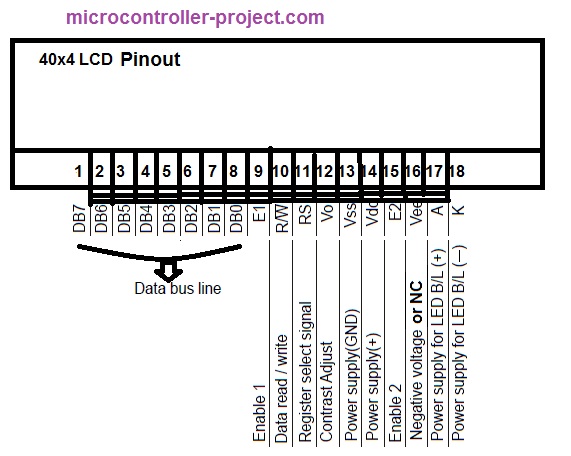
lcd panel pinouts diagram price
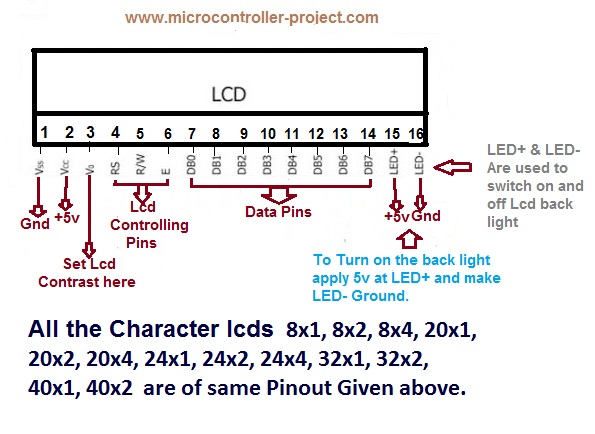
We come across Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) displays everywhere around us. Computers, calculators, television sets, mobile phones, and digital watches use some kind of display to display the time.
An LCD screen is an electronic display module that uses liquid crystal to produce a visible image. The 16×2 LCD display is a very basic module commonly used in DIYs and circuits. The 16×2 translates a display of 16 characters per line in 2 such lines. In this LCD, each character is displayed in a 5×7 pixel matrix.
Contrast adjustment; the best way is to use a variable resistor such as a potentiometer. The output of the potentiometer is connected to this pin. Rotate the potentiometer knob forward and backward to adjust the LCD contrast.
A 16X2 LCD has two registers, namely, command and data. The register select is used to switch from one register to other. RS=0 for the command register, whereas RS=1 for the data register.
Command Register: The command register stores the command instructions given to the LCD. A command is an instruction given to an LCD to do a predefined task. Examples like:
Data Register: The data register stores the data to be displayed on the LCD. The data is the ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD. When we send data to LCD, it goes to the data register and is processed there. When RS=1, the data register is selected.
Generating custom characters on LCD is not very hard. It requires knowledge about the custom-generated random access memory (CG-RAM) of the LCD and the LCD chip controller. Most LCDs contain a Hitachi HD4478 controller.
CG-RAM address starts from 0x40 (Hexadecimal) or 64 in decimal. We can generate custom characters at these addresses. Once we generate our characters at these addresses, we can print them by just sending commands to the LCD. Character addresses and printing commands are below.
LCD modules are very important in many Arduino-based embedded system designs to improve the user interface of the system. Interfacing with Arduino gives the programmer more freedom to customize the code easily. Any cost-effective Arduino board, a 16X2 character LCD display, jumper wires, and a breadboard are sufficient enough to build the circuit. The interfacing of Arduino to LCD display is below.
The combination of an LCD and Arduino yields several projects, the most simple one being LCD to display the LED brightness. All we need for this circuit is an LCD, Arduino, breadboard, a resistor, potentiometer, LED, and some jumper cables. The circuit connections are below.
Abstract: OmniVision CMOS Camera Module rs232 toshiba hdd schematic board GIANTPLUS apple ipod touch schematic diagram tft ipod touch 2 Omnivision OV2640 21 inch Lcd tv circuit schematic diagram NORFLASH schematic diagram of bluetooth headphone
Text: development. An LCD display panel is supplied with the 3-Stack. Figure 1-1 shows the major components of the 3-Stack boards. LCD Display CPU Engine Board Debug Board Personality Board Figure 1-1 , J14 Epson VGA LCD connector J15 Giantplus QVGA Smart display connector J18 mini USBOTG , -Stack should boot and the Windows CE operating system should appear at the Personality board"s LCD display , " 30GB ATA HDD KeyPad LCD /Touch ATA HDD TV Encoder CSI TV /Headphone Jack Chrontel
Abstract: OV2640 Camera Module Hardware schematic diagram usb flash sandisk apple ipod touch schematic diagram tft ipod touch 2 touch screen ipod 40 pin zif connector USB3317 OV26 GIANTPLUS
Text: Joint Test Access Group LAN Local Area Network LCD Liquid Crystal Display LED Light Emitting Diode , board can be run in stand-alone mode for code development. An LCD display panel is supplied with the 3-Stack system. Figure 1-1 shows the major components of the 3-Stack system. LCD Display CPU Engine Board , connector, for USB OTG connection J14 Epson VGA LCD connector J15 Giantplus QVGA Smart display , operating system should appear at the Personality board"s LCD display . Software development mode: ·
Abstract: ov2640 apple tv a4 chip ipod touch circuit diagram USB3317 tft ipod touch 2 GIANTPLUS 32 inch LCD TV SCHEMATIC schematic diagram usb flash sandisk ipod lcd pcb connector
Text: stand-alone mode for code development. An LCD display panel is supplied with the 3-Stack system. Figure 1-1 shows the major components of the 3-Stack system. LCD Display CPU Engine Board Debug Board , connector, for USB OTG connection J14 Epson VGA LCD connector J15 Giantplus QVGA Smart display , system should appear at the Personality board"s LCD display . Software development mode: · Assemble , Accelerometer Tilt Sensor 1.8" or 2.5" 30GB ATA HDD KeyPad LCD /Touch ATA HDD TV Encoder CSI
Abstract: lcd 40 pin diagram lvds ya0m VR12 INTEL dvi to lvds lcd N7 lvds 20 pin lcd panel T3D 34 diode lvds 30 pin lcd panel notebook LCD Panel Control Signal
Text: . 23 4.1. 4.2. 4.3. 5. 5.2. 82807AA VCH LCD Display Modes , VCH 10 R Datasheet 82807AA VCH R 2. Product Features LCD Display · Supports , PCI Bus LVDS or CMOS LCD ICH2-m LAN (Phy) Audio Modem TV TV Encoder and/or DVI , through a DVO port. The display image is then converted to the selected LCD panel interface format. The , TV encoder for TV displaying, or to an external DVI transmitter for DVI Display support. All
Text: PF977-04 S1D13506F00A Color LCD /CRT/ TV Controller s DESCRIPTION The S1D13506 is a color LCD /CRT/ TV graphics controller interfacing to a wide range of CPUs and display devices. The S1D13506, register address space. x Display Support · 4/8-bit monochrome or 4/8/16-bit color LCD interface for , modes on color passive LCD panels using dithering. · Up to 64K colors on TFT/D-TFD, CRT and TV . · 4/8 , 4096 colors. · Separate LUTs for LCD and CRT/ TV . 1 S1D13506F00A· 15/16 bit-per-pixel color
Text: 8 10 12 14 NC TX3+ LCD_VDD TX1TXCTX0+ TX2+ X2 Connectors X2 MSM800 LCD interface J1 LVDS connector Pinout of X2 (MSM800 LCD interface) 1 2 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 , \msm800\manual\ Driver Not required Not required Pinout of J1 (15 Pin Male DSUB connector) 1 6 , settings on the baseboard can damage the LCD Digital-Logic AG | Nordstrasse 11/F | CH , settings for LCD output on the LCD port: - Power up the system - Enter BIOS setup (Press the F1 key to
Abstract: LCD tv display pinout diagram ST20 boot Epson matrix ccd line BGA196 Casio 1.8 colour TFT Matrix CCD "line sensor" Epson ST20 manual SENSOR rgb f13 Casio 1.8" colour TFT
Text: on-chip digital to analog converter q TV display of pictures and clips October 2003 ADCS , NAND SDRAM 2/30 LCD STV0684 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Functional Block Diagram . . , . 22 3.7 LCD controller - Display interface , T2 LCDC LCD Boot ROM Dot selector TVC Audio fifo DMA DMA ADC TV AUDIO , LCD interface TV interface: total 5 pins UOUT D12 CVBS out REXT B14 TV Reference
Abstract: OV2640 32 inch LCD TV SCHEMATIC apple ipod battery tft ipod touch 2 apple tv a4 chip touch screen ipod GIANTPLUS lcd mx27 dc power supply connector USB3317
Text: Area Network LCD Liquid Crystal Display LED Light Emitting Diode MB Megabyte MCU , stand-alone mode for code development. An LCD display panel is supplied with the 3-Stack system. Figure 1-1 , board"s LCD display . Software development mode: · Assemble the three boards together. · Plug the 5.0 , KeyPad Connector I2C LCD /Touch ATA HDD TV Encoder CSI TV /Headphone Jack Chrontel , data enable Active high PA3 TV out and LCD reset Active low PA31 LCD Data Enable
Abstract: how to wire vga to rca jacks RJ45INTLED TD043MTEA1 rca TO VGA pinout CPLD-EPM2210F324 schematic diagram video converter rca to vga schematic diagram vga to composite vga to rca schematic schematic diagram vga to rca cable connector
Text: . 210 LCD Touch Panel Display , Components and Block Diagram The LCD Multimedia HSMC contains the following components. Altera , FineLine BGA package LCD Touch-screen Display 800 X 480 pixel 4.3" Display 13 LCD Multimedia HSMC , Block Diagram Figure 15 shows a functional block diagram of the LCD Multimedia HSMC. 14 LCD , MAX 3378 Dual Low-Voltage Level Translators 28 LCD Touch Screen Display J10 +Touchscreen
Text: S1D13506 Color LCD /CRT/ TV Controller Hardware Functional Specification Document Number: X25B-A, Display Mode Registers . . . . . CRT/ TV Configuration Registers . . . CRT/ TV Display Mode Registers . . . LCD Ink/Cursor Registers . . . . . . . CRT/ TV Ink/Cursor Registers . . . . BitBLT Configuration , . . . . . . . . 13.5 TV Image Display and Positioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . , LCD and CRT (800x600) with EISD Enabled . . . . 18.2.5 Frame Rates for LCD and NTSC TV with EISD
Text: port. Pinout of X1 (MSM800 LCD interface) 1 2 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41 43 Pinout of P1 (DVI connector) 43 44 DE NC +3.3V NC NC D_B1 , \msm800\manual\ Driver Not required Not required P1 X1 Connectors X1 MSM800 LCD , Bios Version : V0.1 Revision :- MSM800 BIOS settings for DVI output on the LCD port: - Power , Graphics Memory: 024 Driver controls init: Disabled Output Display : Auto DOTPLL Bypass: Disabled
Text: . See Figure S. LCD DISPLAY PAN EL PINOUT DESCRIPTION Pin No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 , LCD D IS P L A Y , LED B A C K LIG H T , OPTICS O PTICS Product P review QVGA Color LCD Display , PVV001MQC Module is a virtual display assembly comprised of an LCD transmissive panel, LED backlight source , describe the three components. TABLE OF CONTENTS LCD Display P anel , .18 M O TO R O LA 3 PW O 0 1 M Q C R ev 0 PVV001 M Q C LCD DISPLAY PANEL The LCD panel
Text: . . . . . LCD Display Mode Registers . . . . . CRT/ TV Configuration Registers . . . CRT/ TV Display Mode Registers . . . LCD Ink/Cursor Registers . . . . . . . CRT/ TV Ink/Cursor Registers . . . . BitBLT , -bit Single LCD Display Power S1D13506 GPIOx CRT/ TV Display BUSCLK RESET# RESET# MA[8:0 , S1D13506 Color LCD /CRT/ TV Controller Hardware Functional Specification Document Number: X25B-A, . . . . . . . . . 13.5 TV Image Display and Positioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Text: . 8GB Gigabit Ethernet CRT, Up to 24-bit Dual-channel LVDS LCD , TV , Display Port, HDMI, DVI High , ) Operating Humidity 0% ~ 90% relative humidity, non-condensing MTBF (Hours) â Display Supports CRT/ LCD , CRT/ TV , CRT/DVI, LCD / TV , LCD /DVI simultaneous/ dual view displays Chipset Intel , Wide DC Input Range, +8.5V to +19V COM Express Basic Module Pin-out Type II Specifications System I/O Form Factor COM Express basic module, Pin-out Type II Storage SATA II x 4
Abstract: circuit diagram of flash bios LCD tv display pinout diagram intel 945 circuit diagram lcd tv screen pinout philips crt pinout circuit diagram of usb memory card to tv monitor intel chipset 945 circuit ICH7-M n270 945GSE circuit
Text: Technology Max. Capacity Socket Chipset VRAM Graphics Engine LCD VGA TV Out SDVO Dual Display Chipset Speed COM-Express Basic Module, Type II Pin-out Intel Atom Processor N270 1.6 GHz 533 MHz Intel 945GSE/ ICH7M AWARD , is supported by customized BIOS) CRT + LCD , TV out + LCD , TV out + CRT Intel 82574L Gigabit Ethernet , -bit LVDS TFT LCD Supports one DDR2-533 memory SODIMM socket up to 2 GB Supports 3 PCIe x1, 4 PCI Master , (4.92" x 3.74") Memory Display Ethernet WatchDog Timer Expansion I/O Power Environment
Abstract: SOM-6761Z-S6A1E s-video TO VGA MONITOR PINOUt circuit diagram of usb memory card to tv monitor lcd tv Philips 32 power supply diagram pin diagram intel atom SOM-6761 circuit diagram of flash bios philips lcd tv 32 power board 945gseich7m
Text: Technology Max. Capacity Socket Chipset VRAM Graphics Engine LCD VGA TV Out SDVO Dual Display Chipset Speed COM-Express Compact Module, Type II Pin-out . Embedded Intel Atom Processor N270 1.6 GHz 533 MHz Intel 945GSE, , TV out + LCD , TV out + CRT (Note: SDVO function is supported by customized BIOS) Intel 82574L Gigabit , used to adjust the LCD brightness. Display Power Saving The Brightness Control API allows a , -bit LVDS TFT LCD Supports one DDR2-533 memory SODIMM Socket up to 2 GB Supports 3 PCIe x1, 4 PCI Master
Abstract: LCD tv display pinout diagram HITACHI lcd tv power supply diagrams sharp lcd panel pinout 30 Pinout panel lcd lcd color 176 132 Hsync Vsync RGB signal LCD laptop 8 Pinout monochrome lcd 14 laptop lcd pin configuration WD90C20
Text: VGA flat-panel display controllers and a variety of LCD color display pan els. The WD90C55 also acts , use color or monochrome LCD panels. The WD90C55 interfaces with the following VGA flatpanel display , flat-panel display controllers and a variety of LCD panels. Including TFT and STN color panels. It also acts , from the VGA flat-panel display controllers are passed along to LCD monochrome panels. These inter face , tables and pin diagrams are provided. 3.1 WD90C55 PINOUT Pinout diagram Pin Number to Signal list Pin
Abstract: color crt tv schematic diagram SHARP CRT TV MAIN PROCESSOR, QFP 80 26 Pin GPIO Connector Header Extender 90 Degree Angle MIPS PR31700 S1D13806F00A specification of transistor eb 102h Transistor VMP4 schematic diagram crt tv panasonic
Text: LCD /CRT/ TV graphics controller with embedded memory supporting a wide range of CPUs and display , .1-8 4.1 4.2 Pinout Diagram , . 1-91 8.4.7 LCD Display Mode Registers , . 1-101 8.4.9 CRT/ TV Display Mode Registers , . 1-146 13.4.1 TV Image Display and Positioning
Text: , non-condensing MTBF (Hours) 100,000 Display Supports CRT/ LCD , CRT/ TV , LCD / TV simultaneous/ dual view , -bit Dual-channel LVDS LCD , TV High Definition Audio Interface PATA x 1, SATA II x 3 USB2.0 x 8 PCI x 4 , Pin-out Type II GME965 Specifications System Form Factor COM Express basic module, Pin-out Type , Resolution Up to 2048 x 1536 (QXGA) @ 60Hz for CRT Up to 2048 x 1536 (QXGA) for LCD LCD Interface
Text: for multi-purpose LCD TV and PC display systems. It contains all the logic required to convert , inputs allow digital TV or digital VGA monitor signals to be input for display on the same LCD display , PC display and LCD / TV entertainment systems. The TW88 contains all the logic required to convert , Techwell, Inc. TW88 LCD Flat Panel TV / PC Monitor Controller with Analog NTSC/PAL/SECAM , . TECHWELL, INC. 1 04/02/2001 REV. 0.94 PRELIMINARY TW88 LCD FLAT PANEL TV / PC MONITOR CONTROLLER
Text: 40 VOUT = 25 V IOUT (mA) Figure 18.Load Regulation for LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , 60 80 100 IOUT (mA) Figure 19. Load Regulation for LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Varactor Diode Bias. Using 5 V input. VOUT 5 VIN VSUPPLY C1 1 µF EN 4 Enable Cf 0.01 µF L1 10 µH 1 SW D1 C2 0.22 µF VC Analog Voltage or PWM R1 47 Figure 4. LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Varactor Diode Bias. Using 12 V input. VOUT 5 VIN L1 10 µH 1 SW D1 R1 560 k
Text: . LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Varactor Diode Bias. Using 12 V input. VOUT VOUT Li-ion , Figure 3. LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Varactor Diode Bias. Using 5 V input. L1 10 µH R1 , ) Figure 18.Load Regulation for LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Varactor Diode Bias; VSUPPLY = 5 V , . Load Regulation for LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Varactor Diode Bias; VSUPPLY = 12 V (circuit , £ Ramp Generator EN Enable 1.2 MHz Oscillator GND Device Pin-out Diagram Terminal List
Abstract: SOT95P panasonic plasma tv circuit diagram OLED tv BLOCK diagram oled tv SOT-95 SOT-95p280 plasma tv circuit diagram LCD tv display pinout diagram SON95P300X310-7WEEAN
Text: µF / 50 V C3 0.1 µF Figure 3. LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Varactor Diode Bias. Using 5 , Voltage or PWM R1 47 Figure 4. LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Varactor Diode Bias. Using 12 V , 40 VOUT = 25 V IOUT (mA) Figure 18.Load Regulation for LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , 60 80 100 IOUT (mA) Figure 19. Load Regulation for LCD TV , Plasma TV Bias, FED Display , Internal power FET Ground Feedback input Enable input Input supply Device Pin-out Diagram SW 1 GND 2
Text: CONVERTERS /D DISPLAY C M Operating Supply Voltage Range, V+ CA3162, CA3162A Timing Diagram , N A CONVERTERS /D DISPLAY Figure 3 shows the CA3162E in a typical LCD application. LCDs may , CA3162 fSH H MAC O N DRC T O R R U IS U L I SE I A/D Converter for 3-Digit Display , * and a minimum of external parts to imple ment a complete 3 digit display . The CA3162AE is identical to the CA3162E except for an extended operating tempera ture range. ⢠Multiplexed BCD Display
Abstract: lcd tv block diagram 5X7 LCD internal block diagram of a tv LCD Display pin diagram simple circuit diagram of tv pal lcd display lcd tv controller sed1330
Text: S E D 1 3 3 6 F oa CMOS GRAPHIC LCD / TV CONTROLLER · · · · · For Medium-scale LCD Output to LCD-Screen Virtual Screen Display RAM Enhanced Control Function Simultaneous LCD & TV Display DESCRIPTION , can display the same screen as an LCD display on a TV as well. In addition, it has built-in a simple , Display s iz e . LCD : 640 x 256 dots (Max) TV : 256 x , :. LCD 64 x 256 max TV 2 5 6 x2 0 0 T V

Text: .8 3-4 44-Pin Package LCD Panel Pinout Spec , . 13 3-8 48-Pin Package LCD Panel Pinout Spec , direct Sharp TFT N/A direct direct direct TABLE 1-1 COLOR LCD IMPLEMENTATION PRODUCT , -Bit STN Panels ( Sharp , Seiko) 010 16-Bit STN Panels (Sanyo) 100 Monochrome LCD Panels 1 01 , drive the Sharp TFT color LCD directly without WD90C55. 19-8 ADVANCED INFORMATION 11126191
Text: .16 Flat Panel Header Pinout (P8B) - SHARP .16 LCD Power Supply Header Pinout (P8C , 3-3. Flat Panel Header Pinout (P8B) - SHARP Pin Function Pin 2 Function 1 For +10V or , 3 - Connectors and Headers Table 3-3. Flat Panel Header Pinout (P8B) - SHARP (continued) Pin , LCD power supply header pinout . Table 3-4. LCD Power Supply Header Pinout (P8C) Pin 1 Function
Abstract: LCD tv display pinout diagram HITACHI lcd tv power supply diagrams sharp lcd panel pinout 30 Pinout panel lcd lcd color 176 132 Hsync Vsync RGB signal LCD laptop 8 Pinout monochrome lcd 14 laptop lcd pin configuration WD90C20
Text: monochrome or CONTROLLER TYPE PANEL TYPE STN Color LCD Hitachi TFT Sharp TFT WD90C20 with WD90C55 with , , WD90C20A, WD90C26, and WD90C26A can drive the Sharp TFT color LCD panel directly. 2.7 COLOR PANEL INTERFACE , /Package Descriptions Bus Definition LCD Panel Pinout Specification This section contains the following , NOTE: The WD90C22 controller can drive the Sharp TFT color LCD directly without the WD90C55 device , -BIT STN 8-BIT STN ( Sharp ) (Seiko) MONO LCD SEL|2:0] SEL[2:0] SIGNAL SEL[2:0] PIN =001 =001 NAME =100 NO
Abstract: AA11SB6C-ADFD lt121s1-153 nec lcd inverter schematic schematic logic board lcd monitor samsung 18,5 in samsung lcd inverter pinout LVDS connector 20 pins LCD FUJITSU 12.1 sharp lvds connector pinout RV801 LQ10DS05
Text: Receiver for Sharp XGA LCD Panels . 19 Figure 17: Genesis LVDS , . 21 Table 11: LVDS Card CN3 ( Sharp ) Output Connector Pinout , FRONT BACK Figure 16 : Genesis LVDS Receiver for Sharp XGA LCD Panels For Sharp XGA Panels , : LVDS Card CN3 ( Sharp ) Output Connector Pinout PIN # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 , LCD Panels Table 12: LVDS Card CN4 (Samsung) Output Connector Pinout PIN # 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Text: half the display resolution. 5.8 LCD Panel Interface Table 6: Backlight Connector J801 Pinout Pin # 1 , BACK User Guide Z1FCEV Reference Design FRC LCD Controller Board SED- 0068- C March , Genesis Microchip Z1FCEV Reference Design Z1FCEV Reference Design - FRC LCD Controller User Guide , . 23 5.8 LCD Panel Interface , -bit . 27 5.8.6 LCD Output Formats
Text: LM64032 Additional Info The Datasheet only gives pinout information for a 10 Pir. connector whirh is in the centre of the LCD Pcb. My LCD actually has a 2nd conneztor which is a 14 Pin this is , 11 8 12 9 13 10 Simon Hampton (23-06â99) 21-JUN-99 MON 11:54 SHARP ELECTRONICS UK P. 08 ?«£?AãD Bf: DATE SPEC n* LC 62 921 A SHARP FILE So. APPROVED BY: DATE . . ^ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS GROUP """ SHARP CORPORATION : " ; * SPECIFICATION »sue Sep. 5.198 7 PACE . . = â¢â¢â -. .
Text: LCD Display Connector 60 pin integrated LCD , touch & backlight connector (see Sharp Display Kits , handheld and compact products. provides a common reference pin-out on its expansion connectors, which , Processor Sharp LH75401 16/32 bit ARM7TDMI RISC microprocessor running up to 51.6 MHz SRAM Memory Up to 2 Mbytes Flash Memory Up to 16 Mbytes on board Display Programmable color LCD controller - Built in , I T S Integrated LCD /Touch/Inverter Connector Logic offers the following display kits
Text: × 32 (also serve as functional pins) · LCD controller Frame buffer resides in system memory LCD display modes · · · · · · · · · Integrated Circuits Group · 1 bit/pixel binary mode · Gray mode, 4-level 2-bits/pixel and 16-level 4-bits/pixel LCD display data, 4, 2, 1 , : Overrun SIR (Serial Infra-Red Interface) Using UART IrDA SIR (version 1.0) compatible Sharp DASK , . Copyright ©1998, Sharp Electronics Corp. All rights reserved. All tradenames are the registered property of
Abstract: notebook display tft pinout 65520 cga to vga chips F8680 cga to vga interface chips 65520 flat panel vga notebook display pinout 82C426 Sharp EL Displays
Text: , Sharp Electronics cannot guarantee the accuracy of the information presented. LCD Application Note , up to 1280 x 1024 16 grayscales or 800 x 600 64 grayscales on Sharp "s monochrome LCD and EL panels , Sharp "s color TFT LCD . Table 2. CHIPS 82C9001A PC Video Windowing Controller FEATURES BENEFITS , Sharp "s color TFT LCD . The 82C457 increases the color palette of Sharp "s 512-color TFT LCDs to 24,389 , LCD Application Note Liquid Crystal Displays FLAT PANEL DISPLAY CONTROLLERS FOR PC
Text: External Connections: G 40-pin header for flat panel display, pinout per Sharp LM64P101 monochrome panel , cost PC/104 operator interface solution. It allows flat panel LCD displays to be driven with standard , [See Section 1] LCD Panels Kits, FPKIT-xxx [items above in Section 4] Flat panel displays VGA CRTs , . Typical panels: LG Semicon: LP064V1 color Sharp : LM64K103 mono Read/Write Control AT KBD , Monochrome Panel Kit FPKIT-C02 Active Color Panel Kit CA4029-X Family of cables to LCD panels CA4030
Abstract: cga to vga circuits cga to vga circuit VGA 65530 cga to vga monitor circuits cga ega vga TFT Display controller F8680 chips F8680 apple lcd pinout 65530
Text: grayscales on Sharp "s monochrome LCD and EL panels. The 65520 increases the color palette of Sharp "s 512 , window on a CRT monitor and Sharp "s color TFT LCD . Table 2. CHIPS 82C9001A PC Video Windowing , simultaneously on a CRT monitor and Sharp "s color TFT LCD . The 82C457 increases the color palette of Sharp , Liquid Crystal Displays LCD Application Note FLAT PANEL DISPLAY CONTROLLERS FOR PC , widely different from the CRT. In addition, all of the flat display technologies, LCD , EL and Plasma
Abstract: ncr 53c400 lmg5160xufc 53C400 24 pin 8x8 mono colour Dot Matrix led Display LM64P70 LCM5474-24 SANYO LCM 5483-24 LM64p722 SHARP LCD MATRIX LQ10DH11
Text: . LCD Sharp LMP6470 Planar EL600.400-C 2.8.3 Power Supply for Panels The voltages on connector P6 can be , .12 2.3.3 Pinout of the Floppy Connector , .16 2.4.7 Pinout of the SCSI Interface , .19 2.5.6 Pinout of the IDE Interface , .22 2.6.5 Pinout of the Parallel Interface
Abstract: samsung crt monitor rgb pinout samsung lcd monitor power supply circuit diagram LVDS sony lcd panel Genesis Gmz1 LVDS connector 20 pins LCD FUJITSU lcd sony panel pinout connector 26 pin VGA to RCA and S-Video Pin-out blue BOX sharp lvds connector pinout LVDS connector 26 pins LCD
Text: the display resolution. 5.8 LCD Panel Interface Table 6: Backlight Connector Pinout (J1) Connector J1 , driving the Z1EV circuit, LCD , and backlight. Table 18: Power Supply Connector Pinout (J4) Pin Name +5V , BACK Preliminary User Guide Z1EV Reference Design LCD Controller Board SED , / info@genesis-microchip.on.ca Genesis Microchip Z1EV Reference Design Z1EV Reference Design LCD Controller Preliminary , . 21 5.8 LCD Panel Interface
Abstract: schematic diagram tv sharp ADS7486 S1L50282F23K100 sharp lcd panel pinout transistor D400 SERVICE MANUAL tv sharp sharp lcd service manual NL2432DR22-11B tv schematic diagram SHARP power supply
Text: . . . . . 10 Sharp LCD Timing Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . , Sharp LCD Frontlight Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . , . . . . . . . . . . . 11 Sharp LCD Control Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Sharp LCD OMA5910 Interface . . . , shows the pinout of the timing controller. Connecting TFT LCD Displays to the OMAP5910 5
Abstract: PC28F640P33 sharp 21A U12 circuit diagram HP 30 pin lcd flex cable pinout C117 S4 87A CB-502 sharp CMOS Camera Module CSI 74LVC254 IC SOCKET TSOP48 SMT
Text: dimension .81 14.6 Sharp LQ035Q7DH06 LCD Adapter.81 14.6.1 , ) .65 14.5.17 Universal LCD pin header (X23) .66 14.5.18 Serial LCD (X24 , Figure 4: Pinout of the phyCORE-Connector (Top View, with Cross Section Insert , .64 Figure 18 - LCD Adapter connector location .81 Figure 20 , PHYTEC Messtechnik GmbH 2007 L-700e_0 phyCOREi.MX31 Index of Tables Table 1: Pinout of the
Abstract: LM64C35 Xilinx lcd display controller TFT LCD display Human Machine Interface schematic LJ64H034 VHDL code for dac 128X64* control LMG9520 sharp lcd panel pinout LQ121s1dg11
Text: external register Supports Electroluminescent, Plasma, LCD and CRT displays Support for two video pages , , e.g., various LCD technologies (TNM, STNM, TFT, analogous RGB TFT), electroluminescent displays and , LQ10D36 LQ121S1DG11 LQ150X1DG11 CRT Producer Sharp Sharp Sharp Sharp Sharp Sharp NEC Sharp Sharp Sharp Resolution 320 x 240 B/W 320 x 240 Col STN 320 x 240 Col TFT 640 x 400 Elumin 640 x , TFT 640 x 480 VGA Pinout Signal names are shown in Figure 1 and described in Table 3
Abstract: 04-6298-006-000-883 UL21147 LQ070Y3DG3B SML2CD sharp lcd panel pinout Equivalent Diode sr3a SUMITOMO FFC 15 PIN 04-6277 SUMITOMO FFC 20 PIN 0.5 pitch
Text: Technical Document LCD Specification LCD Group LQ070Y3DG3B LCD Module Product , panel driving Correct the pinout of touch panel FPC. 8-1. Timing characteristics Correct Phase , LD21305B-1 These specification sheets are the proprietary product of SHARP CORPORATION(" SHARP ) and include materials protected under copyright of SHARP . Do not reproduce or cause any third party to , , without the express written permission of SHARP . In case of using the device for applications such as
Abstract: "Infrared TRANSCEIVER" sharp lcd pinout RY6FD11E infrared receiver led 2 pin electronic level transmitter construction diagram encoder output waveform infrared signal waveform Infrared Transceiver
Text: RY6FD11E/RY6FD1SE Technical Information Infrared Transceiver Module FEATURES The Sharp , devices (IrDA 1.0) and SHARP ASK · Compatible with Slower Speeds · Achieving the Longer Communication , DESCRIPTION The Sharp RY6FD11E and RY6FD1SE are 5.0 V infrared transceiver modules, providing the interface , Infrared Transceiver Module RY6FD11E/RY6FD1SE Table 1. Circuit Pinout PIN PINOUTS DESCRIPTION , RY6FD11E-10 Figure 5. Pinout Diagram Table 3. Pinouts PIN DESCRIPTION SYMBOL Analog Vcc
Text: LH77790A/B Thermal & Electrical Specification (Version 1.0) SHARP Table 2-2. Pinout PIN 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 , 1.0) Page 25 SHARP Table 15. LCD Controller Parameter Description PARAMETER DUTY1 BC1 CP1W1 , Electrical Specification (Version 1.0) SHARP Table 16. Typical AC Timing for LCD Controller (3.3 V and , SHARP S H A R P rese rves the right to m ake cha ng es in sp e cifica tio n s de scrib ed herein at , Sharp . T he w a rra n tie s se t forth herein are in lieu of, and exclusive of, all o th e r w a rrantie
Text: 1.0) SHARP Table 15. LCD Controller Parameter Description PARAMETER DESCRIPTION DUTY1 Number of CP1 , support tools are crucial to reducing time-to-market. The SYSTEM ON CHIP Team at Sharp has designed the , engine, a number of essential peripherals (UARTs, Counter/Timers, PIOs, PWMs, etc.), LCD controller , instruction set, and very low power RISC core provide high performance at low current draw. The on-chip LCD , check our website at www.sharpsma.com or with your local SHARP sales office for the latest Thermal and
Text: Electrical Specification 5 LH77790B SHARP Table 1. Pin Descriptions PINS NAME DIRECTION DESCRIPTION LCD , Electrical Specification 7 LH77790B SHARP Table 2. Pinout PIN SIGNAL 1 NC 2 NC 3 XCLK 4 Vss 5 AO 6 A1 7 A2 8 , (Once RESETI Sampled High) 1 1 XCLK 24 Thermal & Electrical Specification SHARP LH77790B LCD , SHARP LH77790B Figure 15. LCD Controller AC Timing Thermal & Electrical Specification 27 LH77790B SHARP , support tools are crucial to reducing time-to-market. The Sytem On Chip team at SHARP has designed the
Abstract: 60 pin LCD connector Hsync Vsync RGB pcb lcd display connector lcd 40pin lcd ribbon vga connector 15 pin lcd lcd 60-pin sharp lcd service manual vga connector female FPGA VGA interface
Text: information and the specification for the Sharp LQ036Q1DA01, visit http://www.sharpsma.com. 5.2 LCD , ColdFire EVB Baseboard Cable Connection 3.2.4 Geode LX LCD Adaptor Board 3.3 Cable Connection to the , Development Kit 4.2 Display an Image on the LCD Screen 11 11 11 5 Display Kit Adjustments 5.1 LCD -3.6-QVGA-10 Vcom Adjustment Knob 5.2 LCD -3.6-QVGA-10 Display Kit Jumper Settings 5.3 LCD -6.4-VGA-10 Display Kit Jumper Settings 13 13 13 13 6 Connector Pinout Description 14 7 Optional Mounting of
Abstract: 10.1 inch lcd with led backlight 40 pin connector pinout vhdl code for rs232 receiver philips lcd 15.4 pinout PL041 vhdl code for a 16*2 lcd schematic diagram tv sharp LM-XCV2000 schematic diagram lcd tv sharp inverter 9PIN MMC socket
Text: 8.4 inch Sharp color full VGA LCD - generic interface to LCD with touch screen - video DAC to , Sharp 8.4" TFT (J14) LCD and touchscreen (J27) EXPA Socket Buffer Touchscreen controller , outputs for a: · VGA or SVGA monitor connected to J30 · Sharp LQ084V1DG21 8.4 inch TFT VGA LCD panel , ] LCD0_ENAB LCD0_R/L LCD0_U/D Generic LCD (J27) B26 Sharp LQ084V1DG2(J14) EXPA Socket B[23:0 , dedicated connector for a 8.4 inch Sharp LCD display and the second (J27) provides a generic interface
Abstract: NL6448BC33-53 nec display lcd backlight inverter 7 pin diagram NEC lcd 17 VGA CABLE CONNECTION DIAGRAM VGA to vga CABLE CONNECTION DIAGRAM TO00 touch screen 5233 connector PCB VGA ARM926EJ-S
Text: the 10.4" VGA LCD from NEC. The shortlist for selection was a 10.4" VGA LCD from Sharp , and the NEC , . Sharp VGA 10.4" TFT LCD Feature NEC 10.4" (NL6448BC33-53) Sharp 10.4" (LQ10D368) 243 x 185.1 x , NEC and Sharp are the only LCD suppliers. Similarly, Freescale Semiconductor cannot recommend one , provided 4.4 VGA Panel Connector Pinout The connector pinout for the i.MX21 ADS LCD connector and , Touch Screen Connector Pinout MC9328MX21 Pin Number/Name on ADS LCD Connector (P7) NEC NL6448BC33
16x2 LCD modules are very commonly used in most embedded projects, the reason being its cheap price, availability, programmer friendly and available educational resources.
16×2 LCD is named so because; it has 16 Columns and 2 Rows. There are a lot of combinations available like, 8×1, 8×2, 10×2, 16×1, etc. but the most used one is the 16×2 LCD. So, it will have (16×2=32) 32 characters in total and each character will be made of 5×8 Pixel Dots. A Single character with all its Pixels is shown in the below picture.
Now, we know that each character has (5×8=40) 40 Pixels and for 32 Characters we will have (32×40) 1280 Pixels. Further, the LCD should also be instructed about the Position of the Pixels. Hence it will be a hectic task to handle everything with the help of MCU, hence an Interface IC like HD44780is used, which is mounted on the backside of the LCD Module itself. The function of this IC is to get the Commands and Data from the MCU and process them to display meaningful information onto our LCD Screen. You can learn how to interface an LCD using the above mentioned links. If you are an advanced programmer and would like to create your own library for interfacing your Microcontroller with this LCD module then you have to understand the HD44780 IC working and commands which can be found its datasheet.
Previous examples connect the white LED backlight to power. The following example is specifically for those using an LCD with a RGB LED backlight. The only difference between the connection is the LED"s backlight on pins 15-18.

Monochrome character, graphic and static displays require different input voltages. All the different LCD voltage symbols can be confusing, but believe it or not, there is a system to the madness.
This LCD voltage terminology originated from the terminals of each type of transistor and their common connections in logic circuits. In other words, VCC is often applied to BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) collectors, VEE to BJT emitters, VDD to FET (Field-Effect Transistor) drains and VSS to FET sources. Most CMOS (Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor) IC data sheets now use VCC and GND to designate the positive and negative supply pins.
Pin three (3) is Vo and is the difference in voltage between VDD and VSS. This LCD voltage is adjusted to provide the sharpest contrast. The adjustment can be accomplished through a fixed resistor or a variable potentiometer. Many products have firmware that monitor the temperature and automatically adjust the contrast voltage.
In a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), V0 is used to vary the screen brightness or contrast. Contrast, simply put is the ratio of the light areas to the dark areas in a LCD. This is usually done in a production setting with values which are optimized for most users. Temperature can have an undesirable effect on the display brightness and for this reason a varying resister or potentiometer is used to accommodate the desires of the user.
Below is a data sheet of a 16x2 Character LCD module that shows various recommended driving voltages. The LCD voltage can range from MIN (minimum) to TYP (Typical) to Max (maximum).
If the supplied LCD voltage drops too low, the display is ‘under-driven’ and will produce segments that are ‘grey’. The lower the LCD voltage falls below the acceptable threshold, the lower the contrast will be.
If the LCD is over-driven, you may see ghosting. This is where segments that should not be ‘on’ are gray. They are not as dark as the segments that should be on, but they can be seen and may cause confusion for the end user.
There are times when a customer needs to replace a display that has been discontinued or EOL (End-Of -Life) by their previous LCD supplier. The previous LCD’s pin-outs may be different than Focus’ standard, off-the-shelf display. This is not a large problem to overcome.
The third option is to pull power from pins one and two. This is the same location from which the LCD is pulling its power. Focus does not recommend this option and can modify the PCB for the customer to connect the backlight from a different location.
Many LCD Modules will require more than one internal voltage/current. This may make it necessary for the customer to supply the needed inputs. They may need to supply 3V, 5V, 9V, -12V etc.
The solution for this is to integrate a charge pump (or booster circuit) into the LCD circuitry. This solution works in most applications, but if the product will be operating in an intrinsic environment, care must be taken with layout of the circuit board.
Intrinsically-safe LCDs are Liquid Crystal Displays that are designed to operate in conditions where an arc or spark can cause an explosion. In these cases, charge pumps cannot be employed. In fact, the total capacitive value of the display needs to be kept to a minimum.
Focus Display Solutions does not build a display that is labeled ‘Intrinsically safe’ but we do design the LCD to meet the requirements of the engineer. In meeting the design engineer’s requirements, the display may need to contain two or three independent inputs. Focus can redesign the PCB and lay out the traces to allow for these additional inputs.
General Specification NMLCD-43480272-CTP-CLB-IPS is a 4.3 inch IPS type TFT LCD with Capacitive Touch and Cover Lens Bezel, with 480*272 resolution. The touch panel is driven by FT5446. This product accords with RoHS. Product Pictures...
General Specification NMLCD-43480272-CTP-IPS is a 4.3 inch IPS type TFT LCD with a Capacitive Touch Panel which is 1:1 scale with the LCD module, with 480*272 resolution. This product accords with RoHS. Product Pictures 4.3 inch 480*272...
General Specification NMLCD-43480272-IPS is a 4.3 inch IPS type TFT LCD, with 480*272 resolution. This product accords with RoHS. Product Pictures 4.3 inch IPS Type TFT LCD with WQVGA Resolution 4.3 inch 480*272 TFT LCD with All Viewng...
General Specification NMLCD-43480272-RTP-IPS is a 4.3 inch IPS type TFT LCD with a Resistive Touch, with 480*272 resolution. This product accords with RoHS. Product Pictures 4.3 inch IPS Type TFT LCD with 480*272 Resolution with...
General Specification This type is a 4.3"" 480*272 full view angle TFT LCD with a Capacaitive Touch Panel with full bonding. Product Picture 4.3"" TFT LCD with Capacitive Touch Panel with Full Bonding 4.3""...
NMLCD-43480272-SB is a colour active matrix LCD module incorporating amorphous silicon TFT (Thin Film Transistor). It is composed of a colour TFT-LCD panel, driver IC, FPC and a back light unit and without a Touch...
General Specification This product is a 4.3"" color active matrix LCD module incorporating amorphous silicon TFT (Thin Film Transistor). It is composed of color TFT-LCD panel, driver IC, FPC and a back light unit and with a...

In this tutorial, I’ll explain how to set up an LCD on an Arduino and show you all the different ways you can program it. I’ll show you how to print text, scroll text, make custom characters, blink text, and position text. They’re great for any project that outputs data, and they can make your project a lot more interesting and interactive.
The display I’m using is a 16×2 LCD display that I bought for about $5. You may be wondering why it’s called a 16×2 LCD. The part 16×2 means that the LCD has 2 lines, and can display 16 characters per line. Therefore, a 16×2 LCD screen can display up to 32 characters at once. It is possible to display more than 32 characters with scrolling though.
The code in this article is written for LCD’s that use the standard Hitachi HD44780 driver. If your LCD has 16 pins, then it probably has the Hitachi HD44780 driver. These displays can be wired in either 4 bit mode or 8 bit mode. Wiring the LCD in 4 bit mode is usually preferred since it uses four less wires than 8 bit mode. In practice, there isn’t a noticeable difference in performance between the two modes. In this tutorial, I’ll connect the LCD in 4 bit mode.
BONUS: I made a quick start guide for this tutorial that you can download and go back to later if you can’t set this up right now. It covers all of the steps, diagrams, and code you need to get started.
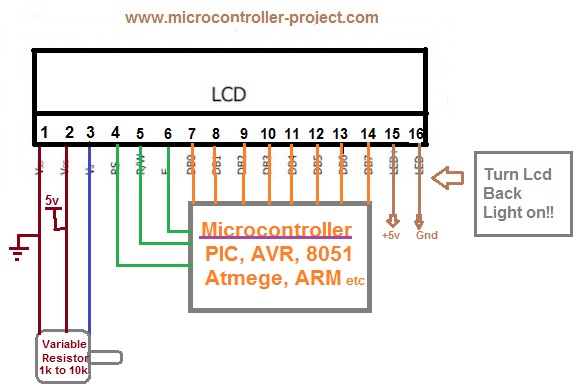
Here’s a diagram of the pins on the LCD I’m using. The connections from each pin to the Arduino will be the same, but your pins might be arranged differently on the LCD. Be sure to check the datasheet or look for labels on your particular LCD:
Also, you might need to solder a 16 pin header to your LCD before connecting it to a breadboard. Follow the diagram below to wire the LCD to your Arduino:
The resistor in the diagram above sets the backlight brightness. A typical value is 220 Ohms, but other values will work too. Smaller resistors will make the backlight brighter.
TheLiquidCrystal() function sets the pins the Arduino uses to connect to the LCD. You can use any of the Arduino’s digital pins to control the LCD. Just put the Arduino pin numbers inside the parentheses in this order:
This function sets the dimensions of the LCD. It needs to be placed before any other LiquidCrystal function in the void setup() section of the program. The number of rows and columns are specified as lcd.begin(columns, rows). For a 16×2 LCD, you would use lcd.begin(16, 2), and for a 20×4 LCD you would use lcd.begin(20, 4).
This function clears any text or data already displayed on the LCD. If you use lcd.clear() with lcd.print() and the delay() function in the void loop() section, you can make a simple blinking text program:
Similar, but more useful than lcd.home() is lcd.setCursor(). This function places the cursor (and any printed text) at any position on the screen. It can be used in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The cursor position is defined with lcd.setCursor(column, row). The column and row coordinates start from zero (0-15 and 0-1 respectively). For example, using lcd.setCursor(2, 1) in the void setup() section of the “hello, world!” program above prints “hello, world!” to the lower line and shifts it to the right two spaces:
You can use this function to write different types of data to the LCD, for example the reading from a temperature sensor, or the coordinates from a GPS module. You can also use it to print custom characters that you create yourself (more on this below). Use lcd.write() in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The function lcd.noCursor() turns the cursor off. lcd.cursor() and lcd.noCursor() can be used together in the void loop() section to make a blinking cursor similar to what you see in many text input fields:
Cursors can be placed anywhere on the screen with the lcd.setCursor() function. This code places a blinking cursor directly below the exclamation point in “hello, world!”:
This function creates a block style cursor that blinks on and off at approximately 500 milliseconds per cycle. Use it in the void loop() section. The function lcd.noBlink() disables the blinking block cursor.
This function turns on any text or cursors that have been printed to the LCD screen. The function lcd.noDisplay() turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD, without clearing it from the LCD’s memory.
This function takes anything printed to the LCD and moves it to the left. It should be used in the void loop() section with a delay command following it. The function will move the text 40 spaces to the left before it loops back to the first character. This code moves the “hello, world!” text to the left, at a rate of one second per character:
Like the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, the text can be up to 40 characters in length before repeating. At first glance, this function seems less useful than the lcd.scrollDisplay() functions, but it can be very useful for creating animations with custom characters.
lcd.noAutoscroll() turns the lcd.autoscroll() function off. Use this function before or after lcd.autoscroll() in the void loop() section to create sequences of scrolling text or animations.
This function sets the direction that text is printed to the screen. The default mode is from left to right using the command lcd.leftToRight(), but you may find some cases where it’s useful to output text in the reverse direction:
This code prints the “hello, world!” text as “!dlrow ,olleh”. Unless you specify the placement of the cursor with lcd.setCursor(), the text will print from the (0, 1) position and only the first character of the string will be visible.
This command allows you to create your own custom characters. Each character of a 16×2 LCD has a 5 pixel width and an 8 pixel height. Up to 8 different custom characters can be defined in a single program. To design your own characters, you’ll need to make a binary matrix of your custom character from an LCD character generator or map it yourself. This code creates a degree symbol (°):
Nowadays, we always use the devices which are made up of LCDs such as CD players, DVD players, digital watches, computers, etc. These are commonly used in the screen industries to replace the utilization of CRTs. Cathode Ray Tubes use huge power when compared with LCDs, and CRTs heavier as well as bigger. These devices are thinner as well power consumption is extremely less. The LCD 16×2 working principle is, it blocks the light rather than dissipate. This article discusses an overview of LCD 16X2, pin configuration and its working.
The term LCD stands for liquid crystal display. It is one kind of electronic display module used in an extensive range of applications like various circuits & devices like mobile phones, calculators, computers, TV sets, etc. These displays are mainly preferred for multi-segment light-emitting diodes and seven segments. The main benefits of using this module are inexpensive; simply programmable, animations, and there are no limitations for displaying custom characters, special and even animations, etc.
A 16×2 LCD has two registers like data register and command register. The RS (register select) is mainly used to change from one register to another. When the register set is ‘0’, then it is known as command register. Similarly, when the register set is ‘1’, then it is known as data register.
The main function of the data register is to store the information which is to be exhibited on the LCD screen. Here, the ASCII value of the character is the information which is to be exhibited on the screen of LCD. Whenever we send the information to LCD, it transmits to the data register, and then the process will be starting there. When register set =1, then the data register will be selected.
Thus, this is all about LCD 16×2 datasheet, which includes what is a 16X2 LCD, pin configuration, working principle, and its applications. The main advantages of this LCD device include power consumption is less and low cost. The main disadvantages of this LCD device include it occupies a large area, slow devices and also lifespan of these devices will be reduced due to direct current. So these LCDs use AC supply with less than 500Hz frequency. Here is a question for you, what are the applications of LCD?
This tutorial includes everything you need to know about controlling a character LCD with Arduino. I have included a wiring diagram and many example codes. These displays are great for displaying sensor data or text and they are also fairly cheap.
As you will see, you need quite a lot of connections to control these displays. I therefore like to use them with an I2C interface module mounted on the back. With this I2C module, you only need two connections to control the LCD. Check out the tutorial below if you want to use an I2C module as well:
These LCDs are available in many different sizes (16×2 1602, 20×4 2004, 16×1 etc.), but they all use the same HD44780 parallel interface LCD controller chip from Hitachi. This means you can easily swap them. You will only need to change the size specifications in your Arduino code.
For more information, you can check out the datasheets below. The 16×2 and 20×4 datasheets include the dimensions of the LCD and in the HD44780 datasheet you can find more information about the Hitachi LCD driver.
Most LCDs have a built-in series resistor for the LED backlight. You should find it on the back of the LCD connected to pin 15 (Anode). If your display doesn’t include a resistor, you will need to add one between 5 V and pin 15. It should be safe to use a 220Ω resistor, but this value might make your display a bit dim. You can check the datasheet for the maximum current rating of the backlight and use this to select an appropriate resistor value.
After you have wired up the LCD, you will need to adjust the contrast of the display. This is done by turning the 10 kΩ potentiometer clockwise or counterclockwise.
Plug in the USB connector of the Arduino to power the LCD. You should see the backlight light up. Now rotate the potentiometer until one (16×2 LCD) or 2 rows (20×4 LCD) of rectangles appear.
In order to control the LCD and display characters, you will need to add a few extra connections. Check the wiring diagram below and the pinout table from the introduction of this article.
We will be using the LCD in 4-bit mode, this means you don’t need to connect anything to D0-D3. The R/W pin is connected to ground, this will pull the pin LOW and set the LCD to WRITE mode.
To control the LCD we will be using the LiquidCrystal library. This library should come pre-installed with the Arduino IDE. You can find it by going to Sketch > Include Library > LiquidCrystal.
The example code below shows you how to display a message on the LCD. Next, I will show you how the code works and how you can use the other functions of the LiquidCrystal library.
After including the library, the next step is to create a new instance of the LiquidCrystal class. The is done with the function LiquidCrystal(rs, enable, d4, d5, d6, d7). As parameters we use the Arduino pins to which we connected the display. Note that we have called the display ‘lcd’. You can give it a different name if you want like ‘menu_display’. You will need to change ‘lcd’ to the new name in the rest of the sketch.
In the loop() the cursor is set to the third column and first row of the LCD with lcd.setCursor(2,0). Note that counting starts at 0, and the first argument specifies the column. If you do not specify the cursor position, the text will be printed at the default home position (0,0) if the display is empty, or behind the last printed character.
Next, the string ‘Hello World!’ is printed with lcd.print("Hello World!"). Note that you need to place quotation marks (” “) around the text. When you want to print numbers or variables, no quotation marks are necessary.
Clears the LCD screen and positions the cursor in the upper-left corner (first row and first column) of the display. You can use this function to display different words in a loop.
This function turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD. The text/data is not cleared from the LCD memory. This means it will be shown again when the function display() is called.
This function turns on automatic scrolling of the LCD. This causes each character output to the display to push previous characters over by one space. If the current text direction is left-to-right (the default), the display scrolls to the left; if the current direction is right-to-left, the display scrolls to the right. This has the effect of outputting each new character to the same location on the LCD.
The following example sketch enables automatic scrolling and prints the character 0 to 9 at the position (16,0) of the LCD. Change this to (20,0) for a 20×4 LCD.
With the function createChar() it is possible to create and display custom characters on the LCD. This is especially useful if you want to display a character that is not part of the standard ASCII character set.
Technical info: LCDs that are based on the Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller have two types of memories: CGROM and CGRAM (Character Generator ROM and RAM). CGROM generates all the 5 x 8 dot character patterns from the standard 8-bit character codes. CGRAM can generate user-defined character patterns.
/* Example sketch to create and display custom characters on character LCD with Arduino and LiquidCrystal library. For more info see www.www.makerguides.com */
After including the library and creating the LCD object, the custom character arrays are defined. Each array consists of 8 bytes, 1 byte for each row. In this example 8 custom characters are created.
In this article I have shown you how to use an alphanumeric LCD with Arduino. I hope you found it useful and informative. If you did, please share it with a friend that also likes electronics and making things!
I would love to know what projects you plan on building (or have already built) with these LCDs. If you have any questions, suggestions, or if you think that things are missing in this tutorial, please leave a comment down below.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey