how to build an lcd display manufacturer

Liquid Crystal Displays or more commonly known as LCDs are one of the most common electronic components which help us interact with an equipment or a device. Most personal portable equipment and even gigantic industrial equipment utilize a custom segment display to display data. For many portable consumer electronics, a segment LCD display is one of the biggest contributors to the overall cost of the device, hence designing a custom segment display can drive the cost down while also utilizing the display area in the most optimum manner. These displays have the lowest cost per piece, low power requirements, and a low tooling fee too.
At first thought, designing a custom segment LCD might look like a Herculean task, but trust me that it is easier than it seems. In this article, we have summarised and compared the display types and available technologies which are required to construct a custom segment LCD. We have also provided a flowchart that can act as a step-by-step guide while you design your own custom LCD. We have also provided the process we followed, a require gathering sheet we used for communicating our needs to the manufacturer, and a few other data and the quotation we received from the manufacturer.
Icons: A silhouette of any shape can be placed on the glass which enhances the ability to display data. For example, a symbol of a heart can be made to denote heart rate or an icon for a low battery to show that the battery needs to be charged. Icons are counted as a single pixel or segment and can give a lot more details than similar-sized text.
LCD Bias– It denotes the number of different voltage levels used in driving the segments, static drives (explained later in this article) only have 2 voltage levels or 2 bias voltage while multiplex drives have multiple voltage levels. For example, 1/3 will have 4 bias voltages.
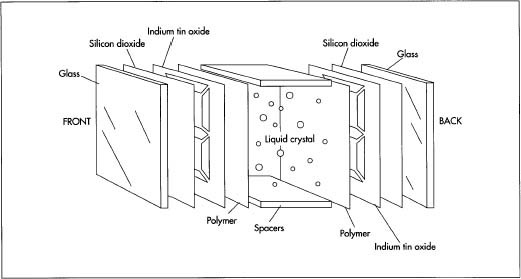
LCDs utilizes the light modulating properties of liquid crystals which can be observed by using polarizing filters. Polarizing filters are special materials that have their molecules aligned in the same direction. If the light waves passing through polarisers have the same orientation as the filter, then the molecules of lights are absorbed by the filter, hence reducing the intensity of light passing through it, making it visible.
In Layman’s language, when an electric current is applied to the electrodes, i.e. to the segment line and common line, it twists the Liquid Crystals w.r.t to the polarizing filter, obstructing the light in that particular area as shown in the figure below. Hence, that area becomes darker and prominent.
A custom LCD is important for maximizing the efficiency of the display area by adding custom symbols and characters. It also helps in reducing the cost and improving energy efficiency of the product. A higher number of custom symbols and specified placement of numerical and alphanumerical characters make the display more informative and readable for the user. This makes it look better than the plain old boring displays we get in the market. Furthermore, we can specify the viewing angle, contrast, and other specifications which can increase durability or give a better value for money for our intended usage. A typical Custom Segment display is shown below, we will also show you how to design and fabricate the same further in the article.
The LCD display doesn’t emit any light of its own, therefore it requires an external source of illumination or reflector to be readable in dark environments.
While designing a custom segment LCD display, we have the leverage of choosing a lot of parameters that affect the final product. From the color of the display to the illumination technique and color of illumination as well as the type of input pins. Some important considerations we need to take while designing a custom 7 segment display are - the type of display, i.e. positive or negative, illumination method, driving technique, polarising type, and connection method. All these design criteria are explained below:
Positive and negative displays can be easily distinguished by the colour of the background and characters. Some common differences between the positive and negative displays are:
So, which one should you choose? When the displays are to be used in areas with higher ambient light, we should select positive segment LCD display as it has better visibility than negative segment LCD displays without using a backlight.
As we know that LED displays don’t emit any light, hence to illuminate it and make it visible in a dark environment, we can use different methods of illumination. The most common LCD Illumination methods are compared below:
For displays that need to be used for budget-friendly devices that should be small and rugged, LED lights are preferred for the displays due to the high durability and low cost of operations. For high brightness, CCFL and Incandescent lights can be used.
A polarizer film is the most important component of an LCD display, which makes it possible to display characters by controlling the light. There are 3 types of polarizers that can be used in the LCD display, the properties and difference are given below:
If your products need to be used with a switchable backlight, then trans-reflective reflectors are best to be used for front reflectors. If the device has to be used without backlight, then we can select a reflective polarizer for the back-panel as it gives the best contrast ratio.
Displays can be categorized into two types, passive displays, and active display, passive displays are simpler to construct as they have 2 connections at each segment, the conductors comprise of an Indium Tin Oxide to create an image, whereas the active displays use thin-film transistors (TFT) arranged in a grid. The name is due to its ability to control each pixel individually.
If your displays have fewer segments, then static LCD drive is preferred as it is easier to control and cheaper to construct, and has a better contrast ratio. But let’s say that if the number of segments in the display are more than 30-40 then a multiplex LCD drive should be preferred as it has multiple common pins, hence reducing the total number of pins required to drive the display.
Choosing a connector type!!! For the prototyping phase or if you need to connect your LCD display on a Microcontroller directly, a pin type connector is the best and most economical option you have. If you need to connect your LCD display in a final product with a high volume of production which also requires to be extremely durable, but at the same time should not take up a lot of space, a Flex type LCD Connector will work best for you
LCDs have limited viewing angles and when seen from an angle they lose contrast and are difficult to be observed. The viewing angle is defined by the angles perpendicular to the center of the display towards its right, left, up, and down which are denoted by the notations 3:00, 9:00, 12:00, and 6:00 respectively. The viewing angle of LCD can be defined as the angle w.r.t. to the bias angle at which the contrast of segments is legible.
To improve the viewing angle in an LCD, a Bias is incorporated in the design which shifts the nominal viewing angle with an offset. Another technique is to increase the Voltage, it affects the bias angle, making the display crisper when viewed from a direction.
For example, the viewing angle of a TN type TFT LCD is 45-65 degrees. Extra-wide polarising film (EWP) can increase the viewing angle by 10 degrees, using an O film polariser can make the viewing angles 75 degrees but these come at a cost of reduced contrast.
Anti-glare filters are bonded with the top polarising filters using adhesive. It improves the viewability by re-directing light waves so they don’t reflect back towards the viewer thus reducing glare. Newer materials are capable of reducing the front glare by up to less than 0.3%.
LCD Control chip or LCD driver chips can be mounted on the flex cable, display, or externally on a PCB. The placement of LCD control chip can affect the cost and size of the display. The 2 most common methods of chip placement are-Chip of Board (COB)and Chip on Glass(COG) which are described below:
COG can be used as it is cheaper and makes the assembly process simpler, but if the dimensions are a constraint, then the COB is also a viable option.
We planned to design an air quality monitoring system for which we needed a custom segment LCD panel for an air quality monitoring device. Our product needs to display the following data: 2.5-micron and 10-micron particulate matter (PM) suspended in the air; the units should be in parts per million (PPM). CO2 in the air in PPM along with total volatile organic compounds present in the air in parts per billion (PPB). To make the product more usable, we included time in 24-hour format, Temperature in ºC, Battery status, loudspeaker status, Bluetooth status, and Wi-Fi status. And for some personal touch, we also added how good the air quality in the room is by using 3 different smileys.
We realized that it was impossible to provide all these data in a generic LCD available in the market, thus decided to build a custom LCD for our project.
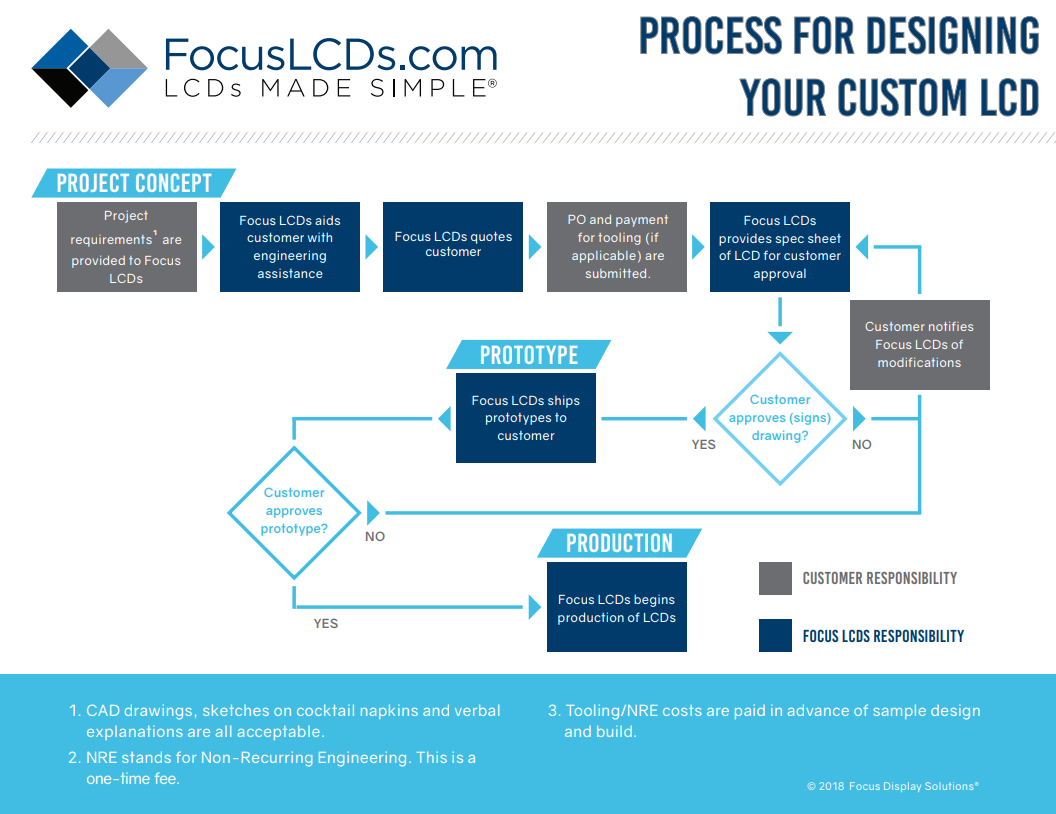
A step-by-step flowchart is shown below to walk you through each and every step of selecting components and getting your custom segment LCD manufactured.
We started by listing down our requirements and drew a mock-up of the display on paper. After finalizing the placement of all the segments and icons on the prototype sketch of the display, we then decided which all icons and segments have to be kept on for the whole time and which needs to be driven. Realizing that there are too many segments, characters and icons, hence we selected a multiplex drive with 8 common pins which helped us bring down the total pins from an estimated 180 pins to less than 40 pins.
Since the device was meant to be used inside houses and offices, which are more often than not well lit and protected from environmental conditions, we opted for a positive mode display. For superior contrast ratio and better viewing angle, we chose a Film Super Twisted Nematic Display (FSTN) with a drive condition of 1/8 Duty and bias of 1/4.
Usually, the displays are mounted at a height of 4.5 feet from the ground, thus the viewing direction was selected to be 12"O clock with an operating frequency of 64Hz. We selected a Transmissive polarizer for the front glass and a reflective polarizer for the rear glass so that the natural light can pass through the front panel and the display can achieve the maximum contrast without the need for backlighting and we opted for the pin type connectors as they are easy for prototyping and are suitable for harsh environment with a lot of vibrations and shocks which best suited our purpose.
In the above image of a custom display design, we sent to the manufacturer, the red lines over multiple characters indicate that all these are considered as a single segment. For the sake of simplicity, we added test like T, S, U, B to denote Text, Symbols, Units, and Battery respectively. These characters were followed by numbers to simplify communication between us and the manufacturer. For example, if we needed any particular text or symbol to remain on, we can easily specify that to the manufacturer by using the corresponding text for that segment.
We mailed our requirements to multiple LCD manufacturers, (you will find a lot of LCD manufacturers on the Internet). Most LCD manufacturers have competitive pricing, and reply within a week. A sample requirement sheet is shown above which a customer needs to fill to specify all the details to the manufacturer.
This is a sample Custom Segment LCD quotation we got from one of the manufacturers. As you can see, the cost is based on the quantity. Higher the quantity, lower the cost. Apart from the cost per quantity, there is one more component called tooling fees. Tooling fee is a one-time fee charged by the manufacturer. It is for the technical design, support, and customization of the product. Customization of PCB or tooling of LCD can drive the tooling price higher or lower.
The tooling time and cost depend on how detailed and accurate designs you sent to the manufacturer. They then send the exact dimensions and technical details of the product they will be manufacturing. Once you confirm the design, they manufacture and ship the product which might take 4-8 weeks to arrive depending on the size of the order and mode of transportation selected.
A custom segment LCD can help you personalize your product while also saving the overall cost of your product. The whole process will take you around 2-3 months, which will include the designing phase, prototyping phase, and getting your custom segment LCDs delivered to your doorstep. Higher ordering quantity will reduce the cost per piece of each unit, thus driving down the cost of your final product.

New Vision Display is a custom LCD display manufacturer serving OEMs across diverse markets. One of the things that sets us apart from other LCD screen manufacturers is the diversity of products and customizations we offer. Our LCD portfolio ranges from low-cost monochrome LCDs to high-resolution, high-brightness color TFT LCDs – and pretty much everything in between. We also have extensive experience integrating LCD screen displays into complete assemblies with touch and cover lens.
Sunlight readable, ultra-low power, bistable (“paper-like”) LCDs. Automotive grade, wide operating/storage temperatures, and wide viewing angles. Low tooling costs.
Among the many advantages of working with NVD as your LCD screen manufacturer is the extensive technical expertise of our engineering team. From concept to product, our sales and technical staff provide expert recommendations and attentive support to ensure the right solution for your project.
In addition, our extensive technology portfolio and manufacturing capabilities enable us to deliver high-quality products that meet the unique specifications of any application. To learn more about what makes us the display manufacturer for your needs, get in touch with us today.
As a leading LCD panel manufacturer, NVD manufactures custom LCD display solutions for a variety of end-user applications: Medical devices, industrial equipment, household appliances, consumer electronics, and many others. Our state-of-the-art LCD factories are equipped to build custom LCDs for optimal performance in even the most challenging environments. Whether your product will be used in the great outdoors or a hospital operating room, we can build the right custom LCD solution for your needs. Learn more about the markets we serve below.
Ready to get started or learn more about how we can help your business? Call us at +1-855-848-1332 or fill out the form below and a company representative will be in touch within 1 business day.
If you have ever wondered what it took to make your own custom graphic LCD from scratch, this video from [Applied Science] is worth a watch. It’s concise and to the point, while still telling you what you need to know should you be interested in rolling your own. There is also a related video which goes into much more detail about experimenting with LCD technology.
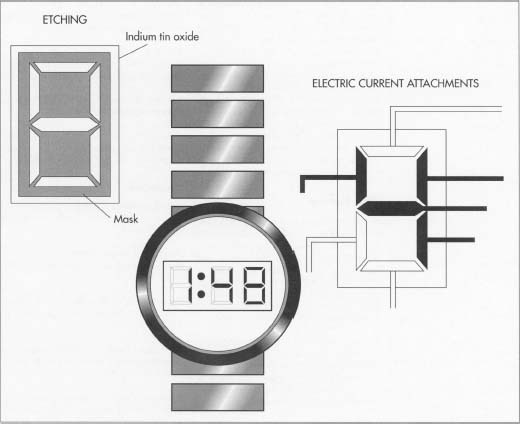
[Applied Science] used microscope slides and parts purchased online to make an LCD that displays a custom graphic when activated. The only step that home experimenters might have trouble following is coating the glass slides with a clear conductive layer, which in the video is done via a process called sputtering to deposit a thin film. You don’t need to do this yourself, though. Pre-coated glass is readily available online. (Search for Indium-Tin Oxide or ‘ITO’ coated glass.)
The LCD consists of a layer of liquid crystal suspended between two layers of conductive glass. An electrical field is used to change the orientation of crystals in the suspension, which modulate the light passing through them. Polarizing filters result in a sharp contrast and therefore a visible image. To show a particular shape, some of the conductive coating is removed from one of the layers in the shape of the desired image. The process [Applied Science] uses to do this is nearly identical to etching a custom PCB.
Parts of LCD technology can be quite hackable. Neither of these videos are brand-new, either. Have any of you taken on the challenge of DIY LCD displays? We’ve seen experiments with electrochromatic glass using old LCD displays, as well as experiments in playing with polarized light to hide secret messages on LCD screens.

Important technical improvements of LCD, such as LED backlighting and wide viewing Angle, are directly related to LCD. And account for an LCD display 80% of the cost of the LCD panel, enough to show that the LCD panel is the core part of the entire display, the quality of the LCD panel, can be said to directly determine the quality of an LCD display.
The production of civil LCD displays is just an assembly process. The LCD panel, the main control circuit, shell, and other parts of the main assembly, basically will not have too complex technical problems.
Does this mean that LCDS are low-tech products? In fact, it is not. The production and manufacturing process of the LCD panels is very complicated, requiring at least 300 process processes. The whole process needs to be carried out in a dust-free environment and with precise technology.
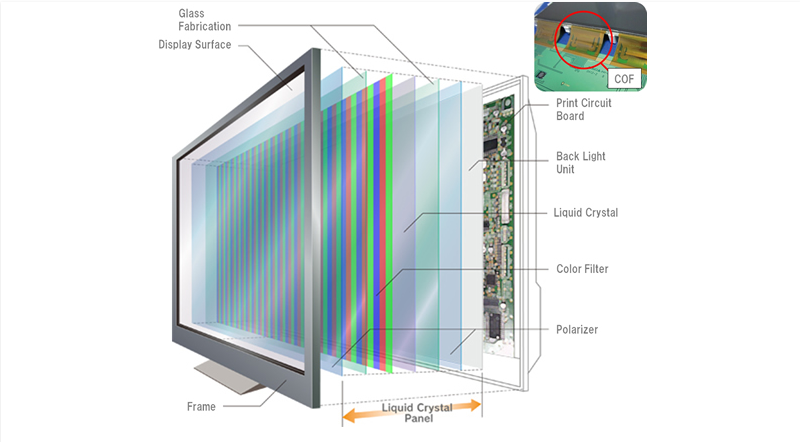
The general structure of the LCD panel is not very complex, now the structure of the LCD panel is divided into two parts: the LCD panel and the backlight system.
Due to the LCD does not shine, so you need to use another light source to illuminate, the function of the backlight system is to this, but currently used CCFL lamp or LED backlight, don’t have the characteristics of the surface light source, so you need to guide plate, spreadsheet components, such as linear or point sources of light evenly across the surface, in order to make the entire LCD panel on the differences of luminous intensity is the same, but it is very difficult, to achieve the ideal state can be to try to reduce brightness non-uniformity, the backlight system has a lot to the test of design and workmanship.
In addition, there is a driving IC and printed circuit board beside the LCD panel, which is mainly used to control the rotation of LCD molecules in the LCD panel and the transmission of display signals. The LCD plate is thin and translucent without electricity. It is roughly shaped like a sandwich, with an LCD sandwiched between a layer of TFT glass and a layer of colored filters.
LCD with light refraction properties of solid crystals, with fluid flow characteristics at the same time, under the drive of the electrode, can be arranged in a way that, in accordance with the master want to control the strength of the light through, and then on the color filter, through the red, green, blue three colors of each pixel toning, eventually get the full-screen image.
According to the functional division, the LCD panel can be divided into the LCD panel and the backlight system. However, to produce an LCD panel, it needs to go through three complicated processes, namely, the manufacturing process of the front segment Array,the manufacturing process of the middle segment Cell, and the assembly of the rear segment module. Today we will be here, for you in detail to introduce the production of the LCD panel manufacturing process.
The manufacturing process of the LCD panel Array is mainly composed of four parts: film, yellow light, etch and peel film. If we just look at it in this way, many netizens do not understand the specific meaning of these four steps and why they do so.
First of all, the motion and arrangement of LCD molecules need electrons to drive them. Therefore, on the TFT glass, the carrier of LCD, there must be conductive parts to control the motion of LCD. In this case, we use ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) to do this.ITO is transparent and also acts as a thin-film conductive crystal so that it doesn’t block the backlight.
The different arrangement of LCD molecules and the rapid motion change can ensure that each pixel displays the corresponding color accurately and the image changes accurately and quickly, which requires the precision of LCD molecule control.ITO film needs special treatment, just like printing the circuit on the PCB board, drawing the conductive circuit on the whole LCD board.
First, the ITO film layer needs to be deposited on the TFT glass, so that there is a smooth and uniform ITO film on the whole TFT glass. Then, using ionized water, the ITO glass is cleaned and ready for the next step.
Next, a photoresist is applied to the glass on which ITO film is deposited, and a uniform photoresist layer is formed on the ITO glass. After baking for a period of time, the solvent of the photoresist was partially volatilized to increase the adhesion of the photoresist material to the ITO glass.
Ultraviolet light (UV) is used to illuminate the surface of the photoresist through a pre-made electrode pattern mask, which causes the photoresist layer to react. The photoresist is selectively exposed under ultraviolet light by covering the photoresist on the glass coated with the photoresist.
The exposed part of the photoresist is then washed away with the developer, leaving only the unexposed part, and the dissolved photoresist is then washed away with deionized water.
Then etch off the ITO film without photoresist covering with appropriate acid etching solution, and only retain the ITO film under the photoresist. ITO glass is conductive glass (In2O3 and SnO2). The ITO film not covered by photoresist is easy to react with acid, while the ITO film covered by photoresist can be retained to obtain the corresponding wire electrode.
Stripping: High concentration of alkali solution (NaOH solution) is used as a stripping solution to peel off the remaining photoresist on the glass so that ITO glass can form ITO graphics exactly consistent with the photolithography mask.
Rinse the basic label of glass with an organic solution and remove the photolithographic tape after reaction to keep the glass clean. This completes the first thin-film conductive crystal process, which generally requires at least five identical processes to form a complex and sophisticated pattern of electrodes on the glass.
This completes the previous Array process. It is not difficult to see from the whole process that ITO film is deposited, photoresist coated, exposed, developed, and etched on TFT glass, and finally, ITO electrode pattern designed in the early stage is formed on TFT glass to control the movement of LCD molecules on the glass. The general steps of the whole production process are not complicated, but the technical details and precautions are very complicated, so we will not introduce them here. Interested friends can consult relevant materials by themselves.
The glass that the LCD board uses makes a craft also very exquisite. (The manufacturing process flow of the LCD display screen)At present, the world’s largest LCD panel glass, mainly by the United States Corning, Japan Asahi glass manufacturers, located in the upstream of the production of LCD panel, these manufacturers have mastered the glass production technology patents. A few months ago, the earthquake caused a corning glass furnace shutdown incident, which has caused a certain impact on the LCD panel industry, you can see its position in the industry.
As mentioned earlier, the LCD panel is structured like a sandwich, with an LCD sandwiched between the lower TFT glass and the upper color filter. The terminal Cell process in LCD panel manufacturing involves the TFT glass being glued to the top and bottom of a colored filter, but this is not a simple bonding process that requires a lot of technical detail.
As you can see from the figure above, the glass is divided into 6 pieces of the same size. In other words, the LCD made from this glass is finally cut into 6 pieces, and the size of each piece is the final size. When the glass is cast, the specifications and sizes of each glass have been designed in advance.
Then, the organic polymer directional material is coated on the surface of the glass, that is, a uniform directional layer is applied to the appropriate position of ITO glass by the method of selective coating. Meanwhile, the directional layer is cured.
Directional friction:Flannelette material is used to rub the surface of the layer in a specific direction so that the LCD molecules can be arranged along the friction direction of the aligned layer in the future to ensure the consistency of the arrangement of LCD molecules. After the alignment friction, there will be some contaminants such as flannelette thread, which need to be washed away through a special cleaning process.
After the TFT glass substrate is cleaned, a sealant coating is applied to allow the TFT glass substrate to be bonded to the color filter and to prevent LCD outflow.
Finally, the conductive adhesive is applied to the frame in the bonding direction of the glass of the color filter to ensure that external electrons can flow into the LCD layer. Then, according to the bonding mark on the TFT glass substrate and the color filter, two pieces of glass are bonded together, and the bonding material is solidified at high temperatures to make the upper and lower glasses fit statically.
Color filters are very important components of LCD panels. Manufacturers of color filters, like glass substrate manufacturers, are upstream of LCD panel manufacturers. Their oversupply or undersupply can directly affect the production schedule of LCD panels and indirectly affect the end market.
As can be seen from the above figure, each LCD panel is left with two edges after cutting. What is it used for? You can find the answer in the later module process
Finally, a polarizer is placed on both sides of each LCD substrate, with the horizontal polarizer facing outwards and the vertical polarizer facing inwards.
A polarizer is an optical plate that allows only light from a certain direction to pass through. It is an optical element that converts natural light into straight polarized light. The mechanism of action is to make the vertical direction light pass through the straight incident light after passing through the vertical polarizer, and the other horizontal direction light is absorbed, or use reflection and scattering and other effects to make its shade.
When making LCD panel, must up and down each use one, and presents the alternating direction, when has the electric field and does not have the electric field, causes the light to produce the phase difference and to present the light and dark state, uses in the display subtitle or the pattern.
The rear Module manufacturing process is mainly the integration of the drive IC pressing of the LCD substrate and the printed circuit board. This part can transmit the display signal received from the main control circuit to the drive IC to drive the LCD molecules to rotate and display the image. In addition, the backlight part will be integrated with the LCD substrate at this stage, and the complete LCD panel is completed.
Firstly, the heteroconductive adhesive is pressed on the two edges, which allows external electrons to enter the LCD substrate layer and acts as a bridge for electronic transmission
Next is the drive IC press. The main function of the drive IC is to output the required voltage to each pixel and control the degree of torsion of the LCD molecules. The drive IC is divided into two types. The source drive IC located in the X-axis is responsible for the input of data. It is characterized by high frequency and has an image function. The gate drive IC located in the Y-axis is responsible for the degree and speed of torsion of LCD molecules, which directly affects the response time of the LCD display. However, there are already many LCD panels that only have driving IC in the X-axis direction, perhaps because the Y-axis drive IC function has been integrated and simplified.
The press of the flexible circuit board can transmit data signals and act as the bridge between the external printed circuit and LCD. It can be bent and thus becomes a flexible or flexible circuit board
The manufacturing process of the LCD substrate still has a lot of details and matters needing attention, for example, rinse with clean, dry, dry, dry, ultrasonic cleaning, exposure, development and so on and so on, all have very strict technical details and requirements, so as to produce qualified eyes panel, interested friends can consult relevant technical information by a search engine.
LCD (LC) is a kind of LCD, which has the properties of light transmission and refraction of solid Crystal, as well as the flow property of Liquid. It is because of this property that it will be applied to the display field.
However, LCD does not emit light autonomously, so the display equipment using LCD as the display medium needs to be equipped with another backlight system.
First, a backplate is needed as the carrier of the light source. The common light source for LCD display equipment is CCFL cold cathode backlight, but it has started to switch to an LED backlight, but either one needs a backplate as the carrier.
CCFL backlight has been with LCD for a long time. Compared with LED backlight, CCFL backlight has many defects. However, it has gradually evolved to save 50% of the lamp and enhance the transmittance of the LCD panel, so as to achieve the purpose of energy-saving.
With the rapid development of LED in the field of lighting, the cost has been greatly reduced.LCD panels have also started to use LED as the backlight on a large scale. Currently, in order to control costs, an LED backlight is placed on the side rather than on the backplate, which can reduce the number of LED grains.
However, no matter CCFL backlight or LED backlight is placed in various ways, the nature of the backlight source cannot be a surface light source, but a linear light source or point light source. Therefore, other components are needed to evenly distribute the light to the whole surface. This task is accomplished by the diffuser plate and diffuser plate.
On the transparent diffuser plate, point-like printing can block part of the light. The LED backlight on the side drives the light from the side of the diffuser plate, and the light reflects and refracts back and forth in the diffuser plate, distributing the light evenly to the whole surface. Point-like printing blocks part of the light, screening the light evenly like a sieve.
At the top of the diffusion plate, there will be 3~4 diffuser pieces, constantly uniform light to the whole surface, improve the uniformity of light, which is directly related to the LCD panel display effect. Professional LCD in order to better control the brightness uniformity of the screen, panel procurement, the later backlight control circuit, will make great efforts to ensure the quality of the panel.
The backlight system also includes a backlight module laminator, located behind the backplane. In the CCFL backlight era, you can often see the long strip laminator like the one above, with each coil responsible for a set of tubes.
However, it is much simpler to use a side white LED as a backlight. The small circuit board on the far left of the figure above is the backlight of the LED.
This is the general structure of the backlight system. Since I have never seen the backlight mode of R.G.B LED, I cannot tell you what the backlight mode is like. I will share it with you when I see it in the future.
Since the LCD substrate and the backlight system are not fixed by bonding, a metal or rubber frame is needed to be added to the outer layer to fix the LCD substrate and the backlight system.
After the period of the Module, the process is completed in LCM (LCDModule) factory, the core of this part of the basic does not involve the use of LCD manufacturing technology, mainly is some assembly work, so some machine panel factories such as chi mei, Korea department such as Samsung panel factory, all set with LCM factories in mainland China, Duan Mo group after the LCD panel assembly, so that we can convenient mainland area each big monitor procurement contract with LCD TV manufacturers, can reduce the human in the whole manufacturing and transportation costs.
However, neither Taiwan nor Korea has any intention to set up factories in mainland China for the LCD panel front and middle manufacturing process involving core technologies. Therefore, there is still a long way to go for China to have its own LCD panel industry.
For over 20 years we"ve been helping clients worldwide by designing, developing, & manufacturing custom LCD displays, screens, and panels across all industries.
Newhaven Display has extensive experience manufacturing a wide array of digital display products, including TFT, IPS, character displays, graphic displays, LCD modules, COG displays, and LCD panels. Along with these products, we specialize in creating high-quality and affordable custom LCD solutions. While our focus is on high-quality LCD products, we also have a variety of graphic and character OLED displays we manufacture.
As a longtime leader in LCD manufacturing, producing top-quality LCD modules and panels is our highest priority. At Newhaven Display, we’re also incredibly proud to uphold our reputation as a trusted and friendly custom LCD manufacturing company.
As a custom LCD manufacturing company, we ensure complete control of our custom displays" reliability by providing the industry"s highest quality standards. Our design, development, production, and quality engineers work closely to help our clients bring their products to life with a fully custom display solution.
Our excellent in-house support sets Newhaven Display apart from other display manufacturers. Modifications in the customization process are completed at our Illinois facility, allowing us to provide an exceptionally fast turnaround time.
Customer support requests sent by phone, email, or on our support forum will typically receive a response within 24 hours. For custom LCD project inquiries, our response time can take a few days or weeks, depending on the complexity of your display customization requirements. With different production facilities and a robust supply chain, we are able to deliver thefastest turnaround times for display customizations.
We work hard to ensure that personalized support is available and highly reliable. Our extended support center is available through our website, including example codes, IC datasheets, font tables, engineering changes, a video library, and answers to frequently asked questions. You can visit our knowledge center and community forum, where you can find answers, browse topics, and talk to other engineers in the display and electronics field.
Our excellent in-house support and custom display modifications set Newhaven Display apart from other LCD display manufacturers. From TFTs, IPS, sunlight readable displays, HDMI modules, EVE2 modules, to COG, character, and graphic LCDs, our modifications in the customization process are completed at our Illinois facility, allowing us to provide quality and fast turnaround times.
As a display manufacturer, distributor, and wholesaler, we are able to deliver the best quality displays at the best prices. Design, manufacturing, and product assembly are completed at our headquarters in Elgin, Illinois. Newhaven Display International ensures the best quality LCD products in the industry in this newly expanded facility with a renovated production and manufacturing space.
With assembly facilities in the US, manufacturing facilities in China, and distribution channels worldwide, we pride ourselves on delivering high-quality custom display solutions quickly to locations worldwide.

In addition to custom LCD displays, we provide custom PCB assemblies and turnkey solutions for products that feature a Displaytech LCD. As a display manufacturer, our engineering and production staff are experienced in handling the design and manufacturing of printed circuit board assemblies for front panels, rack mount equipment, handheld devices and many other products.

Since 1990, AccuView is dedicated to delivering fully customized LCD display solutions for our customers. Our strength lies in understanding and meeting our customers" EXACT requirements coupled with AccuView"s comprehensive manufacturing capabilities and expertise to deliver the right LCD display solution. Let AccuView be your total video solution provider.
Technology trends in backplane technology are driving higher gas demand in display manufacturing. Specific gas requirements of process blocks are discussed, and various supply modes are reviewed.
Since its initial communalization in the 1990s, active matrix thin-film-transistor (TFT) displays have become an essential and indispensable part of modern living. They are much more than just televisions and smartphones; they are the primary communication and information portals for our day-to- day life: watches (wearables), appliances, advertising, signage, automobiles and more.
There are many similarities in the display TFT manufacturing and semiconductor device manufacturing such as the process steps (deposition, etch, cleaning, and doping), the type of gases used in these steps, and the fact that both display and semiconductor manufacturing both heavily use gases.
However, there are technology drivers and manufacturing challenges that differentiate the two. For semiconductor device manufacturing, there are technology limitations in making the device increasingly smaller. For display manufacturing, the challenge is primarily maintaining the uniformity of glass as consumers drive the demand for larger and thinner displays.
While semiconductor wafer size has maxed because of the challenges of making smaller features uniformly across the surface of the wafer, the size of the display mother glass has grown from 0.1m x 0.1m with 1.1mm thickness to 3m x 3m with 0.5mm thickness over the past 20 years due to consumer demands for larger, lighter, and more cost-effective devices.
As the display mother glass area gets bigger and bigger,so does the equipment used in the display manufacturing process and the volume of gases required. In addition, the consumer’s desire for a better viewing experience such as more vivid color, higher resolution, and lower power consumption has also driven display manufacturers to develop and commercialize active matrix organic light emitting displays (AMOLED).
In general, there are two types of displays in the market today: active matrix liquid crystal display (AMLCD) and AMOLED. In its simplicity, the fundamental components required to make up the display are the same for AMLCD and AMOLED. There are four layers of a display device (FIGURE 1): a light source, switches that are the thin-film-transistor and where the gases are mainly used, a shutter to control the color selection, and the RGB (red, green, blue) color filter.
The thin-film-transistors used for display are 2D transitional transistors, which are similar to bulk CMOS before FinFET. For the active matrix display, there is one transistor for each pixel to drive the individual RGB within the pixel. As the resolution of the display grows, the transistor size also reduces, but not to the sub-micron scale of semiconductor devices. For the 325 PPI density, the transistor size is approximately 0.0001 mm2 and for the 4K TV with 80 PPI density, the transistor size is approximately 0.001 mm2.
Technology trends TFT-LCD (thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display) is the baseline technology. MO / White OLED (organic light emitting diode) is used for larger screens. LTPS / AMOLED is used for small / medium screens. The challenges for OLED are the effect of < 1 micron particles on yield, much higher cost compared to a-Si due to increased mask steps, and moisture impact to yield for the OLED step.
Mobility limitation (FIGURE 2) is one of the key reasons for the shift to MO and LTPS to enable better viewing experience from higher resolution, etc.
The challenge to MO is the oxidation after IGZO metalization / moisture prevention after OLED step, which decreases yield. A large volume of N2O (nitrous oxide) is required for manufacturing, which means a shift in the traditional supply mode might need to be considered.
Although AMLCD displays are still dominant in the market today, AMOLED displays are growing quickly. Currently about 25% of smartphones are made with AMOLED displays and this is expected to grow to ~40% by 2021. OLED televisions are also growing rapidly, enjoying double digit growth rate year over year. Based on IHS data, the revenue for display panels with AMOLED technol- ogies is expected to have a CAGR of 18.9% in the next five years while the AMLCD display revenue will have a -2.8% CAGR for the same period with the total display panel revenue CAGR of 2.5%. With the rapid growth of AMOLED display panels, the panel makers have accel- erated their investment in the equipment to produce AMOLED panels.
There are three types of thin-film-transistor devices for display: amorphous silicon (a-Si), low temperature polysilicon (LTPS), and metal oxide (MO), also known as transparent amorphous oxide semiconductor (TAOS). AMLCD panels typically use a-Si for lower-resolution displays and TVs while high-resolution displays use LTPS transistors, but this use is mainly limited to small and medium displays due to its higher costs and scalability limitations. AMOLED panels use LTPS and MO transistors where MO devices are typically used for TV and large displays (FIGURE 3).
This shift in technology also requires a change in the gases used in production of AMOLED panels as compared with the AMLCD panels. As shown in FIGURE 4, display manufacturing today uses a wide variety of gases.
These gases can be categorized into two types: Electronic Specialty gases (ESGs) and Electronic Bulk gases (EBGs) (FIGURE 5). Electronic Specialty gases such as silane, nitrogen trifluoride, fluorine (on-site generation), sulfur hexafluoride, ammonia, and phosphine mixtures make up 52% of the gases used in the manufacture of the displays while the Electronic Bulk gases–nitrogen, hydrogen, helium, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and argon – make up the remaining 48% of the gases used in the display manufacturing.
The key ga susage driver in the manufacturing of displays is PECVD (plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition), which accounts for 75% of the ESG spending, while dry etch is driving helium usage. LTPS and MO transistor production is driving nitrous oxide usage. The ESG usage for MO transistor production differs from what is shown in FIGURE 4: nitrous oxide makes up 63% of gas spend, nitrogen trifluoride 26%, silane 7%, and sulfur hexafluoride and ammonia together around 4%. Laser gases are used not only for lithography, but also for excimer laser annealing application in LTPS.
Silane: SiH4 is one of the most critical molecules in display manufacturing. It is used in conjunction with ammonia (NH3) to create the silicon nitride layer for a-Si transistor, with nitrogen (N2) to form the pre excimer laser anneal a-Si for the LTPS transistor, or with nitrous oxide (N2O) to form the silicon oxide layer of MO transistor.
Nitrogen trifluoride: NF3 is the single largest electronic material from spend and volume standpoint for a-Si and LTPS display production while being surpassed by N2O for MO production. NF3 is used for cleaning the PECVD chambers. This gas requires scalability to get the cost advantage necessary for the highly competitive market.
Nitrous oxide: Used in both LTPS and MO display production, N2O has surpassed NF3 to become the largest electronic material from spend and volume standpoint for MO production. N2O is a regional and localized product due to its low cost, making long supply chains with high logistic costs unfeasible. Averaging approximately 2 kg per 5.5 m2 of mother glass area, it requires around 240 tons per month for a typical 120K per month capacity generation 8.5 MO display production. The largest N2O compressed gas trailer can only deliver six tons of N2O each time and thus it becomes both costly and risky
Nitrogen: For a typical large display fab, N2 demand can be as high as 50,000 Nm3/hour, so an on-site generator, such as the Linde SPECTRA-N® 50,000, is a cost-effective solution that has the added benefit of an 8% reduction in CO2 (carbon dioxide) footprint over conventional nitrogen plants.
Helium: H2 is used for cooling the glass during and after processing. Manufacturers are looking at ways to decrease the usage of helium because of cost and availability issues due it being a non-renewable gas.
N2 On-site generators: Nitrogen is the largest consumed gas at the fab, and is required to be available before the first tools are brought to the fab. Like major semiconductor fabs, large display fabs require very large amounts of nitrogen, which can only be economically supplied by on-site plants.
Cryogenic liquid truck trailers: Oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide are produced at off-site plants and trucked short distances as cryogenic liquids in specialty vacuum-insulated tankers.
Compressed gas truck trailers: Other large volume gases like hydrogen and helium are supplied over longer distances in truck or ISO-sized tanks as compressed gases.
Individual packages: Specialty gases are supplied in individual packages. For higher volume materials like silane and nitrogen trifluoride, these can be supplied in large ISO packages holding up to 10 tons. Materials with smaller requirements are packaged in standard gas cylinders.
Blended gases: Laser gases and dopants are supplied as blends of several different gases. Both the accuracy and precision of the blended products are important to maintain the display device fabrication operating within acceptable parameters.
In-fab distribution: Gas supply does not end with the delivery or production of the material of the fab. Rather, the materials are further regulated with additional filtration, purification, and on-line analysis before delivery to individual production tools.
The consumer demand for displays that offer increas- ingly vivid color, higher resolution, and lower power consumption will challenge display makers to step up the technologies they employ and to develop newer displays such as flexible and transparent displays. The transistors to support these new displays will either be LTPS and / or MO, which means the gases currently being used in these processes will continue to grow. Considering the current a-Si display production, the gas consumption per area of the glass will increase by 25% for LTPS and ~ 50% for MO productions.
To facilitate these increasing demands, display manufacturers must partner with gas suppliers to identify which can meet their technology needs, globally source electronic materials to provide customers with stable and cost- effective gas solutions, develop local sources of electronic materials, improve productivity, reduce carbon footprint, and increase energy efficiency through on-site gas plants. This is particularly true for the burgeoning China display manufacturing market, which will benefit from investing in on-site bulk gas plants and collaboration with global materials suppliers with local production facilities for high-purity gas and chemical manufacturing.
Flat-panel displays are thin panels of glass or plastic used for electronically displaying text, images, or video. Liquid crystal displays (LCD), OLED (organic light emitting diode) and microLED displays are not quite the same; since LCD uses a liquid crystal that reacts to an electric current blocking light or allowing it to pass through the panel, whereas OLED/microLED displays consist of electroluminescent organic/inorganic materials that generate light when a current is passed through the material. LCD, OLED and microLED displays are driven using LTPS, IGZO, LTPO, and A-Si TFT transistor technologies as their backplane using ITO to supply current to the transistors and in turn to the liquid crystal or electroluminescent material. Segment and passive OLED and LCD displays do not use a backplane but use indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent conductive material, to pass current to the electroluminescent material or liquid crystal. In LCDs, there is an even layer of liquid crystal throughout the panel whereas an OLED display has the electroluminescent material only where it is meant to light up. OLEDs, LCDs and microLEDs can be made flexible and transparent, but LCDs require a backlight because they cannot emit light on their own like OLEDs and microLEDs.
Liquid-crystal display (or LCD) is a thin, flat panel used for electronically displaying information such as text, images, and moving pictures. They are usually made of glass but they can also be made out of plastic. Some manufacturers make transparent LCD panels and special sequential color segment LCDs that have higher than usual refresh rates and an RGB backlight. The backlight is synchronized with the display so that the colors will show up as needed. The list of LCD manufacturers:
Organic light emitting diode (or OLED displays) is a thin, flat panel made of glass or plastic used for electronically displaying information such as text, images, and moving pictures. OLED panels can also take the shape of a light panel, where red, green and blue light emitting materials are stacked to create a white light panel. OLED displays can also be made transparent and/or flexible and these transparent panels are available on the market and are widely used in smartphones with under-display optical fingerprint sensors. LCD and OLED displays are available in different shapes, the most prominent of which is a circular display, which is used in smartwatches. The list of OLED display manufacturers:
MicroLED displays is an emerging flat-panel display technology consisting of arrays of microscopic LEDs forming the individual pixel elements. Like OLED, microLED offers infinite contrast ratio, but unlike OLED, microLED is immune to screen burn-in, and consumes less power while having higher light output, as it uses LEDs instead of organic electroluminescent materials, The list of MicroLED display manufacturers:
Sony produces and sells commercial MicroLED displays called CLEDIS (Crystal-LED Integrated Displays, also called Canvas-LED) in small quantities.video walls.
LCDs are made in a glass substrate. For OLED, the substrate can also be plastic. The size of the substrates are specified in generations, with each generation using a larger substrate. For example, a 4th generation substrate is larger in size than a 3rd generation substrate. A larger substrate allows for more panels to be cut from a single substrate, or for larger panels to be made, akin to increasing wafer sizes in the semiconductor industry.
2015, sold to giantplus and tce photomasks, gen 3 still operated by giantplus, gen 4 line sold to giantplus, equipment sold and line demolished, remainder operated by tce
Cantwell, John; Hayashi, Takabumi (January 4, 2019). Paradigm Shift in Technologies and Innovation Systems. Springer Nature. ISBN 9789813293502 – via Google Books.
"Samsung Display has halted local Gen-8 LCD lines: sources". THE ELEC, Korea Electronics Industry Media. August 16, 2019. Archived from the original on April 3, 2020. Retrieved December 18, 2019.
"TCL to Build World"s Largest Gen 11 LCD Panel Factory". www.businesswire.com. May 19, 2016. Archived from the original on April 2, 2018. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
"Panel Manufacturers Start to Operate Their New 8th Generation LCD Lines". 대한민국 IT포털의 중심! 이티뉴스. June 19, 2017. Archived from the original on June 30, 2019. Retrieved June 30, 2019.
"TCL"s Panel Manufacturer CSOT Commences Production of High Generation Panel Modules". www.businesswire.com. June 14, 2018. Archived from the original on June 30, 2019. Retrieved June 30, 2019.
"Business Place Information – Global Operation | SAMSUNG DISPLAY". www.samsungdisplay.com. Archived from the original on 2018-03-26. Retrieved 2018-04-01.
"Samsung Display Considering Halting Some LCD Production Lines". 비즈니스코리아 - BusinessKorea. August 16, 2019. Archived from the original on April 5, 2020. Retrieved December 19, 2019.
Herald, The Korea (July 6, 2016). "Samsung Display accelerates transition from LCD to OLED". www.koreaherald.com. Archived from the original on April 1, 2018. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
Byeonghwa, Yeon. "Business Place Information – Global Operation – SAMSUNG DISPLAY". Samsungdisplay.com. Archived from the original on 2018-03-26. Retrieved 2018-04-01.
www.etnews.com (30 June 2017). "Samsung Display to Construct World"s Biggest OLED Plant". Archived from the original on 2019-06-09. Retrieved 2019-06-09.
Colantonio, Andrea; Burdett, Richard; Rode, Philipp (2013-08-15). Transforming Urban Economies: Policy Lessons from European and Asian Cities. Routledge. ISBN 9781134622160. Archived from the original on 2019-01-01. Retrieved 2019-06-09.
Shilov, Anton. "LG"s New 55+ inch OLED Plant in China Opens: Over 1m+ per Year". www.anandtech.com. Archived from the original on 2019-09-14. Retrieved 2019-12-18.
www.wisechip.com.tw. "WiseChip History – WiseChip Semiconductor Inc". www.wisechip.com.tw. Archived from the original on 2018-02-17. Retrieved 2018-02-17.
"China"s BOE to have world"s largest TFT-LCD+AMOLED capacity in 2019". ihsmarkit.com. 2017-03-22. Archived from the original on 2019-08-16. Retrieved 2019-08-17.
Shilov, Anton. "JOLED Starts Construction of New Printed OLED Facility". www.anandtech.com. Archived from the original on 2019-06-30. Retrieved 2019-06-30.

Except the available standard LCD/TFT/OLED display products, Winstar provides tailor made displays. The extensive portfolio makes it possible to create tailor-made solutions for customers to fit their application. We have the advanced display technologies available to use in your design and if there is anything you want to change about one of our existing LCD/TFT/OLED displays, we can make it happen. With more than 23 years experience, our sales and engineering team will be with you through the entire development process and will ensure the semi or fully customization a successful display tailored made to the individual application.
Our LCD/TFT/OLED custom design solutions are available in different options according to customer requirements. Winstar can offer various options on backlight type, pin and connector, cable, resistive touch screen (RTP) and projected capacitive (PCAP) touch screen or anti-reflective or anti-glare coating, or custom cover lens, ZIF PPC or customized PCB board or a fully custom solution for your product application, as well as System Integrated Solution.

Custom led LCD displays have a variety of different settings. On the other end of the spectrum, some suppliers offer lcd displays that are specific for their components.
There are four types of lcd display lcds wholesale, and one of the most popular ones. Theft of lcd displays in bulk are one of the most popular choices.
Custom built LCD displays create, user-friendly settings and are allowing for customers to save a lot of time and money. Lcd displays are available in a wide range of sizes, styles and and. Itionally, lcd displays are available to all the customers" needs.

When your project demands the imagery and definition of a full-color display, the Color LCD Screen modules available from Phoenix Display International provide a versatile solution to your color display needs. Available in a variety of sizes and capable of displaying a full range of color, the standard TFT color LCD display modules from Phoenix Display can be integrated into any number of projects in multiple applications. In addition, if one of our color LCD display modules doesn’t suit your needs, Phoenix Display can create a Custom LCD Display designed to your unique specifications.
If you’re looking into an outdoor application, Phoenix Display also has full Color TFT Display options in sunlight-readable or true transflective configurations to make you product shine even in the outdoor environment as well as the indoor showroom. And if touch screens are needed, we can use our standard or custom resistive and projected capacitive touch panels for any application.
Our TFT display modules are now Phoenix Display’s most popular Color LCD Screen technology, offering clients super image quality and vivid color reproduction in a versatile and dependable display module. Designed to meet the ever-growing need to display graphical content with high brightness, high contrast, and full-speed video capability, our full-Color LCD Screen modules are suited to handle today’s graphical display needs in stunning, lifelike color.
Not EXACTLY what you need? We specialize in custom and semi-custom display solutions. Contact us about creating something that fits your exact specifications.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey