difference between super amoled and pls tft lcd display pricelist
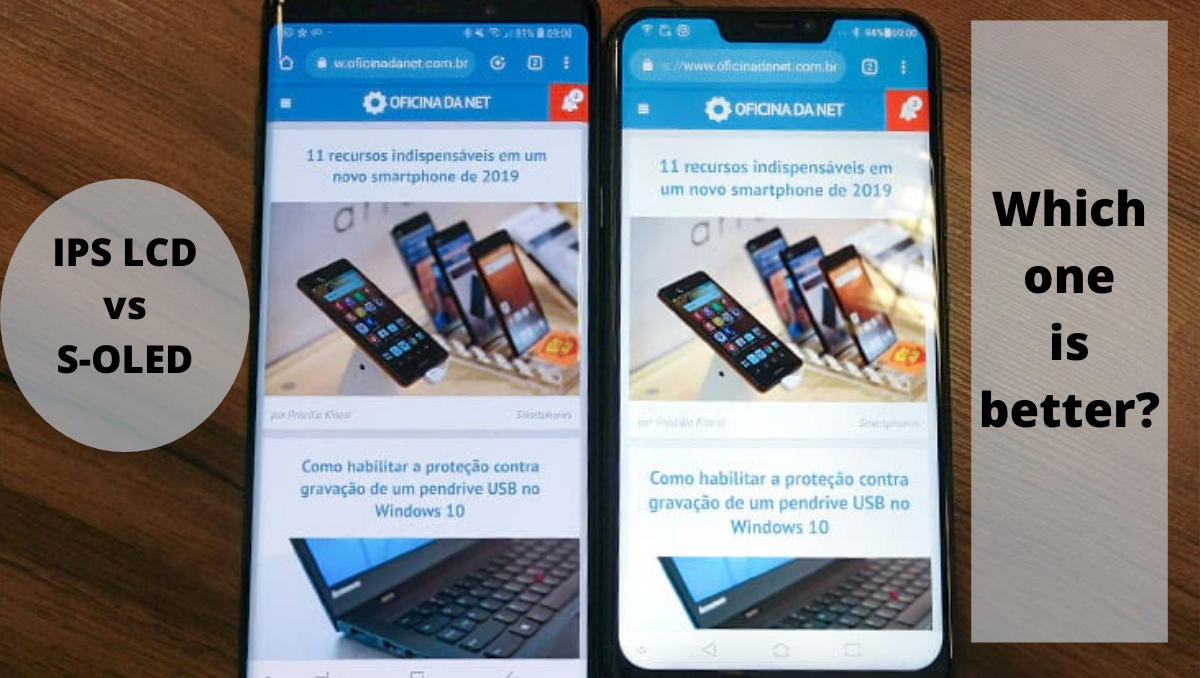
Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Both technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages. So, how do you know which one is best for your needs? We compare these two technologies below.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.
Nauticomp Inc.provides world-class fully customizable touchscreen displays for commercial and industrial settings. With features like sunlight readability, brightness adjustability, infrared lighting, full backlighting, all-weather capabilities, etc., our displays are second to none. Contact us today to learn more.

AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) and TFT (Thin Film Transistor) are the two types of displays that are used in mobile phones. TFT is actually a process of producing the displays and is used even by AMOLED but for most purposes, TFT is used to refer to LCD displays. The difference between them is the material as AMOLED uses organicmaterials, mainly carbon, while TFT does not.
There are differences between the two that are quite tangible. For starters, AMOLED generates its own light rather than relying on a backlight like a TFT-LCD does. This consequently means that AMOLED displays are much thinner than LCD displays; due to the absence of a backlight. It also results in much better colors than a TFT is capable of producing. As each pixel’s color and light intensity can be regulated independently and no light seeps from adjacent pixels. A side by side comparison of the two displays with the same picture should confirm this. Another effect of the lack of a backlight is the much lower power consumption of the device. This is very desirable when it comes to mobile phones where every single feature competes for the limited capacity of the battery. As the screen is on 90% of the time that the device is being used, it is very good that AMOLED displays consume less. Just how much of a difference is not very fixed though as it really depends on the color and intensity of the image. Having a black background with white text consumes much less energy than having black text on a white background.
The biggest disadvantage that AMOLED has is the shorter lifespan of the screen compared to TFT. Each pixel in the display degrades with each second that it is lit and even more so the brighter it is. Â Despite improvements on the lifetime of AMOLED displays, AMOLED still only lasts a fraction of the lifetime of a TFT display. With that said, an AMOLED display is able to outlast the usable lifetime of the device before parts of it start to degrade.
The main hindrance to the massive adaptation of AMOLED is the low production numbers. TFT has been in production for much longer and the infrastructure is already there to meet the demands.

Tried and trusted TFT technology works by controlling brightness in red, green and blue sub-pixels through transistors for each pixel on the screen. The pixels themselves do not produce light; instead, the screen uses a backlight for illumination.
By contrast the Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) display requires no backlight and can light up or turn off each of their pixels independently. As the name suggests, they are made of organic material.
An AMOLED display has many other benefits which make it a superior looking display including exceptional vieiwng angles and a display that looks practically black when it is switched off.
So, why use a TFT display? Well, it is a mature technology meaning the manufacturing processes are efficient, yields high and cost much lower than AMOLED.
TFT displays also have a much longer lifespan than AMOLED displays and are available in a far greater range of standard sizes, which can be cut down to fit a space restricted enclosure for a relatively low cost adder.
Which type of display you choose really depends on your application, environment and users, so why not get in touch with us today to discuss your requirements.

When we purchase a new smartphone we go through a list of specifications that includes the processor, software, cameras, display type, battery, etc. The display of the smartphone is something which has always been a concern for people. And smartphone technology has advanced so much in the past decade that you get several display technology options to choose from.
Today, a smartphone is not just a means to send and receive calls and texts. It has become a general necessity, so choosing the right technology should be your main priority. Coming back to displays, as we said there are plenty of display types available right now.
Two of the main contenders for display technologies that are widely available are AMOLED and LCD. Here in this article, we will be comprising AMOLED vs LCD and find out which one is better for you.
Starting with the AMOLED first, it is a part of the OLED display technology but with some more advanced features. To completely know about it must understand its all three components. The first one is LED, “Light Emitting Diode”. Then we have “O” which stands for organic and makes the OLED.
It actually means that organic material is placed with two conductors in each LED, which helps to produce the light. And the “AM” in AMOLED means Active Matrix, it has the capability to increase the quality of a pixel.
The AMOLED display is similar to the OLED in various factors like high brightness and sharpness, better battery life, colour reproduction, etc. AMOLED display also has a thin film transistor, “TFT” that is attached to each LED with a capacitor.
TFT helps to operate all the pixels in an AMOLED display. This display might have a lot of positives but there are a few negatives too let’s point both of them out.
It comes with individual LEDs so, the pixels can be turned on and off individually. This will show you true black colours, as the pixels on the black part of the image will be turned off.
A major issue with these displays is of burning of pixels. After showing a specific image or colour for a longer period of time, the pixel can get burned. And if there is a problem with a single pixel it will affect the entire display.
Low outdoor visibility, usually the AMOLED Displays are quote not bright in direct sunlight and outdoor readability could be a problem for some devices but average screen brightness.
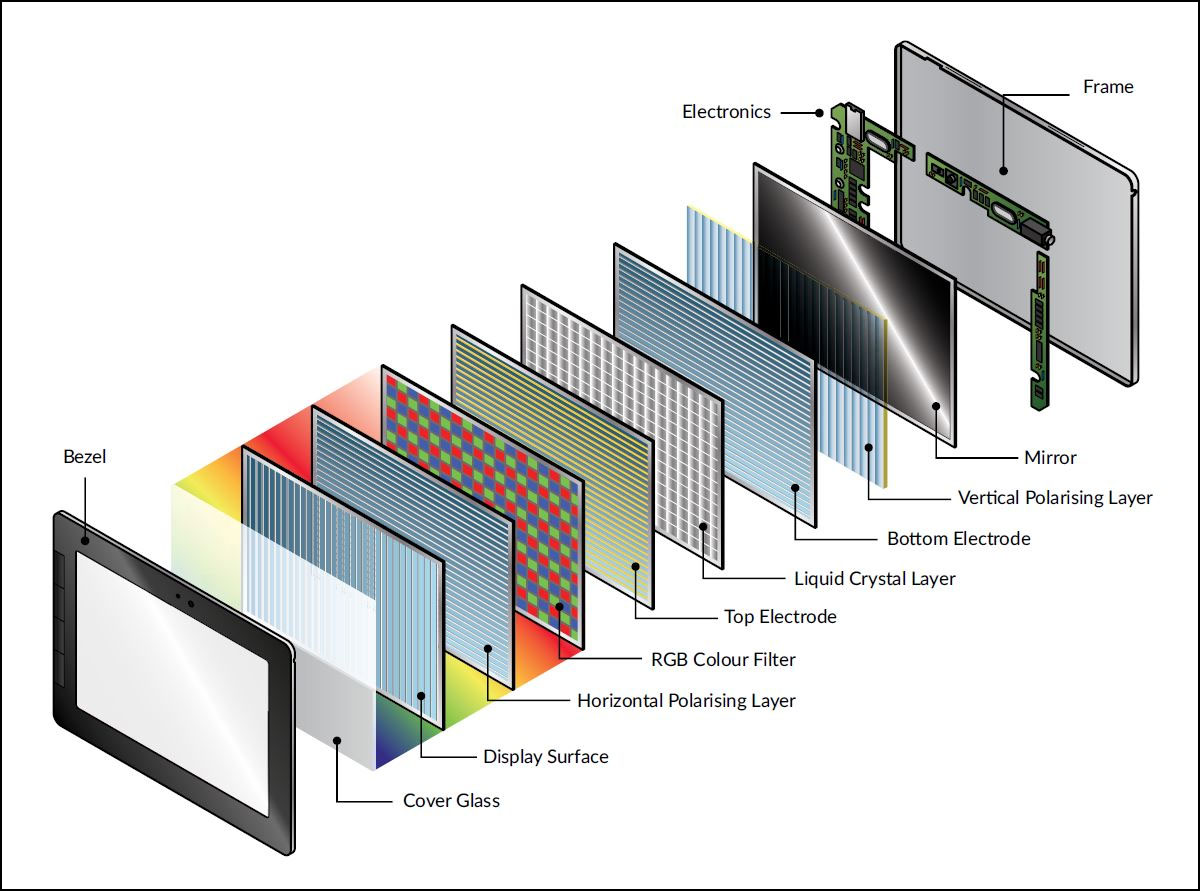
The LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display”, and this display produces colours a lot differently than AMOLED. LCD display uses a dedicated backlight for the light source rather than using individual LED components.
The LCD displays function pretty simply, a series of thin films, transparent mirrors, and some white LED lights that distributes lights across the back of the display.
As we have mentioned, an LCD display always requires a backlight and also a colour filter. The backlight must have to pass through a thin film transistor matrix and a polarizer. So, when you see it, the whole screen will be lit and only a fraction of light gets through. This is the key difference comparing AMOLED vs LCD and this is what differentiates these two display technologies.
The LCD displays are cheaper compared to the AMOLED as there is only one source of light which makes it easier to produce. Most budget smartphones also use LCD displays.
LCD displays have bright whites, the backlight emits lots of light through pixels which makes it easy to read in outdoors. It also shows the “Accurate True to Life” colours, which means it has the colours that reflect the objects of the real world more accurately than others.
LCDs also offer the best viewing angle. Although it may depend on the smartphone you have. But most high-quality LCD displays support great viewing angles without any colour distortion or colour shifting.
The LCD displays can never show the deep blacks like AMOLED. Due to the single backlight, it always has to illuminate the screen making it impossible to show the deep blacks.
The LCDs are also thicker than other displays because of the backlight as it needs more volume. So, LCD smartphones are mostly thicker than AMOLED ones.
Both of these display technologies have their own Pros and Cons. Taking them aside everything ends up with the user preferences as people might have different preferences among different colours and contrast profiles. However, a few factors might help you to decide which one fits perfectly for you.
Let’s start with the pricing. Most AMOLED display smartphones always cost more than an LCD smartphone. Although the trend is changing a bit. But still, if you want to get a good quality AMOLED display you have to go for the flagship devices.
The colors are also very sharp and vibrant with the AMOLED displays. And they look much better than any LCD display. The brightness is something where LCDs stood ahead of the AMOLED display. So using an LCD display outdoors gives much better results.
The last thing is battery consumption, and there is no one near the AMOLED displays in terms of battery. As of now, all smartphones feature a Dark Mode and most of the apps and UI are dark black with a black background. This dark UI on smartphones doesn’t require any other light, it gives the AMOLED displays a boost in battery performance.
Looking at all these factors and comparing AMOLED vs LCD displays, the AMOLED displays are certainly better than the LCDs. Also, the big display OEMs, like Samsung and LG are focusing more the OLED technologies for their future projects. So, it makes sense to look out for AMOLED displays. That being said, if we see further enhancements in the LCD technology in terms of battery efficiency and more, there is no point to cancel them at this moment.

The world of smartphones has been busy for the past few months. There have been numerous revolutionary launches with groundbreaking innovations that have the capacity to change the course of the smartphone industry. But the most important attribute of a smartphone is the display, which has been the focus for all prominent players in the mobile phone industry this year.
Samsung came up with its unique 18:5:9 AMOLED display for the Galaxy S8. LG picked up its old trusted IPS LCD unit for the G6’s display. These display units have been familiar to the usual Indian smartphone buyer. Honor, on the other hand, has just unveiled the new Honor 8 Pro for the Indian market that ships with an LTPS LCD display. This has led to wonder how exactly is this technology different from the existing ones and what benefits does it give Honor to craft its flagship smartphone with. Well, let’s find out.
The LCD technology brought in the era of thin displays to screens, making the smartphone possible in the current world. LCD displays are power efficient and work on the principle of blocking light. The liquid crystal in the display unit uses some kind of a backlight, generally a LED backlight or a reflector, to make the picture visible to the viewer. There are two kinds of LCD units – passive matrix LCD that requires more power and the superior active matrix LCD unit, known to people as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) that draws less power.
The early LCD technology couldn’t maintain the colour for wide angle viewing, which led to the development of the In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD panel. IPS panel arranges and switches the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules of standard LCD display between the glass substrates. This helps it to enhance viewing angles and improve colour reproduction as well. IPS LCD technology is responsible for accelerating the growth of the smartphone market and is the go-to display technology for prominent manufacturers.
The standard LCD display uses amorphous Silicon as the liquid for the display unit as it can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. This though restricts the display resolution and adds to overall device temperatures. Therefore, development of the technology led to replacing the amorphous Silicon with Polycrystalline Silicon, which boosted the screen resolution and maintains low temperatures. The larger and more uniform grains of polysilicon allow faster electron movement, resulting in higher resolution and higher refresh rates. It also was found to be cheaper to manufacture due to lower cost of certain key substrates. Therefore, the Low-Temperature PolySilicon (LTPS) LCD screen helps provide larger pixel densities, lower power consumption that standard LCD and controlled temperature ranges.
The AMOLED display technology is in a completely different league. It doesn’t bother with any liquid mechanism or complex grid structures. The panel uses an array of tiny LEDs placed on TFT modules. These LEDs have an organic construction that directly emits light and minimises its loss by eradicating certain filters. Since LEDs are physically different units, they can be asked to switch on and off as per the requirement of the display to form a picture. This is known as the Active Matrix system. Hence, an Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display can produce deeper blacks by switching off individual LED pixels, resulting in high contrast pictures.
The honest answer is that it depends on the requirement of the user. If you want accurate colours from your display while wanting it to retain its vibrancy for a longer period of time, then any of the two LCD screens are the ideal choice. LTPS LCD display can provide higher picture resolution but deteriorates faster than standard IPS LCD display over time.
An AMOLED display will provide high contrast pictures any time but it too has the tendency to deteriorate faster than LCD panels. Therefore, if you are after greater picture quality, choose LTPS LCD or else settle for AMOLED for a vivid contrast picture experience.

Devices like smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets require a technology that serves better quality visuals and excellent battery life.
The difference Between AMOLED and TFT is their production and quality. The cost of producing Active-Matrix Organic LED is higher than the Thin-Film Transistor LCDs.
Parameters of ComparisonAMOLEDTFTFull FormsThe full form of an AMOLED Display is an Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode.The full form of the TFT is a Thin-Film Transistor.
Co-related VersionsIts closest technology version is its older form, out of which it is improvised, OLEDs (Organic Light-Emitting Diodes).Its closest technology version is its upgraded form, IPS LCDs (In-Plane Switching LCDs) with improvised features.
OLED displays a thin type of film display technology. AMOLED is also a sub-form of it that is consists of organic compounds of the electroluminescent and pixel technology.
The full form of an AMOLED Display is an Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. The AMOLED display is the variant of Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs).
Its closest technology version is its older form, out of which it is improvised, OLEDs (Organic Light-Emitting Diodes). The display looks black after turning it off.
The product is costlier than TFT. All-round viewing angles. Bright and vibrant colors are available with these LEDs. It provides visuals with loss-resolution quality.
Just like AMOLED, this tech also improves image qualities, contrasts, and their addressability. But it provides visuals with high-resolution quality, even better than the former.
The display does not entirely look black after turning it off. And the Color inversion at extreme viewing angles. Limited contrast options are available.
But it is cheaper than the AMOLED. It is available on easily affordable devices and smartphones. Its closest technology version available is its upgraded form, IPS LCDs (In-Plane Switching LCDs) with improvised features.
Active-Matrix Organic LED displays are available in bright and vibrant colors. On the other hand, Thin-Film Transistor LCDs have limited contrast options.

These days you really only have two choices of screens when you are buying a smartphone or tablet: LCD or AMOLED. Many of you probably can’t tell the difference between the two screen types, but both technologies have inherent strengths and weaknesses. LCD has been around for a while, but AMOLED phones are gaining popularity thanks to Samsung and other manufacturers. There isn’t a clear winner at this point in time, so here’s a look at both.
Update:Thisarticle was originally published on June 18, 2012, and updated on Aug. 25, 2014, to reflect recent devices. DT writer Aaron Liu contributed to this article.
LCD, Liquid Crystal Display, has been a part of our lives for years now. Besides mobile devices, we see LCD screens being used with almost every computer monitor, and in the majority of TVs. While these screens are made of wondrous liquid crystals, they also require a couple panes of glass, and a light source. LCD screens produce some of the most realistic colors you can find on a screen, but might not offer as wide of a contrast ratio (darker darks and brighter brights) as an AMOLED screen.
Some common terms you will find associated with LCD displays are TFT and IPS. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, which makes the wiring of LCD screens more efficient by reducing the number of electrodes per pixel. One benefit of TFT displays is an improved image quality over standard LCD screens. Another popular LCD technology is In-Plane Switching, or IPS, which improves upon TFT by offering much wider viewing angles and color reproduction on LCD screens. IPS screens are able to achieve this by keeping all the liquid crystals parallel to the screen. IPS is generally preferable to standard TFT.
AMOLED, Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, technology has grown in popularity in recent years, particularly among Samsung products. AMOLED screens consist of a thin layer of organic polymers that light up when zapped with an electric current. Due to this simple construction, AMOLED screens can be extremely thin and do not require a backlight. The benefit of losing a backlight is readily apparent: these screens are able to produce blacks so deep that the screen pixels can shut right off. Shutting off pixels can also save electricity and battery life in phones and tablets. Just keep your backgrounds close to black and you’ll save energy.
Sometimes when you read about AMOLED screens, you might hear people complaining about something called a “pentile” display. This is a feature of most color AMOLED screens. Instead of having just a single red, blue, and green sub pixel per actual pixel, pentile displays have a RGBG sub pixel layout which has two green sub pixels for each red and blue. The positive of this technology is that you are able to create a screen that is just as bright as normal screens with one third the amount of sub pixels. The negative of pentile screens is that they can appear grainy, or appear to be lower resolution due to the larger, more visible sub pixels. For a while, Samsung begun using a display type called Super AMOLED Plus, which does not use a pentile sub pixel layout and also improves viewability in direct sunlight — traditionally a weakness for AMOLED. Samsung equipped the Galaxy S II with a Super AMOLED plus screen, but then reverted back to Super AMOLED screens for the Galaxy S III, citing screen life as the reason for the switch.
There are pros and cons for each type of screen, and both screen technologies can produce vivid, beautiful displays. The only way to know for sure if the screen on your future device will satisfy you is to try it out for yourself. You will be able to easily see if the screen viewing angles, contrast ratio, and color reproduction will fit your needs after using the phone for just a few minutes.

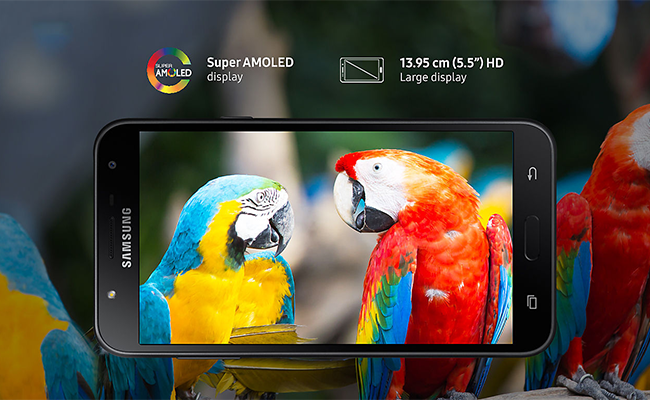
Super AMOLED is Samsung"s own version of AMOLED display which is enhanced for a better output. Most of Samsung"s mid-range and flagship smartphones come with a Super AMOLED display. Even other brands have started using this display off late. There are many benefits of having such a display in a smartphone. With Super AMOLED display, a phone can be thinner, consume less battery, offer higher contrast and better touch sensitivity among other benefits. Samsung has been using this technology in its phones since a long time and it continues enhancing the display for even better output. Below is a list of all the Super AMOLED display phones with their accurate specifications and features.

Smartphone displays may all look the same to some users. Although if you’d compare phones and look at the specs sheet, you may see some unfamiliar abbreviations when you check the technology used on the screen.
In reality, smartphone panels differ in a lot of ways like brightness produced, contrast, power consumption, viewing angles, and more. This quick guide aims to define and identify these technologies that came from different companies.
Let’s first start with the basics. An LCD or Liquid Crystal Display is a type of panel that uses liquid crystals which are back-lit. It’s one of the most common and widely-used technology since they are easily manufactured and doesn’t cost a lot to produce.
In general, it performs well under sunlight since the cells are illuminated from behind. The only drawback is that it doesn’t reproduce color as faithful and accurate as other displays that don’t go for this approach.
Short for Thin Film Transistor, TFT LCD is basically an improved version of LCD wherein an extra transistor and capacitor are both attached to each pixel. This is the same active matrix (AM) technology used in AMOLED displays which we’ll discuss later on.
Because of this, TFT LCDs are able to produce images with better contrast than the usual LCDs. They are also still cheap to produce. Although, viewing angles generally aren’t that impressive while color reproduction is a bit altered. They are now commonly used in low-end devices.
If TFT has one sheet of transistor supporting each pixel, LG Display’s IPS or In-Plane Switching LCDs make use of two transistors for each pixel which is then illuminated with a stronger backlight. This results to way better viewing angles than TFT and a more faithful color reproduction. Any image viewed within 178 degree from all four sides will retain clear details.
One downside, though, is that since it uses a more powerful backlight, it requires slightly more power from the battery as compared to handsets that use non-LCD panels. These are used in majority of handsets today.
A Super-Twisted Nematic display is a type of monochrome passive-matrix LCD that has an even lower cost of production than TFT LCDs. It also consumes less power than both the TFT and IPS displays which is a good thing, but the issue here is that it shows lower image quality and slower response time than TFT panels.
Additionally, STN LCDs can also be reflective which makes it visible even under direct sunlight. Because of this, it is being used for inexpensive phones and informational screens of digital devices.
TFD stands for Thin Film Diode which was made as a sort of getting the best of two things. It has the low power consumption of STN LCDs but since it doesn’t yield very impressive picture quality, it made use of the imaging performance of a TFT LCD.
This is done by pressing diodes together between two pieces of thin glass and the outcome proved that it had faster refresh rates with ghosting kept to a minimum.
A product of Japan Display Inc. (JDI), IPS Neo addresses the issues involved in manufacturing liquid crystal panels such as affecting the production yield due to unwanted foreign particles included in the process.
There’s a detailed scientific process that involves using highly transmissive liquid crystals but basically, because of this unique method from the company, IPS Neo displays give off a higher contrast with flexible viewing angles. This implementation also makes it possible to mass produce these panels which was previously thought to be difficult.
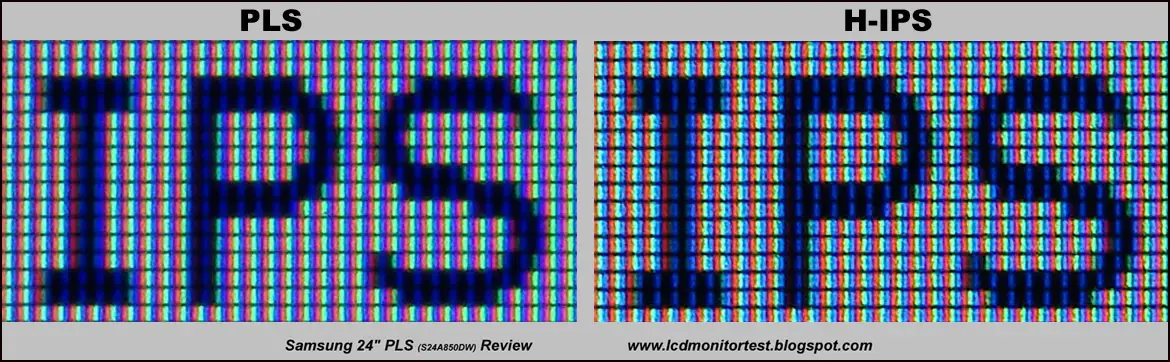
This specific type of screen is from Samsung Mobile Display and was introduced back in 2010. Super PLS (Plane to Line Switching) were made for LCDs and is an improvement to LG Display’s IPS panels. The company claims that Super PLS is ‘about 100%’ better when talking about viewing angles — putting it in the league of AMOLED displays. It is also 10% brighter which would greatly benefit users when used outdoors.
The Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode, or simply AMOLED, was started to be used in mobile phones in 2008. As we’ve mentioned earlier, it uses active matrix but this time for OLED pixels which is simply another term for thin-film display technology . It basically generates light upon electrical activation after combining with a TFT array and has all the characteristics of an OLED display like lively color reproduction, high brightness and sharpness, and is lightweight.
One of the noticeable differences of using AMOLED screens is its deep blacks. This is possible since OLED displays are always off by default unlike LCD panels that are always back-lit. Apart from showing true blacks (since the cell is basically turned off), it also consumes less power.
These are some of the reasons why it quickly gained popularity on high-end devices and because of this, more manufacturers have made the switch from TFT LCDs. Of course, it also has some cons to it. AMOLED displays don’t perform as well as back-lit LCDs under direct sunlight and diode degradation happens over time since they are organic.
Rounding up the list is the Super AMOLED display that we commonly see on mid- to high-end Samsung handsets. They are obviously an advanced counterparts of AMOLED displays from the South Korean company and are built with touch sensors right on the display unlike implementing a separate touch-sensitive layer. This move makes Super AMOLED displays one of the thinnest displays available for electronic devices.
In addition, they are also a lot more responsive when compared to AMOLED displays. Performance outdoors where there is direct sunlight has also improved here while requiring even less power from the battery.
We hope that this quick guide helped you in understanding more about the displays when looking at a smartphone’s specs sheet. If you have any more questions or additions to the article, chime in on the comments section below.

By now you know that (one of) AMOLED"s Achilles" heel is readability in direct sunlight. But Samsung"s been working hard to fix that with its new Super AMOLED technology. Techblog took the display to task by pitting the Samsung Galaxy S (4-inch, 480 x 800 pixel Super AMOLED) against the HTC Desire (3.7-inch 480 x 800 pixel AMOLED) and Sony Ericsson XPERIA X10 (4-inch, 480 x 854 pixel TFT LCD). It"s clear from the video embedded after the break that the LCD still has the edge in the harsh Greek sun, but the Super AMOLED certainly makes a much stronger showing than its AMOLED sib. In fact, differences in visibility between the LCD and Super AMOLED are often indistinguishable, like the picture above. That"ll be good news for us just as soon as Samsung can start meeting demand... regardless of what Stevie J has to say. Check the video after the break and be sure to click the source for some more side-by-side pics, including a few taken indoors where that Super AMOLED display really shines.
There’s nothing more annoying than having to work on a mobile phone that has a cracked screen. Forget the unsightly scar, trying to make sense of what you’re looking at or reading is a real nuisance. It doesn’t matter how hard you try to keep your phone free of damage, sometime or the other, misfortune is bound to strike. That’s the thing about gadgets like this - as tough as they seem, sometimes, even the slightest drop can cause major damage. You cannot undo something like this, but what you can do is save yourself the trouble of buying a brand new phone. You’ll find a cheaper alternative in mobile displays.
For every phone model, there are more than a couple of mobile displays to choose from. When it comes to the display type of these mobile accessories, the popular ones are haptic/tactile touchscreen, IPS LCD, LCD, super AMOLED, and TFT LCD mobile displays. These displays are pretty easy to replace - position the film on your phone’s screen until you’re satisfied with the placing, before gently peeling the layer off.
Planning a road trip with your family? We assume things are going to get pretty tiring once everyone has gotten over the initial excitement of the whole adventure. Well, just because you’re locked in a car, it doesn’t mean you have to cage yourself to feelings of boredom. May be you can get social online or watch a couple of funny clips on your phone. And in a situation like this, mobile displays that double as stands prove to be really useful. Some of these displays feature a 3D video enlarged screen that’s also foldable. The foldable handle of these screens allow you to place your mobile phone at a comfortable angle so your eyes are not irritated, and you can make the most of the whole experience. Compact in size, many of these mobile displays are designed to fit different models of smartphones; like iPhones or mobile phones from brands like Samsung, Nokia, and Micromax.
From HTC, Nokia, Apple, Sony, and Samsung, to Ample Wings, Stylus, Aptroid, and Online for Good, online shopping is your destination for the latest and the best models of mobile displays. This is also the only shopping medium that allows you to check out products, compare their prices in India, and read up a couple of reviews so you can make an informed buying decision.

List of Mobile Phones with Amoled Display (Dec 2022) with price ranging from Rs. 4,740 to Rs. 172,790. We have found 1097 phones. Here is the summary of the results:
Best phones: The best phones to buy are Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra 512GB with a spec score of 97, Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra with a spec score of 97 and OnePlus 10 Pro 256GB with a spec score of 97.
Performance: Phones such as realme GT Neo 3 5G 150W Thor Limited Edition, realme GT Neo 3 5G 256GB and realme GT Neo 3 5G promise smooth and lag-free performance.
Camera: For good image quality, phones such as Samsung Galaxy Note 10, Samsung Galaxy Note 10 Plus (Galaxy Note 10 Pro) and Samsung Galaxy S10 Plus are good buys.
Latest Mobile Phones with Amoled Display (Dec 2022): Phones like Elephone U3H, realme GT Neo 3T 5G 256GB and vivo V25 5G were launched in the last 30 days.

One of the numerous choices you have when purchasing a new cell phone is its display type. Two noteworthy technologies available at the market, AMOLED (or Super AMOLED) and IPS LCD, and both have their own preferences and disadvantages.
So, it’s worth the attention that all the significant manufacturers put a couple of exclusive advancements over the establishments laid by AMOLED or IPS LCD. In other words, the display of the phone is much more than it utilizes So its better to compare AMOLED vs IPS.
Contrasts between these two technologies have change throughout the years and will keep on changing as new overhauls show up, so watch out for the most up to date refreshes from the major producers.
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) is an upgraded version of OLED (organic light emitting diode). The technology utilizes natural compounds which produce (or “discharge”) light when present to an electric flow. Most of the time, this wipes out the requirement for backlighting, which decreases bulk and power consumption.
There’s a better viewing angles in modern AMOLED displays, surpassing the IPS. On the chance that you need profound blacks, nothing beats an AMOLED board! Be that as it may, since AMOLED is harder to create than IPS, costs are higher, and pictures aren’t exactly as sharp.Since each “dot” is basically its own shad light in an AMOLED show, colours are good, and contrast is extraordinary.
The brightness of each spot fluctuates by its shading. So considerations must be taken to make each color dot show up as bright as different colours around it. Because of this restriction, AMOLED screens aren’t as visible in sunshine as IPS shows. At that point, to make an already difficult situation even worse, AMOLED dots corrupt, lessening the shading immersion of the panel after some time.
IPS (in-plane switching) is grow essentially to enable LCD to defeat the constraints of “ordinary” TFT LCD. TFT (thin film transistor) displays ordinarily had slow reaction times which at first tormented PC gamers who require screens with quick response times, yet this in the end became problematic to standard clients when touchscreens ended up used commonly.
View angles on TFT screens were alright when you were sitting directly before one. However, smartphones and tablets require more extensive angles than TFT had the option to give. Moreover, shading replication and sharpness on IPS LCDs were superior to on the TFT predecessors and most contending technologies. When need perfect, splendid whites, IPS is the panel for you!
There truly is no winner with regards to AMOLED versus IPS LCD, but it’s still supportive to comprehend what every technology includes. A significant number of the issues and impediments we discuss are being manage by Samsung, Apple.
The other real players, as everyone changes the displays in their handsets and the innovation lying underneath. Therefore, continue perusing the reviews out to perceive how AMOLED and IPS LCD charge in the years to come.
Eventually, you should concentrate on the qualities of every technology while picking – that is splendid color and profound blacks for AMOLED, and natural color and sharpness for IPS LCD. It is decent to have one technology that does everything superbly, obviously, but we’re not exactly there yet.

The information on this website is provided on "as is, as available basis" without warranty of any kind. DeviceSpecifications is not responsible for any omissions, inaccuracies or other errors in the information it publishes. All warranties with respect to this information are disclaimed. Reproduction of any part of this website in its entirety or partially or in any form or medium without prior written permission is prohibited. The trademarks, marques and logos of the manufacturers of devices, software, hardware, etc. are the property of their respective owners.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
{"backgroundColor":"#e6f4fa","sideMsg":{"t_id":"","language":{"en_us":""},"id":""},"data":[{"bannerInfo":{"t_id":"Page192a42f3-0d83-42f6-9dbf-98c3c84fca20","language":{"en_us":"%3Cp%3ESave%20up%20to%20%7BsavingPercent%7D%20on%20Second%20Chance%20Featured%20Deals%20plus%20earn%202x%20MyLenovo%20Rewards.%26nbsp%3B%3Ca%20href%3D%22%2Fd%2Fdeals%2Fdoorbusters%2F%3FIPromoID%3DLEN944203%22%20target%3D%22_self%22%20textvalue%3D%22Shop%20Now%20%26gt%3B%22%3E%3Cstrong%3EShop%20Now%20%26gt%3B%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fa%3E%3Cbr%2F%3E%3C%2Fp%3E","en":"%3Cp%3ESave%20up%20to%2078%25%20on%26nbsp%3BCyber%20Week%20Doorbusters.%26nbsp%3B%26nbsp%3B%3Ca%20href%3D%22https%3A%2F%2Fadmin.lenovo.com%2Fd%2Fdeals%2Fdoorbusters%2F%3FIPromoID%3DLEN944203%22%20target%3D%22_self%22%20textvalue%3D%22Shop%20Now%20%26gt%3B%22%20style%3D%22white-space%3A%20normal%3B%22%3E%3Cstrong%3EShop%20Now%20%26gt%3B%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fa%3E%3C%2Fp%3E"},"id":"Page192a42f3-0d83-42f6-9dbf-98c3c84fca20"}},{"bannerInfo":{"t_id":"Page55376285-bfd0-4d63-bca5-1b119e582296","language":{"en_us":"%3Cp%3EEarn%203%25-9%25%20in%20rewards%20and%20get%20free%20expedited%20delivery%20on%20select%20products%20when%20joining%20MyLenovo%20Rewards.%26nbsp%3B%26nbsp%3B%3Ca%20href%3D%22%2Frewards%2F%3FIPromoID%3DLEN775755%22%20target%3D%22_self%22%20textvalue%3D%22Join%20for%20Free%20%26gt%3B%22%3E%3Cstrong%3EJoin%20for%20Free%20%26gt%3B%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fa%3E%3C%2Fp%3E","en":"%3Cp%3EMyLenovo%20Rewards%20Members%20earn%203x%20rewards%20when%20you%20configure%20your%20PC%2C%20and%20on%20purchases%20of%20accessories%20%26amp%3B%20electronics.%20Plus%20only%20members%20get%20FREE%20expedited%20delivery%2C%20everyday.%26nbsp%3B%26nbsp%3B%3Ca%20href%3D%22%2Frewards%2F%3FIPromoID%3DLEN775755%22%20target%3D%22_self%22%20textvalue%3D%22Join%20for%20Free%20%26gt%3B%22%3E%3Cstrong%3EJoin%20for%20Free%20%26gt%3B%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fa%3E%3C%2Fp%3E"},"id":"Page55376285-bfd0-4d63-bca5-1b119e582296"}},{"bannerInfo":{"t_id":"Pagef93e1eec-a310-415b-bd6b-7b7e7727acde","language":{"en_us":"%3Cp%3EBad%20credit%20or%20no%20credit%3F%20No%20problem!%20Katapult%20offers%20a%20simple%20lease%20to%20own%20payment%20option%20to%20help%20get%20what%20you%20need.%26nbsp%3B%3Ca%20href%3D%22%2Flandingpage%2Flenovo-financing-options%2F%3FIPromoID%3DLEN771093%22%20target%3D%22_self%22%20textvalue%3D%22See%20if%20you%20Prequalify%20%26gt%3B%22%3E%3Cstrong%3ESee%20if%20you%20Prequalify%20%26gt%3B%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fa%3E%3C%2Fp%3E","en":"%3Cp%3E6%2C%2012%20%26amp%3B%2024%20Months%20Special%20Financing%20on%20qualifying%20purchases%20with%20our%20Lenovo%20Financing%20Credit%20Card.%26nbsp%3B%3Ca%20href%3D%22%2Flandingpage%2Flenovo-financing-options%2F%3FIPromoID%3DLEN771093%22%20target%3D%22_self%22%20textvalue%3D%22See%20if%20you%20Prequalify%20%26gt%3B%22%3E%3Cstrong%3ESee%20if%20you%20Prequalify%20%26gt%3B%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fa%3E%3C%2Fp%3E"},"id":"Pagef93e1eec-a310-415b-bd6b-7b7e7727acde"}},{"bannerInfo":{"t_id":"Page10dad9fe-cc58-4a0b-a2bc-d35fb9df4df7","language":{"en_us":"%3Cp%3EFree%20shipping%20sitewide%2C%20no%20minimum.%20MyLenovo%20Rewards%20members%20receive%20free%20expedited%20delivery*%20with%20their%20free%20membership.%3C%2Fp%3E","en":"%3Cp%3EFree%20shipping%20sitewide%2C%20no%20minimum.%20MyLenovo%20Rewards%20members%20receive%20free%20expedited%20delivery*%20with%20their%20free%20membership.%3C%2Fp%3E"},"id":"Page10dad9fe-cc58-4a0b-a2bc-d35fb9df4df7"}},{"bannerInfo":{"t_id":"Page6cc4df30-8545-4d7d-a7a2-aba27a2a3f64","language":{"en_us":"%3Cp%3ECross%20those%20names%20off%20your%20list%20with%20accessories%20and%20electronics%20under%20%2450.%26nbsp%3B%3Cstrong%3E%26nbsp%3B%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3Ca%20href%3D%22%2Fd%2Faccessories-under-50%2F%3FIPromoID%3DLEN331958%22%20target%3D%22_self%22%20textvalue%3D%22Shop%20Gifts%20%26gt%3B%22%3E%3Cstrong%3EShop%20Gifts%20%26gt%3B%3C%2Fstrong%3E%3C%2Fa%3E%3C%2Fp%3E","en":""},"id":"Page6cc4df30-8545-4d7d-a7a2-aba27a2a3f64"}}],"autoRun":true}




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey