lcd panel test patterns manufacturer
PanelTest™ performs rapid display optical measurements for cell phone, tablet, and laptop sized LCD or OLED displays. It comes standard with three optical instruments for display measurement, an LCD tester for display drive, and can be optionally configured to provide viewing angle and multi-point measurements.
PanelTest provides an entire dark room laboratory in a cabinet. PanelTest can be used on the LCD or OLED production line or in the lab with test times as little as 60 seconds per display. The PanelTest software performs Pass/Fail testing and calculates statistical process parameters, such as Cpk, while logging all test data to a database. Data can be exported to Excel reports
PanelTest™ employs three sensors, each optimized for specific measurement tasks. A high sensitivity spectrometer with a cooled back-thinned CCD provides the highest measurement accuracy throughout the color gamut for luminance, contrast and color measurements. A CCD camera provides rapid uniformity measurements. Westar’s proven
In the past, qualification and QC testing of mobile displays often involved a dark room laboratory with optical instruments mounted on home-made fixtures. Testing was labor intensive and took too long to acquire significant statistical data. This resulted in very long test times for qualification testing and limited QC verification. With its fully integrated instruments, display drive, and powerful software, PanelTest makes rapid qualification testing and QC testing possible!
A certified Westar installer will arrive at your facility to install the PanelTest Display Measurement System. After installing the system, the installer will provide up to 2 days of training on operation.
The PanelTest Display Measurement System comes with a limited 1 year warranty and 1 year of technical support. Contact Westar for extended warranty and support options.

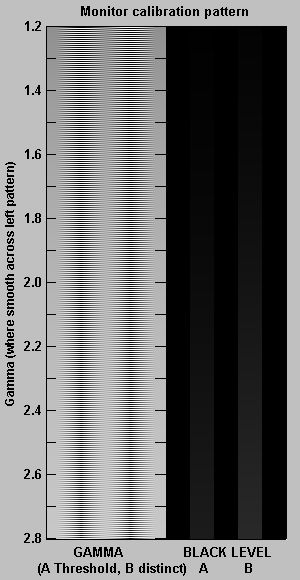
This selection contains several patterns that enable you to check your monitor’s calibration. The gamma patterns (left and middle) must be viewed on a monitor; they do not work in printed media. Reset pattern restores the default values, H = 0, S = 0, L = 1, and Gamma = 2.2.
This chart enables (shown below) you to set the black level (brightness) and estimate display gamma over a range of 1.2 to 2.8 with accuracy close to ±0.05. The gamma pattern is on the left; the black level pattern is on the right. Before using the chart, CRT monitors should be turned for on for at least 15 minutes. For flat screen (LCD) monitors, Screen resolution should be set to the monitor’s native resolution (right-click on the wallpaper, Properties, Settings).
Your monitor’s gamma should be set for 2.2 (for Windows systems).Gamma = 2.2 for the Internet-standard sRGB color space and the popular Adobe RGB (1998) color space. 1.8 was the standard for older Macintosh systems and prepress file interchange (Mac users, see Ian Lyons’ Mac Calibration page.). Many laptop LCD screens cannot be accurately calibrated because gamma is extremely sensitive to viewing angle (though my 2018 Asus Zenbook is better than I expected).You can adjust gamma using Quickgamma (a great free program) or a hardware calibrator (details here).
The image on the right shows the middle gamma pattern enlarged 4x. The upper part of this image, to the right of Standard, uses the same black-to-white sinusoidal variation as the Gamma and black level chart. The color patterns appear when the Alt pattern colors (T & B) box, located just to the right of the Gamma slider, is checked
When this image is displayed normal size (not enlarged; below) on a good quality monitor, the R-C, G-M, B-Y, and Standard patterns appear nearly identical.
Right: HSL rainbow patterns. These patterns are used for a rough visual estimate of the monitor’s color performance. They should appear well-saturated and have smooth color and tonal gradations (no abrupt changes). Laptops typically look very different from well-calibrated LCD or CRT monitors.
In the past decade, LCD monitors have replaced CRT screens for all but the most specialist applications. Although liquid crystal displays boast perfect

The EIZO monitor test lets you quickly and easily assess your monitor’s image quality. You can carry out 13 individual tests to check how uniform the image display is across the entire monitor, for example, or if the text is displayed sharply. You can check your monitor for defective pixels and get a sense of its viewing angle stability. Put your monitor to the test now!
The EIZO monitor test consists of various test scenarios that your monitor can handle to a greater or lesser extent, depending on the model. For example, gaming monitors are distinguished by particularly short response times, whereas graphic monitors impress with a particularly homogenous image display and smooth gradients. You should therefore always assess your monitor within the context of its respective device category. For this reason, please note the manufacturer specifications (especially for the defective pixel test). It is recommended that you carry out the monitor test in a dark room. This allows you to precisely assess even dark image areas.
In order to ensure meaningful test results, your monitor should already be warmed up prior to testing (ideally for 30 minutes). You should also clean the display prior to testing, since reflected light could cause dust particles to look like defective pixels.
Our integrated circuits and reference designs help you create high-density, high-performance, multi-channel flat panel display (FPD) test equipment that minimizes channel-to-channel variations due to reference voltage loading, clocking and power.
New generation flat panel display (FPD) test equipment often requires:Simultaneous high-precision, high-voltage, multi-channel measurement capabilities.

Have you ever properly checked the display quality of the LCD you habitually use? Very often people become aware of previously unnoticed problems in display quality when they run a check using test patterns and so on. This time we are going to talk about the basic points used to assess LCD display quality, and show you a simple way to test it.
Below is the translation from the Japanese of the ITmedia article "The difference in image quality is perfectly obvious! – Let"s check the LCD"s monitor" published April 22, 2010. Copyright 2011 ITmedia Inc. All Rights Reserved.
First of all, bear with us in the following simple test. Below is image data of a row of three squares. In the center of each square is a letter so faint as to be barely distinguishable, so there are three letters in all. Read from the left they make up a word. Can you see that hidden word?
That"s right. The answer is "LCD" (it is displayed if you drag the space between the brackets). We assume that probably many users could read the letters concealed in the squares.
So, the next test is much more difficult. A word is concealed in the four squares below, just as in the image above. The letters are written in colors that are very similar to those of the boxes and we expect that, in many cases, it is hard to distinguish them in your browser. We would like you to download the image and check it closely in photo retouching software or a viewer that is capable of accurate color reproduction.
This time the answer is "EIZO" (it is displayed if you drag the space between the brackets). Depending on the lighting or the user"s environment it may be hard to make out but, if you can read these four letters, the display quality, or more accurately the still image gradation expression, of your LCD is extremely high.
Let"s get down to details then. "Image quality" is the top priority of the LCD, of course. However, recently LCD prices are fiercely competitive and there are surprisingly few products that insist on high image quality and performance. It may be nice to be able to get hold of a wide-screen monitor with full HD (1920 × 1080 dot) resolution or higher fairly cheaply, but it cannot be denied that such LCDs tend not to place too much importance on display quality.
On the other hand, the increasing opportunities to enjoy things like HD videos and games, and high resolution digital photographs on the computer make LCD display quality even more important. As far as possible it"s best to use an LCD with excellent display quality in order to fully enjoy the charms of the visual content.
Even so, perhaps you think that there can"t really be that much wrong with the LCDs that so many people are using at the moment. Here we would like to show you a simple method to check LCD display quality. You can get a good idea of whether the basic display quality is good or bad just by looking at how some simple test images are displayed, just like in the introductory quiz. First of all, we would like you to get a sense of how important it is that "image data can be properly displayed" by checking the display of the LCD that you currently use, (that"s right, the one you are using to view this page!).
The test items use color / monochrome patterned images to check gradation expression, and simple images to check brightness / chromaticity variation. Downloads are available of several test images, such as gradation patterns. We would like you to display the downloaded test images in photo retouching software or a viewer that can reproduce color accurately. As we mentioned at the start of this article, you have to be careful as in many cases colors cannot be displayed accurately in web browsers. (Currently only a few browsers such as Safari and Firefox 3.x can handle color management).
Before starting your visual check of the display quality, please return to your LCD"s setting to default, and select Adobe RGB or sRGB as the image quality mode. If these modes are not available it is fine to set the color temperature to 6500K and gamma to 2.2. If you cannot adjust the color temperature and gamma, simply adjust the brightness and contrast so that they are easier to discern. Of course, if it"s an LCD environment that has been color calibrated it"s OK to leave it as it is.
The average LCD takes some time for the monitor to stabilize after it is switched on so, after start up, please wait at least 30 minutes or so before doing the test. (Most EIZO monitors are an exception to this as they are equipped with our proprietary dimming function and the monitor stabilizes in a short time after start up.)
The surface treatment of an LCD makes a difference to the background reflection. Glare panels impede the surface diffusion of backlight, which does make it easier to achieve high color purity, but also makes distinct reflections of the user or lighting much more likely (photo on the left).
If the lights are similarly trained on a non-glare panel they do not have much effect on the display, only appearing as a fuzzy brightness (photo on the right).
For your reference, we ran a test on an EIZO 24.1-inch wide-screen LCD, the FlexScan SX2462W, for this article. The FlexScan SX series comes with a number of high image quality functions and boasts top class display quality as a general-purpose LCD intended for a computer.
When checking the display quality of an LCD it is comparatively easy to understand the gradation expression capability by a visual check. Let"s display color and monochrome gradation images and check whether the entire image is smoothly reproduced. If there is a problem with the gradation expression it produces things like blocked-up shadows in dark areas and blown-out highlights in light areas, banding (vertical or horizontal stripes) in the middle gradations, and color cast, so you should check for problems like these.
Test images of color / monochrome gradations are shown below. Each test image is prepared for three resolution levels (1280 × 800 dots / 1680 × 1050 dots / 1920 × 1200 dots). When you click on an image it is displayed in that actual resolution. We would like you to download the images in the resolution which matches that of your current LCD. Gradation expression can vary according to whether the image is viewed horizontally or vertically, so it will be more effective if you rotate these images and view them vertically as well.
A gradation pattern where the colors red, green, blue, cyan, magenta and yellow go through 16 gradients as they change to white or black. This is an easy test image so we expect that it can be seen in most environments that each color bar is divided into 16 blocks.
A gradation pattern where the colors red, green, blue, cyan, magenta and yellow go through 64 gradients as they change to white or black. Each color bar is divided into 64 rectangular blocks. With this many gradients we expect that many LCDs will find it hard to make distinctions in the dark areas or the areas that are close to primary colors.
A smooth gradation pattern where the colors red, green, blue, cyan, magenta and yellow go through 256 gradients as they change to white or black. At this level of difficulty you cannot distinguish between adjoining colors from a distance but, if you have an LCD with excellent gradation expression, if you look closely you should be able to see that each color is divided into thin rectangular blocks.
A gradation pattern that changes from black to white. It is divided into 5 horizontal bars: from the top, smooth, 128 gradients, 64 gradients, 32 gradients and 16 gradients. Even if all the differences can be distinguished in the 16 and 32 gradient patterns near the bottom, we expect that there will be some parts in the 64 and 128 gradient patterns where it is hard to see the boundaries between adjoining colors. With this kind of monochrome test image you should also check whether any unnecessary colors are mixed with the gray.
On an average LCD gradations of gray that are close to black tend to appear as blocked-up shadows (gradations of gray that are close to white are displayed comparatively accurately). If your LCD"s OSD menu allows you to adjust the contrast, please try gradually turning down the contrast. Turning down the contrast often makes it possible to see gradations that had been subject to blocked-up shadows or blown-out highlights.
Probably most LCDs will be able to detect some degree of banding and color cast in the middle gradations. Banding in the middle gradations is tone jump (Missing gradations) and, along with color cast, means that the RGB gamma curves are unequal. Unlike blocked-up shadows or blown-out highlights, this is an area that it is hard to improve with adjustments made by the user.
When we looked at these test images on the FlexScan SX2462W, in the smooth gradation there was blocked-up shadows right next to the black but we could distinguish differences in gradations of gray until very close to the black area. When it comes to such subtle gradation distinctions the brightness of the room and the adaptability of the eye come into play, so the range that is visible will vary according to the environment and the individual. The gradation expression was excellent, with almost no blown-out highlights in light areas, middle gradation banding or color cast.
The answer is "The far right" (it is displayed if you drag the space between the brackets). If the other grays looked correct, color may not be being correctly recognized for a variety of reasons, such as the lighting environment or the LCD settings.
The two image patterns below are easy to understand examples of optical illusions. When you look at them you should be able to understand how heavily the human eye is influenced by surrounding colors.
Now let"s assess the gradation expression with some slightly different test images. Below are color patterns with a spread of pale colors in gradations close to the dark range and the light range. They are arranged so that a distinction cannot be made between adjoining colors on an LCD with insufficient gradation expression.
We expect that you could roughly get the whole picture in the gradation patterns on the previous page, but in the patterns this time some parts that cannot be seen may have appeared in some cases. As we mentioned earlier, LCDs tend to display gradations close to black as a blocked-up shadows, and color patterns that are close to black are particularly hard to distinguish.
Since there are some parts that cannot be seen, the possibility arises subtle skin colors and tones cannot be accurately recognized when doing things like retouching photographs, though the misrecognition will vary according to the user"s eyesight. People who place importance on color reproduction should probably bear this in mind when they think about replacing their LCD or buying an extra one.
Incidentally, when we checked the FlexScan SX2462W with these tests we could distinguish everything in both the close to white and the close to black patterns. As well as no blown-out highlights or blocked-up shadows, we saw no unnatural color casts.
This shows the color patterns displayed on the FlexScan SX2462W. It was taken with a digital camera so some parts look a little patchy but they were accurately displayed when we did a visual check.
Every LCD has some degree of brightness and chromaticity variation, but there are many products where the variations become more obvious when the brightness is lowered. A comparison of the brightness and chromaticity variation of a number of LCDs reveals that there is a fairly large difference between products, so this is a point to bear in mind.
If you actually try this test you may be surprised to find more variation than you expected when gray or a near-white pale color is displayed. Generally speaking, the center of an LCD screen is the brightest and it gradually gets darker towards the edges. This is no problem if there is not a big difference in brightness between the central and peripheral areas, but there are some products where this difference is very striking.
Incidentally, this test is also an effective way to test the LCD for dot defects (normal lighting / unlit room). We would like you to check the black display in a darkened environment, for example by switching off all the room lights at night. Although you probably saw the whole screen as uniformly black in a light environment, very often in a dark environment you can find variations in some parts due to light leaks.
The FlexScan SX2462W got good results again when we tried it with the brightness and chromaticity variation tests. The brightness decreased slightly at the edges of the screen, particularly the lower edge, but overall the display was even and pleasing. It is installed with a "digital uniformity equalizer" that measures brightness and chromaticity throughout the screen and makes corrections so that the entire screen is uniform.
Monochrome full-screen displays on a FlexScan SX2462W. Only the screen display is shown. The bottom right is a near-white pale orange. There are not many LCDs that can display this kind of pale color as uniformly as this
However, the pitfall here is that it simply means that "the screen is visible". The thing is that the viewing angle specifications are permitted to use the term "visible" until the display contrast ratio drops to an extremely low 10:1 or 5:1 when the screen is viewed from an angle (the steeper the angle from which the LCD screen is viewed, the more the contrast generally declines). In other words, they do not take into account the display uniformity of the central and peripheral areas of the screen, or the level of chromatic change, when the screen is viewed from an angle.
The ideal viewing angles is that the brightness and chromaticity is very uniform and there is not much chromatic change, even when the screen is viewed from a slight angle. The viewing angles given in the specifications are not really very helpful, but you can judge the standard of the panel type that the LCD (liquid crystal panel) adopts. IPS liquid crystal panels have the least change in brightness or chromaticity when the screen is viewed from an angle, and they are followed by VA panels. An IPS or VA liquid crystal panel can be said to indicate the superior nature of the product itself, so this is often included in the catalog or specifications. It is probably a good idea to look through the catalogs of various products.
On the other hand, monitors installed with cost-effective TN liquid crystal panels are in fact the most numerous. However, the TN type lags far behind the IPS and VA types in terms of characteristic viewing angle changes in brightness and chromaticity. Simply viewing the screen from a slightly different angle makes the coloration change dramatically, and the screen looks completely different according to whether it is viewed vertically or horizontally. If the vertical and horizontal viewing angles in the specifications are different then it is a TN type. There are quite a few products with a 20-inch wide screen or larger where colors look different in the central and peripheral areas even when the screen is viewed straight on.
The display on an IPS panel. Even when viewed from this angle, the displayed content can of course be distinguished completely and the colors also show up really well
The display on a VA panel. Compared with the IPS panel the screen is a little whitish and the chromaticity has slipped, but it is a satisfactory viewing angle for actual use
The display on a TN panel. There is a very clear difference from the IPS and VA panels. The display throughout the entire screen lacks uniformity and there is a yellow cast
The gradation images and monochrome images from earlier in this article can be used as they are to check the viewing angles. Display an image on the whole screen, look at it straight on and check whether the brightness and colors are uniform at the top and bottom of the screen, and in the center and at both sides. Then gradually shift the angle from which you view the screen and check how the brightness and coloration change. If you do this with photographic data as well as the test images, you should be able to get a better sense of the difference in the display.
When we checked the viewing angles of the FlexScan SX2462W there was absolutely nothing to criticize since, in addition to the use of an IPS panel, it is equipped with many high image quality functions, including the afore-mentioned digital uniformity correction circuit. The brightness and chromaticity throughout the whole screen is very uniform, and the coloration hardly changed at all when the viewing angle was changed.
We explained here about easy ways to check LCD monitor quality. How were the results for your current LCD? We think that many people were probably very bothered by the blocked-up shadows and blown-out highlights when the test images to check gradation were displayed, by the middle gradation banding, and by the variations in brightness and chromaticity when the monochrome images were displayed.
As we mentioned at the beginning, recently the number of LCDs with excellent display quality is on the decline. Although we would not go so far as to say that the display quality of inexpensive products is poor. Of course a high quality LCD is indispensable if you want to enjoy using your computer, properly handle the needs of applications that require color reproducibility, and to fully enjoy all the benefits of rich content.
The EIZO FlexScan LCD series has excellent display quality in those regards, and we have no qualms about recommending them to everyone. The product line-up is diverse but each model is clearly ranked according to the purpose to which it is suited and its screen size, and they all guarantee above-standard display quality. They may cost a little more than you had budgeted for but the clear value they offer exceeds their price.
If, after trying these tests, you have doubts about the display quality of the LCD that you usually use, we would certainly urge you to consider an EIZO LCD. We would also recommend that you construct a multi-display environment by making the new LCD your main monitor and the one that you have been using your sub monitor.

To ensure the quality of a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel, extensive quality check in terms of different display patterns is performed after LCD production. Geared to LCD manufacturing facilities with several production lines, this paper presents an LCD testing solution of a server-based test pattern databank (TPD) and units of pattern generation system (PGS). TPD provides a GUI-based tool to facilitate editing and maintenance of test patterns, which are then downloaded to independent PGSs, each connected to LCD panels in a production line, for the pattern testing. Three issues related to the design of the proposed TPD are addressed. First, the definition of file formats used to characterize display patterns and timing parameters utilized for a complete test; second, the underlying graphical user interface (GUI) design of the TPD. Comparison to some existing solutions are also discussed to highlight the benefit of test pattern file consistency as well as cost effectiveness in the proposed TPD
This report examines the gamma relationship between a display’s pixel input values and its luminance output values. We examine how a display’s gamma is specified and how it is normally measured. We see how a display’s gamma measurement and/or adjustment is complicated by dynamic luminance changes that are based on average picture level. We also examine the latest standard for measuring the gamma performance of these displays with dynamic luminance levels.
We then present a type of test pattern that maintains a constant APL, despite changes to its measurement stimulus level. We present an innovative method of maintaining constant APL at any desired window size or APL, as well as constant chromatic, to maintain accurate gamma measurements not only for grayscale levels, but for all colors.
Many display technologies dynamically adjust the luminance levels of the display, depending upon the average picture level (APL) of the currently displayed image. These displays include plasma panels with ABL, LCDs and PDPs with global and local dimming, and projectors with auto iris.
To measure a display’s gamma, we typically display ten or more test patterns, with the stimulus levels (pixel values) of the individual patterns distributed across the grayscale range of interest. We measure the luminance that the display produces with each test pattern and chart the results, to produce a visual representation of the display’s gamma performance (Figure 2).
For this type of display, the luminance of a full white area of the image dynamically changes as the average pixel level of the entire image changes (Figure 4). These displays, that dynamically change their luminance as the average pixel level changes, include all plasma display panels (PDPs), LCDs with global or local dimming enabled, and projectors with auto iris enabled.
Because plasma display panels generate significant heat and a high power supply load when producing high luminance across a significant area of a scene, all plasma displays include an Automatic Brightness Limiter (ABL) to protect their power supplies, to reduce phosphor aging, and to limit their energy consumption.
During a scene with a high proportion of bright elements, the ABL circuit limits the panel’s luminance (dims the entire picture) to limit power consumption. During a scene with a lower proportion of bright pixels there is less limiting effect. Depending upon the proportion of bright pixels in the entire image, this changes the amount of light a plasma panel produces at any particular pixel drive level (Figure 5).
Global or local dimming in LCDs and PDPs, and auto iris in projectors also have the effect of dynamically changing the luminance produced at a particular pixel drive level, depending upon the proportion of bright pixels in the rest of the image. This has the effect of dynamically changing the gamma performance of a display, depending upon picture content. So, what is an appropriate method to measure or adjust the gamma performance for a display that dynamically changes its luminance with picture content changes?
Both full field and window (partial field) test patterns have been used to test display gamma. The APL of both full field and window test patterns changes, though, as the measurement stimulus level changes.
A full-field test pattern produces 100% APL at 100% stimulus, with proportionally lower APLs at lower stimulus levels. The APL varies from 100% to 0%.
This extreme APL change is okay when testing LCD panels with dimming disabled or projectors with auto iris disabled, but is not appropriate for testing displays that dynamically change their luminance levels, depending upon the APL of the currently displayed image.
Window patterns with a black background have been in use for a long time for display measurements. These patterns minimize the APL change when switching between different stimulus levels, as compared to full field test patterns.
You can see that smaller size window patterns, with a black background, result in a smaller APL change as the measurement stimulus level is varied from maximum to minimum. But, any window pattern with a constant background level is not a constant APL test pattern.
Window test patterns have long been thought to be appropriate for measuring displays with dynamically changing luminance levels. However, a window pattern with any constant background level still has a changing APL as the measurement stimulus level changes. This still results in dynamically changing measurement conditions.
The International Committee for Display Metrology (ICDM), part of the Society for Information Display (SID) Definitions and Standards Committee, was charged with updating the Flat Panel Display Measurements Standard that had been used extensively by the industry since its publication by VESA in 2001. The ICDM published its Information Display Measurement Standard (IDMS) in May of 2012, with recommended procedures to quantify electronic display characteristics.
To measure the gamma of display technologies that dynamically adjust luminance based on image content, the IDMS standard specifies test patterns that maintain a fixed average pixel level (APL) (page 86). One IDMS implementation of fixed APL is a test pattern with a center stimulus window and a background that changes pixel level to counterbalance the luminance changes in the center window (Figure 10).
When you are measuring a display that dynamically adjusts its luminance based on image content, you don’t get meaningful gamma measurements with test patterns that each have a different APL. Each test pattern, each with a different APL, causes the display to exhibit a different dynamic luminance characteristic.
A constant APL test pattern maintains the same APL across the measurement stimulus range. As the stimulus level in the center window changes, the background level changes to compensate, keeping the total light output constant.
The center window for the four constant APL test patterns is at the currently selected stimulus level, ranging from 100% white to 0% black. The window size is approximately 5% of the area of the total image frame.
CalMAN also provides a Constant APL test pattern that can be user-defined. The user can select the Pattern Size, to select the size of the center stimulus window, and the Pattern APL, to set the APL of the overall pattern.
As well as maintaining a constant average pixel level for the Constant APL test patterns, CalMAN also maintains the test patterns as constant chromatic.
If you are unable to totally disable either dimming or auto iris, use a constant APL test pattern to minimize their effects on any display measurements.
For plasma panels, to constrain the effect of ABL to the average picture level of the expected content, use constant APL test patterns. We want to measure or adjust gamma in the picture condition that is most prevalent.
You don’t want a different APL for each different test pattern. That would mean that both the stimulus level and the APL are changing during the gamma measurement. We want to test gamma at one or more fixed APLs. Each gamma test will involve only one variable, the stimulus level.
If you want to test multiple variables (i.e. stimulus and APL), test only one variable at a time. Use a constant APL pattern (e.g. 50 APL) to test a display’s gamma at that APL across the stimulus range. Then, switch to another constant APL pattern (e.g. 25 APL) to test the display’s gamma at that APL.
Many display technologies produce different luminance at black, gray, and/or peak white levels, depending upon the average picture level (APL) of the image. These display types include plasma and LCD panels with global or local dimming, plasma panels with ABL, and projectors with auto iris.
A display’s gamma performance, which is critical to accurate image rendering, is determined by measuring test patterns at various stimulus levels. If the test patterns also change average picture level as they change stimulus levels, many displays produce a different luminance, not only in response to the changed stimulus level, but also due to the changed
Because a frame of picture content is always at a single APL and because most picture content averages out to an APL within a moderate range, we normally want to test at one, or possibly two different, APLs to accurately characterize a display’s gamma performance.
A constant APL test pattern allows us to stabilize the ABL effect in plasma panels, stabilize any dimming or auto iris action that can’t be disabled, and test at an APL that is representative of average program content. This allows a gamma test to measure only the effects of stimulus (picture) level changes.
CalMAN constant APL test patterns are available at a number of fixed APLs and at user-defined APLs. The CalMAN test patterns are also constant chromatic, minimizing any display changes due to any effect other than the desired stimulus level change. This enables the most accurate gamma measurements and adjustments that are possible, on any display type.

Important technical improvements of LCD, such as LED backlighting and wide viewing Angle, are directly related to LCD. And account for an LCD display 80% of the cost of the LCD panel, enough to show that the LCD panel is the core part of the entire display, the quality of the LCD panel, can be said to directly determine the quality of an LCD display.
The production of civil LCD displays is just an assembly process. The LCD panel, the main control circuit, shell, and other parts of the main assembly, basically will not have too complex technical problems.
Does this mean that LCDS are low-tech products? In fact, it is not. The production and manufacturing process of the LCD panels is very complicated, requiring at least 300 process processes. The whole process needs to be carried out in a dust-free environment and with precise technology.
The general structure of the LCD panel is not very complex, now the structure of the LCD panel is divided into two parts: the LCD panel and the backlight system.
Due to the LCD does not shine, so you need to use another light source to illuminate, the function of the backlight system is to this, but currently used CCFL lamp or LED backlight, don’t have the characteristics of the surface light source, so you need to guide plate, spreadsheet components, such as linear or point sources of light evenly across the surface, in order to make the entire LCD panel on the differences of luminous intensity is the same, but it is very difficult, to achieve the ideal state can be to try to reduce brightness non-uniformity, the backlight system has a lot to the test of design and workmanship.
In addition, there is a driving IC and printed circuit board beside the LCD panel, which is mainly used to control the rotation of LCD molecules in the LCD panel and the transmission of display signals. The LCD plate is thin and translucent without electricity. It is roughly shaped like a sandwich, with an LCD sandwiched between a layer of TFT glass and a layer of colored filters.
LCD with light refraction properties of solid crystals, with fluid flow characteristics at the same time, under the drive of the electrode, can be arranged in a way that, in accordance with the master want to control the strength of the light through, and then on the color filter, through the red, green, blue three colors of each pixel toning, eventually get the full-screen image.
According to the functional division, the LCD panel can be divided into the LCD panel and the backlight system. However, to produce an LCD panel, it needs to go through three complicated processes, namely, the manufacturing process of the front segment Array,the manufacturing process of the middle segment Cell, and the assembly of the rear segment module. Today we will be here, for you in detail to introduce the production of the LCD panel manufacturing process.
The manufacturing process of the LCD panel Array is mainly composed of four parts: film, yellow light, etch and peel film. If we just look at it in this way, many netizens do not understand the specific meaning of these four steps and why they do so.
First of all, the motion and arrangement of LCD molecules need electrons to drive them. Therefore, on the TFT glass, the carrier of LCD, there must be conductive parts to control the motion of LCD. In this case, we use ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) to do this.ITO is transparent and also acts as a thin-film conductive crystal so that it doesn’t block the backlight.
The different arrangement of LCD molecules and the rapid motion change can ensure that each pixel displays the corresponding color accurately and the image changes accurately and quickly, which requires the precision of LCD molecule control.ITO film needs special treatment, just like printing the circuit on the PCB board, drawing the conductive circuit on the whole LCD board.
This completes the previous Array process. It is not difficult to see from the whole process that ITO film is deposited, photoresist coated, exposed, developed, and etched on TFT glass, and finally, ITO electrode pattern designed in the early stage is formed on TFT glass to control the movement of LCD molecules on the glass. The general steps of the whole production process are not complicated, but the technical details and precautions are very complicated, so we will not introduce them here. Interested friends can consult relevant materials by themselves.
The glass that the LCD board uses makes a craft also very exquisite. (The manufacturing process flow of the LCD display screen)At present, the world’s largest LCD panel glass, mainly by the United States Corning, Japan Asahi glass manufacturers, located in the upstream of the production of LCD panel, these manufacturers have mastered the glass production technology patents. A few months ago, the earthquake caused a corning glass furnace shutdown incident, which has caused a certain impact on the LCD panel industry, you can see its position in the industry.
As mentioned earlier, the LCD panel is structured like a sandwich, with an LCD sandwiched between the lower TFT glass and the upper color filter. The terminal Cell process in LCD panel manufacturing involves the TFT glass being glued to the top and bottom of a colored filter, but this is not a simple bonding process that requires a lot of technical detail.
As you can see from the figure above, the glass is divided into 6 pieces of the same size. In other words, the LCD made from this glass is finally cut into 6 pieces, and the size of each piece is the final size. When the glass is cast, the specifications and sizes of each glass have been designed in advance.
Directional friction:Flannelette material is used to rub the surface of the layer in a specific direction so that the LCD molecules can be arranged along the friction direction of the aligned layer in the future to ensure the consistency of the arrangement of LCD molecules. After the alignment friction, there will be some contaminants such as flannelette thread, which need to be washed away through a special cleaning process.
After the TFT glass substrate is cleaned, a sealant coating is applied to allow the TFT glass substrate to be bonded to the color filter and to prevent LCD outflow.
Finally, the conductive adhesive is applied to the frame in the bonding direction of the glass of the color filter to ensure that external electrons can flow into the LCD layer. Then, according to the bonding mark on the TFT glass substrate and the color filter, two pieces of glass are bonded together, and the bonding material is solidified at high temperatures to make the upper and lower glasses fit statically.
Color filters are very important components of LCD panels. Manufacturers of color filters, like glass substrate manufacturers, are upstream of LCD panel manufacturers. Their oversupply or undersupply can directly affect the production schedule of LCD panels and indirectly affect the end market.
As can be seen from the above figure, each LCD panel is left with two edges after cutting. What is it used for? You can find the answer in the later module process
Finally, a polarizer is placed on both sides of each LCD substrate, with the horizontal polarizer facing outwards and the vertical polarizer facing inwards.
When making LCD panel, must up and down each use one, and presents the alternating direction, when has the electric field and does not have the electric field, causes the light to produce the phase difference and to present the light and dark state, uses in the display subtitle or the pattern.
The rear Module manufacturing process is mainly the integration of the drive IC pressing of the LCD substrate and the printed circuit board. This part can transmit the display signal received from the main control circuit to the drive IC to drive the LCD molecules to rotate and display the image. In addition, the backlight part will be integrated with the LCD substrate at this stage, and the complete LCD panel is completed.
Firstly, the heteroconductive adhesive is pressed on the two edges, which allows external electrons to enter the LCD substrate layer and acts as a bridge for electronic transmission
Next is the drive IC press. The main function of the drive IC is to output the required voltage to each pixel and control the degree of torsion of the LCD molecules. The drive IC is divided into two types. The source drive IC located in the X-axis is responsible for the input of data. It is characterized by high frequency and has an image function. The gate drive IC located in the Y-axis is responsible for the degree and speed of torsion of LCD molecules, which directly affects the response time of the LCD display. However, there are already many LCD panels that only have driving IC in the X-axis direction, perhaps because the Y-axis drive IC function has been integrated and simplified.
The press of the flexible circuit board can transmit data signals and act as the bridge between the external printed circuit and LCD. It can be bent and thus becomes a flexible or flexible circuit board
The manufacturing process of the LCD substrate still has a lot of details and matters needing attention, for example, rinse with clean, dry, dry, dry, ultrasonic cleaning, exposure, development and so on and so on, all have very strict technical details and requirements, so as to produce qualified eyes panel, interested friends can consult relevant technical information by a search engine.
LCD (LC) is a kind of LCD, which has the properties of light transmission and refraction of solid Crystal, as well as the flow property of Liquid. It is because of this property that it will be applied to the display field.
However, LCD does not emit light autonomously, so the display equipment using LCD as the display medium needs to be equipped with another backlight system.
First, a backplate is needed as the carrier of the light source. The common light source for LCD display equipment is CCFL cold cathode backlight, but it has started to switch to an LED backlight, but either one needs a backplate as the carrier.
CCFL backlight has been with LCD for a long time. Compared with LED backlight, CCFL backlight has many defects. However, it has gradually evolved to save 50% of the lamp and enhance the transmittance of the LCD panel, so as to achieve the purpose of energy-saving.
With the rapid development of LED in the field of lighting, the cost has been greatly reduced.LCD panels have also started to use LED as the backlight on a large scale. Currently, in order to control costs, an LED backlight is placed on the side rather than on the backplate, which can reduce the number of LED grains.
At the top of the diffusion plate, there will be 3~4 diffuser pieces, constantly uniform light to the whole surface, improve the uniformity of light, which is directly related to the LCD panel display effect. Professional LCD in order to better control the brightness uniformity of the screen, panel procurement, the later backlight control circuit, will make great efforts to ensure the quality of the panel.
Since the LCD substrate and the backlight system are not fixed by bonding, a metal or rubber frame is needed to be added to the outer layer to fix the LCD substrate and the backlight system.
After the period of the Module, the process is completed in LCM (LCDModule) factory, the core of this part of the basic does not involve the use of LCD manufacturing technology, mainly is some assembly work, so some machine panel factories such as chi mei, Korea department such as Samsung panel factory, all set with LCM factories in mainland China, Duan Mo group after the LCD panel assembly, so that we can convenient mainland area each big monitor procurement contract with LCD TV manufacturers, can reduce the human in the whole manufacturing and transportation costs.
However, neither Taiwan nor Korea has any intention to set up factories in mainland China for the LCD panel front and middle manufacturing process involving core technologies. Therefore, there is still a long way to go for China to have its own LCD panel industry.
In both LCD and OLED displays, producing these cells – which are highly complex – is by far the most difficult element of the production process. Indeed, the complexity of these cells, combined with the levels of investment needed to achieve expertise in their production, explains why there are less than 30 companies in the whole world that can produce them. China, for instance, has invested more than 300 billion yuan (approximately $45 billion USD) in just one of these companies – BOE – over the past 14 years.
Panox Display has been involved in the display industry for many years and has built strong and long-term partner relationships with many of the biggest OLED and LCD panel manufacturers. As a result, we are able to offer our clients guaranteed access to display products from the biggest manufacturers.
LG Display was, until 2021, the No. 1 display panel manufacturer in the world. Owned by LG Group and headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, it has R&D, production, and trade institutions in China, Japan, South Korea, the United States, and Europe.
Founded in 2001, AUO – or AU Optronics – is the world’s leading TFT-LCD panel manufacturer (with a 16% market share) that designs, develops, and manufactures the world’s top three liquid crystal displays. With panels ranging from as small as 1.5 inches to 46 inches, it boasts one of the world"s few large-, medium -and small-sized product lines.
AUO offers advanced display integration solutions with innovative technologies, including 4K2K ultra-high resolution, 3D, ultra-thin, narrow bezel, transparent display, LTPS, OLED, and touch solutions. AOU has the most complete generation production line, ranging from 3.5G to 8.5G, offering panel products for a variety of LCD applications in a range of sizes, from as small as 1.2 inches to 71 inches.
Now Sharp is still top 10 TV brands all over the world. Just like BOE, Sharp produce LCDs in all kinds of size. Including small LCD (3.5 inch~9.1 inch), medium LCD (10.1 ~27 inch), large LCD (31.5~110 inch). Sharp LCD has been used on Iphone series for a long time.
Beside those current LCDs, the industrial LCD of Sharp is also excellent and widely used in public facilities, factories, and vehicles. The Sharp industrial LCD, just means solid, high brightness, super long working time, highest stability.
Since its establishment, Truly Semiconductors has focused on researching, developing, and manufacturing liquid crystal flat panel displays. Now, after twenty years of development, it is the biggest small- and medium-sized flat panel display manufacturer in China.
Truly’s factory in Shanwei City is enormous, covering an area of 1 million square meters, with a net housing area of more than 100,000 square meters. It includes five LCD production lines, one OLED production line, three touch screen production lines, and several COG, LCM, MDS, CCM, TAB, and SMT production lines.
Its world-class production lines produce LCD displays, liquid crystal display modules (LCMs), OLED displays, resistive and capacitive touch screens (touch panels), micro camera modules (CCMs), and GPS receiving modules, with such products widely used in the smartphone, automobile, and medical industries. The LCD products it offers include TFT, TN, Color TN with Black Mark (TN type LCD display for onboard machines), STN, FSTN, 65K color, and 262K color or above CSTN, COG, COF, and TAB modules.
In its early days, Innolux attached great importance to researching and developing new products. Mobile phones, portable and mounted DVD players, digital cameras, games consoles, PDA LCDs, and other star products were put into mass production and quickly captured the market, winning the company considerable market share.
Looking forward to the future, the group of photoelectric will continue to deep LCD display field, is committed to the development of plane display core technology, make good use of global operations mechanism and depth of division of labor, promise customers high-quality products and services, become the world"s top display system suppliers, in 2006 in the global mobile phone color display market leader, become "Foxconn technology" future sustained rapid growth of the engine.
Founded in June 1998, Hannstar specializes in producing thin-film transistor liquid crystal display panels, mainly for use in monitors, notebook displays and televisions. It was the first company in Taiwan to adopt the world’s top ultra-wide perspective technology (AS-IPS).
The company has three LCD factories and one LCM factory. It has acquired state-of-the-art TFT-LCD manufacturing technology, which enables it to achieve the highest efficiency in the mass production of thin-film transistor liquid crystal display production technology. Its customers include many of the biggest and most well-known electronics companies and computer manufacturers in Taiwan and overseas.
TCL CSOT – short for TCL China Star Optoelectronics Technology (TCL CSOT) – was founded in 2009 and is an innovative technology enterprise that focuses on the production of semiconductor displays. As one of the global leaders in semiconductor display market, it has bases in Shenzhen, Wuhan, Huizhou, Suzhou, Guangzhou, and India, with nine panel production lines and five large modules bases.
TCL CSOT actively produces Mini LED, Micro LED, flexible OLED, printing OLED, and other new display technologies. Its product range is vast – including large, medium, and small panels and touch modules, electronic whiteboards, splicing walls, automotive displays, gaming monitors, and other high-end display application fields – which has enabled it to become a leading player in the global panel industry.
In the first quarter of 2022, TCL CSOT’s TV panels ranked second in the market, 55 inches, 65 " and 75 inches second, 8K, 120Hz first, the first, interactive whiteboard and digital sign plate; LTPS flat panel, the second, LTPS and flexible OLED fourth.
EDO (also known as EverDisplay Optonics) was founded in October 2012 and focuses on the production of small- and medium-sized high-resolution AMOLED semiconductor display panels.
Tianma Microelectronics was founded in 1983 and listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange in 1995. It is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the production of liquid crystal displays (LCD) and liquid crystal display modules (LCM).
After more than 30 years of development, it has grown into a large publicly listed company integrating LCD research and development, design, production, sales, and servicing. Over the years, it has expanded by investing in the construction of STN-LCD, CSTN-LCD, TFT-LCD and CF production lines and module factories across China (with locations in Shenzhen, Shanghai, Chengdu, Wuhan and Xiamen), as well R&D centers and offices in Europe, Japan, South Korea and the United States.
JDI (Japan Display Inc.) was established on November 15, 2011, as a joint venture between the Industrial Innovation Corporation, Sony, Hitachi, and Toshiba. It is dedicated to the production and development of small-sized displays. It mainly produces small- and medium-sized LCD display panels for use in the automotive, medical, and industrial fields, as well as personal devices including smartphones, tablets, and wearables.
Although Sony’s TVs use display panels from TCL CSOT (VA panel), Samsung. Sony still produces the world’s best micro-OLED display panels. Sony has many micro OLED model such as 0.23 inch, 0.39 inch, 0.5 inch, 0.64 inch, 0.68 inch, 0.71 inch. Panox Display used to test and sell many of them, compare to other micro OLED manufacuturers, Sony`s micro OLEDs are with the best image quality and highest brightness (3000 nits max).




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey