tft display vs capacitive display quotation

IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.
Take your product to the next level with a capacitive touch screen LCD by Displaytech. Our PCAP (projected capacitive) touch screen technology is a premium alternative to a resistive touchscreen. We offer capacitive touchscreens for our 2.8-inch, 3.5-inch, 4.3-inch, 5-inch and 7-inch TFT LCD displays.
Capacitive touch technology allows for an enhanced product user interface since it supports gestures and proximity sensing. Unlike resistive touch screens which rely on pressure, capacitive touch responds to an electric current and can handle multi-finger touch points. This means that capacitive touchscreens can be used with your bare finger and it supports gestures such as pinch-to-zoom or swipe.
Capacitive touch panels are the more modern and advanced touchscreen option because of their advanced capabilities. They are commonly found in consumer products like smartphones, tablets, appliances, and monitors.
A capacitive touchscreen detects and responds to changes in capacitance caused by the screen"s electrostatic field when the screen"s surface is touched.
Capacitive touchscreen displays allow for touch gestures and respond to multi-touch inputs. You’ll typically be able to enter one to five touch inputs simultaneously, but some capacitive touchscreens can process even more.
Capacitive touchscreens deliver brighter, higher contrast images due to the makeup of their panels. Displays with capacitive touch screens are more durable than resistive touch screens because they are designed with cover glass on their top layer. In fact, all of our capacitive TFT displays have standard 0.7mm thick built-in cover glass and can be further
While the cost is currently higher than resistive touchscreens, capacitive touchscreens are quickly becoming the industry standard in touchscreen technology.
The enhanced responsiveness can be a downside depending on how and where the display is used. For example, a capacitive touchscreen would not easily respond to the user while wearing certain types of gloves. Although capacitive touchscreens don’t respond to inorganic inputs, they can still be accidentally activated by other conductive elements. One of the the most common elements that causes interruptions is water.
Rain, humidity, and condensation on the surface of capacitive touchscreens will often cause accidental inputs and reduced accuracy until the water is removed. This is one of the main reasons why a resistive touchscreen would be chosen over a capacitive touchscreen in certain situations.
Any device that utilizes touch gestures like swiping, pinching, or multi-touch will require a capacitive touchscreen. These features often help make capacitive touchscreen displays more intuitive and user-friendly than resistive touchscreens. Capacitive touchscreens are best suited for applications requiring improved touch responsiveness with better image brightness and contrast.
sense pressure on the display"s top layer and send a signal to the circuit layer to activate the touchscreen functionality. Because they use pressure to activate the touch inputs, resistive touchscreen displays can be used with a stylus, gloves, and other items. Resistive touchscreens are built without cover glass and made of plastic, making them more susceptible to dents and scratches.
Resistive touchscreens are often seen as the less advanced variety of touch panel compared to capacitive touch panels. However, being able to interact with non-organic inputs keeps these touchscreens relevant in specific industries.
Resistive touchscreen displays are less sensitive than capacitive touchscreen displays. This is considered an advantage in some cases and is why they’re chosen for specific applications. Resistive touchscreens will not respond to accidental inputs from the environment, so they won’t be interrupted by things like water spills or lightweight debris landing on the screen.
This type of touchscreen requires more intentional inputs from the user, making them more reliable in rugged and unstable environments. For example, a resistive touchscreen is the perfect solution on a construction site where water or debris might land on the screen. They’re also the best touchscreen display option for situations where the user is wearing gloves.
Resistive touchscreen panels are unfortunately more susceptible to dents and scratches. Their poor visibility in direct sunlight does not make them ideal for outdoor applications. Their inability to respond to multi-touch inputs can be a disadvantage in fast-paced applications requiring such. Because resistive touchscreens rely on the pressure applied to the top layer, they tend to be abused and mishandled, which makes them less durable over time than capacitive touchscreens.
While it’s clear that capacitive touchscreens are dominating the consumer electronics market, resistive touchscreens still have an advantage in some ways.
If you’re looking for a cost-effective touchscreen that can operate with simple tap inputs in rugged environments, resistive is the way to go. For more advanced and intuitive touchscreen technology with higher quality applications, choose capacitive touchscreens.

Capacitive touchscreen TFT LCDs are available in 2.8", 3.5", 4.3", 5.0", 7.0", and 10.1" diagonal sizes. Capacitive touch TFTs offer excellent contrast and clarity, have a built-in I2C interface, excellent dragging performance, and accept multi-point inputs, also known as multi-touch.

The Capacitive touch panel is activated with anything containing an inductive load such as a finger or stylus. It allows for multi-touch options. When using the capacitive touch screen, the display needs a separate controller to interface with the touch panel. The display for capacitive touch is brighter since the touch panel is transparent.
The Transmissive polarizer is best used for displays that run with the backlight on all the time. This polarizer provides the brightest backlight possible. If you have a need for a bright backlight with lower power drain, transmissive is a good choice for this TFT LCD display.
Focus LCDs can provide many accessories to go with your display. If you would like to source a connector, cable, test jig or other accessory preassembled to your LCD (or just included in the package), our team will make sure you get the items you need.Get in touch with a team member today to accessorize your display!
Focus Display Solutions (aka: Focus LCDs) offers the original purchaser who has purchased a product from the FocusLCDs.com a limited warranty that the product (including accessories in the product"s package) will be free from defects in material or workmanship.

The Capacitive touch panel is activated with anything containing an inductive load such as a finger or stylus. It allows for multi-touch options. When using the capacitive touch screen, the display needs a separate controller to interface with the touch panel. The display for capacitive touch is brighter since the touch panel is transparent.
The Transmissive polarizer is best used for displays that run with the backlight on all the time. This polarizer provides the brightest backlight possible. If you have a need for a bright backlight with lower power drain, transmissive is a good choice for this TFT LCD display.
Focus LCDs can provide many accessories to go with your display. If you would like to source a connector, cable, test jig or other accessory preassembled to your LCD (or just included in the package), our team will make sure you get the items you need.Get in touch with a team member today to accessorize your display!
Focus Display Solutions (aka: Focus LCDs) offers the original purchaser who has purchased a product from the FocusLCDs.com a limited warranty that the product (including accessories in the product"s package) will be free from defects in material or workmanship.
Digital graphic touch screen overlays transform any large display into a state-of-the-art interactive touch screen and whiteboard. Touch Screen Overlays attach to the front of your existing LCD, TFT, or Plasma display monitor giving it instant touch interaction with your device transforming your display into a Human Machine Interface. Touch Screen Overlays can provide an excellent way to seal your display from dust, particulate contaminants, and moisture ingress up to IP67 with proper design.
In addition to our many product capabilities, at Dyna-Graphics, we provide fully customized touchscreen panel overlays for your interactive touchscreen needs. Our capacitive and resistive touch screen overlay systems allow for complete interactive capabilities with any type of Plasma, TFT, or LCD display monitor.
Contact us for more information regarding our resistive and capacitive touch screen overlay product options, or call us at 800-959-0108 and we will gladly assist you with your specific touchscreen panel overlay questions. Dyna-Graphics is your premier source for technologically advanced touch screen overlays.
There are a few key differences between capacitive and resistive touch screen technologies. A resistive touchscreen is comprised of several layers, out of which the flexible plastic and glass layers are the two most important electrically resistive layers. When a finger or stylus tip presses down on the outer surface, both the ITO films meet, which leads to an accurate measurement of the touch position.
In comparison, a capacitive touchscreen also consists of two spaced layers of glass, which are coated with conductor such as Indium Tin Oxide (ITO). The human body is then used as a conductor, so when a finger touches the glass of the capacitive surface, it changes the local electrostatic field, which creates the interaction. The system continuously monitors the movement of each tiny capacitor to locate the next area of touch.
Touch Screen overlays incorporate sophisticated optical imaging technology and a robust design to provide a durable touch solution perfect for high-traffic public applications. The hard coated plastic overlay preserves the displays optics and protects it from damage or abuse. Touch Screen overlays are easy to install and use, making it easy to take your standard display screen and convert it to touch screen HMI capable. In addition, overlay tough technology is designed with a wealth of features to ensure long-lasting durability and functionality. Give us a call at 800-959-0108 to discuss your project requirements.
Dyna-Graphics utilizes hard coated lenses in all our custom touch screen overlays and panel displays. These lenses enhance incandescent, LED, fluorescent gas, and liquid crystal displays for superior visibility. Light sources can be exposed or totally sealed, as your application requires.
Two options are available for lighted displays: always on, or “dead front” (viewable only when on or activated). Dead front displays can be adjusted for the strength of the light source. We can also install multiple light sources in the same switch panel. We can include individual LEDs, fluorescent gas displays, and digital LED displays, as needed.
Capacitive and resistive touch screen overlay systems provide numerous advantages for a wide range of industries and applications. Our touch screen overlays are simple to operate and are ideal for applications that span various industries throughout the world. As a premium touchscreen panel overlay provider our capacitive and resistive touch screen overlay are regularly used within the following industries and applications.
Contact Dyna-Graphics for more information regarding our custom resistive and capacitive touch screen overlay options that provides a simple and convenient conversion of your standard computer monitor into an overlay touch panel. Or request a quote for further pricing details today. Dyna-Graphics is your trusted source for touchscreen panel overlay systems.
.jpg)
Leadtek has paid great efforts on research and development of TFT-LCM, especially on its application of consumable and industrial products. The sizes of LCM includes 1.4”, 2.4”, 3.5", 3.51", 4.3", 4", 5", 7", 8", 10.1” and 11.6". And among them the 3.5”, 4.3", 5", 7” and 10.1" LCM has achieved the leading level of the industry, and mainly applied to vehicle-applications, tablet PCs, smartphones, medical equipment, measurement equipment, E-books, EPC and industrial products, and provides powerful and reliable supports on supplies and qualities. We are cooperating with famous foreign companies on research and developments, and will bring out the series products of industrial control. Also, we explore the overseas market, and build up a long-term relationship with our overseas partners and agents, Leadtek products will be worldwide in the near future.

Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (5" diagonal) bright (18 white-LED backlight) and colorful 800x480 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a capacitive touch panel attached on screen by default.
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. You can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs.

This 7" EVE demonstration kit includes just about everything needed for a functioning demonstration of the Crystalfontz 7" EVE display with a capacitive touch screen (just add backlight power). Through the EVE breakout board, the EVE display is connected to an Arduino-clone microcontroller (Seeeduino). The kit comes loaded with demonstration software, so simply connecting the two cables, plugging in the Seeeduino, and supplying backlight power starts the demo.

This TFT display module comprises a 7" TFT with capacitive touch and an EVE accelerator PCB. The EVE accelerator PCB simplifies interfacing with the display as it makes the display, touch, backlight, and any added audio features appear to the host MCU as a memory-mapped SPI device. The host controller can send high-level commands to the EVE chip to quickly and easily describe images, text, buttons, tables, and more.
At 7" on the diagonal, this display offers plenty of space, making it a great choice for an information panel, menu, etc. Plus, thanks to the extremely wide viewing angle achieved using in-plane switching (IPS), this display can be read equally well above or below eye level.

ASI-T-17711A1SPN/D is a 1.77 inch transflective TFT with a resolution of 160 x 128, SPI interface and with a brightness of 110 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight.
ASI-T-20043A5PMN/AY is a 2.0 inch TFT with a resolution of 480 x 360, 3W SPI+16 bit RGB or MIPI interface, IPS all view, with a high brightness of 500 Nits.
ASI-T-240DA8BN/D is a 2.4 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 240 X 320, CPU 16-bit interface and with a brightness of 800 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight.
ASI-T-240DA10SMN/AQ is a 2.4 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 240 x 320, SPI & MCU interface, IPS all-angle view and with a brightness of 1000 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight. It also features an extra wide operating temperatures of -30 to +80C; perfect for extreme environmental applications.
ASI-T-240DAKBN/D is a 2.4 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 240 x 320, MCU interface and with a brightness of 1000 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight.
ASI-T-283DAKCRN/A is a 2.83 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 240 x 320, CPU, RGB, SPI interface and with a brightness of 1000 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight
ASI-T-3501RA1EN/A is a 3.5 inch TFT with a resolution of 480 x 640, 18 bit RGB, All View interface and with a brightness of 120 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight
ASI-T-3501RA1EN/D is a 3.5 inch TFT with a resolution of 480 x 640, 18-bit DBI Type B, All View interface and with a brightness of 120 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight
ASI-T-350EA8RCY6/A is a 3.5 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 320 x 240, 24-bit Parallel RGB/Serial RGB/CCIR/YUV interface and with a brightness of 850 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight with Capacitive Touch Panel
ASI-T-350EA10SRN/A is a 3.5 inch TFT with a resolution of 320 x 240, SPI & RGB interface and with a high brightness of 1,000 Nits and wide temperature range of -30 - +85 C.
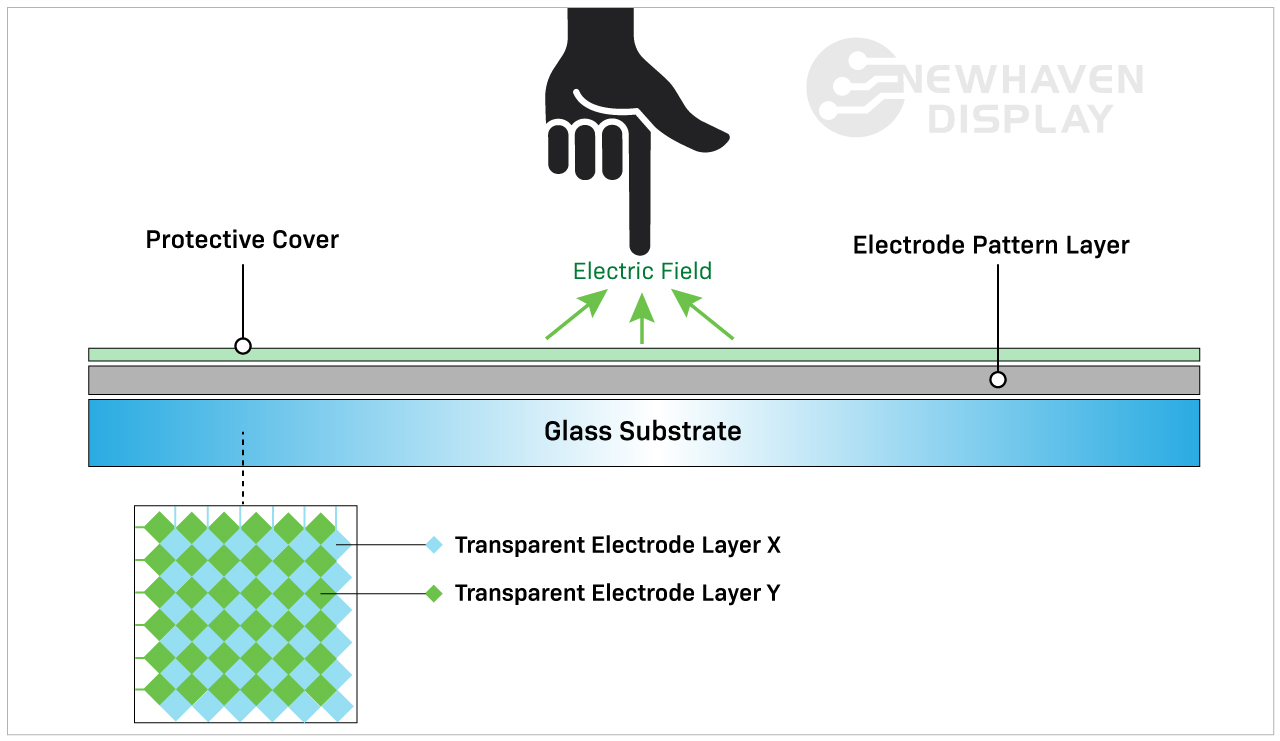
Capacitive touch technology is increasingly used in user interfaces for a variety of devices. A capacitive touch display is created by attaching a capacitive layer on top of a glass panel substrate. These components are then covered with a protective outer layer, and the surface of the device will maintain a static charge. As a person’s finger or a stylus touches the surface, the charge will transfer from the panel surface to the device or finger. This allows the capacitive device to register the touch location.
Thin-film transistor (TFT) LCD capacitive touch screens have become a popular choice when compared to the other leading touch screen technology – resistive touch. While resistive touch screens have been around for a longer time and can be built at a lower cost, capacitive touch displays offer several significant advantages over other display technologies. In this post, we’ll explore what makes capacitive touch technology unique and how it performs across several parameters.
Capacitive touch technology offers excellent screen sensitivity when used with a finger or stylus. The surface of these devices will respond to varying degrees of pressure, as opposed to a resistive touch screen where firm and direct pressure must be used. A TFT LCD capacitive touch screen is also sensitive enough to be used only with fingers without the need for a stylus.
Capacitive stylus devices can be used for added precision and niche applications such as digital drawing. Another related benefit is support for multi-touch operation using multiple fingers simultaneously. This includes advanced gestures such as pinch-zoom that is a popular feature in many device applications today.
TFT LCD capacitive displays are known for their excellent optical quality. The glass substrate that sits below the electrode film transmits most of the available light to the surface resulting in crisp sharpness and display contrast. These screens are also known for outstanding color fidelity that supports the viewing of high-quality images, video, and software content. This also has a positive impact on the user experience when integrated into larger kiosks and interactive displays.
Capacitive touch devices are very stable, with little to no shift in the image being transferred to the screen. This is an important advantage over other display types, as image shift can get worse over time and require manual correction with other types of displays. A capacitive touch device, therefore, does not require the periodic calibrations that are commonly necessary with many older display technologies. Maintaining a stable image is an essential requirement in high-performance display applications, such as those found in the broadcasting and entertainment industries.
The glass substrate of a capacitive touch display is very strong, and the protective layer helps prevent scratches and other marks. Like most displays, a capacitive touch screen can crack if dropped or exposed to significant pressure. It should be noted that a cracked resistive touch screen most often ceases to operate, while a cracked capacitive device will usually maintain some functionality. This has made capacitive screens popular for commercial applications that are exposed to significant wear and tear.
The screen of a capacitive touch device can be completely sealed, preventing contaminants from entering the seams on the outer edges of the display. Preventing dust and condensation from getting inside the display is important for long-term use. This also makes a capacitive touch display easy to clean. Due to the ease of cleaning and other advantages, capacitive touch technology is often used for public digital displays in high-traffic areas.
The sensitivity of a capacitive touch display also contributes to excellent response times. As a user touches the screen at different locations, the surface can register these movements with a high degree of accuracy. A capacitive touch screen also performs very well when the user’s finger or stylus is dragged across the surface. This makes capacitive touch a preferred choice for graphic design and audio-visual applications.
One final advantage of capacitive touch technology is false touch rejection. A resistive display can be easily confused if multiple fingers touch the screen at the same time, making it unable to register accurate movement. The improved sensitivity of a capacitive display increases the ability of the surface to differentiate between multiple points of contact. In addition to enabling the custom gestures, sliding motions, and light touches mentioned above, this also eliminates the potential for a missed touchpoint.
Capacitive touch is a relatively new touchscreen technology that is having a significant impact on the display industry. With several advantages over competing design options, the use of TFT LCD capacitive touch technology is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. This will be an important trend for device manufactures, designers, and end-users to follow as an opportunity to improve product quality and performance.

Touchscreens have changed the way people expect to interact with their devices. When it comes to smartphones and tablets, touch is the way to go. Even handheld game consoles, laptops, and car navigation systems are moving towards touch. Manufacturers of these devices need to give their respective consumers the responsiveness these consumers are looking for. Selecting the right TFT-LCD display to use for different devices is important.
For touch-sensitive displays, two types of technologies are used: resistive and capacitive. The main difference is in how they respond to touch. Mobile phone comparison site Omio indicates that resistive technology is more accurate but capacitive technology is more responsive.
Capacitive touchscreens, on the other hand, offer more responsiveness with better optical clarity and multi-touch performance. They detect more complex finger gestures. These qualities are shown to be more important for general interaction so it’s more dominant in smartphones and tablets, as well as in other devices with small to medium screen sizes.
As you can see, capacitive screens get general usage while resistive screens cater to more specific applications. With this, TFT-LCD module manufacturers, like Microtips Technology, focus on continuously improving capacitive screen technology.
Electronic Design states that many technological advances can be used to integrate touch sensors directly into the display. In some, manufacturers stack-up the touch sensors and integrate the controller with the display driver ICs. These advances allowed thinner and smarter capacitive touchscreens – a trend that you see in many devices today. For example, Windows phones originally worked exclusively with resistive touchscreen technology but later on moved over to capacitive. If the continuous development of capacitive touchscreen technology becomes successful, these screens may soon have abilities they don’t possess at the moment, such as hover support, non-finger support, and many more.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The liquid crystal displays used in calculators and other devices with similarly simple displays have direct-driven image elements, and therefore a voltage can be easily applied across just one segment of these types of displays without interfering with the other segments. This would be impractical for a large display, because it would have a large number of (color) picture elements (pixels), and thus it would require millions of connections, both top and bottom for each one of the three colors (red, green and blue) of every pixel. To avoid this issue, the pixels are addressed in rows and columns, reducing the connection count from millions down to thousands. The column and row wires attach to transistor switches, one for each pixel. The one-way current passing characteristic of the transistor prevents the charge that is being applied to each pixel from being drained between refreshes to a display"s image. Each pixel is a small capacitor with a layer of insulating liquid crystal sandwiched between transparent conductive ITO layers.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
In 2004, Hydis Technologies Co., Ltd licensed its AFFS patent to Japan"s Hitachi Displays. Hitachi is using AFFS to manufacture high end panels in their product line. In 2006, Hydis also licensed its AFFS to Sanyo Epson Imaging Devices Corporation.
Less expensive PVA panels often use dithering and FRC, whereas super-PVA (S-PVA) panels all use at least 8 bits per color component and do not use color simulation methods.BRAVIA LCD TVs offer 10-bit and xvYCC color support, for example, the Bravia X4500 series. S-PVA also offers fast response times using modern RTC technologies.
A technology developed by Samsung is Super PLS, which bears similarities to IPS panels, has wider viewing angles, better image quality, increased brightness, and lower production costs. PLS technology debuted in the PC display market with the release of the Samsung S27A850 and S24A850 monitors in September 2011.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
The bare display panel will only accept a digital video signal at the resolution determined by the panel pixel matrix designed at manufacture. Some screen panels will ignore the LSB bits of the color information to present a consistent interface (8 bit -> 6 bit/color x3).
With analogue signals like VGA, the display controller also needs to perform a high speed analog to digital conversion. With digital input signals like DVI or HDMI some simple reordering of the bits is needed before feeding it to the rescaler if the input resolution doesn"t match the display panel resolution.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
Brody, T. Peter; Asars, J. A.; Dixon, G. D. (November 1973). "A 6 × 6 inch 20 lines-per-inch liquid-crystal display panel". 20 (11): 995–1001. Bibcode:1973ITED...20..995B. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1973.17780. ISSN 0018-9383.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Kim, Sae-Bom; Kim, Woong-Ki; Chounlamany, Vanseng; Seo, Jaehwan; Yoo, Jisu; Jo, Hun-Je; Jung, Jinho (15 August 2012). "Identification of multi-level toxicity of liquid crystal display wastewater toward Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa". Journal of Hazardous Materials. Seoul, Korea; Laos, Lao. 227–228: 327–333. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.059. PMID 22677053.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey