lcd screen size comparison for sale
A lot goes into determining the best viewing distance, and there are several different criteria you can use. Aside from size, things like resolution and even how strong your eyesight is can affect how you see the screen. Because everyone"s eyesight is different, this is less an exact science and more of a general guide based on scientific principles of vision and resolution.
That doesn"t mean you should be sitting a foot away from your TV. Having the largest screen possible isn"t always ideal. The human visual system has a total horizontal field of view of about 200 degrees, although a portion of that is peripheral vision. While it makes some sense to get as large a TV as you can for movies, not all content is made to fill the entire field of view. This becomes very apparent if you try to watch sports from up close while fixating on a single part of the screen, which quickly starts to feel nauseating.
The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers recommends sitting at a distance where the screen fills up a minimum of 30° of your field of vision for a good experience.
This is generally good guidance, but people who use their TVs mostly for watching movies might benefit from sitting a bit closer to get a more theater-like experience. The SMPTE "reference" position for movie theaters and the THX recommendation is about 40°. The minimum angle of vision works well for most usages, though, and sitting at a distance where the screen fills 30° of your horizontal field of view should be comfortable for most people.
Our size and distance tool above is based on the 30° guideline that is suitable for mixed usage, but you can find distances for a variety of sizes at 40° here.Learn more about the human visual field.
For instance, sitting close to a 1080p TV can look almost like watching through a screen door because you can see the individual pixels, even if it"s playing a high-quality 1080p HD movie. Increasing your distance to the TV also increases the density of details, producing a better image. Since 4k TVs have such a large density of pixels, it"s much more difficult for this issue to arise. You need to be quite close to a fairly large TV for the pixels to be noticeably distracting.
With 8k TVs, that density increases further, making it even harder to notice flaws with the resolution unless you"re sitting extremely close. However, this also decreases the point at which the perceived difference in picture quality becomes noticeable. Because the pixels are more densely packed with an 8k resolution, you need to sit closer to actually resolve those details. For that reason—content aside—8k only really makes sense if you want a really big screen and plan on sitting close to it. Learn more about the difference between 4k and 8k.
This chart shows the point at which an upgrade in resolution becomes worth it depending on size and distance to the TV. Each line represents the optimal viewing distance for each resolution, but any TV that falls within the range of that color will be suitable to notice a difference in picture quality. So, for example, if you have a 65 inch TV, the viewing distance at which the eye can actually process the details of 4k content is about 4 feet. However, any distance between 4 and about 8.5 feet will be enough to appreciate the difference between 4k and 1080p on a 65 inch TV. Go too far, and the image will look identical to 1080p HD.
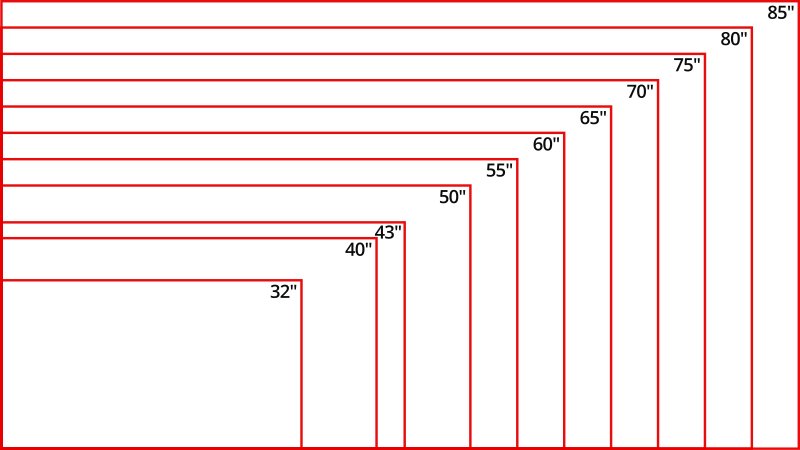
You"re probably thinking something along the lines of "My couch is 10" away from my TV, which according to the chart means I need a 75 inch TV. This is insane!" It"s true that if you want to take full advantage of higher resolutions, that"s the ideal size you should get. That said, this may not be possible for everyone, which brings us to budget.
The price of a TV is usually exponential to its size. Size isn"t the only factor though, as resolution, panel type, and features all play into it as well. Looking at 65 inch TVs, for instance, an OLED like the LG CX OLED is inevitably going to cost more than a budget LED TV like the Hisense H8G, and both of these will seem downright cheap compared to an 8k TV like the Samsung Q900TS 8k QLED. Fortunately, though, as technology improves and the availability of higher resolution TVs expands, larger TVs have become more common and therefore more affordable. Feel free to compare the prices of our picks for the best 65 inch TVs, the best 70 to 75 inch TVs, and the best 80 to 85 inch TVs to really see the difference that size makes.
We recommend a field of vision of about 30 degrees for mixed usage. In general, we also recommend getting a 4k TV since lower resolution TVs are becoming harder to find. To easily find out what size you should buy, you can divide your TV viewing distance (in inches) by 1.6 (or use our TV size calculator above) which roughly equals a 30-degree angle. If the best size is outside your budget, just get the biggest TV you can afford. These are guidelines, after all, and since most TVs nowadays are 4k, you can"t really go wrong with the size that works for you, especially since picture quality also depends a lot on the content and viewing conditions. Ideally, you would optimize the capacity of your TV by getting one that"s large enough for you to notice all the visual detail that 4k has to offer, but ultimately, you should watch however feels most comfortable to you, whatever the size and distance may be.

If you ask TV and theatrical industry groups, they"ll tell you to measure your seating distance to determine the ideal screen size. The farther away you sit, obviously, the smaller your TV appears. The ideal is to have a screen that fills a certain amount of your field of view, though how much is "ideal" is up for debate.
The other major factor to consider is something I"ll call "room domination." How big does a TV have to be before that looming black rectangular slab seems to be the only thing in the room? This factor is definitely subjective. As someone who"s had a 12-foot-wide projection screen in his house for over a decade, and has also reviewed large TVs, I"ll take the big projection screen over a TV any day (not least because when the "TV" is off, a projector"s screen is white or gray, a TV is glossy black). An 80-plus inch TV can easily just dominate a space. Wall mounting can help a bit, but your TV room risks becoming the TV"s room.
I"ll be honest, I don"t subscribe to any of the established "rules" for viewing distance and screen size. I think the SMPTE and the lesser THX numbers are too TV-biased. I think they vastly underestimate what"s easily possible with modern technology, for those who want more.
I sit nine feet from a 102-inch screen. That"s just the 16x9 portion. The full screen is 2.35:1 and 128 inches diagonal. I can just barely make out pixels when I expand a 1080p projector to the full width of the screen, but in standard 16x9 viewing, I can"t. 4K looks amazing.
Do you want to go that big? Well, that"s a different question. I find larger screen sizes easier on the eyes, as more of your field of view is taken up with the roughly uniform brightness of the screen. In an otherwise dark room, your pupils are more naturally closed to the amount of light thanks to the big screen.
Conversely, I find watching a small screen in a dark room more fatiguing, as your pupils are more open (because of the dark room) with this one annoying pinprick of bright light (the TV). Many people complain about headaches when they watch TV in a dark room. One possible cause is the
The ultimate decision is one of personal preference. My goal here was to point out a rough idea of what"s possible or recommended. For me, I would always err on the side of "too big." An old boss of mine used to say that no one regretted buying a TV they thought might be "too big." My opinion is that a 50-inch TV is too small for most rooms. That"s not to say I think everyone should get a 102-inch screen, but the reality is a 50-inch flat panel is really not that much larger than the 36-inch CRTs of the old days. Since 65- and even 75-inch TVs

LCD display doesn’t operate the same way as CRT displays , which fires electrons at a glass screen, a LCD display has individual pixels arranged in a rectangular grid. Each pixel has RGB(Red, Green, Blue) sub-pixel that can be turned on or off. When all of a pixel’s sub-pixels are turned off, it appears black. When all the sub-pixels are turned on 100%, it appears white. By adjusting the individual levels of red, green, and blue light, millions of color combinations are possible
The pixels of the LCD screen were made by circuitry and electrodes of the backplane. Each sub-pixel contains a TFT (Thin Film Transistor) element. These structures are formed by depositing various materials (metals and silicon) on to the glass substrate that will become one part of the complete display “stack,” and then making them through photolithography. For more information about TFT LCDs, please refer to “
The etched pixels by photolith process are the Native Resolution. Actually, all the flat panel displays, LCD, OLED, Plasma etc.) have native resolution which are different from CRT monitors
Although we can define a LCD display with resolution, a Full HD resolution on screen size of a 15” monitor or a 27” monitor will show different. The screen “fineness” is very important for some application, like medical, or even our cell phone. If the display “fineness” is not enough, the display will look “pixelized” which is unable to show details.
PPI stands for number of pixels per inch. It is kind of pixel density. PPI describes the resolution of a digital image, not a print. PPI is used to resize images in preparation for printing
But you see other lower resolution available, that is because video cards are doing the trick. A video card can display a lower LCD screen resolution than the LCD’s built-in native resolution. The video cards can combine the pixels and turn a higher resolution into lower resolution, or just use part of the full screen. But video cards can’t do the magic to exceed the native resolution.
Aspect Ratio: You might hear 4:3 which is full screen, 16:9 is for widescreen; 21:9 is for ultrawide computer monitors and televisions, as well as cinematic widescreen projectors. Some ultrawide monitors are trying to replace dual monitor.
The Hisense U8H matches the excellent brightness and color performance of much pricier LCD TVs, and its Google TV smart platform is a welcome addition. But it’s available in only three screen sizes.
The Hisense U8H is the best LCD/LED TV for most people because it delivers the performance of a much pricier TV yet starts at under $1,000, for the smallest (55-inch) screen size. This TV utilizes quantum dots, a full-array backlight with mini-LEDs, and a 120 Hz refresh rate to deliver a great-looking 4K HDR image. It’s compatible with every major HDR format. And it’s equipped with two full-bandwidth HDMI 2.1 inputs to support 4K 120 Hz gaming from the newest Xbox and PlayStation consoles. Add in the intuitive, fully featured Google TV smart-TV platform, and the U8H’s price-to-performance ratio is of inarguable value.
That’s not to say the U8H has pixel-precise light control—it’s not an OLED TV, after all—but it does a terrific job most of the time. In fact, in our tests, the U8H bested last year’s upgrade pick, the Samsung QN90A, in certain scenarios: The intro to Guillermo del Toro’s Cabinet of Curiosities on Netflix features the filmmaker against a pitch-black backdrop. Though last year’s QN90A failed to maintain perfect control over dimming elements during this scene (the black backdrop brightened distractingly once a sufficient amount of brighter content appeared on screen), the U8H did not. (For the record, the newer QN90B also passed this test.) The U8H’s mini-LEDs also help the screen look uniformly bright: Although the U8H is still not as good as an OLED TV in this respect, it shows very little indication of being a backlight-driven display, even during tricky scenes with large swaths of dim lighting.
The onboard Google TV smart platform is another feather in this TV’s cap. As usual, however, it will be much more satisfying to use if you have a Google account and already take advantage of Google’s connected services, like Photos. The experience of navigating the TV’s smart features—scanning QR codes to sign into apps, using the onscreen keyboard, and browsing your Google Photos to set a photo as a screensaver—was very satisfying in terms of responsiveness and speed. Powering on the TV and booting into an app took just seconds. The included Bluetooth remote is also equipped with a handy “Hey Google” button, allowing you to pull up Google’s assistant and use voice commands to search for content or set a reminder. If you have multiple users with their own Google accounts, you can designate separate profiles (attached to a Gmail account) so that each user can customize the experience to their liking, as well as access their own Google Drive or Photos. While some reviewers have reported instances of momentary freezing while using the U8H’s platform, I didn’t personally experience any instances of slowdown that were egregiously worse than with any other smart-TV platform.
In terms of design, the Hisense U8H is not as svelte as our upgrade pick, but it’s plenty sturdy and doesn’t look or feel cheap. Two narrow, metal feet jut out from beneath the panel and steadily hold the TV. They can be attached in two separate spots, either closer in toward the middle of the panel or out toward the edges, to account for different-size TV stands. The feet are also equipped with cable organization clasps—a nice touch for keeping your TV stand free of cable clutter. Though the TV is primarily plastic, its bezels are lined with metal strips, providing a bit more durability in the long run. I moved it around my home, and it was no worse for wear, but we’ll know more after doing some long-term testing.
The Hisense U8H has some difficulties with banding, or areas of uneven gradation, where transitions that should appear smooth instead look like “bands” of color (sometimes also called posterization). Like many current 4K HDR TVs, the U8H uses an 8-bit panel rather than a 10-bit panel, which affects the color decoding and color presentation process. This is usually relevant only with HDR video and games. When playing games on the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X, I saw a few instances where the content wasn’t rendered correctly and displayed ugly splotches of color on the screen. However, this almost always occurred during static screens (such as a pause menu or loading screen); I rarely spotted it during actual gameplay. Hisense has stated that it would address the problem in a future firmware update, but at the time of writing it was still present. This is a flaw that may give dedicated gamers pause, but we don’t consider it to be a dealbreaker for most people.
Finally, like most TVs that use vertical alignment (VA) LCD panels, the U8H has a limited horizontal viewing angle, which may be a bit annoying if you’re hoping to entertain a large crowd. Our upgrade pick uses a special wide-angle technology to address this.
Consider the space you have available when choosing which size screen you want. The 15 to 19-inch screen LCDs are the most popular, but LCD monitors do come in even larger sizes.
Find out what the screen ratio is while you look at screen size. Compare LCD monitor"s display capabilities as well. Some are sold as the typical 4:3 dimension displays while others now display a wide-screen option just like televisions.

Apple makes quite a few iPhones nowadays and they’re all slightly different – both with respect to specs and size. Here’s a handy iPhone size comparison chart to give you a visual idea of the differences
As of right now, Apple’s latest iPhone is the iPhone 13 – and iPhone 13 range, including the iPhone 13 mini, iPhone 13 Pro, and iPhone 13 Pro Max. As you can see from the table above, Apple’s iPhone 13 is pretty much exactly the same size as the iPhone 12 – it is slightly thicker, however, to accommodate larger batteries.
iPhone 13 Pro Max & iPhone 14 Pro Max / 14 Plus:The iPhone 14 Pro Max and iPhone 14 Plus both run 6.8in OLED displays. The iPhone 13 Pro Max also runs the same size Super Retina XDR OLED screen. As of 2022, these are the biggest iPhones you can currently buy. The iPhone 14 Plus does not have Apple’s ProMotion display though. For that, you’ll need to go Pro or Pro Max.
iPhone 7 Plus/iPhone 8 Plus – The iPhone 7 Plus and iPhone 8 Plus look the same. The only difference between them is to do with the camera and the internal specs. In the hand and with respect to performance, there’s not much to separate these two phones. Both have a 5.5in 1080p LCD display and while this isn’t as good as OLED, it is still a very good display. And the really cool thing about Apple’s older flagship models is that you can now buy them for hardly any money at all.
Apple’s entry-level iPhones for the last couple of years have also been fairly large too; the iPhone XR has a 6.1in LCD screen size and so too does the iPhone 11, iPhone 12, iPhone 13, and the iPhone 14. The iPhone 11 used an LCD screen, whereas the iPhone 12 and iPhone 13 use OLED.
In 2020, all iPhone models (inside the iPhone 12 range) will feature OLED displays. You also have the most choice with respect to size with the iPhone 12 too – it comes in three distinct screen sizes: 5.4in, 6.1in, and 6.7in.

The "p-display" nomenclature used in this article refers to the number of pixels displayed across the width of a given phone"s screen. Earlier phones with lower than 720p (lower than HD ready resolution) are not included in this listing. The lists below are dynamic lists and may be sorted into alphabetical order by clicking on the "sort icons" at the top of the first column.
LCD panels" resolutions are often quoted in terms of raw subpixels, misnamed "pixels" in manufacturer"s specifications. Each real pixel includes one subpixel for each of three colors, so calling subpixels "pixels" inflates the claimed resolution by a factor of three. This bit of marketing obfuscation is calculated as horizontal resolution × vertical resolution × 3. For example: 640 × 480 VGA is 921,600 subpixels, or 307,200 pixels, 800 × 600 SVGA is 1,440,000 subpixels, or 480,000 pixels, and 1024 × 768 XGA is 2,359,296 subpixels, but only 786,432 full-color pixels.

How big is big enough? When it comes to computer monitors, you want something that can fit comfortably on your desk while giving you plenty of screen real estate. While in the past sub-20-inch monitors were commonplace, today, unless you’re really constrained for space, there’s no real need to buy anything under 22 inches. For most, 24 inches is going to be a baseline, as you can pick up a number of screens at that size for around $100, and they look fantastic at 1080p.
For those who want more than that, though, there are plenty of sizes to choose from. Monitors that stretch 27 inches diagonally are increasingly popular, and there are plenty of options beyond 30 inches that are affordable. If you want to go extreme, we’ve even tried some great computer monitors that get close to 50 inches, like Samsung’s CHG90.
While you’ll need to sit well back from those, there’s no denying that they look amazing. They give you the same screen as multiple smaller monitors without a bezel dividing them down the middle. They tend to be rather expensive, though, and if you go really wide, you’ll struggle to find media that can display at close to its native resolution, leaving the picture to either look stretched or surrounded by black.
Anywhere between 24 and 30 inches is going to be perfectly fine for most users. They let you make the most of modern resolutions and color clarity, and they also fit a couple of different web pages open at the same time without needing to use two monitors, which is handy for many professionals. They don’t tend to be too expensive at that size, either, unless you opt for the top-end models.
Today, all the best screens are still LCD monitors that use LED technology for a slim product that saves energy while providing ideal backlighting. We’ve been waiting years for OLED technology to make the transition to PC monitors, it isfinally beginning thanks to brands like LG, but the technology is still relatively rare.
One aspect of PC monitors that you do need to consider, though, is resolution. While 1080p was once the gold standard, today, it’s just the baseline. If you’re happy to spend a little more, there are a few other options worth considering, especially if you want to improve screen space or gaming visuals. Resolution isn’t the be-all and end-all of monitor features, though. In fact, too much resolution on too small of a screen can often be annoying because it shrinks all images down and forces you to enlarge everything to easily read it.
Aspect ratio: The aspect the screen shows images in (length compared to height). A common standard, and your best bet, is 16:9. It works with plenty of content, and it’s great for movies or games. Some fancy monitors like to stretch things out with ratios like 21:9, but that is more suitable for unusual work situations or hardcore gaming. Another common format, 16:10, provides slightly more vertical space for viewing multiple open documents or images. 3:2 is becoming more commonplace in laptops for better web viewing, but that’s rare on stand-alone displays.
Contrast ratio: Contrast ratios tell you the difference between how white and how black a monitor screen can get. Higher contrast ratios are a good sign because that means colors will be more differentiated. However, multiple measurements for contrast ratios exist, and stated specs aren’t very reliable, so take it all with a grain of salt.
Refresh rate: Rated in hertz (Hz), a monitor’s refresh rate is how often it updates the image on your screen. While most support up to 60Hz, some displays now offer much higher refresh rates. That can result in smoother movements on your desktop and support for higher frame rates in games, which can make a big difference in high-paced titles by reducing your input lag. 120Hz to 144Hz is a great range to target, but you could opt for the fastest screens out there with up to 240Hz support. Just make sure you have a high-powered graphics card to back it up.
Response time: Response time indicates how quickly the monitor shows image transitions. A low response time is good for fast-paced action video, twitchy gameplay, and similar activities. Response times are measured in milliseconds, with the best screens able to switch pixels at only a couple of milliseconds, but not everyone needs such fast reactions.
Viewing angle: Viewing angle isn’t as important for a monitor as it is for a TV screen, but if you like to watch shows on your computer with groups of friends, aim for a larger viewing angle so people at the sides can see easily. Anything above 170 degrees is good news here.
There are also curved monitors to consider. They don’t have different resolutions than their flat counterparts, but present a concave curved screen, which can make a difference to the experience and tasks they’re best suited for.
A curved screen can provide a more immersive experience, especially when it comes to certain games (racing games are a favorite for curved ultrawides). This largely benefits single-player games where a user will be comfortable sitting at the center of the screen.

The original A7R IV has been discontinued and quietly replaced by the A7R IVA. The changes are very subtle, with the most noticeable difference being the higher resolution of the LCD screen (2.36M vs 1.44M dots on the original model). Other details are included in the chapters below.
The 10 Main Differences in a NutshellImage Quality: the A7R IV produces impressive results concerning sharpness and details, in addition to giving you greater crop possibilities. It also performs very well up to ISO 12800. The A7 IV has updated picture profiles, and lots to offer when it comes to dynamic range.Autofocus: the A7 IV is more precise with face and eye detection, and also delivers a better keeper rate for birds in flight. The A7R IV is not too far behind concerning the latter, but struggles more with Eye AF.Buffer: the A7 IV has superior capabilities by a long margin when using the CF express card, which is however more expensive than a SD card. Both cameras go as fast as 10fps, which is quite the effort for the R model considering it has almost double the megapixels.Pixel Shift Multi Shooting: the performance concerning in-body stabilisation is pretty similar, but the R model uses the technology for an extra feature that produces a 240MP file!Movie Recording: the A7 IV has more features and advanced options, including 10-bit 4:2:2 internal recording and 4K 60p (in Super35 mode). The R model produces the best results in crop mode and has slightly more dynamic range in the highlights.Viewfinder and LCD monitor: the ‘R’ has more resolution for both. The A7 IV has more touch functionalities thanks to the new menu system.Design and Functionality: the A7 IV makes it easier to separate the still and photo modes, while also giving you more customisation options for each (including the memory recall that works in movie mode). The newest camera also sports a full sized HDMI port and a faster USB C port.Memory cards: both can work with two SD UHS-II cards, but only the A7 IV takes one CFexpress Type A card, which helps the buffer among other things.Tidbits: the A7 IV offers extra functionalities, including the possibility of USB streaming without any plugin or software required.Price: the A7R IV(A) is $1000 more expensive.
The A7R IV has a lower score, not so much because of out of focus images, but because of the bigger presence of slightly soft results, where the eyes are a bit soft in comparison to the nose or ears of the subject (meaning focus is a little too short or far). It also struggled more when the subject was further away at the beginning of the sequence, as well as when she turned 360˚ near the end.
The difference between the Creative Looks of the A7 IV and the Creative Styles of the R model that I highlighted in the first chapter of this article are valid for video too but it is less visible in comparison to photographs.
In my overheating test, the A7 IV was able to record non-stop for two hours without any problem, and without the overheating warning appearing on the screen. The A7R IV managed the same result (ambient temperature between 21˚C and 22˚C).
Finally, the A7 IV has extra settings and features you won’t find in the R model, such as:Active mode: makes the footage more stable by using the gyro sensor’s data. There is a slight crop of 1.1x. I don’t find it makes a huge difference.Post stabilisation with Catalyst: the camera can record the data from its gyro sensor, and the Sony Catalyst software can use that information to stabilise the footage in post with better results (IBIS must be off during recording). It’s the best solution when you walk with the camera.Breathing compensation: it reduces the breathing effect that occurs when focusing from one point to the other (the field of view is cropped a little as a result). It works really well, but not every lens is compatible (check the list on the Sony website)Shockless WB: it makes manual changes to white balance smoother while recordingFlexible Exposure Mode: it allows you to switch between auto and manual exposure settings separately for the aperture and shutter speed (like in professional cinema cameras). It is an alternative to the P/A/S/M modes.Emphasized REC Display: enables a red frame around the edge of the LCD monitor to show the camera is recording.
As for the rear LCD screen, the one on the A7R IV has more resolution (1.44M on the original model, 2.36M dots on the A7R IVA) but it only tilts up and down.
Both LCDs are touch sensitive but there is more you can do on the A7 IV, including navigating the menu and changing settings. On the R model, you can only move the focus point or activate magnification (with a double tap).
The A7 IV also improves a few things concerning live view in general (EVF and LCD). For example, there is an option to keep the exposure preview optimised for flash work. In video mode, the magnification option is sharper and much more usable.
Concerning the connections, the A7 IV has a full sized HDMI (vs Micro Type D for the R model) and can work with a wired LAN connection with an optional LAN to USB C adapter. The A7R IV has a flash sync port.
Concerning battery life, they use the same BP-FZ100 battery, but the A7R IV has a slightly higher rating of 670 shots when using the LCD (660 for the A7R IVA), as opposed to 610 for the A7 IV.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey