ips-lcd hd vs tft lcd manufacturer

IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

If you want to buy a new monitor, you might wonder what kind of display technologies I should choose. In today’s market, there are two main types of computer monitors: TFT LCD monitors & IPS monitors.
The word TFT means Thin Film Transistor. It is the technology that is used in LCD displays. We have additional resources if you would like to learn more about what is a TFT Display. This type of LCDs is also categorically referred to as an active-matrix LCD.
These LCDs can hold back some pixels while using other pixels so the LCD screen will be using a very minimum amount of energy to function (to modify the liquid crystal molecules between two electrodes). TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These two elements play a key part in ensuring that the TFT display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy while still generating vibrant, consistent images.
Industry nomenclature: TFT LCD panels or TFT screens can also be referred to as TN (Twisted Nematic) Type TFT displays or TN panels, or TN screen technology.
IPS (in-plane-switching) technology is like an improvement on the traditional TFT LCD display module in the sense that it has the same basic structure, but has more enhanced features and more widespread usability.
These LCD screens offer vibrant color, high contrast, and clear images at wide viewing angles. At a premium price. This technology is often used in high definition screens such as in gaming or entertainment.
Both TFT display and IPS display are active-matrix displays, neither can’t emit light on their own like OLED displays and have to be used with a back-light of white bright light to generate the picture. Newer panels utilize LED backlight (light-emitting diodes) to generate their light hence utilizing less power and requiring less depth by design. Neither TFT display nor IPS display can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red, green, blue) color filter in each LCD pixels to produce the color consumers see. If you use a magnifier to inspect your monitor, you will see RGB color in each pixel. With an on/off switch and different level of brightness RGB, we can get many colors.
Winner. IPS TFT screens have around 0.3 milliseconds response time while TN TFT screens responds around 10 milliseconds which makes the latter unsuitable for gaming
Winner. the images that IPS displays create are much more pristine and original than that of the TFT screen. IPS displays do this by making the pixels function in a parallel way. Because of such placing, the pixels can reflect light in a better way, and because of that, you get a better image within the display.
Winner. While the TFT LCD has around 15% more power consumption vs IPS LCD, IPS has a lower transmittance which forces IPS displays to consume more power via backlights. TFT LCD helps battery life.
Normally, high-end products, such as Apple Mac computer monitors and Samsung mobile phones, generally use IPS panels. Some high-end TV and mobile phones even use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) displays. This cutting edge technology provides even better color reproduction, clear image quality, better color gamut, less power consumption when compared to LCD technology.
This kind of touch technology was first introduced by Steve Jobs in the first-generation iPhone. Of course, a TFT LCD display can always meet the basic needs at the most efficient price. An IPS display can make your monitor standing out.

Before you get a new monition for your organization, comparing the TFT display vs IPS display is something that you should do. You would want to buy the monitor which is the most advanced in technology. Therefore, understanding which technology is good for your organization is a must. click to view the 7 Best Types Of Display Screens Technology.
Technology is changing and becoming advanced day by day. Therefore, when you are looking to get a new monitor for your organization, LCD advantages, and disadvantage, you have to be aware of the pros and cons of that monitor. Moreover, you need to understand the type of monitor you are looking to buy.
That is why it is important to break it down and discuss point by point so that you can understand it in a layman’s language devoid of any technical jargon. Therefore, in this very article, let’s discuss what exactly TFT LCDs and IPS LCDs are, and what are their differences? You will also find out about their pros and cons for your organization.
The word TFT means Thin-Film-Translator. Click to view: what is TFT LCD, It is the technology that is used in LCD or Liquid Crystal Display. Here you should know that this type of LCD is also categorically referred to as active-matrix LCDs. It tells that these LCDs can hold back some pixels while using other pixels. So, the LCD will be using a very minimum amount of energy to function. TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
Now, it is time to take a look at its features that are tailored to improve the experience of the monitor users significantly. Here are some of the features of the TFT monitor;
No radiation, no scintillation, no harm to the user’s health. In particular, the emergence of TFT LCD electronic books and periodicals will bring humans into the era of a paperless office and paperless printing, triggering a revolution in the civilized way of human learning, dissemination, and recording.
It can be normally used in the temperature range from -20℃ to +50℃, and the temperature-hardened TFT LCD can operate at low temperatures up to -80 ℃. It can not only be used as a mobile terminal display, or desktop terminal display but also can be used as a large screen projection TV, which is a full-size video display terminal with excellent performance.
The manufacturing technology has a high degree of automation and good characteristics of large-scale industrial production. TFT LCD industry technology is mature, a mass production rate of more than 90%.
TFT LCD screen from the beginning of the use of flat glass plate, its display effect is flat right angles, let a person have a refreshing feeling. And LCDs are easier to achieve high resolution on small screens.
The word IPS refers to In-Plane-Switching which is a technology used to improve the viewing experience of the usual TFT displays. You can say that the IPS display is a more advanced version of the traditional TFT LCD module. However, the features of IPS displays are much more advanced and their applications are very much widespread. You should also know that the basic structure of the IPS LCD is the same as TFT LCD if you compare TFT LCD vs IPS.
As you already know, TFT displays do have a very quick response time which is a plus point for it. But, that does not mean IPS displays a lack of response time. In fact, the response time of an IPS LCD is much more consistent, stable, and quick than the TFT display that everyone used to use in the past. However, you will not be able to gauge the difference apparently by watching TFT and IPS displays separately. But, once you watch the screen side-by-side, the difference will become quite clear to you.
The main drawback of the TFT displays as figured above is the narrow-angle viewing experience. The monitor you buy for your organization should give you an experience of wide-angle viewing. It is very much true if you have to use the screen by staying in motion.
So, as IPS displays are an improved version of TFT displays the viewing angle of IPS LCDs is very much wide. It is a plus point in favor of IPS LCDs when you compare TFT vs IPS. With a TFT screen, you cannot watch an image from various angles without encountering halo effects, blurriness, or grayscale that will cause problems for your viewing.
It is one of the major and remarkable differences between IPS and TFT displays. So, if you don’t want to comprise on the viewing angles and want to have the best experience of viewing the screen from wide angles, the IPS display is what you want. The main reason for such a versatile and wonderful viewing angle of IPS display is the screen configuration which is widely set.
Now, when you want to achieve wide-angle viewing with your display screen, you need to make sure it has a faster level of frequency transmittance. It is where IPS displays overtake TFT displays easily in the comparison because the IPS displays have a much faster and speedier transmittance of frequencies than the TFT displays.
Now the transmittance difference between TFT displays and IPS displays would be around 1ms vs. 25ms. Now, you might think that the difference in milliseconds should not create much of a difference as far as the viewing experience is concerned. Yes, this difference cannot be gauged with a naked eye and you will find it difficult to decipher the difference.
However, when you view and an IPS display from a side-by-side angle and a TFT display from a similar angle, the difference will be quite evident in front of you. That is why those who want to avoid lagging in the screen during information sharing at a high speed; generally go for IPS displays. So, if you are someone who is looking to perform advanced applications on the monitor and want to have a wider viewing angle, then an IPS display is the perfect choice for you.
As you know, the basic structure of the IPS display and TFT displays are the same. So, it is quite obvious that an IPS display would use the same basic colors to create various shades with the pixels. However, there is a big difference with the way a TFT display would produce the colors and shade to an IPS display.
The major difference is in the way pixels get placed and the way they operate with electrodes. If you take the perspective of the TFT display, its pixels function perpendicularly once the pixels get activated with the help of the electrodes. It does help in creating sharp images.
But the images that IPS displays create are much more pristine and original than that of the TFT screen. IPS displays do this by making the pixels function in a parallel way. Because of such placing, the pixels can reflect light in a better way, and because of that, you get a better image within the display.
As you already know the features of both TFT and IPS displays, it would be easier for you to understand the difference between the two screen-types. Now, let’s divide the matters into three sections and try to understand the basic differences so that you understand the two technologies in a compressive way. So, here are the difference between an IPS display and a TFT display;
Now, before starting the comparison, it is quite fair to say that both IPS and TFT displays have a wonderful and clear color display. You just cannot say that any of these two displays lag significantly when it comes to color clarity.
However, when it comes to choosing the better display on the parameter of clarity of color, then it has to be the IPS display. The reason why IPS displays tend to have better clarity of color than TFT displays is a better crystal oriental arrangement which is an important part.
That is why when you compare the IPS LCD with TFT LCD for the clarity of color, IPS LCD will get the nod because of the better and advanced technology and structure.
IPS displays have a wider aspect ratio because of the wide-set configuration. That is why it will give you a better wide-angle view when it comes to comparison between IPS and TFT displays. After a certain angle, with a TFT display, the colors will start to get a bit distorted.
But, this distortion of color is very much limited in an IPS display and you may see it very seldom after a much wider angle than the TFT displays. That is why for wide-angle viewing, TFT displays will be more preferable.
When you are comparing TFT LCD vs. IPS, energy consumption also becomes an important part of that comparison. Now, IPS technology is a much advanced technology than TFT technology. So, it is quite obvious that IPS takes a bit more energy to function than TFT.
Also, when you are using an IPS monitor, the screen will be much larger. So, as there is a need for much more energy for the IPS display to function, the battery of the device will drain faster. Furthermore, IPS panels cost way more than TFT display panels.
1. The best thing about TFT technology is it uses much less energy to function when it is used from a bigger screen. It ensures that the cost of electricity is reduced which is a wonderful plus point.
2. When it comes to visibility, the TFT technology enhances your experience wonderfully. It creates sharp images that will have no problems for older and tired eyes.
1. One of the major problems of TFT technology is that it fails to create a wider angle of view. As a result, after a certain angle, the images in a TFT screen will distort marring the overall experience of the user.
Although IPS screen technology is very good, it is still a technology based on TFT, the essence of the TFT screen. Whatever the strength of the IPS, it is a TFT-based derivative.
Finally, as you now have a proper understanding of the TFT displays vs IPS displays, it is now easier for you when it comes to choose one for your organization. Technology is advancing at a rapid pace. You should not be surprised if you see more advanced display screens in the near future. However, so far, TFT vs IPS are the two technologies that are marching ahead when it comes to making display screens.
STONE provides a full range of 3.5 inches to 15.1 inches of small and medium-size standard quasi TFT LCD module, LCD display, TFT display module, display industry, industrial LCD screen, under the sunlight visually highlight TFT LCD display, industrial custom TFT screen, TFT LCD screen-wide temperature, industrial TFT LCD screen, touch screen industry. The LCD module is very suitable for industrial control equipment, medical instruments, POS system, electronic consumer products, vehicles, and other products.

As you might already be aware, there’s a large variety of versatile digital display types on the market, all of which are specifically designed to perform certain functions and are suitable for numerous commercial, industrial, and personal uses. The type of digital display you choose for your company or organization depends largely on the requirements of your industry, customer-base, employees, and business practices. Unfortunately, if you happen to be technologically challenged and don’t know much about digital displays and monitors, it can be difficult to determine which features and functions would work best within your professional environment. If you have trouble deciphering the pros and cons of using TFT vs. IPS displays, here’s a little guide to help make your decision easier.
TFT stands for thin-film-transistor, which is a variant of liquid crystal display (LCD). TFTs are categorized as active matrix LCDs, which means that they can simultaneously retain certain pixels on a screen while also addressing other pixels using minimal amounts of energy. This is because TFTs consist of transistors and capacitors that respectively work to conserve as much energy as possible while still remaining in operation and rendering optimal results. TFT display technologies offer the following features, some of which are engineered to enhance overall user experience.
The bright LED backlights that are featured in TFT displays are most often used for mobile screens. These backlights offer a great deal of adaptability and can be adjusted according to the visual preferences of the user. In some cases, certain mobile devices can be set up to automatically adjust the brightness level of the screen depending on the natural or artificial lighting in any given location. This is a very handy feature for people who have difficulty learning how to adjust the settings on a device or monitor and makes for easier sunlight readability.
One of the major drawbacks of using a TFT LCD instead of an IPS is that the former doesn’t offer the same level of visibility as the latter. To get the full effect of the graphics on a TFT screen, you have to be seated right in front of the screen at all times. If you’re just using the monitor for regular web browsing, for office work, to read and answer emails, or for other everyday uses, then a TFT display will suit your needs just fine. But, if you’re using it to conduct business that requires the highest level of colour and graphic accuracy, such as completing military or naval tasks, then your best bet is to opt for an IPS screen instead.
Nonetheless, most TFT displays are still fully capable of delivering reasonably sharp images that are ideal for everyday purposes and they also have relatively short response times from your keyboard or mouse to your screen. This is because the pixel aspect ration is much narrower than its IPS counterpart and therefore, the colours aren’t as widely spread out and are formatted to fit onto the screen. Primary colours—red, yellow, and blue—are used as the basis for creating brightness and different shades, which is why there’s such a strong contrast between different aspects of every image. Computer monitors, modern-day HD TV screens, laptop monitors, mobile devices, and even tablets all utilize this technology.
IPS (in-plane-switching) technology is almost like an improvement on the traditional TFT display module in the sense that it has the same basic structure, but with slightly more enhanced features and more widespread usability. IPS LCD monitors consist of the following high-end features.
IPS screens have the capability to recognize movements and commands much faster than the traditional TFT LCD displays and as a result, their response times are infinitely faster. Of course, the human eye doesn’t notice the difference on separate occasions, but when witnessing side-by-side demonstrations, the difference is clear.
Wide-set screen configurations allow for much wider and versatile viewing angles as well. This is probably one of the most notable and bankable differences between TFT and IPS displays. With IPS displays, you can view the same image from a large variety of different angles without causing grayscale, blurriness, halo effects, or obstructing your user experience in any way. This makes IPS the perfect display option for people who rely on true-to-form and sharp colour and image contrasts in their work or daily lives.
IPS displays are designed to have higher transmittance frequencies than their TFT counterparts within a shorter period of time (precisely 1 millisecond vs. 25 milliseconds). This speed increase might seem minute or indecipherable to the naked eye, but it actually makes a huge difference in side-by-side demonstrations and observations, especially if your work depends largely on high-speed information sharing with minimal or no lagging.
Just like TFT displays, IPS displays also use primary colours to produce different shades through their pixels. The main difference in this regard is the placement of the pixels and how they interact with electrodes. In TFT displays, the pixels run perpendicular to one another when they’re activated by electrodes, which creates a pretty sharp image, but not quite as pristine or crisp as what IPS displays can achieve. IPS display technologies employ a different configuration in the sense that pixels are placed parallel to one another to reflect more light and result in a sharper, clearer, brighter, and more vibrant image. The wide-set screen also establishes a wider aspect ratio, which strengthens visibility and creates a more realistic and lasting effect.
When it comes to deciphering the differences between TFT vs. IPS display technologies and deciding which option is best for you and your business, the experts at Nauticomp Inc. can help. Not only do we offer a wide variety of computer displays, monitors, and screen types, but we also have the many years of experience in the technology industry to back up our recommendations and our knowledge. Our top-of-the-line displays and monitors are customized to suit the professional and personal needs of our clients who work across a vast array of industries. For more information on our high-end displays and monitors, please contact us.

If you want to buy a monitor, normally there are only two choices: TFT display or IPS display. In order to make the right purchase decision, it is important to know the technologies behind the two displays.
The word TFT means thin film transistor. It is the technology that is used in LCD or Liquid Crystal Display. Here you should know that this type of LCDs is also categorically referred to as active-matrix LCDs. It says that these LCDs can hold back some pixels while using other pixels. So, the LCD will be using a very minimum amount of energy to function (actually to make the liquid crystal molecules between two electrodes twisting). TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the TFT display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
The brightest feature TFT displays have is its low cost because of the simpler process of manufacturing, low cost material and one of the oldest technologies for LCD displays. But they are not the best quality considering poor viewing angles, lower contrast ratio, slower response time, lower aperture ratio (each pixel not bright enough) and the worst is that there is one view angle with Gray Scale Inversion (reversed image), see the bottom one of picture 1 below.
IPS (in-plane-switching) technology is like an improvement on the traditional TFT LCD display module in the sense that it has the same basic structure, but with more enhanced features and more widespread usability. IPS LCD monitors consist of the following high-end features. It has a much wider viewing angle, more consistent, accurate color in all viewing directions, it has higher contrast, faster response time. But IPS display is not perfect as its higher manufacturing cost. See the Fig.2 below
Both TFT display and IPS display are active matrix displays, neither can’t emit light like OLED, it has to be used with a back-light of white bright light to generate the picture. Newer panels utilize LED backlight (light emitting diodes) to generate their light and therefore utilize less power and require less depth by design. Actually neither TFT display nor IPS display can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red,green,blue) color filter in each LCD pixel to make the LCD show color. If you use a magnifier to see your monitor, you will see RGB color. By switching on/off and different levels of RGB brightness, we can produce a spectrum of many colors.
Faster Response Time: IPS Display Wins. IPS TFT Screens have around 0.3 milliseconds response time while TN TFT Screens respond around 10 milliseconds which makes the latterpoor for gaming purposes.
Cost: TFT Display Wins (around 30%-50% lower). The TFT lcd production technology is more mature than IPS LCD, it has a better production yield than IPS LCD.
Lower Energy Consumption: TFT Display wins. TN TFT LCD has more than around 15% power consumption than IPS lcd. The reason still comes from the array way of liquid crystal inside the IPS LCD screen. Because the liquid crystal molecules are arrayed in the electrode plane, the power would be saved for switching on liquid crystal in IPS screen than twisting it in TFT lcd screens, that is the reason IPS screen is better than TN TFT lcd in power consumption. Regarding the IPS LCD screen have better contrast, but in the same time, it have less transmissive ratio (transmittance), so we need more light from lcd backlight, if used more led chips, so it also need more power to the lcd backlight, so the total display module might need more power consumption if the backlight driving current for IPS LCD panel. so we need to be moreconcerned about the backlight current consumption instead of the IPS TFT panel itself. The main power consumption would be from the lcd backlight, not the IPS TFT panel. Battery life will likely be longer if other hardware is the same.
Better “Image or Pixel Sticking” or “Ghosting” (Image Sticking is when an image will stay on for a short time when instead it should be off): Hard to say depending on different display screen manufacturers. Generally speaking, TFT Display has aslightly better chance not to have the issue.
In summary, normally high-end products like Apple Mac monitors and Samsung mobile phones most likely use IPS panels. Some of the even high end TV and mobile phones use AMOLED( Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) Displays. The technology provides even better color reproduction, image quality, better color gamut, less power than LCD technology. Please note that OLED includes AMOLED and PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes). What you need to choose is AMOLED for your TV and mobile phones instead of PMOLED. If you have more budget, you can have your screen with touch screen, most of the touch nowadays uses PCAP (Projective Capacitive) touch panel. This kind of touch technology was first introduced by Steven Jobs in the first generation iPhone. Of course, a TFT LCD display can always meet the basic needs with reasonable price.
The two buzzwords the tech world has been chatting about for a number of years now is IPS, (In-Plane Switching) screen technology used for liquid crystal displays or LCD’s for short, and TFT (Thin-Film-Transistor) an active matrix screen technology, which is more expensive, but a sharper image.
Designed in the 1980’s, but not introduced until nearly a decade later, in 1996, by Hitachi, IPS technology is nothing new, and a type of LCD design that affords greater viewing angles and higher-quality color reproduction than the traditional TN or Twisted Nematic LCDs.
TFT (Thin-Film-Transistor) Liquid Crystal Display is a thin display type, where a transistor embedded into each crystal gate; these transistors are then printed on thin-transparent film. The technology was designed to improve image qualities, such as contrast and addressability.
Also designed in the late 1980’s, TFT display technologies is just another variation of LCD displays that offer greater color, contrast, and response times as opposed to available passive matrix LCD’s. One of the primary differences between IPS and TFT display technologies is the cost. IPS is more expensive than TN technology. However, there are some key differences between the two that should be noted.
Before we go into the differences, let’s talk about features of each technology. Note that we’re not talking TVs, computer, or tablets, but screens on a much smaller scale, (think 7” or smaller) which uses different rules to fit that scale. First, it’s interesting to discover that the TFT display technologies is the most common type of color display technology; more monochrome displays still out-sell color, due to lower cost and lower power consumption, however, the narrow poor visibility of TFTs in direct sunlight is their downside; but I’m getting ahead of myself here.
IPS technology has come a long way in regards to cell phones and other LCD screens that are even much smaller. (Picture digital clocks on a radio, microwave, and hand-held games) Some of the features of an IPS screen include:Wider viewing angles – crystals are aligned horizontally rather than vertically, so it allows for better angled viewing, perfect for smaller screens, where you need to rotate the screen for better viewing
TFT display technologies have developed over the years and have become quite popular in tech circles. The features offered with this advancing technology are:Superior color display – for technology that requires it or for consumers that desire color screens
Variety of displays, which can be interfaced through a variety of bus types, including 18 and 24 bit for red/green/blue, LVDS, and 8 bit and 16 bit for a CPU – many controllers allow for two or more different types of interfaces on the same TFT screen
Let me explain. As you can see, both have excellent color display and clarity; however, IPS screens offer greater color reproduction and viewing angles because of the way crystal orientation and polarizers are arranged. In a TFT screen, the structure of the crystals results in angular retardation in the light. The IPS screens thus offer less distortion properties. Other differences include power consumption and cost. With IPS screens, it takes more power (up to 15% more) than with a TFT screen. If you’re on a monitor, such as a computer screen that’s bigger than 7 inches, it will drain your battery faster than if you’re on a 3.5” screen. Regarding cost, IPS panels are more expensive to produce than TFT panels.
If you want the benefits of having a Smartphone without a huge price tag, then TFT devices are your best bet. Another difference is that IPS screens have longer response times than TFT screens, so the lag output is greater. A few other key differences to be aware of are that with IPS panels, you get a bigger variety of panels, as was discussed above, with their super, advanced, and so forth developments, giving the consumer options, and IPS screens that can display 24-bit TrueColor; they also stay color-accurate and remain stable.
Now we will go over the downside of IPS screens, which we briefly touched on above, which includes a major disadvantage: cost. If you’re just looking for an average Smartphone or don’t need all the fancy coloring and clarity for LCD displays, then cost may not be a big factor; however, this is the main reason why IPS technology is beginning to come down. As with every new invention, discovery or technology, demand is everything. Another disadvantage is that colors may not always transcribe correctly or accurately, which may or may not be a deterrent. Also, high resolutions are not always readily available for personal applications. In certain circumstances, the brightness may not be enough, especially in darkness.
Steve Jobs said it best: “Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.” I tend to agree with him. With TFT display technologies, less energy consumption is a big deal, especially when dealing with bigger screens, and of course less electricity means lower cost, overall. The visibility is sharper, meaning no geometric distortion, which is great for these tired, old eyes. The response time and physical design of the screens are also appealing. TFT displays can also save space and be placed virtually anywhere in an office or home, because of the brightly lit feature and crisp clear images.
Some cons of TFT screens deal with the viewing angle, which create distortion, resulting in a less-than-perfect image. Static resolution, meaning the resolution can’t be changed, may also cause a problem, but newer models seem to have tackled that issue. The accuracy of the display of colors is not perfect, specifically strong blacks and bright whites, so when printing an image, it may not display the spectrum of colors.
And there you have it. In the future, even this superb technology will change and new, more exciting technology will take its place. But until then, IPS & TFT screens are forging ahead with their own advances and improvements, so stayed tune. You don’t want to miss it.
Focus Display Solutions (www.FocusLCDs.com) offers off-the-shelf Color TFT display technologies in both TN and IPS. Many of the color modules contain built in touch panels.

The tried and trusted TFT is the display of choice for most industrial designs, but it does have its limitations in viewability and colour vibrancy. But what about the relatively new technology, IPS (in plane switching) which has turned the TFT into a super-TFT? What are the benefits and drawbacks of each?
IPS derives its name from the fact that the liquid-crystal molecules are aligned in parallel with the glass plates, whereas the TN principle adopted in conventional TFT displays is based on perpendicular alignment of the molecules. In an IPS display, the crystals remain oriented in parallel whether the pixel is turned on or off.
A TFT display is a form of Liquid Crystal Displaywith thin film transistors for controlling the image formation. The TFT technology works by controlling brightness in red, green and blue sub-pixels through transistors for each pixel on the screen. The pixels themselves do not produce light; instead, the screen uses a backlight for illumination. Discover our TFT Products
Because the pixels block light when in the off state (the opposite situation to conventional TFT), IPS TFT exhibits high contrast and the background is true black when the display is powered down.
Display choice really does depend on your application, end user and environment. It may be a higher-grade IPS is needed to satisfy outdoor requirements, or a lower cost standard TFT display is sufficient. Before you make your choice, why speak with us and we will be happy to talk you through your options.

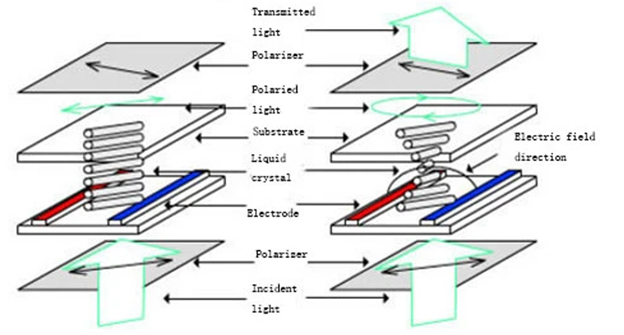
IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

The word TFT means Thin Film Transistor. It is the technology that is used in LCD or Liquid Crystal Display. It is also called Active Matrix LCD which differentializes from Passive Matrix LCD. A TFT substrate is composed of a matrix of pixels and ITO electrode (Indium Tin Oxide, a transparent electric conducting film) each with a TFT device and is so called array. Thousands or millions of these pixels together create an image on the display. The diagram below shows the simple structure of a pixel.
As long as there are TFT in the LCD, the LCD should be called a TFT LCD. But when the TFT LCD display was first commercialized, 100% TFT LCDs were TN (twisted Nematic) type TFT displays. As TN is a very technical term so most of the users ignored TN and named TN type TFT display as TFT display. While the newly developed TFT LCD display technologies such as IPS (in-plane-switching ) type TFT display, O-Film type TFT display (derived from TN type TFT display), MVA( Multi-domain Vertical Alignment) type TFT display, AFFS (Advanced Fringe Field Switching) type TFT display, they are widely call IPS display, O-Film display, MVA display and AFFS display. As the above terms have been used for long and widely accepted in the market, we will not try to correct the misunderstanding here. We will still use the TFT display (should be TN type TFT display) and IPS display (should be IPS type TFT display) in the following.
The twisted nematic effect (TN-LCD) was a main technology breakthrough that made LCDs practical. TN LCDs first make battery powered devices popular. TN-LCD displays led to the rapid expansion in the display field, quickly replacing other displays like LEDs, plasma, CRTs etc. By the 1990s, TN LCDs were widely used in portable electronics.
The TN display takes advantage of the ability of the nematic substance to rotate the polarization of light beams passing through it. Two polarizing filters, parallel planes of glass with their polarizing lines oriented at right angles with respect to each other, are positioned on either side of the liquid crystal. When light enters the display, it is polarized by the input filter. In the absence of an electric field, all the incoming light is transmitted. This is because the light polarization is rotated 90 degrees by the nematic liquid crystal, and the light therefore passes easily through the output filter, which is oriented to match the 90-degree shift. With the application of a voltage, an electric field is produced in the nematic liquid crystal. Under these conditions the polarization effect is reduced. If the voltage is large enough, the polarization effect disappears altogether, and the light is blocked by the output polarizing filter. The diagram below shows how a TN LCD works.
The best feature of TFT displays is the low cost due to a simpler manufacturing process, low-cost raw materials, and one of the oldest technologies for LCD displays. But they are not the best quality considering poor viewing angles, lower contrast ratio, slower response time, lower aperture ratio (each pixel not bright enough), and the worst is that there is one view angle with gray scale inversion (reversed image), see the below picture for reference.
IPS (in-plane-switching) technology is also one type of TFT LCD display. The basic LCD structure is similar to TN type TFT display but the inside display schematic is different.
In 1992, Hitachi researchers in Japan first developed details of the IPS technology. NEC and Hitachi became early manufacturers of active-matrix addressed LCDs based on the IPS technology. In 1996, Samsung developed the optical patterning technique that enables multi-domain LCD. Multi-domain and in-plane switching subsequently remained the dominant LCD designs through 2006. IPS technology is widely used in LCD panels for TVs, laptops, monitors, and smartphones. Apple Inc. products branded with the label Retina Display (such as iPhone 4 onward, iPad 3 on, iPad Mini 2 on, MacBook Pro with Retina display adopted IPS LCDs with LED backlighting.
An IPS LCD panel, when no electric field is applied to the liquid crystal cells, the cells naturally align in liquid crystal cells in a horizontal direction between two glass substrates which blocks the transmission of light from the backlight. This makes the display dark and results in a black display screen. When an electric field is applied, the liquid crystal cells are able to rotate through 90° allowing light to pass through resulting in a white display screen. IPS panels have superior image quality, good contrast ratio and wide viewing angles of up to 170°. IPS panels are well suited for graphics design and other applications which require accurate and consistent color reproduction.
In summary, normally high-end products such as Apple Mac computer monitors and Samsung mobile phones generally use IPS panels. Some high-end TV and mobile phones even use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) displays. This cutting-edge technology provides even better color reproduction, clear image quality, better color gamut, less power consumption when compared to LCD technology. Of course, a TFT LCD display can always meet the basic needs at the most efficient price.
This article is an original piece of content written by Bill Cheung, a marketing manager who has an engineering and technical support background at Orient Display. We are a LCD and display technology provider with over two decades of industry experience in delivering cutting edge display solutions. Please browse our knowledge base if you would like to learn more about LCDs!

Have you ever wonder where TFT derive from? Why is TFT referred to as LCD? The phenomenon started in early days, when bulky CRT displays were thing of the past and LCD was its replacement, but as time progresses, there were still room for improvement, which leads to the birth of TFT’s.
TFT is a variant of an LCD which uses thin film transistor technology to improve an image quality, while an LCD is class of displays that uses modulating properties of liquid crystals to form what we call an LCD (liquid crystals display) which in fact does not emits light directly.
Even though LCDs were very energy efficient, light weight and thin in nature, LCD were falling behind to the CRT display, which then leads to a change in LCD manufacturing, where performance became a big problem.
For example, having a 2001 Mustang vs a 2014 Mustang, the dimensions and engine of the 2014 has been redesign for performance reasons, not mentioning user friendly, so does the LCD to TFT.
As the birth of TFT, the elements are deposited directly on the glass substrate which in fact the main reason for the switch was because TFTs are easier to produce, better performance in terms of adjusting the pixels within the display to get better quality.
LCDs became ineffective over a period of time, almost all aspect of watching a TV, playing video games or using a handheld device to surf the net became daunting, this phenomenon is known as high response time with low motion rate.
Another problem with LCD was crosstalking, in terms of pixelating, this happens when signals of adjacent pixels affects operations or gives an undesired effect to the other pixel.
As TFT’s become very popular throughout the century due to its elaborate low charge associate and outstanding response time, LCDs became a thing of the past, and TFT became the predominant technology with their wider viewing angles and better quality this technology will be around for a long time.

In-Plane Switching (IPS) is a technology that overcomes the viewing limitations of conventional TFT-LCDs. It is also known as Super TFT.IPS derives its name from the fact that the liquid-crystal molecules are aligned in parallel with the glass plates, whereas the TN principle adopted in conventional TFT displays is based on perpendicular alignment of the molecules.
Pricing for small size IPS displays, particularly2.4 and 2.8", is comparable, if not favourable to TN-TFTs, meaning that you can upgrade from a monochrome display to a superior colour display without breaking the budget..
Our IPS-TFT displays are available from 1" to 23" and ideal for outdoor applications. To further enhance the displays where environmental challenges including sunlight, extreme temperatures, water or salt, or vandalism, can be an issue we have a number of

In recent years, smartphone displays have developed far more acronyms than ever before with each different one featuring a different kind of technology. AMOLED, LCD, LED, IPS, TFT, PLS, LTPS, LTPO...the list continues to grow.
There are many display types used in smartphones: LCD, OLED, AMOLED, Super AMOLED, TFT, IPS and a few others that are less frequently found on smartphones nowadays, like TFT-LCD. One of the most frequently found on mid-to-high range phones now is IPS-LCD. But what do these all mean?
LCD means Liquid Crystal Display, and its name refers to the array of liquid crystals illuminated by a backlight, and their ubiquity and relatively low cost make them a popular choice for smartphones and many other devices.
LCDs also tend to perform quite well in direct sunlight, as the entire display is illuminated from behind, but does suffer from potentially less accurate colour representation than displays that don"t require a backlight.
Within smartphones, you have both TFT and IPS displays. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, an advanced version of LCD that uses an active matrix (like the AM in AMOLED). Active matrix means that each pixel is attached to a transistor and capacitor individually.
The main advantage of TFT is its relatively low production cost and increased contrast when compared to traditional LCDs. The disadvantage of TFT LCDs is higher energy demands than some other LCDs, less impressive viewing angles and colour reproduction. It"s for these reasons, and falling costs of alternative options, that TFTs are not commonly used in smartphones anymore.Affiliate offer
IPS technology (In-Plane Switching) solves the problem that the first generation of LCD displays experience, which adopts the TN (Twisted Nematic) technique: where colour distortion occurs when you view the display from the side - an effect that continues to crop up on cheaper smartphones and tablets.
The PLS (Plane to Line Switching) standard uses an acronym that is very similar to that of IPS, and is it any wonder that its basic operation is also similar in nature? The technology, developed by Samsung Display, has the same characteristics as IPS displays - good colour reproduction and viewing angles, but a lower contrast level compared to OLED and LCD/VA displays.
This is a very common question after "LED" TVs were launched, with the short answer simply being LCD. The technology used in a LED display is liquid crystal, the difference being LEDs generating the backlight.
One of the highlights from TV makers at the CES 2021 tradeshow, mini-LED technology seemed far removed from mobile devices until Apple announced the 2021 iPad Pro. As the name implies, the technique is based on the miniaturization of the LEDs that form the backlight of the screen — which still uses an LCD panel.
Despite the improvement in terms of contrast (and potentially brightness) over traditional LCD/LED displays, LCD/mini-LEDs still divide the screen into brightness zones — over 2,500 in the case of the iPad and 2021 "QNED" TVs from LG — compared to dozens or hundreds of zones in previous-generation FALD (full-array local dimming) displays, on which the LEDs are behind the LCD panel instead of the edges.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. While this may sound complicated it actually isn"t. We already encountered the active matrix in TFT LCD technology, and OLED is simply a term for another thin-film display technology.
OLED is an organic material that, as the name implies, emits light when a current is passed through it. As opposed to LCD panels, which are back-lit, OLED displays are "always off" unless the individual pixels are electrified.
This means that OLED displays have much purer blacks and consume less energy when black or darker colours are displayed on-screen. However, lighter-coloured themes on AMOLED screens use considerably more power than an LCD using the same theme. OLED screens are also more expensive to produce than LCDs.
Because the black pixels are "off" in an OLED display, the contrast ratios are also higher compared to LCD screens. AMOLED displays have a very fast refresh rate too, but on the downside are not quite as visible in direct sunlight as backlit LCDs. Screen burn-in and diode degradation (because they are organic) are other factors to consider.Affiliate offer
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. An OLED display is comprised of thin sheets of electroluminescent material, the main benefit of which is they produce their own light, and so don"t require a backlight, cutting down on energy requirements. OLED displays are more commonly referred to as AMOLED displays when used on smartphones or TVs.
Super AMOLED is the name given by Samsung to its displays that used to only be found in high-end models but have now trickled down to more modestly specced devices. Like IPS LCDs, Super AMOLED improves upon the basic AMOLED premise by integrating the touch response layer into the display itself, rather than as an extra layer on top.
The latest evolution of the technology has been christened "Dynamic AMOLED". Samsung didn"t go into detail about what the term means, but highlighted that panels with such identification include HDR10+ certification that supports a wider range of contrast and colours, as well as blue light reduction for improved visual comfort.
Resolution describes the number of individual pixels (or points) displayed on the screen and is usually presented for phones by the number of horizontal pixels — vertical when referring to TVs and monitors. More pixels on the same display allow for more detailed images and clearer text.
To make it easier to compare different models, brands usually adopt the same naming scheme made popular by the TV market with terms like HD, FullHD and UltraHD. But with phones adopting a wide range of different screen proportions, just knowing that is not enough to know the total pixels displayed on the screen.Common phone resolutions
Speaking of pixel density, this was one of Apple"s highlights back in 2010 during the launch of the iPhone 4. The company christened the LCD screen (LED, TFT, and IPS) used in the smartphone as "Retina Display", thanks to the high resolution of the panel used (960 by 640 pixels back then) in its 3.5-inch display.
With the iPhone 11 Pro, another term was introduced to the equation: "Super Retina XDR". Still using an OLED panel (that is supplied by Samsung Display or LG Display), the smartphone brings even higher specs in terms of contrast - with a 2,000,000:1 ratio and brightness level of 1,200 nits, which have been specially optimized for displaying content in HDR format.
As a kind of consolation prize for iPhone XR and iPhone 11 buyers, who continued relying on LCD panels, Apple classified the display used in the smartphones with a new term, "Liquid Retina". This was later applied also to the iPad Pro and iPad Air models, with the name defining screens that boast a high range and colour accuracy, at least based on the company"s standards.
TFT(Thin Film Transistor) - a type of LCD display that adopts a thin semiconductor layer deposited on the panel, which allows for active control of the colour intensity in each pixel, featuring a similar concept as that of active-matrix (AM) used in AMOLED displays. It is used in TN, IPS/PLS, VA/PVA/MVA panels, etc.
LTPS(Low Temperature PolySilicon) - a variation of the TFT that offers higher resolutions and lower power consumption compared to traditional TFT screens, based on a-Si (amorphous silicon) technology.
IGZO(Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide) - a semiconductor material used in TFT films, which also allows higher resolutions and lower power consumption, and sees action in different types of LCD screens (TN, IPS, VA) and OLED displays
LTPO(Low Temperature Polycrystaline Oxide) - a technology developed by Apple that can be used in both OLED and LCD displays, as it combines LTPS and IGZO techniques. The result? Lower power consumption. It has been used in the Apple Watch 4 and the Galaxy S21 Ultra.
Among televisions, the long-standing featured technology has always been miniLED - which consists of increasing the number of lighting zones in the backlight while still using an LCD panel. There are whispers going around that smartphones and smartwatches will be looking at incorporating microLED technology in their devices soon, with it being radically different from LCD/LED displays as it sports similar image characteristics to that of OLEDs.
On the other hand, the use of multiple diodes for each pixel poses a challenge in terms of component miniaturization. For example, a Full HD resolution has just over two million pixels (1,920 x 1,080 dots), which requires 6 million microscopic LEDs using a traditional RGB (red, green, and blue) structure.
In the case of LCD displays, the main advantage lies in the low manufacturing cost, with dozens of players in the market offering competitive pricing and a high production volume. Some brands have taken advantage of this feature to prioritize certain features - such as a higher refresh rate - instead of adopting an OLED panel, such as the Xiaomi Mi 10T.

TFT and LCD are two different types of electronic displays used in computers, TVs, and smartphones. However, they are not as different as you might think. Let’s start with what those abbreviations mean.
A key weakness of TFT panels is that they do not have wide viewing angles, so they are better suited to displays that require you to view head-on. This can be a good or a bad thing, depending on your needs. For example, the narrower viewing angles mean people sitting or standing around you are less likely to be able to snoop on what you are doing on your mobile phone.
TFT panels are cheaper to manufacture, but they also consume much more power than regular LCD panels. Lastly, they have poorer sunlight visibility. You will find TFT displays on feature phones, smart feature phones, and low-end Android phones.
LCD: This is an abbreviation for “liquid crystal display”. It is a flat panel display with wider viewing angles compared to TFT. They also have lower power consumption and so deliver much better battery life than their TFT counterparts.
In summary, while TFT panels have some distinct advantages, they fall short in other areas and so their use have been limited to low end phones, from feature phones to entry-level Android phones. Plastic feels inferior to touch than glass, which means that TFT screens don’t get to feature much on mid-range and premium devices.
As we see improvements to TFT technology, we will see them deployed on higher end devices over time. In 2022, Samsung used TFT displays in its mid-range Galaxy A13 and Galaxy A23. Perhaps those improvements are happening already.
For now, LCD is the most widely used display type in modern smartphones. At the very top end, we have premium flagships using OLED and AMOLED displays.
TFT displays are higher quality components than regular LCD displays. TFT displays are sharper, brighter, and refresh better than LCD panels. However, they have weaknesses that make them unsuitable for higher end phones.
AMOLED panels have all the benefits of OLED screens, which means they are better than LCD panels. They are expensive though, and so are used in high-end smartphones only.

With regard to gaming, some criticisms IPS monitors include more visible motion blur coming as a result of slower response times, however the impact of motion blur will vary from user to user. In fact, mixed opinions about the “drawbacks” of IPS monitor for gaming can be found all across the web. Take this excerpt from one gaming technology writer for example: “As for pixel response, opinions vary. I personally think IPS panels are quick enough for almost all gaming. If your gaming life is absolutely and exclusively about hair-trigger shooters, OK, you’ll want the fastest response, lowest latency LCD monitor. And that means TN. For the rest of us, and certainly for those who place even a modicum of importance on the visual spectacle of games, I reckon IPS is clearly the best panel technology.” Read the full article here.
IPS monitors deliver ultra-wide 178-degree vertical and horizontal viewing angles. Graphic designers, CAD engineers, pro photographers, and video editors will benefit from using an IPS monitor. Many value the color benefits of IPS monitors and tech advances have improved IPS panel speed, contrast, and resolution. IPS monitors are more attractive than ever for general desktop work as well as many types of gaming. They’re even versatile enough to be used in different monitor styles, so if you’ve ever compared an ultrawide vs. dual monitor setup or considered the benefits of curved vs. flat monitors, chances are you’ve already come into contact with an IPS panel.
TN monitors, or “Twisted Nematic” monitors, are the oldest LCD panel types around. TN panels cost less than their IPS and VA counterparts and are a popular mainstream display technology for desktop and laptop displays.
These high-end VA-type monitors rival IPS monitors as the best panel technology for professional-level color-critical applications. One of the standout features of VA technology is that it is particularly good at blocking light from the backlight when it’s not needed. This enables VA panels to display deeper blacks and static contrast ratios of up to several times higher than the other LCD technologies. The benefit of this is that VA monitors with high contrast ratios can deliver intense blacks and richer colors.
There is another type of panel technology that differs from the monitor types discussed above and that is OLED or “Organic Light Emitting Diode” technology. OLEDs differ from LCDs because they use positively/negatively charged ions to light up every pixel individually, while LCDs use a backlight, which can create an unwanted glow. OLEDs avoid screen glow (and create darker blacks) by not using a backlight. One of the drawbacks of OLED technology is that it is usually pricier than any of the other types of technology explained.
When it comes to choosing the right LCD panel technology, there is no single right answer. Each of the three primary technologies offers distinct strengths and weaknesses. Looking at different features and specs helps you identify which monitor best fits your needs.
LCD or “Liquid Crystal Display” is a type of monitor panel that embraces thin layers of liquid crystals sandwiched between two layers of filters and electrodes.
While CRT monitors used to fire electrons against glass surfaces, LCD monitors operate using backlights and liquid crystals. The LCD panel is a flat sheet of material that contains layers of filters, glass, electrodes, liquid crystals, and a backlight. Polarized light (meaning only half of it shines through) is directed towards a rectangular grid of liquid crystals and beamed through.
Note: When searching for monitors you can be sure to come across the term “LED Panel” at some point or another. An LED panel is an LCD screen with an LED – (Light Emitting Diode) – backlight. LEDs provide a brighter light source while using much less energy. They also have the ability to produce white color, in addition to traditional RGB color, and are the panel type used in HDR monitors.
Early LCD panels used passive-matrix technology and were criticized for blurry imagery. The reason for this is because quick image changes require liquid crystals to change phase quickly and passive matrix technology was limited in terms of how quickly liquid crystals could change phase.
As a result, active-matrix technology was invented and transistors (TFTs) began being used to help liquid crystals retain their charge and change phase more quickly.
Thanks to active-matrix technology, LCD monitor panels were able to change images very quickly and the technology began being used by newer LCD panels.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey