lcd module technology comparison manufacturer
Asia has long dominated the display module TFT LCD manufacturers’ scene. After all, most major display module manufacturers can be found in countries like China, South Korea, Japan, and India.
However, the United States doesn’t fall short of its display module manufacturers. Most American module companies may not be as well-known as their Asian counterparts, but they still produce high-quality display products for both consumers and industrial clients.
In this post, we’ll list down 7 best display module TFT LCD manufacturers in the USA. We’ll see why these companies deserve recognition as top players in the American display module industry.
STONE Technologies is a leading display module TFT LCD manufacturer in the world. The company is based in Beijing, China, and has been in operations since 2010. STONE quickly grew to become one of the most trusted display module manufacturers in 14 years.
Now, let’s move on to the list of the best display module manufacturers in the USA. These companies are your best picks if you need to find a display module TFT LCD manufacturer based in the United States:
Planar Systems is a digital display company headquartered in Hillsboro, Oregon. It specializes in providing digital display solutions such as LCD video walls and large format LCD displays.
Microtips Technology is a global electronics manufacturer based in Orlando, Florida. The company was established in 1990 and has grown into a strong fixture in the LCD industry.
What makes Microtips a great display module TFT LCD manufacturer in the USA lies in its close ties with all its customers. It does so by establishing a good rapport with its clients starting from the initial product discussions. Microtips manages to keep this exceptional rapport throughout the entire client relationship by:
Displaytech is an American display module TFT LCD manufacturer headquartered in Carlsbad, California. It was founded in 1989 and is part of several companies under the Seacomp group. The company specializes in manufacturing small to medium-sized LCD modules for various devices across all possible industries.
The company also manufactures embedded TFT devices, interface boards, and LCD development boards. Also, Displaytech offers design services for embedded products, display-based PCB assemblies, and turnkey products.
Displaytech makes it easy for clients to create their own customized LCD modules. There is a feature called Design Your Custom LCD Panel found on their site. Clients simply need to input their specifications such as their desired dimensions, LCD configuration, attributes, connector type, operating and storage temperature, and other pertinent information. Clients can then submit this form to Displaytech to get feedback, suggestions, and quotes.
A vast product range, good customization options, and responsive customer service – all these factors make Displaytech among the leading LCD manufacturers in the USA.
Products that Phoenix Display offers include standard, semi-custom, and fully-customized LCD modules. Specifically, these products comprise Phoenix Display’s offerings:
Clients flock to Phoenix Display because of their decades-long experience in the display manufacturing field. The company also combines its technical expertise with its competitive manufacturing capabilities to produce the best possible LCD products for its clients.
True Vision Displays is an American display module TFT LCD manufacturing company located at Cerritos, California. It specializes in LCD display solutions for special applications in modern industries. Most of their clients come from highly-demanding fields such as aerospace, defense, medical, and financial industries.
The company produces several types of TFT LCD products. Most of them are industrial-grade and comes in various resolution types such as VGA, QVGA, XGA, and SXGA. Clients may also select product enclosures for these modules.
All products feature high-bright LCD systems that come from the company’s proprietary low-power LED backlight technology. The modules and screens also come in ruggedized forms perfect for highly-demanding outdoor industrial use.
LXD Incorporated is among the earliest LCD manufacturers in the world. The company was founded in 1968 by James Fergason under the name International Liquid Xtal Company (ILIXCO). Its first headquarters was in Kent, Ohio. At present, LXD is based in Raleigh, North Carolina.
All of their display modules can be customized to fit any kind of specifications their clients may require. Display modules also pass through a series of reliability tests before leaving the manufacturing line. As such, LXD’s products can withstand extreme outdoor environments and operates on a wide range of temperature conditions.
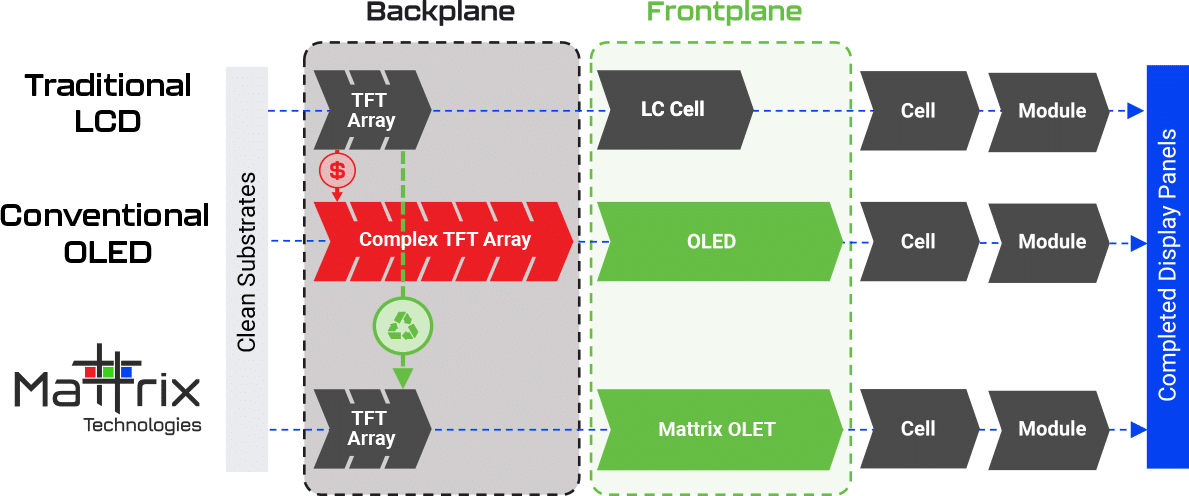
We’ve listed the top 7 display module TFT LCD manufacturers in the USA. All these companies may not be as well-known as other Asian manufacturers are, but they are equally competent and can deliver high-quality display products according to the client’s specifications. Contact any of them if you need a US-based manufacturer to service your display solutions needs.
We also briefly touched on STONE Technologies, another excellent LCD module manufacturer based in China. Consider partnering with STONE if you want top-of-the-line smart LCD products and you’re not necessarily looking for a US-based manufacturer. STONE will surely provide the right display solution for your needs anywhere you are on the globe.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) screens are a staple in the digital display marketplace and are used in display applications across every industry. With every display application presenting a unique set of requirements, the selection of specialized LCDs has grown to meet these demands.
LCD screens can be grouped into three categories: TN (twisted nematic), IPS (in-plane switching), and VA (Vertical Alignment). Each of these screen types has its own unique qualities, almost all of them having to do with how images appear across the various screen types.
This technology consists of nematic liquid crystal sandwiched between two plates of glass. When power is applied to the electrodes, the liquid crystals twist 90°. TN (Twisted Nematic) LCDs are the most common LCD screen type. They offer full-color images, and moderate viewing angles.
TN LCDs maintain a dedicated user base despite other screen types growing in popularity due to some unique key features that TN display offer. For one,
Displays with VA screens deliver wide viewing angles, high contrast, and good color reproduction. They maintain high response rates similar to TN TFTs but may not reach the same sunlight readable brightness levels as comparable TN or IPS LCDs. VA displays are generally best for applications that need to be viewed from multiple angles, like digital signage in a commercial setting.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) technology improves image quality by acting on the liquid crystal inside the display screen. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate parallel (or “in-plane”) rather than upright to allow light to pass through. This behavior results in several significant improvements to the image quality of these screens.
Based on current trends, IPS and TN screen types will be expected to remain the dominant formats for some time. As human interface display technology advances and new product designs are developed, customers will likely choose IPS LCDs to replace the similarly priced TN LCDs for their new projects.

The most basic LCD introduced above is called passive matrix LCDs which can be found mostly in low end or simple applications like, calculators, utility meters, early time digital watches, alarm clocks etc. Passive matrix LCDs have a lot of limitations, like the narrow viewing angle, slow response speed, dim, but it is great for power consumption.
In order to improve upon the drawbacks, scientists and engineers developed active matrix LCD technology. The most widely used is TFT (Thin Film Transistor) LCD technology. Based on TFT LCD, even more modern LCD technologies are developed. The best known is IPS (In Plane Switching) LCD. It has super wide viewing angle, superior image picture quality, fast response, great contrast, less burn-in defects etc.
IPS LCDs are widely used in LCD monitors, LCD TVs, Iphone, pads etc. Samsung even revolutionized the LED backlighting to be QLED (quantum dot) to switch off LEDs wherever light is not needed to produce deeper blacks.
– Twisted Nematic Display: The TN (Twisted Nematic) LCDs production can be done most frequently and used different kinds of displays all over the industries. These displays are most frequently used by gamers as they are cheap & have quick response time as compared with other displays. The main disadvantage of these displays is that they have low quality as well as partial contrast ratios, viewing angles & reproduction of color. But, these devices are sufficient for daily operations.
– In-Plane Switching Display:IPS displays are considered to be the best LCD because they provide good image quality, higher viewing angles, vibrant color precision & difference. These displays are mostly used by graphic designers & in some other applications, LCDs need the maximum potential standards for the reproduction of image & color.
– Vertical Alignment Panel: The vertical alignment (VA) panels drop anywhere in the center among Twisted Nematic and in-plane switching panel technology. These panels have the best viewing angles as well as color reproduction with higher quality features as compared with TN type displays. These panels have a low response time. But, these are much more reasonable and appropriate for daily use.
– Advanced Fringe Field Switching (AFFS): AFFS LCDs offer the best performance & a wide range of color reproduction as compared with IPS displays. The applications of AFFS are very advanced because they can reduce the distortion of color without compromising on the broad viewing angle. Usually, this display is used in highly advanced as well as professional surroundings like in the viable airplane cockpits.
– Passive and Active Matrix Displays: The Passive-matrix type LCDs works with a simple grid so that charge can be supplied to a specific pixel on the LCD. One glass layer gives columns whereas the other one gives rows that are designed by using a clear conductive material like indium-tin-oxide. The passive-matrix system has major drawbacks particularly response time is slow & inaccurate voltage control. The response time of the display mainly refers to the capability of the display to refresh the displayed image.
– Active-matrix type LCDs mainly depend on TFT (thin-film transistors). These transistors are small switching transistors as well as capacitors which are placed within a matrix over a glass substrate. When the proper row is activated then a charge can be transmitted down the exact column so that a specific pixel can be addressed, because all of the additional rows that the column intersects are switched OFF, simply the capacitor next to the designated pixel gets a charge.
LCD technologies have great advantages of light, thin, low power consumption which made wall TVs, laptops, smartphones, pad possible. On its way to progress, it wiped out the competition of many display technologies. We don’t see CRT monitors on our desks and plasma displays TV at our home anymore. LCD Technologies dominant the display market now. But any technology has the limitations.
LCD technologies have slow response times especially at low temperature, limited viewing angles, backlighting is needed. Focus on LCD drawbacks, OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diodes) technology was developed. Some high-end TV and mobile phones start to use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) displays.
This cutting-edge technology provides even better color reproduction, clear image quality, better color gamut, less power consumption when compared to LCD technology. Please note, OLED displays include AMOLED and PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes). What you need to choose is AMOLED for your TV and mobile phones instead of PMOLED.
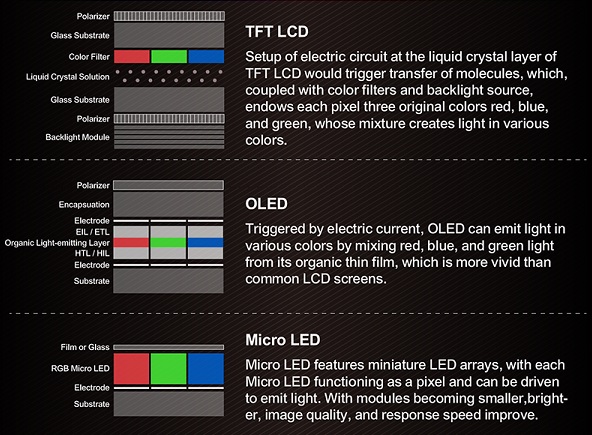
There are two main competing display technologies in the market today: LCD and OLED. The mature and dominant technology is the Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), while the up-and-coming challenger is the Organic Light Emitting Diode Display (OLED display). The main difference between LCD and OLED displays is how they create the light and the colors of the image being displayed. This leads to application dependent strengths and weaknesses of either technology.
OLEDs operate via a solid-state technology, where the individual pixels can emit light in various colors and intensity without the need for an additional light source or color filter. The light-emitting portion of an OLED display is comprised of multiple layers of very specific organic semiconductor materials which can be adjusted to emit light in specific wavelengths. These organic layers have a typical thickness in the order of 100nm. In addition, no backlight is required, allowing for a very thin display module.
In LCD display technology, the individual pixels modulate light. An applied voltage changes the orientation of liquid crystal molecules that – in conjunction with a pair of polarizers – function as a light shutter by either blocking or allowing light to pass through. LCD displays, therefore, require an additional light source, either from reflected ambient light or more commonly from a “backlight” (an array of LEDs arranged behind or next to the LCD panel). LCD color can be created by adding color filters to the individual pixels. Because OLED displays don’t require the additional backlight, polarizers, or color filter components of an LCD module, they can be made much thinner than LCD displays of equivalent size and resolution.
OLED display technology can offer power-saving advantages over LCDs, which is important, especially for battery-powered applications such as mobile phones. An OLED’s power consumption will vary with image content and brightness, as light is generated only at the individual pixels needed to display the image. A dark image or a graphic on a black background will consume much less power than bright images or graphics. In contrast, LCD backlights must be ON while the display operates. It’s possible to control individual zones of the backlight separately to save power, but this added complexity is usually only applied in larger displays.
OLEDs can achieve a much higher contrast ratio if reflections from the front surface are carefully controlled. If no current flows through an OLED pixel, it does not emit any light. In contrast the shutter effect of an LCD pixel does not block 100% of the light. Depending on the specific LCD technology used and the angle of observation, a small percentage of the light generated in the backlight can escape. This can wash out dark areas of an image. It is possible but expensive to limit this light leakage to a point where the contrast of an LCD and OLED display become perceptually equivalent.
RGB OLEDs naturally generate a narrow bandwidth of light. This leads to very saturated primary colors and a wide color gamut. This enables OLED technology to display colors which are not easily accessible to LCDs unless RGB backlights or quantum dots are used. Often OLED colors are used “as is”, however, for very high image color fidelity, such high color saturation needs to be electronically ‘tuned down’, to match the color bandwidth of the rendering chain.
LCDs offer an advantage over OLEDs in applications where a continuous static image is required. The light emitting materials in OLEDs are affected by luminance decay as a function of the total amount of current that has passed through the pixel. This decay differs for red, green and blue. The dimming effect is subtle, but when adjacent pixels are illuminated at the same time it can become noticeable as an undesired brightness variation or color shift. LCDs don’t suffer from this dimming effect, which makes them a more suitable solution for applications with static images or images with static elements.
Another advantage of LCD technology is the wide variety of different variations to choose from. Depending on the application certain trade-offs can be very attractive. An example is much lower cost for a laptop display compared to a tablet. This is achieved by allowing poor image performance when viewed from the direction the is usually blocked by the keyboard. In a tablet where good viewing performance is required from any direction, much higher cost LCDs or OLEDs must be used.
They can be used to replace old TN LCDs or add dynamic push buttons on industrial equipment. They can be customized to various resolutions, FPC configurations, colors, custom shaped OLED displays (e.g. octagonal, round, etc.) and can even be made into flexible and transparent displays. Thanks to their versatility, OLED display panel suppliers can offer some exciting capabilities for their customers – things that were previously impossible with LCDs.
As an experienced LCD and OLED panel supplier, New Vision Display can help you find the right technology for your application. Contact us via the below form to discuss your project.

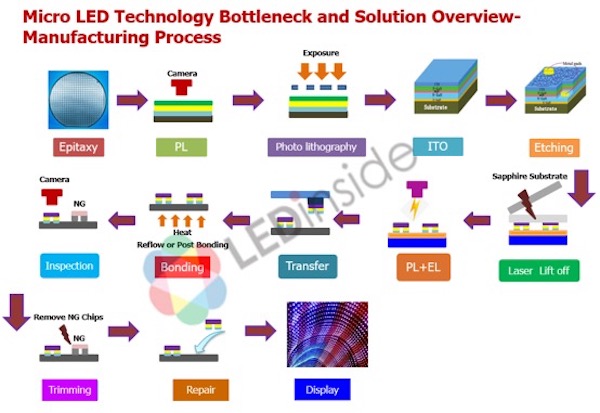
Major technologies are CRT, LCD and its derivatives (Quantum dot display, LED backlit LCD, WLCD, OLCD), Plasma, and OLED and its derivatives (Transparent OLED, PMOLED, AMOLED). An emerging technology is Micro LED and cancelled and now obsolete technologies are SED and FED.

There are plenty of new and confusing terms facing TV shoppers today, but when it comes down to the screen technology itself, there are only two: Nearly every TV sold today is either LCD or OLED.
The biggest between the two is in how they work. With OLED, each pixel provides its own illumination so there"s no separate backlight. With an LCD TV, all of the pixels are illuminated by an LED backlight. That difference leads to all kinds of picture quality effects, some of which favor LCD, but most of which benefit OLED.
LCDs are made by a number of companies across Asia. All current OLED TVs are built by LG Display, though companies like Sony and Vizio buy OLED panels from LG and then use their own electronics and aesthetic design.
So which one is better? Read on for their strengths and weaknesses. In general we"ll be comparing OLED to the best (read: most expensive) LCD has to offer, mainly because there"s no such thing as a cheap OLED TV (yet).
The better LCDs have local dimming, where parts of the screen can dim independently of others. This isn"t quite as good as per-pixel control because the black areas still aren"t absolutely black, but it"s better than nothing. The best LCDs have full-array local dimming, which provides even finer control over the contrast of what"s onscreen -- but even they can suffer from "blooming," where a bright area spoils the black of an adjacent dark area.
One of the main downsides of LCD TVs is a change in picture quality if you sit away from dead center (as in, off to the sides). How much this matters to you certainly depends on your seating arrangement, but also on how much you love your loved ones.
A few LCDs use in-plane switching (IPS) panels, which have better off-axis picture quality than other kinds of LCDs, but don"t look as good as other LCDs straight on (primarily due to a lower contrast ratio).
OLED doesn"t have the off-axis issue LCDs have; its image looks basically the same, even from extreme angles. So if you have a wide seating area, OLED is the better option.
Nearly all current TVs are HDR compatible, but that"s not the entire story. Just because a TV claims HDR compatibility doesn"t mean it can accurately display HDR content. All OLED TVs have the dynamic range to take advantage of HDR, but lower-priced LCDs, especially those without local-dimming backlights, do not. So if you want to see HDR content it all its dynamic, vibrant beauty, go for OLED or an LCD with local dimming.
In our tests comparing the best new OLED and LCD TVs with HDR games and movies, OLED usually looks better. Its superior contrast and lack of blooming win the day despite LCD"s brightness advantage. In other words LCD TVs can get brighter, especially in full-screen bright scenes and HDR highlights, but none of them can control that illumination as precisely as an OLED TV.
The energy consumption of LCD varies depending on the backlight setting. The lower the backlight, the lower the power consumption. A basic LED LCD with its backlight set low will draw less power than OLED.
LG has said their OLED TVs have a lifespan of 100,000 hours to half brightness, a figure that"s similar to LED LCDs. Generally speaking, all modern TVs are quite reliable.
Does that mean your new LCD or OLED will last for several decades like your parent"s last CRT (like the one pictured). Probably not, but then, why would you want it to? A 42-inch flat panel cost $14,000 in the late 90"s, and now a 65-inch TV with more than 16x the resolution and a million times better contrast ratio costs $1,400. Which is to say, by the time you"ll want/need to replace it, there will be something even better than what"s available now, for less money.
OLED TVs are available in sizes from 48 to 88 inches, but LCD TVs come in smaller and larger sizes than that -- with many more choices in between -- so LCD wins. At the high end of the size scale, however, the biggest "TVs" don"t use either technology.
You can get 4K resolution, 50-inch LCDs for around $400 -- or half that on sale. It"s going to be a long time before OLEDs are that price, but they have come down considerably.
LCD dominates the market because it"s cheap to manufacture and delivers good enough picture quality for just about everybody. But according to reviews at CNET and elsewhere, OLED wins for overall picture quality, largely due to the incredible contrast ratio. The price difference isn"t as severe as it used to be, and in the mid- to high-end of the market, there are lots of options.
Thinner, bigger, faster, cheaper. Direct view LCD screens are just starting to break the size barrier that once held them back (with some models getting as large as 100+" though don"t expect volume shipments) and it will be up to the manufacturing plants to convert or expand to the point where these larger screens become affordable and economical to produce. LCDs are not yet the best for black levels, but they are getting better due to LED backlighting and the "blur" effect, where the pixels cannot refresh fast enough for the screen motion, is all but extinct in newer 120Hz models.
Plasma screens are sometimes viewed as a wonder of the modern world, and most of their attention comes from their flat presentation and large screen sizes. They are able to be produced in sizes up to 103" (don"t look for mass production of this size, however) and yield a very nice picture. The downside is that they are power-hungry (not to be confused with the environmentally-friendly LCD screens). You may enjoy watching commercials with plasma screens hanging on the ceiling, but even Philips will tell you that their screens do much better hanging on a wall or placed on a stand.
Extinction. While it has taken far longer than originally estimated, we maintain that LCD panels are on a trend to become a commodity. This year, Pioneer announced it is leaving the plasma panel manufacturing business and taking on LCD panels from Sharp. The LCD manufacturing process is getting better, additional manufacturing plants open up each year to turn out more and more panels and performance is increasingly getting better. Add to that the low cost of manufacturing and additional technologies coming on board and you have a tough road ahead for plasma. Plasma displays are indeed competing in terms of longevity, brightness, (true) contrast ratio, power consumption and burn-in. Their black levels and color saturation are very impressive. Due to these advancements it is very likely that plasma and LCD will maintain parallel development for some time. As LCD displays become thinner, cheaper, faster and more competitive, however, plasma will become obsoleted.
1080p has also finally made in-roads with plasma. Beginning with Hitachi (who unlike many other companies actually demoed a working unit at last year"s CEDIA) 2007 seems to be the year of 1080p plasma technology - albeit at a price.

One of the most important aspects of any display you can understand is the panel technology being used. Specifications alone won’t give you the full picture of a displays performance, and we all know that manufacturers can exaggerate specs on paper to suit their marketing. With an understanding of the panel technology being used you will get a feel for the overall performance characteristics of the display and how it should perform in real terms. Our extensive panel search database helps you identify the panel technology (and manufacturer and part number where known) of many screens in the market. This article which follows will help you understand what the different panel technologies can offer you. A lot of manufacturers now list the panel technology as well in their specs, something which wasn’t included a in the past.
TN Film panels are the mostly widely used in the desktop display market and have been for many years since LCD monitors became mainstream. Smaller sized screens (15″, 17″ and 19″) are almost exclusively limited to this technology in fact and it has also extended into larger screen sizes over the last 7 years or so, now being a popular choice in the 20 – 28″ bracket as well. The TN Film panels are made by many different manufacturers, with the big names all having a share in the market (Samsung, LG.Display, AU Optronics) and being backed up by the other companies including most notably Innolux and Chunghwa Picture Tubes (CPT). You may see different generations of TN Film being discussed, but over the years the performance characteristics have remained similar overall.
TN Film has always been so widely used because it is comparatively cheap to produce panels based on this technology. As such, manufacturers have been able to keep costs of their displays down by using these panels. This is also the primary reason for the technology to be introduced into the larger screen sizes, where the production costs allow manufacturers to drive down retail costs for their screens and compete for new end-users.
The other main reason for using TN Film is that it is fundamentally a responsive technology in terms of pixel latency, something which has always been a key consideration for LCD buyers. It has long been the choice for gaming screens and response times have long been, and still are today, the lowest out of all the technologies overall. Response times typically reach a limit of around 5ms at the ISO quoted black > white > black transition, and as low as 1ms across grey to grey transitions where Response Time Compensation (overdrive) is used. TN Film has also been incorporated into true 120Hz+ refresh rate desktop displays, pairing low response times with high refresh rates for even better moving picture and gaming experiences, improved frame rates and adding 3D stereoscopic content support. Modern 120Hz+ refresh rate screens normally also support NVIDIA 3D Vision 2 and their LightBoost system which brings about another advantage for gaming. You can use the LightBoost strobed backlight system in 2D gaming to greatly reduce the perceived motion blur which is a significant benefit. Some screens even include a native blur reduction mode instead of having to rely on LightBoost ‘hacks’, providing better support for strobing backlights and improving gaming experiences when it comes to perceived motion blur. As a result, TN Film is still the choice for gamer screens because of the low response times and 120Hz+ refresh rate support.
The main problem with TN Film technology is that viewing angles are pretty restrictive, especially vertically, and this is evident by a characteristic severe darkening of the image if you look at the screen from below. Contrast and colour tone shifts can be evident with even a slight movement off-centre, and this is perhaps the main drawback in modern TN Film panels. Some TN Film panels are better than others and there have been improvements over the years to some degree, but they are still far more restrictive with fields of view than other panel technologies. The commonly quoted 170/160 viewing angles are an unfair indication of the actual real-life performance really, especially when you consider the vertical contrast shifts. Where viewing angles are quoted by a manufacturer as 160/160 or 170/160 that is a clear sign that the panel technology will be TN Film incidentally.
Movie playback is often hampered by ‘noise’ and artifacts, especially where overdrive is used. Black depth was traditionally quite poor on TN Film matrices due to the crystal alignment, however, in recent years, black depth has improved somewhat and is generally very good on modern screens, often surpassing IPS based screens and able to commonly reach contrast ratios of ~1000:1. TN Film is normally only a true 6-bit colour panel technology, but is able to offer a 16.7 million colour depth thanks to dithering and Frame Rate Control methods (6-bit + FRC). Some true 8-bit panels have become available in recent years (2014 onwards) but given the decent implementation of FRC on other 6-bit+FRC panels, the real-life difference is not something to concern yourself with too much.
VA technology was first developed by Fujitsu in 1996. However the limited viewing angles were its main disadvantage, and so further investment focused on addressing this problem. It was eventually solved by dividing each pixel into domains which worked synchronously. This lead the birth of the following technologies:
MVA technology, was later developed by Fujitsu in 1998 as a compromise between TN Film and IPS technologies. On the one hand, MVA provided a full response time of 25 milliseconds (that was impossible at the time with IPS, and not easily achievable with TN), and on the other hand, MVA matrices had wide viewing angles of 160 – 170 degrees, and thus could better compete with IPS in that parameter. The viewing angles were also good in the vertical field (an area where TN panels suffer a great deal) as well as the horizontal field. MVA technology also provided high contrast ratios and good black depth, which IPS and TN Film couldn’t quite meet at the time.
While some improvements have been made, the color-reproduction properties of these modern MVA technologies can still be problematic in some situations. Such panels give you vivid and bright colors, but due to the peculiarities of the domain technology many subtle color tones (dark tones often) are lost when you are looking at the screen strictly perpendicularly. When you deflect your line of sight just a little, the colors are all there again. This is a characteristic “VA panel contrast shift” (sometimes referred to as ‘black crush’ due to the loss of detail in dark colours) and some users pick up on this and might find it distracting. Thus, MVA matrices are somewhere between IPS and TN technologies as concerns color rendering and viewing angles. On the one hand, they are better than TN matrices in this respect, but on the other hand the above-described shortcoming prevents them from challenging IPS matrices, especially for colour critical work.
AU Optronics have more recently (around 2005) been working on their latest generation of MVA panel technology, termed ‘Advanced Multi Domain Vertical Alignment’ (AMVA). This is still produced today although a lot of their focus has moved to the similarly named, and not to be confused AHVA (Advanced Hyper Viewing Angle, IPS-type) technology. Compared with older MVA generations, AMVA is designed to offer improved performance including reduced colour washout, and the aim to conquer the significant problem of colour distortion with traditional wide viewing angle technology. This technology creates more domains than conventional multi-domain vertical alignment (MVA) LCD’s and reduces the variation of transmittance in oblique angles. It helps improve colour washout and provides better image quality in oblique angles than conventional VA LCD’s. Also, it has been widely recognized worldwide that AMVA technology is one of the few ways to provide optimized image quality through multiple domains.
AMVA still has some limitations however in practice, still suffering from the off-centre contrast shift you see from VA matrices. Viewing angles are therefore not as wide as IPS technology and the technology is often dismissed for colour critical work as a result. As well as this off-centre contrast shift, the wide viewing angles often show more colour and contrast shift than competing IPS-type panels, although some recent AMVA panel generations have shown improvements here (see BenQ GW2760HS for instance with new “Color Shift-free” technology). Responsiveness is better than older MVA offerings certainly, but remains behind TN Film and IPS/PLS in practice. The Anti-Glare (AG) coating used on most panels is light, and sometimes even appears “semi glossy” and so does not produce a grainy image.
AUO developed a series of vertical-alignment (VA) technologies over the years. This is specifically for the TV market although a lot of the changes experienced through these generations applies to monitor panels as well over the years. Most recently, the company developed its AMVA5 technology not only to improve the contrast ratio, but also to enable a liquid crystal transmission improvement of 30% compared to AMVA1 in 2005. This was accomplished by effectively improving the LC disclination line using newly developed polymer-stabilized vertical-alignment (PSA) technology. PSA is a process used to improve cell transmittance, helping to improve brightness, contrast ratio and liquid crystal switching speeds.
We have included this technology in this section as it is a modern technology still produced by Sharp as opposed to the older generations of MVA discussed above. Sharp are not a major panel manufacturer in the desktop space, but during 2013 began to invest in new and interesting panels using their MVA technology. Of note is their 23.5″ sized MVA panel which was used in the Eizo Foris FG2421 display. This is the first MVA panel to offer a native 120Hz refresh rate, making it an attractive option for gamers. Response times had been boosted significantly on the most part, bringing this MVA technology in line with modern IPS-type panels when it comes to pixel latency. The 120Hz support finally allowed for improved frame rates and motion smoothness from VA technology, helping to rival the wide range of 120Hz+ TN Film panels on the market.
Of particular note also are the excellent contrast ratios of this technology, reaching up to an excellent 5000:1 in practice, not just on paper. Viewing angles are certainly better than TN Film and so overall these MVA panels can offer an attractive all-round option for gaming, without some of the draw-backs of the TN Film panels. Viewing angles are not as wide as IPS panel types and there is still some noticeable gamma shift at wider angles, and the characteristic VA off-centre contrast shift still exists.
PVA was developed by Samsung as an alternative to MVA in the late 1990’s. The parameters and the development methods for PVA and MVA are so different that PVA can be truly regarded as an independent technology, although it is still a ‘Vertical Alignment’ technology type and has many similar characteristics. PVA is a Samsung only technology.
There was the same problem with traditional PVA matrices as with MVA offerings – their response time grew considerably when there’s a smaller difference between the initial and final states of the pixel. Again, PVA panels were not nearly as responsive as TN Film panels. With the introduction of MagicSpeed (Samsung’s overdrive / RTC) with later generations (see below), response times have been greatly improved and are comparable to MVA panels in this regard on similarly spec-ed panels. They still remain behind TN Film panels in gaming use, but the overdrive really has helped improve in this area. There are no PVA panels supporting native 120Hz+ refresh rates and Samsung have no plans to produce any at this time. In fact Samsung’s investment in PVA seems to have been cut back significantly in favour of their IPS-like PLS technology.
The contrast ratio of PVA matrices is a strong point, as it is with MVA. Older PVA panels offered contrast ratios of 1000 – 1200:1 typically, but remained true to their spec in many cases. As such at the time of their main production they were better than TN Film, IPS and even MVA in this regard. Movie playback is perhaps one area which is a weak point for PVA, especially on Samsung’s overdriven panels. Noise and artifacts are common unfortunately and the panels lose out to MVA in this regard. Most PVA panels were true 8-bit modules, although some generations (see below) began to use 6-bit+FRC instead. There are no 10-bit supporting PVA panels available, either native 10-bit or 8-bit+FRC. Panel coating is generally light on PVA panels, quite similar to a lot of MVA panels.
The introduction of overdrive to PVA panels lead to the next generation of Super Patterned Vertical Alignment (S-PVA) technology in 2004. Like P-MVA panels were to MVA, these are really just an extension of the existing PVA technology, but with the MagicSpeed (overdrive) technology, they have managed to make them more suitable for gaming than the older panels. One other difference is that the liquid crystal cell structure is a boomerang shape, splitting each sub pixel into two different sections with each aligned in opposite directions. This is said to help improve viewing angles and colour reproduction when viewed from the side. Limitations still exist with S-PVA and they don’t offer as wide viewing angles as IPS-type panels, and still suffer from the off-centre contrast shift we’ve described. Most S-PVA panels offered a true 8-bit colour depth, but some did feature Frame Rate Control (FRC) to boost a 6-bit panel (6-bit+FRC).
In late 2009 Samsung started to produce their latest generation of so called “cPVA” panels. These new panels featured a simpler sub-pixel structure in comparison with S-PVA, but allowed Samsung to produce the panels at a lower cost, and drive down the retail cost of their new screens. It’s unclear what the “c” stands for. This is a similar approach to e-IPS which we discuss a little later on.
There is very little official information about this technology but some Samsung monitors started to be labelled as having an A-PVA panel around 2012 onwards. We suspect that nothing has really changed from S-PVA / cPVA panels, but that the term “Advanced” has been added in to try and distinguish the new models, and perhaps compete with LG.Display’s successful IPS technology and AU Optronics AMVA technology where they have also added the word “Advanced” for their latest generations (see AMVA and AH-IPS).
In Plane Switching (IPS – also known as ‘Super TFT’) technology was developed by Hitachi in 1996 to try and solve the two main limitations of TN Film matrices at the time, those being small viewing angles and low-quality color reproduction. The name In-Plane Switching comes from the crystals in the cells of the IPS panel lying always in the same plane and being always parallel to the panel’s plane (if we don’t take into account the minor interference from the electrodes). When voltage is applied to a cell, the crystals of that cell all make a 90-degrees turn. By the way, an IPS panel lets the backlight pass through in its active state and shutters it in its passive state (when no voltage is applied), so if a thin-film transistor crashes, the corresponding pixel will always remain black, unlike with TN matrices.
The original IPS technology became a foundation for several improvements: Super-IPS (S-IPS), Dual Domain IPS (DD-IPS), and Advanced Coplanar Electrode (ACE). The latter two technologies belong to IBM (DD-IPS) and Samsung (ACE) and are in fact unavailable in shops. The manufacture of ACE panels is halted, while DD-IPS panels are coming from IDTech, the joint venture of IBM and Chi Mei Optoelectronics – these expensive models with high resolutions occupy their own niche, which but slightly overlaps with the common consumer market. NEC is also manufacturing IPS panels under such brands as A-SFT, A-AFT, SA-SFT and SA-AFT, but they are in fact nothing more than variations and further developments of the S-IPS technology.
Since their initial production in 1998 S-IPS panels have gained the widest recognition, mostly due to the efforts of LG.Philips LCD (now known as LG.Display), who were outputting rather inexpensive and high-quality 19″ – 30″ matrices. The response time was among the serious drawbacks of the IPS technology – first panels were as slow as 60ms on the “official” black-to-white-to-back transitions (and even slower on grey-to-grey ones!) Fortunately, the engineers dragged the full response time down to 25 ms and then 16ms later, and this total is equally divided between pixel rise and pixel fall times. Moreover, the response time doesn’t greatly grow up on black-to-gray transitions compared to the specification, so some older S-IPS matrices at the time could challenge TN Film panels in this parameter.
The IPS technology has always been at the top end when it comes to colour reproduction and viewing angles. Colour accuracy has always been a strong point, and even in modern displays the IPS matrices can surpass the performance of TN Film and VA equivalents. The viewing angles are a key part in this, since IPS matrices are free of the off-centre contrast shift that you can see from VA type panels. This is the reason why IPS is generally considered the preferred choice for colour critical work and professional colour displays, combining the excellent colour accuracy with truly wide viewing angles (178/178). S-IPS panels can show a purple colour when viewing dark images from a wide angle.
One main problem of the S-IPS technology traditionally was the low contrast ratio. Black depth was often a problem with S-IPS panels and contrast ratios of 500 – 600:1 were common for the early S-IPS offerings. However, these have been improved significantly, and contrast ratios are now much better as a result with modern IPS generations (see following sections). One other area which remains problematic for modern IPS panels is movie playback, again with noise being present, and only accentuated by the heavy application of overdrive technologies. S-IPS panels are sometimes criticized for their Anti-Glare (AG) coating, which can appear quite grainy and dirty looking, especially when viewing white/light backgrounds in office applications. Again that has been improved significantly in recent generations.
Sometimes you will see these terms being used, but S-IPS is still widely used as an umbrella for modern IPS panels. In 2002 Advanced Super IPS (AS-IPS) boosted the amount of light transmitted from the backlighting by around 30% compared with the standard Super IPS technology developed in 1998. This did help boost contrast ratios somewhat, but they could still not compete with VA panel types. In 2005 with the introduction of RTC technologies (Overdrive Circuitry – ODC) and dynamic contrast ratios, LG.Display started to produce their so called “Enhanced IPS” (E-IPS, not to be confused with e-IPS) panels. Pixel response times were reduced across G2G transitions to as low as 5ms on paper.
Enhanced S-IPS builds on S-IPS technology by providing the same 178° viewing angle from above and below and to the sides, and greatly improves the off-axis viewing experience by delivering crisp images with minimal colour shift, even when viewed from off-axis angles such as 45°. You will rarely see this E-IPS term being used to be honest. You may also occasionally see the name “Advanced S-IPS” (AS-IPS) being used, but this was just a name given specifically by NEC to the E-IPS panel developed and used in their very popular NEC 20WGX2 screen, released in 2006. The AS-IPS name was also (confusingly) used by Hitachi in some of their earlier IPS generations as shown below, back in 2002.
Above: Evolution of IPS as detailed by Hitachi Displays: “IPS technology was unveiled by Hitachi, Ltd. in 1995, and put to practical use in 1996. Since then, it has evolved into Super-IPS, Advanced-Super IPS, and IPS-Pro.”
Close inspection of modern IPS panels can show this new H-IPS pixel structure, although not all manufacturers refer to their models as featuring an H-IPS panel. Indeed, LG.Display don’t really make reference to this H-IPS version, although from a technical point of view, most modern IPS panels are H-IPS in format. As an example of someone who has referred to this new generation, NEC have used the H-IPS name in their panel specs for models such as the LCD2690WXUi2 and LCD3090WUXi screens.
The following technical report has feedback from the LG.Philips LCD laboratory workers: “Wedesigned a new pixel layout to improve the aperture ratioof IPS mode TFT-LCD (H-IPS). This H-IPS pixel layout design has reducedthe width of side common electrode used to minimize thecross talk and light leakage which is induced by interferencebetween data bus line and side common electrode of conventionalIPS mode. The side common electrodes of a pixel canbe reduced by horizontal layout of inter-digital electrode pattern whereconventional IPS pixel designs have vertical layout of inter-digital electrodes.We realized 15 inch XGA TFT LCD of H-IPS structurewhich has aperture ratio as much as 1.2 times ofcorresponding conventional IPS pixel design.” ©2004 Society for Information Display.
During 2009 LG.Display began to develop a new generation of e-IPS (it is unclear what the “e” actually stands for) panels which is a sub-category of H-IPS. They simplified the sub-pixel structure in comparison with H-IPS (similar to cPVA vs. S-PVA) and increased the transparency of the matrix by producing a wider aperture for light transmission. In doing so, they have managed to reduce production costs significantly by integrating the panels with lower cost, lower power backlight units. This allowed LG.Display to compete with the low cost TN Film panels and Samsung’s new cPVA generation. Because transparency is increased, they are able to reduce backlight intensity as you need less light to achieve the same luminance now.
The drawback of e-IPS in comparison with S-IPS is that the viewing angles are slightly smaller. When you take a look at an e-IPS matrix from a side, the image will lose its contrast as black turns into grey. On the other hand, there is no tonal shift (as with TN and cPVA matrixes) and the viewing angles, especially vertical ones, are still much larger than with TN Film. Many e-IPS panels are actually 6-bit + AFRC modules (as opposed to true 8-bit) which might explain how the costs are kept very low in some cases, although in practice the FRC algorithm is very well implemented and you are unlikely to see any obvious side affects. Like H-IPS panels from years prior, e-IPS panels are sometimes criticized for their Anti-Glare (AG) coating, which can appear quite grainy and dirty looking, especially when viewing white backgrounds in office applications.
Some spec sheets from LG.Display give some clues as to the differences. The lines separating the sub-pixels are smaller than with H-IPS and therefore the UH-IPS technology has an 18% higher aperture ratio. The drive for increased LCD panel transmissivity is not for the purpose specifically of increasing on screen brightness, but rather to maintain brightness and reduce backlight lamps, inverters, and optical films in order to lower panel costs. LG have used this terminology with some of their LED backlight monitors.
This was a new name which NEC introduced in early 2010 with their new PA series of screens. Thankfully they’ve been kind enough to tell us what the ‘p’ stands for in their marketing, giving rise to the generation of ‘Performance IPS’ panels. This new panel name is being used in the new 24″ – 30″ sized screens (PA241W, PA271W and PA301W). In fact the p-IPS name is just a sub-category of H-IPS technology, being created as a way for NEC to distinguish their new “10-bit” models from the rest of their range. In addition, when you look into the details of it the panels are actually an 8-bit module with 10-bit receiver, giving you an 8-bit + FRC module. This is capable of producing a 1.07 billion colour palette (10-bit) through FRC technology but it is not a true 10-bit colour depth.
There are very few true 10-bit panels out there in the market, although a 24″ 10-bit module was features in the HP LP2480zx for instance, but at a much higher cost. Some other high end models use true 10-bit panels as well, but you need to be a little wary of manufacturers specified 10-bit figures as they are not always 100% accurate.
PLS was introduced by Samsung at the end of 2010 and designed to compete with LG.Display’s long-established and very popular IPS technology. It is an IPS-type technology and for all intents and purposes can be considered IPS, just being manufactured by another company. Samsung claimed they had reduced production costs compared with IPS by about 15% and so were making a play at the market of IPS panels when it was launched. At the time it was also being dubbed “S-PLS” (Super-PLS) but that name seemed to be dropped quite quickly in favour of just “PLS”. It wasn’t until mid 2011 that the first PLS displays started to appear, fittingly they were manufactured by Samsung themselves. The Samsung S27A850D was the first of its kind and its overall performance certainly reminded users of IPS panels.
Again like Samsung’s PLS technology, AU Optronics have invested in their own IPS-type technology since 2012, dubbed AHVA. This technology is designed by AU Optronics as another alternative to IPS. Confusingly the AHVA name makes it sound like it’s a VA-type panel, which AU Optronics have been manufacturing for many years. It should not be confused with AMVA which is their current “true” VA technology produced. The BenQ BL2710PT was the first display featuring this new technology and gave us some insight into the performance characteristics of AHVA, confirming how closely it resembled an LG.Display IPS panel.
In very recent times (2015) AU Optronics have been the first to release official high refresh rate (144Hz) IPS-type panels, through their AHVA technology. The first display to use one of these panels was the Acer Predator XB270HU which was impressive when it came to refresh rate support and response times. We expect further panels to emerge at a later date with 120Hz+ refresh rates which can only be a good thing when it comes to gaming. With the addition of this high refresh rate we also saw the first inclusion of a blur reduction backlight (from the NVIDIA ULMB mode) on an IPS-type panel. Again a positive sign when it comes to the gaming future of IPS-type panels.

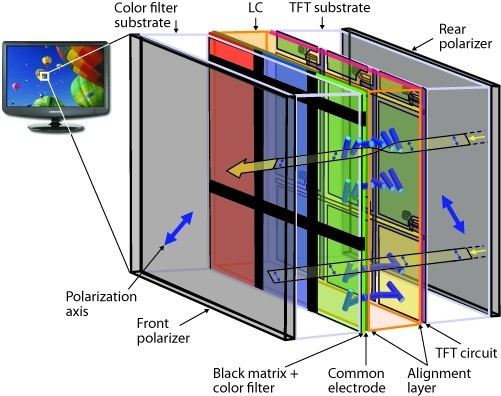
Liquid crystal module (LCM) is simply the LCD screen and backlight assembly. For example, the display component of an LCD TV is a liquid crystal module, and its low temperature is equivalent to a picture tube in a CRT. Other parts include power supply circuits, signal processing circuits, etc., and of course the casing.
Liquid crystal modules are mainly divided into screen and backlight components. The two parts are assembled together but work independently of each other. The principle of liquid crystal display is that the backlight component emits light, and the light is displayed through the liquid crystal screen. The role of the LCD screen is to control and process these lights on a pixel-by-pixel basis to display images.
The LCD panel is the main component of the LCD and accounts for nearly 80% of the cost of the LCD. At present, there are not many manufacturers with panel manufacturing technology in the world. Only SHARP (Sharp), Samsung, LGD, Innolux, AUO and other manufacturers have core technologies. In the past, most terminal manufacturers used their LCD panels. Of course, with the rapid development of mainland panel manufacturers, domestic companies such as BOE, Shentianma, CSOT, etc. have also begun to accumulate their own patented technologies, and the panels produced by them are also widely used by terminal manufacturers.
The so-called dead pixel is a general term for pixels that cannot be displayed normally on the LCD panel. The liquid crystal panel is composed of many pixel points, and the liquid crystal material on each display point is completed by changing the light transmission and the same state under the control of electric signal. At 1024*768 resolution, the LCD panel has a total of 786,432 display points, so it is difficult to completely guarantee that there will be some problems with so many points. At present, the technology cannot completely overcome the occurrence of no dead pixels. Therefore, the level division of the panel is also judged according to the number of dead pixels. Manufacturers generally avoid dead pixels and divide LCD panels, selling LCD panels with no dead pixels or very few dead pixels at a high price, while those with a large number of dead pixels are dealt with at a low price.
Brightness is also a more important indicator. The brighter the liquid crystal is, it stands out from a row of liquid crystal walls when viewed from a distance. The principle of LCD display brightness is realized by the brightness of the backlight tube behind the panel.
Typical LCDs are edge-lit by a strip of white LEDs. The 2D backlighting system in Pro Display XDR is unlike any other. It uses a superbright array of 576 blue LEDs that allows for unmatched light control compared with white LEDs. Twelve controllers rapidly modulate each LED so that areas of the screen can be incredibly bright while other areas are incredibly dark. All of this produces an extraordinary contrast that’s the foundation for XDR.
With a massive amount of processing power, the timing controller (TCON) chip utilizes an algorithm specifically created to analyze and reproduce images. It controls LEDs at over 10 times the refresh rate of the LCD itself, reducing latency and blooming. It’s capable of multiple refresh rates for amazingly smooth playback. Managing both the LED array and LCD pixels, the TCON precisely directs light and color to bring your work to life with stunning accuracy.

The display industry has come a long way in recent years. With so many competing standards on the market today, it’s often hard to tell if an emerging technology is worth paying extra for. OLED and QLED, for instance, sound similar enough on the surface but are, in fact, completely different display types.
LCDs, or liquid crystal displays, are the oldest of all display types on this list. They are made up of two primary components: a backlight and a liquid crystal layer.
Since liquid crystals don’t produce any light by themselves, LCDs rely on a white (or sometimes blue) backlight. The liquid crystal layer then simply has to let this light pass through, depending on the image that needs to be displayed.
You may have noticed that the term LCD has started to disappear of late, especially in the television industry. Instead, many manufacturers now prefer branding their televisions as LED models instead of LCD. Don’t be fooled, though — this is just a marketing ploy.
These so-called LED displays still use a liquid crystal layer. The only difference is that the backlights used to illuminate the display now use LEDs instead of cathode fluorescent lamps, or CFLs. LEDs are a better light source than CFLs in almost every way. They are smaller, consume lesser power, and last longer. However, the displays are still fundamentally LCDs.
Twisted nematic, or TN, was the very first LCD technology. Developed in the late 20th century, it paved the way for the display industry to transition away from CRT.
TN panels have been around for decades in devices like handheld calculators and digital watches. In these applications, you only need to power sections of the display where you don’t want light. In other words, it is an incredibly energy-efficient technology. Twisted nematic panels are also cheap to manufacture.
Instead of a twisted orientation, liquid crystals in an IPS display are oriented parallel to the panel. In this default state, light is blocked — the exact opposite of what happens in a TN display. Then, when a voltage is applied, the crystals simply rotate in the same plane and let light through. As a side note, this is why the technology is called in-plane switching.
Having said that, IPS displays do come with a few minor compromises. The technology isn’t nearly as energy-efficient as TN, nor is it as cheap to manufacture at scale. Still, if you care about color accuracy and viewing angles, IPS is likely your only option.
This default vertical arrangement blocks a lot more of the backlight from coming through to the front of the display. Consequently, VA panels are known for producing deeper blacks and offering better contrast compared to other LCD display types. As for bit-depth and color gamut coverage, VA is capable of doing just as well as IPS.
On the downside, the technology is still relatively immature. Early VA implementations suffered from extremely slow response times. This led to ghosting, or shadows behind fast-moving objects. The reason for this is simple — it takes longer for VA’s perpendicular arrangement of crystals to change orientation.
From this description alone, it’s easy to see how OLED differs from LCD and prior display types. Since the compounds used in OLEDs emit their own light, they are an emissive technology. In other words, you don’t need a backlight for OLEDs. This is why OLEDs are universally thinner and lighter than LCD panels.
Since each organic molecule in an OLED panel is emissive, you can control whether a particular pixel is lit up or not. Take away the current and the pixel turns off. This simple principle allows OLEDs to achieve remarkable black levels, outperforming LCDs that are forced to use an always-on backlight. Besides delivering a high contrast ratio, turning off pixels also reduces power consumption.
The contrast alone would make the technology worth it, but other benefits exist too. OLEDs boast high color accuracy and are extremely versatile. Foldable smartphones such as the Samsung Galaxy Flip series simply wouldn’t exist without AMOLED’s physical flexibility.
In summary, OLED subtypes aren’t nearly as varied as LCDs. Furthermore, only a handful of companies manufacture OLEDs so there’s even less quality variance than you’d expect. Samsung manufactures the majority of OLEDs in the smartphone industry. Meanwhile, LG Display has a near-monopoly on the large-sized OLED market. It supplies panels to Sony, Vizio, and other giants in the television industry.
In the section on LCDs, we saw how the technology can vary based on differences in the liquid crystal layer. Mini-LED, however, attempts to improve contrast and image quality at the backlight level instead.
The backlights in conventional LCDs have only two modes of operation — on and off. This means that the display has to rely on the liquid crystal layer to adequately block light in darker scenes. Failing to do that results in the display producing grays instead of true black.
This technique, known as local dimming, has become ubiquitous in higher-end LCD televisions. Until recently, though, it wasn’t viable for smaller displays like those found in laptops or smartphones. And even in larger devices like monitors and TVs, you run the risk of not having enough dimming zones.
Take the 2021 iPad Pro, for example. It was among the first consumer devices to adopt mini-LED technology. Even with 2,500 zones across 12.9 inches, however, some users reported blooming or halos around bright objects.
Still, it’s not hard to see how mini-LEDs can eventually deliver better contrast than conventional local dimming implementations. Furthermore, since mini-LED displays still rely on traditional LCD technologies, they aren’t prone to burn-in like OLEDs.
Quantum dot technology has become increasingly common — usually positioned as a key selling point for many mid-range televisions. You may also know it by Samsung’s marketing shorthand: QLED. Similar to mini-LED, however, it isn’t some radically new panel technology. Instead, quantum dot displays are basically conventional LCDs with an additional layer sandwiched in between.
When combined with traditional LCD color filters, quantum dot displays can cover a greater percentage of the visible light spectrum. Put simply, you get richer and ore accurate colors — enough to deliver a satisfactory HDR experience. And since the crystals emit their own light, you also get a tangible bump in brightness compared to traditional LCDs.
However, quantum dot technology does not improve other pain points of LCDs such as contrast and viewing angles. For that, you’d have to combine quantum dots with local dimming or mini-LED technologies. And until those mature, you’re unlikely to find a quantum dot display that can rival OLED in all aspects.
Quantum-dot OLED, or QD-OLED, is an amalgamation of two existing technologies — quantum dots and OLED. More specifically, it aims to eliminate the drawbacks of both traditional OLEDs and LCD-based quantum dot displays.
Modern OLED implementations combat this by leaving the fourth sub-pixel white (without any color filters) to improve the perception of brightness. However, they still usually fall short in terms of brightness, especially against high-end LCDs with larger backlights.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey