lcd screen temperature range price

Liquid crystal displays (LCD) have become an essential component to the industry of display technology. Involved in a variety of contexts beyond the indoors like LCD TVs and home/office automation devices, the LCD has expanded its usage to many environments, such as cars and digital signage, and, thus, many temperature variations as well.
As with any substance that requires a specific molecular characteristic or behavior, LCDs have an operating temperature range in which the device, if within, can continue to function properly and well. In addition to that, there is also an ideal storage temperature range to preserve the device until used.
This operating temperature range affects the electronic portion within the device, seen as falling outside the range can cause LCD technology to overheat in hot temperatures or slow down in the cold. As for the liquid crystal layer, it can deteriorate if put in high heat, rendering it and the display itself defective.
In order for the LCD panel to avoid defects, a standard commercial LCD’s operation range and storage range should be kept in mind. Without adaptive features, a typical LCD TV has an operating range from its cold limit of 0°C (32°F) to its heat limit of 50°C (122°F) (other LCD devices’ ranges may vary a bit from these numbers).
The storage range is a bit wider, from -20°C (-4°F) to 60°C (140°F). Though these ranges are quite reasonable for many indoor and even outdoor areas, there are also quite a few regions where temperatures can drop below 0°C or rise above 32°C, and in these conditions, LCDs must be adapted to ensure functionality.
Heat, can greatly affect the electronics and liquid crystals under an LCD screen. In consideration of heat, both external heat and internally generated heat must be taken into consideration.
Seen as the liquid crystals are manipulated in a device by altering their orientations and alignments, heat can disrupt this by randomizing what is meant to be controlled. If this happens, the LCD electronics cannot command a certain formation of the liquid crystal layer under a pixel, and the LED backlighting will not pass through as expected, which can often lead to dark spots, if not an entirely dark image. This inevitably disrupts the display’s readability.
Depending on the upper limit of the operation temperature range, LCD device can be permanently damaged by extreme heat. With long exposure to extreme heat, besides the destruction of the liquid crystals, battery life can shorten, hardware can crack or even melt, response time may slow to prevent even more heat generation from the device.
The LED backlight and the internal circuitry, typically TFT-based in the common TFT LCDs, are components that can generate heat that damages the device and its display. To address this concern with overheating, many devices use cooling fans paired with vents.
Some devices that are used in extremely high ambient temperatures may even require air conditioning. With air vents to carry the heat out, the device can expel it into the surroundings.
In the opposite direction is extreme cold. What typically occurs in the cold is “ghosting” (the burning of an image in the screen through discoloration) and the gradual slowing and lagging of response times. Like heat-affected LCD modules, the extreme temperature can affect the liquid crystals. This layer is a medium between the liquid and solid state, so it is still susceptible to freezing.
An LCD device can be left in freezing temperatures because it will likely not be permanently damaged like in the heat, but it is important to understand the device’s limits and how to take precautions when storing the device. The standard and most common lower-bound storage range limit is -20°C, below freezing, but if possible, it would be best to keep it above that limit, or else there is still a risk of permanent damage.
If the device is not adapted for the cold, it would be good to keep it bundled up, trapping the heat within layers. However, this is only a temporary solution. Adapted, rugged devices have advantages such as screen enclosure insulation for heat level preservation and, in more extreme cases, heaters to generate extra heat to raise the internal temperature to a level above the minimum.
When selecting the appropriate module, it is necessary to understand the device’s expected primary application. The application will decide factors such as display type, environmental conditions, whether or not power consumption is a factor, and the balance between performance and cost. These factors can have an effect on the operation and storage temperature ranges for the device.
Display types have a lot of variation. Choices like alphanumeric or graphic LCD, human-machine interactive LCD modules and touchscreen panels capabilities, the width of the viewing angle, level of contrast ratios, types of backlighting, and liquid crystal alignment methods are often considered. For example, the twisted nematic LCD provides for the fastest response time at the lowest cost, but cannot offer the highest contrast ratio or widest viewing angle.
Environment-based factors must consider things besides the obvious temperature like UV exposure and humidity/moisture, as they all are necessary in finding the perfect fit extreme temperature LCD module.
Besides the LCD modules, recent new products have opened doors in wide temperature range displays, such as OLED displays. OLED displays offer better displays in regard to contrast, brightness, response times, viewing angles, and even power consumption in comparison to traditional LCD displays.
These benefits, in addition to its ability to achieve a wide temperature range, provide more options for consumers in search of high quality displays for extreme climates.

Modern LCD screens have a great many uses. Not only are they now the system of choice for our home TVs and computers but their use in digital signage has made them a common sight in many shopping malls, airports and other locations with high quantities of people.
Even outdoor locations are no barrier to the use of modern LCD screens with outdoor digital signage a rising medium now seen in many town centers, car parks, front of stores and train station platforms.
All this out of home use means many screens operate in locations test the temperature limits of LCD displays. While waterproof screens and LCD enclosures designed for rugged applications provide the ability of the screen to operate-even in outdoor locations, one consideration often overlooked, is that of temperature.
LCD screens have a limited temperature range. Not only will the electronics inside an TV screen overheat and cause failure if the screen gets too hot, but the liquid crystal itself will begin to deteriorate under hot conditions.
The same is true of environments where temperatures fall below zero, causing a screen to stop functioning. A typical LCD TV has an operating range between 0°C (32°F) and 32°C (90°F).
Of course, many indoor and outdoor locations don’t suffer temperatures outside of this range, but many locations do and placing screens in these areas can prove challenging.
One of the problems with using a screen in hot locations is that the screen itself produces quite a bit of heat. When housed in an outdoor enclosure, the heat has to be continuously removed. While cooling fans combined with an air-vent normally carry out this task on an LCD, the need to prevent moisture from getting to the screen makes the task more complicated.
To get around this problem, specially shaped vents provide an exit for hot air while preventing rainfall and other moisture from getting in. In some locations where ambient temperatures are extremely high, screens need air conditioning to ensure they don’t exceed the maximum operating temperature.
In cold climates the opposite problem occurs. The need to keep heat in often requires insulation of the screen enclosure. Often this can trap enough of the heat generated by the screen itself to keep the internal temperature above minimum, but in some locations, even this isn’t enough. Heaters, controlled by thermostats provide extra heat in these circumstances, which enables the use of LCD displays in extremely cold locations such as ski-resorts and in Arctic regions.

Typically, standard LCD modules provide a temperature range of -20°C to +70°C. To meet the need of customers, EVERVISION has developed a series of wide temperature TFT LCD modules with operating temperatures ranging from -30°C to +80°C, and the maximum for some models can reach 85°C.
EVERVISION developed LCD Heater to integrate with our TFT Display Module so that can show optimal view even in low temperature. For materials, heaters can be used with transparent resins, such as glass and poly-carbonate. Our LCD Transparent Heater is made of glass substrate, so we name it “Glass Heater”. It can not only improve the LCD image sticking issue efficiently, but also have heat and humidity resistance advantage.
As the result, it shows 4.3 inch TFT LCD Module display functionally under normal operating conditions. However, there is an overlapping at low temperature, because of LC"s physical characteristics. From this experiment, we know that overlapping can be solved by turning on Glass Heater.

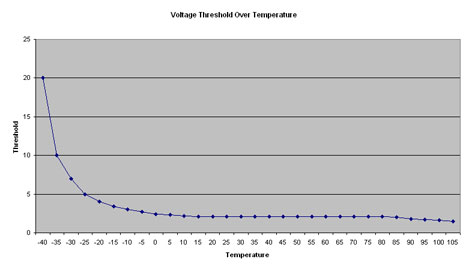
The higher the mux rate, the less time a given group of segments is being addressed , and the worse the display will look. If you refer to our "Basic Operation of an LCD" page, it is easy to see that this is not a good situation.

LCD stands for “liquid crystal display,” but this is a bit of a misnomer. In reality, the technology has no liquid components, so it isn’t susceptible to freezing and expansion in extreme cold. (Remember, many vehicles nowadays have LCD displays on their in-dash radios and CD players, and these have not been known to crack in freezing climates.)
An LED (light-emitting diode) TV is nothing more than an LCD TV that uses LED backlighting. Compared to the LCD’s fluorescent-style backlighting, LEDs are more energy-efficient, but they don’t respond to cold temperatures much differently. One exception is that LED lights may actually shine brighter in cooler temperatures, as long as it is not too cold. But what is too cold?
When it comes to durability in cold temperatures, there is no real difference between LCD and LED TVs. An LCD or LED TV may not perform well under extreme temperature conditions. In the cold, the response time of an HDTV picture may lag. For this reason, many LCD and LED television manuals will specify a safe-operating-temperature range. In most HDTVs, this range is about 50–90°F.
The temperature range for safe storage is typically even wider. Most LCD and LED sets are rated for storage in temps as low as -4°F. Always refer to your television’s manual for actual safe-temperature ranges.
If your cabin gets colder than this in the winter, you may want to consider erring on the side of caution. Cover the set in a soft blanket to protect it from dust and direct sunlight, and then store it in a dry place with above-freezing temperatures for the season, or for however long you plan to be away.
If you decide to leave the TV at the cabin for impromptu winter visits, exercise caution when turning it on in a cold room. Allow time for the cabin to warm up before turning on the TV, otherwise the extreme change in temperature may result in condensation inside the set and subsequent damage to the screen.
So, when you arrive at the cottage and fire up the woodstove, fireplace or heater, wait at least an hour (longer is better) for the screen to reach a temperature within the safe operating range. Sounds like a long time to wait, we know. But just think – you’ll have more time for card games and conversation!
There are several industrial applications that require LCD displays to operate in extreme temperature environments such as in military, food processing, gas/fuel pumps, medical, manufacturing, and non-climate-controlled facilities, among others. Take note that typical monitors can only be used in environments with 0�C~50�C temperature range. UV exposure, moisture, and humidity also affect the overall temperature within a specific environment. iTech Company offers a range of LCD monitors that can function properly in a wide working temperature range from -30℃ to +80℃. These products are already proven and tested to maintain its original luminance under such temperatures.
While the range of operating temperature is a relevant consideration for the device to withstand extreme hot or cold environments, other factors must also be taken into account for the overall performance of the device. These includethe clarity of the image, environmental protection, LED backlighting, quality of the components, andvarious options available.
iTech Company’s products are equipped with these useful features to deliver great performance even in harsh working conditions. These are available in different monitor sizes and resolutions. It offers superior image quality with wide viewing angle. Some of the optional features include the touch screen functionality for interactive application and the level of brightness to ensure that the screen content is highly visible in all lighting conditions. Moreover, these wide operating temperature LCD displays are available in different types including open frame, panel mount, andchassis mount.

I always finding it interesting when a new customer of ours calls to let us know that they can find cheap LCD displays, the same LCD we supply, for almost half the price. After all, cheap LCD displays are the same no matter where you purchase it. Right?
Let me assure you that the phrase, ‘You get what you pay for’ is just as true for LCD displays as it is for insurance, fine jewelry, car repairs and open heart surgery. You will always be able to find a lower cost product or service, but many times you are not comparing apples to apples.
The word “cheap” is so polarized in that in one instance you can revel in the victory of finding that super low price and yet simultaneously it is no victory at all if someone looks at your product and says, “Wow, that looks cheap.” So, let’s talk about Cheap LCD displays.
The long and short of it is that LCD’s are in investment. In many cases, they are the most expensive component in your product, but you need to balance that with the fact that they are also what the customer looks at the most. If you are building a hand held device that measures the PH of pool water, it’s a safe bet that people will be looking at the display far more than the battery compartment on the back of the unit. The cheap LCD display may save you a fraction of what other suppliers are quoting, but what is it costing you? Return customers. Good online reviews. Word-of-mouth advertising.
There is a rule of thumb statistic that says it costs a company 7 times more money to earn a new customer, than it does to keep a current customer. So why would you save 20% or even 40% off the cost of an LCD and in return lose your current customers. The savings will not offset the increased advertising cost to bring in new customers.
There are three main fluids used in a monochrome LCD module. They are TN, STN and FSTN. Each fluid has its own niche in which it operates well. One of the main factors impacted by the different fluids is acceptable viewing angle of the display.
LCD displays are quite diverse when it comes to the temperatures in which they can operate well. Some even have as much and more than 100 degrees window of successful operation. There are three main temperature ranges of an LCD unit:Normal temperature (indoor temps—think of your living room)
Ultra wide temperature (-40C/-40F--think of extreme cold and hot environments like in Alaska, Minnesota, and Wisconsin or Florida, and specifically Phoenix where it gets hot, hot, hot!).
The cost difference between normal temp and ultra wide temperatures can be as much as 30%. Therefore, identifying the appropriate temperature range is critical to have the best device for the best price.
Take for instance one customer of ours who needed the display to work properly on oil rigs near the North Pole. Their product monitors the safety equipment on the rig. Is it worth spending the extra $5 on a display that can survive working in all conditions? Is the LCD display an investment or expendable?
When a supplier is promising you the cheapest deal out there, you need to make sure that you are again dealing with an apples-to-apples comparison. Make sure that they aren’t saving you money by offering you a display that has the cheapest temperature range or the narrowest viewing angle, especially when those aren’t what will suit your product and your situation. They may just be choosing the cheapest alternatives of all the many options available, all to have you wind up with a unusable or inferior product. Then, you not only have a product you aren’t thrilled about but you face the problem of shipping the product back to the foreign country from which it came. This is not a convenient way to deal with the fallout from the “cheap” product! There is a real advantage to buying a product that has American support and part of that advantage is simply the convenience of speaking the same language and being within one shipping day apart from your customer support.
The engineer took our price and specs and called back a few days later saying that another LCD vendor came in with a similar product that would cost in the low $5 range. Red flags immediately went up in my mind. Something was not right about this cheap LCD display. The display was similar, but upon inspection there were some ‘strings’ attached.
This is critical if you plan to build your product for the next few years. You will need to purchase more of these exact LCD displays in the future. When that time comes and you find out that the LCD modules are discontinued, you are in deep trouble. Your only option is to redesign your product for the current LCD.
Keep in mind that if you plan to repair your customer’s product, it is critical to have a supply of the original LCD. You cannot use a new LCD in an old product in the same way you cannot use a VHS tape (for those of you over the age of 20) in a blue ray player.
A simple tip is to do a little research on the product. Google can be your best friend. When someone offers you a screaming deal on a cheap LCD display, type in the part # and manufacture into Google; you may quickly find out why the prices are so cheap.
There are companies that contact us to buy our surplus/returns. These companies are providing a valuable service by keeping displays out of the landfills. If you need to be able to purchase the exact same LCD in the future, stay away from refurbished units. Once they are gone, there are no rain checks. Many of these displays can be found on eBay and other online auctions.
That engineer quickly realized that asking the three critical questions makes all the difference in the price of the product! Getting cheap LCD displays is not always a mistake, just remember to ask questions and really think through whether this is an investment or an expendable item.

Segment LCDs, also called static displays or glass-only displays, are constructed of two pieces of ITO (Indium tin oxide) glass with a twisted nematic fluid sandwiched in between. A static display is a segment display with one pin for every one segment.
These displays are still one of the most popular technologies in use and the majority of them are custom. Many people think the process of designing a custom segment liquid crystal display is complicated and too complex to be understood except for a few experienced people. But after designing custom LCDs for over 14 years, it can be said that just about anyone can select the best options for their product.
In other words, you don’t have to be an engineer, or have a PHD from MIT to design a custom LCD for your application. So instead of offering a list of technical terms and equations, these are the different options available.
The tooling fee for a custom display is the lowest of all the technologies and allows the customer to receive a LCD that is manufactured to the exact dimensions requested, including custom icons and segments.
Focus LCDs offers a one-time NRE (Non-recurring engineering) or tooling fee. This includes all design, technical support, and samples. A PDF showing an overview of our tooling process can be found by clicking here: Custom LCD flowchart
Segment displays require less power than other display technology such as TFT, OLED, and UWVD. This makes these LCDs ideal for applications that are battery powered or solar powered. They require the lowest power to drive, an estimated 2uA per centimeter squared. Glass only displays (no backlight and no controller) require an estimated 10% of the power that is required for a LED backlight. In other words, a static display without a backlight will draw around 1mA; the same display with a LED backlight will demand from 10mA up to 25mA. Most displays can be driven at 3.3V or 5V since microprocessors can operate at both voltages. 3.3V is becoming more popular since two double ‘AA’ batteries can produce between 3.0V and 3.3V.
A segment is any line, dot or symbol that can be turned on and off independently. The photo below is of a segment LCD that contains numbers, a small clock symbol, the word ‘Jul’, and the letters ‘PM.’
There are four numbers in the above LCD (0 8 4 7) all are seven segments. In other words the ‘0’ has seven segments, the ‘8’ has seven segments and so on. Each number has seven independent segments. Each segment can be turned on and off independently to create other numbers and some letters such as E, F C and others. This is an example of a ‘seven’ segment. But there are some letters that a seven segment cannot display such as the letter ‘M’ or ‘V’. In this case a fourteen segment configuration can be used.
An icon is a small symbol or set of words that is only one segment. In other words, when the segment is ‘on,’ the full word or symbol turns on. When it is “off,” the word or symbol turns off. In the photo above: the clocksymbol is one segment, the word ‘JUL’ is one segment, the letters FOCUSLCDS.COM are one segment and the letters ‘PM’ are one segment.
It is possible to burn a segment into the glass so that it is always “on”. In this case, the ‘FOCUSLCDS.COM’ has been burned into the glass and can always be seen by the customer even when the power is “off”. Some customers will have their company name burned into the glass.
Segment LCDs, like all LCD display technologies, operate best between specific temperature ranges. You choose the temperature ranges that it will operate in. There are two standard configurations: normal temperature and wide temperature. The wider the temperature range, the more expensive the display.
The standard operating temperature range for a segment LCD is 0C to 50C. It is possible to build the display with a different fluid that will allow it to operate from -30C to 80C (F). With the addition of a heater, the display can operate down to -50C.
When the display becomes too cold, the fluid between the two layers of glass starts to freeze; when the display does freeze, the segments that were “on” when it froze will stay on. The display will not change until the temperature increases. When the display becomes too hot, a black spot will develop in the center of the glass. Basically the fluid is boiling. When the temperate comes down, the display will operate normally.

A lot of consumers wonder how manufacturers determine the LCD display panel prices. After all, display solutions such as TFT LCDs and HMI touch screens do not always come cheap. And sometimes, a few products that can indeed be purchased for lower prices may come with several quality issues.
Hence, we’ve rounded up a list of factors that influence how to display modules such as TFTs, LCD, and touch screens are priced. You can also use these factors to evaluate to whom you should place your next orders for your display solutions.
LCD fluids are used in altering the light orientation passing through glass substrates. Hence, this causes the panel’s active pixels to darken. Different kinds of LCD panel fluids provide unique characteristics and change a panel’s viewing angle, temperature range, and display clarity.
Another characteristic of this fluid is that it works well even in colder temperatures. It’s because TN fluid has the quickest response time among the other LCD fluid types.
TN fluid is considered the cheapest LCD fluid type. However, this doesn’t mean that TN isn’t widely used. The display technology is greatly utilized in digital clocks, pagers, and gas pumps.
LCD modules with STN fluid enjoy a wider display angle, greater multiplexing, higher image contrast, and sharper response than devices using TN fluids. However, modules with STN fluids may have slower response times when used in lower temperatures due to the fluid freezing inside the device.
STN fluid falls under the moderately cheap LCD module price. Furthermore, STN fluid is widely utilized in several monochrome LCD devices such as POS machines, inexpensive feature phones, and informational screens of some devices.
CSTN is a bit pricier than TN and STN fluids. But it’s a good choice if you need to display color images on your LCD device. In fact, a lot of color feature phones use CSTN as an alternative to the TFT displays, saving almost half the manufacturing costs.
In terms of cost, the LCD display module price of a unit with FSTN is higher compared to TN and STN. But this is concerning the better visual quality that FSTN offers.
To cap off this part, the fluids used in a screen is a big factor in determining the overall LCD screen display panel price. As you can see, the four fluid types often used in LCD screens rise in costs with respect to the visual quality produced by each technology.
The temperature range in which LCD screen displays may work varies intensely. Some displays continue to work at optimal performance even when used in cold or hot outdoor temperatures. Lower-quality LCD panels may start having glitches at the slightest change of temperature and humidity. Hence, the temperature range may have a huge impact on the LCD display panel price as well.
In hot environments– The liquid crystals may begin to deteriorate, while the electrical components will start overheating and cause damage to the display screen performance.
Now, most LCD screen panels don’t experience such temperature extremes. In fact, a typical LCD TV can operate properly between approximately o°C and 32°C (32° – 90° F). Meanwhile, other screen modules (usually the industrial-grade ones) have unique capabilities to work in even more extreme ends of the temperature scale.
If you want to look for the most cost-effective type of LCD panel for your device, then you must consider the following standard LCD unit temperature types:
Normal temperature units work well in environments that have indoor temperatures at approximately 20-35°C (68-95°F). Some LCD modules may work well above up to 50°C (122°F). Such LCD modules can be used in daily settings by the typical consumer public.
LCD units under this type are made to withstand lower and higher temperature ranges. Extreme operating temperatures may range anywhere from -30°C to 85°C (-22-185°F). Most LCD modules with wide/extreme temperature capabilities are used in extremely cold areas such as Artic places and ski resorts, as well as humid and moisture-rich hot outdoor areas.
Generally, the LCD module price goes up if the entire display unit can withstand higher temperature ranges. Those who can operate under normal temperature ranges only are usually cheaper.
Hence, you must consider the places where you’ll be installing your LCD display devices. You can’t just use cheaper LCD modules for an industrial-grade display machine. Treat your LCD panel as an investment and select a panel that will yield better screen performance that’ll last several years for you and your business.
Color LCDs have three subpixels that hold red, blue, and green color filters. Each subpixel can have as much as 256 color shades, depending on the variation and control of the voltage applied to it.
Now, when you combine 256 shades of both red, blue, and green subpixels, color LCDs can display a color palette of up to 16.8 million colors. And all these are made possible by millions of transistors etched onto the glass modules.
Display size also plays a large role in an LCD device’s color capability. Smaller screens need fewer pixels and transistors since they have smaller display sizes. These screens are also less costly to make. Now, larger screens with high color resolution and huge display sizes require more transistors and pixels, justifying the higher prices of such monitors.
A touch screen display module is more costly than a non-touch monitor module. Touch capability is integrated into Human Machine Interface (HMI) modules and is generally used in kiosks, bank ATMs, hospital equipment, and similar devices in other industries.
HMI touch screen price is also dependent on what kind of touch screen technology it uses. Here are some of the common touch technologies integrated to HMI touch screen devices:
This type of touch screen technology is made up of a top polythene layer and a glass-bottom layer separated by microdots or an air gap. This module is then attached to a touch screen controller.
Resistive touch screen panels are used in most bank ATMs and some older models of cellular phones. They carry the lowest HMI touch screen price among all other touch screen technologies.
Capacitive touch screens are the most common in the display industry today. This technology uses transparent conductors, insulators, and glass to create the panel. An electrostatic field change in the screen’s module happens when a human finger touches the screen surface. This ultimately creates signals that are sent to the touch screen controller for processing.
In general, capacitive touch screens are the most cost-effective choice for HMI machines. Since they are considered the gold standard of commercial touch screen technologies, they do come with a high price tag.
Infrared grid technology uses photodetector pairs and X-Y infrared LED components to allow sensors to pick up the touch and its exact location. Infrared grids have been used in several touch screen modules before the capacitive touch screen technology took over.
We’ve explained the following factors at length for both public consumers and business clients to understand the variations in TFT, LCD, and HMI touch screen prices.
Cheap doesn’t necessarily mean low-quality. Also, expensive options aren’t always a wise choice, either. You can maximize your buying or manufacturing options if you know how to compare LCD modules and panels depending on the specifications you truly need for your display machines and devices.

Modeling simple, elegant, LCD panels inline connections, moisture-resistant, strong anti-interference, applies to refrigerated cabinets, display counters and other needs of temperature measurement and display of variousread more... Brochure
Accuracy: +-1 DegreeC IN THE RANGE OF -30 DegreeC ~ +250 DegreeC , OTHERWISE MORE THAN +- 2 DegreeC, +-1.8 DegreeF IN THE RANGE OF -22 DegreeF ~ +482 Degree
This is one of the best TDS meters that we tested at this price point. Order today because we sell out quickly. This TDS Meter Water Quality Tester and EC Meter is a Professional quality Total Dissolved Solids combination TDS Meter, TDS EC Meter and Temperature Meter. Ideal for all water quality testing, water purificationread more...
This is a Digital thermometer and hygrometer. This meter can be used to measure temperature and humidity. The meter comes with a sensor with an extended wire

The display screen can be divided into three types: normal temperature, wide temperature and ultra-wide temperature according to the supported working temperature range. The normal temperature display supports the working temperature between 0 °C and 50 °C, and the wide temperature display supports the working temperature between -20 °C and +70 °C. ℃, the ultra-wide temperature display supports the working temperature between -40℃~+90℃.
Usually, the display screen with good low temperature performance will have poor high temperature performance. The wider the operating temperature range, the higher the price. Users can choose suitable display products according to actual use conditions.

Temperature and Humidity Sensor with LCD Screen:New updated smart sensor to monitor home temperature and humidity timely for most comfortable living environment, featured with LCD screen to check the temperature and humidity,together with the date and time for your convenience;charged by USB adapter for flexible usage.
Compatible with Tuya Smart/Smart Life APP:Smartly monitor temperature and humidity data by smart phone via Tuya Smart APP with no hub required,functional well in the APP to check with data graph by day,month and year record.Even with facial expression as the guardian mode to offer the best air and temperature for baby care.
Infrared Inductive Switch for Bright Backlight:Designed with the infrared sensing area to trigger the backlight on the large LCD screen,offering the best viewing effect in the dark to protect your eyes.Temp. unit convert between ℃ / ℉ in the APP or via the reset button on the device for much easier reading.
Work with Alexa and Google Home:Voice control is available for this version of smart sensor,to know current temperature and humidity status via voice command;device share to family for convenience;fast pairing with Bluetooth on under 2.4G WiFi;includes full 2-year warranty and 60-day refund guarantee for complete satisfaction.

Size:Our standard TFT LCD display size range from 0.96 inch to 13.3 inch, including 0.96”, 1.44", 1.77", 2", 2.2"", 2.4", 2.8", 3.2", 3.5", 4.3", 5", 5.5”, 7", 8", 10.1", 13.3”.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey