lcd display mode free sample

You can adjust the LCD contrast setting for a sharper, more vivid display. If you are having difficulty reading the LCD display, try changing its contrast setting for improved visibility:
You can adjust the backlight brightness of the LCD display. If you are having difficulty reading the LCD display after adjusting its contrast setting, try changing the backlight brightness:
You can change the amount of time the LCD display stays on after the last key press. This is a power-saving feature. Your Brother machine can print, scan, and receive faxes and voice calls while its LCD is off.

provides a dual stack implementation for both IPv4 and IPv6 management environments. In Network Configuration mode, you can use the LCD panel to configure the network settings for a Firepower device’s management interface: the IP address, subnet mask or prefix, and default gateway.
If you edit the IP address of a Firepower device using the LCD panel, confirm that the changes are reflected on the managing Management Center. In some cases, you may need to edit the device management settings manually. See the for more information.
By default, the ability to change network configuration using the LCD panel is disabled. You can enable it during the initial setup process, or using the device’s web interface. For more information, see Allowing Network Reconfiguration Using the LCD Panel.
CautionEnabling this option may present a security risk. You need only physical access, not authentication, to configure network settings using the LCD panel.
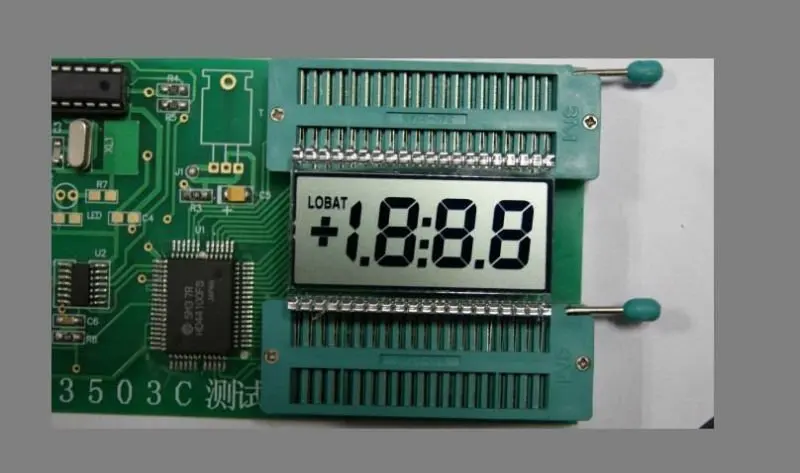
The first line on the panel indicates whether you are editing the IPv4 or IPv6 address. The second line displays the IP address you are editing. A cursor underlines the first digit, and represents the digit you are editing. The two symbols correspond with the multi-function keys to the right of each row.
Note that the IPv6 address does not fit completely on the display. As you edit each digit and move the cursor to the right, the IPv6 address scrolls to the right.
With the cursor on the first digit, the LCD panel displays the cancel and right arrow symbols at the end of the IP address. With the cursor on any other digit, the LCD panel displays the left and right arrow symbols.
Because it presents a security risk, the ability to change network configuration using the LCD panel is disabled by default. You can enable it during the initial setup process (see the see the Firepower 8000 Series Getting Started Guide

The Firepower System provides a dual stack implementation for both IPv4 and IPv6 management environments. In Network Configuration mode, you can use the LCD panel to configure the network settings for a Firepower device’s management interface: the IP address, subnet mask or prefix, and default gateway.
If you edit the IP address of a Firepower device using the LCD panel, confirm that the changes are reflected on the managing Management Center. In some cases, you may need to edit the device management settings manually. See the for more information.
By default, the ability to change network configuration using the LCD panel is disabled. You can enable it during the initial setup process, or using the device’s web interface. For more information, see Allowing Network Reconfiguration Using the LCD Panel.
The first line on the panel indicates whether you are editing the IPv4 or IPv6 address. The second line displays the IP address you are editing. A cursor underlines the first digit, and represents the digit you are editing. The two symbols correspond with the multi-function keys to the right of each row.
Note that the IPv6 address does not fit completely on the display. As you edit each digit and move the cursor to the right, the IPv6 address scrolls to the right.
With the cursor on the first digit, the LCD panel displays the cancel and right arrow symbols at the end of the IP address. With the cursor on any other digit, the LCD panel displays the left and right arrow symbols.
Because it presents a security risk, the ability to change network configuration using the LCD panel is disabled by default. You can enable it during the initial setup process (see Understanding the Setup Process), or using the device’s web interface as described in the following procedure.

The display driver is able to display predefined setups of text or user defined text. To display text using DisplayText set DisplayMode to 0, or set DisplayMode to 1 for the HT16K33 dot-matrix display.
To use the seven-segment-specific TM1637, TM1638 and MAX7219 Display- commands, set DisplayMode to 0. Parameter LCD Display OLED Display TFT Display 7-segment Display (TM163x and MAX7219) 0 DisplayText DisplayText DisplayText All TM163x Display- functions
The DisplayText command is used to display text as well as graphics and graphs on LCD, OLED and e-Paper displays (EPD). The command argument is a string that is printed on the display at the current position. The string can be prefixed by embedded control commands enclosed in brackets [].
In order to use the DisplayText command the DisplayMode must be set to 0 (or optional 1 on LCD displays) or other modes must be disabled before compilation with #undef USE_DISPLAY_MODES1TO5.
In the list below p stands for parameter and may be a number from 1 to n digits. On monochrome graphic displays things are drawn into a local frame buffer and sent to the display either via the d command or automatically at the end of the command.
Pfilename: = display an rgb 16-bit color (or jpg on ESP32) image when file system is present, Scripteditor contains a converter to convert jpg to special RGB16 pictures See ScriptEditor Ffilename: = load RAM font file when file system is present. the font is selected with font Nr. 5, these fonts are special binary versions of GFX fonts of any type. they end with .fnt. an initial collection is found in Folder BinFonts
When a file system is present you may define displaytext batch files. If a file named "display.bat" is present in the file system this batch file is executed. The file may contain any number of diplaytext cmds, one at a line. You may have comment lines beginning with a ;
E-Paper displays have 2 operating modes: full update and partial update. While full update delivers a clean and sharp picture, it has the disadvantage of taking several seconds for the screen update and shows severe flickering during update. Partial update is quite fast (300 ms) with no flickering but there is the possibility that erased content is still slightly visible. It is therefore useful to perform a full update in regular intervals (e.g., each hour) to fully refresh the display.
The data sheets of the TFT and OLED displays mention burn-in effects when a static display is shown for extended periods of time. You may want to consider turning on the display on demand only.
The EPD font contains 95 characters starting from code 32, while the classic GFX font contains 256 characters ranging from 0 to 255. Custom characters above 127 can be displayed. To display these characters, you must specify an escape sequence (standard octal escapes do not work). The ~character followed by a hex byte can define any character code.
The I2C address must be specified using DisplayAddress XX, e.g., 60. The model must be specified with DisplayModel, e.g., 2 for SSD1306. To permanently turn the display on set DisplayDimmer 100. Display rotation can be permanently set using DisplayRotate X (x = 0..3).
E-Paper displays are connected via software 3-wire SPI (CS, SCLK, MOSI). DC should be connected to GND , Reset to 3.3 V and busy may be left unconnected. The jumper on the circuit board of the display must be set to 3-wire SPI.
Waveshare has two kinds of display controllers: with partial update and without partial update. The 2.9 inch driver is for partial update and should also support other Waveshare partial update models with modified WIDTH and HEIGHT parameters. The 4.2 inch driver is a hack which makes the full update display behave like a partial update and should probably work with other full update displays.
In black and white displays, a local RAM buffer must be allocated before calling the driver. This must be set to zero on character or TFT color displays.
Universal Display Driver or uDisplay is a way to define your display settings using a simple text file and easily add it to Tasmota. uDisplay is DisplayModel 17. It supports I2C and hardware or software SPI (3 or 4 wire).
Initial register setup for the display controller. (IC marks that the controller is using command mode even with command parameters) All values are in hex. On SPI the first value is the command, then the number of arguments and the the arguments itself. Bi7 7 on the number of arguments set indicate a wait of 150 ms. On I2C all hex values are sent to I2C.
bit 2: enable async DMA, 0 wait for DMA to complete before returning, 4 run DMA async in the background. This later mode is only valid if the SPI bus is not shared between the display and any other SPI device like SD Card Reader.
# Scripter is the nost convenient way to edit and develop a uDisplay driver. On every scripter save the display is reinitialized and you immediately see results of your changes.
There are also many variants of each display available and not all variants may be supported. #define directive Description USE_DISPLAY Enable display support. Also requires at least one of the following compilation directives

The control bar offers a default set of buttons and other controls, providing commonly used options. In the center of the control bar is the LCD, which shows the playhead position and the project tempo, key, and time signature.
You can set a SMPTE offset for the project. As songs don’t always need to start precisely at bar 1, you can select any bar position to be played at the set SMPTE time.In Logic Pro, click the triangle on the right side of the LCD, then choose Use SMPTE View Offset from the pop-up menu.
With Milliseconds:The frame fractions are displayed in milliseconds instead of SMPTE bits (also called subframes). Remember that this value is dependent on the frame rate: at 25 fps, a frame is 40 milliseconds long, at 30 fps, approximately 33 ms.
Choose one of the following settings in the Display Tempo as pop-up menu:Beats Per Minute (BPM, Maelzel): Beats per minute, to four individually adjustable decimal places.

With the revival of the “Start Menu” from Windows 8 to Windows 10, this user-friendly desktop UI (user interface) realizes a more operable multi-display function. Let’s take a look at how we can use this multi-display tool on a Windows 10 notebook or desktop PC.
When using Windows 10 in your notebook PC or desktop computer you’ll notice one major change – the revival of the desktop UI. This UI was revived after the complete removal of the Start Menu in Windows 8/8.1 - previously present in Windows 7 and earlier - was met with mixed reactions. The latest UI has become much easier to use, with the modern UI “tile format” being integrated with a virtual desktop feature in order to enhance multitasking and workability.
With the new focus on the desktop UI, Windows 10 has naturally improved the display settings. For example the “multi-display” function (Multiple displays connected to one’s PC for simultaneous use) has been greatly improved. Let’s go through some of these surprisingly not well known Windows 10 multi-display functions found on both notebook PCs and Desktop PCs.
Example: EIZO LCD display FlexScan EV2455 connected to 13.3" 2in1 notebook PC (VAIO Z). Projecting the 13.3" notebook PC display to a 24.1" WUXGA (1920 x 1200 pixels) external display greatly enhances one’s work efficiency.
Example: The expanded display of two EIZO FlexScan EV2455 monitors connected to a desktop PC. Aligning two 24.1" WUXGA (1920 x 1200 pixels) monitors side by side achieves a combined resolution of 3840 x 1200 pixels.
Setting up a multi-display environment on Windows 10 is incredibly simple. When you connect a second display to your PC, Windows automatically detects the display and displays the desktop UI.
In this case we opened the multi-display function from the desktop UI by selecting the OS “Project” menu. From the taskbar, click on the Action Center (bottom right of screen) and select “Project,” or if you want to use the shortcut keys, press the Windows Key andP key and the “Project” menu will appear. There are four types of display methods that can be chosen. If you want to expand the desktop UI over two screens, select the “Extend” option.
Find the “Action Center” icon in the lower right taskbar, and click on the “Project” icon (left image). In the “Project” menu, out of the four options, choose how you want to display your monitors (right image)
From here the two screens’ position relative to each other, display size such as text (expansion rate), display orientation, the previous four display method settings, and the main / sub-display monitor settings can be changed. Additionally, if you cannot see your connected display, click on “detect” to try to find the display (if this doesn’t work we recommend reconnecting the cable and/or restarting your PC).
In the enclosed grey squares [1] and [2], the position of the two monitors relative to each other is displayed. It’s best to drag these two squares to suit the actual position of your monitors.
These days notebook PCs equipped with very high definition displays of pixel densities greater than full HD are growing, but when these units are connected to external displays the character and icon sizes can vary significantly between the original notebook PC and external monitor, making it difficult to work with. If that’s the case, the “Change the size of text, apps, and other items” slider bar can be used to effectively adjust the display sizes close to the each other.
In the “System > Display” menu the screen position, display size (enlargement ratio), display orientation, display method of the multi-display, and main/sub display can be set.
If you scroll down to the bottom of the “Display” menu there is an “advanced display settings” link. If you click on this, you can set the resolutions of the display monitors. Additionally, if you click on the “Advanced sizing of text and other items” link, you can change the settings for more detailed things like the size of items and text.
As shown above, Windows 10 has a new settings application installed which we recommend you use. But you can also use the “control panel” found in Windows 8 and earlier. To any familiar PC user, the conventional method of using the control panel to display various settings is still possible.
In Windows 10, after a window has been snapped to either the left or right side using the snap function, the empty area in the opposite side will display all other available windows as thumbnails. Choose one of these windows and it will fill that side of the screen.
Furthermore in Windows 10, if a window is moved to one of the four corners of the screen, it will shrink to 1/4 the size of the screen, so that four windows can be displayed at once. Additionally, in a multi-display environment, if you are displaying too many windows and your desktop has become messy, click and drag the window you want to view and quickly shake it to minimize all other windows. You can also press Windows and Home.
Let’s take a look at how the Taskbar can be used to increase the efficiency of the multi-display function. Right click on the taskbar and select “Settings” to display the “Settings > Taskbar” menu. Let’s look at the multi-display settings that can be found here. If you want to display the taskbar on your second device, slide the “Show taskbar on all displays” option to “on” and the taskbar will appear on both devices.
Right click on the taskbar, and select “Settings” (Left image). In the “Settings > Taskbar” menu, scroll down to “Multiple displays” and you can choose how the taskbar will be displayed on each device.
There are three options to choose how the taskbar can be viewed. The “All taskbars” option will display the taskbar the same on both displays, with all the running program icons displayed on both display’s taskbars. The “Main taskbar and taskbar where window is open” will display all running program’s icons on the first display’s taskbar and also display the programs running on the second display in the second display’s taskbar. Finally if you select “Taskbar where window is open” the taskbar will be displayed on both displays, but a running program’s taskbar icon will only be displayed on the taskbar of the monitor that the program is displayed on.
The above image shows the difference between the “All taskbars,” “Main taskbar and taskbar where window is open,” and “Taskbar where window is open” settings. The Windows 10 voice-enabled personal assistant “Cortana,” time icons and the notification area will always display on the first monitor.
If you connect an external display to a notebook PC, being able to create a large-screen, high resolution dual-display environment can significantly improve one’s work efficiency. These days products with high density pixel displays larger than full HD are becoming more common, but if a notebook PC with a screen size of 13 or 14 inches is displayed on one of these high resolution displays, the screen will end up shrinking so that it’s difficult to read, and so it has to be enlarged by 150% or 200%. Therefore it’s not that resolution = workspace, but rather that your workspace is limited to the size of your screen.
But an external display with a mainstream 23 – 24" full HD (1920 x 1080 pixels) or WUXGA (1920 x 1200 pixels) model, connected to a notebook PC, will display in a similar size to the notebook PC making it familiar to the user, and providing a lot of work space.
Example: An EIZO 24.1 inch WUXGA display (FlexScan EV2455) connected to a high-spec 2in1 VAIO Z notebook PC (from here on the examples will display the same set-up). The VAIO Z notebook display has a high definition resolution of 2560 x 1440 pixels, but because the screen is only a “mobile” 13.3 inches, on Windows it is expanded to 200%. Adding this to the FlexScan EV2455’s 24.1 inch 1920 x 1200 pixel display, gives a vast area of work space. Of course, because the FlexScan EV2455 has a large screen and 1920 x 1200 pixels, the notebook’s display can be displayed at 100% without needing to increase the 1920 x 1200 pixels. This makes for comfortable browsing of multiple web pages as shown.
Example: On a large external display, you can watch an online video while searching for relevant information on your notebook. Of course you can surf the internet on anything, but the large external screen is perfect for enjoying video content.
If you have an external monitor with excellent color display, you can use the graphics software in your notebook PC whilst replicating (mirroring) the display onto the external monitor; creating color-accurate images while you work. The above image is an example of the “Fresh Paint” application.
A word of advice when choosing a monitor to connect to your notebook PC, in a dual display environment — having the two taskbars at the bottom of the screen be uniform makes it easier to use, but a notebook PC’s height cannot be adjusted, so choosing a product that can be easily adjusted is desirable. Furthermore, because a notebook’s display is situated at a fairly low height, an external monitor that can be lowered to the table surface is better.
If an LCD display’s height adjustment range is wide, you can create a vertical multi-display environment like this, reducing the required width of your working space. The image gives the example of a VAIO Z and FlexScan EV2455, but if you tilt the screen of the VAIO Z, the FlexScan EV2455 can be made to not overlap as shown; naturally creating two screens.
If the external display is set in the vertical position, portrait photos and long lists of information can be displayed. The notebook PC cannot be used in the vertical position.
In our examples we used the EIZO 24.1-inch WUXGA display FlexScan EV2455 because it is a monitor with a height adjustment range of 131 mm and the ability to be vertically rotated, so it can be easily combined with a notebook PC. Additionally, because of the narrow “frameless” design, the black border and bezel (i.e. noise) is minimized as much as possible. It’s easy to appreciate how the visual transition from one screen to the other becomes naturally gentler on the eyes. This monitor will also suit any photo-retouching and content creation by correctly displaying the sRGB color gamut; i.e. displaying colors the same as those found in most notebook PCs.
It should be noted that in Windows 10, the “tablet mode” cannot be used in a multi-display environment. In Windows 8/8.1 a notebook PC could display the modern UI start screen while an external display could display the desktop UI, but in Windows 10 the multi-display environment is restricted to only using the desktop UI. This is one of the revived functions that were found to be most useful in Windows 7.
Although the notebook PC has become mainstream in recent years, the desktop PC is still popular for users who require high-performance or work efficient computers. So to these users who want to take advantage of their high-powered PCs and increase their productivity, we recommend the multi-display environment. Using large, high resolution displays in a multi-display environment gives you an unbeatable advantage.
Because there are no screen size or resolution restrictions like in a notebook PC, the desktop multi-display environment can use a flexible combination of screen sizes and resolutions according to your location, budget or application. If so inclined, using the previous EIZO monitor, a resolution of 5760 x 1080 pixels could be made from 3 monitors, 5760 x 2160 pixels from 6 monitors, and many more variations can be made.
An example of how a multi-display environment can be used in the business scene. The left display can display tables and calculations of statistical data, while comparing the graphs, and the right screen can be used to summarize the findings in a document. If this were just one monitor, you would be constantly switching between windows, but with two monitors you can see all the necessary data without needing to switch between windows; improving work efficiency and reducing transcribing errors.
An example of how map-based services can be used. On just one screen, the display range of a map is quite narrow, but with two screens, a map, aerial photo, information about the location, and photos from the location can all be displayed at the same time. You can take advantage of the realism of the large screen by doing virtual tours of tourist destinations.
An example of how the multi-display environment can help with photo re-touching. Rotating one monitor to the vertical position can help with retouching portrait photos, or editing long documents and websites. If you want to take advantage of a vertical screen, you need to choose a monitor that can be rotated or buy a separate rotating mount to attach your monitor to.
Most commonly when people want to build a multi-display environment, they start with one monitor, and then later add another one. Ideally, it’s best to purchase multiple monitors of the same model in the beginning. This way the screen size and resolution can be aligned, but also the color and aesthetics will match. But perhaps more importantly, because the monitors are the same age, any defects in the screen such as color variations can be found early-on by comparing the two monitors next to each other.
Another note for those who might be thinking about trying to build a multi-display environment, is that the more monitors you align, the wider your viewing angle will need to be. In order to be able to see each monitor clearly without having to move, you need to buy a product that has wide viewing angles. Furthermore, the more screens you have the harder it is to avoid light reflecting on your screen and into your eyes. To prevent this, we recommend buying a monitor with a glare reducing surface, which will make the screens easier to see and will be easier on your eyes. Additionally, as mentioned above we recommend a monitor with a narrow bezel and black border as it is space-saving and increases visibility among other advantages.
The 24.1-inch WUXGA display FlexScan EV2455 that we used, uses an IPS LCD panel with wide viewing angles and a glare reducing screen. Furthermore it has a narrow-frame design of only 6.2 mm (1 mm bezel and 5.2 mm black border). Therefore two monitors side by side will only have a gap of 12.4 mm, so you can make an almost noiseless multi-display environment. Another feature is the automatic dimming function (Auto EcoView) which leads to less eye fatigue, and less power consumption.
Earlier we introduced the set-up procedure for Windows 10 “multi-display,” and also showed some concrete examples. Whether you use a notebook PC or the more conventional desktop PC, if you want to increase the work efficiency of Windows 10, using multi-display is highly effective.
Even compared to a PC, a monitor is still a possible long-term investment. Therefore we recommend that you do not compromise on quality; in the medium to long term if you think of the comprehensive savings made through increased work productivity, reduced burdens on your body, and reduced power consumption, high-quality display products may offer higher value. Considering that, the FlexScan EV2455 that we used from EIZO’s “FlexScan EV” series meets all of these elements and includes a 5 year warranty, making it one of the best products suited to a multi-display environment.

AOur production quality follow ISO9000 standard system, stable design team,22 years experience of QC team and strictly quality control system guarantee the production quality. accept third part inspection,we have mechanical checking,display checking,high&low temperature storage&operating test during high humidity condition,EMC test(optional) for every design .
Accessing Dell Display Manager (DDM) features and the most recent Easy Arrange layouts is easier than ever. Simply enter preset hotkeys to bring up Dell Display Manager (DDM) UI at the touch of the keyboard. Also, switch easily between your favorite Easy Arrange layouts and templates.
A more intuitive way to configure monitor settings. Simply drag and drop the Dell Display Manager UI menu from one monitor to another. Allows users to control and change monitor settings easily in a multimonitor configuration.
Viewing and using Dell Display Manager (DDM) in portrait mode is now possible. Dell Display Manager (DDM) Easy Arrange templates automatically switch to portrait mode when monitor orientation is pivoted vertically.
KVM Wizard to simplify the KVM setup. Follow step-by-step pop-up windows guide at the click of the KVM Wizard icon on the Dell Display Manager (DDM) user interface. (available on select Dell monitors with KVM capability only.)
IT managers can issue specific instructions using command lines to Dell Display Manager (DDM) to perform tasks within specific times to individual monitor or an entire fleet
Remote Control capabilities (includes Power on/off, restoring factory defaults, changing monitor front of screen settings, optimal resolution, display modes, disabling OSD menu access, input switching).
Up to 38 layouts: With Dell Display Manager’s Easy Arrange, you can organize multiple applications on your screen and snap them into a template of your choice, making multitasking easy and effortless.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey