esp32 cam tft display manufacturer

A beautiful 3.5” touchscreen display, based on ESP32-WROVER, with a built-in 2M pixel OV2640 camera, makes it an ever perfect platform for your ESP32 projects.
Makerfabs ESP32 3.5” Touch with camera is absolutely open for makers, and besides, Makerfabs provide plenty of Demos to help the users on the usage. Have a try at this fantastic display in your next ESP32 project!~
A beautiful 3.5 inch touchscreen display, based on ESP32-WROVER, with built-in 2M pixel OV2640 camera, which makes it an ever perfect platform for your ESP32 projects.
Makerfabs ESP32 3.5 inch Touch with camera is absolutely open for makers, and besides, Makerfabs provide plenty of Demos to help the users on the usage. Have a try at this fantastic display in your next ESP32 project!~

ESP32 development boards with a camera are becoming very popular among the maker community. There are several models with different features like microSD card support, microphone, screen, and much more for a very reasonable price. These boards allow you to build projects with image, video streaming, face recognition and detection, and other AI applications. Do you know what’s the best ESP32 camera board for your project?
All cameras have an OV2640 camera and usually, these come with a small flex cable. There are camera probes sold separately with longer flex cables and with a fish-eye lens. The fish-eye lens capture a wider area, which is really useful for surveillance projects.
The ESP32-CAM AI-Thinker is one of the most popular ESP32 development boards with a camera – it comes with a lot of useful features and costs around $7 or less!
It features an ESP32-S chip and comes with a “regular” 2MP OV2640 camera. This board has 4MB PSRAM, which is used for buffering images from the camera into video streaming or other tasks and allows you to use higher quality in your pictures without crashing the ESP32.
It supports a microSD cardand has 10 accessible GPIOs and power pins. However, not all GPIOs can be used because some are either being used by the camera or by the microSD card. So, you need to be careful with which GPIOs you’ll use.
The ESP32-CAM board comes with an on-board antenna, but also with an IPEX connector allowing you to alternatively use an external antenna to improve the Wi-Fi communication range.
One of the major drawbacks of the ESP32-CAM is that it doesn’t have USB-to-UART interface. This means that you can’t connect the ESP32-CAM directly to your computer using a USB cable. You need to use an FTDI programmer. Nonetheless, this is one of the most versatile and cheapest ESP32 development boards with a camera.
This development board comes with the ESP32-Wrover-E chip (with PSRAM). It comes with the OV2640 camera and it is easy to use and set up. It has a USB-to-UART converter so it’s straightforward to upload code to the board. You just need to connect a USB cable to the board and connect it to your computer to upload code or apply power. There’s no need for extra circuitry or an FTDI programmer.
It comes with several exposed GPIOs if you want to connect other peripherals. Additionally, if you’re not using the camera, you can use it as a regular ESP32 with a wide number of available GPIOs. It comes with RESET and BOOT buttons, which makes it easy to reset the board or put it in flashing mode if needed.
When programming this board using Arduino IDE, make sure you select the board ESP32 Wrover Module and in the partition scheme select Huge APP (3MB No OTA/1MB SPIFFS).
Just with 21mm by 41mm, it is equipped with a 2 MP OV2640 camera, on-board microphone, reset, boot, and function buttons, and two LEDs. It features 4MB Flash, 8MB PSRAM, and a Micro USB type-C connector (easy to upload code). It comes with on-board antenna and IPEX connector if you want to add an external antenna.
There are several different versions of M5-Stack ESP32 boards with cameras. The M5-Camera A or M5-Camera B like all the other boards featured here comes with the OV2640 camera. It has 4MB PSRAM—so, you shouldn’t have problems taking pictures and streaming with higher quality.
The TTGO T-Camera Plus comes with all the functionalities we would want in such a development board and for a very reasonable price. The board comes with microSD card support, a microphone, support for a 3.7V lithium battery as well as a battery management circuit, a 1.3 TFT display (color screen), microUSB interface, and on-board reset button.
Finally, the board has an on-board antenna, but also an IPEX connector if you want to add an external antenna. When we got our board it came loaded with an example that shows what the camera “sees” on the screen. This is a very versatile board and we really like it. Read our in-depth review of the TTGO T-Camera Plus.
This camera features a OV2640 camera, a 0.96 inch SSD1306 OLED display, a grove connector (ideal to connect I2C devices), a battery connector, a PIR motion sensor, an on-board RESET button, and a function button connected to GPIO 34. It also features 8MB PSRAM, but it doesn’t support a microSD card.
If you want to include some motion detection in your projects, this is the camera to go with. For more details, you can take a look at the camera GitHub page.
The TTGO T-Journal is a $12-$15 ESP32 Camera Development Board with an OV2640 camera, an external antenna, an I2C SSD1306 0.91 inch OLED display, some exposed GPIOs, function button, a battery connector, and a micro-USB interface.
The OLED display is a great addition to the board. You can display the board IP address, or any errors while debugging. There are four accessible GPIOs. Two of them are for I2C communication and the other two are perfect to connect servo motors (you can also connect other peripherals).
This is another ESP32 board with a camera from M5-Stack. This ESP32-Camera doesn’t have PSRAM. In practical terms, this means the camera is not able to do face recognition and detection and doesn’t support picture resolution higher than SVGA (800×600). You may also have a hard time with video streaming. Some people reported that his camera heats up very fast with video streaming. Usually, when you get one of these boards, you also get a heat sink precisely because of that.
In this article, we’ve reviewed 8 different ESP32 camera development boards. All boards feature the OV2640 2MP camera and you can program them using Arduino IDE. The best camera for you will really depend on your project requirements. We compiled all this information so that it’s easier for you to pick up the best board for what you have in mind.
In our opinion, the ESP32-CAM AI-Thinker is the most versatile for beginners (and it’s also cheaper) but it needs an FTDI programmer to upload code, or an ESP32-CAM MB programmer. If you don’t want to use the FTDI programmer there are other boards to choose from, I personally like the Freenove ESP32 Wrover board.
The TTGO T-Plus is the one with more functionalities: microphone, microSD card, a color screen, and much more. If you don’t intend to connect any peripherals to your board, the M5-camera might be a better option (and you can easily connect other M5-stack expansions). At this point, taking into account the variety of available boards, I would not choose a board without PSRAM.
Register in our brand new ESP32 course with Arduino IDE. This is our complete guide to program the ESP32 with Arduino IDE, including projects, tips, and tricks! The registrations are open, so

The TTGO T-Camera Plus is an ESP32 Camera Development Board that features an OV2640 camera, microSD card support, 1.3 inch TFT display, built-in programmer, access to I2C GPIOs, 8MB PSRAM and much more.
You can get the TTGO T-Camera Plus in different stores. You can choose whether you want the board with a normal lens or a fish-eye lens in many stores. You can also choose if you want a longer flex cable to have a rear camera.
The camera that comes with this board is a 2MP OV2640 camera, which is the same camera that comes with the ESP32-CAM, T-Journal, ESP-EYE, and other similar boards. When you get your T-Camera Plus, most stores allow you to choose between a camera with a normal lens or a fish-eye lens.
You also have the option to choose a longer or shorter flex cable. A longer flex cable allows you to have a rear camera (the display facing one side and the camera facing the other).
The board comes with a microSD card slot. This can be very useful to store photos, data collected from I2C sensors, or to store files to serve to clients (files to build a web page with the ESP32, for example).
To interface the microSD card with the ESP32 using Arduino IDE, you can use the SD_MMC library. The connections between the microSD and the ESP32 are shown in the next table.
The T-Camera Plus comes with a MSM261S4030H0 microphone (right above the reset button). This is very cool because you can add voice features to your projects, like voice wake-up, or trigger a task when the sound level goes above a certain threshold.
To interface the microphone with the ESP32, you can use the esp32-i2s mems library. Unfortunately, at the moment there isn’t much information about microphones and I2S interface with the ESP32.
The T-Camera Plus comes with some GPIOs exposed that were used to come with an onboard BME280 sensor. However, the sensor would get really hot on the board, so the manufacturer decided to remove the sensor as shown below (we don’t recommend soldering the BME280 sensor).
The TTGO T-Camera Plus comes flashed with an example. Apply power to your board using the microUSB interface. After a few seconds, the display will display a message. You should say the word that appears on the screen to “unlock” the device.
If you pronounce it correctly (it can be a bit difficult, so you may have to try several times), you’ll start seeing what the camera “sees”. This is a great example to check if everything is working with the board hardware.
There are many other ESP32 development boards with camera. We have a comparison table with the most popular ESP32 camera boards so that it is easier for you to pick up the most suitable camera for your projects.
In this article, we’ve taken a quick look at the T-Camera Plus. It features an OV2640 camera, a 1.3 inch OLED display, microSD card support, microphone, battery connector, microUSB interface, and 8MB PSRAM. This is a great board given its price and versatility.
Register in our brand new ESP32 course with Arduino IDE. This is our complete guide to program the ESP32 with Arduino IDE, including projects, tips, and tricks! The registrations are open, so
At first it was not successful, since most examples useTJpg_Decoderand it use a lot of memory, causing the ESP32-CAM crash then reboot. Then I found out that there"s an function from the ESP32 library to convert JPEG into RGB565 (which is the format used by the Adafruit driver). I can even scale the image to 1/2 side size (= 1/4) so it fit the ST7735S 160x128 or 128x128 displays nicely. Everything works and problem solved.
You can find some more details about wiring, the training data (Kaggle Cats and Dogs Dataset) and the model (MobileNetV1 96x96 0.25 with transfer learning) on my repo. There"s also a copy of my model library and a boilerplate version (without using button and TFT).
The train accuracy is 89.8% and test accuracy is 86.97% on Edge Impulse. Captured image is 240x240 (resized to 120x120 on TFT and 96x96 for the model). Model inference (predict) time on ESP32-CAM is 2607 ms (2.6 secs). It"s not fast, but the setup is so cheap I think this can actually be useful as real world applications...?
This ESP32-CAM Project covers how to use ESP32-CAM with a TFT display to show the picture captured by the cam. We have covered several times how to use ESP32-CAM in different projects and we have described how to use ESP32-CAM in Machine Learning projects. Even if we can use ESP32-CAM with a Web server to show pictures, in this post we want to cover how to show a picture on a TFT screen (ST7735). Therefore, we would like to visualize the picture taken by the ESP32-CAM directly on the display. In this case, we use an ST7735s display, anyway, you can select a different TFT if you like.
You should already know how to take a picture using an ESP32-CAM therefore we will focus on two aspects only:How to connect the ESP32-CAM to TFT display
This is the most interesting part because here we will show the picture taken by the ESP32-CAM on the TFT display. To do it, we will use the TJpg_Decoder library because it simplifies our work. First of all, we use a low-resolution such as 120×160 so that the picture fits in the TFT.
defining the scale and the callback method used to render the picture:bool tft_output(int16_t x, int16_t y, uint16_t w, uint16_t h, uint16_t* bitmap){
At the end of this tutorial, you have learned how to use ESP32-CAM with TFT display. In this project we have integrated ESP32-CAM with ST7735 to show the image captured. We have build a simple camera machine using ESP32-CAM.

In today"s project, we are going to make a Digital Action Camera of our own with a Capacitive Touchscreen on it. We made a similar DIY camera using the ESP32 Cam a few projects back but there was no touchscreen on that module. You can check that project from hereand its Video description from here.
We will be using an ESP32 Cam touchscreen module from MakersFab which is based on theESP32 wrover module. We will also use it for playing some fun games and at the end, we will make a Screenshot receiver as well. We also have with us an A9G module and a SIM808 module from Makerfabs but we will make something with them in the future. Though I have made a project using the A9G module in the past you can check that out from hereand its video description from here.
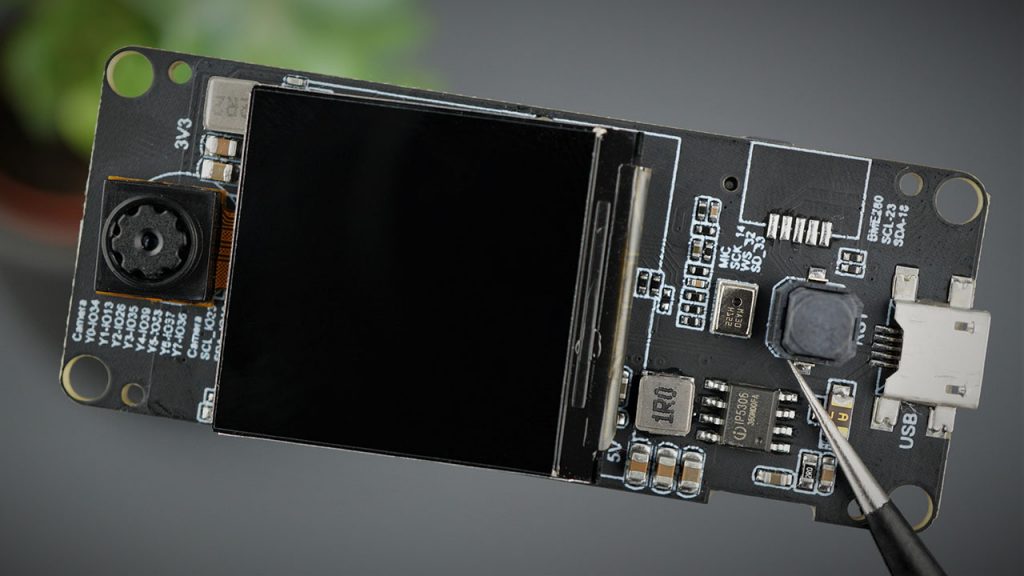
The ESP32 Touch Cam Module is a beautiful 3.5” touchscreen display, based on ESP32-WROVER, with a built-in 2M pixel OV2640 camera, which makes it an excellent platform for ESP32 projects. It is a pretty sleek and good looking module that can be used in several different display based projects. It comes up with a built-in micro SD card slot because an SD card is required for Image Capturing and Streaming purposes. It has an onboard CP2102 programmer and other display and Capacitive connectors on the backside.
It has ILI9488 as the 3.5” 320x480 TFT LCD driver which uses SPI for communication with ESP32. The SPI main clock could be up to 60M~80M, which makes the display smooth enough for videos. The camera OV2640 with pixel 2M can make applications such as remote photography, face recognition, etc. The module also has GPIO pins which we can use with the breakout connectors to connect the ESP32 display with sensors/actuators. The ESP32 TFT Touch support Arduino or MicroPython programming. The module we are using here has a Capacitive Touch, you can also get the module with resistive touch as well.
Here we will use the ESP32 Touch Cam module from Makerfabs to build a DIY Digital Camera. For that, we do not need to do any extra connections. we just need to connect the module to our PC, and uploading the code will make it ready to use. For building the camera we need to follow some simple steps given below:-
First of all, connect the Touchscreen Camera module to your PC using a USB type C cable. After that head over to the Github repository of the project from here.
In the Github repository, you will see a folder named Touch Camera. You simply need to download the folder and when the folder gets downloaded. You need to open the Camera_v2.ino file. It is the Arduino Code for the project you need to upload on the module.
When the code opens in the Arduino IDE. You need to head over to Tools and select the correct board which is the "ESP32 Wrover module". After that, we need to select the correct Partition Scheme which is the "Huge APP(3MB No OTA)". As this is done, you need to select the correct COM Port and hit the upload button.
As the code gets uploaded, you will see that the screen will become completely white and as the code gets uploaded the screen will start displaying whatever will be in front of the camera. You will see "Streaming" written on the bottom left corner of the screen and on the right side of the screen you will see 3 options which are "Take Photo", "Last Photo" and "Start Streaming". Take photo button will click a photo and save that in the SD Card. The Last Photo option will display the last photo which was clicked and the start streaming option will start streaming. In this way, you can click photos and also stream camera data over Wifi as well. So in this way, you will have a digital camera built by yourself. Now let"s try some other applications of this module as well.
In the last step, we built a digital camera using the Touch Cam module now in this step we will try another interesting application of the ESP32 Touch Cam module which is the Screenshot Receiver. What a Screenshot Receiver does is that it captures data from the screen of your PC sends it over Wi-Fi to the ESP32 module and displays the same data on your module"s display. So to build that we need to follow the steps given below:-
Once you have that IP address, you need to head over to the repository again. There you will see a ScreenShot Sender application. You need to open that application and enter the IP Address you obtained on the module display and hit the connect button.
Once the module gets connected you will see a Square box on your display and whatever on your screen would be covered by the box will also become visible on the module display as well. You can move that box on your PC screen and the contents on the module"s display will change simultaneously as well. All this Screenshot data transmission happens over Wifi and there is no wired connection between the module and the PC meant for the transmission. So in this way, we built a Screenshot Receiver and tested it as well.
So in this way, we got to know about the ESP32 Touch Camera module from Makerfabs. It is very compact and good for use in certain projects. We made two such projects as well which were the Wifi-based Screenshot receiver and the ESP32 Digital camera as well but the possibilities of making projects from these are endless. One example I can give you is ESP32 based gaming.
So this was about the ESP32 Touch Cam module from Makerfabs and its applications. You can attach sensors/ actuators with it and make something of your own.
![]()
In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
In which “Hello, World!” is the text you want to display and the (x, y) coordinate is the location where you want to start display text on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
Note: some people find issues with this display when trying to read from the SD card. We don’t know why that happens. In fact, we tested a couple of times and it worked well, and then, when we were about to record to show you the final result, the display didn’t recognized the SD card anymore – we’re not sure if it’s a problem with the SD card holder that doesn’t establish a proper connection with the SD card. However, we are sure these instructions work, because we’ve tested them.
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.

I CAN WALK AGAIN! yaaay.. Back in the lab making videos.This video is the first of a miniseries showing how to interface a camera to a microcontroller (ESP32...






 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey