What is an Alphanumeric LCD Display?
In the realm of electronics and display technology, alphanumeric LCD displays stand as a prime example of functionality fused with simplicity. These displays, often referred to as LCD screens or LCD panels, are characterized by their ability to present a combination of alphabetic characters, numeric digits, and special symbols in a clear, crisp manner. They are widely used in a range of applications, from basic calculators and electronic watches to more complex devices like multi-functional meters and industrial control panels.
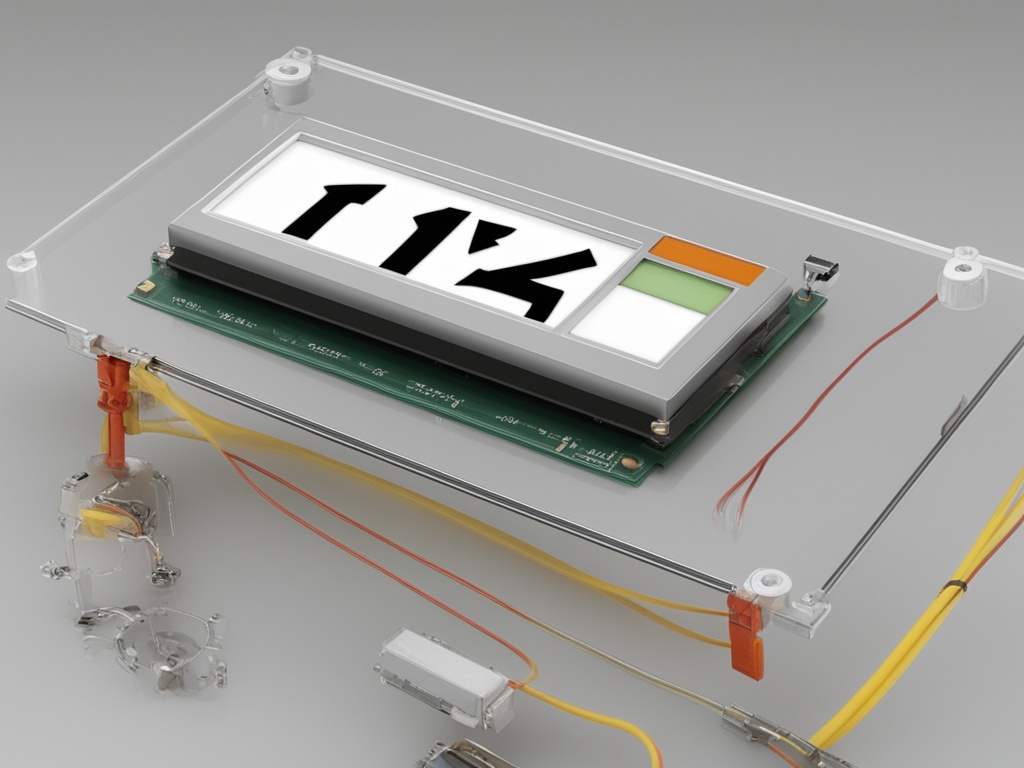
A key aspect of alphanumeric LCD displays is their configuration, which typically follows a standard nomenclature. This nomenclature breakdown is crucial for understanding the specifications and capabilities of these displays. The configuration is typically expressed as a series of numbers, with the first number indicating the number of characters in each row, followed by the number of rows. For instance, a display described as "16×2" indicates that there are 16 characters in each row, with two rows in total.
This configuration not only affects the overall size and shape of the display but also its resolution, which is essentially the number of distinct points or pixels that can be displayed. A higher resolution means more characters or more complex graphics can be shown. For alphanumeric LCD displays, the resolution is typically fixed and cannot be changed, making it crucial to select the right configuration based on the intended application.
In addition to the standard configurations like 16×2, 8×1, and 40×4, alphanumeric LCD displays can also be found in a range of sizes and formats, designed to meet specific requirements. Some displays are designed for monochrome (black and white) display, while others offer color options for added visual appeal. The choice of display type depends largely on the end use case and the desired level of functionality.
The operation of alphanumeric LCD displays relies on a combination of backlighting and liquid crystal display technology. The backlighting, typically provided by LEDs, ensures that the display is visible even in low-light conditions. The liquid crystal display (LCD) technology, on the other hand, works by manipulating the polarization of light passing through the display, creating the illusion of pixels and therefore images or text.
Alphanumeric LCD displays are also known for their durability and longevity. The LCD panels are typically made from high-quality materials that can withstand repeated use and exposure to various environmental conditions. This makes them suitable for use in a wide range of settings, from indoor environments to outdoor locations where exposure to moisture, dust, and other contaminants may be a concern.
Moreover, alphanumeric LCD displays are energy-efficient, consuming relatively little power compared to other types of displays. This is especially important in battery-powered devices where extended battery life is crucial. The low power consumption of LCD displays helps extend the operational lifespan of these devices, making them more suitable for mobile and remote applications.
In summary, alphanumeric LCD displays are a versatile and reliable solution for a wide range of display needs. Their simplicity, durability, and energy efficiency make them ideal for use in a diverse array of applications, from basic consumer electronics to complex industrial systems. By understanding the configuration and specifications of these displays, it becomes easier to select the right model for a given application, ensuring optimal performance and user experience.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey