’ll also need a 220 ohm resistor to drop the voltage for the displays LED backlight.
The Arduino IDE includestheLiquidCrystallibraryand this library has a number of example sketches. I’ll go over three of them here but you can also try the other ones.
The sketch starts with a number of credits and a description of the required hardware hookup. You’ll note that this is the same hookup you just performed on your Arduino and LCD module.
We then initialize an object that we call “lcd” using the pinouts of the LCD display. If you decide to hook up your display to different pins then you’ll need to modify this section.
In the beginning of the loop we set our cursor to the first position in the second row. Note that the row numbers start with zero so the second row is row 1.
That ends the loop, so we start back at the top of the loop and repeat. The result will be a counter on the second line that counts seconds from the htime the Arduino was last reset.
Load the sketch up to your Arduino and observe your display. If you don’t see anything try adjusting the brightness control that you wired to the display.
The second example we will try isthe Scroll sketch. Scrolling is a useful technique when you can’t get your text to fit on one line of the LCD display.
Custom characters are useful when you want to display a character that is not part of the standard 127-character ASCII character set. Thi scan be useful for creating custom displays for your project.
A character on the display is formed in a 5 x 8 matrix of blocks so you need to define your custom character within that matrix. To define the character you’ll use thecreateCharfunctionof the LiquidCrystal library. You are limited to defining a maximum of eight characters.
To usecreateCharyou first set up an array of bytes with 8 elements. Each element in the array defines one row of the character in the 5 x 8 matrix. You then use createCharto assign a number from 0 to 7 to that array.
The Custom Character demonstration requires one additional component to be wired to the Arduino, a potentiometer (10K or greater) wired up to deliver a variable voltage to analog input pin A0.
As with the previous sketches we examined this one starts by loading theLiquidCrystallibrary and defining an object calledlcdwith the connection information for the display. It then moves on to define the custom characters.
Each character is defined as an array with 8 elements, the zeros and ones in the array indicate which elements in the character should be on and which ones should be off. Five arrays are defined, although the sketch actually only used four of them.
Finally the setup routine ends by printing a line to the first row of the LCD display. The line makes use of two of the custom characters, the “heart” and the “smiley”.
We begin by reading the value of the voltage on pin A0 using the ArduinoanalogReadfunction. As the Arduino has a 10-bit analog to digital converter this will result in a reading ranging from 0 to 1023.
We then use an Arduinomapfunction to convert this reading into a range from 200 to 1000. This value is then assigned to an integer calleddelayTime, which as its name implies represents a time delay period.
One thing you may have noticed about using the LCD display module with the Arduino is that it consumes a lot of connections. Even in 4-wire mode there are still a total of seven connections made to the Arduino digital I/O pins. As an Arduino Uno has only 14 digital I/O pins that’s half of them used up for the display.
In other cases you would need to resort to using some of the analog pins as digital pins or even moving up to an Arduino Mega which has many more I/O pins.
But there is another solution. Use the I2C bus adapter for the LCD display and connect using I2C. This only consumes two I/O pins and they aren’t even part of the set of digital I/O pins.
The bus has evolved to be used as an ideal method of communicating between microcontrollers, integrated circuits, sensors and micro computers. You can use it to allow multiple Arduinos to talk to each other, to interface numerous sensors and output devices or to facilitate communications between a Raspberry Pi and one or more Arduinos.
In I2C communications there is the concept of Master and Slave devices. There can be multiples of each but there can only be one Master at any given moment. In most Arduino applications one Arduino is designated Master permanently while the other Arduinos and peripherals are the Slaves.
The Master transmits the clock signal which determines how fast the data on the bus is transferred. There are several clock speeds used with the I2C bus. The original design used 100 KHz and 400 KHz clocks. Faster rates of 3.4 MHz and higher are available on some I2C configurations.
Every device on the I2C bus has a unique address. When the Master wants to communicate with a Slave device it calls the Slaves address to initiate communications.
The I2C Adapter for the LCD display is a tiny circuit board with 16 male header pins soldered to it. These pins are meant to be connected directly to the 16-pin connection on the LCD1602 display (or onto other displays that use the same connection scheme).
The device also has a 4-pin connector for connection to the I2C bus. In addition there is a small trimpot on the board, this is the LCD display brightness control.
Most of these devices have three jumpers or solder pads to set the I2C address. This may need to be changed if you are using multiple devices on the same I2C bus or if the device conflicts with another I2C device.
Most Arduino Unos also have some dedicated pins for I2C, these are internally connected to A4 and A5 and are usually located above the 14 digital I/O pins. Some models of the Uno have additional I2C connectors as well.
Note how much easier it is to use the I2C connection, which does not consume any of the Arduino Unos 14 digital I/O pins. Since A4 and A5 are being used for the I2C bus they can’t be used as analog inputs in this configuration.
Nick has written a simple I2C scanner sketch that he’s put into the public domain. It scans your I2C bus and gives you back the address of every I2C device it finds. I’ve repeated Nick’s sketch here, it’s also in the ZIP file that you can download with all of the code for this article.
Load this sketch into your Arduino then open your serial monitor. You’ll see the I2C address of your I2C LCD display adapter. You can then make note of this address and use it in the sketches we’ll be looking at now.
In order to run the subsequent sketches you’ll need to install another library. This is theNewLiquidCrystallibrarywhich, as its name implies, is an improved version of the LiquidCrystal library packaged with your Arduino IDE.
The sketch starts by loading the ArduinoWirelibrary. This is the Arduino library that facilitates communications over I2C and it’s part of your Arduino IDE installation.
On the next line we define the connections to the LCD display module from the I2C Adapter,. Note that these are NOT the connections from the Arduino, they are the connections used by the chip on the adapter itself.
Load the sketch and run it on your Arduino. If you can’t get it to work check out the address and connection information to be sure you have it right.
We need to make a minor wiring adjustment to the hookup with our I2C adapter, specifically we will need to add a DHT22 temperature and humidity sensor into the circuit. The wiring is shown here:
As you can see the DHT22 is connected with its output tied to pin 7 of the Arduino. The other two connections are 5 volts and ground. Note that pin 3 of the DHT22 is not used.
This sketch also makes use of theDHTlibrary from Adafruit. We used this library in a previous article, “Using the HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Distance Sensor with Arduino” so you may want to take a look at that one in order to get it installed.
The key thing to note is that this library is dependant upon another Adafruit library, theirUnified Sensorlibrary. Both can be installed using the Library Manager in your Arduino IDE.
The sketch is similar to our demo sketch in that it creates an “lcd” object with the I2C and display connection information. It also defines a couple of parameters for the DHT22 sensor, as well as some floating variables to hold the temperature and humidity values.
Note that this displays the temperature in Celsius. If you want to change this to Fahrenheit its a simple matter of using some math. The formula( temp * 1.8 ) + 32will convert the results to Fahrenheit.
So far we have used the LCD1602 display module for all of our experiments. For our final demonstration we’ll switch to a popular Arduino shield that contains a LCD1602 along with some push buttons.
The LCD Keypad Shield is available from several different manufacturers. The device fits onto an Arduino Uno or an Arduino Mega and simplifies adding an LCD display to your project.
The Reset button is simply connected to the Arduino Reset pin and works just like the Reset button on the Arduino itself. This is common on many shields as the shields physically cover the Reset button.
Instead the buttons are connected to a resistor array that acts as a voltage divider. The entire array is connected to the Arduino’s analog A0 pin. One pin for five push buttons.
Note that the LCD is being used in 4-wire mode. The LCD itself is the same one used on the LCD1602 module, so all of the code for that module will work with the LCD Keypad Shield as well.
Now that you know how the LCD Keypad module works and which Arduino pins it uses all that remains is to install it onto your Arduino and load the demo sketch.
One thing – once the shield is installed on the Arduino you won’t have easy access to the unused I/O pins to connect any sensors or output devices you may want to use (although the demo sketch doesn’t need anything else connected). There are a couple of ways to get around this:
Use a shield that exposes the pins for prototyping before you install the LCD Keypad shield. In the video associated with this article I use a “Screw Shield” that brings all of the Arduino I/O pins out to a series of screw connectors. There are other similar shields. Using one of these shields is the easiest way to work with the LCD Keypad shield, as well as other Arduino shields.
The sketch begins by including theLiquidCrystallibrary. You can use the original one or the one includes with theNewLiquidCrystallibrary. We then set up an object with the LCD connections, note that these are just hard-coded as they won’t change.
Next we define a number of constants, one for each of the push buttons. Note that nothing is defined for the Reset button as it simply mimics the Arduino Reset button, however a constant is defined for the “none” condition.
After that we define a function calledread_LCD_buttons(). This function reads the value on analog port A0 and returns an integer corresponding to the button integers we defined earlier. Note that the function adds approximately 50 to each of the manufacturers specified values to account for intolerances in the resistors in the voltage divider.
We start the loop by placing the cursor 9 spaces over on the second line. We then use themillisfunction to display a counter that counts the time since the Arduino was reset. This is to test the Reset button.
We then call ourread_LCD_buttons()function and use it to display the value of the push button, right before the counter. Then we end the loop and do it again.
Load the code onto the Arduino and run it. You should see the value of each button as you press it, along with a counter that increments each second. If you press Reset the counter should reset itself back to zero.
As you can see LCD displays are pretty simple to use thanks to the availability of some excellent libraries for the Arduino. As these displays are also very inexpensive they will make an ideal addition to many of your Arduino projects.
And finally the LCD Keypad Shield is a convenient method of adding both a display and a simple keypad to your project, no wiring or soldering required.
In this tutorial, I’ll explain how to set up an LCD on an Arduino and show you all the different ways you can program it. I’ll show you how to print text, scroll text, make custom characters, blink text, and position text. They’re great for any project that outputs data, and they can make your project a lot more interesting and interactive.
The display I’m using is a 16×2 LCD display that I bought for about $5. You may be wondering why it’s called a 16×2 LCD. The part 16×2 means that the LCD has 2 lines, and can display 16 characters per line. Therefore, a 16×2 LCD screen can display up to 32 characters at once. It is possible to display more than 32 characters with scrolling though.
The code in this article is written for LCD’s that use the standard Hitachi HD44780 driver. If your LCD has 16 pins, then it probably has the Hitachi HD44780 driver. These displays can be wired in either 4 bit mode or 8 bit mode. Wiring the LCD in 4 bit mode is usually preferred since it uses four less wires than 8 bit mode. In practice, there isn’t a noticeable difference in performance between the two modes. In this tutorial, I’ll connect the LCD in 4 bit mode.
Here’s a diagram of the pins on the LCD I’m using. The connections from each pin to the Arduino will be the same, but your pins might be arranged differently on the LCD. Be sure to check the datasheet or look for labels on your particular LCD:
Also, you might need to solder a 16 pin header to your LCD before connecting it to a breadboard. Follow the diagram below to wire the LCD to your Arduino:
All of the code below uses the LiquidCrystal library that comes pre-installed with the Arduino IDE. A library is a set of functions that can be easily added to a program in an abbreviated format.
In order to use a library, it needs be included in the program. Line 1 in the code below does this with the command #include
Now we’re ready to get into the programming! I’ll go over more interesting things you can do in a moment, but for now lets just run a simple test program. This program will print “hello, world!” to the screen. Enter this code into the Arduino IDE and upload it to the board:
TheLiquidCrystal() function sets the pins the Arduino uses to connect to the LCD. You can use any of the Arduino’s digital pins to control the LCD. Just put the Arduino pin numbers inside the parentheses in this order:
This function sets the dimensions of the LCD. It needs to be placed before any other LiquidCrystal function in the void setup() section of the program. The number of rows and columns are specified as lcd.begin(columns, rows). For a 16×2 LCD, you would use lcd.begin(16, 2), and for a 20×4 LCD you would use lcd.begin(20, 4).
This function clears any text or data already displayed on the LCD. If you use lcd.clear() with lcd.print() and the delay() function in the void loop() section, you can make a simple blinking text program:
This function places the cursor in the upper left hand corner of the screen, and prints any subsequent text from that position. For example, this code replaces the first three letters of “hello world!” with X’s:
Similar, but more useful than lcd.home() is lcd.setCursor(). This function places the cursor (and any printed text) at any position on the screen. It can be used in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The cursor position is defined with lcd.setCursor(column, row). The column and row coordinates start from zero (0-15 and 0-1 respectively). For example, using lcd.setCursor(2, 1) in the void setup() section of the “hello, world!” program above prints “hello, world!” to the lower line and shifts it to the right two spaces:
You can use this function to write different types of data to the LCD, for example the reading from a temperature sensor, or the coordinates from a GPS module. You can also use it to print custom characters that you create yourself (more on this below). Use lcd.write() in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The function lcd.noCursor() turns the cursor off. lcd.cursor() and lcd.noCursor() can be used together in the void loop() section to make a blinking cursor similar to what you see in many text input fields:
Cursors can be placed anywhere on the screen with the lcd.setCursor() function. This code places a blinking cursor directly below the exclamation point in “hello, world!”:
This function creates a block style cursor that blinks on and off at approximately 500 milliseconds per cycle. Use it in the void loop() section. The function lcd.noBlink() disables the blinking block cursor.
This function turns on any text or cursors that have been printed to the LCD screen. The function lcd.noDisplay() turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD, without clearing it from the LCD’s memory.
This function takes anything printed to the LCD and moves it to the left. It should be used in the void loop() section with a delay command following it. The function will move the text 40 spaces to the left before it loops back to the first character. This code moves the “hello, world!” text to the left, at a rate of one second per character:
This function takes a string of text and scrolls it from right to left in increments of the character count of the string. For example, if you have a string of text that is 3 characters long, it will shift the text 3 spaces to the left with each step:
Like the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, the text can be up to 40 characters in length before repeating. At first glance, this function seems less useful than the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, but it can be very useful for creating animations with custom characters.
lcd.noAutoscroll() turns the lcd.autoscroll() function off. Use this function before or after lcd.autoscroll() in the void loop() section to create sequences of scrolling text or animations.
This function sets the direction that text is printed to the screen. The default mode is from left to right using the command lcd.leftToRight(), but you may find some cases where it’s useful to output text in the reverse direction:
This code prints the “hello, world!” text as “!dlrow ,olleh”. Unless you specify the placement of the cursor with lcd.setCursor(), the text will print from the (0, 1) position and only the first character of the string will be visible.
This command allows you to create your own custom characters. Each character of a 16×2 LCD has a 5 pixel width and an 8 pixel height. Up to 8 different custom characters can be defined in a single program. To design your own characters, you’ll need to make a binary matrix of your custom character from an LCD character generator or map it yourself. This code creates a degree symbol (°):
If you found this article useful, subscribe via email to get notified when we publish of new posts! And as always, if you are having trouble with anything, just leave a comment and I’ll try to help you out.

This article gives you a step-by-step guide to becoming a pro in using Liquid Crystal Display. We will use a free Arduino Simulator to try all the examples without leaving your PC. No hardware is needed.
There are two versions of the chip"s ROM with two different fonts: HD44780UA00, Japanese katakana characters, and HD44780UA02, which includes Western European characters.
You can see that the first eight characters are user-defined. It allows you to create custom shapes and store them. You will see how to create custom characters and load them in your following Arduino projects. Let us start with a basic example.
We will print a simple text on the LCD using Arduino UNO in this example. In this case, you control what is displayed on the Arduino readily. You only need four cables. Power, Ground, I2C data, and I2C clock.
Use the link above to run the code. You can tinker with the code to change the text displayed or the position. The best thing about the link is that it will save the project as your version. It will be automatically saved under my projects tab on the wokwi site if you are logged in.
The below line code adds the LCD library to your project. This consists of all the LCD-related functions. Since we are using the I2C version, we have included the standard LCD library made for the I2C version.#include
The following line of the code resets and initializes all the LCD registers and prepares them for project usage. This function will be called only once in thesetup()function.lcd.init();
To turn on the backlight, you can use the below code. You will be able to see the contents of the display without a backlight, too, if it is a green LCD. Backlight, nevertheless, makes the project more beautiful and reading crisper.lcd.backlight();
The first parameter tells the position column-wise (0indicated first place,1indicates the second place, and so on). The second parameter tells the row number. We have only two rows (0and1).lcd.setCursor(1, 0);
This completes a basic introduction to the LCD as well as an example project to start the LCD exploration. In the coming sections, we will see different projects as soon as possible




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey