tft lcd pros and cons for sale
Responsible for performing installations and repairs (motors, starters, fuses, electrical power to machine etc.) for industrial equipment and machines in order to support the achievement of Nelson-Miller’s business goals and objectives:
• Perform highly diversified duties to install and maintain electrical apparatus on production machines and any other facility equipment (Screen Print, Punch Press, Steel Rule Die, Automated Machines, Turret, Laser Cutting Machines, etc.).
• Provide electrical emergency/unscheduled diagnostics, repairs of production equipment during production and performs scheduled electrical maintenance repairs of production equipment during machine service.

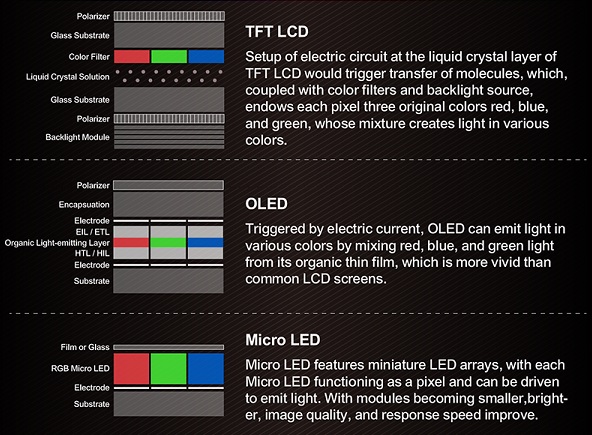
The worlds of high-end Color LCD Modules are taken over. As our world evolved and embedded devices becoming more, and more sophisticated and prevalent, we tend to look at the art of design. Steve Jobs sums it up just right. “Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.” TFT LCD modules are a type of variant of an LCD which uses thin film, appliances such as: TV, computer monitors, kindles, mobile phone, and navigation system. The construction of a color LCD module or TFT LCD is quite extraordinary because of the circuit layout process; this form of layout is similar to the layout of a semiconductor product. Even though as we observe the TFT LCD display we came across few pros and cons which are most needed for this discussion. The advantages of TFT LCD are as follows: less energy consumption, visibility is sharper in other words has superb quality, physical design, response time, and less eye strain etc… With every great product there are few disadvantages associated, such as, cost and viewing angles.
TFT LCD displays are very convenient because of the energy consumption associate with this display, knowingly in today’s society saving energy is a number one priority to reduce greenhouse gas and ensure a better future generations. Due to the construction of TFT structures Pixel like materials does not consume much energy to begin with except this material consume far less power than a comparable CRT monitor. The images of a TFT display does not rely on the scanning of electron beams instead they are free from flicker and has a crisp image, with no geometric distortion. The physical design of TFT display are space savors which can be position anywhere in ones office, or house with a rotations mechanism in place for less constrains on space.
As mention before TFT LCD has few disadvantages, due to the nature of the design TFT LCD display may cost a little more than a regular monochrome display. Other disadvantages may arise when the viewing the display at the 6 0’clock direction but in fact the optimal viewing is at the 12’oclock direction this may also lead to inversion which or common in situation like this; however TFT displays are superior and will be in production for years to come.

TFT (Thin Film Transistor) LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) we are talking here is TN (Twisted Nematic) type TFT displays which is align with the term in the TV and computer market. Now, TFT displays have taken over the majority of low-end color display market. They have wide applications in TV, computer monitors, medical, appliance, automotive, kiosk, POS terminals, low end mobile phones, marine, aerospace, industrial meters, smart homes, consumer electronic products etc. For more information about TFT displays, please visit our knowledge base.
Talking about Pros and Cons of TFT displays, we need to clarify which display they are compared to. To some displays, TFT displays might have advantages, but compared with another display, the same character might become the disadvantages of TFT displays. We will try our best to make clear as below.
Less Energy Consumption: Compared with CRT(Cathode-Ray Tube) VFD ( Vacuum Fluorescent Display) and LED (Light Emitting Diode) display, which made laptop possible.
Excellent physical design. TFT displays are very easy to design and integrated with other components, such as resistive and capacitive touch panels (RTP, CTP, PCAP) etc.
Minimum Eye Strain: Because TFT panel itself doesn’t emit light itself like CRT, LED, VFD. The light source is LED backlight which is filtered well with the TFT glass in front for the blue light.
More Energy Consumption: Compared with monochrome displays and OLED (PMOLED and AMOLED) display, which makes TFT displays less attractive in wearable device.
Poor response time and viewing angle: Compared with IPS LCD displays, AMOLED displays and recent micro-LED display. TFT displays still need to note viewing angle of 6 o’clock or 12 o’clock in the datasheet and still have the gray scale inversion issue.
High tooling cost: Depending on which generation production line to produce and also depending on its size. Building a TFT display fab normally need billions of dollars. For a big size display which needs high generation production line to produce. The NRE cost can be millions dollars.
Sunlight Readability: Because it is very expensive to produce transflective TFT LCD displays, in order to be readable under the sunlight, very bright LED backlight (> 1,000 nits) has to be used. The power needed is high and also need to deal with heat management. If used together with touch panel, expensive optical bonding (OCA or OCR) and surface treatment (AR, AF) technologies have to be used.

TFT stands for thin-film transistor, which means that each pixel in the device has a thin-film transistor attached to it. Transistors are activated by electrical currents that make contact with the pixels to produce impeccable image quality on the screen. Here are some important features of TFT displays.Excellent Colour Display.Top notch colour contrast, clarity, and brightness settings that can be adjusted to accommodate specific application requirements.Extended Half-Life.TFT displays boast a much higher half-life than their LED counterparts and they also come in a variety of size configurations that can impact the device’s half-life depending on usage and other factors.TFT displays can have either resistive or capacitive touch panels.Resistive is usually the standard because it comes at a lower price point, but you can also opt for capacitive which is compatible with most modern smartphones and other devices.TFT displays offer exceptional aspect ratio control.Aspect ratio control contributes to better image clarity and quality by mapping out the number of pixels that are in the source image compared to the resolution pixels on the screen.Monitor ghosting doesn’t occur on TFT displays.This is when a moving image or object has blurry pixels following it across the screen, resembling a ghost.
TFT displays are incredibly versatile.The offer a number of different interface options that are compatible with various devices and accommodate the technical capabilities of all users.
There are two main types of TFT LCD displays:· Twisted nematic TFT LCDs are an older model. They have limited colour options and use 6 bits per each blue, red, and green channel.
In-plane switching TFT LCDs are a newer model. Originally introduced in the 1990s by Hitachi, in-plane switching TFT LCDs consist of moving liquid pixels that move in contrast or opposite the plane of the display, rather than alongside it.
The type of TFT LCD monitor or industrial display you choose to purchase will depend on the specifications of your application or project. Here are a few important factors to consider when selecting an appropriate TFT LCD display technology:Life expectancy/battery life.Depending on the length of ongoing use and the duration of your project, you’re going to want to choose a device that can last a long time while maintaining quality usage.
Touch type and accuracy.What type of activities are you planning on using your device for? If it’s for extended outdoor use, then you should go with projected capacitive touch as this is more precise and accurate. Touch accuracy is important for industrial and commercial applications.
Image clarity.Some TFT displays feature infrared touchscreens, while others are layered. The former is preferable, especially in poor lighting conditions or for outdoor and industrial applications, because there’s no overlay and therefore no obstructions to light emittance.
The environmental conditions make a difference in operation and image clarity. When choosing a TFT for outdoor or industrial applications, be sure to choose one that can withstand various environmental elements like dust, wind, moisture, dirt, and even sunlight.
As a leading manufacturer and distributor of high-quality digital displays in North America, Nauticomp Inc. can provide custom TFT LCD monitor solutions that are suitable for a multitude of industrial and commercial indoor and outdoor applications. Contact us today to learn more.

When you put them together, you get a TFT LCD, which is a flat panel display or screen that can be found everywhere from smartphones and tablets to TV sets and monitors.
TFT displays have a longer half-life than LEDs and are available in a wider number of configurations, all of which might affect the device"s half-life depending on usage and other circumstances.
TFC displays can have a resistive or capacitive touch panel. Because resistive is less expensive, it is frequently used in numerous applications. A capacitive touch screen, on the other hand, is a fantastic choice because it works with most recent smartphones and mobile devices.
This is not an issue with TFT displays since the display maps out the number of pixels in the source image relative to the resolution pixels on display, resulting in greater image quality and clarity. Monitor ghosting occurs when a moving image or object is followed across the screen by a hazy image (and resembling a ghost).
TFT displays are available in a variety of interface configurations, making them compatible with a wide range of devices and allowing for a wide range of technological capabilities.
1. Glass paneling may limit utility – for example, a TFT LCD display may be a poor choice for outdoor environments where the glass can showcase glares from natural lighting.
4. Glass paneling may limit utility – for example, a TFT LCD display may be a poor choice for outdoor environments where the glass can showcase glares from natural lighting.
5. Because it does not emit its light, this sort of display relies on backlighting to provide brightness. As a result, producers must use LEDs and construct a backlighting structure.
Although the selecting procedure for your LCD display may not appear to be stressful, it is in reality due to the countless products that have invaded the market.

Everyone is familiar with the TFT-LCD display screen. It is currently the most popular display product in the display industry. Its high reliability and good display effect are sure to have a wave of loyal fans. Then do you know the advantages and disadvantages of TFT-LCD display screen?
The hourly effect of the TFT-LCD display screen is very lifelike, and the color reproduction is far superior to other types of display screens. The picture presented to the user is bright in color, high in saturation, and the pure white and pure black pictures are very pure. It is very pure for professionals, one of the approved display screens.
The IPS series of the TFT-LCD display screen can reach a full viewing angle of 178 degrees, which means that no matter which angle the user views the TFT-LCD display screen from, the effect is very good.
The application of TFT-LCD display screen is very wide, used in industry, transportation, medical treatment, smart home, electric power, aviation and other fields. There must be a reason behind the widespread use. The size is complete, the interface types are many, and the development is simple. This is an important reason why the terminal chooses the TFT-LCD display screen.
Any product that is good will also have its bad aspects, and the shortcomings of the TFT-LCD display screen are reflected in the limitation of brightness. Due to its ultra-thin shape, it cannot meet the needs of ultra-high brightness. There are certain restrictions.
The display technology of TFT-LCD display screens has become mature, and the yield and production capacity of products are getting higher and higher, and the price of TFT-LCD display screens is becoming more and more affordable. These are all the reasons behind for the popularity of TFT-LCD display screens.
Shenzhen CDTech Electronics established in 2011, is a national high-tech enterprise specializing in TFT LCDs, Touch Displays, HDMI Displays and other display products.
The factory covers an area of 5,000 square meters, including thousand-level dust-free workshop area of over 1000 square meters. CDTech has industry-leading automatic production and testing equipment which can provide customers with standard and customized display and touch total solutions. Our products are widely used in Industrial Control Equipment, Medical, Smart-Home, Automotive and Vehicle Displays, Instrumentation, and other Information Terminal applications.

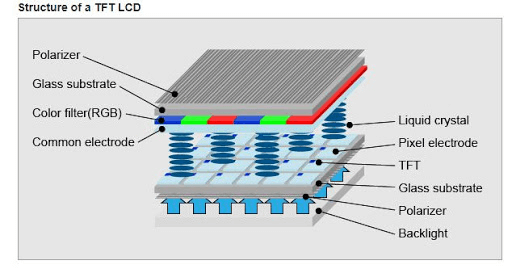
IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.
Before you get a new monition for your organization, comparing the TFT display vs IPS display is something that you should do. You would want to buy the monitor which is the most advanced in technology. Therefore, understanding which technology is good for your organization is a must. click to view the 7 Best Types Of Display Screens Technology.
Technology is changing and becoming advanced day by day. Therefore, when you are looking to get a new monitor for your organization, LCD advantages, and disadvantage, you have to be aware of the pros and cons of that monitor. Moreover, you need to understand the type of monitor you are looking to buy.
Now, understanding the technology from the perspective of a tech-savvy person may not be the ideal thing to do unless you are that tech-savvy person. If you struggle to understand technology, then understanding it in a layman’s language would be the ideal thing to do.
That is why it is important to break it down and discuss point by point so that you can understand it in a layman’s language devoid of any technical jargon. Therefore, in this very article, let’s discuss what exactly TFT LCDs and IPS LCDs are, and what are their differences? You will also find out about their pros and cons for your organization.
The word TFT means Thin-Film-Translator. Click to view: what is TFT LCD, It is the technology that is used in LCD or Liquid Crystal Display. Here you should know that this type of LCD is also categorically referred to as active-matrix LCDs. It tells that these LCDs can hold back some pixels while using other pixels. So, the LCD will be using a very minimum amount of energy to function. TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
Now, it is time to take a look at its features that are tailored to improve the experience of the monitor users significantly. Here are some of the features of the TFT monitor;
The display range covers the application range of all displays from 1 inch to 40 inches as well as the large projection plane and is a full-size display terminal.
No radiation, no scintillation, no harm to the user’s health. In particular, the emergence of TFT LCD electronic books and periodicals will bring humans into the era of a paperless office and paperless printing, triggering a revolution in the civilized way of human learning, dissemination, and recording.
It can be normally used in the temperature range from -20℃ to +50℃, and the temperature-hardened TFT LCD can operate at low temperatures up to -80 ℃. It can not only be used as a mobile terminal display, or desktop terminal display but also can be used as a large screen projection TV, which is a full-size video display terminal with excellent performance.
The manufacturing technology has a high degree of automation and good characteristics of large-scale industrial production. TFT LCD industry technology is mature, a mass production rate of more than 90%.
It is a perfect combination of large-scale semiconductor integrated circuit technology and light source technology and has great potential for further development.
TFT LCD screen from the beginning of the use of flat glass plate, its display effect is flat right angles, let a person have a refreshing feeling. And LCDs are easier to achieve high resolution on small screens.
The word IPS refers to In-Plane-Switching which is a technology used to improve the viewing experience of the usual TFT displays. You can say that the IPS display is a more advanced version of the traditional TFT LCD module. However, the features of IPS displays are much more advanced and their applications are very much widespread. You should also know that the basic structure of the IPS LCD is the same as TFT LCD if you compare TFT LCD vs IPS.
As you already know, TFT displays do have a very quick response time which is a plus point for it. But, that does not mean IPS displays a lack of response time. In fact, the response time of an IPS LCD is much more consistent, stable, and quick than the TFT display that everyone used to use in the past. However, you will not be able to gauge the difference apparently by watching TFT and IPS displays separately. But, once you watch the screen side-by-side, the difference will become quite clear to you.
The main drawback of the TFT displays as figured above is the narrow-angle viewing experience. The monitor you buy for your organization should give you an experience of wide-angle viewing. It is very much true if you have to use the screen by staying in motion.
So, as IPS displays are an improved version of TFT displays the viewing angle of IPS LCDs is very much wide. It is a plus point in favor of IPS LCDs when you compare TFT vs IPS. With a TFT screen, you cannot watch an image from various angles without encountering halo effects, blurriness, or grayscale that will cause problems for your viewing.
It is one of the major and remarkable differences between IPS and TFT displays. So, if you don’t want to comprise on the viewing angles and want to have the best experience of viewing the screen from wide angles, the IPS display is what you want. The main reason for such a versatile and wonderful viewing angle of IPS display is the screen configuration which is widely set.
Now, when you want to achieve wide-angle viewing with your display screen, you need to make sure it has a faster level of frequency transmittance. It is where IPS displays overtake TFT displays easily in the comparison because the IPS displays have a much faster and speedier transmittance of frequencies than the TFT displays.
Now the transmittance difference between TFT displays and IPS displays would be around 1ms vs. 25ms. Now, you might think that the difference in milliseconds should not create much of a difference as far as the viewing experience is concerned. Yes, this difference cannot be gauged with a naked eye and you will find it difficult to decipher the difference.
However, when you view and an IPS display from a side-by-side angle and a TFT display from a similar angle, the difference will be quite evident in front of you. That is why those who want to avoid lagging in the screen during information sharing at a high speed; generally go for IPS displays. So, if you are someone who is looking to perform advanced applications on the monitor and want to have a wider viewing angle, then an IPS display is the perfect choice for you.
As you know, the basic structure of the IPS display and TFT displays are the same. So, it is quite obvious that an IPS display would use the same basic colors to create various shades with the pixels. However, there is a big difference with the way a TFT display would produce the colors and shade to an IPS display.
The major difference is in the way pixels get placed and the way they operate with electrodes. If you take the perspective of the TFT display, its pixels function perpendicularly once the pixels get activated with the help of the electrodes. It does help in creating sharp images.
But the images that IPS displays create are much more pristine and original than that of the TFT screen. IPS displays do this by making the pixels function in a parallel way. Because of such placing, the pixels can reflect light in a better way, and because of that, you get a better image within the display.
As the display screen made with IPS technology is mostly wide-set, it ensures that the aspect ratio of the screen would be wider. This ensures better visibility and a more realistic viewing experience with a stable effect.
As you already know the features of both TFT and IPS displays, it would be easier for you to understand the difference between the two screen-types. Now, let’s divide the matters into three sections and try to understand the basic differences so that you understand the two technologies in a compressive way. So, here are the difference between an IPS display and a TFT display;
Now, before starting the comparison, it is quite fair to say that both IPS and TFT displays have a wonderful and clear color display. You just cannot say that any of these two displays lag significantly when it comes to color clarity.
However, when it comes to choosing the better display on the parameter of clarity of color, then it has to be the IPS display. The reason why IPS displays tend to have better clarity of color than TFT displays is a better crystal oriental arrangement which is an important part.
That is why when you compare the IPS LCD with TFT LCD for the clarity of color, IPS LCD will get the nod because of the better and advanced technology and structure.
IPS displays have a wider aspect ratio because of the wide-set configuration. That is why it will give you a better wide-angle view when it comes to comparison between IPS and TFT displays. After a certain angle, with a TFT display, the colors will start to get a bit distorted.
But, this distortion of color is very much limited in an IPS display and you may see it very seldom after a much wider angle than the TFT displays. That is why for wide-angle viewing, TFT displays will be more preferable.
When you are comparing TFT LCD vs. IPS, energy consumption also becomes an important part of that comparison. Now, IPS technology is a much advanced technology than TFT technology. So, it is quite obvious that IPS takes a bit more energy to function than TFT.
Also, when you are using an IPS monitor, the screen will be much larger. So, as there is a need for much more energy for the IPS display to function, the battery of the device will drain faster. Furthermore, IPS panels cost way more than TFT display panels.
1. The best thing about TFT technology is it uses much less energy to function when it is used from a bigger screen. It ensures that the cost of electricity is reduced which is a wonderful plus point.
2. When it comes to visibility, the TFT technology enhances your experience wonderfully. It creates sharp images that will have no problems for older and tired eyes.
1. One of the major problems of TFT technology is that it fails to create a wider angle of view. As a result, after a certain angle, the images in a TFT screen will distort marring the overall experience of the user.
Although IPS screen technology is very good, it is still a technology based on TFT, the essence of the TFT screen. Whatever the strength of the IPS, it is a TFT-based derivative.
Finally, as you now have a proper understanding of the TFT displays vs IPS displays, it is now easier for you when it comes to choose one for your organization. Technology is advancing at a rapid pace. You should not be surprised if you see more advanced display screens in the near future. However, so far, TFT vs IPS are the two technologies that are marching ahead when it comes to making display screens.
STONE provides a full range of 3.5 inches to 15.1 inches of small and medium-size standard quasi TFT LCD module, LCD display, TFT display module, display industry, industrial LCD screen, under the sunlight visually highlight TFT LCD display, industrial custom TFT screen, TFT LCD screen-wide temperature, industrial TFT LCD screen, touch screen industry. The LCD module is very suitable for industrial control equipment, medical instruments, POS system, electronic consumer products, vehicles, and other products.

TFT LCD is a mature technology. OLED is a relatively new display technology, being used in more and more applications. As for Micro LED, it is a new generation technology with very promising future. Followings are the pros and cons of each display technology.
TFT Liquid Crystal Display is widely used these days. Since LCD itself doesn"t emit light. TFT LCD relies on white LED backlight to show content. This is an explanation of how TFT LCD works.
Relatively lower contrast:Light needs to pass through LCD glasses, liquid crystal layer, polarizers and color filters. Over 90% is lost. Also, LCD can not display pure black.
Organic Light-Emitting Diode is built from an electro-luminescent layer that contains organic compounds, which emit light in response to an electric current. There are two types of OLED, Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) and Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED). These driving methods are similar to LCD"s. PMOLED is controlled sequentially using a matrix addressing scheme, m + n control signals are required to address a m x n display. AMOLED uses a TFT backplane that can switch individual pixels on and off.
Low power consumption and flexible: OLED doesn"t rely on backlight and consumes less power. OLED is essentially created on plastic film. It is bendable and easy to process.
High contrast and vivid color: OLED emits light itself, can produce very bright image with beautiful color. And because OLED can be turned off, it can produce true black.
Stroboscopic effect: most OLED screen uses PWM dimming technology. Some people who are easy perceive stroboscopic frequency may have sore eyes and tears.
Micro LED, sometimes called μLED is made up of tiny LED, measure less than 100μm. Another way of looking at this is that MicroLEDs are simply traditional LEDs shrunk down and placed into an array.
Replacing organic material with inorganic GaN material eliminates the need of polarizing and encapsulation layer, found in OLED. Micro LED is smaller and thinner, consumes less power.
TFT Liquid crystal display products are diversified, convenient and versatile, simple to keep up, upgrade, update, long service life, and have many alternative characteristics.
The display range covers the appliance range of all displays from one to forty inches and, therefore, the giant projection plane could be a large display terminal.
In particular, the emergence of TFT LCD electronic books and periodicals will bring humans into the era of paperless offices and paperless printing, triggering a revolution in the civilized way of human learning, dissemination, and recording.
It can be generally used in the temperature range from -20℃ to +50℃, and the temperature-hardened TFT LCD can operate at low temperatures up to -80 ℃. It can be used as a mobile terminal display or desktop terminal display and can be used as a large screen projection TV, which is a full-size video display terminal with excellent performance.
The manufacturing technology has a high degree of automation and sound characteristics of large-scale industrial production. TFT LCD industry technology is mature, with a more than 90% mass production rate.
It is an ideal combination of large-scale semiconductor integrated circuit technology and light source technology and has good potential for more development.
From the beginning of flat glass plates, its display effect is flat right angles, letting a person have a refreshing feeling. LCDs are simple to achieve high resolution on small screens.

TFT is an abbreviation for Thin Film Transistor, a flat panel display used to improve the operation and utility of LCD screens. In order to portray an appearance to the audience, a liquid crystal display (LCD) utilizes a crystalline-filled fluid to modify rear lighting polarized origin through the use of an electromagnetic force among two relatively thin metal wires such as indium oxide (ITO). However, color TFT displays are associated with this method, which can be employed in both divided and pixelated display systems.
With motion pictures displayed on an LCD, the intrinsic sluggish rate of increase between liquid phases over a significant number of pixel components can be an issue due to capacitance impacts, which can create a blurring of the visuals. Placing a high-velocity LCD control device inside the formation of a thin-film transistor immediately next to the cell component just on a glass screen, the issue of LCD picture speed may be substantially improved, and image blur can be eliminated for all useful purposes entirely.
Organic light-emitting diodes (AMOLEDs) are a type of flat light-emitting advanced technologies that are created by interspersing a succession of organic thin sheets over two conducting conductors. An electrical charge causes a brilliant light to be produced when the current flows. AMOLED displays are light-emitting screens that do not require a backlight, making them thinner and more energy-efficient than liquid crystal displays (LCDs) (which will need a white backlight).
AMOLED displays are not only thin and fuel-intensive, but they also deliver the highest image quality available, so they can be made translucent, elastic, bendable, or even rollable and stretchy in the future, allowing for a variety of applications. AMOLEDs are a revolutionary technology in terms of display devices! It is possible to create an AMOLED by sandwiching a sequence of thin films across phase conductors. Electric charge causes a brilliant light to be emitted when the current flows through the coil.
The color display is fantastic. Color intensity, sharpness, and luminance settings that are second to none and can be customized to meet the needs of any application.
Half-Life has been expanded. TFT displays have a far longer half-life than its LED equivalents, and they are available in a number of sizes, which might have an effect on the device"s half-life based on the phone"s usage as well as other variables. Touch panels for TFT screens can be either resistant or capacitance in nature.
As it is more affordable than capacitive, resistive is typically the preferred option. However, capacitive technology is compatible with a wide range of contemporary smartphones and digital gadgets.
They rely on backlight to give illumination rather than generating their own light. Hence they require constructed light-creating diodes (LEDs) in their backlit display framework to ensure enough brightness.
Backlighting is unnecessary for AMOLEDs. LCDs produce images by selectively blocking parts of the illumination, whereas AMOLEDs produce light. AMOLEDs utilize less energy than LCDs since they don"t need backlighting. This is critical for battery-powered devices such as phones.
While AMOLED light-emitting sheets are lightweight, the substrate can also be elastic rather than stiff. AMOLED films are not limited to glass-like LEDs and LCDs.
AMOLEDs offer 170-degree ranges of vision. LCDs operate by obscuring the light. Hence they have intrinsic viewing obstacles. In addition, AMOLEDs have a substantially wider viewing spectrum.
AMOLEDs outperform LEDs. Since AMOLED organic coatings are less than LED inorganic crystal levels, AMOLED conducting and particle emitters layers can just be multi-layered. Also, LEDs and LCDs need glass backing, which absorbs light. AMOLEDs don"t need it.
AMOLEDs seem to be simpler to implement and larger. AMOLEDs are constructed of polymers and may be produced into big sheets. It takes a lot of extra liquid crystals to build and set down.
While red and green AMOLED sheets have a greater lifespan (46,000 to 230,000 hours), azure compounds have significantly shorter longevity (up to roughly 14,000 hours).
Due to the fact that AMOLED displays inherently emit illumination, they do not need a backlight when used on a monitor screen. Conversely, LCDs require backlights since the liquid crystals themselves are incapable of producing light under their own. Direct light emission from AMOLED displays also allows for the developing of lightweight display devices than others using TFT LCDs.
LCD displays have a higher brightness than AMOLED panels. This is owing to the LCD"s usage of led backlight, which may provide a brilliant illumination of the entire display. Despite the fact that AMOLEDs produce high levels of brilliance from their illumination, they will never be able to match the intensity of LCD lighting.
LCD screens use less power than AMOLED displays, which provides a slight advantage. The amount of energy consumed by AMOLED displays is dependent on the intensity of the screen. Lowered luminance results in lower energy usage, however, it might not be the best solution because the contrast would suffer as a result of the decreased brightness. In some situations, such as when to use an AMOLED device in direct sunlight, it is not an optimal situation.
However, the backlit keys of TFT displays account for the majority of their power usage. TFT screens" efficiency is considerably improved when the backlight is set to a lesser brightness level than the default setting. For example, replacing the light of an LCD TV with just an Led flash will have no effect on the image quality, but will result in lower power usage than replacing the light of an AMOLED TV.
With the exception of phones, numerous other technologies make use of displays to allow customers to engage in direct communication with them. To determine whether or not TFT LCD will be able to withstand the development of AMOLED innovation, we should first review the benefits of LCD technology. The backlighting quality ensures that whites are strong and brightness is superb but will deplete a battery much more quickly than just an AMOLED display. Furthermore, the cost of LCD screens is a considerable consideration. In addition to being less expensive and more easily accessible, they are produced in standard industry sizes, allowing them to be purchased for innovative products with relative ease.

TFT stands for thin-film transistor and is used with LCD to improve image quality over older digital display technologies. Each pixel on a TFT LCD has its own transistor on the glass itself, which offers greater control over the images and colors that it renders.
TFT is also an abbreviation for other technical terms including time from transmission, text fix test, Trinitron flat tube, and trivial file transfer protocol.
Since the transistors in a TFT LCD screen are so small, the technology offers the added benefit of requiring less power. However, while TFT LCDs can deliver sharp images, they also tend to offer relatively poor viewing angles. The result is that TFT LCDs look best when viewed head-on, but viewing images from the side is often difficult.
TFT LCDs are found on low-end smartphones as well as basic cell phones. The technology is also used on TVs, handheld video game systems, computer monitors, and GPS navigation systems.
All the pixels on a TFT screen are configured in a row-and-column format, and each pixel is attached to an amorphous silicon transistor that rests directly on the glass panel. This allows each pixel to be given a charge and for the charge to be kept even when the screen is refreshed to produce a new image.
With this type of setup, the state of a particular pixel is being actively maintained even while other pixels are being used. This is why TFT LCDs are considered active matrix displays (as opposed to a passive matrix displays).
Lots of smartphone manufacturers use IPS-LCD (Super LCD), which provides wider viewing angles and richer colors, but newer phones feature displays that utilize OLED or Super-AMOLED technology. For example, Samsung"s flagship smartphones boast OLED panels, while most of Apple"s iPhones and iPads come equipped with an IPS-LCD. Super LCD and Super-AMOLED have their own pros and cons, but they both far exceed the capabilities of TFT LCD technology.

Let us start with the basics first; refresh the knowledge about TN and LCD displays in general, later we will talk about TFTs (Thin Film Transistors), how they differ from regular monochrome LCD displays. Then we will go on to the ghosting effect, so we will not only discuss the technology behind the construction of the TFT, but also some phenomena, like the ghosting effect, or grayscale inversion, that are important to understand when using an LCD TFT display.
Next, we will look at different technologies of the TFT LCD displays like TN, IPS, VA, and of course about transmissive and transflective LCD displays, because TFT displays also can be transmissive and transflective. In the last part we will talk about backlight.
Let us start with a short review of the most basic liquid crystal cell, which is the TN (twisted nematic) display. On the picture above, we can see that the light can be transmit through the cell or blocked by the liquid crystal cell using voltage. If you want to learn more about monochrome LCD displays and the basics of LCD displays, follow this link.
What is a TFT LCD display and how it is different from a monochrome LCD display? TFT is called an active display. Active, means we have one or more transistors in every cell, in every pixel and in every subpixel. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, transistors that are very small and very thin and are built into the pixel, so they are not somewhere outside in a controller, but they are in the pixel itself. For example, in a 55-inch TV set, the TFT display contains millions of transistors in the pixels. We do not see them, because they are very small and hidden, if we zoom in, however, we can see them in every corner of each pixel, like on the picture below.
On the picture above we can see subpixels, that are basic RGB (Red, Green, Blue) colors and a black part, with the transistors and electronic circuits. We just need to know that we have pixels, and subpixels, and each subpixel has transistors. This makes the display active, and thus is called the TFT display. TFT displays are usually color displays, but there are also monochrome TFT displays, that are active, and have transistors, but have no colors. The colors in the TFT LCD display are typically added by color filters on each subpixel. Usually the filters are RGB, but we also have RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) LCD displays with added subpixels without the filter (White) to make the display brighter.
What is interesting, the white part of the RGB and RGBW screen will look exactly the same from a distance, because the lights are mixed and generate white light, but when we come closer to the screen, we will not see white light at all.
Going a little bit deeper, into the TFT cell, there is a part inside well known to us from the monochrome LCD display Riverdi University lecture. We have a cell, liquid crystal, polarizers, an ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) layer for the electrodes, and additionally an electronic circuit. Usually, the electronic circuit consists of one transistor and some capacitors to sustain the pixel state when we switch the pixel OFF and ON. In a TFT LCD display the pixels are much more complicated because apart from building the liquid crystal part, we also need to build an electronic part.
That is why TFT LCD display technologies are very expensive to manufacture. If you are familiar with electronics, you know that the transistor is a kind of switch, and it allows us to switch the pixel ON and OFF. Because it is built into the pixel itself, it can be done very quickly and be very well controlled. We can control the exact state of every pixel not only the ON and OFF states, but also all the states in between. We can switch the light of the cells ON and OFF in several steps. Usually for TFT LCD displays it will be 8-bit steps per color, so we have 256 steps of brightness for every color, and every subpixel. Because we have three subpixels, we have a 24-bit color range, that means over 16 million combinations, we can, at least theoretically, show on our TFT LCD display over 16 million distinct colors using RGB pixels.
Now that we know how the TFT LCD display works, we can now learn some practical things one of which is LCD TFT ghosting. We know how the image is created, but what happens when we have the image on the screen for a prolonged time, and how to prevent it. In LCD displays we have something called LCD ghosting. We do not see it very often, but in some displays this phenomenon still exists.
If some elements of the picture i.e., your company logo is in the same place of the screen for a long period of time, for couple of weeks, months or a year, the crystals will memorize the state and later, when we change the image, we may see some ghosting of those elements. It really depends on many conditions like temperature and even the screen image that we display on the screen for longer periods of time. When you build your application, you can use some techniques to avoid it, like very rapid contrast change and of course to avoid the positioning the same image in the same position for a longer time.
You may have seen this phenomenon already as it is common in every display technology, and even companies like Apple put information on their websites, that users may encounter this phenomenon and how to fix it. It is called image ghosting or image persistence, and even Retina displays are not free of it.
Another issue present in TFT displays, especially TN LCD displays, is grayscale inversion. This is a phenomenon that changes the colors of the screen according to the viewing angle, and it is only one-sided. When buying a TFT LCD display, first we need to check what kind of technology it is. If it is an IPS display, like the Riverdi IPS display line, then we do not need to worry about the grayscale inversion because all the viewing angles will be the same and all of them will be very high, like 80, 85, or 89 degrees. But if you buy a more common or older display technology type, like the TN (twisted nematic) display, you need to think where it will be used, because one viewing angle will be out. It may be sometimes confusing, and you need to be careful as most factories define viewing direction of the screen and mistake this with the greyscale inversion side.
On the picture above, you can see further explanation of the grayscale inversion from Wikipedia. It says that some early panels and also nowadays TN displays, have grayscale inversion not necessary up-down, but it can be any angle, you need to check in the datasheet. The reason technologies like IPS (In-Plane Switching), used in the latest Riverdi displays, or VA, were developed, was to avoid this phenomenon. Also, we do not want to brag, but the Wikipedia definition references our website.
We know already that TN (twisted nematic) displays, suffer from grayscale inversion, which means the display has one viewing side, where the image color suddenly changes. It is tricky, and you need to be careful. On the picture above there is a part of the LCD TFT specification of a TN (twisted nematic) display, that has grayscale inversion, and if we go to this table, we can see the viewing angles. They are defined at 70, 70, 60 and 70 degrees, that is the maximum viewing angle, at which the user can see the image. Normally we may think that 70 degrees is better, so we will choose left and right side to be 70 degrees, and then up and down, and if we do not know the grayscale inversion phenomena, we may put our user on the bottom side which is also 70 degrees. The viewing direction will be then like a 6 o’clock direction, so we call it a 6 o’clock display. But you need to be careful! Looking at the specification, we can see that this display was defined as a 12 o’clock display, so it is best for it to be seen from a 12 o’clock direction. But we can find that the 12 o’clock has a lower viewing angle – 60 degrees. What does it mean? It means that on this side there will be no grayscale inversion. If we go to 40, 50, 60 degrees and even a little bit more, probably we will still see the image properly. Maybe with lower contrast, but the colors will not change. If we go from the bottom, from a 6 o’clock direction where we have the grayscale inversion, after 70 degrees or lower we will see a sudden color change, and of course this is something we want to avoid.
To summarize, when you buy older technology like TN and displays, which are still very popular, and Riverdi is selling them as well, you need to be careful where you put your display. If it is a handheld device, you will see the display from the bottom, but if you put it on a wall, you will see the display from the top, so you need to define it during the design phase, because later it is usually impossible or expensive to change the direction.
We will talk now about the other TFT technologies, that allow us to have wider viewing angles and more vivid colors. The most basic technology for monochrome and TFT LCD displays is twisted nematic (TN). As we already know, this kind of displays have a problem with grayscale inversion. On one side we have a higher retardation and will not get a clear image. That is why we have other technologies like VA (Vertical Alignment), where the liquid crystal is differently organized, and another variation of the TFT technology – IPS which is In-Plane Switching. The VA and IPS LCD displays do not have a problem with the viewing angles, you can see a clear image from all sides.
Nowadays all TV sets, tablets and of course mobile phones are IPS or VA. You can turn them around and see the image clear from all sides. But, for monitor applications the TN technology is still widely used, because the monitor usually is in front of you and most of the time you look directly at it, from top, left or right side, but very rarely from the bottom, so the grayscale inversion viewing angle can be placed there. This technology still is very practical because it is affordable and has some advantages for gamers because it is very fast.
Apart from the different organization of the liquid crystals, we also organize subpixels a little bit differently in a VA and IPS LCD displays. When we look closer at the TN display, we will just see the subpixels with color filters. If we look at the VA or IPS display they will have subpixels of subpixels. The subpixels are divided into smaller parts. In this way we can achieve even wider viewing angles and better colors for the user, but of course, it is more complicated and more expensive to do.
The picture above presents the TN display and grayscale inversion. For IPS or VA technology there is no such effect. The picture will be the same from all the sides we look so these technologies are popular where we need wide viewing angles, and TN is popular where we don’t need that, like in monitors. Other advantages of IPS LCD displays are they give accurate colors, and wide viewing angles. What is also important in practice, in our projects, is that the IPS LCD displays are less susceptible to mechanical force. When we apply mechanical force to the screen, and have an optically bonded touch screen, we push the display as well as squeeze the cells. When we have a TN display, every push on the cell changes the image suddenly, with the IPS LCD displays with in-plane switching, different liquid crystals organization, this effect is lesser. It is not completely removed but it is much less distinct. That is another reason IPS displays are very popular for smartphones, tablets, when we have the touchscreens usually optically bonded.
If we wanted to talk about disadvantages, there is a question mark over it, as some of them may be true, some of them do not rely on real cases, what kind of display, what kind of technology is it. Sometimes the IPS displays can have higher power consumption than others, in many cases however, not. They can be more expensive, but not necessarily. The new IPS panels can cost like TN panels, but IPS panels definitely have a longer response time. Again, it is not a rule, you can make IPS panels that are very fast, faster than TN panels, but if you want the fastest possible display, probably the TN panel will be the fastest. That is why the TN technology is still popular on the gaming market. Of course, you can find a lot of discussions on the internet, which technology is better, but it really depends on what you want to achieve.
Now, let us look at the backlight types. As we see here, on the picture above, we have four distinct types of backlight possible. The most common, 95 or 99 per cent of the TFT LCD displays on the market are the transmissive LCD display type, where we need the backlight from the back. If you remember from our Monochrome LCD Displays lecture, for transmissive LCD displays you need the backlight to be always on. If you switch the backlight off, you will not see anything. The same as for monochrome LCD displays, but less popular for TFT displays, we have the transflective LCD display type. They are not popular because usually for transflective TFT displays, the colors lack in brightness, and the displays are not very practical to use. You can see the screen, but the application is limited. Some transflective LCD displays are used by military, in applications where power consumption is paramount; where you can switch the backlight off and you agree to have lower image quality but still see the image. Power consumption and saving energy is most important in some kind of applications and you can use transflective LCD displays there. The reflective type of LCD displays are almost never used in TFT. There is one technology called Low Power Reflective Displays (LPRD) that is used in TFT but it is not popular. Lastly, we have a variation of reflective displays with frontlight, where we add frontlight to the reflective display and have the image even without external light.
Just a few words about Low Power Reflective Displays (LPRD). This kind of display uses environmental light, ambient light to reflect, and produce some colors. The colors are not perfect, not perfectly clear, but this technology is becoming increasingly popular because it allows to have color displays in battery powered applications. For example, a smartwatch would be a case for that technology, or an electrical bike or scooter, where we can not only have a standard monochrome LCD display but also a TFT LCD color display without the backlight; we can see the image even in
You have app. 15% of the article left. That content is exclusive for our Riverdi University members only. Please fill out the Riverdi University Membership form below and join our community!
strong sunlight and not need backlight at all. So, this kind of TFL LCD display technology is getting more and more popular when we have outdoor LCD displays and need a low power consumption.
On the picture above, we have some examples of how transmissive and reflective LCD displays work in the sunlight. If we have a simple image, like a black and white pattern, then on a transmissive LCD display, even with 1000 candela brightness, the image probably will be lower quality than for a reflective LCD display; if we have sunlight, we have very strong light reflections on the surface of the screen. We have talked about contrast in more detail in the lecture Sunlight Readable Displays. So, reflective LCD displays are a better solution for outdoor applications than transmissive LCD displays, where you need a really strong backlight, 1000 candela or more, to be really seen outdoors.
To show you how the backlight of LCD displays is built, we took the picture above. You can see the edge backlight there, where we have LEDs here on the small PCB on the edge, and we have a diffuser that distributes the light to the whole surface of LCD screen.
In addition to the backlight, we have something that is called a frontlight. It is similar to backlight, it also uses the LEDs to put the light into it, but the frontlight needs to be transparent as we have the display behind. On the example on the picture above we can see an e-paper display. The e-paper display is also a TFT display variation, but it is not LCD (liquid crystal), it is a different technology, but the back of the display is the same and it is reflective. The example you see is the Kindle 4 eBook reader. It uses an e-paper display and a frontlight as well, so you can read eBooks even during the night.
Please remember to SUBSCRIBE to our YouTube channel and fill out the MEMBERSHIP FORM, to be informed about our Riverdi University materials and live events!
I agree to the Riverdi Sp. z o.o Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy. I also agree to receive emails from Riverdi Sp. z o.o and I understand that I may opt out of Riverdi Sp. z o.o subscriptions at any time.

Welcome to Riverdi University. In this lecture we will be talking about OLED displays. OLED displays are a little bit different than the TFT displays that we normally sell and Riverdi does not sell standard OLED displays. We sell them as custom modules only for particular projects. So, if you require an OLED display in your application, please contact us and for sure we will be able to find a solution for you and make the right display. Anyway, because we share the knowledge about displays, we have today’s University lesson about OLEDs because it is important to understand how they work and how to use them and just acknowledge this fantastic technology that exists and for sure in the future we will have standard displays based on OLED technology as well.
In the picture above we have a short agenda of the lecture. We will talk about basic rules, how OLED displays are built and how they differ from TFT modules. Then a little bit about physics and about application rules, how to use OLED displays. We will also talk about passive OLEDs, we will see the comparison between OLED technology and STN, which is a monochrome LCD, and a VFD which is the Vacuum Display. Vacuum Display is an old technology, but we can find some displays on the market that still use this this technology. We will talk about Active OLEDs that are AMOLEDs and Super AMOLEDs and last, we will talk about interfaces for OLED displays.
and just acknowledge this fantastic technology that exists and for sure in the future we will have standard displays based on OLED technology as well.
OLED is abbreviation from Organic Light Emitting Diode. It is like LED but based on organic materials. The emitting light is pretty much the same as with the LED, just the materials used here are different. They are not silicone based but organic based layers. As you can see the structure and construction is pretty simple, the physics here is like in any LED diode or laser diode. We have the recombination of electrons, so with the current they go to the higher levels energy states and then they go to the lower levels and emit light. Using various materials, we can generate distinct colors, and this is different than in TFT.
As you may remember from our TFT sessions, we said that TFT or LCD in general is just blocking the light from the backlight. Usually, the backlight in TFT is white. We block the light, or we transmit the light and to achieve the color in TFT we need to use color filters. Normally there are three color filters on the top of the TFT screen, which are RGB. For OLED screens it is different. We have a material that emits the color itself. So, using varied materials, we can emit distinct colors. If we have a full color OLED display which will typically be an AMOLED display, that you can see nowadays in mobile phones or tablets or even laptops or TV sets, it uses RGB cells or RGBW cells and then the colors are mixed. Remember that the OLED is emitting light itself, and we do not have any backlight.
In the picture above, you can see a simple comparison between a TFT display and an OLED display. The first thing that is always noticeable is that OLED display is much simpler. We have less layers than in a TFT. As you may remember from the TFT lecture it is pretty complicated. At first, we need a backlight, then we need some diffusers, light guides to prepare the light, we have polarizers, we have a TFT itself, which is simplified in the picture, and then we have color filters and the top polarizer. With OLED the construction is very simple. We need a base as the backbone for every display, then we have the emission layer and some conductive layers on the top and the bottom.
A passive display – PMOLED is very simple compared to an LCD monochrome display. An Active Matrix – AMOLED is more like a TFT and we additionally have transistors in the cells. But in the simplified version we do not have transistors, just simple layers and there is no color filters and no backlight. So, we have no back and no front layers, just the middle that is emitting light itself, and this gives us a really big advantage. Of course, it is simpler, it may be cheaper to build in mass production OLED displays, but if we do not have a backlight, that means if we do not emit any light, we have a true black background and this is a huge advantage of OLED displays, where we have a contrast in very high values. OLED displays are perfect displays to achieve high contrast. If we do not have reflected light or if we decrease the reflected light, we do not have the light that is coming from the backlight, because there is no backlight. If you have ever seen an OLED display, especially in a TV store, you could see OLED TV sets, from LG or Samsung or other brands, and you may notice that the contrast there is very high and the black is true black. It is even an unnatural thing to see that. The companies there use special demo movies where we have like the cosmos or something and the sun in the middle of the screen. You can see that the background is black, and it is true black. It is different than in TFT displays. If you have a TFT display next to the OLED display, you will notice the difference. The contrast in OLED is much higher because there is no backlight and no issue with the light that is going through TFT always, a little but always, that is the main difference.
In the picture above, we have the main advantages of OLED displays. We have excellent contrast, very high contrast. As you can see the background is really black and it looks like that in reality, not only in the photo. No backlight, high brightness, we can achieve pretty high brightness of the pixels in OLED, we have fantastic color reproduction, because we do not use color filters, we are able to generate very saturated colors in a wide gamut. Typically, OLEDs have the widest gamut color on the market, and it is really superior to a typical TFT
We can also achieve this with a TFT, with special color filters or Quantum Dot filters, but in general OLED is superior here without any special effort. The true black is related to the contrast. Super viewing angles, that is another advantage over the TFT. If we have a typical TFT, a TN display discussed in the previous lectures, we have grayscale inversion from one viewing angle. Then we have displays like IPS or MVA types, where we can see a picture from all the viewing angles but still the viewing angle would be like 85 degrees 87 or the best would be up to 89 degrees. In OLED displays we have 89 degrees without any effort because it is like a LED diode. It emits light, and we can see exactly the same from all the viewing angles. OLEDs can be very thin, because there are only a few layers, no backlight, no front layers, so they can be very thin and very light. We can build OLED displays on elastic surfaces that we can bend or can be curved, for example Samsung foldable mobile phones or some curved LG TV sets. OLEDs have low power consumption. If we have an LCD or a TFT, we need a backlight. The backlight is consuming a lot of power because the light is being consumed by all the layers that th




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey