pantalla tft lcd vs super amoled pricelist
Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
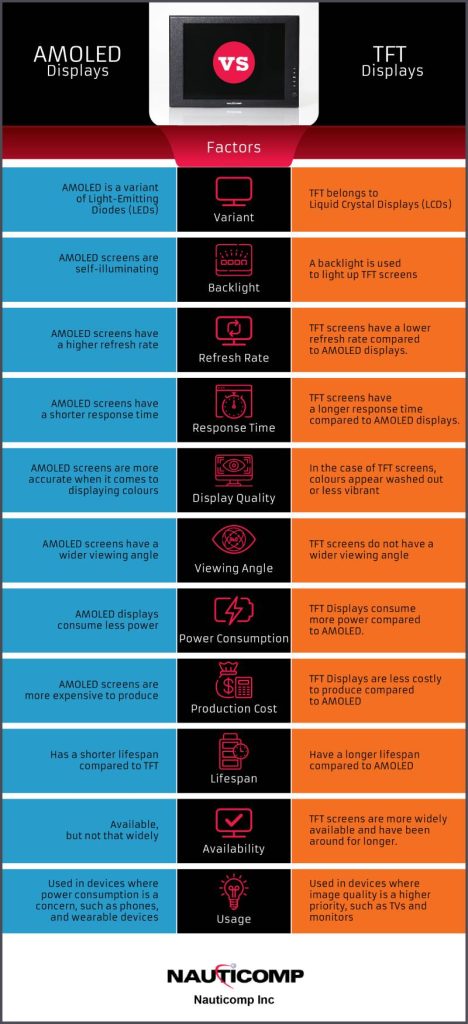
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.

Some of the amoled display available can operate with no noise, bounce, and reaction, and are able to operate without any sensitivity to vibrations and shock. The amoled display come with the core components: coils, an oscillator, an output amplifier, as well as a Schmitt trigger. There are different versions of this sensor available, including unshielded (which allows for wider sensing distances) and shielded (with an electromagnetic field that is concentrated at the front).
Wholesale amoled display, full-feature to economy series, and top brand models. Phones (or cellphones, or mobile phones) are the devices we use every day, for chatting with friends to communicating essential work information, from checking memes to streaming the latest dramas, from gaming to reading novels, our phones are integrated into our lives. Not a day goes by when someone doesn"t need a new amoler display or a new phone component, and we"ve got what you need. Visit our wholesaler catalogue now, and complete your inventory of all the phones available for your market.
Browse cutting-edge amoled display on Alibaba.com at reasonable prices. amoled display in varying display size and resolution are accessible on the site. The merchandise are useful in automotive, medical, and industrial screen displays. amoled display having multiple interface types and display technology are in stock. amoled display on Alibaba.com have high resolution and luminance to display precise details. They have a capacitive touch for convenient use. They can show multiple characters per line. amoled display can be manufactured to suit smaller wearable devices or large projectors. They can be integrated with smart home systems for face recognition and office equipment. They feature multiple interfacing types like MPU or RS232. They are sturdy, thanks to a toughened glass structure with a considerable operating temperature range. The life span of amoled display stretches up to several thousand pages hours get.

AMOLED displays are popular for the pure blacks and energy efficient "glance" displays they enable. Thus they are seen as a premium option for smartphone and laptop users, and AMOLED panels are only seen in really high-end TVs. However, thanks to competition and demand spurring greater production, prices are starting to become more competitive with TFT LCD panels, reports IT industry journal DigiTimes.
According to the source report "The production cost for a 5.5-inch HD AMOLED panel has drifted to US$12.10 recently, compared to US$12.20 for a 5.5-inch HP LTPS LCD panel". This is a big change to the previous state of affairs where AMOLED panels had "much higher,"prices due to the increased production costs. Thanks to the levelling off of prices and demand it"s expected that AMOLED panels will be equipped on up to 50 per cent of smartphones by 2020.
In other recent AMOLED smartphone news, the Nikkei Asian Review asserts that Apple will "use OLED screens in all new iPhones launching in 2018". Industry sources say Apple is considering launching three smartphones in 2018 and all will come equipped with this type of display.
Later this year Apple will launch its first OLED iPhone - but only the premium version will get this type of display, in a design that eschews its iconic Home button. Two other iPhone models released this year will use TFT LCDs.
Back to the AMOLED panel pricing news, and there is hope that larger displays, not just those aimed at smartphones and tablets, will come down in price. LG Display"s E4-2 fab, its second production line for AMOLED displays for TVs, will enter volume production in H2 2017, says DigiTimes. Thanks to the new production line AMOLED TV display production is set to more than double to 1.5 million units, say sources. Furthermore, several Chinese panel makers have been investing in AMOLED production facilities with output set to increase fivefold (comparing 2016 output to that estimated to come on line in 2018).

LCD is an acronym that stands for Liquid Crystal Display and it is one of the most commonly used display by OEMs on their devices. LCD displays are further categorised into two types on the basis of the technology used to make them. The two types are IPS LCD and TFT LCDs.
TFT stands Thin-film Transistor and de facto, it really isn’t a type of display. TFT is only the technology used to produce LCD display panels. TFT LCD displays use an ‘Active Matrix Technology” where the display transistor and capacitor have individual pixels attached to them. In fact, each pixel can have as many as four transistors; for switching them off and on easily. TFT displays are widely known for having high contrast ratios, resolution and image quality. They are also cheaper to produce but not as cheap as IPS LCD.
IPS stands for In-Plane Switching and it is the most popularly used type of LCD panels for a number of reasons. First, compared to TFT, the crystal/pixel orientation on IPS LCD is different. This modification allows for improved colour reproduction, better viewing angles, and reduced energy consumption. This is why IPS LCD is preferred over TFT by most gadgets manufacturers.
Generally, LCDs are known as the “backlit displays” because the pixels on the display are powered by a polarized light engineered to the screen. The light passes through the (horizontal and vertical) filters which help determine the pixel’s brightness. Although the inclusion of a backlight makes LCD displays (and phones) thicker, pixels are generally more closely packed, colours are more natural, and images — sharper.
OLED stands for “Organic light-emitting diode”. OLED is one of the latest display innovation used in many gadgets and electronics like smartphones and TVs. Unlike LCD displays, OLED panels produce their own light and do not rely on a backlight. This self-emission is achieved when an electrical current passes through two conductors with an organic carbon-based film between them.
Regarding quality, OLED are generally better at displaying blacks. They are also slimmer, dissipate less heat, and possess better contrast ratio when compared to LCDs. However, they are more expensive to produce and in turn lead to an increase in the price of smartphones they are used on. Shorter lifespan is also a downside to OLED displays.
AMOLED is an advanced type of OLED display that uses an “Active Matrix” technology. AMOLED is the acronym for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED). Like OLED, AMOLED pixels also emit their own light and further uses an active matrix system attached to a thin-film transistor (TFT) to exert more control over each pixels. This results to better visual experience; darker blacks, deeper brights, and higher refresh rates.
AMOLED panels are mostly used in big-sized smartphones as it supports almost any display size. One downside to AMOLED panels, though, is poor usability under sunlight.
Also called S-AMOLED, Super AMOLED is an upgrade of AMOLED panels. Unlike regular AMOLED, this upgrade uses almost the same technology but with architectural modifications that makes it better. In S-AMOLED, the touch sensor component have been integrated with the screen; both are separated in regular AMOLED.
This difference results in brighter display, reduced power consumption, reduced sunlight reflection, enhanced outdoor readability, and wider viewing angles. Super AMOLED is one the best displays out there and can be found on many flagship devices like the Samsung Galaxy A7 (2018) with three rear cameras, Samsung Galaxy Note9.
You can easily identify your smartphone’s screen type through a simple Google search of your phone specifications. You should see your device’s screen type under the display department. The image below shows the screen type (IPS LCD) of the Coolpad Note 5.
Estamos en un momento en el que damos mucha más importancia a la pantalla de los teléfonos inteligentes que a cualquier otra especificación. Además, el tamaño de la pantalla parece haber quedado relegado, ya que los usuarios están más interesados en la calidad real que proporciona la pantalla que en sus pulgadas.
Pasamos muchas horas delante de ellas: no nos vale cualquier cosa. Así pues, veamos por medio de un breve repaso los distintos tipos de pantalla que podemos encontrar en el mercado. Con sus pros y contras.
Vamos con un puñado de siglas: AMOLED es el acrónimo de Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Las pantallas AMOLED usan materiales orgánicos que emiten luz cuando se aplica electricidad.
Los AMOLED permiten mostrar imágenes brillantes, delgadas, flexibles y eficientes. Las pantallas AMOLED están siempre apagadas a menos que los píxeles individuales estén eléctricamente excitados. Esto significa que las pantallas AMOLED tienen negros mucho más puros y consumen menos energía cuando se muestran colores negros o más oscuros en la pantalla. Además, dado que son muy flexibles, pueden doblarse.
Las pantallas AMOLED son relativamente caras de producir y están muy saturadas. Sin embargo, las pantallas AMOLED son vibrantes y son mejores para la reproducción del color.
LCD significa pantalla de cristal líquido. Las pantallas LCD están formadas por una serie de cristales líquidos que se iluminan con una luz de fondo. Requieren menos energía y, por lo tanto, son muy populares en dispositivos portátiles como teléfonos móviles. Las pantallas LCD también tienden a funcionar bastante bien a la luz solar directa, ya que la iluminación del panel viene por detrás. Son ideales para muchos tipos de teléfonos inteligentes.
TFT significa "Transductor de película delgada", una versión avanzada de LCD que usa una matriz activa. La matriz activa significa que cada píxel está conectado a un transistor y condensador individualmente. La ventaja de tener pantallas TFT es que tienen una alta relación de contraste y un bajo costo de producción, lo que reduce el precio de su dispositivo. Sin embargo, no tienen buenos ángulos de visión e impresionante reproducción del color.
IPS significa In-Plane Switching (cambio en el plano) y es una mejora adicional en TFT LCD. De hecho, es un tipo específico de panel LCD que se creó para mejorar el TFT-LCD. La forma en que los cristales se excitan eléctricamente sobre ellos es diferente y la orientación de la matriz de cristal se rota. Este cambio de orientación mejora los ángulos de visión, la relación de contraste y la reproducción del color. El consumo de energía también se reduce en comparación con las pantallas LCD TFT. Debido a que los LCD IPS tienden a ser mejores que los LCD TFT, también son más caros cuando se los coloca en un teléfono inteligente.
La introducción de IPS redujo en gran medida muchas deficiencias de TFT-LCD. La reproducción del color mejoró mucho, el ángulo de visión aumentó y el tiempo de respuesta de la pantalla mejoró drásticamente.
IPS se ha convertido en una mejor opción para los jugadores debido a su tiempo de respuesta mínimo. Esto, a su vez, nos brinda una mejor respuesta táctil, mucho mejor que AMOLED y pantallas TFT-LCD normales.
Los paneles son más delgados: permite dispositivos más delgados. Para un grosor idéntico al de AMOLED, los fabricantes de dispositivos IPS deben esforzarse más y sacrificarse.
Baja vida útil: los paneles OLED y AMOLED se degradan más rápido que el IPS LCD. La mayoría de las estimaciones indican 14,000 horas como tiempo de vida del panel. IPS fácilmente tiene una vida útil de hasta 60,000 horas. En el caso de los teléfonos inteligentes no es un problema importante. 14,000 horas es equivalente a 8 horas diarias durante 5 años. Pero en general, el color azul es el primero que comienza a degradarse en AMOLED. Los recientes avances en AMOLED han logrado una vida útil de 62,000 horas para el azul y 198,000 para el verde.
Color blanco intenso: un alto brillo, en comparación con AMOLED. La diferencia de intensidad es claramente visible, dejando al oponente más cerca de gris o blanco.
Una pantalla IPS, también conocida como panel de conmutación en el plano, es un tipo de tecnología de visualización de alta calidad que generalmente se implementan en monitores, tabletas y teléfonos inteligentes de computadora y portátiles de alto rendimiento.
IPS ofrece una mejor experiencia de usuario debido a su ángulo más amplio y calidad de color mejorada, características de visualización que han evolucionado bastante con el tiempo desde que se introdujeron las pantallas LCD con efecto TN y se utilizaron de forma ubicua en la década de 1990.
Las tabletas y teléfonos inteligentes de alto rendimiento tienen esta tecnología de pantallas IPS porque estos productos nacieron para estas funciones: ver pelis, chatear por video, y almacenar y editar fotos. Las características mejoradas de la tecnología de ángulo y color proporcionan una mejor experiencia general para el usuario.
Tecnología como la Super IPS+ del nuevo Zenfone 4 rinden perfectamente bajo luz directa gracias a su límite lumínico de 600 nits, a que sumar la tecnología Splendid —que es capaz de ajustar la temperatura del color según las condiciones de la luz ambiente—
Y los profesionales creativos también se benefician de un monitor IPS: una pantalla IPS+ proporciona una gama de colores más amplia y mayores ángulos de visión, con los que obtener una mayor precisión estética y resultados más coherentes. Dicho de otro modo: lo que ven es una traducción sin artificios.

Apple has used the Super AMOLED screen developed by Samsung since the iPhone X. If the original OLED is replaced after the warranty period of the mobile phone screen, the iPhone X and iPhone XS will cost $549. The high cost of replacing screens is not something that every consumer is willing to accept. Soft OLED and hard OLED replacement screens have gradually become hot selling products in mobile phone repair shops. Recently, the appearance of in cell LCD adapted to the iPhone X has broken this calm. It uses lower-cost LCD instead of OLED screens and enters the iPhone X repair industry with an absolute price advantage. What are the advantages and disadvantages of in cell LCD and OLED screen?
Take iFixit, a more authoritative website in the smartphone repair industry, and launched an in-cell LCD screen suitable for iPhone X / iPhone XS / iPhone XS Max. The prices are $75, $85, and $165.Its price is only half of OLED. The
In-cell LCD screen is darker than OLED, and the screen display color gamut and resolution are lower. When the mobile phone is in standby, the OLED screen can display pure black, while the LCD cannot.
The biggest advantage of the OLED screen is that the power consumption is small, the power consumption of the TFT LCD screen is larger than that of the OLED, and the standby time is shortened after the LCD screen is replaced.
In low-light environments, users who use OLED mobile phone screens are prone to eye pain. Because LCD can directly reduce the brightness of the screen, and OLED uses the method of adjusting the brightness and non-light duty cycle to deceive the brain to adjust the brightness. This means that in the dark light environment when the human pupil is naturally enlarged to allow more light to enter, the OLED actually enters the pupil at the highest brightness.
According to the iPhone customer experience feedback information, the LCD screen is more in line with the current user habits on the market. Apple is developing LCD screens for both the iPhone Xr and iPhone 11. Compared with OLED, iPhone in cell TFT LCD has a larger display effect than the original screen, and the price is much cheaper than OLED.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey