16x2 lcd module jhd162a data sheet in stock
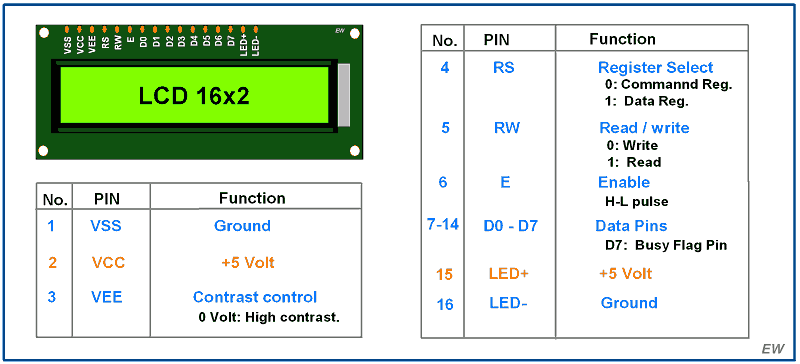
16×2 LCD is named so because; it has 16 Columns and 2 Rows. There are a lot of combinations available like, 8×1, 8×2, 10×2, 16×1, etc. But the most used one is the 16*2 LCD, hence we are using it here.
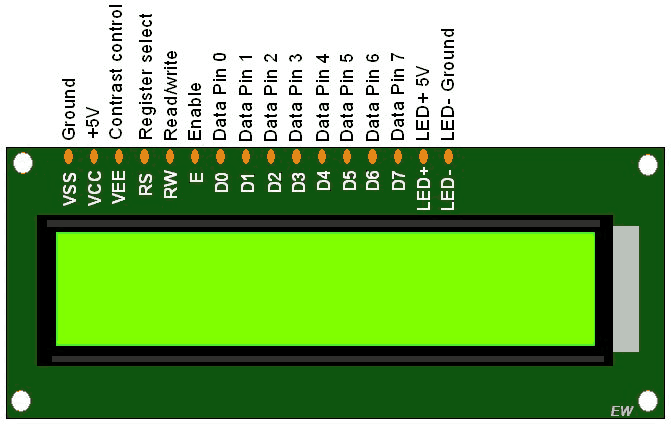
All the above mentioned LCD display will have 16 Pins and the programming approach is also the same and hence the choice is left to you. Below is the Pinout and Pin Description of 16x2 LCD Module:
These black circles consist of an interface IC and its associated components to help us use this LCD with the MCU. Because our LCD is a 16*2 Dot matrix LCD and so it will have (16*2=32) 32 characters in total and each character will be made of 5*8 Pixel Dots. A Single character with all its Pixels enabled is shown in the below picture.
So Now, we know that each character has (5*8=40) 40 Pixels and for 32 Characters we will have (32*40) 1280 Pixels. Further, the LCD should also be instructed about the Position of the Pixels.
It will be a hectic task to handle everything with the help of MCU, hence an Interface IC like HD44780 is used, which is mounted on LCD Module itself. The function of this IC is to get the Commands and Data from the MCU and process them to display meaningful information onto our LCD Screen.
The LCD can work in two different modes, namely the 4-bit mode and the 8-bit mode. In 4 bit mode we send the data nibble by nibble, first upper nibble and then lower nibble. For those of you who don’t know what a nibble is: a nibble is a group of four bits, so the lower four bits (D0-D3) of a byte form the lower nibble while the upper four bits (D4-D7) of a byte form the higher nibble. This enables us to send 8 bit data.
Now you must have guessed it, Yes 8-bit mode is faster and flawless than 4-bit mode. But the major drawback is that it needs 8 data lines connected to the microcontroller. This will make us run out of I/O pins on our MCU, so 4-bit mode is widely used. No control pins are used to set these modes. It"s just the way of programming that change.
As said, the LCD itself consists of an Interface IC. The MCU can either read or write to this interface IC. Most of the times we will be just writing to the IC, since reading will make it more complex and such scenarios are very rare. Information like position of cursor, status completion interrupts etc. can be read if required, but it is out of the scope of this tutorial.
The Interface IC present in most of the LCD is HD44780U,in order to program our LCD we should learn the complete datasheet of the IC. The datasheet is given here.
There are some preset commands instructions in LCD, which we need to send to LCD through some microcontroller. Some important command instructions are given below:

16x2 LCD modules are very commonly used in most embedded projects, the reason being its cheap price, availability, programmer friendly and available educational resources.
16×2 LCD is named so because; it has 16 Columns and 2 Rows. There are a lot of combinations available like, 8×1, 8×2, 10×2, 16×1, etc. but the most used one is the 16×2 LCD. So, it will have (16×2=32) 32 characters in total and each character will be made of 5×8 Pixel Dots. A Single character with all its Pixels is shown in the below picture.
Now, we know that each character has (5×8=40) 40 Pixels and for 32 Characters we will have (32×40) 1280 Pixels. Further, the LCD should also be instructed about the Position of the Pixels. Hence it will be a hectic task to handle everything with the help of MCU, hence an Interface IC like HD44780is used, which is mounted on the backside of the LCD Module itself. The function of this IC is to get the Commands and Data from the MCU and process them to display meaningful information onto our LCD Screen. You can learn how to interface an LCD using the above mentioned links. If you are an advanced programmer and would like to create your own library for interfacing your Microcontroller with this LCD module then you have to understand the HD44780 IC working and commands which can be found its datasheet.
16×2 LCD is a basic 16 character by 2 line display Yellow/Green Backlight. Utilizes the extremely most common HD44780 parallel interface chipset (datasheet). Even more, it has JHD162A Compatible Pinout Diagram, and Command Interface code is freely available. Finally, You will need 7 general I/O pins (If used in 4-bit Mode) to interface to this LCD screen. it also includes an LED back-light.
Features of 16×2 Display LCD:Commonly Used in Student Project, College, copiers, fax machines, laser printers, industrial test equipment, networking equipment such as routers and storage devices

The 16x2 is the most commonly used LCD display module. It can display 16 characters in a column for 2 rows thus a total of 32 characters. The characters can either be number, alphabets or symbol. It is also possible to create your own custom character and display it if required. The LCD has the HD44780U display driver IC which is responsible for displaying characters on the LCD
This 16x2 LCD display has a blue background and back light which makes it unique and more visible than the commonly used green color. If you need the green backlight you can use this Green Backlight LCD. The required supply voltage is from 4.7V to 5.3V and the LCD can operate either in 8-bit mode or in 4-bit mode allowing you to save more GPIO pins on the controller side. The current consumption is about 1mA without the back light.
The 16x2 LCD pinout diagram is shown below. As you can see the module has (from right) two power pins Vss and Vcc to power the LCD. Typically Vss should be connected to ground and Vcc to 5V, but the LCD can also operate from voltage between 4.7V to 5.3V. Next, we have the control pins namely Contrast (VEE), Register Select (RS), Read/Write (R/W) and Enable (E). The Contrast pin is used to set the contrast (visibility) of the characters, normally it is connected to a 10k potentiometer so that the contrast can be adjusted. The Read/Write pin will be grounded in most cases because we will only be writing characters to the LCD and not read anything from it. The Register Select (RS) and Enable pin (E) pin are the control pins of the LCD and will be connected to the digital pins GPIO pins of the microcontroller. These pins are used to instruct the LCD where place a character when to clear it etc.
From DB0 to DB7 we have our eight Data Pins which are used to send information about the characters that have to be displayed on the LCD. The LCD can operate in two different modes, in the 4-bit Modeonly pins DB4 to DB7 will be used and the pins DB0 to DB3 will be left idle. In 8-bit Mode, all the eight-pin DB0 to DB7 will be used. Most commonly the 4-bit mode is preferred since it uses only 4 Data pins and thus reduces complexity and GPIO pin requirement on the microcontroller.Finally, we have the LED+ and LED- pins which are used to power the backlight LED inside our Display module. Normally the LED+ pin is connected to 5V power through a 100 ohm current limiting resistor and the LED- pin is connected to Ground.

We come across Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) displays everywhere around us. Computers, calculators, television sets, mobile phones, and digital watches use some kind of display to display the time.
An LCD screen is an electronic display module that uses liquid crystal to produce a visible image. The 16×2 LCD display is a very basic module commonly used in DIYs and circuits. The 16×2 translates a display of 16 characters per line in 2 such lines. In this LCD, each character is displayed in a 5×7 pixel matrix.
Contrast adjustment; the best way is to use a variable resistor such as a potentiometer. The output of the potentiometer is connected to this pin. Rotate the potentiometer knob forward and backward to adjust the LCD contrast.
Sends data to data pins when a high to low pulse is given; Extra voltage push is required to execute the instruction and EN(enable) signal is used for this purpose. Usually, we set en=0, when we want to execute the instruction we make it high en=1 for some milliseconds. After this we again make it ground that is, en=0.
A 16X2 LCD has two registers, namely, command and data. The register select is used to switch from one register to other. RS=0 for the command register, whereas RS=1 for the data register.
Command Register: The command register stores the command instructions given to the LCD. A command is an instruction given to an LCD to do a predefined task. Examples like:
Data Register: The data register stores the data to be displayed on the LCD. The data is the ASCII value of the character to be displayed on the LCD. When we send data to LCD, it goes to the data register and is processed there. When RS=1, the data register is selected.
Generating custom characters on LCD is not very hard. It requires knowledge about the custom-generated random access memory (CG-RAM) of the LCD and the LCD chip controller. Most LCDs contain a Hitachi HD4478 controller.
CG-RAM address starts from 0x40 (Hexadecimal) or 64 in decimal. We can generate custom characters at these addresses. Once we generate our characters at these addresses, we can print them by just sending commands to the LCD. Character addresses and printing commands are below.
LCD modules are very important in many Arduino-based embedded system designs to improve the user interface of the system. Interfacing with Arduino gives the programmer more freedom to customize the code easily. Any cost-effective Arduino board, a 16X2 character LCD display, jumper wires, and a breadboard are sufficient enough to build the circuit. The interfacing of Arduino to LCD display is below.
The combination of an LCD and Arduino yields several projects, the most simple one being LCD to display the LED brightness. All we need for this circuit is an LCD, Arduino, breadboard, a resistor, potentiometer, LED, and some jumper cables. The circuit connections are below.

I have a written a header file for routines which will used frequently and every time I want to interface with LCD using Atmega 16a I use this header file.
Then when I reset later it displays random variables(infact I can see that the second line doesnt change at all, it means that the screen is not cleared but a command was written to LCD_init() to clear screen)

In this project we will only be using a LCD, Arduino uno, jumper wires to display text on the LCD. We will use the digital pin 6 to control the contrast value of the LCD. The function to display text on the lcd will be | lcd.print (“Your text here”) |
Nowadays, we always use the devices which are made up of LCDs such as CD players, DVD players, digital watches, computers, etc. These are commonly used in the screen industries to replace the utilization of CRTs. Cathode Ray Tubes use huge power when compared with LCDs, and CRTs heavier as well as bigger. These devices are thinner as well power consumption is extremely less. The LCD 16×2 working principle is, it blocks the light rather than dissipate. This article discusses an overview of LCD 16X2, pin configuration and its working.
The term LCD stands for liquid crystal display. It is one kind of electronic display module used in an extensive range of applications like various circuits & devices like mobile phones, calculators, computers, TV sets, etc. These displays are mainly preferred for multi-segment light-emitting diodes and seven segments. The main benefits of using this module are inexpensive; simply programmable, animations, and there are no limitations for displaying custom characters, special and even animations, etc.
Pin4 (Register Select/Control Pin): This pin toggles among command or data register, used to connect a microcontroller unit pin and obtains either 0 or 1(0 = data mode, and 1 = command mode).
Pins 7-14 (Data Pins): These pins are used to send data to the display. These pins are connected in two-wire modes like 4-wire mode and 8-wire mode. In 4-wire mode, only four pins are connected to the microcontroller unit like 0 to 3, whereas in 8-wire mode, 8-pins are connected to microcontroller unit like 0 to 7.
A 16×2 LCD has two registers like data register and command register. The RS (register select) is mainly used to change from one register to another. When the register set is ‘0’, then it is known as command register. Similarly, when the register set is ‘1’, then it is known as data register.
The main function of the data register is to store the information which is to be exhibited on the LCD screen. Here, the ASCII value of the character is the information which is to be exhibited on the screen of LCD. Whenever we send the information to LCD, it transmits to the data register, and then the process will be starting there. When register set =1, then the data register will be selected.
Thus, this is all about LCD 16×2 datasheet, which includes what is a 16X2 LCD, pin configuration, working principle, and its applications. The main advantages of this LCD device include power consumption is less and low cost. The main disadvantages of this LCD device include it occupies a large area, slow devices and also lifespan of these devices will be reduced due to direct current. So these LCDs use AC supply with less than 500Hz frequency. Here is a question for you, what are the applications of LCD?

In this project, we will have brief discussion on how to interface 16×2 LCD module to AT89C51, which is an 8051 family microcontroller. We use LCD display for the displaying messages in a more interactive way to operate the system or displaying error messages etc. Interfacing 16×2 LCD with 8051 microcontroller is very easy if you understanding the working of LCD.
16×2 Liquid Crystal Display which will display the 32 characters at a time in two rows (16 characters in one row). Each character in the display is of size 5×7 pixel matrix. This matrix differs for different 16×2 LCD modules, if you take JHD162A, this matrix goes to 5×8. There are 16 pins in the LCD module, the pin configuration us given below
4RSRS is the register select pin used to write display data to the LCD (characters), this pin has to be high when writing the data to the LCD. During the initializing sequence and other commands this pin should low.
Commands:There are some preset commands which will do a specific task in the LCD. These commands are very important for displaying data in LCD. The list of commands given below:
The data pins of the LCD are connected to PORT0 (first, the PORT0 pins must be pulled-HIGH with the help of a 1KΩ Resistor Pack). RS and E are connected to PORT2 pins P2.0 and P2.1.
The programs given below will use above functions and display the complete string which is given by the programmer to display the data. We have provided two demo codes working properly and easy to understand.

The Displaytech 162J series is a lineup of 16x2 character LCD modules. These modules have an 80x36 mm outer dimension with 66x16 mm viewing area on the display. The 162J 16x2 LCD displays are available in STN or FSTN LCD modes with or without an LED backlight. The backlight color options include yellow green, white, blue, pure green, or amber color. Get a free quote direct from Displaytech for a 16x2 character LCD display from the 162J series.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey