difference between tft lcd and crt in stock

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

TFT monitors don"t have refresh rates "as such", a CRT with it"s rate set low would certainly give you a headache because it illuminates and draws line by line at say 65Hz.

Since the production of cathode ray tubes has essentially halted due to the cost and environmental concerns, CRT-based monitors are considered an outdated technology. All laptops and most desktop computer systems sold today come with LCD monitors. However, there are a few reasons why you might still prefer CRT over LCD displays.
While CRT monitors provide better color clarity and depth, the fact that manufacturers rarely make them anymore makes CRTs an unwise choice. LCD monitors are the current standard with several options. LCD monitors are smaller in size and easier to handle. Plus, you can buy LCD monitors in a variety of sizes, so customizing your desktop without all the clutter is easy.
The primary advantage that CRT monitors hold over LCDs is color rendering. The contrast ratios and depths of colors displayed on CRT monitors are better than what an LCD can render. For this reason, some graphic designers use expensive and large CRT monitors for their work. On the downside, the color quality degrades over time as the phosphors in the tube break down.
Another advantage that CRT monitors hold over LCD screens is the ability to easily scale to various resolutions. By adjusting the electron beam in the tube, the screen can be adjusted downward to lower resolutions while keeping the picture clarity intact. This capability is known as multisync.
The biggest disadvantage of CRT monitors is the size and weight of the tubes. An equivalently sized LCD monitor can be 80% smaller in total mass. The larger the screen, the bigger the size difference. CRT monitors also consume more energy and generate more heat than LCD monitors.
For the most vibrant and rich colors, CRTs are hard to beat if you have the desk space and don"t mind the excessive weight. However, with CRTs becoming a thing of the past, you may have to revisit the LCD monitor.
The biggest advantage of LCD monitors is the size and weight. LCD screens also tend to produce less eye fatigue. The constant light barrage and scan lines of a CRT tube can cause strain on heavy computer users. The lower intensity of the LCD monitors coupled with the constant screen display of pixels being on or off is easier on the eyes. That said, some people have issues with the fluorescent backlights used in some LCD displays.
The most notable disadvantage to LCD screens is the fixed resolution. An LCD screen can only display the number of pixels in its matrix. Therefore, it can display a lower resolution in one of two ways: using only a fraction of the total pixels on the display, or through extrapolation. Extrapolation blends multiple pixels together to simulate a single smaller pixel, which often leads to a blurry or fuzzy picture.
For those who are on a computer for hours, an LCD can be an enemy. With the tendency to cause eye fatigue, computer users must be aware of how long they stare at an LCD monitor. While LCD technology is continually improving, using techniques to limit the amount of time you look at a screen alleviates some of that fatigue.
Significant improvements have been made to LCD monitors over the years. Still, CRT monitors provide greater color clarity, faster response times, and wider flexibility for video playback in various resolutions. Nonetheless, LCDs will remain the standard since these monitors are easier to manufacture and transport. Most users find LCD displays to be perfectly suitable, so CRT monitors are only necessary for those interested in digital art and graphic design.

LCD displays were created as an alternative to the CRT display screens which were big and bulky when compared to the later LCD displays. It stands for Liquid Crystal Display.
LCD displays can be divided into two – monochrome LCD displays and colour LCD displays. The colour LCD displays can again be divided into two and the TFT display is one of the two colours LCD displays. STN or Super Twisted Nematic display is the other type of LCD colour display.
As mentioned, a TFT display is a kind of colour LCD display which uses thin film transistors in order to produce images with more quality. TFT stands for thin film transistors.
The elements of the TFT are placed directly on the glass substrate while the traditional method involves the process of producing silicon transistors.
The images produced on TFT display screens are much better when compared to the images produced on an LCD screen. In the case of a TFT screen, the images produced will also not be prone to any crosstalk.
The TFT screens also require only less charge when compared to the LCD display screens to get activated. LCD screens, on the other hand, will use or consume more charge to work properly because of using traditional methods.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CRT-vs-LCD-monitor-cfe0b6f375b542928baf22a0478a57a3.jpg)
The short name of TFT:Thin Film Transistor in Chinese. What is the difference between TFT and LCD? Our laptops and desktops now use relatively advanced TFT displays, which consist of LCD pixels and are powered by thin-film transistors integrated behind the pixels. Therefore, the TFT type display screen also belongs to a class of display devices with a source matrix.
TFT type display screen is currently a better LCD color display, TFT type display has many advantages: high responsiveness, high brightness, high contrast, and so on.TFT displays are closest to CRT displays. The TFT screen also often appears on the screen of each big mobile phone, there are 65536 colors, 160,000 colors, 16 million colors three, its display effect is also very good.
TFT means that every LCD pixel on an LCD is driven by a thin-film transistor integrated behind it. Thus can achieve high speed, high brightness, high contrast display screen information, TFT-LCD(thin-film transistor liquid crystal display) is one of the majority of LIQUID crystal displays.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD). The structure of the LCD is placed in the middle of the two pieces of parallel glass liquid crystal box, the substrate glass set on TFT (thin-film transistor), set the color filter substrate glass on, on the TFT signal, and the voltage change to control the rotation direction of the liquid crystal molecules, so as to achieve control of each pixel display emergent polarized light or not and to achieve. Now THAT LCD has replaced CRT as the mainstream, the price has dropped a lot and become widely available.
The TFT(Thin Film Field-effect Transistor) is a video in which every single pixel in the liquid crystal display is actuated by a Thin Film Transistor embedded in the rear. Thus can achieve high speed, high brightness, high contrast display screen information.
Color screens of mobile phones vary depending on LCD quality and research and development technology. The types of color screens include STN (CSTN), TFT(LTPS), TFD, UFB, and OLED.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD). Generally divided into monochrome and color LCD two kinds, the current monochrome LCD has almost out of the notebook computer market, and color LCD still continues to develop. The color LCD can be divided into two types: STN and TFT. The TFT(Thin Film Transistorized)LCD, also known as the active transistorized Transistor LIQUID crystal display (LCD), is the true-color LIQUID crystal display that many people describe as the Thin Film Transistor.DSTN (Dual Scan Twisted Nematic)LCD, namely double scan LIQUID crystal display. It is a display mode of STN LCD, which is no longer on the market.
What is the difference between TFT and LCD? Read here I believe you have a general understanding and cognition of TFT and LCD, LCD refers to liquid crystal display, TFT is a kind of LCD. The former is for laptops and the latter is for desktop computers. There are several different technologies for LCD, FED, PDP, OLED, TFT-LCD, they are all LCD. Only the desktop with several fronts more, lower cost, TFT technology cost is higher, generally used for notebook, or MOTO, etc., now most of the display is TFT type display, I believe we will pay more attention to the choice and purchase of digital goods.

Cathode Ray Tubes (CRT) were once the only way to convey pictures. They are large, bulky and consume a lot of power. Liquid Crystal Displays or more commonly known as LCDs are beginning to replace CRTs in most applications today. They are essentially the reverse of what CRTs are, light, thin, and energy efficient. Also, because of the high power consumption of CRT displays, it needs to dissipate a greater amount of energy which makes it run hotter compared to LCDs.
The only aspect where CRT wins over LCD in performance is in the response time. Older LCDs have been plagued with very slow response times that create ghosting effects on the screen whenever there is high speed motion. This made early LCD screens unsuitable for most gaming needs and even in viewing movies, but newer LCDs have improved on it and this is no longer such a big issue.
Understandably, LCDs cost significantly more compared to CRTs in displays of the same size due to the more complex production process that is needed to produce LCDs. But consumers often rationalize that the extra cost is recovered after a while due to the significantly lower power consumption. The physical dimensions of the LCD also meant that it is usable in so many applications where CRTs would simply be impractical to use. Aside from the usual TV screen or computer monitor, LCDs are also used in mobile phones, digital cameras, music players, GPS navigators, and so much more.
A problem that is unique to LCD screens is the dead pixel, which is unheard of in CRT screens. Since LCDs are a matrix of pixels, one or more of these pixels may not function due to irregularities in the production process. This leaves a small dot on the screen that doesn’t change with the display, appearing like a small piece of dirt stuck in there. Most manufacturers would accept and replace screens that have dead pixels in them but it is always best to inquire about the warranty and their dead pixel policy.

No native resolution. Currently, the only display technology capable of multi-syncing (displaying different resolutions and refresh rates without the need for scaling).Display lag is extremely low due to its nature, which does not have the ability to store image data before output, unlike LCDs, plasma displays and OLED displays.
Text and images (scans of census records) are crisper and sharper and the LCD monitor is easier on your eyes. Monitor"s size: Traditional monitors are similar to a TV because both of them have the CRT (Cathode Ray Tube). That is the reason for its bigger size. It therefore occupies more space at the desk. It is also heavy.
However, LCD monitors have thin flat screen. Therefore occupies very less space and is lighter than the CRT monitor. LCD monitors can be fixed even on wall. Display Size: Even though the display size of a CRT monitor is calculated diagonally, the actual display size is smaller. For instance a 17" CRT monitor will actually have a display size of only 16" However, the display size of 17" LCD monitor will have 17" display size. Resolution: CRT monitors can show different resolutions. The resolution can be changed as required. LCD Monitors will have Native Resolution and therefore has a fixed resolution. The best resolution will be the native resolution for that LCD monitor. Viewing Direction: A CRT screen can be viewed from all directions. And from different distance. But LCD monitors cannot be viewed from all directions. LCD monitors can only be viewed straight. Therefore its viewing direction is limited. If viewed from other directions the colors will change and sometimes the vision will be unclear if not viewed straight. But in recent years the new LCD monitors have improved on this defect. Radiation Emission: The radiation emission in CRT monitors are higher. This will not be visible normally but it will affect eyesight and may cause head ache. Long term use of these monitors may even affect the eyes adversely. LCD monitors do not have this type of Radiation emission. Therefore LCD monitors are good for the eyes. Price: CRT monitors are priced very cheap. However they consume more power. LCD monitors are priced higher, but they consume less electricity. Though the electricity consumption is not very significant for personal use, it is very cost efficient in big organizations with many computers.
Text and images (scans of census records) are crisper and sharper and the LCD monitor is easier on your eyes. Dot pitch: This is the space between dots and is measured in fractions of a millimeter, e.g., .25mm. The smaller the number the better because the dots are tighter. Many manufacturers don%u2019t even list the dot pitch anymore and you probably won%u2019t be able to tell the difference between a .22 and .27 pitch anyway. So, if you like the monitor then don%u2019t worry about the dot pitch. Passive-matrix vs. active-matrix: Do not buy a passive-matrix monitor. I seriously doubt you%u2019ll even see one for sale, but%u2026just in case. Having said that, there are some new passive-matrix technologies that are worth buying. If the monitor isn"t TFT (a type of active-matrix), look for CSTN or DSTN (the latest passive technologies). Brightness: How bright is the picture, expressed as cd/m (I have no idea what the units mean). Look for a brightness level of 200 cd/m or greater. Again, if the monitor specs don%u2019t list this value (not all do) be sure you can get your money back. If the lighting in your office (kitchen table) is subdued the brightness factor won%u2019t be as important as if you have a lot of sunlight streaming in. Don%u2019t pay extra for extra brightness unless you%u2019re worried about bright sunlight. Overall, the contrast ratio will have a bigger impact on picture quality. Monitor"s size: Traditional monitors are similar to a TV because both of them have the CRT (Cathode Ray Tube). That is the reason for its bigger size. It therefore occupies more space at the desk. It is also heavy. However, LCD monitors have thin flat screen. Therefore occupies very less space and is lighter than the CRT monitor. LCD monitors can be fixed even on wall. Display Size: Even though the display size of a CRT monitor is calculated diagonally, the actual display size is smaller. For instance a 17" CRT monitor will actually have a display size of only 16" However, the display size of 17" LCD monitor will have 17" display size. Resolution: CRT monitors can show different resolutions. The resolution can be changed as required. LCD Monitors will have Native Resolution and therefore has a fixed resolution. The best resolution will be the native resolution for that LCD monitor.
Speaking of easy on your eyes, there isn"t any glare, and the flat screen means no distortion. By the way, even those expensive old-fashioned flat screen CRT monitors have some distortion. Monitor"s size: Traditional monitors are similar to a TV because both of them have the CRT (Cathode Ray Tube). That is the reason for its bigger size. It therefore occupies more space at the desk. It is also heavy. However, LCD monitors have thin flat screen. Therefore occupies very less space and is lighter than the CRT monitor. LCD monitors can be fixed even on wall. Display Size: Even though the display size of a CRT monitor is calculated diagonally, the actual display size is smaller. For instance a 17" CRT monitor will actually have a display size of only 16" However, the display size of 17" LCD monitor will have 17" display size. Resolution: CRT monitors can show different resolutions. The resolution can be changed as required. LCD Monitors will have Native Resolution and therefore has a fixed resolution. The best resolution will be the native resolution for that LCD monitor. Viewing Direction: A CRT screen can be viewed from all directions. And from different distance. But LCD monitors cannot be viewed from all directions. LCD monitors can only be viewed straight. Therefore its viewing direction is limited. If viewed from other directions the colors will change and sometimes the vision will be
Liquid Crystal Displays or LCDs were created as an alternative to big and bulky CRT displays. They were energy efficient, thin, and light. But problems plagued earlier LCD models and made them far too inferior to CRT displays. As a remedy, traditional LCD construction methods were adapted to improve the performance of these diplays. TFT or Thin Film Transistor was the solution they found. Instead of the traditional method of producing silicon transistors in wafers, TFT elements are deposited directly to the glass substrate.
The new method of producing the screen had a few immediate improvements. TFT made it possible to reduce the crosstalk between individual pixels resulting in a significant improvement in image quality. Crosstalk is when the signal of adjacent pixels affect the operation of the pixel. This deviates the brightness of pixels, making it brighter or dimmer than it was intended to be. TFT also solved, or at least minimized, the inherent problem of LCD that made it unusable for a lot of applications. LCD screens used to have a very high response time and it was not capable of reproducing fast motion. This problem made gaming and watching movies on these displays pretty terrible. The small transistor elements in a TFT display requires a smaller amount of charge to change its state. The lower charge needed translates directly to a faster response time. As development continued on TFT displays, the response time became lower and lower until LCDs were almost competitive with CRTs with respect to response time.
TFT was so successful that it became the standard in producing LCD screens. Today, all the LCDs being made are built with TFT. Even the newer screens being developed that use LEDs still utilize a TFT layer to drive the display. TFT might be totally replaced in the future by a superior technology but for now, it is the dominant element in all LCDs.

The obsolescence of CRT monitors requires replacing stimulators used for eliciting VEPs with new monitors. Currently, LCD monitors are the only suitable alternative, however other technologies, like OLED, may become a viable option [23]. So far, the ISCEV extended protocol for VEP methods of estimation of visual acuity recommends ensuring luminance artifacts caused by non-CRT stimulators [9], which can be achieved by reducing the stimulus contrast [23]. However, this may not be possible without falling below the minimum contrast values recommended for VEP [1, 23]. Since LCD stimulators have been shown to result in mostly a delay in the VEP responses [2,3,4, 23] but seem not to affect the size of the amplitudes [2], we expected no difference between the estimated visual acuity by using LCD or CRT monitors used as a stimulator for the sweep VEP.
The results of the first experiment show statistically significant effects of the monitor type on the time-to-peak after stimulus onset and the peak-to-trough amplitude (Table 1). The mean delay of the time-to-peak after stimulus onset between recordings obtained using the LCD and the CRT monitor was about 60 ms, which is quite high and possibly caused by the relatively old LCD monitor used. Accordingly, statistically significant effects on the time-to-peak after stimulus onset and the peak-to-trough amplitude were found for the monitor/contrast combination in the results of the second experiment (Table 4). Surprisingly, the mean delay of the time-to-peak after stimulus onset of the CRT monitors with high contrast was with up to 151 ms, longer (Table 5) than that of the LCD monitors (with low and high contrast), although one would expect modern monitors to have shorter or even no delays [24, 25]. Additionally, a statistically significant interaction between the spatial frequency and the monitor type was revealed in both experiments, causing an increased time delay for the intermediate spatial frequencies (1.4–10.3 cpd) with LCD stimulation (Fig. 2, top left) in the first experiment and an almost linear increase with the spatial frequencies in the second experiment (Fig. 2, bottom left). This may be explained by the semi-manual cursor placement, which is necessary because the amplitudes are less pronounced at frequencies below and above this frequency band. Another cause might be an input lag resulting from the time required by the monitor to prepare the image data to be displayed. This could be caused by, e.g., internal scaling for non-native resolutions, which may even be present when using the monitor’s native resolution. In the worst case, this leads to nonlinearities of the response timing of the LCD monitor when presenting patterns of low or high frequency [26, 27]. In doubt, the precise duration of the input lag should be measured using a photodiode attached to the display [28] and in case of being constant, the delay could then be subtracted from the respective time-to-peak values. Finally, the higher latencies may also be caused by the different software used for generating the stimuli: whereas in the first experiment, a custom-developed Java-based software was used, in the second experiment, the Python-based PsychoPy was employed. Nevertheless, these differences seem not to affect the estimated visual acuity. The mean peak-to-trough amplitude using the LCD monitor in the first experiment is reduced by about 0.9 µV with a confidence interval from − 1.6 to − 0.2 µV compared to the CRT stimulator, but increased by about 2.6 µV (confidence interval from 1.2 to 4.0 µV) when comparing the new LCD monitor with the CRT monitor (both with high contrast) in the second experiment (Table 5). However, these differences were, despite being statistically significant, within the expected standard deviation from about 0.5 to 7 µV of the P100 amplitude found in the literature [29,30,31] and therefore probably of no clinical relevance (Fig. 2, right). Interestingly, the results of Nagy et al. [2] suggest a similar reduction in the peak-to-trough amplitude when using an LC display for stimulation. In the first experiment, no statistically significant interaction between monitor type and spatial frequency on peak-to-trough amplitude was found but a tendency to smaller amplitudes at intermediate frequencies (Table 1), whereas in the second experiment, the effect of the interaction of stimulator and spatial frequency was statistically significant (Table 4). It has to be taken into account that the residuals of the models were heteroscedastic and therefore the statistical significance of the effects may be overestimated [32].
In the first experiment, the difference between the subjective visual acuity and that estimated by the second-order polynomial method, or by the modified Ricker function, was not statistically significant from a hypothetical assumed value of 0 logMAR (Table 2). Neither were the variances between CRT and LCD statistically different. Accordingly, the linear mixed-effects models revealed no statistically significant effects of neither the monitor type, the recording cycle, nor their interaction on the difference between subjective and estimated visual acuity for both estimation methods (Table 3).
In contrast in the second experiment, the differences between subjective visual acuity determined using FrACT and the visual acuities estimated using the modified Ricker function along with the conversion formula used in the first experiment were significantly different from the hypothesized difference of 0 logMAR for both, the new gaming LCD monitor and the old LCD monitor, at high and low contrast, but not for the CRT monitor. After using an individually adjusted conversion formula for each monitor/contrast combination, no statistically significant difference from the hypothesized difference of 0 logMAR was found (Table 7). However, one should keep in mind that using the results to calculate the conversion formula used to predict the results is circular reasoning. Nevertheless, it indicates, that using individual established conversion formulas calculated from a sufficiently large number of normative data will minimize the error between true visual acuity and estimated visual acuity.
Table 6 lists the signal-to-noise ratio calculated from the fitted Ricker model for the different combinations of monitors and contrasts. The highest SNR was found for the CRT monitor using high contrast. The LCDs showed lower SNR values. The on average higher amplitudes obtained using LCD monitors (Table 5) indicate that more noise is present when stimulating using LCDs. However, this effect could be caused by the different software used for the stimulus presentation and the lower number of sweeps recorded for averaging compared to the recordings using the CRT monitor. Nevertheless, none of the differences between the SNR values obtained from the different monitor types was statistically significant (Table 6), which corresponds to the findings of Fox et al. [28].
We want to point out the limitations of the current study: We included only healthy participants, so the possible effects of LCD stimulators on patients with reduced visual acuity remain unclear and should be further investigated, especially since we found a statistically significant, albeit not clinically relevant, effect of the monitor/contrast combination on peak-to-trough amplitude and time-to-peak after stimulus onset in the second experiment (Tables 4, 5). Further limitations are that the participants were not stratified by age and that the subjective visual acuity in the first experiment was determined using an eye chart projector, in contrast to the second experiment, where FrACT was used, limiting the accuracy of the estimated value. Finally, this study compared only three specific monitors; therefore, the results are not universally valid.
In conclusion, based on the results of this study, LCD monitors may substitute CRT monitors for presenting the stimuli for the sweep VEP to objectively estimate visual acuity. Newer LCD screens, especially with low response times in the range of 1–2 ms, therefore, allow for a reduction in luminance artifacts at required contrast levels [23], albeit the luminance artifact may not have a large effect on the recorded signals [28]. New technologies like OLED displays [23] may even be better suited, since one the one hand, the onset will be the same for the whole pattern, and on the other hand, LCDs and OLEDs provide a constant luminance level during stimulation, whereas CRTs need a constants pulses to keep the phosphor lit up, causing fast local luminance flashes all the time [28]. Therefore, in contrast to CRTs, LCD and OLED stimulators, e.g., may allow for recording true offset responses [33]. However, caution should be taken when leveraging modern displays for stimulation, since their in-built electronics perform all kinds of sophisticated image-enhancing procedures including color-correction, brightness boosting, contrast enhancement by real-time adjustments of the colors or the backlight, or eyestrain-reducing blue light filtering, with the aim to improve the users’ experience, or to increase the monitors lifetime. This applies in particular to consumer electronics like TVs. Gaming monitors, in addition, use special acceleration drivers, which shut down the backlight, insert black frames (Black Frame Insertion, BFI), or employ variable refresh rates (e.g., Nvidia G-SYNC or AMD FreeSync) to clean the retained image from the eye. Therefore, one should disable any image processing or enhancing functionality in the monitor settings, before using the monitor as stimulator for electrophysiological experiments. Finally, it is advisable to perform a calibration with healthy volunteers using best-corrected and artificially reduced visual acuity and to collect normative data for the employed setup, as always recommended by ISCEV [34], in order to establish an individual conversion formula between the sweep VEP outcome and the estimated visual acuity.

Monitor displays are commonly used peripheral output devices in computers. These peripheral devices are also called ‘display monitors’ or ‘monitors’ or ‘displays’. They display information to a computer user.[1] There are a few important reasons why practicing radiologists should have a working knowledge of monitor displays and these are described below.
Impact of digital imaging: Computers play an important role in contemporary radiology practice. Most radiology modalities today use monitor displays to aid analysis of images. Monitors have become integral components of digital radiography, USG, CT / MRI consoles and workstations, and PACS terminals.
Image chain: There is an image chain that radiologists need to be aware of while working on computers with monitor displays. At one end of the image chain is the modality. Here pixels, gray scale values, processing, postprocessing, and window level and width are important parameters that govern the appearance of any given image. In the middle of the image chain is the computer with its display controller, graphic cards, and look-up tables (LUT) memory, which influence the digital generation of an image. The human observer"s visual system is the final element of the image chain. Its performance is strongly affected by ambient light, environment, reflection, veiling glare, angular response, and visual acuity.
Shift in analysis model: In the traditional model of radiology practice, hardcopy images displayed on viewboxes were the first point of analysis. Today, in most instances, softcopy images displayed on monitors are the first point of analysis. As a result, key steps like viewing, analysis, processing, and postprocessing of softcopy images are executed directly at monitors of consoles, workstations, and office desktops.[2]
Heterogeneity of data: The data displayed on the monitors in a radiology department is heterogeneous. It is often a variable combination of monochrome and gray-scale and/or color images viewed alongside text, audio, and/or video.[3] In such circumstances, radiologists need to possess a working knowledge of important performance parameters like resolution, brightness, contrast ratio, and viewing angles.
Growth of RIS, PACS, and teleradiology: Image transfer across a variety of networks and radiology modalities is common practice these days. Images are increasingly being stored as part of a patient"s electronic medical records, to be analyzed as and when required; images are often transferred over departmental networks and to teleradiology workstations for analysis[3] In such a diverse set of locations, it is common to find different types of monitors used for displaying assorted types of data.
Original dataset: The American College of Radiology (ACR) has devised guidelines for monitor displays, based on the matrix size of the original digital image dataset. Monitors for small matrix datasets [typically sourced from CT, MRI, USG, nuclear medicine (NM), digital fluorography, and digital subtraction angiography (DSA)] have different performance guidelines as compared to monitors required for large matrix datasets [e.g., sourced from digital radiography (DR), computed radiography (CR), digitized films, and digital mammography][4]. The large matrix datasets require monitors with higher performance. As a rule of thumb, the resolution of the selected display system, ideally, should match the matrix of the image acquisition data.[4]
Image consistency: Each and every computer and its monitor at our workplace, handles gray-scale images in a different way. This is governed by factors such as acquisition parameters, application technique, graphics board, video board memory and processing, LUTs, and display signal processing. Therefore, there is a growing awareness of the need to maintain image consistency and gray-scale calibration across a broad variety of monitor displays.[5]

We all are familiar with the computer monitors. We spend time sitting in front of them for hours working, gaming or watching movies. A monitor is used to display the output of any computer system. A good display makes all the difference and no doubt enhances the user experience. The innovation in the display technologies has improved the quality of the display devices including monitors. Now the desktop computers are available with a variety of displays ranging from technologically obsolete CRT monitors to latest slim LCD, LED or OLED monitors.
A computer monitor, technically termed as visual display unit is an output device that presents the information from the CPU on the screen working as an interface between CPU and the user. A cable connects the monitor to a video adaptor or video card which is set up on the motherboard of the computer. The CPU (Central Processing Unit) sends instruction to the video adaptor telling what needs to be displayed on the screen. The video adaptor converts the instructions into a set of corresponding signals and sends to the monitor. Monitor contains a circuitry that generates the picture on the screen from the set of signals.
The major parameters that measure the performance of a monitor are luminance, contrast ratio, resolution, dot pitch, response time, refresh rate and power consumption. The common problem that arises in monitors is dead pixels, blurred screen, phosphor-burn, etc.
which were the boxy Video Display Terminals (VDTs). VDTs were monochrome monitors which used CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) technology. They were capable of working with any type of computer by connecting through a serial interface.
IBM’s CRT– IBM launched its first computer also known as a ‘three piece computer’ in 1981. It had three different units – CPU, monitor and keyboard separately. By 1984, IBM introduced the new CRT monitor with enhanced Color Graphics Adaptor (CGA) with 16 colors and a resolution of 640 x 350 pixels. In 1987 IBM started offering the Video Graphics Array as part of its new PCs which allowed 256 different colors and a resolution of 640 x 480 pixels.
XGA and UXGA– A new technology named Enhanced Graphics Array or XGA was introduced in 1990 which allowed 16.8 million colors with a resolution of 800 x 600 pixels. The new monitors were now offering true colors that matched the human eye (human eye can detect 10 million different colors). Later the technology extended as UXGA, Ultra Extended Graphics Array which allowed 1600 x 1200 pixels.
In the 90s the LCD monitors came in the scene and gradually started competing with the CRT monitors. By the end of the 20th century, the CRT era was declining with the increasing popularity of Liquid Crystal Technology (LCD). This technology produces sharper images than the CRT monitors and the LCD monitors are significantly thinner having lower radiation emissions.
Few years’ back, LED displays came in the scene and they are gradually making its space in the market. LED technology has various advantages over LCD technology like better image quality, low power consumption, etc.
Since the beginning of computer era, there have been a number of technologies used for the display of output. The major technologies are CRT, LCD, Plasma, LED and OLED displays.
signals through a cable and the signal is decoded by the display controller which finally appears on a phosphor screen. The detailed working is as following:
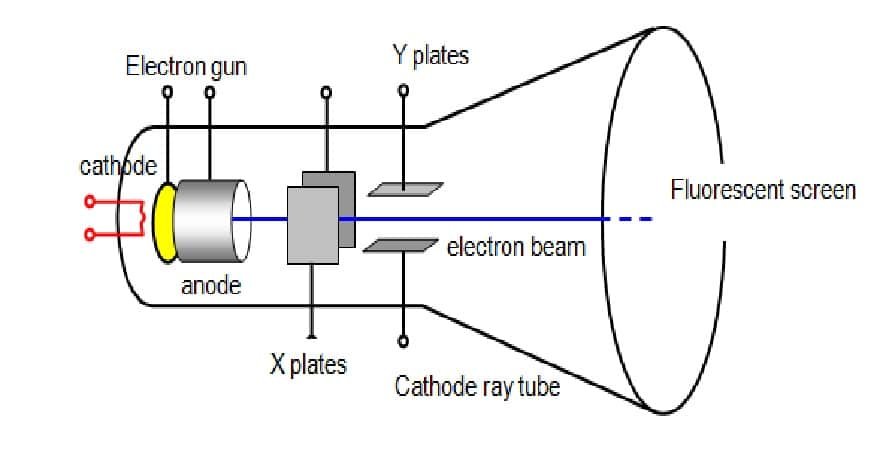
As shown in the image CRTs have a conical shape and there is an electron gun or cathode ray gun at the back end of the monitor and a phosphor screen in the front. The electron gun fires a stream of electrons towards the display screen through a vacuum tube. This stream of electrons is also known as cathode rays. At the middle of the monitor, there are magnetic anodes which are magnetized in accordance with the instruction from the display controller. When electrons (cathode rays) pass through the magnetic anodes, they are pushed or pulled in one direction or other depending on the magnetic field on the anodes. This directs the electrons towards the correct part of phosphor coating inside the display glass. When electrons strikes the phosphor coated screen passing through a mesh (shadow mask or aperture grill), the phosphor lights up making a displayable dot on the computer screen. There are three different colored phosphors (Red, Green and Blue) for each pixel and the color of the pixel depends on the phosphor on which the electrons strike.
has three different phosphors for each pixel. A cathode ray strikes to one or more of these phosphors and the corresponding colored pixel appear on the screen. However high quality monitors use individual electron gun for each color which improves the image quality. Distance for two same colored phosphors (for single electron gun monitors) is known as dot pitch. Lesser the dot pitch higher is the quality of monitors.
brightness on the screen. Shadow mask is an obsolete technology in which there is a metal sheet with millions of holes to pass electrons in order to hit the phosphor coating. The shadow mask covers the entire screen thereby protecting the phosphors from stray ions (due to vacuum) and also limits the strength of the rays reducing the brightness on the monitor.
What is the resolution of the screen?–Resolution of a monitor tells how densely pixels are arranged on the screen. A combination of dot pitch and the viewable image area defines the maximum resolution of the screen. For example if a 21 inch monitor screen with a viewable area of 401mm x 298mm has a dot pitch of 0.26 mm, then its resolution is 1843 x 1370 pixels derived from a formula.
currently. LCD monitors are lightweight, compact, occupy less space, consume low power and are available in a reasonable price. Currently there are two types of LCD technology in use – Active matrix LCD technology or TFT and Passive matrix technology. The TFT technology is more reliable with better image quality while the passive matrix technology has a slower response and gradually becoming outdated.
As the name indicates, liquid crystals are the key elements of the display screen. By manipulating the crystal we can change the way they interacts with the light. There is a display controller in the monitor which receives the display signals from the video adaptor in the motherboard. The display controller controls two things – the electric signals to the liquid crystals and the back light. Structure of an LCD is shown in the below images (Also see how LCD works).
The liquid crystals used in the LCD are Twisted Nemantic (TN), a type of liquid crystals that are twisted at 90owith the surface. In this state, crystals allow the light to pass through the polarizer but on applying a voltage, they get untwisted and block the light to passing through the polarizer. The display controller starts the backlight that passes through the first piece of the glass. At the same time the display controller also send the electrical currents to the liquid crystal molecules to align and allowing the varying level of light to pass through the second piece of glass, forming the desired picture on the screen. In color monitors, each pixel is made of three liquid crystal cells fronted with red, green and blue filters. The light passing through the filtered screen forms the color what you see on the monitor. A wide range of colors are formed by varying the intensity of colored pixels.
The backlight is made of cathodes, and depending on the quality of the monitor, there may be a single cathode at the top or one at the top and one at the bottom, or two at the top and two at the bottom to improve the brightness and clarity of the monitor. These cathodes are diffused through a layer of plastic and diffusing materials.
Resolution– Unlike the CRT monitors there is no complex equation for the dot pitch and the resolution. The resolution of a monitor is simply the number of pixels contained in the matrix. Typically a 17 inch monitor has a resolution of 1280 x 1024 pixels.
In the below video Bill Hammack explains how a TFT monitor works, how it uses liquid crystals, thin film transistors and polarizers to display information.
In this field. LED monitors use light emitting diodes that acts as a performance booster in the monitors. Basically LED monitors are the LCD monitors with a LED backlight to power up the LCD panel. It means that LEDs are placed behind or around the LCD panel to enhance the luminosity and video definition of the monitor screen.
As we have seen in the above section of LCD monitors, they use a cold cathode light as backlight. In the LED monitors all the concepts are same except this backlight, which is replaced by LEDs.
There are three different types of LED monitors available based on the manner how the diodes are arranges in the monitor. These are – Direct LEDs, Edge LEDs and RGB LEDs. Both Edge and Direct LED display monitors use white diodes that are used to illuminate the LCD panel to produce the improved picture quality. The arrangement of LEDs in the monitor is shown in the below image:
In the Direct LEDs display, white diodes are placed all over the panel to produce higher quality image while the Edge LEDs display uses LEDs only on the borders of the LCD panel. Direct LEDs are generally used in the production of high definition TV whereas the Edge LEDs is mainly used in the production of computer screens. RGB LEDs display is better among the three types of LED monitors as it uses red, green and blue diodes to produce the lifelike images with amazing contrast ratio.
Both types of monitors work on the same technology. LED monitors are LCD monitors with replaced cold cathode backlight to LED backlight. Here are the differences that make the LED displays better than the LCDs
Contrast and Black level of the LED screen is better than the LCD screens because the liquid crystals cannot stop 100% of the backlight from cold cathode backlight and hence when the black screen is to be shown on the monitor, it is not completely black (as shown in the below image). But Edge LED screens perfectly show the black screen as there is no backlight at all.
illuminate tiny colored fluorescent lights to create image pixels. Each pixel is made of three such fluorescent lights – red, green and blue lights. To create a wide range of colors, intensity of these lights is varied accordingly.
There are millions of tiny cells filled with the gas like xenon and neon. They are positioned between two plates of glass known as front plate glass and rear plate glass. Two transparent electrodes covered by an insulating dielectric material and a magnesium oxide protective layer are also sandwiched between the glass plates on both sides of the cells on the entire screen.
When the CPU sends the signals to the Plasma monitor, the corresponding electrodes are charged which ionizes the gas in the intersecting cells by passing an electric current. Due to the collisions between the gas ions they release energy in the form of the photons of light which illuminate the respective cells. This process occurs thousands of times in a small fraction of second making the display faster. The released ultraviolet photons strike the phosphor material coated on the inner wall of the cell and hence phosphor electrons jump to the higher energy level. When the electron falls back to its normal state, it releases the energy as a visible light photon. Every pixel on the screen is made of three different colored phosphors – red, green and blue.
are some organic material (containing carbon, like wood, plastic or polymers.) that is used to convert the electric current into light. Since the LEDs are capable of producing different colored light, they are directly used to produce the correct color and there is no need of a backlight which saves power and space. With fast response time, wide viewing angles, outstanding contrast levels and perfect brightness, OLED displays are surely better than the existing other display technologies.
The heart of the OLED display is a stack of thin organic layers which is sandwiched between two conductors – a transparent anode and a metallic cathode, which in turn are sandwiched between two glass plates known as seal and substrate. The organic layer consists of a hole-injection layer, a hole-transport layer, an emissive layer and an electron-transport layer. When an appropriate voltage is applied, an electric current flows from cathode to anode through the organic layers. The cathode give electrons to the emissive layer of organic molecules while the anode takes equivalent electrons from the conducting layer of organic molecules. At the boundary of emissive and conductive layers, electrons and the holes are gathered. Here electrons are recombined with the holes by releasing energy in the form of photon of light. Hence the organic layer emits the light to produce the display. The color of the light depends on the type of organic molecules while the brightness depends on the amount of the current applied. By maximizing the recombination process in the emissive layer the output light can be improved in OLED devices. Thus the emissive layer is slightly doped with highly fluorescent molecules to enhance the electro-luminescent efficiency and control of color.
·Comparing it with the LCD devices, OLED displays can be viewed from different angles as they are “emissive” devices i.e. they emit light rather than modulating transmitted or reflected light.
LCD stands for liquid crystal displays, which were basically created so as to provide an alternative for big and bulky CRT display screens. LCDs were efficient when it came to energy and were very thin and light too.
The best part about TFT displays is that the elements of TFT are deposited directly to the glass substrate rather than the traditional solution of producing silicon transistors.
The difference between TFT and LCD is that TFT is a part or can say a variant of LCD that is used to improve the quality of the image on the screen while LCD is a whole class of a number of displays that uses liquid crystal property to form what it is, which actually does not emit the light directly.
TFT is abbreviated for the thin-film transistor. It is basically used for the flat planes in order to get high-quality liquid crystal displays that are the LCDs.
LCD stands for liquid crystal displays, which were basically created so as to provide an alternative for big and bulky CRT display screens. LCDs were efficient when it came to energy and were very thin and light too.
Parameters of comparisonTFTLCDWhat is it?TFT is one of the many methods that are now used to create LCDs.LCD is a class of different displays that are used to create images with the help of transistors.
ProcessTFT displays the elements of TFT are deposited directly to the glass substrate rather than the traditional solution of producing silicon transistors.LCD does not have such a process.
DisplaysThe TFT-produced displays are much better and are not prone to any crosstalk.Displays made with LCDs are prone to crosstalk and do not have good quality.
TFT is abbreviated for the thin-film transistor. It is basically used for flat planes in order to get high-quality liquid crystal displays that are LCDs.
The best part about TFT displays is that the elements of TFT are deposited directly to the glass substrate rather than the traditional solution of producing silicon transistors.
LCD stands for liquid crystal displays, which were basically created so as to provide an alternative for big and bulky CRT display screens. LCDs were efficient when it came to energy and were very thin and light too.
LEDs, though, have a very common and mostly used set of systems as it literally is used anywhere, like in smartphones, computers, laptops, and other instrumental places.
Piyush Yadav has spent the past 25 years working as a physicist in the local community. He is a physicist passionate about making science more accessible to our readers. He holds a BSc in Natural Sciences and Post Graduate Diploma in Environmental Science. You can read more about him on his bio page.

What are the key differences between leading electronic visual displays available in the market? Such are the times that we live in that today most of us cannot possibly imagine a life without an electronic device. In fact, we have managed to surround ourselves and depend on a growing number of electronic appliances. Several of these devices - as it happens - also have an electronic visual display; be it a mobile phone, a tablet, a desktop monitor or the television set. Without a doubt, these electronic screen devices have revolutionised the way we lead our lives now as all of the four devices have become increasingly commonplace to the point of becoming basic necessities. Which brings to our blog topic: what exactly is an electronic screen and which are the leading screen technologies available today? Read on to know more…
An electronic screen or an electronic visual display, informally called a screen, is basically a device used to display / present images, text, or video transmitted electronically, without creating a permanent record. As mentioned earlier, electronic visual displays include television sets, computer monitors, and digital signage in information appliances. As per the definition, an overhead projector (along with screen onto which the text, images, or video is projected) can also be called an electronic visual display.
1. Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) display:A vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns and a phosphorescent screen, the cathode-ray tube (CRT) is used to display images. It modulates, accelerates, and deflects electron beams onto the screen to make the images. The images could be electrical waveforms (oscilloscope), pictures (television, computer monitor) or radar targets. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, wherein the visible light from the fluorescent material (if any) does not really have any significant meaning to a visual observer, but the visible pattern on the tube face could cryptically represent the stored data. In television sets and computer monitors, the front area of the tube is scanned systematically and repetitively in a pattern called a raster. Thanks to the intensity of each of the three electron beams - one for each additive primary color (red, green, and blue) - being controlled with a video signal as a reference, an image is produced. In modern CRT monitors and TVs, magnetic deflection bends the beams; magnetic deflection is essentially a varying magnetic field generated by coils and driven by electronic circuits around the neck of the tube, although electrostatic deflection is often used in oscilloscopes, a type of electronic test instrument. CRT is one of the older screen/ display technologies.
2. Flat-Panel display: Flat-panel displays are electronic viewing technologies that are used to allow people to see content (still images, moving images, text, or other visual material) in a range of entertainment, consumer electronics, personal computer, and mobile devices, and several kinds of medical, transportation and industrial equipment. They are much lighter and thinner than traditional cathode ray tube (CRT) television sets and video displays and are typically less than 10 centimetres (3.9 in) thick. Flat-panel displays can be classified under two display device categories: volatile and static. Volatile displays need pixels to be periodically electronically refreshed to retain their state (say, liquid-crystal displays). A volatile display only shows an image when it has battery or AC mains power. Static flat-panel displays rely on materials whose color states are bistable (say, e-book reader tablets from Sony), and they retain the text or images on the screen even when the power is off. In recent times, flat-panel displays have almost completely replaced old CRT displays. Most flat-panel displays from the 2010s use LCD and/or LED technologies. Majority of the LCD screens are back-lit as color filters are used to display colors. Being thin and lightweight, flat-panel displays offer better linearity and have higher resolution than the average consumer-grade TV from the earlier decades. The highest resolution for consumer-grade CRT TVs was 1080i, whereas many flat-panels can display 1080p or even 4K resolution.
3. Plasma (P) display: A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing plasma; ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Earlier, plasma displays were commonly used in larger televisions (30 inches and larger). But since more than a decade now, they have lost almost all market share due to competition from low-cost LCDs and more expensive but high-contrast OLED flat-panel displays. Companies stopped manufacturing plasma displays for the United States retail market in 2014, and for the Chinese market in 2016.
4. Electroluminescent display (ELD):Electroluminescent Displays (ELDs) are screens that make use of electroluminescence. Electroluminescence (EL) is an optical and electrical phenomenon where a material emits light in response to an electric current passed through it, or to a strong electric field.
So ELD then is a kind of flat panel display produced by sandwiching a layer of electroluminescent material between two layers of conductors. When the current flows, the layer of material emits radiation in the form of visible light. Basically, electroluminescence works by exciting atoms by passing an electric current through them, leading them to emit photons. By varying the material being excited, the color of the light being emitted is changed. The actual ELD is built using flat, opaque electrode strips running parallel to each other, covered by a layer of electroluminescent material, followed by another layer of electrodes, running perpendicular to the bottom layer. This top layer has to be transparent so as to allow light to escape. At each intersection, the material lights, creating a pixel.
5. Liquid Crystal Display (LCD): A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that makes use of the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not give out light directly; they use a backlight or reflector to create images in color or monochrome. LCDs display arbitrary images like in a general-purpose computer display or fixed images with low information content, that can be displayed or hidden, such as preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays, like in a digital clock. They use the same core technology, apart from the fact that arbitrary images are made up of a large number of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs could be on (positive) or off (negative), as per the polarizer arrangement. For instance, a character positive LCD with a backlight has black lettering on a background the same color as the backlight, and a character negative LCD has a black background with the letters matching the backlight color. Blue LCDs typically get their characteristic appearance from optical filters being added to white.
LCD screens are being used in several applications such as LCD televisions, computer monitors, instrument panels, aircraft cockpit displays, and indoor and outdoor signage. Small LCD screens are seen in portable consumer devices such as digital cameras, watches, calculators and mobile telephones, including smartphones. LCDs are also found in consumer electronics products such as DVD players, video game devices and clocks. It is interesting to note that these displays are available in a wide range of screen sizes as compared to CRT and plasma displays. Also, while LCD screens have replaced heavy, bulky cathode ray tube (CRT) displays in almost all applications, they are slowly being replaced by OLEDs, which can be easily made into different shapes, and boast other advantages such as having a lower response time, wider color gamut, virtually infinite color contrast and viewing angles, lower weight for a given display size and a slimmer profile and potentially lower power consumption. OLEDs, however, are more expensive for a given display size and they can suffer from screen burn-in when a static image is displayed on a screen for a long time (for instance, the table frame for an airline flight schedule on an indoor sign), not to mention that there is currently no way to recycle OLED displays. LCD panels, on the other hand, are susceptible to image persistence but they rarely suffer image burn-in as they do not use phosphors, plus they can be recycled, although this technology is not exactly common as yet. Not surprisingly, attempts have been made to increase the lifespan of LCDs in the form of quantum dot displays, which provide performance to that of an OLED display, but the Quantum dot sheet that gives these displays their characteristics can not yet be recycled. LCDs are also more energy-efficient and can be disposed of more safely than a CRT display.
6. Light-Emitting Diode (LED) display:An LED display is a flat panel display that uses an array of light-emitting diodes as pixels for a video display. Their brightness lets them be used outdoors where they are visible in the sun for store signs and billboards. It was in 1962 that LED diodes first came into being; this was when the first practical LED was invented by General Electric’s Nick Holonyak Jr. This was also when they were mainly red in color. While the early models had a monochromatic design, the efficient Blue LED completing the color triad became available in the market only in the late 1980s. Today, large displays use high-brightness diodes to generate a wide spectrum of colors. In fact, recently, LEDs have also become a popular choice among destination signs on public transport vehicles and variable-message signs on highways. LED displays can offer general illumination in addition to visual display, as when used for stage lighting or other decorative (as opposed to informational) purposes. Several big corporations such as Apple, Samsung and LG are currently looking to develop MicroLED displays. These displays are easily scalable, and help with making the production process more streamlined. That said, production costs continue to be quite high and thus remain a limiting factor.
7. Organic Light-Emitting Diode OLED display: An organic light-emitting diode (OLED), also called an organic EL (organic electroluminescent) diode, is a light-emitting diode (LED), where the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that gives out light in response to an electric current. The organic layer is located between two electrodes, at least one of which is transparent. OLEDs are used to build digital displays in devices such as television screens, computer monitors, portable systems such as smartphones, handheld game consoles and digital assistants. Typically, an OLED display works without a backlight because it emits visible light. This means that it can display deep black levels and can be thinner and lighter than a liquid crystal display (LCD). In low ambient light conditions, say in a dark room, an OLED screen can achieve a higher contrast ratio than an LCD, irrespective of whether the LCD uses an LED backlight or cold cathode fluorescent lamps.
Also important to note an OLED display can be driven with a passive-matrix (PMOLED) or active-matrix (AMOLED) control scheme. In the former, each row (and line) in the display is controlled sequentially, one by one, as opposed to in the AMOLED where a thin-film transistor backplane is used to directly control and switch each individual pixel on or off, thus offering higher resolution and larger display sizes.
Lastly, there are two main families of OLED: those based on small molecules and those making use of polymers. A big area of research is the development of white OLED devices for use in solid-state lighting applications.
8. Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display: AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a display device technology being used in smartwatches, mobile devices, laptops, televisions, media players and digital cameras. As mentioned earlier, it is a type of OLED; rather a specific type of thin-film-display technology where organic compounds form the electroluminescent material. What distinguishes it from PMOLED is the active matrix technology behind the addressing of pixels. An AMOLED display basically comprises an active matrix of OLED pixels generating light (luminescence) upon electrical activation that have been positioned or integrated onto a thin-film transistor (TFT) array, which in turn operates as a series of switches to control the current flowing to each individual pixel. AMOLED technology has continued to work towards consuming low power, becoming low-cost and offering scalability (mainly by offering larger sizes.
9. Super AMOLED display: Super AMOLED is essentially an AMOLED display but it is a term coined for marketing purposes by leading device manufacturers. It is used to denote AMOLED displays that come with an integrated digitizer, i.e. the layer that detects touch is integrated into the screen, instead of overlaid on top of it. The display technology however is not an improvement on the AMOLED. For instance, Samsung claims that Super AMOLED displays reflect one-fifth as much sunlight as the first generation AMOLED. In fact, Super AMOLED displays that are part of the Pentile matrix family, are also at times known as SAMOLED. Other variations of this term include Super AMOLED Advanced, Super AMOLED Plus, HD Super AMOLED, HD Super AMOLED Plus and Full HD Su




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey