acronym abbreviation for tft lcd touch screen pricelist

TFT is a Thin Film Transistor, TFT refers to each LCD liquid crystal display pixels that are driven by integration in the behind of the Thin Film Transistor. Therefore, the TFT-type display has the advantages of high responsiveness, high brightness, and high contrast, and its display effect is close to that of CRT display, TFT-LCD is one of the most liquid crystal displays.TFT display is also a kind of active-matrix liquid crystal display equipment. TFT-LCD is one of the best LCD color displays, TFT-LCD has the advantages of fine and vivid image, lightweight, low power consumption, and good environmental protection performance, widely used in TV, laptop, mobile phone, monitor, medical beauty, and other equipment.
Unlike TN, TFT displays are “backlit” – the imaginary light path is not from top to bottom, as in TN, but from bottom to top. In this way, a special light tube is set on the back of the liquid crystal, and the light source shines upward through the lower polarizer. Since the upper and lower interlayer electrodes are changed into FET electrodes and common electrodes, the performance of liquid crystal molecules will also change when the FET electrode is switched on. The display purpose can be achieved through shading and light transmission, and the response time is greatly improved to about 80ms.TFT is commonly known as “true color” because it has higher contrast and richer colors than TN-LCD, and the screen updates faster.
The main feature of TFT-LCD, as opposed to TN, is one semiconductor switch per pixel. Because each pixel can be directly controlled by point pulses. Therefore, each node is relatively independent and can be controlled continuously. Such a design method not only improves the response speed of the display screen but also can accurately control the display grayscale, which is why TFT color is more realistic than DSTN.
The TFT panel is cut from a larger substrate. LCD products also have a large array of transistors to control the three primary colors, and current manufacturing technology is difficult to ensure that tens or even hundreds of millions of transistors on a large substrate are without a single problem. If there is a problem with one of the transistors, then the corresponding color of the corresponding point of the transistor will go wrong (only a certain fixed color can be displayed), and this point is commonly called “bad point”. The probability of bad spots is not fixed in position, so a substrate is likely to be wasted a lot. Generally, LCD requires that the bad point is less than 5, and some large manufacturers have narrowed the standard to 3, or even 0, which will reduce the yield rate. Some smaller manufacturers expand the bad points, which naturally reduces costs and quality, which is one reason why some manufacturers have been able to slash prices.
Although there are many manufacturers capable of producing LCDs, there are only a handful of manufacturers capable of producing TFT panels.ACER, as a well-known enterprise in the IT industry, is quite powerful. Although IT does not have the ability to produce TFT panels by itself,
The display sets the electron, the communication and the information processing technology in one body, is considered as the electron industry after the 20th-century microelectronics, the computer another important development opportunity.
The principle of field emission flat display is similar to that of CRT, which only has one to three electron guns and up to six. The field emission display adopts an electron gun array (electron emission micro tip array, such as diamond film tip cone), and the display with a resolution of VGA (640×480×3) needs 921,600 electron emission micro tips with uniform performance.
Glow plasma display are through small vacuum plasma discharge excitation discharge cavity light-emitting materials, luminous effect, and low power consumption is its shortcomings (only 1.2 lm/W, and lamp luminous efficiency more than 80 lm/W, 6 watts per square inch display area), but in 102 ~ 152 cm diagonal field of the large-screen display has a strong competitive advantage.
The semiconductor light-emitting diode (LED) display scheme, due to the successful development of GaN blue light-emitting diode, has won absolute control over the market of the video display with very large screens, but this kind of display is only suitable for large outdoor displays, and video display with a small and medium screen does not have its market.
Special TFT – LCD, LCD flat panel display, is the only one in the brightness, contrast, such as power, life, volume and weight of integrated performance to catch up with and surpass that of the CRT display device, it features good performance, large-scale production, a high degree of automation, low cost of raw materials, the vast development space, will quickly become the mainstream product of the new century, is one of the highlights of the 21st-century global economic growth.
TFT-LCD, which USES liquid crystal as the excellent characteristic of the light valve, divides the luminous display device into two parts, namely the light source and the control of the light source. As a light source, no matter from luminous efficiency, full color, or life, has achieved brilliant results, but also in continuous deepening. Since the invention of the LCD, the backlight has been continuously improved, from monochrome to color, from thick to thin, from side fluorescent lamps to flat fluorescent lamps. The latest achievements in light sources will provide a new backlight for LCD. With the progress of light source technology, there will be newer and better light sources and LCD applications. Is the control of the light source, the rest of the large scale integrated circuit technology and semiconductor technology transplanted, successfully developed the thin film transistor (TFT) production technology, implements the matrix addressing the control of the liquid crystal light valve, solved the LCD light valve and the controller, so that the advantages of liquid crystal display (LCD).
The TFT thin-film transistor (matrix) — which “actively” controls individual pixels on the screen — is the origin of the so-called active matrix TFT.So how exactly do images come about? The basic principle is simple: a display screen consists of a number of pixels that can emit light of any color, and controlling each pixel to display a corresponding color does the trick. In TFT LCD, backlight technology is generally adopted. In order to accurately control the color and brightness of each pixel, a switch similar to a shutter needs to be installed after each pixel. When the “shutter” is opened, light can come through, but when the “shutter” is closed, light cannot come through.
Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) are filamentous, and their molecular structure changes as the environment change, giving them different physical properties — allowing light to pass through or block it — in the case of louvers.
TFT color filter is divided into red, green, and blue according to the color, which is successively arranged on the glass substrate to form a group (dot pitch) corresponding to a pixel. Each monochrome filter is called a sub-pixel. That said, if a TFT display supports a maximum resolution of 1280×1024, it needs at least 1280×3×1024 sub-pixels and transistors. For a 15-inch TFT display (1024 x 768), a pixel is about 0.0188 inches.
As you know, pixels are critical to a display, and the smaller each pixel, the larger the maximum possible resolution of the display. But because of the physical limitations of transistors, the TFT is roughly 0.0117 inches (0.297mm) per pixel, so the maximum resolution for a 15-inch display is 1,280 by 1,024.[1]
TFT technology is the basis of liquid crystal (LC), inorganic and organic thin-film electroluminescence (EL and OEL) flat panel displays.TFT is a kind of film necessary for manufacturing circuits formed by sputtering and chemical deposition process on the non-single wafers such as glass or plastic substrate, and large-scale semiconductor integrated circuit (LSIC) is produced by processing of the film. Using non-single-crystal substrate can greatly reduce the cost, which is the extension of traditional LSI to large-area, multi-function, and low-cost direction.
The first generation of large-area glass substrate (300mm×400mm) TFT-LCD production line was put into production in the early 1990s. By the first half of 2000, the area of glass substrate has been expanded to 680mm×880mm), and the recent 950mm×1200mm glass substrate will also be put into operation. In principle, there is no area limit.
The 1.3-inch TFT chip used for liquid crystal projection has a resolution of one million pixels in XGA.The resolution of the SXGA (1280×1024) 16.1-inch TFT array amorphous silicon film thickness is only 50nm, and the TAB ON GLASS and SYSTEM ON GLASS technology, its IC integration, requirements for equipment and supply technology, technical difficulty than the traditional LSI.
TFT was first used as a matrix location circuit to improve the optical valve characteristics of liquid crystals. For high-resolution displays, the accurate control of object elements is realized through voltage adjustment in the range of 0-6v (its typical value is 0.2 to 4V), thus making it possible for LCD to achieve a high-quality high-resolution display.TFT-LCD is the first flat panel display in human history to surpass CRT in display quality. Now people are starting to integrate the drive IC into the glass substrate, and the whole TFT will be more powerful than traditional large-scale semiconductor integrated circuits.
The glass and plastic substrates fundamentally solve the cost problem of large-scale semiconductor integrated circuits and open up wide application space for large-scale semiconductor integrated circuits.
In addition to traditional film formation processes such as sputtering and CVD (chemical vapor deposition) and MCVD (molecular chemical vapor deposition), laser annealing technology has also been applied, which can produce amorphous and polycrystalline films as well as monocrystalline films. Not only can make silicon membrane but also can make other Ⅱ – Ⅵ and Ⅲ – Ⅴ semiconductor thin film.
Low voltage applications, low drive voltage, solid use safety, and reliability improvement; Flat, light, and thin, saving a lot of raw materials and space; Low power consumption, its power consumption is about one-tenth of the CRT display, reflective TFT-LCD is only about one percent of the CRT, saving a lot of energy; TFT-LCD products also have specifications, models, size series, variety, convenient and flexible use, maintenance, update, upgrade easy, long service life and many other characteristics. The display range covers the application range of all monitors from 1 inch to 40 inches and the large projection plane, which is a full-size display terminal; Display quality from the simplest monochrome character graphics to high resolution, high color fidelity, high brightness, high contrast, the high response speed of various specifications of video display; Display mode has direct vision type, projection type, perspective type, and reflection type.
No radiation, no flicker, no harm to the user’s health. In particular, the appearance of TFT-LCD electronic books and periodicals will bring mankind into the era of a paperless office and paperless printing, and trigger the revolution of human learning, communication, and recording civilization.
The temperature range from -20℃ to +50℃ can be used normally, and the low temperature working temperature of TFT-LCD after temperature reinforcement can reach -80 ℃. It can be used as a mobile terminal display, desktop terminal display, and large screen projection TV. It is a full-size video display terminal with excellent performance.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The liquid crystal displays used in calculators and other devices with similarly simple displays have direct-driven image elements, and therefore a voltage can be easily applied across just one segment of these types of displays without interfering with the other segments. This would be impractical for a large display, because it would have a large number of (color) picture elements (pixels), and thus it would require millions of connections, both top and bottom for each one of the three colors (red, green and blue) of every pixel. To avoid this issue, the pixels are addressed in rows and columns, reducing the connection count from millions down to thousands. The column and row wires attach to transistor switches, one for each pixel. The one-way current passing characteristic of the transistor prevents the charge that is being applied to each pixel from being drained between refreshes to a display"s image. Each pixel is a small capacitor with a layer of insulating liquid crystal sandwiched between transparent conductive ITO layers.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
The transmittance of a pixel of an LCD panel typically does not change linearly with the applied voltage,sRGB standard for computer monitors requires a specific nonlinear dependence of the amount of emitted light as a function of the RGB value.
It achieved pixel response which was fast for its time, wide viewing angles, and high contrast at the cost of brightness and color reproduction.Response Time Compensation) technologies.
Less expensive PVA panels often use dithering and FRC, whereas super-PVA (S-PVA) panels all use at least 8 bits per color component and do not use color simulation methods.BRAVIA LCD TVs offer 10-bit and xvYCC color support, for example, the Bravia X4500 series. S-PVA also offers fast response times using modern RTC technologies.
When the field is on, the liquid crystal molecules start to tilt towards the center of the sub-pixels because of the electric field; as a result, a continuous pinwheel alignment (CPA) is formed; the azimuthal angle rotates 360 degrees continuously resulting in an excellent viewing angle. The ASV mode is also called CPA mode.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
The bare display panel will only accept a digital video signal at the resolution determined by the panel pixel matrix designed at manufacture. Some screen panels will ignore the LSB bits of the color information to present a consistent interface (8 bit -> 6 bit/color x3).
With analogue signals like VGA, the display controller also needs to perform a high speed analog to digital conversion. With digital input signals like DVI or HDMI some simple reordering of the bits is needed before feeding it to the rescaler if the input resolution doesn"t match the display panel resolution.
The statements are applicable to Merck KGaA as well as its competitors JNC Corporation (formerly Chisso Corporation) and DIC (formerly Dainippon Ink & Chemicals). All three manufacturers have agreed not to introduce any acutely toxic or mutagenic liquid crystals to the market. They cover more than 90 percent of the global liquid crystal market. The remaining market share of liquid crystals, produced primarily in China, consists of older, patent-free substances from the three leading world producers and have already been tested for toxicity by them. As a result, they can also be considered non-toxic.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.

In-Plane Switching (IPS) is a technology that overcomes the viewing limitations of conventional TFT-LCDs. It is also known as Super TFT.IPS derives its name from the fact that the liquid-crystal molecules are aligned in parallel with the glass plates, whereas the TN principle adopted in conventional TFT displays is based on perpendicular alignment of the molecules.
With more and more consumer products such as smart phones and tablets using IPS displays, the production yield and cost has come down significantly in recent years. This is great news for manufacturers wanting to upgrade their design.
Pricing for small size IPS displays, particularly2.4 and 2.8", is comparable, if not favourable to TN-TFTs, meaning that you can upgrade from a monochrome display to a superior colour display without breaking the budget..
Anders have partnered with world leading brand Kastus®to offer a globally patentedantimicrobial & antiviralsurface coating which has a proven kill rate of up to 99.99% against harmful bacteria, fungi and antibiotic-resistant superbugs, which makes it particularly useful for products including glass and ceramics. This year, an independent testing report found Kastus to be effective against human Coronavirus on screens.
Our IPS-TFT displays are available from 1" to 23" and ideal for outdoor applications. To further enhance the displays where environmental challenges including sunlight, extreme temperatures, water or salt, or vandalism, can be an issue we have a number of
Here at Anders we don"t just strive to design a best in class display solution for your product, but we also want to make sure the display is driven with the right embedded system. We can help achieve a hardware solution that ensures your display works perfectly within your application. Hardware solutions include:
Marine user interface systems have a lot of challenges: for both safety and user experience, the displays need to have outstanding clarity, be easy to read in any conditions and and from any angle, whilst withstanding rain and seawater, all whilst delivering clear, concise information and reliable connectivity for a seamless user experience. We can help you design a display and embedded system truly fit for purpose.
The medical environment is quite rightly rigorous and demanding, requiring display and embedded solutions that are accessible and safe to use.Understanding where and how a medical product will be used and by whom is important for us to help you design a solution truly fit for purpose.
With ever increasing pressure in all of our lives, having easy to use and reliable home appliances plays a key role in easing thosestresses.We can help you achieve an innovative display and embedded design fit for those demanding user expectations.
Putting your own stamp on your product is more than a logo on the start-up screen. Discover how we can help you design a unique display solution with our customisation services:

TFT and LCD are two different types of electronic displays used in computers, TVs, and smartphones. However, they are not as different as you might think. Let’s start with what those abbreviations mean.
A key weakness of TFT panels is that they do not have wide viewing angles, so they are better suited to displays that require you to view head-on. This can be a good or a bad thing, depending on your needs. For example, the narrower viewing angles mean people sitting or standing around you are less likely to be able to snoop on what you are doing on your mobile phone.
TFT panels are cheaper to manufacture, but they also consume much more power than regular LCD panels. Lastly, they have poorer sunlight visibility. You will find TFT displays on feature phones, smart feature phones, and low-end Android phones.
LCD: This is an abbreviation for “liquid crystal display”. It is a flat panel display with wider viewing angles compared to TFT. They also have lower power consumption and so deliver much better battery life than their TFT counterparts.
In summary, while TFT panels have some distinct advantages, they fall short in other areas and so their use have been limited to low end phones, from feature phones to entry-level Android phones. Plastic feels inferior to touch than glass, which means that TFT screens don’t get to feature much on mid-range and premium devices.
As we see improvements to TFT technology, we will see them deployed on higher end devices over time. In 2022, Samsung used TFT displays in its mid-range Galaxy A13 and Galaxy A23. Perhaps those improvements are happening already.
For now, LCD is the most widely used display type in modern smartphones. At the very top end, we have premium flagships using OLED and AMOLED displays.
TFT displays are higher quality components than regular LCD displays. TFT displays are sharper, brighter, and refresh better than LCD panels. However, they have weaknesses that make them unsuitable for higher end phones.
AMOLED panels have all the benefits of OLED screens, which means they are better than LCD panels. They are expensive though, and so are used in high-end smartphones only.
These are improved versions of AMOLED screens and were developed by Samsung. They are also thinner. The name explains it: think of Super AMOLED as AMOLED on steroids.
Founder of MobilityArena. Yomi’s journey in mobile started in 2001. Besides obsessing over mobile phones, he also started creating WAP sites (early mobile-friendly websites created with WML). He began writing about phones in 2004 and has been at it since then. He has owned over 200 devices, from Symbian, Palm, PocketPC/Windows Mobile, BlackBerry/BB10, webOS, Windows Phone, Firefox, Ubuntu Touch, to Android, iOS, and KaiOS operating systems.
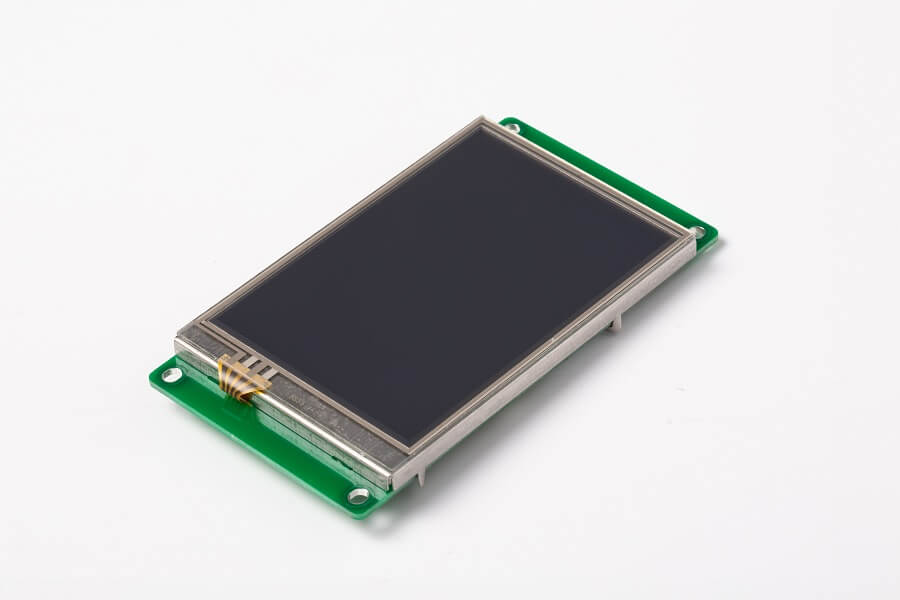

TFT-based displays have a transistor for each pixel on the screen. This allows the electrical current that illuminates the display to be turned on and off at a faster rate, which makes the display brighter and shows motion smoother. LCDs that use TFT technology are called "active-matrix" displays, which are higher-quality than older "passive-matrix" displays. TFT technology provides the best resolution of all the flat display technologies, but it is also expensive than monochrome lcd. So TFTs are used in high-quality LCD displays, if you see a LCD monitor at your local computer market, it should be an active tft lcd display, Basically, it is a high-quality tft lcd monitor.
Passive-matrix display. A passive-matrix display is anLCD screen display that contains a series of wires that cross each other. See the dual scan display for a full definition on this term.
What is an Active-matrix Display (TFT)? Alternatively referred to as TFT ( thin-film transistor) and AMLCD ( active-matrix LCD ), an active-matrix display is an LCD ( liquid crystal display) introduced with the IBM ThinkPad in 1992.
It uses a matrix of thin film transistors(TFTs) and capacitors to control the image produced by thedisplay. The brightness of each pixel is controlled by modifying the electrical charge of the corresponding capacitors.

As a display device TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor and is used to enhance the operation and usefulness of LCD displays. An LCD is a fluidic display device that uses a crystalline filled liquid to manipulate a rear illumination polarized source by means of an electrostatic field between two thin transparent metal conductors such as indium tin oxide (ITO) in order to present an image to the viewer. This process can be used in both segmented or pixelated display devices but is found synonymous with color TFT displays.
When an LCD is used to display moving images the inherent slow rate of change between fluid states over a large number of pixel elements can be a problem due in part to capacitive effects, which causes moving image blurring. By putting a high speed LCD controlling device in the form of a thin film transistor right at the pixel element on the glass surface, the LCD image speed issue can be greatly enhanced and for all practical purposes eliminates image blurring.
Other benefits of these thin film transistors are they allow for thinner display designs and different pixel designs and arrangements to vastly improve display viewing angles.
TFT displays are found in many applications these days, from mobile devices, appliance, medical devices, instrumentation, aircraft and certainly computer display devices as well as TV’s. The addition of the thin film transistor in LCD design vastly improved the use of LCD’s in all market areas.

Thin film transistors (TFT) is commonly known as an active-matrix LCD, which is complemented with higher image-quality transistor, in which each transistor is assigned to a pixel.
Osaka, June 27, 2013 - (JCN Newswire) - Sharp Corporation ("Sharp") announced that Sharp has passed a resolution at its board of directors meeting held on June 27, 2013, to enter into a business alliance relating to liquid crystal displays ("LCDs") with China Electronics Corporation.
Industry insiders say that Haier leads the refrigerator and washing machine segments in China, but faces strong pressure from leading LCD TV brands as Hisense, Konka and Skyworth, so outsourcing is a good and reasonable way for Haier to take on major counterparts in the LCD TV segment.
In the April-June quarter, however, the company said it expects to book a net loss of 50 billion yen due to 27 billion yen in special losses resulting from suspension of operations at large-sized LCD plants due to the disaster, it said.
Sharp will collaborate with the new company on construction of the LCD panel plant adopting the 6th generation glass substrates in Nanjing-city and production of LCD panels, by providing its LCD production technology and know-how as well as the sales of 6th generation production equipment of Kameyama Plant No.1 incorporating cutting-edge production technology.
Overall we see total TV average selling prices rising slightly on a weighted average basis from $522 in 2007 to $536 in 2008 due to the share gains by LCD and Plasma TVs which sell for higher average prices than CRT TVs.
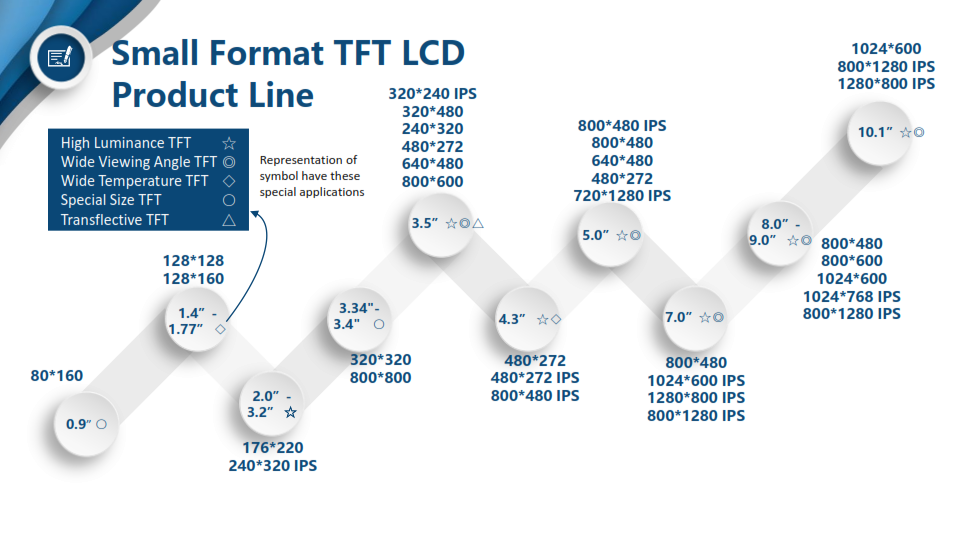
As you might already be aware, there’s a large variety of versatile digital display types on the market, all of which are specifically designed to perform certain functions and are suitable for numerous commercial, industrial, and personal uses. The type of digital display you choose for your company or organization depends largely on the requirements of your industry, customer-base, employees, and business practices. Unfortunately, if you happen to be technologically challenged and don’t know much about digital displays and monitors, it can be difficult to determine which features and functions would work best within your professional environment. If you have trouble deciphering the pros and cons of using TFT vs. IPS displays, here’s a little guide to help make your decision easier.
TFT stands for thin-film-transistor, which is a variant of liquid crystal display (LCD). TFTs are categorized as active matrix LCDs, which means that they can simultaneously retain certain pixels on a screen while also addressing other pixels using minimal amounts of energy. This is because TFTs consist of transistors and capacitors that respectively work to conserve as much energy as possible while still remaining in operation and rendering optimal results. TFT display technologies offer the following features, some of which are engineered to enhance overall user experience.
The bright LED backlights that are featured in TFT displays are most often used for mobile screens. These backlights offer a great deal of adaptability and can be adjusted according to the visual preferences of the user. In some cases, certain mobile devices can be set up to automatically adjust the brightness level of the screen depending on the natural or artificial lighting in any given location. This is a very handy feature for people who have difficulty learning how to adjust the settings on a device or monitor and makes for easier sunlight readability.
One of the major drawbacks of using a TFT LCD instead of an IPS is that the former doesn’t offer the same level of visibility as the latter. To get the full effect of the graphics on a TFT screen, you have to be seated right in front of the screen at all times. If you’re just using the monitor for regular web browsing, for office work, to read and answer emails, or for other everyday uses, then a TFT display will suit your needs just fine. But, if you’re using it to conduct business that requires the highest level of colour and graphic accuracy, such as completing military or naval tasks, then your best bet is to opt for an IPS screen instead.
Nonetheless, most TFT displays are still fully capable of delivering reasonably sharp images that are ideal for everyday purposes and they also have relatively short response times from your keyboard or mouse to your screen. This is because the pixel aspect ration is much narrower than its IPS counterpart and therefore, the colours aren’t as widely spread out and are formatted to fit onto the screen. Primary colours—red, yellow, and blue—are used as the basis for creating brightness and different shades, which is why there’s such a strong contrast between different aspects of every image. Computer monitors, modern-day HD TV screens, laptop monitors, mobile devices, and even tablets all utilize this technology.
IPS (in-plane-switching) technology is almost like an improvement on the traditional TFT display module in the sense that it has the same basic structure, but with slightly more enhanced features and more widespread usability. IPS LCD monitors consist of the following high-end features.
IPS screens have the capability to recognize movements and commands much faster than the traditional TFT LCD displays and as a result, their response times are infinitely faster. Of course, the human eye doesn’t notice the difference on separate occasions, but when witnessing side-by-side demonstrations, the difference is clear.
Wide-set screen configurations allow for much wider and versatile viewing angles as well. This is probably one of the most notable and bankable differences between TFT and IPS displays. With IPS displays, you can view the same image from a large variety of different angles without causing grayscale, blurriness, halo effects, or obstructing your user experience in any way. This makes IPS the perfect display option for people who rely on true-to-form and sharp colour and image contrasts in their work or daily lives.
IPS displays are designed to have higher transmittance frequencies than their TFT counterparts within a shorter period of time (precisely 1 millisecond vs. 25 milliseconds). This speed increase might seem minute or indecipherable to the naked eye, but it actually makes a huge difference in side-by-side demonstrations and observations, especially if your work depends largely on high-speed information sharing with minimal or no lagging.
Just like TFT displays, IPS displays also use primary colours to produce different shades through their pixels. The main difference in this regard is the placement of the pixels and how they interact with electrodes. In TFT displays, the pixels run perpendicular to one another when they’re activated by electrodes, which creates a pretty sharp image, but not quite as pristine or crisp as what IPS displays can achieve. IPS display technologies employ a different configuration in the sense that pixels are placed parallel to one another to reflect more light and result in a sharper, clearer, brighter, and more vibrant image. The wide-set screen also establishes a wider aspect ratio, which strengthens visibility and creates a more realistic and lasting effect.
When it comes to deciphering the differences between TFT vs. IPS display technologies and deciding which option is best for you and your business, the experts at Nauticomp Inc. can help. Not only do we offer a wide variety of computer displays, monitors, and screen types, but we also have the many years of experience in the technology industry to back up our recommendations and our knowledge. Our top-of-the-line displays and monitors are customized to suit the professional and personal needs of our clients who work across a vast array of industries. For more information on our high-end displays and monitors, please contact us.

Kitchen display systems (KDS) are digital kitchen monitoring screens that display incoming orders in restaurant kitchens. KDS route orders from the point-of-sale (POS) system to the correct kitchen stations. An excellent kitchen display system streamlines kitchen communication, reduces human error, and monitors cook times for each dish. The best restaurant KDS systems show a dish’s ingredients at the touch of a button and text customers when orders are ready.
Most kitchen display systems are built into restaurant POS systems and offered at an additional fee for hardware and software. We examined each kitchen display system and its corresponding POS systems based on price, ease of use, and features to arrive at our top recommendations.
Toast POS is one of our top-rated cloud-based restaurant POS systems, and its KDS offering is likewise a top performer. Toast’s KDS is the most customizable system on this list. You canhighlight individual ingredients and common allergens. Plus, users can choose their font size and how information is arranged on order tickets. This system also sendstext messages to customers when their orders are ready, and alerts servers in the POS app when they have food waiting in the kitchen.
Toast’s KDS earned a 4.52 out of a possible 5 on our scoring criteria. It earned high marks for price—the underlying Toast POS offers both a free Starter software subscription and Pay-as-you-Go options for hardware. It also earned perfect scores for order management, advanced functions, and reporting.
Toast’s KDS operates on industry-grade hardware built to withstand the steam, grease, and hot temperatures of a restaurant kitchen. Toast’s touch-screen KDS tablets are rated at IP-54 for resistance to dust, steam, and water droplets. Apple’s iPads, on the other hand, are not IP-rated at all. iPads can also struggle in temperatures above 95 degrees Fahrenheit.
IP Rating:IP stands for Ingress Protection. IP ratings are two-digit codes established by the International Electrotechnical Commission to rate how well electronic devices withstand dust and water intrusion. The first number rates dust avoidance on a scale of 1 to 6; the second digit rates water-tightness on a scale of 1 to 9.
Touch-screen navigation Quick access buttons on the top right corner of the screen allow you to Show All-Day View. You can also show fulfilled orders or recall fulfilled tickets. Accessing the overflow menu allows you to see device connectivity status, adjust text size, or switch users.
All-day count view “All day” is restaurant-speak for “total” or “altogether.” Cooks say “all day” to refer to the total number of an item they need to prepare to fill all open orders. As in “how many burgers all day?” Toast’s All-Day count screen shows your all-day counts at a glance, so your kitchen team is never second-guessing what orders they have on deck.
Auto-firing by prep time If you input cook times with your recipes in the Toast POS, you can configure your Toast KDS to organize newly-ordered items by their cook time to ensure all dishes on a ticket are ready at the same time. When an order is “fired” in the POS, your KDS will show a running timer on each ticket. This way, you always know how long a customer has waited for their order.
Toast’s KDS software is currently offered at $25 per screen, per month. If you need multiple screens, however, Toast will likely work out a lower per-terminal price for you. To get the best pricing, reach out to the Toast sales team for a custom quote.
Revel Systems is a hybrid POS that operates on iPads. Though, like Toast, Revel users have the option to use a touch-screen KDS or rely on the Epson KDS integration if they need more robust hardware or bump bars. Revel’s KDS only operates on the Revel POS, which has the strongest drive-thru management tools of any cloud POS on the market.
Revel’s KDS earned a 3.92 out of 5on our KDS scoring criteria. It earned points for its advanced features like customizable ticket layouts and screen views. However, it lost points for price. Revel was the only option on this list that received no points for price. The POS does not offer a free subscription or free trial, and the KDS does not operate on more than one system.
Revel users can track countless order types and customize their screen views with multiple colors to highlight order types or ticket status. (Image from Revel Systems)
Revel’s KDS communicates with the customer-facing Order Ready screen to show live updates when take out, drive-thru, or other orders are ready. (Image from Revel Systems)
Revel Systems’ KDS offers several dynamic viewing options: Expedite, Expedite Tile, Kitchen Screen, Production View, and Order Display, so cooks and expeditors can choose their preferred view. Revel Systems also supports a customer-facing Order Ready screen to display orders by customer name to identify which orders are ready for pick up. Orders on this screen can be further color-coded to separate to-go, drive-thru, and curbside pickups, a massive timesaver for restaurants that rely on multiple third-party delivery platforms.
Like most systems on this list, Revel runs its KDS on iPads. But if you want more rugged hardware or a larger screen, you can opt for a ViewSonic VSD243 smart display instead. Like Toast, Revel users need to purchase their KDS hardware directly through Revel, even if they plan to use iPads. Revel does not support hardware that is purchased through third parties.
Revel integrates with the third-party messaging app Twilio to support automated text messaging from the KDS screen. You can create custom messages for in-house, takeout, curbside, or delivery orders. The system will automatically text customers when your cooks or expediter marks the order as “complete” in the KDS.
Order Ready screen Revel’s built-in Order Ready screen is customer-facing and shows real-time order status. This is an excellent tool for communicating with delivery drivers or for keeping things organized in a high-volume, quick service environment. Orders can be flagged with order numbers and customer names and will be color-coded by order type.
Drive-thru tools The Revel POS includes a detailed workflow for drive-thru restaurants it calls Drive Thru XT. This module condenses order and payment screens to reduce button presses and logs vehicle information to ensure the correct orders are given to the correct customers. You can also track drive-thru orders separately from in-house orders on the Revel KDS.
See what makes Revel POS such a great fit for delivery restaurants and quick service restaurants in general. Explore Revel’s full features by reading our full Revel review.
Epson’s KDS is afreestanding hardware solution that partners with several POS brands. Epson is well known for its workhorse receipt and kitchen printers. In addition to their standard printers, Epson also designs and manufactures printers that support a robust KDS system. With printer-driven, ethernet-connected screens, Epson’s KDS does not need an internet connection to work, making this system the best for offline functionality.
The Epson KDS is available as touch-screen monitors with integrated printers, or as monitors outfitted with bump bars. This system also operates with virtually any restaurant POS system that accepts Epson printers. So if your POS supports Epson printers and you need a KDS, Epson likely has you covered, making this system the best for POS integrations.
Compatible POS Systems:Lavu, Cake, Upserve, Focus POS, Future POS, MICROS, Mojo, PAR, PosiTouch, Revel, Revention, Rpower, Shift4, Speedline, Talech, Toast, Touch Dynamic and more
Epson’s KDS earned a 3.77 out of 5 on our scoring criteria. It earned points for integrating with multiple POS systems and offering both touch-screen and bump bar hardware. However, it lost some points for price and ease of use. You have to purchase the system through a third-party reseller (which may be your POS company), which means that pricing and contract terms can vary widely.
Because Epson’s KDS leverages the information routed to your kitchen printers, it functions as more of a hardware than a software solution. In most cases, the only cost to add an Epson KDS to a compatible POS system is the hardware cost. However, your POS provider may charge a separate software fee for adding the KDS integration—so be sure to ask.
KDS screen, wall mounting bracket, bump bar, KDS driver-enabled impact kitchen printerBump bar navigation panelPrices vary by resellerLinerless label printer with built-in KDS driver
Epson’s KDS screens are driven by the printers they are attached to. You can print paper tickets on demand, or even linerless sticker labels—which are ideal for labeling takeout and delivery orders.
Epson’s black-and-white, grid-based user interface is a little old-school. Plus, some cooks find bump bar navigation a bit dated. However, others prefer bump bars because they are easier to operate with gloved hands or damp fingertips. Epson includes options for both bump bar enabled and touch-screen monitors.
Like Lightspeed and Toast, Epson allows your staff to access recipe information directly from the KDS screen so there are never any mistakes from the kitchen. You just need to be sure to attach a recipe to each dish.
Epson makes some of the hardest-working printers in the restaurant industry. See our guides to the best thermal receipt printers to find the best printers for your restaurant.
Fresh KDS is a standalone, iPad-based KDS system that integrates with several popular POS systems like Square and Clover. There are currently more integrations in the works, with industry stalwarts Toast, Revel, Lightspeed, TouchBistro, and Aloha.
With pricing starting at $19 per month and a seven-day free trial that allows you to test the system before committing, Fresh KDS is a strong choice for restaurants that want a touch-screen KDS that integrates with their existing POS system.
Fresh KDS earned a 3.32 out of 5 in our KDS evaluation. This system scored well for price—the seven-day free trial gave it a boost—and number of POS integrations. Advanced features like customer text messaging and an integrated order-ready display also earned points.
Fresh KDS operates on iPads running iOS 13 or later and Android 6.0 or later tablets. Simply download the KDS app from Google Play or the Apple App store onto tablets you already own. For industry-grade hardware, Fresh KDS supports projective capacitive (PCAP) touch-screen monitors and offers an optional bump bar.
As with Toast, Fresh KDS lets you customize virtually every color on the screen. Choose which colors you want to label your ticket status, order type, and order modifications. You can even choose a light or dark mode for the entire KDS screen.
You can choose to arrange your Fresh KDS tickets in neat, individual columns or squeeze tickets into all available screen space with the Tile view. Split View allows you to separate your screen into two order streams, helpful for separating eat-in orders from to-go or pickup orders from delivery orders.
Like Toast and Revel, Fresh KDS sends automated SMS text alerts when you mark orders as complete. With Fresh KDS, however, you have even more messaging options. You can set messages for when new orders are received and when your team begins preparing orders. You can also set custom messages for different order types—eat-in, curbside, pick-up, or delivery.
Like Revel, Fresh KDS includes an optional customer-facing order tracking screen. This is ideal for counter-service restaurants or those that do a high volume of takeout orders. When your kitchen marks a KDS ticket as completed, the order status on the tracking screen automatically updates to show customers their food is ready.
Fresh KDS offers three subscription tiers: Basic, Advanced, and Enterprise. Basic starts at $19 per month, Advanced comes in at $35 per month, and Enterprise requires a custom quote. Each subscription includes software for two KDS screens, though the system can support up to 10 screens at a single location.
At the Advanced subscription level, Fresh KDS includes standout features like automated customer SMS text messaging (like Toast and Revel) and a customer-facing order tracking screen (like Revel). Though you’ll also need the Advanced level if you simply want to print tickets from the KDS screen; Basic subscriptions do not include ticket printing functions.
Fresh KDS integrates with several restaurant POS systems. If you need a POS for your business, see our rankings of the best restaurant POS systems, best quick service POS systems, and best POS systems for delivery.
Square for Restaurants is a cloud-based POS system best suited for restaurants on a budget, as the POS software has a forever free plan and an advanced plan that’s just $60 per month. In particular, we recommend Square for Restaurants for food trucks, QSRs, cafes, slice shops, and bakeries.
If you’re using the free version of Square for Restaurants, the KDS is just $20 per device. If you’re on Square for Restaurants Plus or Premium, KDS software for unlimited devices is included for free.
Square earned a3.22 out of 5 on our KDS scoring system. Square’s affordable pricing—it outscored the other systems on this list for price—and the ability to use hardware you already own make Square for Restaurants the best KDS for restaurants on a budget.
While you can customize your KDS views in dozens of ways, from the ticket size to the alert colors, Square is not overwhelmingly customizable. So it’s an excellent fit for small restaurants that want a simple KDS solution. If you want more customization options, you should try Toast (for a POS option) or Epson (for a freestanding solution).
Square’s KDS operates on iPads running iOS 13 or later. You can download the KDS software from the Apple App Store, then operate the KDS on iPads you already own. Alternatively, you can purchase iPads from Square. The Square KDS can receive orders from Square for Restaurants operating on Square Register or iPads, Square POS operating on iPads, Android devices, Square Register, and Square Terminal devices, orders from the Square Online store, and any third-party delivery partner or kiosk partner sending orders to your Square POS.
Countertop iPad POS terminal with built-in card reader*Countertop or wall mounting bracket for iPad in Square Stand case*POS terminal with built-in card reader and customer-facing display
Customizable views On each Square KDS, you can individually adjust the text size, the number of tickets displayed per page, and notification settings for new orders. This way, your cooks can view orders the way they prefer.
Free online ordering All of the systems on this list display online orders in the KDS. But Square for Restaurants is the only POS that includes a free online ordering site. In addition to receiving online orders directly in your KDS order stream, Square users have the comfort of knowing they aren’t paying any extra fees for those orders.
For Free Square for Restaurants users, the Square KDS costs $20 per tablet, per month. Plus and Premium subscribers can use the KDS for free on unlimited devices.
See why we recommend Square for Restaurants for food trucks and learn more about Square for Restaurants POS features in our full Square for Restaurants review.
Lightspeed POS is a cloud-based POS that operates on iPads. Like the underlying POS, Lightspeed’s KDS module—called Lightspeed Kitchen—also runs on iPads. Pricing for Lightspeed Restaurant’s POS starts at $39 per month. The KDS software is an additional custom-quoted price. In the past, the KDS was available for just $12 per screen, per month.
Withfour available subscription tiers and both user-friendly templated reports and advanced analytics, Lightspeed offers the widest range of tools. So small restaurants won’t pay for tools they don’t use, but large restaurants don’t need to find a new POS provider when their business grows. This system can grow as your business grows so you don’t lose the tools you love.
Lightspeed Kitchen earned a 3.19 out of 5.00on our KDS ranking, putting it right on Square’s heels. It earned points for its recipe lookup “Show and Tell” functions and for its affordability. But Lightspeed Kitchen is not quite as customizable as Toast and Revel’s KDS (though restaurants looking for a simplified solution might prefer this).
Since Lightspeed Kitchen operates via a browser-hosted app, it needs an internet connection to work (unlike Toast, Revel, and Epson). Overall, however, the streamlined nature of Lightspeed Kitchen is excellent for keeping quick service restaurants and small, independent restaurants organized.
Lightspeed compiles information from the KDS into easy-to-read reports so users can see which items take the longest to prepare. (Image from Lightspeed)
Lightspeed offers a 14-day free trial of the underlying POS so you can test all of Lightspeed Restaurant’s POS functions before you commit to the system. Unfortunately, the KDS is not included in the free trial. Contact Lightspeed for a demo of the KDS.
Tickets in different stages of the preparation pipeline appear with pre-configured colors: gray for New or Archived, orange for Preparing, green for Done, and red for Voided. Unlike Toast, Revel, and Epson, however, you cannot customize these colors; they are programmed into the KDS.
From the top left corner of the Lightspeed Kitchen screen, you can filter tickets by active, new, preparing, done, or archived status. Tickets can be moved from one order phase to the next with single or double taps.
Order tags Lightspeed labels online orders with the name of the referring platform. And—via a Deliverect integration—Lightspeed integrates with virtually every third-party platform you can imagine. You can keep your third-party orders organized, even if you partner with several platforms.
Show and Tell function Lightspeed Kitchen’s KDS includes a Show and Tell function that shows a detailed image and item description on the KDS screen when a cook clicks on the menu item. This stops short of the recipe look-up function supported by Epson and Toast, but ensures your cooks are reminded how to plate a dish and review a list of its ingredients.
Lightspeed Kitchen is a paid add-on to the Lightspeed Restaurant POS. The software is offered at a custom-quoted price from Lightspeed. Contact their sales department for full pricing.
See why we recommend Lightspeed Restaurant for cafes and as the best available iPad POS for restaurants. Plus, explore Lightspeed Kitchen’s POS features in our full Lightspeed Restaurant review.
We rewarded KDS systems that are included in the cost of your restaurant POS. For systems that operate with more than one POS, we looked for free trials, free baseline subscriptions, or a monthly cost of $20 or less for the KDS software.
We considered how much each KDS can be customized, and looked for systems that accept in-person, online, and third-party orders. We awarded points for systems that allow you to recall whole tickets and individual menu items, as well as systems that track all-day counts.
We prioritized tools that send automated text updates to customers when their orders are ready or support multiple hardware types. We also looked for kitchen monitoring systems that include recipe lookups and menu images at the click of a button.
We looked for systems that log preparation times and provide reports that measure your kitchen’s productivity. We also awarded points for KDS screens that work during an internet outage in offline mode.
Toast POS has our favorite KDS module. With options like text message notifications, customizable alerts, and kitchen-specific features like all-day counts, Toast’s KDS supports the widest range of restaurant styles. Combined with Toast’s excellent online ordering, delivery management, team management, and reporting functions, the Toast KDS creates a full spectrum restaurant management solution at a competitive price. Visit Toast for a demo, or to get started for free today.

The world of smartphones has been busy for the past few months. There have been numerous revolutionary launches with groundbreaking innovations that have the capacity to change the course of the smartphone industry. But the most important attribute of a smartphone is the display, which has been the focus for all prominent players in the mobile phone industry this year.
Samsung came up with its unique 18:5:9 AMOLED display for the Galaxy S8. LG picked up its old trusted IPS LCD unit for the G6’s display. These display units have been familiar to the usual Indian smartphone buyer. Honor, on the other hand, has just unveiled the new Honor 8 Pro for the Indian market that ships with an LTPS LCD display. This has led to wonder how exactly is this technology different from the existing ones and what benefits does it give Honor to craft its flagship smartphone with. Well, let’s find out.
The LCD technology brought in the era of thin displays to screens, making the smartphone possible in the current world. LCD displays are power efficient and work on the principle of blocking light. The liquid crystal in the display unit uses some kind of a backlight, generally a LED backlight or a reflector, to make the picture visible to the viewer. There are two kinds of LCD units – passive matrix LCD that requires more power and the superior active matrix LCD unit, known to people as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) that draws less power.
The early LCD technology couldn’t maintain the colour for wide angle viewing, which led to the development of the In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD panel. IPS panel arranges and switches the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules of standard LCD display between the glass substrates. This helps it to enhance viewing angles and improve colour reproduction as well. IPS LCD technology is responsible for accelerating the growth of the smartphone market and is the go-to display technology for prominent manufacturers.
The standard LCD display uses amorphous Silicon as the liquid for the display unit as it can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. This though restricts the display resolution and adds to overall device temperatures. Therefore, development of the technology led to replacing the amorphous Silicon with Polycrystalline Silicon, which boosted the screen resolution and maintains low temperatures. The larger and more uniform grains of polysilicon allow faster electron movement, resulting in higher resolution and higher refresh rates. It also was found to be cheaper to manufacture due to lower cost of certain key substrates. Therefore, the Low-Temperature PolySilicon (LTPS) LCD screen helps provide larger pixel densities, lower power consumption that standard LCD and controlled temperature ranges.
The AMOLED display technology is in a completely different league. It doesn’t bother with any liquid mechanism or complex grid structures. The panel uses an array of tiny LEDs placed on TFT modules. These LEDs have an organic construction that directly emits light and minimises its loss by eradicating certain filters. Since LE




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey