pantalla tft lcd vs super amoled free sample

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.

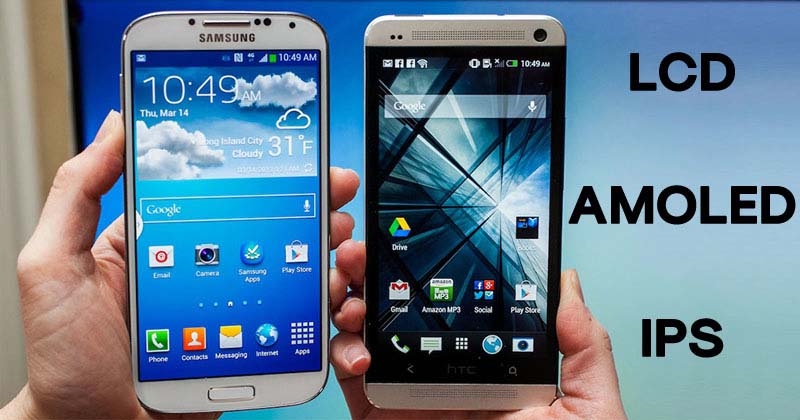
These days you really only have two choices of screens when you are buying a smartphone or tablet: LCD or AMOLED. Many of you probably can’t tell the difference between the two screen types, but both technologies have inherent strengths and weaknesses. LCD has been around for a while, but AMOLED phones are gaining popularity thanks to Samsung and other manufacturers. There isn’t a clear winner at this point in time, so here’s a look at both.
LCD, Liquid Crystal Display, has been a part of our lives for years now. Besides mobile devices, we see LCD screens being used with almost every computer monitor, and in the majority of TVs. While these screens are made of wondrous liquid crystals, they also require a couple panes of glass, and a light source. LCD screens produce some of the most realistic colors you can find on a screen, but might not offer as wide of a contrast ratio (darker darks and brighter brights) as an AMOLED screen.
Some common terms you will find associated with LCD displays are TFT and IPS. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, which makes the wiring of LCD screens more efficient by reducing the number of electrodes per pixel. One benefit of TFT displays is an improved image quality over standard LCD screens. Another popular LCD technology is In-Plane Switching, or IPS, which improves upon TFT by offering much wider viewing angles and color reproduction on LCD screens. IPS screens are able to achieve this by keeping all the liquid crystals parallel to the screen. IPS is generally preferable to standard TFT.
AMOLED, Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, technology has grown in popularity in recent years, particularly among Samsung products. AMOLED screens consist of a thin layer of organic polymers that light up when zapped with an electric current. Due to this simple construction, AMOLED screens can be extremely thin and do not require a backlight. The benefit of losing a backlight is readily apparent: these screens are able to produce blacks so deep that the screen pixels can shut right off. Shutting off pixels can also save electricity and battery life in phones and tablets. Just keep your backgrounds close to black and you’ll save energy.
Sometimes when you read about AMOLED screens, you might hear people complaining about something called a “pentile” display. This is a feature of most color AMOLED screens. Instead of having just a single red, blue, and green sub pixel per actual pixel, pentile displays have a RGBG sub pixel layout which has two green sub pixels for each red and blue. The positive of this technology is that you are able to create a screen that is just as bright as normal screens with one third the amount of sub pixels. The negative of pentile screens is that they can appear grainy, or appear to be lower resolution due to the larger, more visible sub pixels. For a while, Samsung begun using a display type called Super AMOLED Plus, which does not use a pentile sub pixel layout and also improves viewability in direct sunlight — traditionally a weakness for AMOLED. Samsung equipped the Galaxy S II with a Super AMOLED plus screen, but then reverted back to Super AMOLED screens for the Galaxy S III, citing screen life as the reason for the switch.

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.

One of such trade-offs that buyers often have to bear is choosing between a higher refresh rate or an AMOLED panel. But which is more important for a better experience: a fast 120Hz LCD panel or a 60Hz AMOLED one? Let"s find out.
Unlike a regular LCD, an AMOLED display provides more vivid image quality, consumes less power, and does a better job at reducing screen glare. This means that any content you consume on your phone—from games to movies to social media—will appear brighter and more colorful, all while saving your battery life.
Each pixel produces its own light on an AMOLED panel, unlike LCD or IPS panels that use a backlight to illuminate the screen. Because of this, the former can show darker colors and deep blacks more accurately since it can just turn a pixel off to represent an absence of light. On the latter, the same colors appear washed out or faded.
When using Dark Mode (or Night Mode) on an AMOLED panel, the workload of the display is reduced since a measurable portion of the screen is basically turned off. Only the pixels that show colors need to be illuminated, whereas the black pixels can remain shut off. As a result, you save battery life while viewing dark content on an AMOLED screen.
If you"re a gamer, a high refresh rate display will serve you better than an AMOLED one, making your gaming experience much smoother. However, note that the higher the refresh rate, the faster you will drain your battery. Also, keep in mind that many mobile games only support 60Hz, so the benefit of having a 90Hz or 120Hz screen may be redundant.
On the flip side, if you"re someone who consumes a lot of video content like movies, TV shows, YouTube videos, or TikTok clips, then having an AMOLED panel is clearly the better choice since it will improve the color accuracy and vividness dramatically.
As premium features become more common, they"re quickly making their way into budget phones. Having a high refresh rate AMOLED display is obviously better if you can find such a device in the budget category. But if you can"t, you have to trade one for the other.
Since budget phones come with weaker chips, the games you play may not always take advantage of that high refresh rate screen, making them a bit unnecessary apart from smoother scrolling of social media feeds. However, an AMOLED panel will continue to enrich your viewing experience no matter what.

In this edition of Primed, we"ll be examining the different qualities and underlying technologies of several displays, starting with the ubiquitous TFT-LCD and moving through the nascent realm of glasses-free 3D and beyond. We"ll also be addressing the importance of resolution and pixel density. Finally, we"ll be scoping out a handful of upcoming technologies -- while some are thoroughly intriguing, others are just plain wacky. Go ahead... buy the ticket, take the ride, and join us after the break. It"s Primed time.
Generally speaking, two display types rule today"s mobile phones: the Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), and the Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED). While each technology carries a set of strengths and weaknesses, a very important distinction can be drawn between the two. The LCD uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals (LCs), but LCs don"t emit light directly. As such, a light source is necessary for proper viewing. Conversely, the OLED uses organic compounds that illuminate when exposed to electric currents. As backlights aren"t necessary for OLEDs, they"re significantly thinner than traditional LCDs. All things equal, OLED phones should be slimmer than their LCD counterparts, but this isn"t always the case. Take for example the MEDIAS N-04C, which uses a TFT-LCD and measures 7.7mm thin, versus the Galaxy S II, which uses the latest Super AMOLED Plus display and is 8.5mm thick.
The most desirable phone displays today are variants of these two technologies. In the LCD camp, there"s the Super LCD (S-LCD) and the IPS display -- with the latter as the basis for the Retina Display and the NOVA display. Likewise, the OLED territory is filled with options such as Super AMOLED, Super AMOLED Plus and ClearBlack. We"ll discuss the important distinctions between these competing display types shortly, but first let"s develop a fundamental understanding of how these brilliant creations work and how they came to be.
The story of the LCD began in 1888 when cholesterol was extracted from carrots. Think we reached too far back? Not if you"ve ever wondered what liquid crystals are. You see, a botanist named Friedrich Reinitzer discovered this extract had two distinct boiling points and observed the molecule"s ability to transmute from liquid to a crystalline structure in the interim. Even more shocking, the cloudy substance was able to reflect circularly polarized light and rotate the light"s polarization. (This little tidbit will become important when we discuss how LCDs operate.) While liquid crystals appear throughout nature, it wasn"t until 1972 -- when 5CB (4-Cyano-4"-pentylbiphenyl) was synthesized -- that they became commercially viable. A first of its kind, 5CB was chemically stable and entered its nematic phase at room temperature. While there"s actually three phases of liquid crystals, we"re most interested in the nematic one. This describes a state where molecules flow like liquid and self-align in a thread-like helix -- and coincidentally, are easily manipulated with electricity.
Now that you"ve got a little background about liquid crystals, let"s examine how they"re used in LCDs. Let"s start by making a sandwich. As our bread, we"ll take two polarizing filters, one which polarizes light on the horizontal axis and the other on the vertical axis. If we take the slices of bread and hold them up to a light source, nothing is going to pass through. Remember when we said liquid crystals have the ability to rotate light"s polarization? Yeah, they"re a critical ingredient in our sandwich because they determine light"s passage. When nematic crystals are in their natural (or relaxed) state, they form a twisted helix. As light travels through the molecule structure, its polarization is rotated by 90 degrees and light is allowed to pass through the top filter. Conversely, when voltage is applied to the LCs, the helix is broken and light can"t escape the polarizing filters. If you"re keeping score, this is known as the twisted nematic field effect. Going back to the sandwich analogy, the nematic crystals are placed between two layers of transparent electrodes which apply voltage to the liquid crystals. It"s a rather simplistic sandwich, but it describes the fundamentals of how LCDs work. For you visual learners, Bill Hammack does an excellent job of explaining these concepts in the following video.
Now let"s apply this knowledge to the modern TFT-LCD that you"re familiar with. It"s the basis for twisted nematic (TN) and in-plane switching (IPS) displays, and both technologies rely upon the thin film transistor (TFT) for the quick response time and image clarity that we take for granted. Fundamentally, the TFT is a matrix of capacitors and transistors that address the display pixel by pixel -- although at a blistering speed. Every pixel consists of three sub-pixels -- red, green and blue -- each with its own transistor, and a layer of insulated liquid crystals are sandwiched between conductive indium tin oxide layers. Shades are made possible by delivering a partial charge to the underlying LCs, which controls the amount of light that passes through the polarizing filter, thus regulating the intensity of each sub-pixel.
The most common LCD display is based on TN technology, which has been successful due to its relatively inexpensive production costs and fast refresh rates. Many of you will remember the shadow-trail that plagued early LCDs, and faster refresh rates reduce this effect and make the displays better suited for movies and games. Unfortunately, TN displays are famous for exhibiting poor viewing angles and most aren"t capable of showing the entire 24-bit sRGB color gamut. In attempt to mimic the full range of 16.7 million colors, many screens implement a form of dithering to simulate the proper shade. Basic TN screens are hardly fantastic, but they"re also good enough to survive the day without eliciting too many complaints.
Another technology that"s gotten plenty of airtime is the Super LCD (S-LCD), which is a display that"s manufactured by a joint-venture between Sony and Samsung. It employs an alternate method to IPS and TN that"s known as super patterned vertical alignment (S-PVA). Here, the liquid crystals have varying orientations, which help colors remain uniform when viewed from greater angles. S-LCDs also feature improved contrast ratios over traditional TN displays, which exposes a greater amount of details in dark images. Further, these displays feature dual sub-pixels that selectively illuminate based on the brightness of the screen. As you can imagine, this provides power-saving benefits, along with refined control of colors on the screen.
You"re most likely familiar with the active-matrix OLED (AMOLED), which relies on a TFT backplane to switch individual pixels on and off. Coincidentally, active-matrix displays consume significantly less power than their passive-matrix OLED (PMOLED) counterparts, which makes them particularly well-suited for mobile devices. These displays are typically manufactured by printing electroluminescent materials onto a substrate, and that relatively simplistic process suggests that OLEDs will ultimately become cheaper and easier to manufacture than LCDs. Shockingly, the most challenging step is the creation of the substrate itself, which remains a difficult and expensive endeavor. Currently, the limited supply and high demand of AMOLED screens has restricted their availability, and you"re most likely to find them in high-end smartphones.
While all screens suffer from reduced visibility in direct sunlight, the original AMOLED screens were particularly vulnerable to this drawback. To resolve this, Samsung introduced the Super AMOLED display. With this new technology, the touch sensors were integrated into the screen itself. Naturally, this allowed for a thinner display, but this also improved brightness by eliminating the extra layer. Additionally, the screen"s reflection of ambient light and power consumption were significantly reduced. While colors were now bright and vibrant -- and acceptable in direct sunlight -- the displays still couldn"t match the crispness and clarity of LCD screens, particularly with respect to text. Samsung"s PenTile matrix is to blame, which is a hallmark of its AMOLED and Super AMOLED displays. Here, a single pixel is composed of two sub-pixels, either red and green, or blue and green, and the green sub-pixel is significantly more narrow than the other two. While the scheme works fine for images because the human eye is more sensitive to green, it makes the anti-aliasing of text rather imprecise, and the end result is a bit blurry. Like Super AMOLED, Nokia"s ClearBlack display was created to make the AMOLED screen more visible in direct sunlight. This was accomplished by adding a polarized filter to the display, which allows the viewer to see through the screen"s reflection and view the images as they would appear under more ideal conditions.
In its most recent incarnation, the Super AMOLED Plus features a traditional three sub-pixels of equal proportion within one pixel, along with an increased sub-pixel count and density. Both of these measures create a display that"s much more crisp, especially when it comes to text. Further, the tighter spacing between pixels results in better visibility under direct sunlight. The new Super AMOLED Plus screens are also thinner and brighter to boot.
If you find your current smartphone far too rigid, 2012 could be quite a milestone, as Samsung is readying flexible AMOLED displays for production next year. While we plan to see smartphones with large screens that can be folded into a smaller form -- a definite improvement over current hinge-based designs -- we"d love to see an outlandish solution that fully incorporates the flexible spirit.

AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode, OLED display device technology. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescent material, and active matrix refers to the technology behind the addressing of pixels.
An AMOLED display consists of an active matrix of OLED pixels generating light (luminescence) upon electrical activation that have been deposited or integrated onto a thin-film transistor (TFT) array, which functions as a series of switches to control the current flowing to each individual pixel.
Typically, this continuous current flow is controlled by at least two TFTs at each pixel (to trigger the luminescence), with one TFT to start and stop the charging of a storage capacitor and the second to provide a voltage source at the level needed to create a constant current to the pixel, thereby eliminating the need for the very high currents required for passive-matrix OLED operation.
TFT backplane technology is crucial in the fabrication of AMOLED displays. In AMOLEDs, the two primary TFT backplane technologies, polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si) and amorphous silicon (a-Si), are currently used offering the potential for directly fabricating the active-matrix backplanes at low temperatures (below 150 °C) onto flexible plastic substrates for producing flexible AMOLED displays.
AMOLED was developed in 2006. Samsung SDI was one of the main investors in the technology, and many other display companies were also developing it. One of the earliest consumer electronics products with an AMOLED display was the BenQ-Siemens S88 mobile handsetiriver Clix 2 portable media player.Nokia N85 followed by the Samsung i7110 - both Nokia and Samsung Electronics were early adopters of this technology on their smartphones.
Manufacturers have developed in-cell touch panels, integrating the production of capacitive sensor arrays in the AMOLED module fabrication process. In-cell sensor AMOLED fabricators include AU Optronics and Samsung. Samsung has marketed its version of this technology as "Super AMOLED". Researchers at DuPont used computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software to optimize coating processes for a new solution-coated AMOLED display technology that is competitive in cost and performance with existing chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technology. Using custom modeling and analytic approaches, Samsung has developed short and long-range film-thickness control and uniformity that is commercially viable at large glass sizes.
The amount of power the display consumes varies significantly depending on the color and brightness shown. As an example, one old QVGA OLED display consumes 0.3 watts while showing white text on a black background, but more than 0.7 watts showing black text on a white background, while an LCD may consume only a constant 0.35 watts regardless of what is being shown on screen.
AMOLED displays may be difficult to view in direct sunlight compared with LCDs because of their reduced maximum brightness.Super AMOLED technology addresses this issue by reducing the size of gaps between layers of the screen.PenTile technology is often used for a higher resolution display while requiring fewer subpixels than needed otherwise, sometimes resulting in a display less sharp and more grainy than a non-PenTile display with the same resolution.
The organic materials used in AMOLED displays are very prone to degradation over a relatively short period of time, resulting in color shifts as one color fades faster than another, image persistence, or burn-in.
As of 2010, demand for AMOLED screens was high and, due to supply shortages of the Samsung-produced displays, certain models of HTC smartphones were changed to use next-generation LCD displays from the Samsung-Sony joint-venture SLCD in the future.
Flagship smartphones sold in 2020 and 2021 used either a Super AMOLED. Super AMOLED displays, such as the one on the Samsung Galaxy S21+ / S21 Ultra and Samsung Galaxy Note 20 Ultra have often been compared to IPS LCDs, found in phones such as the Xiaomi Mi 10T, Huawei Nova 5T, and Samsung Galaxy A20e.ABI Research, the AMOLED display found in the Motorola Moto X draws just 92 mA during bright conditions and 68 mA while dim.
"Super AMOLED" is a marketing term created by Samsung for an AMOLED display with an integrated touch screen digitizer: the layer that detects touch is integrated into the display, rather than overlaid on top of it and cannot be separated from the display itself. The display technology itself is not improved. According to Samsung, Super AMOLED reflects one-fifth as much sunlight as the first generation AMOLED.One Glass Solution (OGS).
Future displays exhibited from 2011 to 2013 by Samsung have shown flexible, 3D, transparent Super AMOLED Plus displays using very high resolutions and in varying sizes for phones. These unreleased prototypes use a polymer as a substrate removing the need for glass cover, a metal backing, and touch matrix, combining them into one integrated layer.
Lee, Myung Ho; Seop, Song Myoung; Kim, Jong Soo; Hwang, Jung Ho; Shin, Hye Jin; Cho, Sang Kyun; Min, Kyoung Wook; Kwak, Won Kyu; Jung, Sun I; Kim, Chang Soo; Choi, Woong Sik; Kim, Sung Cheol; Yoo, Eu Jin (2009). "Development of 31-Inch Full-HD AMOLED TV Using LTPS-TFT and RGB FMM". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. 40: 802. doi:10.1889/1.3256911. S2CID 110948118.
Hamer, John W.; Arnold, Andrew D.; Boroson, Michael L.; Itoh, Masahiro; Hatwar, Tukaram K.; Helber, Margaret J.; Miwa, Koichi; Levey, Charles I.; Long, Michael; Ludwicki, John E.; Scheirer, David C.; Spindler, Jeffrey P.; Van Slyke, Steven A. (2008). "System design for a wide-color-gamut TV-sized AMOLED display". Journal of the Society for Information Display. 16: 3. doi:10.1889/1.2835033. S2CID 62669850.
Lin, Chih-Lung; Chen, Yung-Chih (2007). "A Novel LTPS-TFT Pixel Circuit Compensating for TFT Threshold-Voltage Shift and OLED Degradation for AMOLED". IEEE Electron Device Letters. 28 (2): 129. Bibcode:2007IEDL...28..129L. doi:10.1109/LED.2006.889523. S2CID 11194344.
Sarma, Kalluri R.; Chanley, Charles; Dodd, Sonia R.; Roush, Jared; Schmidt, John; Srdanov, Gordana; Stevenson, Matthew; Wessel, Ralf; Innocenzo, Jeffrey; Yu, Gang; O"Regan, Marie B.; MacDonald, W. A.; Eveson, R.; Long, Ke; Gleskova, Helena; Wagner, Sigurd; Sturm, James C. (2003). "Active-matrix OLED using 150°C a-Si TFT backplane built on flexible plastic substrate (Proceedings Paper)". SPIE Proceedings. 5080: 180. doi:10.1117/12.497638. S2CID 12958469. "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 June 2011. Retrieved 2010-09-06.link)
Reid Chesterfield, Andrew Johnson, Charlie Lang, Matthew Stainer, and Jonathan Ziebarth, "Solution-Coating Technology for AMOLED Displays Archived 16 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine", Information Display Magazine, January 2011.
"AMOLED vs LCD: differences explained". Android Authority. 8 February 2016. Archived from the original on 27 December 2016. Retrieved 6 February 2017.
Tim Carmody (10 November 2010). "How Super AMOLED displays work". Wired. Wired.com. Archived from the original on 28 September 2012. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
Ashtiani, Shahin J.; Reza Chaji, G.; Nathan, Arokia (2007). "AMOLED Pixel Circuit With Electronic Compensation of Luminance Degradation". Journal of Display Technology. 38 (1): 36. Bibcode:2007JDisT...3...36A. doi:10.1109/JDT.2006.890711. S2CID 44204246.
"AMOLED vs LCD: Which screen is best for your phone?". digitaltrends.com. 29 August 2014. Archived from the original on 29 March 2018. Retrieved 6 May 2018.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
The transmittance of a pixel of an LCD panel typically does not change linearly with the applied voltage,sRGB standard for computer monitors requires a specific nonlinear dependence of the amount of emitted light as a function of the RGB value.
IPS has since been superseded by S-IPS (Super-IPS, Hitachi Ltd. in 1998), which has all the benefits of IPS technology with the addition of improved pixel refresh timing.
Less expensive PVA panels often use dithering and FRC, whereas super-PVA (S-PVA) panels all use at least 8 bits per color component and do not use color simulation methods.BRAVIA LCD TVs offer 10-bit and xvYCC color support, for example, the Bravia X4500 series. S-PVA also offers fast response times using modern RTC technologies.
A technology developed by Samsung is Super PLS, which bears similarities to IPS panels, has wider viewing angles, better image quality, increased brightness, and lower production costs. PLS technology debuted in the PC display market with the release of the Samsung S27A850 and S24A850 monitors in September 2011.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/AMOLED-975451056-a78e63853020468d97d2b5d19d2d9e3d-6b76a0af45c8492c811cd88e97dea36a.jpg)
Some of the amoled display available can operate with no noise, bounce, and reaction, and are able to operate without any sensitivity to vibrations and shock. The amoled display come with the core components: coils, an oscillator, an output amplifier, as well as a Schmitt trigger. There are different versions of this sensor available, including unshielded (which allows for wider sensing distances) and shielded (with an electromagnetic field that is concentrated at the front).
Wholesale amoled display, full-feature to economy series, and top brand models. Phones (or cellphones, or mobile phones) are the devices we use every day, for chatting with friends to communicating essential work information, from checking memes to streaming the latest dramas, from gaming to reading novels, our phones are integrated into our lives. Not a day goes by when someone doesn"t need a new amoler display or a new phone component, and we"ve got what you need. Visit our wholesaler catalogue now, and complete your inventory of all the phones available for your market.
Browse cutting-edge amoled display on Alibaba.com at reasonable prices. amoled display in varying display size and resolution are accessible on the site. The merchandise are useful in automotive, medical, and industrial screen displays. amoled display having multiple interface types and display technology are in stock. amoled display on Alibaba.com have high resolution and luminance to display precise details. They have a capacitive touch for convenient use. They can show multiple characters per line. amoled display can be manufactured to suit smaller wearable devices or large projectors. They can be integrated with smart home systems for face recognition and office equipment. They feature multiple interfacing types like MPU or RS232. They are sturdy, thanks to a toughened glass structure with a considerable operating temperature range. The life span of amoled display stretches up to several thousand pages hours get.

When buying a new Android phone, the device screen plays a determining role. Not only the size of said panel, but also the type of panel that is used in it. Currently we are mainly with two options: AMOLED screen or iPS. They are two names that surely sound familiar to you, but that must be compared.
Next, we will talk more about these two types of screen, so that you can know which one is better or which one to choose on your mobile. Since there are differences between an AMOLED or IPS screen, which is good to know and take into account in this process of buying a new Android smartphone. We leave you with information about each type of panel and more about its strengths or weaknesses, for example.
AMOLED is the acronym for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. These types of screens are composed of organic materials that emit light when electricity is applied. In this type of panel, each pixel works independently, so if there are black areas, those pixels are not working or are inactive, something that helps save energy in the device, this is in fact one of the great advantages of this type of panels.
IPS panel is a type of LCD screen, something that many may not know. LCDs are liquid crystal panels, they are screens composed of a series of liquid crystals that are illuminated with a backlight. They are screens that require less energy, so they are widely used in Android phones. These are also screens that work well even when the sun hits them directly, they can still be read well in these types of conditions.
The IPS is a type of LCD screen, as we have said. IPS stands for In-Plane Switching. and it is an improvement of this type of panels. In this case, the crystals are activated in a different way than the normal LCD panel and have a matrix orientation that rotates, which is something that helps to obtain better viewing angles, better contrast and better colors. In addition, it consumes less power than TFT LCD panels (the other type of panel that is itself an improvement on the traditional LCD panel). Although it is the most expensive type of LCD panel on the market, it is more expensive than the TFT, which has also been losing some presence in some segments.
In an article about AMOLED or IPS screen, it is good to know the advantages and disadvantages that each type of panel leaves us. Now that we know more about each of them, it is necessary to know in which fields they are strong and in which fields they can or should improve still. Since they are the two most common types of panel in the Android phone market and choosing one or the other is important, because it will clearly affect the experience of using said phone. These are the advantages and disadvantages that AMOLED screens currently leave us:
The AMOLED screen is something that has gained a lot of presence in the high end on Android. These are very thin panels, which leave us with good colors and great contrast, something that undoubtedly helps a good experience when viewing photos or streaming content from the phone. In addition, the fact that each pixel works independently is something that helps in the energy consumption of the panel, which is usually lower, thus taking better advantage of the capacity of the phone"s battery.
The IPS panel or screen is something that has been in Android for a long time and that we see especially in the mid-range or upper-middle range of the operating system. It is a cheaper panel to produce than AMOLED, one of its points in favor, but since it is thicker and has a fairly high power consumption, it is not used in the high range of Android. Although it is a type of panel that leaves us with a good user experience, thanks to its good viewing angles, brightness and good colors. Therefore, it is not uncommon for many to even prefer this type of panel to an AMOLED one.
As we have said before, It will depend on the use you want to make of the mobile. IPS panels are ideal for gaming, as well as for creative work, due to their good colors, response time, and viewing angles. While AMOLED panels are good options for general mobile use, streaming content or viewing photos. It also depends on whether you are looking for a high-end or mid-range phone. Since in the high range most panels are AMOLED today. If you take this into account, you will be able to determine which is the best type of panel for you, also depending on the money you want to spend on said phone.
This rise of small, powerful components has also led to significant developments in display technology. The most recent of which, AMOLED, is now the main competitor for the most common display used in quality portable electronics – the TFT–LCD IPS (In-Plane Switching) display. As more factories in the Far East begin to produce AMOLED technology, it seems likely we will enter a battle of TFT IPS versus AMOLED, or LCD vs LED. Where a large percentage of a product’s cost is the display technology it uses, which provides best value for money when you’re designing a new product?
TFT IPSdisplays improved on previous TFT LCD technology, developed to overcome limitations and improve contrast, viewing angles, sunlight readability and response times. Viewing angles were originally very limited – so in-plane switching panels were introduced to improve them.
Modern TFT screens can have custom backlights turned up to whatever brightness that their power limit allows, which means they have no maximum brightness limitation. TFT IPS panels also have the option for OCA bonding, which uses a special adhesive to bond a touchscreen or glass coverlens to the TFT. This improves sunlight readability by preventing light from bouncing around between the layers of the display, and also improves durability without adding excess bulk; some TFT IPS displays now only measure around 2 mm thick.
AMOLED technology is an upgrade to older OLED technology. It uses organic compounds that emit light when exposed to electricity. This means no backlight, which in turn means less power consumption and a reduction in size. AMOLED screens tend to be thinner than TFT equivalents, often produced to be as thin as 1 mm. AMOLED technology also offers greater viewing angles thanks to deeper blacks. Colours tend to be greater, but visibility in daylight is lower than IPS displays.
As manufacturers increasingly focus on smaller devices, such as portable smartphones and wearable technology, the thinness and high colour resolution of AMOLED screens have grown desirable. However, producing AMOLED displays is far more costly as fewer factories offer the technology at a consistent quality and minimum order quantities are high; what capacity there is is often taken up the mobile phone market Full HD TFT IPS displays have the advantage of being offered in industry standard sizes and at a far lower cost, as well as offering superior sunlight visibility.
The competition between displays has benefitted both technologies as it has resulted in improvements in both. For example, Super AMOLED, a marketing brand by Samsung, involves the integration of a touchscreen layer inside the screen, rather than overlaid on it. The backlight in TFT technology means they can never truly replicate the deep blacks in AMOLED, but improvements have been made in resolution to the point where manufacturers like Apple have been happy to use LCD screens in their smartphones, even as they compete with Samsung’s Super AMOLED.
Aside from smartphones, many technologies utilise displays to offer direct interaction with customers. To decide whether TFT LCD will survive the rise of AMOLED technology, we must first recap the advantages of LCD. The backlit quality means that whites are bright and contrast is good, but this will wear down a battery faster than AMOLED. Additionally, cost is a significant factor for LCD screens. They are cheaper, more freely available and are offered in industry standard sizes so can be ordered for new products without difficulty.
It seems hard to deny that AMOLED will someday become the standard for mobile phones, which demand great colour performance and are reliant on battery life. Where size is an issue, AMOLED will also grow to dominance thanks to its superior thinness. But for all other technologies, particularly in industrial applications, TFT-LCD offers bright, affordable display technology that is continually improving as the challenge from AMOLED rises.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey