pantalla tft lcd vs super amoled brands

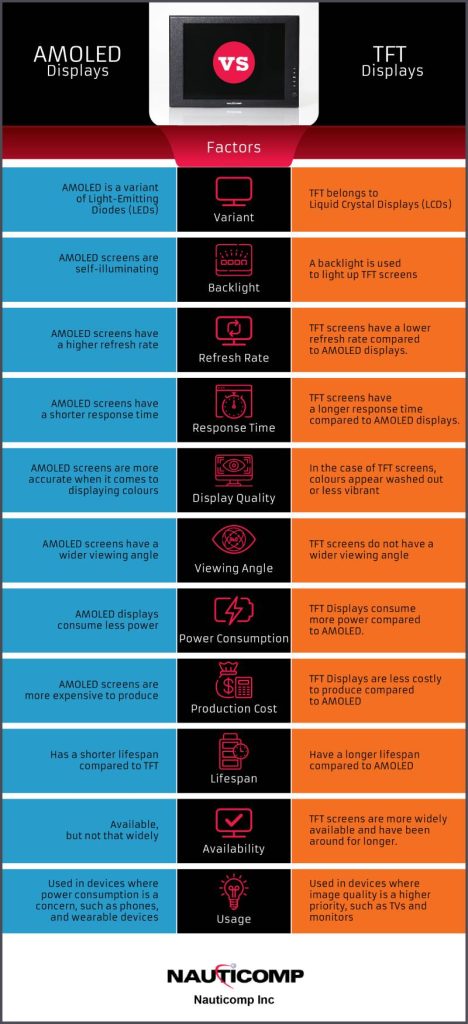
AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.

Tried and trusted TFT technology works by controlling brightness in red, green and blue sub-pixels through transistors for each pixel on the screen. The pixels themselves do not produce light; instead, the screen uses a backlight for illumination.
By contrast the Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) display requires no backlight and can light up or turn off each of their pixels independently. As the name suggests, they are made of organic material.
An AMOLED display has many other benefits which make it a superior looking display including exceptional vieiwng angles and a display that looks practically black when it is switched off.
So, why use a TFT display? Well, it is a mature technology meaning the manufacturing processes are efficient, yields high and cost much lower than AMOLED.
TFT displays also have a much longer lifespan than AMOLED displays and are available in a far greater range of standard sizes, which can be cut down to fit a space restricted enclosure for a relatively low cost adder.
Mobile display technology is firmly split into two camps, the AMOLED and LCD crowds. There are also phones sporting OLED technology, which is closely associated with the AMOLED panel type. AMOLED and LCD are based on quite different underlying technologies, leading manufacturers to tout a number of different benefits depending on which display type they’ve opted for. Smartphone manufacturers are increasingly opting for AMOLED displays, with LCD mostly reserved for less expensive phones.
We’ll start alphabetically with AMOLED, although to be a little broader we should probably start with a little background about OLED technology in general.
The arrangement of these sub-pixels alters the performance of the displays slightly. Pentile vs striped pixel layouts, for example, results in superior image sharpness, but lower pixel life spans due to the smaller pixel sizes.
Finally, the AM part in AMOLED stands in for Active Matrix, rather than a passive matrix technology. This tells us how each little OLED is controlled. In a passive matrix, a complex grid system is used to control individual pixels, where integrated circuits control a charge sent down each column or row. But this is rather slow and can be imprecise. Active Matrix systems attach a thin film transistor (TFT) and capacitor to each LED. This way, when a row and column are activated to access a pixel, the capacitor at the correct pixel can retain its charge in between refresh cycles, allowing for faster and more precise control.
One other term you will encounter is Super AMOLED, which is Samsung’s marketing term for a display that incorporates the capacitive touchscreen right into the display, instead of it being a separate layer on top of the display. This makes the display thinner.
The use of LEDs and minimal substrates means that these displays can be very thin. Furthermore, the lack of a rigid backlight and innovations in flexible plastic substrates enables flexible OLED-based displays. Complex LCD displays cannot be built in this way because of the backlight requirement. Flexy displays were originally very promising for wearables. Today, premium-tier smartphones make use of flexible OLED displays. Although, there are some concerns over how many times a display can flex and bend before breaking.
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display and reproduces colors quite differently from AMOLED. Rather than using individual light-emitting components, LCD displays rely on a backlight as the sole light source. Although multiple backlights can be used across a display for local dimming and to help save on power consumption, this is more of a requirement in larger TVs.
Scientifically speaking, there’s no individual white light wavelength. White light is a mixture of all other visible colors in the spectrum. Therefore, LCD backlights have to create a pseudo white light as efficiently as possible, which can then be filtered into different colors in the liquid crystal element. Most LCDs rely on a blue LED backlight which is filtered through a yellow phosphor coating, producing a pseudo white light.
All combined, this allows an LCD display to control the amount of RGB light reaching the surface by culling a backlight, rather than producing colored light in each pixel. Just like AMOLED, LCD displays can either be active or passive matrix devices, but most smartphones are active these days.
This wide variation in the way that light is produced has quite a profound difference to the user experience. Color gamut is often the most talked-about difference between the two display types, with AMOLED providing a greater range of color options than LCD, resulting in more vibrant-looking images.
OLED displays have been known for additional green and blue saturation, as these tend to be the most powerful colors in the sub-pixel arrangement, and very little green is required for white light. Some observers find that this extra saturation produces results that they find slightly unnatural looking. Although color accuracy has improved substantially in the past few years and tends to offer better accuracy for wider color gamuts like DCI-P3 and BT-2020. Despite not possessing quite such a broad gamut, LCD displays typically offer 100% sRGB gamut used by most content and can cover a wide gamut and most of the DCI-P3 color space too.
As we mentioned before, the lack of a backlight and filtering layers weighs in favor of OLED over LCD. LCD displays often suffer from light bleed and a lower contrast ratio as the backlight doesn’t switch off even when pixels are supposed to be black, while OLED can simply switch off its pixels. LCD’s filtering layer also inherently blocks some light and the additional depth means that viewing angles are also reduced compared to OLED.
One downside of AMOLED is that different LEDs have different life spans, meaning that the individual RBG light components eventually degrade at slightly different rates. As well as the dreaded but relatively rare burn-in phenomenon, OLED display color balance can drift very slightly over time, while LED’s single backlight means that color balance remains more consistent across the display. OLED pixels also often turn off and on slower, meaning that the highest refresh rate displays are often LCD. Particularly in the monitor market where refresh rates exceed 120Hz. That said, plenty of OLED smartphones offer 90, 120, and even 144Hz support.
There are some pros and cons to both technologies and some reasonable user preferences between the different color and contrast profiles. Although the prevalence of multiple display modes available in modern smartphones makes this somewhat less of an issue these days. However, the falling production costs and additional benefits of OLED displays have made them a more popular choice than ever across a wide range of price segments. OLED dominates the high-end smartphone and TV spaces owing to its wider color gamut, superior contrast ratio, while still supporting decent refresh rates. Not to mention its flexible characteristics for brand new mobile form factors.
Major display manufacturers, such as LG Display and Samsung Display, are betting big on OLED technology for the future, making major investments into additional production facilities. Particularly when it comes to its use in flexible display technology. The AMOLED panel market is expected to be worth close to $30 billion in 2022, more than double its value in 2017 when this article was first published.
That said, developments in Quantum Dot and mini LED displays are closing the already small performance gap between LCD and OLED, so certainly don’t count LCD out of the race just yet.

These days you really only have two choices of screens when you are buying a smartphone or tablet: LCD or AMOLED. Many of you probably can’t tell the difference between the two screen types, but both technologies have inherent strengths and weaknesses. LCD has been around for a while, but AMOLED phones are gaining popularity thanks to Samsung and other manufacturers. There isn’t a clear winner at this point in time, so here’s a look at both.
LCD, Liquid Crystal Display, has been a part of our lives for years now. Besides mobile devices, we see LCD screens being used with almost every computer monitor, and in the majority of TVs. While these screens are made of wondrous liquid crystals, they also require a couple panes of glass, and a light source. LCD screens produce some of the most realistic colors you can find on a screen, but might not offer as wide of a contrast ratio (darker darks and brighter brights) as an AMOLED screen.
Some common terms you will find associated with LCD displays are TFT and IPS. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, which makes the wiring of LCD screens more efficient by reducing the number of electrodes per pixel. One benefit of TFT displays is an improved image quality over standard LCD screens. Another popular LCD technology is In-Plane Switching, or IPS, which improves upon TFT by offering much wider viewing angles and color reproduction on LCD screens. IPS screens are able to achieve this by keeping all the liquid crystals parallel to the screen. IPS is generally preferable to standard TFT.
AMOLED, Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, technology has grown in popularity in recent years, particularly among Samsung products. AMOLED screens consist of a thin layer of organic polymers that light up when zapped with an electric current. Due to this simple construction, AMOLED screens can be extremely thin and do not require a backlight. The benefit of losing a backlight is readily apparent: these screens are able to produce blacks so deep that the screen pixels can shut right off. Shutting off pixels can also save electricity and battery life in phones and tablets. Just keep your backgrounds close to black and you’ll save energy.
Sometimes when you read about AMOLED screens, you might hear people complaining about something called a “pentile” display. This is a feature of most color AMOLED screens. Instead of having just a single red, blue, and green sub pixel per actual pixel, pentile displays have a RGBG sub pixel layout which has two green sub pixels for each red and blue. The positive of this technology is that you are able to create a screen that is just as bright as normal screens with one third the amount of sub pixels. The negative of pentile screens is that they can appear grainy, or appear to be lower resolution due to the larger, more visible sub pixels. For a while, Samsung begun using a display type called Super AMOLED Plus, which does not use a pentile sub pixel layout and also improves viewability in direct sunlight — traditionally a weakness for AMOLED. Samsung equipped the Galaxy S II with a Super AMOLED plus screen, but then reverted back to Super AMOLED screens for the Galaxy S III, citing screen life as the reason for the switch.

Samsung came up with its unique 18:5:9 AMOLED display for the Galaxy S8. LG picked up its old trusted IPS LCD unit for the G6’s display. These display units have been familiar to the usual Indian smartphone buyer. Honor, on the other hand, has just unveiled the new Honor 8 Pro for the Indian market that ships with an LTPS LCD display. This has led to wonder how exactly is this technology different from the existing ones and what benefits does it give Honor to craft its flagship smartphone with. Well, let’s find out.
The LCD technology brought in the era of thin displays to screens, making the smartphone possible in the current world. LCD displays are power efficient and work on the principle of blocking light. The liquid crystal in the display unit uses some kind of a backlight, generally a LED backlight or a reflector, to make the picture visible to the viewer. There are two kinds of LCD units – passive matrix LCD that requires more power and the superior active matrix LCD unit, known to people as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) that draws less power.
The early LCD technology couldn’t maintain the colour for wide angle viewing, which led to the development of the In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD panel. IPS panel arranges and switches the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules of standard LCD display between the glass substrates. This helps it to enhance viewing angles and improve colour reproduction as well. IPS LCD technology is responsible for accelerating the growth of the smartphone market and is the go-to display technology for prominent manufacturers.
The standard LCD display uses amorphous Silicon as the liquid for the display unit as it can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. This though restricts the display resolution and adds to overall device temperatures. Therefore, development of the technology led to replacing the amorphous Silicon with Polycrystalline Silicon, which boosted the screen resolution and maintains low temperatures. The larger and more uniform grains of polysilicon allow faster electron movement, resulting in higher resolution and higher refresh rates. It also was found to be cheaper to manufacture due to lower cost of certain key substrates. Therefore, the Low-Temperature PolySilicon (LTPS) LCD screen helps provide larger pixel densities, lower power consumption that standard LCD and controlled temperature ranges.
The AMOLED display technology is in a completely different league. It doesn’t bother with any liquid mechanism or complex grid structures. The panel uses an array of tiny LEDs placed on TFT modules. These LEDs have an organic construction that directly emits light and minimises its loss by eradicating certain filters. Since LEDs are physically different units, they can be asked to switch on and off as per the requirement of the display to form a picture. This is known as the Active Matrix system. Hence, an Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display can produce deeper blacks by switching off individual LED pixels, resulting in high contrast pictures.
The honest answer is that it depends on the requirement of the user. If you want accurate colours from your display while wanting it to retain its vibrancy for a longer period of time, then any of the two LCD screens are the ideal choice. LTPS LCD display can provide higher picture resolution but deteriorates faster than standard IPS LCD display over time.
An AMOLED display will provide high contrast pictures any time but it too has the tendency to deteriorate faster than LCD panels. Therefore, if you are after greater picture quality, choose LTPS LCD or else settle for AMOLED for a vivid contrast picture experience.

This rise of small, powerful components has also led to significant developments in display technology. The most recent of which, AMOLED, is now the main competitor for the most common display used in quality portable electronics – the TFT–LCD IPS (In-Plane Switching) display. As more factories in the Far East begin to produce AMOLED technology, it seems likely we will enter a battle of TFT IPS versus AMOLED, or LCD vs LED. Where a large percentage of a product’s cost is the display technology it uses, which provides best value for money when you’re designing a new product?
TFT IPSdisplays improved on previous TFT LCD technology, developed to overcome limitations and improve contrast, viewing angles, sunlight readability and response times. Viewing angles were originally very limited – so in-plane switching panels were introduced to improve them.
Modern TFT screens can have custom backlights turned up to whatever brightness that their power limit allows, which means they have no maximum brightness limitation. TFT IPS panels also have the option for OCA bonding, which uses a special adhesive to bond a touchscreen or glass coverlens to the TFT. This improves sunlight readability by preventing light from bouncing around between the layers of the display, and also improves durability without adding excess bulk; some TFT IPS displays now only measure around 2 mm thick.
AMOLED technology is an upgrade to older OLED technology. It uses organic compounds that emit light when exposed to electricity. This means no backlight, which in turn means less power consumption and a reduction in size. AMOLED screens tend to be thinner than TFT equivalents, often produced to be as thin as 1 mm. AMOLED technology also offers greater viewing angles thanks to deeper blacks. Colours tend to be greater, but visibility in daylight is lower than IPS displays.
As manufacturers increasingly focus on smaller devices, such as portable smartphones and wearable technology, the thinness and high colour resolution of AMOLED screens have grown desirable. However, producing AMOLED displays is far more costly as fewer factories offer the technology at a consistent quality and minimum order quantities are high; what capacity there is is often taken up the mobile phone market Full HD TFT IPS displays have the advantage of being offered in industry standard sizes and at a far lower cost, as well as offering superior sunlight visibility.
The competition between displays has benefitted both technologies as it has resulted in improvements in both. For example, Super AMOLED, a marketing brand by Samsung, involves the integration of a touchscreen layer inside the screen, rather than overlaid on it. The backlight in TFT technology means they can never truly replicate the deep blacks in AMOLED, but improvements have been made in resolution to the point where manufacturers like Apple have been happy to use LCD screens in their smartphones, even as they compete with Samsung’s Super AMOLED.
Aside from smartphones, many technologies utilise displays to offer direct interaction with customers. To decide whether TFT LCD will survive the rise of AMOLED technology, we must first recap the advantages of LCD. The backlit quality means that whites are bright and contrast is good, but this will wear down a battery faster than AMOLED. Additionally, cost is a significant factor for LCD screens. They are cheaper, more freely available and are offered in industry standard sizes so can be ordered for new products without difficulty.
It seems hard to deny that AMOLED will someday become the standard for mobile phones, which demand great colour performance and are reliant on battery life. Where size is an issue, AMOLED will also grow to dominance thanks to its superior thinness. But for all other technologies, particularly in industrial applications, TFT-LCD offers bright, affordable display technology that is continually improving as the challenge from AMOLED rises.

There are two main families of OLED: those based on small molecules and those employing polymers. Adding mobile ions to an OLED creates a light-emitting electrochemical cell (LEC) which has a slightly different mode of operation. An OLED display can be driven with a passive-matrix (PMOLED) or active-matrix (AMOLED) control scheme. In the PMOLED scheme, each row and line in the display is controlled sequentially, one by one,thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane to directly access and switch each individual pixel on or off, allowing for higher resolution and larger display sizes.
An OLED display works without a backlight because it emits its own visible light. Thus, it can display deep black levels and can be thinner and lighter than a liquid crystal display (LCD). In low ambient light conditions (such as a dark room), an OLED screen can achieve a higher contrast ratio than an LCD, regardless of whether the LCD uses cold cathode fluorescent lamps or an LED backlight. OLED displays are made in the same way as LCDs, but after TFT (for active matrix displays), addressable grid (for passive matrix displays) or indium-tin oxide (ITO) segment (for segment displays) formation, the display is coated with hole injection, transport and blocking layers, as well with electroluminescent material after the first 2 layers, after which ITO or metal may be applied again as a cathode and later the entire stack of materials is encapsulated. The TFT layer, addressable grid or ITO segments serve as or are connected to the anode, which may be made of ITO or metal.transparent displays being used in smartphones with optical fingerprint scanners and flexible displays being used in foldable smartphones.
The bottom-emission organic light-emitting diode (BE-OLED) is the architecture that was used in the early-stage AMOLED displays. It had a transparent anode fabricated on a glass substrate, and a shiny reflective cathode. Light is emitted from the transparent anode direction. To reflect all the light towards the anode direction, a relatively thick metal cathode such as aluminum is used. For the anode, high-transparency indium tin oxide (ITO) was a typical choice to emit as much light as possible.thin film transistor (TFT) substrate, and the area from which light can be extracted is limited and the light emission efficiency is reduced.
In "white + color filter method," red, green, and blue emissions are obtained from the same white-light LEDs using different color filters.uneven degradation rate of blue pixels vs. red and green pixels. Disadvantages of this method are low color purity and contrast. Also, the filters absorb most of the light waves emitted, requiring the background white light to be relatively strong to compensate for the drop in brightness, and thus the power consumption for such displays can be higher.
In contrast to a conventional OLED, in which the anode is placed on the substrate, an Inverted OLED uses a bottom cathode that can be connected to the drain end of an n-channel TFT especially for the low cost amorphous silicon TFT backplane useful in the manufacturing of AMOLED displays.
Transfer-printing is an emerging technology to assemble large numbers of parallel OLED and AMOLED devices efficiently. It takes advantage of standard metal deposition, photolithography, and etching to create alignment marks commonly on glass or other device substrates. Thin polymer adhesive layers are applied to enhance resistance to particles and surface defects. Microscale ICs are transfer-printed onto the adhesive surface and then baked to fully cure adhesive layers. An additional photosensitive polymer layer is applied to the substrate to account for the topography caused by the printed ICs, reintroducing a flat surface. Photolithography and etching removes some polymer layers to uncover conductive pads on the ICs. Afterwards, the anode layer is applied to the device backplane to form the bottom electrode. OLED layers are applied to the anode layer with conventional vapor deposition, and covered with a conductive metal electrode layer. As of 2011mm × 400mm. This size limit needs to expand for transfer-printing to become a common process for the fabrication of large OLED/AMOLED displays.
For a high resolution display like a TV, a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane is necessary to drive the pixels correctly. As of 2019, low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS)– TFT is widely used for commercial AMOLED displays. LTPS-TFT has variation of the performance in a display, so various compensation circuits have been reported.excimer laser used for LTPS, the AMOLED size was limited. To cope with the hurdle related to the panel size, amorphous-silicon/microcrystalline-silicon backplanes have been reported with large display prototype demonstrations.indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) backplane can also be used.
OLEDs can be printed onto any suitable substrate by an inkjet printer or even by screen printing,plasma displays. However, fabrication of the OLED substrate as of 2018 is costlier than that for TFT LCDs.registration — lining up the different printed layers to the required degree of accuracy.
OLEDs enable a greater contrast ratio and wider viewing angle compared to LCDs, because OLED pixels emit light directly. This also provides a deeper black level, since a black OLED display emits no light. Furthermore, OLED pixel colors appear correct and unshifted, even as the viewing angle approaches 90° from the normal.
LCDs filter the light emitted from a backlight, allowing a small fraction of light through. Thus, they cannot show true black. However, an inactive OLED element does not produce light or consume power, allowing true blacks.nm. The refractive value and the matching of the optical IMLs property, including the device structure parameters, also enhance the emission intensity at these thicknesses.
OLEDs also have a much faster response time than an LCD. Using response time compensation technologies, the fastest modern LCDs can reach response times as low as 1ms for their fastest color transition, and are capable of refresh frequencies as high as 240Hz. According to LG, OLED response times are up to 1,000 times faster than LCD,μs (0.01ms), which could theoretically accommodate refresh frequencies approaching 100kHz (100,000Hz). Due to their extremely fast response time, OLED displays can also be easily designed to be strobed, creating an effect similar to CRT flicker in order to avoid the sample-and-hold behavior seen on both LCDs and some OLED displays, which creates the perception of motion blur.
The biggest technical problem for OLEDs is the limited lifetime of the organic materials. One 2008 technical report on an OLED TV panel found that after 1,000hours, the blue luminance degraded by 12%, the red by 7% and the green by 8%.hours to half original brightness (five years at eight hours per day) when used for flat-panel displays. This is lower than the typical lifetime of LCD, LED or PDP technology; each rated for about 25,000–40,000hours to half brightness, depending on manufacturer and model. One major challenge for OLED displays is the formation of dark spots due to the ingress of oxygen and moisture, which degrades the organic material over time whether or not the display is powered.
However, some manufacturers" displays aim to increase the lifespan of OLED displays, pushing their expected life past that of LCD displays by improving light outcoupling, thus achieving the same brightness at a lower drive current.cd/m2 of luminance for over 198,000hours for green OLEDs and 62,000hours for blue OLEDs.hours for red, 1,450,000hours for yellow and 400,000hours for green at an initial luminance of 1,000cd/m2.
Degradation occurs three orders of magnitude faster when exposed to moisture than when exposed to oxygen. Encapsulation can be performed by applying an epoxy adhesive with dessicant,Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD). The encapsulation process is carried out under a nitrogen environment, using UV-curable LOCA glue and the electroluminescent and electrode material deposition processes are carried out under a high vacuum. The encapsulation and material deposition processes are carried out by a single machine, after the Thin-film transistors have been applied. The transistors are applied in a process that is the same for LCDs. The electroluminescent materials can also be applied using inkjet printing.
Improvements to the efficiency and lifetime of blue OLEDs is vital to the success of OLEDs as replacements for LCD technology. Considerable research has been invested in developing blue OLEDs with high external quantum efficiency, as well as a deeper blue color.
As an emissive display technology, OLEDs rely completely upon converting electricity to light, unlike most LCDs which are to some extent reflective. E-paper leads the way in efficiency with ~ 33% ambient light reflectivity, enabling the display to be used without any internal light source. The metallic cathode in an OLED acts as a mirror, with reflectance approaching 80%, leading to poor readability in bright ambient light such as outdoors. However, with the proper application of a circular polarizer and antireflective coatings, the diffuse reflectance can be reduced to less than 0.1%. With 10,000 fc incident illumination (typical test condition for simulating outdoor illumination), that yields an approximate photopic contrast of 5:1. Advances in OLED technologies, however, enable OLEDs to become actually better than LCDs in bright sunlight. The AMOLED display in the Galaxy S5, for example, was found to outperform all LCD displays on the market in terms of power usage, brightness and reflectance.
While an OLED will consume around 40% of the power of an LCD displaying an image that is primarily black, for the majority of images it will consume 60–80% of the power of an LCD. However, an OLED can use more than 300% power to display an image with a white background, such as a document or web site.
Nokia introduced OLED mobile phones including the N85 and the N86 8MP, both of which feature an AMOLED display. OLEDs have also been used in most Motorola and Samsung color cell phones, as well as some HTC, LG and Sony Ericsson models.ZEN V, the iriver clix, the Zune HD and the Sony Walkman X Series.
The Google and HTC Nexus One smartphone includes an AMOLED screen, as does HTC"s own Desire and Legend phones. However, due to supply shortages of the Samsung-produced displays, certain HTC models will use Sony"s SLCD displays in the future,Nexus S smartphone will use "Super Clear LCD" instead in some countries.
DuPont stated in a press release in May 2010, that they can produce a 50-inch OLED TV in two minutes with a new printing technology. If this can be scaled up in terms of manufacturing, then the total cost of OLED TVs would be greatly reduced. DuPont also states that OLED TVs made with this less expensive technology can last up to 15 years if left on for a normal eight-hour day.
The number of automakers using OLEDs is still rare and limited to the high-end of the market. For example, the 2010 Lexus RX features an OLED display instead of a thin film transistor (TFT-LCD) display.
By 2004, Samsung Display, a subsidiary of South Korea"s largest conglomerate and a former Samsung-NEC joint venture, was the world"s largest OLED manufacturer, producing 40% of the OLED displays made in the world,AMOLED market.million out of the total $475million revenues in the global OLED market in 2006.
Samsung"s 2010 AMOLED smartphones used their Super AMOLED trademark, with the Samsung Wave S8500 and Samsung i9000 Galaxy S being launched in June 2010. In January 2011, Samsung announced their Super AMOLED Plus displays, which offer several advances over the older Super AMOLED displays: real stripe matrix (50% more sub pixels), thinner form factor, brighter image and an 18% reduction in energy consumption.
At the 2007, Las Vegas Consumer Electronics Show (CES), Sony showcased a 11-inch (28 cm), (resolution 960×540) and 27-inch (69 cm), full HD resolution at 1920 × 1080 OLED TV models.contrast ratios and total thicknesses (including bezels) of 5mm. In April 2007, Sony announced it would manufacture 1000 11-inch (28 cm) OLED TVs per month for market testing purposes.XEL-1, was the first commercial OLED TV
In October 2008, Sony published results of research it carried out with the Max Planck Institute over the possibility of mass-market bending displays, which could replace rigid LCDs and plasma screens. Eventually, bendable, see-through displays could be stacked to produce 3D images with much greater contrast ratios and viewing angles than existing products.
A third model of Nintendo"s Switch, a hybrid gaming system, features an OLED panel in place of the original model"s LCD panel. Announced in the summer of 2021, it was released on 8 October 2021.
Ishibashi, Tadashi; Yamada, Jiro; Hirano, Takashi; Iwase, Yuichi; Sato, Yukio; Nakagawa, Ryo; Sekiya, Mitsunobu; Sasaoka, Tatsuya; Urabe, Tetsuo (25 May 2006). "Active Matrix Organic light Emitting Diode Display Based on "Super Top Emission" Technology". Japanese Journal of Applied Physics. 45 (5B): 4392–4395. Bibcode:2006JaJAP..45.4392I. doi:10.1143/JJAP.45.4392. ISSN 0021-4922. S2CID 121307571.
Tsujimura, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Murayama, K.; Tanaka, A.; Morooka, M.; Fukumoto, E.; Fujimoto, H.; Sekine, J.; Kanoh, K.; Takeda, K.; Miwa, K.; Asano, M.; Ikeda, N.; Kohara, S.; Ono, S.; Chung, C. T.; Chen, R. M.; Chung, J. W.; Huang, C. W.; Guo, H. R.; Yang, C. C.; Hsu, C. C.; Huang, H. J.; Riess, W.; Riel, H.; Karg, S.; Beierlein, T.; Gundlach, D.; Alvarado, S.; et al. (2003). "4.1: A 20-inch OLED Display Driven by Super-Amorphous-Silicon Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. 34: 6. doi:10.1889/1.1832193. S2CID 135831267.
"Comparison of OLED and LCD". Fraunhofer IAP: OLED Research. 18 November 2008. Archived from the original on 4 February 2010. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
"World"s Largest 21-inch OLED for TVs from Samsung". Physorg.com. 4 January 2005. Archived from the original on 12 January 2009. Retrieved 17 August 2009.

Estamos en un momento en el que damos mucha más importancia a la pantalla de los teléfonos inteligentes que a cualquier otra especificación. Además, el tamaño de la pantalla parece haber quedado relegado, ya que los usuarios están más interesados en la calidad real que proporciona la pantalla que en sus pulgadas.
Pasamos muchas horas delante de ellas: no nos vale cualquier cosa. Así pues, veamos por medio de un breve repaso los distintos tipos de pantalla que podemos encontrar en el mercado. Con sus pros y contras.
Vamos con un puñado de siglas: AMOLED es el acrónimo de Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Las pantallas AMOLED usan materiales orgánicos que emiten luz cuando se aplica electricidad.
Los AMOLED permiten mostrar imágenes brillantes, delgadas, flexibles y eficientes. Las pantallas AMOLED están siempre apagadas a menos que los píxeles individuales estén eléctricamente excitados. Esto significa que las pantallas AMOLED tienen negros mucho más puros y consumen menos energía cuando se muestran colores negros o más oscuros en la pantalla. Además, dado que son muy flexibles, pueden doblarse.
Las pantallas AMOLED son relativamente caras de producir y están muy saturadas. Sin embargo, las pantallas AMOLED son vibrantes y son mejores para la reproducción del color.
LCD significa pantalla de cristal líquido. Las pantallas LCD están formadas por una serie de cristales líquidos que se iluminan con una luz de fondo. Requieren menos energía y, por lo tanto, son muy populares en dispositivos portátiles como teléfonos móviles. Las pantallas LCD también tienden a funcionar bastante bien a la luz solar directa, ya que la iluminación del panel viene por detrás. Son ideales para muchos tipos de teléfonos inteligentes.
TFT significa "Transductor de película delgada", una versión avanzada de LCD que usa una matriz activa. La matriz activa significa que cada píxel está conectado a un transistor y condensador individualmente. La ventaja de tener pantallas TFT es que tienen una alta relación de contraste y un bajo costo de producción, lo que reduce el precio de su dispositivo. Sin embargo, no tienen buenos ángulos de visión e impresionante reproducción del color.
IPS significa In-Plane Switching (cambio en el plano) y es una mejora adicional en TFT LCD. De hecho, es un tipo específico de panel LCD que se creó para mejorar el TFT-LCD. La forma en que los cristales se excitan eléctricamente sobre ellos es diferente y la orientación de la matriz de cristal se rota. Este cambio de orientación mejora los ángulos de visión, la relación de contraste y la reproducción del color. El consumo de energía también se reduce en comparación con las pantallas LCD TFT. Debido a que los LCD IPS tienden a ser mejores que los LCD TFT, también son más caros cuando se los coloca en un teléfono inteligente.
La introducción de IPS redujo en gran medida muchas deficiencias de TFT-LCD. La reproducción del color mejoró mucho, el ángulo de visión aumentó y el tiempo de respuesta de la pantalla mejoró drásticamente.
IPS se ha convertido en una mejor opción para los jugadores debido a su tiempo de respuesta mínimo. Esto, a su vez, nos brinda una mejor respuesta táctil, mucho mejor que AMOLED y pantallas TFT-LCD normales.
Los paneles son más delgados: permite dispositivos más delgados. Para un grosor idéntico al de AMOLED, los fabricantes de dispositivos IPS deben esforzarse más y sacrificarse.
Baja vida útil: los paneles OLED y AMOLED se degradan más rápido que el IPS LCD. La mayoría de las estimaciones indican 14,000 horas como tiempo de vida del panel. IPS fácilmente tiene una vida útil de hasta 60,000 horas. En el caso de los teléfonos inteligentes no es un problema importante. 14,000 horas es equivalente a 8 horas diarias durante 5 años. Pero en general, el color azul es el primero que comienza a degradarse en AMOLED. Los recientes avances en AMOLED han logrado una vida útil de 62,000 horas para el azul y 198,000 para el verde.
Color blanco intenso: un alto brillo, en comparación con AMOLED. La diferencia de intensidad es claramente visible, dejando al oponente más cerca de gris o blanco.
Una pantalla IPS, también conocida como panel de conmutación en el plano, es un tipo de tecnología de visualización de alta calidad que generalmente se implementan en monitores, tabletas y teléfonos inteligentes de computadora y portátiles de alto rendimiento.
IPS ofrece una mejor experiencia de usuario debido a su ángulo más amplio y calidad de color mejorada, características de visualización que han evolucionado bastante con el tiempo desde que se introdujeron las pantallas LCD con efecto TN y se utilizaron de forma ubicua en la década de 1990.
Las tabletas y teléfonos inteligentes de alto rendimiento tienen esta tecnología de pantallas IPS porque estos productos nacieron para estas funciones: ver pelis, chatear por video, y almacenar y editar fotos. Las características mejoradas de la tecnología de ángulo y color proporcionan una mejor experiencia general para el usuario.
Tecnología como la Super IPS+ del nuevo Zenfone 4 rinden perfectamente bajo luz directa gracias a su límite lumínico de 600 nits, a que sumar la tecnología Splendid —que es capaz de ajustar la temperatura del color según las condiciones de la luz ambiente—
Y los profesionales creativos también se benefician de un monitor IPS: una pantalla IPS+ proporciona una gama de colores más amplia y mayores ángulos de visión, con los que obtener una mayor precisión estética y resultados más coherentes. Dicho de otro modo: lo que ven es una traducción sin artificios.

When it comes to choosing what to use for your displays, going with the standard can get you farther ahead than thinking outside the box. TFT LCD display gives you an edge for your advertising needs, television screens, or even phone screens.
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is one of the technologies commonly used for building LCDs. With this technology, your LCD is guaranteed a sharp, clear, and full-color display and high-quality performance.
When a signal sent to a pixel also affects the pixels next to it, crosstalk This runs the risk of distorting the quality of your image. With TFT, crosstalk is significantly reduced with the TFT layer integrated into the screen itself. With every pixel corresponding to the signals meant only for them, you are guaranteed the best resolution and image quality.
In the LCD industry, the most popular kinds of displays are manufactured and innovated the most. Unlike other types of LCD technologies, the TFT module is available in different sizes, ranging from cellphone sizes to larger TV sizes, to suit your needs.
All LCD displays have a determined number of hours of use before they become half as bright than when they were turned on for the first time. This is called half-life. Although research is still ongoing regarding half-life, TFT displays are said to have more than 14,000 hours of half-life.
This does not mean, however, that the LCD will burn out after reaching its half-life. It means that its brightness will only be half of when it was new.
Compared to CRTs, TFT LCD modules have lower heat release. Moreover, they emit lower electromagnetic emissions which significantly decrease visual fatigue. This means that TFTs are ideal for devices and displays that require an audience’s prolonged attention, such as cell phones and television screens.
While the TFT’s power consumption is significantly lower than OLEDs in white displays, there are also emerging TFT displays in the market that integrate smart technologies that can save up to 50% energy on battery-operated devices.
One of the notable disadvantages of TFTs, however, is its cost. The characteristics detailed in the previous section, however, must be considered worthy of investment. Moreover, as the number of TFTs floods the LCD display market, the price for TFTs are decreasing by the day.
At Microtips Technology USA, we only provide you with the best among the best of TFT modules. Our TFT LCD displays assure only full RGB brilliance with up to 16.7 million colors, better picture quality with high resolutions and IPS technology, and affordability.

Have you ever wonder where TFT derive from? Why is TFT referred to as LCD? The phenomenon started in early days, when bulky CRT displays were thing of the past and LCD was its replacement, but as time progresses, there were still room for improvement, which leads to the birth of TFT’s.
TFT is a variant of an LCD which uses thin film transistor technology to improve an image quality, while an LCD is class of displays that uses modulating properties of liquid crystals to form what we call an LCD (liquid crystals display) which in fact does not emits light directly.
Even though LCDs were very energy efficient, light weight and thin in nature, LCD were falling behind to the CRT display, which then leads to a change in LCD manufacturing, where performance became a big problem.
For example, having a 2001 Mustang vs a 2014 Mustang, the dimensions and engine of the 2014 has been redesign for performance reasons, not mentioning user friendly, so does the LCD to TFT.
As the birth of TFT, the elements are deposited directly on the glass substrate which in fact the main reason for the switch was because TFTs are easier to produce, better performance in terms of adjusting the pixels within the display to get better quality.
LCDs became ineffective over a period of time, almost all aspect of watching a TV, playing video games or using a handheld device to surf the net became daunting, this phenomenon is known as high response time with low motion rate.
Another problem with LCD was crosstalking, in terms of pixelating, this happens when signals of adjacent pixels affects operations or gives an undesired effect to the other pixel.
As TFT’s become very popular throughout the century due to its elaborate low charge associate and outstanding response time, LCDs became a thing of the past, and TFT became the predominant technology with their wider viewing angles and better quality this technology will be around for a long time.

It"s an organic light-emitting display. OLED display technology is different from the traditional LCD display mode, without backlight. It uses a very thin coating of organic materials and a glass substrate, which emit light when an electric current passes through. Moreover, OLED screen module can be made lighter and thinner, with larger viewing angle, and can significantly save power.
AMOLED is panel-self luminous. The TFT is illuminated on the LCD panel by backlight. AMOLED effect is more colorful and brighter. The screen can be seen clearly outside during the day. The most important is that the power consumption of AMOLED is much lower. AMOLED screen is more expensive than TFT LCD touch screen. The life of AMOLED screens is also longer.
AMOLED, after all, is a new technology, which has a bright future. TFT LCD touch screen can be thinned, and LTPS technology is still relatively stable. AMOLED module has low qualified rate and long lead time. So if the size and resolution are the same, buy the cheapest one.
Kingtech LCD is one of the leading TFT LCD OEM / ODM LCD display manufacturers in China. Customizing industrial equipment, medical, POS, logistics equipment, smart home applications and other projects is allowed.
In recent years, smartphone displays have developed far more acronyms than ever before with each different one featuring a different kind of technology. AMOLED, LCD, LED, IPS, TFT, PLS, LTPS, LTPO...the list continues to grow.
As if the different available technologies weren"t enough, component and smartphone manufacturers adopt more and more glorified names like "Super Retina XDR" and "Dynamic AMOLED", which end up increasing the potential for confusion among consumers. So let"s take a look at some of these terms used in smartphone specification sheets and decipher them.
There are many display types used in smartphones: LCD, OLED, AMOLED, Super AMOLED, TFT, IPS and a few others that are less frequently found on smartphones nowadays, like TFT-LCD. One of the most frequently found on mid-to-high range phones now is IPS-LCD. But what do these all mean?
LCD means Liquid Crystal Display, and its name refers to the array of liquid crystals illuminated by a backlight, and their ubiquity and relatively low cost make them a popular choice for smartphones and many other devices.
LCDs also tend to perform quite well in direct sunlight, as the entire display is illuminated from behind, but does suffer from potentially less accurate colour representation than displays that don"t require a backlight.
Within smartphones, you have both TFT and IPS displays. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, an advanced version of LCD that uses an active matrix (like the AM in AMOLED). Active matrix means that each pixel is attached to a transistor and capacitor individually.
The main advantage of TFT is its relatively low production cost and increased contrast when compared to traditional LCDs. The disadvantage of TFT LCDs is higher energy demands than some other LCDs, less impressive viewing angles and colour reproduction. It"s for these reasons, and falling costs of alternative options, that TFTs are not commonly used in smartphones anymore.Affiliate offer
IPS technology (In-Plane Switching) solves the problem that the first generation of LCD displays experience, which adopts the TN (Twisted Nematic) technique: where colour distortion occurs when you view the display from the side - an effect that continues to crop up on cheaper smartphones and tablets.
The PLS (Plane to Line Switching) standard uses an acronym that is very similar to that of IPS, and is it any wonder that its basic operation is also similar in nature? The technology, developed by Samsung Display, has the same characteristics as IPS displays - good colour reproduction and viewing angles, but a lower contrast level compared to OLED and LCD/VA displays.
According to Samsung Display, PLS panels have a lower production cost, higher brightness rates, and even superior viewing angles when compared to their rival, LG Display"s IPS panels. Ultimately, whether a PLS or IPS panel is used, it boils down to the choice of the component supplier.
This is a very common question after "LED" TVs were launched, with the short answer simply being LCD. The technology used in a LED display is liquid crystal, the difference being LEDs generating the backlight.
One of the highlights from TV makers at the CES 2021 tradeshow, mini-LED technology seemed far removed from mobile devices until Apple announced the 2021 iPad Pro. As the name implies, the technique is based on the miniaturization of the LEDs that form the backlight of the screen — which still uses an LCD panel.
Despite the improvement in terms of contrast (and potentially brightness) over traditional LCD/LED displays, LCD/mini-LEDs still divide the screen into brightness zones — over 2,500 in the case of the iPad and 2021 "QNED" TVs from LG — compared to dozens or hundreds of zones in previous-generation FALD (full-array local dimming) displays, on which the LEDs are behind the LCD panel instead of the edges.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. While this may sound complicated it actually isn"t. We already encountered the active matrix in TFT LCD technology, and OLED is simply a term for another thin-film display technology.
OLED is an organic material that, as the name implies, emits light when a current is passed through it. As opposed to LCD panels, which are back-lit, OLED displays are "always off" unless the individual pixels are electrified.
This means that OLED displays have much purer blacks and consume less energy when black or darker colours are displayed on-screen. However, lighter-coloured themes on AMOLED screens use considerably more power than an LCD using the same theme. OLED screens are also more expensive to produce than LCDs.
Because the black pixels are "off" in an OLED display, the contrast ratios are also higher compared to LCD screens. AMOLED displays have a very fast refresh rate too, but on the downside are not quite as visible in direct sunlight as backlit LCDs. Screen burn-in and diode degradation (because they are organic) are other factors to consider.Affiliate offer
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. An OLED display is comprised of thin sheets of electroluminescent material, the main benefit of which is they produce their own light, and so don"t require a backlight, cutting down on energy requirements. OLED displays are more commonly referred to as AMOLED displays when used on smartphones or TVs.
As we"ve already covered, the AM part of AMOLED stands for Active Matrix, which is different from a Passive Matrix OLED (P-OLED), though these are less common in smartphones.
Super AMOLED is the name given by Samsung to its displays that used to only be found in high-end models but have now trickled down to more modestly specced devices. Like IPS LCDs, Super AMOLED improves upon the basic AMOLED premise by integrating the touch response layer into the display itself, rather than as an extra layer on top.
As a result, Super AMOLED displays handle sunlight better than AMOLED displays and also require less power. As the name implies, Super AMOLED is simply a better version of AMOLED. It"s not all just marketing bluster either: Samsung"s displays are regularly reviewed as some of the best around.
The latest evolution of the technology has been christened "Dynamic AMOLED". Samsung didn"t go into detail about what the term means, but highlighted that panels with such identification include HDR10+ certification that supports a wider range of contrast and colours, as well as blue light reduction for improved visual comfort.
In the same vein, the term "Fluid AMOLED" used by OnePlus on its most advanced devices basically highlights the high refresh rates employed, which results in more fluid animations on the screen.Affiliate offer
Resolution describes the number of individual pixels (or points) displayed on the screen and is usually presented for phones by the number of horizontal pixels — vertical when referring to TVs and monitors. More pixels on the same display allow for more detailed images and clearer text.
Speaking of pixel density, this was one of Apple"s highlights back in 2010 during the launch of the iPhone 4. The company christened the LCD screen (LED, TFT, and IPS) used in the smartphone as "Retina Display", thanks to the high resolution of the panel used (960 by 640 pixels back then) in its 3.5-inch display.
With the iPhone 11 Pro, another term was introduced to the equation: "Super Retina XDR". Still using an OLED panel (that is supplied by Samsung Display or LG Display), the smartphone brings even higher specs in terms of contrast - with a 2,000,000:1 ratio and brightness level of 1,200 nits, which have been specially optimized for displaying content in HDR format.
As a kind of consolation prize for iPhone XR and iPhone 11 buyers, who continued relying on LCD panels, Apple classified the display used in the smartphones with a new term, "Liquid Retina". This was later applied also to the iPad Pro and iPad Air models, with the name defining screens that boast a high range and colour accuracy, at least based on the company"s standards.
TFT(Thin Film Transistor) - a type of LCD display that adopts a thin semiconductor layer deposited on the panel, which allows for active control of the colour intensity in each pixel, featuring a similar concept as that of active-matrix (AM) used in AMOLED displays. It is used in TN, IPS/PLS, VA/PVA/MVA panels, etc.
LTPS(Low Temperature PolySilicon) - a variation of the TFT that offers higher resolutions and lower power consumption compared to traditional TFT screens, based on a-Si (amorphous silicon) technology.
IGZO(Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide) - a semiconductor material used in TFT films, which also allows higher resolutions and lower power consumption, and sees action in different types of LCD screens (TN, IPS, VA) and OLED displays
LTPO(Low Temperature Polycrystaline Oxide) - a technology developed by Apple that can be used in both OLED and LCD displays, as it combines LTPS and IGZO techniques. The result? Lower power consumption. It has been used in the Apple Watch 4 and the Galaxy S21 Ultra.
Among televisions, the long-standing featured technology has always been miniLED - which consists of increasing the number of lighting zones in the backlight while still using an LCD panel. There are whispers going around that smartphones and smartwatches will be looking at incorporating microLED technology in their devices soon, with it being radically different from LCD/LED displays as it sports similar image characteristics to that of OLEDs.
As previously stated, OLED/AMOLED screens have the advantage of a varied contrast level, resulting from individual brightness control for the pixels. Another result of this is the more realistic reproduction of black, as well as low power consumption when the screen shows off dark images - which has also helped to popularize dark modes on smartphones.
In the case of LCD displays, the main advantage lies in the low manufacturing cost, with dozens of players in the market offering competitive pricing and a high production volume. Some brands have taken advantage of this feature to prioritize certain features - such as a higher refresh rate - instead of adopting an OLED panel, such as the Xiaomi Mi 10T.

Key Difference: AMOLED is a type of screen used in consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Gorilla Glass is a type of protection that is used on the screen.
There are many different types of screens available, such as TFT LCD, IPS-LCD, Resistive Touchscreen LCD, OLED, AMOLED, Super AMOLED, etc. Each of these types has something that helps them stand apart from the others.
AMOLED stands for Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode or "Active Matrix OLED" for short. It is a hybrid display technology that combines the active matrix backplane from a traditional TFT display with an OLED display. The advantage of this is that it has a faster pixel switching response time than the traditional OLED displays.
Currently, AMOLED is very popular for use in mobile phones, media players and digital cameras. However, it is not currently popular for use in larger applications such as televisions or laptops.
AMOLED screen have been made popular by phone manufactures, such as Samsung, who tout its benefits. Samsung uses what it calls a Super AMOLED display in its popular Samsung Galaxy line of phones. Super AMOLED is essentially an AMOLED display that Samsung has integrated it with a digitizer, which means that the layer that detects touch is integrated into the screen, rather than overlaid on top of it.
As compared to other screens on the market, AMOLED has a faster pixel switching response than traditional OLED displays, consumes less power and has better contrast ratios than LCDs. However, AMOLED displays may be difficult to view in direct sunlight as they have reduced brightness. Also organic materials used in AMOLED displays are very prone to degradation, which may result is fading of one color over the others.
The main difference between Gorilla Glass and AMOLED is the fact that AMOLED is a type of display used in electronics, whereas Gorilla Glass is a type of toughened glass that acts as a screen protection, usually laid on top of the display such as AMOLED.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey