tft display vs super amoled display for sale

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
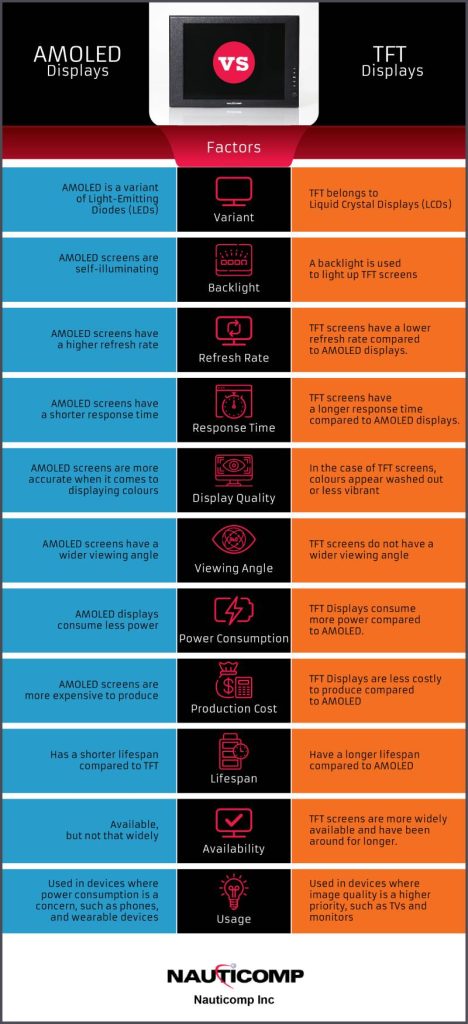
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.
Nauticomp Inc.provides world-class fully customizable touchscreen displays for commercial and industrial settings. With features like sunlight readability, brightness adjustability, infrared lighting, full backlighting, all-weather capabilities, etc., our displays are second to none. Contact us today to learn more.

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.

TFT is an abbreviation for Thin Film Transistor, a flat panel display used to improve the operation and utility of LCD screens. In order to portray an appearance to the audience, a liquid crystal display (LCD) utilizes a crystalline-filled fluid to modify rear lighting polarized origin through the use of an electromagnetic force among two relatively thin metal wires such as indium oxide (ITO). However, color TFT displays are associated with this method, which can be employed in both divided and pixelated display systems.
With motion pictures displayed on an LCD, the intrinsic sluggish rate of increase between liquid phases over a significant number of pixel components can be an issue due to capacitance impacts, which can create a blurring of the visuals. Placing a high-velocity LCD control device inside the formation of a thin-film transistor immediately next to the cell component just on a glass screen, the issue of LCD picture speed may be substantially improved, and image blur can be eliminated for all useful purposes entirely.
Organic light-emitting diodes (AMOLEDs) are a type of flat light-emitting advanced technologies that are created by interspersing a succession of organic thin sheets over two conducting conductors. An electrical charge causes a brilliant light to be produced when the current flows. AMOLED displays are light-emitting screens that do not require a backlight, making them thinner and more energy-efficient than liquid crystal displays (LCDs) (which will need a white backlight).
AMOLED displays are not only thin and fuel-intensive, but they also deliver the highest image quality available, so they can be made translucent, elastic, bendable, or even rollable and stretchy in the future, allowing for a variety of applications. AMOLEDs are a revolutionary technology in terms of display devices! It is possible to create an AMOLED by sandwiching a sequence of thin films across phase conductors. Electric charge causes a brilliant light to be emitted when the current flows through the coil.
The color display is fantastic. Color intensity, sharpness, and luminance settings that are second to none and can be customized to meet the needs of any application.
Half-Life has been expanded. TFT displays have a far longer half-life than its LED equivalents, and they are available in a number of sizes, which might have an effect on the device"s half-life based on the phone"s usage as well as other variables. Touch panels for TFT screens can be either resistant or capacitance in nature.
Due to the apparent glass panels, there is limited functionality. For instance, there are ineffective for outdoor use because the glass can display glares from its natural lighting)
They rely on backlight to give illumination rather than generating their own light. Hence they require constructed light-creating diodes (LEDs) in their backlit display framework to ensure enough brightness.
Backlighting is unnecessary for AMOLEDs. LCDs produce images by selectively blocking parts of the illumination, whereas AMOLEDs produce light. AMOLEDs utilize less energy than LCDs since they don"t need backlighting. This is critical for battery-powered devices such as phones.
While AMOLED light-emitting sheets are lightweight, the substrate can also be elastic rather than stiff. AMOLED films are not limited to glass-like LEDs and LCDs.
AMOLEDs offer 170-degree ranges of vision. LCDs operate by obscuring the light. Hence they have intrinsic viewing obstacles. In addition, AMOLEDs have a substantially wider viewing spectrum.
AMOLEDs outperform LEDs. Since AMOLED organic coatings are less than LED inorganic crystal levels, AMOLED conducting and particle emitters layers can just be multi-layered. Also, LEDs and LCDs need glass backing, which absorbs light. AMOLEDs don"t need it.
AMOLEDs seem to be simpler to implement and larger. AMOLEDs are constructed of polymers and may be produced into big sheets. It takes a lot of extra liquid crystals to build and set down.
While red and green AMOLED sheets have a greater lifespan (46,000 to 230,000 hours), azure compounds have significantly shorter longevity (up to roughly 14,000 hours).
Due to the fact that AMOLED displays inherently emit illumination, they do not need a backlight when used on a monitor screen. Conversely, LCDs require backlights since the liquid crystals themselves are incapable of producing light under their own. Direct light emission from AMOLED displays also allows for the developing of lightweight display devices than others using TFT LCDs.
LCD displays have a higher brightness than AMOLED panels. This is owing to the LCD"s usage of led backlight, which may provide a brilliant illumination of the entire display. Despite the fact that AMOLEDs produce high levels of brilliance from their illumination, they will never be able to match the intensity of LCD lighting.
LCD screens use less power than AMOLED displays, which provides a slight advantage. The amount of energy consumed by AMOLED displays is dependent on the intensity of the screen. Lowered luminance results in lower energy usage, however, it might not be the best solution because the contrast would suffer as a result of the decreased brightness. In some situations, such as when to use an AMOLED device in direct sunlight, it is not an optimal situation.
However, the backlit keys of TFT displays account for the majority of their power usage. TFT screens" efficiency is considerably improved when the backlight is set to a lesser brightness level than the default setting. For example, replacing the light of an LCD TV with just an Led flash will have no effect on the image quality, but will result in lower power usage than replacing the light of an AMOLED TV.
With the exception of phones, numerous other technologies make use of displays to allow customers to engage in direct communication with them. To determine whether or not TFT LCD will be able to withstand the development of AMOLED innovation, we should first review the benefits of LCD technology. The backlighting quality ensures that whites are strong and brightness is superb but will deplete a battery much more quickly than just an AMOLED display. Furthermore, the cost of LCD screens is a considerable consideration. In addition to being less expensive and more easily accessible, they are produced in standard industry sizes, allowing them to be purchased for innovative products with relative ease.

AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode) and TFT (Thin Film Transistor) are the two types of displays that are used in mobile phones. TFT is actually a process of producing the displays and is used even by AMOLED but for most purposes, TFT is used to refer to LCD displays. The difference between them is the material as AMOLED uses organicmaterials, mainly carbon, while TFT does not.
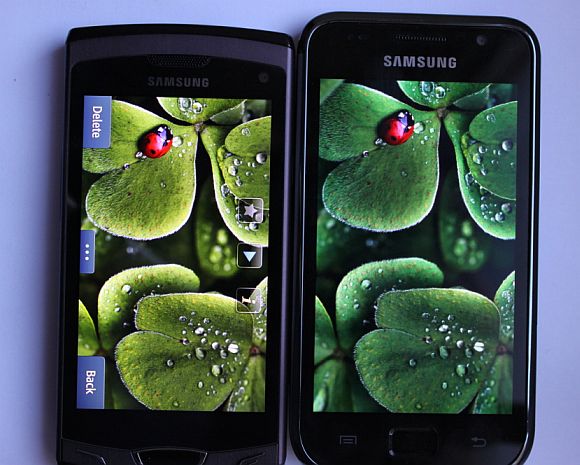
There are differences between the two that are quite tangible. For starters, AMOLED generates its own light rather than relying on a backlight like a TFT-LCD does. This consequently means that AMOLED displays are much thinner than LCD displays; due to the absence of a backlight. It also results in much better colors than a TFT is capable of producing. As each pixel’s color and light intensity can be regulated independently and no light seeps from adjacent pixels. A side by side comparison of the two displays with the same picture should confirm this. Another effect of the lack of a backlight is the much lower power consumption of the device. This is very desirable when it comes to mobile phones where every single feature competes for the limited capacity of the battery. As the screen is on 90% of the time that the device is being used, it is very good that AMOLED displays consume less. Just how much of a difference is not very fixed though as it really depends on the color and intensity of the image. Having a black background with white text consumes much less energy than having black text on a white background.
The biggest disadvantage that AMOLED has is the shorter lifespan of the screen compared to TFT. Each pixel in the display degrades with each second that it is lit and even more so the brighter it is. Â Despite improvements on the lifetime of AMOLED displays, AMOLED still only lasts a fraction of the lifetime of a TFT display. With that said, an AMOLED display is able to outlast the usable lifetime of the device before parts of it start to degrade.
The main hindrance to the massive adaptation of AMOLED is the low production numbers. TFT has been in production for much longer and the infrastructure is already there to meet the demands.
This rise of small, powerful components has also led to significant developments in display technology. The most recent of which, AMOLED, is now the main competitor for the most common display used in quality portable electronics – the TFT–LCD IPS (In-Plane Switching) display. As more factories in the Far East begin to produce AMOLED technology, it seems likely we will enter a battle of TFT IPS versus AMOLED, or LCD vs LED. Where a large percentage of a product’s cost is the display technology it uses, which provides best value for money when you’re designing a new product?
TFT IPSdisplays improved on previous TFT LCD technology, developed to overcome limitations and improve contrast, viewing angles, sunlight readability and response times. Viewing angles were originally very limited – so in-plane switching panels were introduced to improve them.
Modern TFT screens can have custom backlights turned up to whatever brightness that their power limit allows, which means they have no maximum brightness limitation. TFT IPS panels also have the option for OCA bonding, which uses a special adhesive to bond a touchscreen or glass coverlens to the TFT. This improves sunlight readability by preventing light from bouncing around between the layers of the display, and also improves durability without adding excess bulk; some TFT IPS displays now only measure around 2 mm thick.
AMOLED technology is an upgrade to older OLED technology. It uses organic compounds that emit light when exposed to electricity. This means no backlight, which in turn means less power consumption and a reduction in size. AMOLED screens tend to be thinner than TFT equivalents, often produced to be as thin as 1 mm. AMOLED technology also offers greater viewing angles thanks to deeper blacks. Colours tend to be greater, but visibility in daylight is lower than IPS displays.
As manufacturers increasingly focus on smaller devices, such as portable smartphones and wearable technology, the thinness and high colour resolution of AMOLED screens have grown desirable. However, producing AMOLED displays is far more costly as fewer factories offer the technology at a consistent quality and minimum order quantities are high; what capacity there is is often taken up the mobile phone market Full HD TFT IPS displays have the advantage of being offered in industry standard sizes and at a far lower cost, as well as offering superior sunlight visibility.
The competition between displays has benefitted both technologies as it has resulted in improvements in both. For example, Super AMOLED, a marketing brand by Samsung, involves the integration of a touchscreen layer inside the screen, rather than overlaid on it. The backlight in TFT technology means they can never truly replicate the deep blacks in AMOLED, but improvements have been made in resolution to the point where manufacturers like Apple have been happy to use LCD screens in their smartphones, even as they compete with Samsung’s Super AMOLED.
Aside from smartphones, many technologies utilise displays to offer direct interaction with customers. To decide whether TFT LCD will survive the rise of AMOLED technology, we must first recap the advantages of LCD. The backlit quality means that whites are bright and contrast is good, but this will wear down a battery faster than AMOLED. Additionally, cost is a significant factor for LCD screens. They are cheaper, more freely available and are offered in industry standard sizes so can be ordered for new products without difficulty.
It seems hard to deny that AMOLED will someday become the standard for mobile phones, which demand great colour performance and are reliant on battery life. Where size is an issue, AMOLED will also grow to dominance thanks to its superior thinness. But for all other technologies, particularly in industrial applications, TFT-LCD offers bright, affordable display technology that is continually improving as the challenge from AMOLED rises.

Tried and trusted TFT technology works by controlling brightness in red, green and blue sub-pixels through transistors for each pixel on the screen. The pixels themselves do not produce light; instead, the screen uses a backlight for illumination.
By contrast the Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) display requires no backlight and can light up or turn off each of their pixels independently. As the name suggests, they are made of organic material.
An AMOLED display has many other benefits which make it a superior looking display including exceptional vieiwng angles and a display that looks practically black when it is switched off.
So, why use a TFT display? Well, it is a mature technology meaning the manufacturing processes are efficient, yields high and cost much lower than AMOLED.
TFT displays also have a much longer lifespan than AMOLED displays and are available in a far greater range of standard sizes, which can be cut down to fit a space restricted enclosure for a relatively low cost adder.
Which type of display you choose really depends on your application, environment and users, so why not get in touch with us today to discuss your requirements.

OLED displays are commonplace on all high-end phones, tablets, smartwatches, televisions, and even many of the many budget phones. However, there isn"t one type of OLED technology. Depending on your device, you may have an OLED, AMOLED, or POLED display.
OLED promises inky blacks, high contrast, low response times, and incredible brightness. There are a few downsides (primarily the burn-in phenomenon), but overall it"s the best screen technology you"ll find. We explain the background behind the acronyms, the difference between POLED and AMOLED, and which is better, helping you choose the right phone.
Every OLED screen comprises millions of diodes, hence the name organic light-emitting diode. Viewed under a microscope, each screen consists of a series of red, green, and blue diodes that can be individually turned on and off. Behind this, the light-emitting pixels of an OLED display emit blue and yellow light. The yellow and blue light combine to form white light, passing through the red, green, and blue subpixels to produce a single pixel. Because each pixel handles its light and color, OLED displays do not need a separate backlight.
As an OLED screen doesn"t need a backlight, black is produced by turning off the pixels, resulting in deep, consistent blacks. This allows manufacturers to implement things like an always-on display without quickly burning through battery life.
Another critical advantage of OLED tech is high contrast ratios. Technically, OLED displays offer "infinite contrast," or 1,000,000:1 contrast ratios. This is because OLED displays reproduce black by turning off pixels entirely, and contrast is measured by comparing the brightest part of the screen to the darkest part. Improved contrast makes on-screen content more vivid and makes bright highlights look more impressive. This also means that OLED screens can reach higher brightness than the best IPS LCD screens.
OLED displays can display more colors with greater color accuracy than their LCD peers. This is great for photographers and videographers using their phones to preview, edit, and create content.
OLED displays have near-instantaneous pixel response times. Older LCD screens often have lower response times because to change from one color to another, they must physically change the orientation of a liquid crystal, which takes time. An OLED display turns a subpixel on or off with an electrical charge, giving them a faster pixel response time.
The omission of a separate backlight and the use of fewer components means OLED displays can be thinner than LCDs, making them more versatile in their applications. This means they are more fragile and prone to damage in high-impact or high-stress situations. Engineers combat this by using technologies like Gorilla Glass and robust metal frames. Mitigation strategies like these raise the cost of OLED screens.
OLED displays can also be transparent, depending on the materials used. Transparent displays are helpful for in-display fingerprint readers and under-display cameras, which allow manufacturers to design smartphones with fewer and smaller bezels, notches, and display cutouts. When notches and cutouts are necessary, OLED displays have more even brightness around those cutouts and notches compared with LCDs, where the backlight has to make it around the cutout, and things get a little messy.
Of particular import to smartphones, OLED displays often consume less power, especially when displaying dark images or UI elements, thanks to the pixel-level regulation of brightness. However, at max brightness, an OLED screen usually uses more power than an equivalent LCD.
As with any new technology, OLED tech is not without its flaws.OLED displays are prone to degradation from age and UV exposure, resulting from the organic nature of the molecules that make up the diodes. The organic nature of OLED displays also leads to a phenomenon called screen burn-in, where static UI elements like menus, navigation bars, and status bars (elements that are on-screen for long periods) leave a permanent ghost image, even when they are not displayed. However, burn-in has been somewhat mitigated by pixel shifting and technological advancements in recent years.
Early OLED screens placed all the organic materials on a glass substrate. However, glass is rigid, so a flexible plastic substrate is needed to create foldable display screens, leading to the creation of POLED screens.
POLED (polymer organic light-emitting diode) offers advantages in terms of durability and versatility. The replacement ofglass substrates with plastic ones makes them more shock-resistant. Another unique advantage is in the implementation. Designers can reduce bezel size by folding the electronics underneath an edge of the display instead of having it be on the same plane. POLED displays are also significantly thinner than OLED displays with glass substrates.
Note the difference between P OLED and pOLED. pOLED is the trademark that LG Display uses to brand its plastic OLED displays. It produces these displays for a variety of applications and companies. Google used pOLED displays on the Pixel 2 XL, LG used them on theLG Velvet and several wearables,and Apple reportedly used LG pOLED displays on some Apple Watch models. LG"s pOLED displays seem to suffer from an increased risk of burn-in, as users of the Google Pixel 2 XL complained of burn-in after a few months of use.
To get to the resolution and size of a phone, an AMOLED screen (active matrix organic light emitting diode) is needed. Older, passive matrix OLED displays (PMOLED) require higher voltages for higher pixels/resolutions. The higher the voltage, the lower the screen"s lifetime.
Thin-film transistor (TFT) arrays used in modern active-matrix OLED displays control the charging of the display"s storage capacitors. These TFTs control current flow, resulting in more energy-efficient OLED panels than PMOLED displays. This allows a larger display size without compromising resolution, lifetime, or power consumption.
QLED isn"t related to OLED displays—despite what the name may suggest—but it"s often slated as a competitor to OLED, and it aims to replace the technology by targeting both OLED"s successes and failures. QLED stands for quantum dot light-emitting diode. The core principle of QLED technology is the same as a regular OLED. A backlight is passed through red, green, and blue subpixel layers to generate an image. However, the backlight isn"t one large, uniformly-lit layer. Instead, QLED displays use an array of tiny individually-controlled LEDs to supply the backlight. Using individually-controlled LEDs means the display can produce a more accurate image with a higher contrast.
Generally speaking, QLED displays have similar benefits to OLED displays—high peak brightness, high contrast, perfect blacks, and good saturation. Still, they lack some OLED advantages, like image retention and reduced overall and sustained brightness.
QLED is found in TVs and large computer monitors because that"s where it sees the most benefit. OLED displays in phones are small enough, bright enough, and cheap enough that QLED wouldn"t be able to compete or offer any practical benefit to the end user.
Display type is only one part of the puzzle.What use is exotic technology if it doesn"t make any difference to the end user? Smartphone manufacturers use many approaches to improve their displays. Let"s look at a few things you should look for apart from the display type.
Resolution is the number of pixels a screen has. It is usually written as a ratio: pixels on the long side by pixels on the short side, for example, 1920 x 1080. Most smartphone displays have a resolution between 720p (1280 x 720) on the low-end and 4k (3480 x 2160) on some Sony models. While 4k is excessive and rare for anything under 15 inches, 720p, 1080p, and 1440p are all common smartphone resolutions.
The ideal smartphone screen resolution depends on the screen size. A metric called pixels per inch (PPI) describes the display"s number of pixels in a vertical or horizontal inch. For a 6-inch display, you should aim for at least 1080p or above 350 PPI. This will ensure that the text is crisp.
A subpixel is one of the light-emitting parts of a pixel—in the case of most displays, these are red, blue, and green—that combine in different quantities to display various colors in an image. Although RGB subpixel layouts have been the prevalent option for a long time, some display manufacturers elect to use subpixel arrangements like BGR, PenTile, RGBG, and WRGB. The reason these subpixel layouts exist is to combat the various shortcomings of the display technology.
As with resolution, the subpixel layout can affect perceived image quality. Over the brief course of display history, manufacturers and designers have settled on RGB as a standard, meaning content is generally optimized for that layout. When manufacturers decided to invent new subpixel layouts, the perceived quality took a bit of a hit.
So why do manufacturers use odd-pixel layouts? It depends on the manufacturer and its goals. Samsung uses PenTile displays, which use RGBG instead of RGB subpixels, to combat image retention on its AMOLED displays. WRGB displays add a separate white subpixel to boost brightness on OLED displays—a technology that is otherwise notoriously dim.
Refresh rate is the number of times per second a display refreshes, and higher refresh rates mean motion and animations look smoother. Generally, 60Hz is the lowest commonly-found refresh rate and is perfectly serviceable. Many modern flagship phones and a few mid-range phonesoffer 90Hz, 120Hz, 144Hz, and even 240Hz displays.
Response times on OLED displays are generally lower, meaning displays can reach these high refresh rates and look better at these higher refresh rates thanks to the reduced ghosting.
Smartphones are often used outside in bright sunlight, so display brightness is a huge factor. Display brightness is measured in nits or cd/m². Peak brightness is the momentary maximum brightness of a small portion of a screen, while sustained brightness is a more realistic representation of the brightness of the whole display. Aim for above 600 nits of sustained brightness since anything below may cause legibility issues in bright conditions. On the other hand, brightness is measured logarithmically, not linearly, meaning 1,200 nits is only twice as bright as 300 nits. This is important since many manufacturers lean heavily on high brightness metrics as a marketing point.
Display specifications are no different. While it is true that OLED displays may be the best option for some people, they command a premium, and a lot of people wouldn"t notice the difference.
Brightness, refresh rate, and resolution are all key factors, and performance as a whole should be the determining factor in selecting a display, not the shiny new technology involved. If you"re looking for a phone with an OLED display and a high refresh rate, check out the best Android phones you can buy.

Both screens are made up of Pixels. A pixel is made up of 3 sections called sub-pixels. The three sections are red, green and blue (primary colors for display tech).
The light is generated from a “backlight”. A series of thin films, transparent mirrors and an array of white LED Lights that shine and distribute light across the back of the display.
On some lower quality LCD screens, you can see bright spots in the middle or on the perimeters of screens. This is caused by uneven light distribution. The downside to using backlights, is that black is never true black, because no matter what, light has to be coming through, so it will never have as dark of a screen as an AMOLED screen. Its comparable to being able to slow a car down to 2 mph versus coming to a complete stop.
Each pixel is its own light source, meaning that no backlight is necessary. This allows the screen assembly to be thinner, and have more consistent lighting across the whole display.

Super AMOLED (S-AMOLED) and Super LCD (IPS-LCD) are two display types used in different kinds of electronics. The former is an improvement on OLED, while Super LCD is an advanced form of LCD.
All things considered, Super AMOLED is probably the better choice over Super LCD, assuming you have a choice, but it"s not quite as simple as that in every situation. Keep reading for more on how these display technologies differ and how to decide which is best for you.
S-AMOLED, a shortened version of Super AMOLED, stands for super active-matrix organic light-emitting diode. It"s a display type that uses organic materials to produce light for each pixel.
One component of Super AMOLED displays is that the layer that detects touch is embedded directly into the screen instead of existing as an entirely separate layer. This is what makes S-AMOLED different from AMOLED.
Super LCD is the same as IPS LCD, which stands forin-plane switching liquid crystal display. It"s the name given to an LCD screen that utilizes in-plane switching (IPS) panels. LCD screens use a backlight to produce light for all the pixels, and each pixel shutter can be turned off to affect its brightness.
There isn"t an easy answer as to which display is better when comparing Super AMOLED and IPS LCD. The two are similar in some ways but different in others, and it often comes down to opinion as to how one performs over the other in real-world scenarios.
However, there are some real differences between them that do determine how various aspects of the display works, which is an easy way to compare the hardware.
For example, one quick consideration is that you should choose S-AMOLED if you prefer deeper blacks and brighter colors because those areas are what makes AMOLED screens stand out. However, you might instead opt for Super LCD if you want sharper images and like to use your device outdoors.
S-AMOLED displays are much better at revealing dark black because each pixel that needs to be black can be true black since the light can be shut off for each pixel. This isn"t true with Super LCD screens since the backlight is still on even if some pixels need to be black, and this can affect the darkness of those areas of the screen.
What"s more is that since blacks can be truly black on Super AMOLED screens, the other colors are much more vibrant. When the pixels can be turned off completely to create black, the contrast ratio goes through the roof with AMOLED displays, since that ratio is the brightest whites the screen can produce against its darkest blacks.
However, since LCD screens have backlights, it sometimes appears as though the pixels are closer together, producing an overall sharper and more natural effect. AMOLED screens, when compared to LCD, might look over-saturated or unrealistic, and the whites might appear slightly yellow.
When using the screen outdoors in bright light, Super LCD is sometimes said to be easier to use, but S-AMOLED screens have fewer layers of glass and so reflect less light, so there isn"t really a clear-cut answer to how they compare in direct light.
Another consideration when comparing the color quality of a Super LCD screen with a Super AMOLED screen is that the AMOLED display slowly loses its vibrant color and saturation as the organic compounds break down, although this usually takes a very long time and even then might not be noticeable.
Without backlight hardware, and with the added bonus of only one screen carrying the touch and display components, the overall size of an S-AMOLED screen tends to be smaller than that of an IPS LCD screen.
This is one advantage that S-AMOLED displays have when it comes to smartphones in particular, since this technology can make them thinner than those that use IPS LCD.
Since IPS-LCD displays have a backlight that requires more power than a traditional LCD screen, devices that utilize those screens need more power than those that use S-AMOLED, which doesn"t need a backlight.
That said, since each pixel of a Super AMOLED display can be fine-tuned for each color requirement, power consumption can, in some situations, be higher than with Super LCD.
For example, playing a video with lots of black areas on an S-AMOLED display will save power compared to an IPS LCD screen since the pixels can be effectively shut off and then no light needs to be produced. On the other hand, displaying lots of color all day would most likely affect the Super AMOLED battery more than it would the device using the Super LCD screen.
An IPS LCD screen includes a backlight while S-AMOLED screens don"t, but they also have an additional layer that supports touch, whereas Super AMOLED displays have that built right into the screen.
For these reasons and others (like color quality and battery performance), it"s probably safe to say that S-AMOLED screens are more expensive to build, and so devices that use them are also more expensive than their LCD counterparts.

Over time, the purpose of using mobile phones or Smartphones has changed. Comparatively, it has now become a basic necessity of every individual. Smartphone has dramatically transformed the lives of individuals. It has now become a mini-computer that everyone carries in their pocket. Instead, you can have multiple things at your fingertips in a few seconds. While there are plenty of things to look for, AMOLED vs OLED is also a part of it.
Before purchasing any Smartphone, everyone goes through a list of specifications. This list includes display type, screen size, battery backup, supported operating system, total internal memory, and many others. Today, we have brought a comprehensive study of the significant display technologies available nowadays.
This article will introduce you to AMOLED vs OLED display technologies. Then, we will discuss the properties of both display technologies, followed by the difference between AMOLED vs OLED.
It stands for Natural Light-Emitting Diode, a type of LED technique that utilises LEDs wherein the light is of organic molecules that cause the LEDs to shine brighter. These organic LEDs are in use to make what are thought to be the best display panels in the world.
When you make an OLED display, you put organic films among two conductors to make them. As a result, a bright light comes out when electricity is used—a simple design with many advantages over other ways to show things.
OLEDs can be used to make emissive displays, which implies that each pixel can be controlled and emits its very own light. As a result, OLED displays have excellent picture quality. They have bright colours, fast motion, and most importantly, very high contrast. Most of all, “real” blacks are the most important. The simple design of OLEDs also makes it easy to create flexible displays that can bend and move.
PMOLED stands for Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. The PMOLEDs are easy to find and much cheaper than other LEDs, but they cannot work for a long duration as their lifespan is very short. Therefore, this type of display is generally for small devices up to 3 inches.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. This type of display is generally for large platforms. It contains TFT, which further consists of a storage capacitor. It also works on the same principle as OLED displays.
AMOLED offers no restriction on the size of the display. The power consumption of AMOLED is much less than other display technologies. The AMOLED provides incredible performance. It is thinner, lighter, and more flexible than any other display technology like LED, or LCD technology.
The AMOLED display is widely used in mobiles, laptops, and televisions as it offers excellent performance. Therefore, SAMSUNG has introduced AMOLED displays in almost every product. For example, Full HD Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy S4 and Samsung Galaxy Note 3, Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy S3, HD Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy Note, and HD Super AMOLED Plus in Samsung Galaxy S3. Apart from this, it is also used in AMOLED vs OLED creating the following:
So far, we have discussed OLED and AMOLED display technologies. Now, we will look at some of the differences between OLED and AMOLED display technology:
OLED comprises thin layers of the organic component, which emits light when the current passes through it. In this technology, each pixel transmits its own light. On the other side, AMOLED consists of an additional layer of thin-film transistors (TFTs). In AMOLED, the storage capacitors are used to maintain the pixel states.
While the technology is different among various manufacturers, Samsung’s edge AMOLED displays use plastic substrates with poly-Si TFT technology similar to how LG uses it in their POLED technology. This technology is what makes the possibility to build curved displays using an active-matrix OLED panel.
OLED display much deeper blacks as compared to AMOLED displays. You cannot see the screen in AMOLED display under direct sunlight. The AMOLED display quality is much better than the OLEDs as it contains an additional layer of TFTs and follows backplane technologies.
These organic compounds are present between the protective layers of glass or plastic. Comparatively, AMOLED comprises an active matrix of OLED pixels along with an additional layer of TFTs. This extra layer is responsible for controlling the current flow in each pixel.
The OLED display offers a high level of control over pixels. Hence, it can be turned off completely, resulting in an excellent contrast ratio compared to the AMOLED displays and less power consumption. On the other side, AMOLED has faster refresh rates than OLEDs. Also, they offer a tremendous artificial contrast ratio as each pixel transmits light but consumes more power than OLEDs.
OLED displays are comparatively much thinner compared to LCDs. Hence, it provides more efficient and bright presentations. In addition, OLED offers support for large display sizes compared to traditional LCDs. AMOLEDs remove the limitation of display sizes. one can fit it into any display size.
Putting all the points mentioned above in view, the key difference to understand appropriately is that POLED is an OLED display with a plastic substrate. On the other hand, AMOLED is Samsung’s word for its display technology which is mainly for marketing. Therefore, most phone manufacturers having AMOLED displays mean that they are using Samsung displays. It is as simple as that. To add to that, all the curved display technology is made possible because of the usage of the plastic substrate.
So, based on the points mentioned above, the difference between OLED and AMOLED displays, you can choose any of the two display technology at your convenience. Both are good, offer excellent performance, and are customised according to your requirements.
The AMOLED display has a higher quality than OLEDs since it has an additional layer of TTs and uses backplane technologies. When compared to OLED screens, AMOLED displays are far more flexible. As a result, they are substantially more expensive than an OLED display.
Window to the digital world, the display is one of the first seen features when selecting a smartphone, so a show must be good, and an AMOLED display offers the same. Offering a great viewing experience, here are the top 3 AMOLED screen smartphones available in the market right now:
Realme 10 Pro Plus 5G features a 6.7-inch AMOLED display with 394 PPI display. It runs on MediaTek Dimensity 1080. On the rear, the Realme 10 Pro Plus 5G has a triple-camera setup with 108-megapixel primary sensor, 8-megapixel ultra-wide angle sensor, 2-megapixel sensor.
Coming to the front, it has a 16-megapixel selfie camera housed in the punch-hole display. It comes with a 5000mAh battery that supports 67W smart flash charging. The Realme 10 Pro Plus 5G is one of the best segments with a AMOLED FHD display.
The Xiaomi Redmi Note 12 Pro 5G runs on MediaTek Dimensity 1080 chipset bundled with Mali-G68 MC4 graphics processor and up to 12GB RAM. The display front comes with a 6.67-inch AMOLED display with FHD and 395 PPI.
The cameras have a triple rear camera setup with a 50-megapixel primary sensor, an 8-megapixel ultra-wide angle sensor, and a 2-megapixel macro sensor. In addition, it has a 16-megapixel selfie camera. It has a 5,000 mAh battery with 67W fast charging. The AMOLED display on the Redmi Note 12 Pro 5G is a treat for all media enthusiasts.
OPPO has recently launched the OPPO Reno8 5G with MediaTek Dimensity 1300 chipset coupled with Arm Mali-G77 MC9 GPU and up to 8GB of RAM. In addition, it comes with a 6.43-inch curved AMOLED display with support for HDR10+.
On the rear, it comes with a triple-camera setup with a 50-megapixel primary sensor, an 8MP ultra-wide angle sensor, a 2-megapixel macro camera. In addition, it has a 32-megapixel selfie camera integrated inside the punch-hole on display on the front. It comes with a 4,500mAh battery that supports 80W fast charging and can charge the phone 100 per cent in just 15 minutes. Since it comes with an Full HD+ AMOLED display on the display front, it is a treat for gamers and media consumption lovers.
Smartphone displays have advanced significantly in recent years, more so than most people realise in this technological age. Display screens are similar to windows in the mobile world, which has seen a tremendous transformation in innovative products in the last several years. People have gotten more selective when buying a phone in recent years, and although all of the functions are important, the display is always the most noticeable.
Major smartphone manufacturers attempt to provide their consumers with the most delicate devices possible that incorporate the most up-to-date technologies. In AMOLED vs OLED, AMOLED is a type of OLED and a more prominent example of both OLED and POLED, so there’s no debate about which is superior.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey