tft display layers quotation

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The liquid crystal displays used in calculators and other devices with similarly simple displays have direct-driven image elements, and therefore a voltage can be easily applied across just one segment of these types of displays without interfering with the other segments. This would be impractical for a large display, because it would have a large number of (color) picture elements (pixels), and thus it would require millions of connections, both top and bottom for each one of the three colors (red, green and blue) of every pixel. To avoid this issue, the pixels are addressed in rows and columns, reducing the connection count from millions down to thousands. The column and row wires attach to transistor switches, one for each pixel. The one-way current passing characteristic of the transistor prevents the charge that is being applied to each pixel from being drained between refreshes to a display"s image. Each pixel is a small capacitor with a layer of insulating liquid crystal sandwiched between transparent conductive ITO layers.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
In 2004, Hydis Technologies Co., Ltd licensed its AFFS patent to Japan"s Hitachi Displays. Hitachi is using AFFS to manufacture high end panels in their product line. In 2006, Hydis also licensed its AFFS to Sanyo Epson Imaging Devices Corporation.
A technology developed by Samsung is Super PLS, which bears similarities to IPS panels, has wider viewing angles, better image quality, increased brightness, and lower production costs. PLS technology debuted in the PC display market with the release of the Samsung S27A850 and S24A850 monitors in September 2011.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
The bare display panel will only accept a digital video signal at the resolution determined by the panel pixel matrix designed at manufacture. Some screen panels will ignore the LSB bits of the color information to present a consistent interface (8 bit -> 6 bit/color x3).
With analogue signals like VGA, the display controller also needs to perform a high speed analog to digital conversion. With digital input signals like DVI or HDMI some simple reordering of the bits is needed before feeding it to the rescaler if the input resolution doesn"t match the display panel resolution.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
Brody, T. Peter; Asars, J. A.; Dixon, G. D. (November 1973). "A 6 × 6 inch 20 lines-per-inch liquid-crystal display panel". 20 (11): 995–1001. Bibcode:1973ITED...20..995B. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1973.17780. ISSN 0018-9383.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Kim, Sae-Bom; Kim, Woong-Ki; Chounlamany, Vanseng; Seo, Jaehwan; Yoo, Jisu; Jo, Hun-Je; Jung, Jinho (15 August 2012). "Identification of multi-level toxicity of liquid crystal display wastewater toward Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa". Journal of Hazardous Materials. Seoul, Korea; Laos, Lao. 227–228: 327–333. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.059. PMID 22677053.
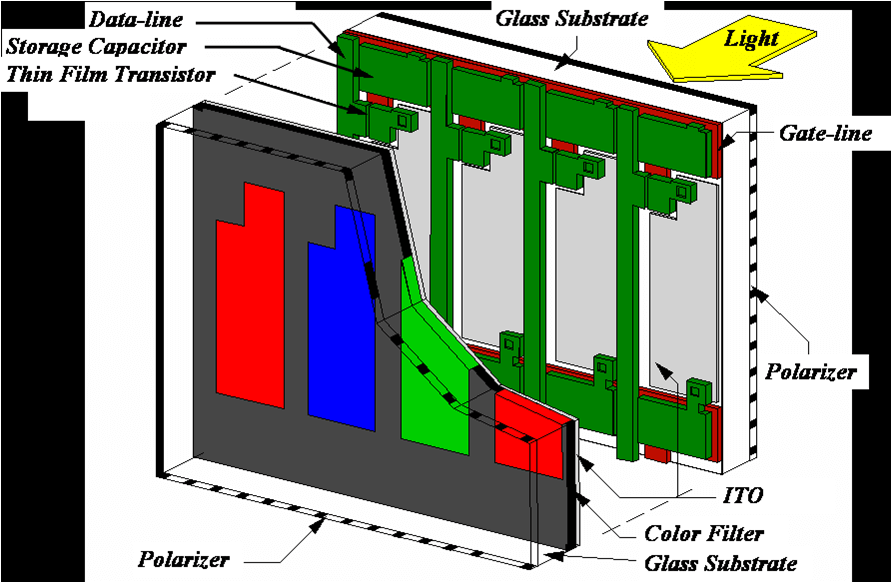
TFT displays have become increasingly common in our daily lives. They are used in cars, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, as well as in industrial applications and many more. But what are TFT displays and why are they so important?
A TFT (Thin Film Transistor) display is a type of display technology that uses a thin layer of transparent material to produce an image on the screen. The display is made up of thin layers of organic material called organic transistors, which are stacked together on a glass substrate and covered with a thin layer of plastic or metal oxide.
TFT displays are also used in many other industrial applications, such as industrial control systems, medical devices, automotive infotainment systems, and more.
The basic concept behind a TFT display is simple: it uses light to create an image on a screen. Light passes through the glass substrate and the organic transistors until it reaches the top layer of the display.
The number of pixels that can be displayed depends on how many organic transistors are used in each pixel or subpixel (a single-pixel is made up of multiple subpixels). For example, a 4-inch (10 cm) display has a pixel pitch of 0.0625 inches (1.57 mm).
The basic design of a TFT display has remained unchanged for more than 20 years. In this design, the sub-pixels are arranged in a grid pattern, with each subpixel connected to its neighbor by wires that form rows and columns.
The first large format TFT display was introduced in 1987 by NEC Corporation, which used a 1024×768 pixel screen for its PC monitor line, called CRT Professional Display System or “Videotronic” system. The technology was licensed to NEC’s competitors such as Hitachi and Toshiba for use in their own monitors and televisions. The system was marketed as “Super Video” and replaced the aging “Videotron” CRT monitors that were still being used at the time. The first LCD TV was also produced in 1987 by Sony.
In 1989, Sharp’s first TFT-LCD TV set was introduced with a resolution of 576×320 pixels, while the world’s first large format high definition screen with a resolution of 1024×768 pixels was introduced by NEC in 1994.
Over the years, TFT display technology has developed by leaps and bounds. It has been used in tablets, smartphones, notebooks, game consoles, and computer monitors. The technology is also used in digital cameras, camcorders, MP3 players, and GPS devices.
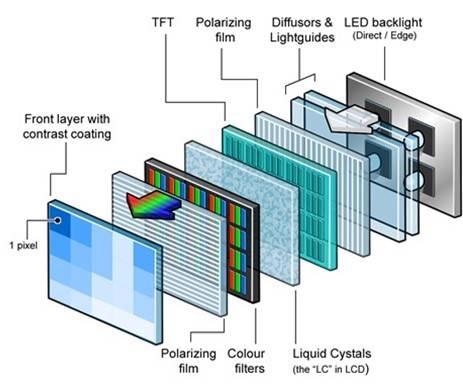
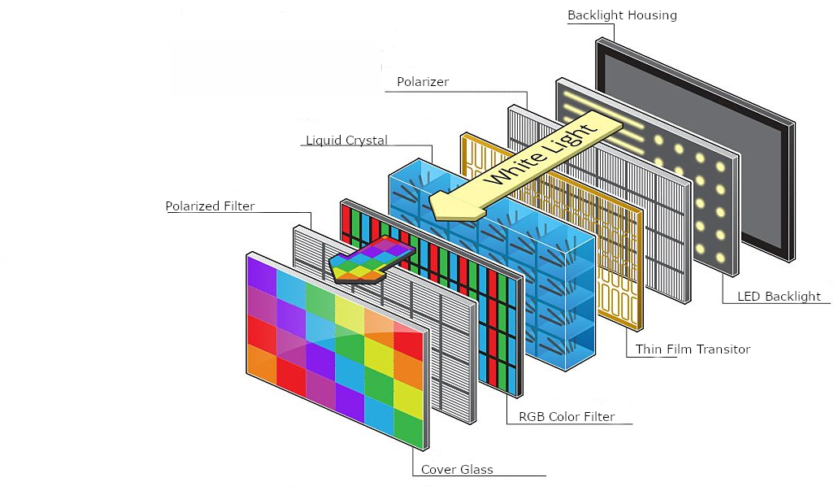
What does the TFT display technology comprise? From far, you can easily assume TFT to be a single unit. But in reality, it comprises different components that work together.
The backlight of the TFT display is a very important component. It provides the light for the pixels and is also responsible for illuminating the display. The light emitted by a backlight can be controlled by varying the amount of current running through it.
When it comes to LCD displays, there are two types of backlights; Active matrix and Passive matrix. Active matrix backlight has several layers of electrodes, which are used to control the amount of current flowing through them.
The pixel is the smallest unit in a TFT display. It is the basic unit of information that is displayed on the screen. The pixel consists of three sub-elements, namely; Red, Green, and Blue (RGB).
The number of sub-pixels that are used in each pixel varies with different display technologies. In full-color LCDs, there are three types of sub-pixel: red, green, and blue (RGB). Full color TFT displays use a combination of Red, Green, and Blue (RGB) sub-pixels to represent full color.
The light that is transmitted through each TFT is controlled by applying voltages of different values to each pixel in turn. To do this, a control circuit called a driver circuit is required. The driver circuit controls the voltage applied to each pixel with reference to a set of parameters known as “pixel information”.
This information includes color, brightness, and other characteristics that define how an individual pixel should be operated for display purposes. The parameters also include how many red, green and blue sub-pixels are used to produce each pixel.
The control system can be further divided into 3 sub-systems: the interface, the timing, and the data transfer system (DTS). These systems work together to provide all of the necessary functions for controlling TFT displays from external sources such as computers, printers, or TVs.
This is another component of a TFT display system. It consists of a liquid crystal material sandwiched between two glass plates. This material is responsible for controlling the light by changing its refractive index.
-Wide viewing angle: The viewing angle of the TFT display is larger than that of the CRT set. It is generally considered to be the best choice for applications requiring an extended viewing angle.
-Transparency: TFT display has better transparency than CRT set, which makes it more suitable for applications requiring high transparency such as window displays and computer monitors.
-High resolution: TFT display can produce higher resolution than CRT display. For example, the pixel density of TFT is about 3 million pixels per square inch (PPI), which is about three times that of conventional liquid crystal displays (LCDs) whose pixel density is about 100 ppi.
-Reliability: Since it uses no moving parts, the TFT screen does not need any maintenance or repair, and therefore the reliability is higher than that of LCDs and plasma displays.
-Power saving: TFT display consumes much less power than CRT. The power consumption of a mainstream TFT display is about 1/10 that of a typical LCD. In some applications, the power consumption can be reduced to 1/100 or less of that of a CRT.
-High brightness: The picture displayed on the screen can be bright enough to be seen in bright sunlight without any need for glare reduction filters.
-Compatibility: Since it uses no moving parts, the TFT screen does not have any mechanical problems such as screen flicker and image sticking problems found in plasma displays and LCDs.
-High resolution: Although the pixel density of TFT is about 3 million pixels per square inch (ppi), the resolution is more than 100 ppi which makes it more suitable for many applications where high resolution is needed.
-Consistency: Since it uses no moving parts, the image displayed on the TFT display is not affected by temperature and humidity, which makes it more consistent than LCDs and plasma displays.
-Cost: The cost of a TFT display is lower than that of LCDs and plasma displays. For example, in some applications where image quality is not critical, the cost of a TFT display may be only a few tens to a few hundreds of dollars while the cost of LCDs or plasma displays may be several thousand to several tens of thousands.
-Excellent color display: We can’t deny the fact that TFTs have a superior color display. This simply means that the color of pixels can be accurately reproduced.
-Very thin: When compared with LCDs and plasma displays, which are very thick, TFTs are very thin and lightweight. In addition, the cost of mounting a large size TFT screen to a wall panel is relatively low.
-No ghosting: ‘Ghosting’ refers to the fact that the display shows a bright spot on the screen when the screen is turned off. TFT screens do not show ghosting. TFTs produce a sharp image even when they are turned off.
-No geometric distortion: Geometric distortion refers to the shape of the display on a flat surface. TFTs produce a sharp image even when they are turned off.
-No radiation: TFTs do not emit any harmful radiation, and there is no need for shielding or shielding materials to protect people from harmful radiation.
Considering that TFTs use less power, it is possible to reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared with LCDs. In addition, if you use LED backlights in TFT displays, you can reduce power consumption by up to 75% compared with conventional backlights.
If a product uses a backlight, there is a high possibility that the color of the screen will be affected after some time due to dust or dirt that comes into contact with it. But it is possible to prevent this problem by using TFTs with LED backlights, which have no problems such as those caused by dust and dirt.
Workability refers to the ease with which you can operate a product. When working with a screen that has TFTs, it is possible to increase the amount of information that can be displayed at one time. It is also possible to reduce the number of times you must change settings on a product by increasing its usability.
Design refers to what you can create with the use of a product. Using TFTs, it is possible to create products that have a thin profile and are lightweight, which makes them more convenient for transportation and storage.
Human interface refers to what you touch when using a product or what you see on the screen when using a product (e.g., buttons and other controls). By integrating the TFTs into the display part of a product, it is possible to make the human interface easier.
Amoled refers to a technology that replaces the traditional liquid crystal display (LCD) with an organic light-emitting diode (OLED). Modern TFTs are similar to Amoled in terms of their structure, but they differ from Amoled in terms of their performance.
The TFTs of the present invention have superior characteristics compared to Amoled, such as high contrast ratio and response speed. The TFTs also have superior characteristics compared to conventional display devices such as CRT and plasma display panels, which cannot be achieved by these conventional display devices.
IPS refers to a technology that replaces the traditional liquid crystal display (LCD) with in-plane switching technology. The IPS display has superior features to TFT due to its high contrast ratio, wide viewing angle, and high response speed.
There are certain limitations to TFTs. For example, there is a limit to the size of the display and the resolution of the image that can be displayed on a display. Also, because TFTs are considered to be a kind of organic semiconductor displays, they have a short life span and therefore need frequent replacement.
Because of their high resolution, TFT displays are used in display monitors. The type of TFT used in display monitors can be categorized as either active matrix or passive matrix. Active matrix TFTs use a thin film transistor (TFT) as its active component, whereas passive matrix uses a liquid crystal display (LCD).
TFTs are also being used in portable electronic devices such as mobile phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and cameras. These devices require high-resolution screens because the user must be able to view accurate images and text on the screen. TFTs are also being used in laptops, which have a much larger screen size than many other portable electronic devices.
Because of their size and high resolution, laptop computers use passive matrix TFT displays instead of LCDs for larger displays than those found on smaller-sized portable electronics devices that use LCDs for their displays (e.g., mobile phones and PDAs).
TFT displays are used in front-projection TVs. The type of TFT used in front-projection TVs can be categorized as either active matrix or passive matrix. Active matrix TFTs use a thin film transistor (TFT) as its active component, whereas passive matrix uses a liquid crystal display (LCD).
Head-mounted displays (HMDs) use liquid crystal on silicon technology to create small, inexpensive, low-power VR headsets that can be worn on the head. Some HMDs use active matrix TFT technology while others use passive matrix TFT technology. Active matrix HMDs use shorting bars or glass electrodes to control each pixel; passive matrix HMDs use a liquid crystal material that allows for the creation of an image by controlling the voltage applied to each pixel.
TFTs are used in projectors to create the on-screen image from the input signal. TFTs are used in both active matrix and passive matrix projectors. Active matrix projectors use shorting bars or glass electrodes to control each pixel, while passive matrix projectors use a liquid crystal material that allows for the creation of an image by controlling the voltage applied to each pixel.
CCDs are used in digital cameras and DV camcorders to capture still images and video, respectively. CCDs use a single array of photosites that each receives an electrical charge during exposure to light, resulting in an electrical signal that is output as an image. TFTs are used in CCDs as display circuits for previewing pictures.
TFTs are used in the display of gaming systems such as consoles, personal computers, and hand-held devices. TFTs are also used in the display of mobile telephones and in digital signs.
There are many factors to consider when buying a TFT display. The most important factors are the size of the display, the resolution of the display, and whether or not it is touch-sensitive.
It is also vital to consider where you are buying your TFT display system. A good place to buy a TFT display is from an authorized dealer or an online store. You should also consider whether or not the TFT display system you are looking for has a warranty.
At ICRFQ, we can connect you to the best TFT display suppliers and manufacturers in China. Just contact us and we will do what a reliable sourcing agent should do!
Optical and SEM (scanning electron microscopy) images of fabricated (a, b) CL and (c, d) CLSE pixel structures. The five white line patterns in (d) are the ITO interdigitated pixel and common electrodes. (e) Images from the normal direction and from 50 degrees to the left and right of a 2.3-inch-diagonal display incorporating the IPS TFT-LCD panel. (f) The three-black matrix (BM) patterns (top: BM covering both gate and data lines, middle: BM covering only the data lines, and bottom: without BM) and (g) optical images of pixels without BM (left: LC on and off voltages supplied to every other data line, right: LC off voltage supplied to all data lines).
Figure 3e shows images from the normal direction and from 50 degrees to the left and right of a 2.3-inch-diagonal display incorporating the IPS TFT-LCD panel fabricated in our laboratory, (f) the three black matrix (BM) patterns (top: BM covering both gate and data lines, middle: BM covering only the data lines, and bottom: without BM), and (g) optical images of panel areas without the BM (left: LC on and off voltages supplied to every other data line, right: LC off voltage supplied to all data lines). As can be seen in the image from the normal direction, the brightness and contrast of the display area with the top BM and middle BM patterns are almost the same, but the contrast of the display area without the BM is relatively lower because of the lower darkness level of the LC off pixels indicating “HITACHI”. As shown in Fig. 3g, this is due to light leaking through the aperture between the data line and adjacent common lines. Therefore, in the CL structure, the BM on the drain line is necessary to obtain a high contrast ratio by shielding light leakage. This is the same as in the conventional structure. On the contrary, there is no light leakage along the gate line through the gaps between the gate line and edges of the pixel/common electrodes, as is clearly shown in Fig. 3g. This is a unique advantage of the CL structure because the conventional structure must shield these gaps with the BM to prevent light leakage. The suppression of light leakage along the gate line in the CL structure is due to the driving scheme (see Fig. 2b,a for a comparison with the conventional structure). During the holding period (tOFF) in the conventional structure, regardless of the pixel voltage, Vp (including Vp = 0), nonzero Vgp and Vgc are always applied to keep the TFT off, and these voltages are applied to the LC layer, inducing light leakage as reported in
Figure 4a shows the gate voltage (Vg) dependence of the panel brightness, while the inset shows that of the TFT current (transfer characteristics). The gray curves are for the conventional IPS TFT-LCD with the TFT before enhancement, the common line, and the matrix BM (MBM) shown at the top of Fig. 3f. The blue curves are for the proposed CL structure with the enhanced TFT and the stripe BM (SBM) shown in the middle of Fig. 3f. In this case, enhanced TFT characteristics were obtained by using an MNOS TFT without back-channel oxidation that was enhanced by the BTS process. In both structures, the threshold voltages for panel brightness, defined by extrapolating the straight part of the brightness curves, reflect those of the TFT transfer curves defined as Vg at a drain current of 10−12 A, and they are well matched to be 4 V and 9 V, respectively. The maximum brightness for the CL structure is 137% higher than that for the conventional structure, which is due to the increase in the aperture ratio from 38 to 52% that results from the elimination of the common line and the BM covering the gate line.
(a) Dependence of panel brightness and TFT current on gate voltage for the conventional pixel structure of 38% aperture ratio (AR) with matrix black matrix (MBM) over both drain and gate lines and proposed CL pixel structure of 52% AR with strip black matrix (SBM) over only the drain lines. Transfer characteristics before and after bias temperature stress (BTS) treatment are shown in the inset. (b) Charging and (c) holding characteristics of enhanced TFT of the CL structure with gate as a common line. Vg and Vd in the TFT ON state are 30 V and +/−7 V, respectively.
To estimate the charging and holding characteristics of the MNOS-enhanced TFT in the panel, the gate TFT ON and OFF time dependences of the panel brightness were measured (Fig. 4b,c). The charging characteristics in Fig. 4b are plotted as a function of tON at tOFF = 16.6 ms, Vg = 30 V, and Vd = ± 7 V. The holding characteristics in Fig. 4c are plotted as a function of tOFF at tON = 34 μs. 95.1% charging at tON = 34 μs and 95.3% holding at tOFF = 16.6 ms indicate that the enhanced TFT has sufficient charging and holding performance to drive a standard VGA (640 × 480 pixels) panel (the number of scanning lines is estimated as tOFF/tON = 16.6/0.034 = 488).
To confirm the driving conditions for the CL structure without the BM along the gate line (with the SBM), the tOFF dependence of the contrast ratio (CR) in the CL panel was further investigated as shown in Fig. 5a, where CR is plotted as a function of tOFF for the CL panels with the matrix BM (MBM) and the strip BM (SBM). The inset shows the brightness in the bright (Vd = 7 V) and dark (Vd = 0 V) states of the CL panel with the SBM as a function of tOFF and an optical image of the panel with tOFF = 6.4 ms. The SBM and MBM panels keep CR higher than 240 with tOFF > 16.6 ms, the frame period of a display panel without flicker being noticeable to the human eye. both panels decrease CR when tOFF is less than 16.6 ms; the CR of the SBM panel decreases faster than the CR of the MBM panel. As shown in the inset, the decrease in CR was due to the increase in dark-state brightness with decreasing tOFF as light leakage increases along the gate line. This light leakage is induced by the voltage Vgp = Vgc = VgON = 30 V applied only for 34 μs during the TFT ON (charging) state, which is 1/488th the duration, tOFF = 16.6 ms, of the TFT OFF (holding) state with Vgp = Vgc = VgOFF = 0 V, but the ratio increases with decreasing tOFF and becomes effective enough to switch on LC layer and induce light leakage. However, it should be stressed again that the CL panel with the normal holding (TFT OFF) time of 16.6 ms does not suffer from the light leakage along the gate line, so the aperture ratio can be increased by removing the BM along the gate line.
Figure 6 indicates the effect of bias temperature stress (BTS) on the TFT characteristics. As the stressing time, tS, of the positive gate stress voltage, Vst = + 77 V, increases from 0 to 3600 s, the transfer (Id-Vg) curve shifts in the positive direction (Fig. 6a). Vth is defined as Vg at which Id = 10−12 A and ΔVth is defined as the Vth shift from the initial value via BTS. As shown in Fig. 6b, ΔVth increases logarithmically with increasing tS: ΔVth = 2.17 + 4.93 × log (tS). The mechanism behind the gate-stress-induced Vth shift is electron tunnel injection from the a-Si:H semiconductor into the SiOx gate insulator. For confirmation, ΔVth of MNOS TFTs with different SiOx thicknesses is plotted as a function of the electric field applied to the SiOx layer in Fig. 6c. Here, the thickness of the SiOx was varied (5, 10, 20, 50 nm), while the SiN thickness was fixed at 200 nm. The electric field applied to SiOx, Eox, was calculated using the following equation,
Effect of bias temperature stress (BTS) on TFT characteristics. (a) The transfer (Id–Vg) curve shifts in the positive direction with positive gate bias stress of Vst = + 77 V over the duration of 0–3600 s. (b) ΔVth, defined as the Vth shift from the initial value via BTS, increases logarithmically with increasing tS, following ΔVth = 2.17 + 4.93 × log (tS). (c) ΔVth of MNOS TFTs with different SiOx thicknesses from 5 to 50 nm as a function of the electric field applied to the SiOx layer.
Figure 7a shows the effect of back-channel oxidation (BCO) and passivation (PAS) on the Id-Vg characteristics of the MNOS TFT. The Id-Vg curve with Vth = 5.1 V is further enhanced to Vth = 10.9 V after BCO, although there is a slight degradation of the slope of the current increase in the sub-threshold region. The slope recovers after PAS without any change to the enhanced characteristics
(a) Effect of back-channel oxidation (BCO) and passivation (PAS) on Id–Vg characteristics of MNOS TFT. (b) Vth and Vth standard deviation, σVth, after BTS and after BCO without BTS treatments and (c) SiOX thickness as a function of position along gate-line, x.
The advantage of BCO over BTS is the uniformity of the enhanced characteristics; Fig. 7b shows the distribution of the enhanced Vth as a function of position along gate-line, x, for the MNOS TFTs connected with a 90-mm-long gate line in the TFT substrate after BTS and BCO treatments. The average value of Vth and the standard deviation, σVth, for pristine TFTs before BTS or BCO, are 5.1 V and 0.35 V, respectively. After BCO, Vth is uniformly enhanced, with an average Vth = 11 V and σVth = 0.4 V without increasing σVth. On the other hand, after BTS, Vth is nonuniformly enhanced with an average Vth = 9.3 V and σVth of 1.4 V. In particular, Vth increases linearly as a function of position along gate-line, x. As the gate SiOx thickness linearly decreases, from (54 nm) to (47 nm) with increasing x as shown in Fig. 7c, the increase in ΔVth after BTS with x is due to increase in the electric field applied to SiOx as shown in Fig. 6c and Eq. 1.
It has been shown that the Vth of the MNOS TFT is independent of the gate SiOx thickness when the thickness is more than 5 nm8a, Vth of the MNOS TFT with the BCO treatment becomes almost independent of the BCO SiOx thickness. As shown in the inset, the thickness of BCO SiOx composed of oxidized a-Si:H linearly increases with BCO processing time, and the Vth increase almost saturates at a BCO SiOx thickness greater than 5 nm. Therefore, the enhanced MNOS TFT after BCO has a uniformly high Vth that is robust to thickness fluctuations of the gate and BCO SiOx layers. BCO also has an advantage over BTS in terms of the stability of Vth as shown in Fig. 8b, which plots the annealing time dependence of Vth for BCO and BTS. In this experiment, the stoichiometry (x) of the gate SiOx was 1.78 for BTS and 1.78 and 1.9 for BCO. The annealing temperature in the N2 atmosphere was 200 °C. In the case of BTS, Vth decreased to the pristine value after approximately 5 h of annealing, while Vth decreased more slowly in the case of BCO. In particular, the annealing time required for Vth to fall to 7 V was 7.5 times longer than that of BTS. Increasing the stoichiometry (x) of the gate SiOx dramatically improved the BCO-enhanced Vth to as much as 11 V, which was stably maintained after 24 h of annealing at 200 °C.
(a) Dependence of Vth on thickness of back-channel oxidized (BCO) SiOX. The inset shows the SiOx thickness dependence on the BCO process time for RF powers of 200 W and 500 W. (b) Stability of Vth as a function of annealing time for three different TFTs with gate SiOx stoichiometry, x = 1.78 and bias temperature stress (BTS), x = 1.78 and BCO, and x = 1.9 and BCO. The temperature of annealing in the N2 atmosphere was 200 °C. (c) Band diagram of back-channel oxidized MNOS TFT. The red arrows show the electric dipoles at the SiOX/a-Si:H and a-Si:H/BCO SiOX interfaces.
A schematic band model for the MNOS TFT with the BCO treatment and the sectional structure of the interface between the a-Si:H and gate and BCO SiOx are shown in Fig. 8c. The uniformly high Vth that is independent of SiOx thickness is due to the dipoles generated at the channel and back-channel interfaces between a-Si:H and SiOx8 of reference

On most touchscreens there are usually two layers that make up just the digitizer. The glass on top that you touch and the actual digitizer sheet which consists of the touch matrix circuitry. The digitizer sheet is adhered to the glass so it often appears to be one piece. So you where correct to assume glass cover, digitizer and then lcd. The digitizer sheet and glass have a small gap that has an adhesive in it. On both the glass(bottom) and digitizer(top) is a transparent metallic conductive coating which is usually indium tin oxide. The human touch is conductive which allows for the electical sensors in the digitizer and glass sheets to sense the touch at a specific location.
Some of the newest technology such as Super AMOLED is able to get away from the two conductive sheets and has the touch sensors built into only one sheet, so these touchscreens would be an exception. So most forms of touchscreens consist of three or more layers.

A TN or Twisted Nematic TFT LCD is a cost-effective high performance LCD. It offers good brightness performance and fast response times. However, it suffers in one key area and that is its viewing cone. TN LCD’s typically have three good viewing angle directions. In these directions the image is typically clear and colors are consistent up to 80 degrees from the center of the LCD. The remaining viewing direction is usually good through 40-50 degrees from center. Afterwards, the image is likely to invert, almost appearing like an x-ray.

Compared with ordinary LCDs, TFT LCDs provide very clear images/text with shorter response times. TFT LCDs are increasingly being used to bring better visual effects to products.
TFT stands for “thin film transistor”. The transistor of a color TFT LCD is composed of a thin film of amorphous silicon deposited on glass. It acts as a control valve to provide the appropriate voltage to the liquid crystal for each sub-pixel. This is why TFT LCDs are also known as active matrix displays.
TFT LCDs have a liquid crystal layer between a glass substrate formed by the TFT and transparent pixel electrodes and another glass substrate with a color filter (RGB) and a transparent counter electrode. Each pixel in the active matrix is paired with a transistor that includes a capacitor, which gives each sub-pixel the ability to retain its charge without sending a charge every time it needs to be replaced. This means that TFT LCDs are more responsive.
To understand how a TFT LCD works, we must first grasp the concept of a field effect transistor (FET), which is a transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current. It is a component with three terminals: source, gate and drain. fet controls the flow of current by applying a voltage to the gate, thereby changing the conductivity between the drain and source.
Using the FET, we can build a circuit as follows. The data bus sends a signal to the source of the FET, and when SEL SIGNAL applies a voltage to the gate, a drive voltage is generated on the TFT LCD panel. A sub-pixel is lit. A TFT LCD display contains thousands or millions of such driver circuits.
Color TFT LCD from 1.8 inch ~ 15 inch, there are different resolutions and interfaces. How to choose the right TFT LCD, you can refer to the previous article “LCD | How to choose a liquid crystal display module
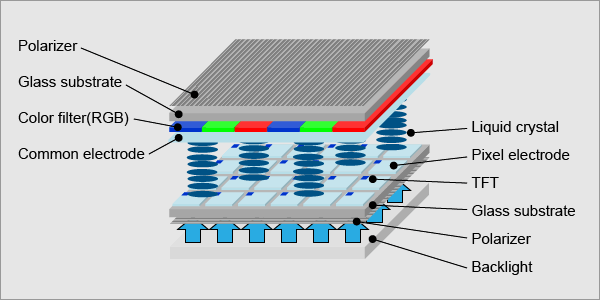
A TFT LCD, or a thin film transistor liquid crystal display, is one of the fastest growing forms of display technology today. The thin film transistor (TFT) is a type of semiconductor device used in display technology to enhance efficiency, compactness, and cost of the product. In conjunction with its semiconductor properties, the TFT LCD is an active matrix display, controlling pixels individually and actively rather than passively, furthering the benefits of this semiconductor device.
The TFT LCD is built with three key layers. Two sandwiching layers consist of glass substrates, though one includes TFTs while the other has an RGB, or red green blue, color filter. The layer between the glass layers is a liquid crystal layer.
The Architecture of a TFT Pixelbelow) from the other substrate layer of the device and control the amount of voltage applied to their respective sub-pixels. This layer also has pixel electrodes between the substrate and the liquid crystal layer. Electrodes are conductors that channel electricity into or out of something, in this case, pixels.
On the surface level is the other glass substrate. Just beneath this glass substrate is where the actual pixels and sub-pixels reside, forming the RGB color filter. In order to counteract the electrodes of the previously mentioned layer, this surface layer has counter (or common) electrodes on the side closer to the liquid crystals that close off the circuit that travels between the two layers. In both these substrate layers, the electrodes are most frequently made of indium tin oxide (ITO) because they allow for transparency and have good conductive properties.
The outer sides of the glass substrates (closest to the surface or closest to the back) have filter layers called polarizers. These filters allow only certain beams of light to pass through if they are polarized in a specific manner, meaning that the geometric waves of the light are appropriate for the filter. If not polarized correctly, the light does not pass through the polarizer which creates an opaque LCD screen.
Between the two substrate layers lie liquid crystals. Together, the liquid crystal molecules may behave as a liquid in terms of movement, but it holds its structure as a crystal. There are a variety of chemical formulas available for use in this layer. Typically, liquid crystals are aligned to position the molecules in a certain way to induce specific behaviors of passing light through the polarization of the light waves. To do this, either a magnetic or electric field must be used; however, with displays, for a magnetic field to be usable, it will be too strong for the display itself, and thus electric fields, using very low power and requiring no current, are used.
Before applying an electric field to the crystals between the electrodes, the alignment of the crystals is in a 90 degree twisted pattern, allowing a properly crystal-polarized light to pass through the surface polarizer in a display’s “normal white” mode. This state is caused by electrodes that are purposely coated in a material that orients the structure with this specific twist.
However, when the electric field is applied, the twist is broken as the crystals straighten out, otherwise known as re-aligning. The passing light can still pass through the back polarizer, but because the crystal layer does not polarize the lights to pass through the surface polarizer, light is not transmitted to the surface, thus an opaque display. If the voltage is lessened, only some crystals re-align, allowing for a partial amount of light to pass and creating different shades of grey (levels of light). This effect is called the twisted nematic effect.
Fig. 3:The top row characterizes the nature of alignment in using IPS as well as the quality of viewing angles. The bottom row displays how the twisted nematic is used to align the crystals and how viewing angles are affected by it.
The light that passes through the device is sourced from the backlight which can shine light from the back or the side of the display. Because the LCD does not produce its own light, it needs to use the backlight in the OLED) have come into use as well. Typically white, this light, if polarized correctly, will pass through the RGB color filter of the surface substrate layer, displaying the color signaled for by the TFT device.
Within an LCD, each pixel can be characterized by its three sub-pixels. These three sub-pixels create the RGB colorization of that overall pixel. These sub-pixels act as capacitors, or electrical storage units within a device, each with their own independent structural and functional layers as described earlier. With the three sub-pixels per pixel, colors of almost any kind can be mixed from the light passing through the filters and polarizer at different brightness based on the liquid crystal alignment.
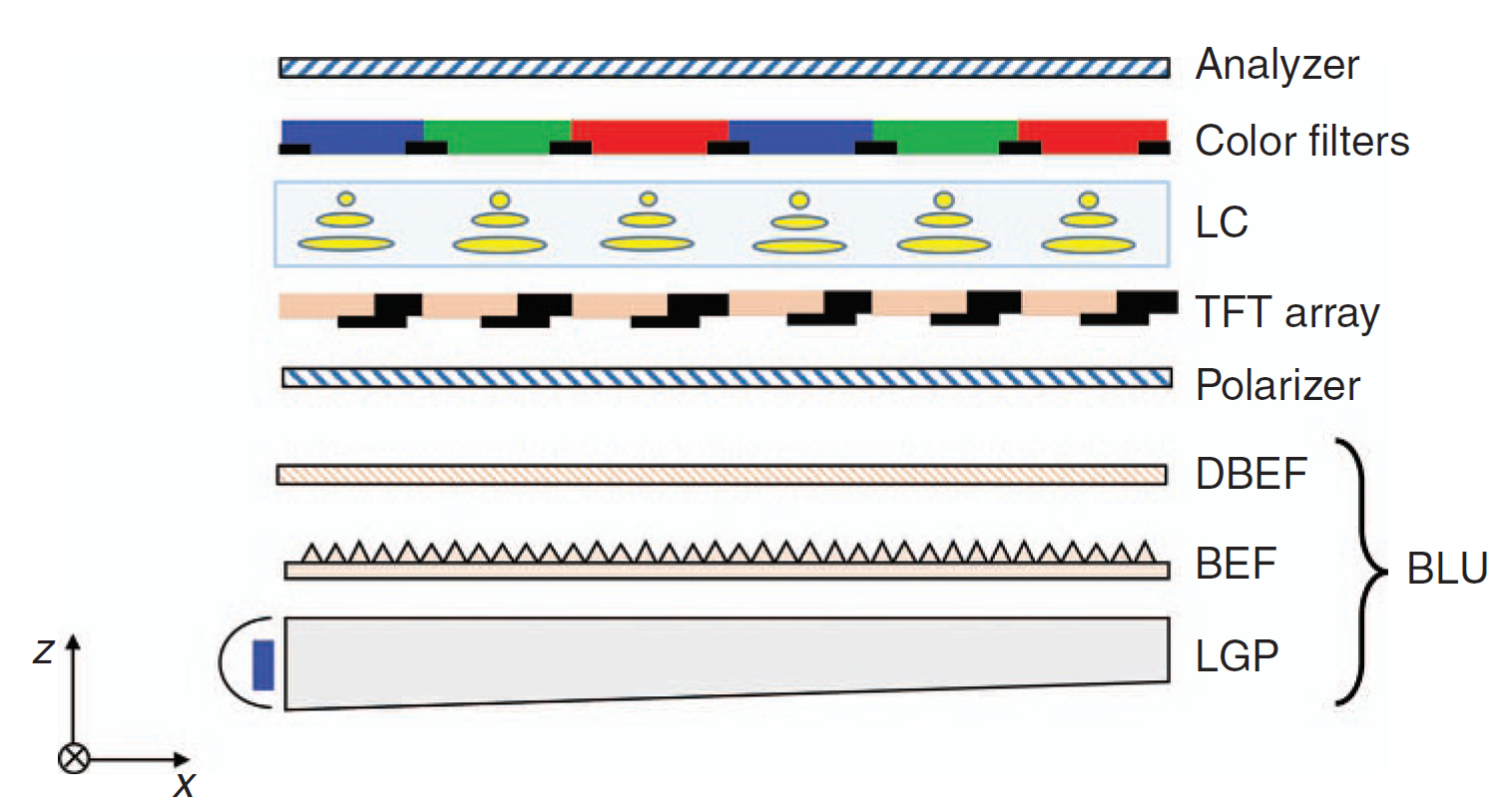
A TFT is a type of transistor used in active-matrix LCD screens. TFT LCD screens use a separate transistor to control each pixel in the display. They allow the electrical current that controls each pixel to turn on and off quickly, which decreases response time and makes on-screen motion smoother. TFT LCDs are often used as computer monitors, televisions, mobile phone screens, and other flat-panel color displays.
The name "Thin Film Transistor" is derived from the manufacturing process. The manufacturer first applies thin films of a semiconductor (like amorphous silicon) and dielectric materials to a flat, non-conductive surface (like glass). Unneeded silicon is etched away, leaving only a grid of transistors and the transparent glass surface. These transistor panels are thin enough to fit between a polarized backlight and the layer of liquid crystals. These transistors apply an electrical current to the liquid crystals, altering their arrangement to block light in certain ways. The light then passes through other layers of the screen, including a color filter and polarized light filter, to display the final image.
Not all TFT LCD screen are made the same. There are several types of TFT panels, made by distinct methods, and with different performance characteristics. The two most common types are TN and IPS.
Twisted Nematic (TN) panels contain liquid crystals that twist as an electric current is applied. As the crystals twist, they allow varying amounts of polarized light to pass through. TN panels are the easiest type of TFT LCD to produce and offer the quickest response times. However, TN panels don"t display colors as accurately as other types of panels, particularly when viewed at an angle.
TRIZ, Russian acronym for "Theory of Inventive Problem Solving" is now becoming well known and being applied to the various engineering field in the Western and Asian countries. However, as only few successful examples on the problems in microelectronics are found in the literature. Therefore, the previous work on a small high resolution TFT-LCD (Thin Film Transistor Addressed Liquid Crystal Display) for projection display was investigated and analyzed from TRIZ point of view to see its usefulness to solve engineering problems in the microelectronics field.There was a conflict between existence of spacers necessary to keep cell gap of LCD (Liquid crystal Display) uniform, which is related to the transmission uniformity of the screen, and serious degradation of image quality due to existence of spacers, which are recognized as a bright spot on the dark screen, as the spacer size compared with pixel size becomes large. The problem was analyzed by the TRIZ framework, and the solution to the above conflict in manufacturing an LCD for projection display was found systematically by utilizing TRIZ framework.Also, further problem of conflicting features between “productivity” and “manufacturing precision” and several other issues in production of small TFT-LCD for projection displays are studied by using TRIZ framework, and get to a new device structure and fabrication process as a FIR (Final Ideal Result). In this approach, TFT array formed on the Si wafer is transferred onto the other substrate such as glass with high strain-point, Eagle XG, and AN100, etc. used in the TFT-LCD industry. The hydrogen exfoliation technique and fragile layer are exploited to transfer device layers to the other substrates. In the present proposal, TFTs are perfect single crystal, in contrast to the poly-Si TFT used in the current LCDs, and this eliminates issue of characteristics variation stemming from the grain boundary of Poly-Si.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey