kmr-1.8 tft display price

@david_prentice: I meant Himax, well spotted! I remember seeing a 1.8" display with a HX---- driver advertised, but I am not sure where I saw it. Yes you are right, ILI9163/S6D02A1/ST7735 are all options often advertised for 1.8" displays.
Interestingly it reports my display as having an ILI9163 but I am using initialisation code from this library for a S6D02A1 and it works OK but that may just be by luck and a degree of initialisation address compatibility.

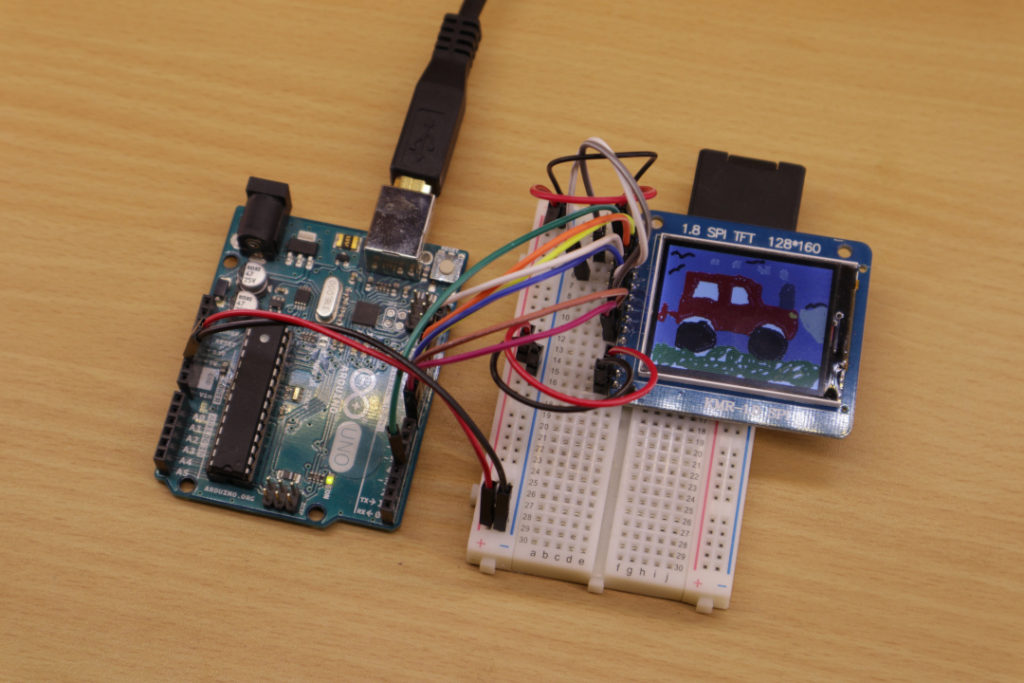
Recently, I had the idea to make a digital picture frame—one of these kinds which load images from SD cards and show each image for some time. I was remembering myself that I already own a small TFT display, the KMR-1.8 SPI, that works out of the box with an Arduino Uno. When I digged up my KMR-1.8 SPI, I realized that it has also an in-built SD card reader. Moreover, I looked up the Internet and found ready-to-use libraries for the in-built SD card reader as well as showing images on the TFT display. For these reasons, I thought making such an digital picture frame will turn out very easy.
When I started to implement my first lines of codes and started to connect my Arduino Uno to the KMR-1.8 SPI, I ran into two major problems. First, the colors of my image file did not match to the colors displayed by the KMR-1.8 (red and blue were interchanged). Second, my first prototypes stopped to work after about 5 minutes. The application started to freeze and showed the same image forever instead of displaying the next image after a chosen time.
There exists various versions of so-called “1.8 TFT displays” from different manufacturers. Not all of them are 100% compatible to each other. Therefore, if you own a TFT display and want to use my tutorial to make it work, please check if your TFT display really matches the version I used in this tutorial:
The source code relies on three header files (and libraries): SPI.h (Link), SD.h (Link) and TFT.h (Link). Please make sure that all of them are correctly installed before trying out my source code (In Arduino IDE: Tools -> Manage Libraries…).
I overcame the first problem by not using the default initialization method (“TFTscreen.begin();”) of the TFT library. Instead, I looked up whats inside the “begin”-method. I found a method called “initR” which has a parameter that allows to perform the initialization for a specific chip. Here, the parameter value “INITR_BLACKTAB” worked for me as the colors were then shown correctly. In addition, I call the method “setRotation” with parameter value “1” in order to be conform to the default initialization method. In the end, the code for the setting up the TFT library object looks like this:// ...
The code looks for image files (*.BMP) on the SD card and shows each image for 60 seconds. You can change the display time by setting “DELAY_IMAGE_SWAP” to a new value.

In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
In which “Hello, World!” is the text you want to display and the (x, y) coordinate is the location where you want to start display text on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
Note: some people find issues with this display when trying to read from the SD card. We don’t know why that happens. In fact, we tested a couple of times and it worked well, and then, when we were about to record to show you the final result, the display didn’t recognized the SD card anymore – we’re not sure if it’s a problem with the SD card holder that doesn’t establish a proper connection with the SD card. However, we are sure these instructions work, because we’ve tested them.
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.

Specification:Driver IC: ST7735RResolution: 128 x 160 pixelsFeatures:- Can help you to get rid of the Arduino serial monitor.- Some tests and provide UTFT library, AdaFruit Library and instruction on DropBox.- Tested with Latest Arduino 1.6.5.IO interface:1. RESET --directly to the microcontroller IO2. CS --directly to the microcontroller IO3. A0 --IO control registers select4. SDA --IO control data transmission5. SCL --IO control SPI bus6. BL--High Level 3.3V backlight onNote:Please contact us for documents and driver if you need. Please noted this LCD is 3.3V, which can not receive 5V signals from the Arduino, so please use a 1k series resistors between GPIO lines on a 5V arduino and this LCD, power this LCD with 5V but drive it with "level shifted resistor" GPIO lines.Besides, you could use mcifriend 2.8 inch TFT LCD library to get it to work, it will work fine with the Mega or Uno.

Features for the 1.8 Inch LCD TFT Display 128X160 SPI Serial Port With SD Card Holder is the best way to add a small, colourful, and bright display to any project. Since the display uses 4-wire SPI to communicate and has its pixel-addressable frame buffer, you can use it with every kind of microcontroller.
Even a tiny one with low memory and few pins available! The 1.8″ display has 128×160 color pixels. Unlike the low-cost Nokia 6110 and similar LCDs, which are CSTN type and thus have poor colour and slow refresh, this display is a true TFT! The TFT driver (ST7735R) can display full 18-bit color (262,144 shades!). And the 4.6 cm (1.8 “) SPI 128×160 TFT LCD Display Module will always come with the same driver chip, so there are no worries that your code will not work from one to the other. The breakout has the TFT display soldered on (it uses a delicate flex-circuit connector), an ultra-low-dropout 3.3V regulator, and a 3/5V level shifter to use it with 3.3V or 5V power and logic. It features a microSD card holder so you can quickly load full-colour bitmaps from a FAT16/FAT32 formatted microSD card

Tags: Arduino Uno, Arduino,1.8" SPI TFT LCD, 128x160 module, SD card,ST7735R,ST7735S, Adafruit,Adafruit_ST7735, Adafruit_GFX,ST7735B, UTFT,flickering streaks ,мерцающие полосы, вертикальные горизонтальные помехи при обновлении картинки с SD карты,HY-1.8 SPI, S6D02A1,Adafruit_QDTech, KMR-1.8 SPI,TFT_ILI9163, Arduino Esplora,SainSmart
This lovely little display breakout is the best way to add a small, colorful and bright display to any project. Since the display uses 4-wire SPI to communicate and has its own pixel-addressable frame buffer, it can be used with every kind of microcontroller. Even a very small one with low memory and few pins available.
The 1.8" display has 128x160 color pixels. Unlike the low cost "Nokia 6110" and similar LCD displays, which are CSTN type and thus have poor color and slow refresh, this display is a true TFT! The TFT driver (ST7735R, ST7735S, ST7735B) can display full 18-bit color (262K shades). And the LCD will always come with the same driver chip so there"s no worries that your code will not work from one to the other.
The breakout has the TFT display soldered on (it uses a delicate flex-circuit connector) as well as a ultra-low-dropout 3.3V regulator and a 3/5V level shifter so you can use it with 3.3V or 5V power and logic. We also had a little space so we placed a microSD card holder so you can easily load full color bitmaps from a FAT16/FAT32 formatted microSD card.
This color display uses SPI to receive image data. That means you need at least 4 pins - CLOCK, DATA IN, TFT CS and D/C. If you"d like to have SD card usage too, add another 2 pins - DATA OUT and card CS.
MISO(or SD_MISOorSDO) (Master In Slave Out) - this is the SPI Master In Slave Out pin, its used for the SD card. It isn"t used for the TFT display which is write-only
MOSI (or DIN or SD_MOSIorSDA) (Master Out Slave In) - this is the SPI Master Out Slave In pin, it is used to send data from the microcontroller to the SD card and/or TFT
TFT_CS (Chip Select or Slave Select) - the pin on each device that the master can use to enable and disable specific devices. This is the TFT SPI chip select pin
RST (or RESETorRES) - this is the TFT reset pin. Connect to ground to reset the TFT! Its best to have this pin controlled by the library so the display is reset cleanly, but you can also connect it to the Arduino Reset pin, which works for most cases.
There are two ways to wire up these displays - one is a more flexible method Software SPI (you can use any pins on the Arduino) and the other Hardware SPI is much faster (4-8x faster, but you are required to use the hardware SPI pins)
You have got one of these really cheap 1.8" TFT SPI LCD module. Great value for the price. You have got it up and running in no time. Just one little problem... flickering streaks - horizontal, vertical or combined. You did a search on the Web and can"t find right answer. We will help you. It"s very easy.
The root cause of what often described as flicker, to me it is more like flickering lines when loading data into display. Actualy, if you have more than one device on SPI - any SPI activity will cause that.
Most Arduino"s running at 5V. Present display powered internally, including IOs, at 3.3v. Atmel"s IOs drive current is pretty high. Display"s inputs have clamps to VCC. Most signals idle high. When signals are 5V - current from signals through clamp diodes back feeding VCC and actually raising voltage on 3.3V regulator on display board to ~3.9V. During intense communications this voltage drops a bit and display"s analog circuitry thrown a out of wack causing streaks on display.
What I did, is to insert resistive dividers into each signal from Atmel to TFT. It consists of one in series of 180 Ohm and one 330 Ohm parallel to the inputs to ground, for each input.
Insert resistive dividers into each signal from Arduino board to TFT display. It consists of one in series of 180 Ohm and one 330 Ohm parallel to the inputs to ground, for each input.
Convert your Arduino board and TFT display to 3.3V. Many ways to do that for Arduino. For example, on display board you have to put solder blob across JP1.
3.TFTBitmapLogo sketch. Displays your picture.The display can load images bigger or smaller than the display size (160 x 128 px), but for better results, edit your image size to 160 x 128 px.The image should be in .bmp format. To do that, you can use a photo editing software and save the image as.bmpformat. If you want to later use your own image, use an image editing tool and crop your image to no larger than 128 pixels high and 160 pixels wide. Save it as a 24-bit color BMP file - it must be 24-bit color format to work, even if it was originally a 16-bit color image - becaue of the way BMPs are stored and displayed!You can download example here.
6.spitftbitmap sketch. The display can load images bigger or smaller than the display size (160 x 128 px), but for better results, edit your image size to 160 x 128 px.The image should be in .bmp format. To do that, you can use a photo editing software and save the image as.bmpformat. If you want to later use your own image, use an image editing tool and crop your image to no larger than 160 pixels high and 128 pixels wide. Save it as a 24-bit color BMP file - it must be 24-bit color format to work, even if it was originally a 16-bit color image - becaue of the way BMPs are stored and displayed!You can download example here.
7. ST7735_SD sketch. Scrolls you pictures like Photo frame. The display can load images bigger or smaller than the display size (160 x 128 px), but for better results, edit your image size to 160 x 128 px.The image should be in .bmp format. To do that, you can use a photo editing software and save the image as.bmpformat. If you want to later use your own image, use an image editing tool and crop your image to no larger than 160 pixels high and 128 pixels wide. Save it as a 24-bit color BMP file - it must be 24-bit color format to work, even if it was originally a 16-bit color image - becaue of the way BMPs are stored and displayed! You can change the rotation of pictures to landscape or vertical. You can find examples of pictures used here.
11. TFT_graphicstest_small sketch for TFT_ILI9163 library. Supports ILI9163 chip. Do not forget to check the User_Setup.h file configuration in library folder.
TFT_ILI9163library. Download, unzip and add to libraries in our PC, for example C:\Users\toshiba\Documents\Arduino\libraries. This link you can find in Preferences of Adruino IDE program which installed in your PC. You can read about it here. Supports ILI9163 chip
TFT_S6D02A1ibrary. Download, unzip and add to libraries in our PC, for example C:\Users\toshiba\Documents\Arduino\libraries. This link you can find in Preferences of Adruino IDE program which installed in your PC. You can read about it here. Supports S6D02A1 chip.
UTFTlibrary. Download, unzip and add to libraries in our PC, for example C:\Users\toshiba\Documents\Arduino\libraries. This link you can find in Preferences of Adruino IDE program which installed in your PC. You can read about it here. SD card is not supported.

I needed to install this library from Bodmer; then edit the User_Setup.h file ( in sketchbook/libraries/TFT_ESPI ) to match my display and the connections used.
This User_Setup.h works fine for the ESP32; except that in the UTFT_DEMO_FAST Example the final screen (orange rectangle on blue background) no text was displayed.
There are several displays that go by the name of ST7735 - I used one without a card reader and one with - the one with a card reader had a red (rot) PCB - just to give you a hint - check the distance of the mounting holes in the diplay"s PCB to be...
SummaryThis is a box for ST 7735 128x160 pixel color display. ...There is also the 3d model of display, that can be used to create other type of box.Print SettingsPrinter Brand: RepRapPrinter: PRUSA I3 r2Rafts: Doesn"t MatterSupports: ...
Code and circuit :- https://github.com/sandy9159/Arduino-based-Mini-radar-HC-SR04-ST7735-Display Material Required Arduino nano :- https://amzn.to/2Eq3tSK HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor :- https://amzn.to/2SEU4vQ SG 90 Servo :- https://amzn.to/2NG807N...
I made this to contain a 1.8"TFT screen ST7735 and attach it to a project box which contained an Arduino. The template allowed me to precisely cut out the holes for the cables and the screws to hold it in place and then seal the main box from the...
This project is an Arduino Weather Station widget that was implemented using two electronic components, Wemos D1 Mini and the ST7735 1.8" Color TFT Display Implementation available on github:...
supprot for color display ST7735, can be used to create a clock / weather station etc... next time I will upload the Arduino code and schematics for a Clock.
Summarysupprot for color display ST7735, can be used to create a clock / weather station etc... next time I will upload the Arduino code and schematics for a Clock.
8/21/17- sandwiching the breakout boards together around the perfboard has obscured the mounting holes, working on an alternative mounting arrangement Some handy reference for the ST7735 display driver and the FLIR Lepton:...
... is integrated in the middle,And a display (e.g. ...ST7735) in the bottom.The display is surrounded by six holes for ButtonsIn the front, there is another hole for an antenna.Inside, there are supports for an arduino due and two 9V block Batteries
... it sits completely flush to the wall just like a light switch or a power outlet. I used the ST7735 display which has an SD card slot on the back of it, I didn"t need the SD card for the project but this mount allows for its installation. ...
SourceCode & Description: https://github.com/twistedmcbane/Arduino-Bitcoin-Price-Ticker TFT Display (ST7735): https://www.amazon.de/gp/product/B078JBBPXK/ref=ppx_yo_dt_b_asin_title_o00__o00_s00?ie=UTF8&psc=1 Arduino NodeMcu v3:...
The display shows: - Job name - Printer status - Remaining time - Current print height and progress (based on height) - Elapsed time and estimated total print time - Bed Temperature (current | setpoint) and extruder temperature (current | setpoint)...

Of course I’ve not just been working on the pretty colours – I’ve revamped the control codes for the ESP8266-driven controller twice, discovered and fixed an OTA flaw in the code, re-hashed the Node-Red driving code, found and fixed countless other bits and pieces… you know – in other words – pretty much revamped everything just to improve a simple display.
PLEASE NOTE: If you wish to use the display module depicted above – make sure it is based on the s6d02a1 chip (board says 1.8″ TFT) – try this link: Cheap LCDs https://tech.scargill.net/yourls/cheaplcd. Boards have the marking “1.8 TFT MODULE” on the bottom. The ones with a single connector (as against one on each side) generally do NOT use this chip and hence are not compatible). Also, AliExpress do this board cheaply.
So the box is just an Ebay job, I think it was £3 – sadly I can’t find them right now, lovely job with rounded corners and top/bottom vents. We did find a sluightly larger one however. The display is one I call the QD-tech display, based on the 6sd02a1 controller and very cheap, see above. 120×160 pixel LCD and supported in ESP-NOW.
Glued to the back of this display is a Wemos D1 Mini from AliExpress, dirt cheap ESP-12 based board and they communicate via SPI – simplified to the minimum. I’ve connected resets together, CE to ground and so the only actual connections to the display are 5v and 3v3 (backlight) from the Wemos D1) and ground of course, for signals: clock, data, D/C. That’s it.
I use my well-developed ESP-NOW ESP8266 code for this and had to make some improvements on the way. As I was updating the board over and over and over, learning about the display chip, I noted memory issues occasionally when doing over the air updates – fixed that. I noted that I had no way to tell if the ESP8266 (and hence the display) had reset at any time (to know to do the init code) – fixed that (my ESP8266 code now sends a status message when rebooting). I got sick of the clumsy way I had to update the display, sending line, box, text commands so I amalgamated them all into string commands – and that was such a good idea I went back and made the code for other displays follow the same format. You can see how all of this might’ve taken up a lot of time.
Above you see the Node-Red code, running on a Raspberry Pi using my usual setup – there are in fact 2 displays – one on my desk and one in the hallway. I check for the ESP12s coming out of reset and send start-up code via MQTT to the displays separately. Overkill, could have just done the one. That includes setting up the display itself, clearing the screen and putting in that nice white framework of lines and rectangles. Meanwhile I have timed functions updating the time (once a second) and everything else once a minute. The weather forecast (see icons in a previous post) comes from Dark Sky and I was having difficulty getting what I wanted out of the Node for that service, when it occurred to me that was just as easy to do an HTTP request – as the HTTP node is able to capture information and convert it to a JSON object. How handy is that.
You may notice a reference to England – this display is running in Spain but I have a Node-Red setup with sensors back in the UK so the two Node-Red installations will soon exchange temperature/humidity and other info – so I figured I may as well show temperature and humidity from back in the UK.
I’ll not go into the entire code sent off to the display, as mentioned above I’ve very much simplified that now and it is all detailed in the manual I put together for home control.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey