que significa tft lcd brands

TFT-LCD, pantalla de cristall líquid-TFT (transistor de pel·lícula fina) o pantalla de cristall líquid amb tecnologia de transistor de pel·lícula fina, és una variant de pantalla de cristall líquid (LCD) que fa servir tecnologia de transistor de pel·lícula fina (TFT) per a millorar la qualitat d"imatge. Els LCD de TFT són un tipus de LCD de matriu activa, encara que generalment aquest terme es considera sinònim de LCD. Es fan servir en televisors, visualitzadors de pantalla plana i projectors. En computació, els monitors de TFT estan desplaçant la tecnologia de CRT, i estan comunament disponibles en grandàries de 12 a 30 polzades. El 2006 van entrar al mercat de les televisions desplaçant de mica en mica una part del mercat de pantalla de plasma.
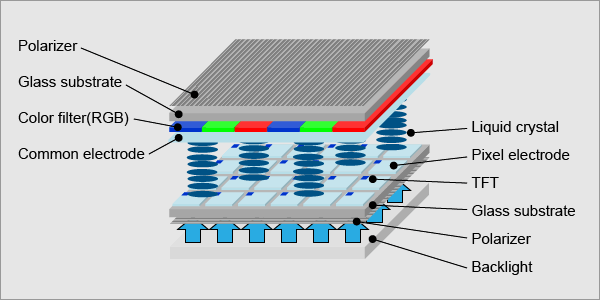
Les pantalles de cristall líquid normals, com les de les calculadores, presenten elements d"imatge excitats en forma directa –es pot aplicar una tensió a través d"un segment sense que hi hagi interferències amb altres segments de la pantalla. Açò no és possible en pantalles grans amb un gran nombre de píxels, ja que es requeririen milions de connexions -connexions en la part superior i inferior per a cadascun dels tres colors (roig, verd i blau) de cada píxel. Per a evitar açò, els píxels són direccionats en files i columnes, el que redueix el nombre de connexions de milions a milers. Si tots els píxels d"una fila són excitats mitjançant una tensió positiva i tots els píxels d"una columna són excitats amb una tensió negativa, llavors el píxel que es troba en la intersecció té el voltatge aplicat més elevat i és commutat. L"inconvenient d"aquesta solució és que tots els píxels de la mateixa columna reben una fracció de la tensió aplicada, com ocorre amb tots els píxels de la mateixa fila, així encara que no siguen commutats completament, tendeixen a enfosquir-se. La solució al problema és proporcionar a cada píxel el seu propi transistor commutador, açò permet controlar a cada píxel per separat. La baixa corrent de fugida del transistor implica que la tensió aplicada al píxel no es perd durant les actualitzacions de refresc de la imatge en la pantalla. Cada píxel és un menut condensador amb una capa transparent d"òxid d"indi i estany en el frontal, una capa transparent en la part posterior, i entre mitjà una capa aïllant de cristall líquid.
La distribució dels circuits en un TFT-LCD és molt similar a la utilitzada en la memòria DRAM. No obstant això, en comptes de realitzar els transistors usant hòsties de silici, aquests són fabricats dipositant una pel·lícula prima de silici sobre un panell de vidre. Els transistors ocupen només una menuda fracció de l"àrea de cada píxel i la pel·lícula de silici de la superfície romanent és eliminada permetent que la llum passe a través d"ella.
La capa del silici per a TFT-LCDs es diposita generalment usant el procés denominat PECVD (Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition) d"un precursor de gas silano (SiH4) per a produir una pel·lícula amorfa de silici. El silici policristal·lí també s"utilitza en algunes pantalles on es requereixen TFTs amb un rendiment més alt, típicament en pantalles on es requereix una resolució molt alta o en aquelles on es desitja realitzar algun processament de dades en si mateix. Ambdós tipus de TFTs, els de silici amorf i els de silici policristal·lí presenten una prestació molt pobra enfront dels transistors fabricats a partir de cristalls de silici simples.
TN+Film (Twisted nematic+Film, Torsió Nemàtica+Pel·lícula) o TN, és el tipus de visualització més comú, atribuïble al seu cost de producció baix i ampli desenvolupament. El temps de resposta d"un píxel en els panells TN moderns, és prou ràpid per evitar rastres d"ombres i efectes fantasmes (problemes de refresc), que eren un problema dels monitors LCDs de tecnologia passiva. Els temps de resposta ràpids han estat la virtut més important d"aquesta tecnologia, encara que en la majoria dels casos aquest nombre no reflecteix el rendiment a través de les transicions dels possibles colors. Els temps de resposta tradicionals van ser donats acord a un estàndard ISO com la transició des del negre cap al blanc i no van reflectir la velocitat de les transicions dels tons grisos (una transició molt més comú per cristalls líquids en la pràctica). L"ús modern de tecnologies RTC (Response Time Compensation - Overdrive) han permès que els fabricants redueixin el temps de les transicions de gris (G2G) significativament, mentre que el temps de resposta ISO queda gairebé igual. Les temps de resposta són donades ara en les xifres de G2G, amb 4 ms i 2 ms com valors comuns per als models fonamentats en la tecnologia de TN+film. Aquesta estratègia de màrqueting, combinat amb el cost relativament més baix de la producció per a pantalles TN, ha resultat en el domini de TN en el mercat del consumidor.
Un dels desavantatges de les pantalles basades en TN és el seu escàs angle de visió, especialment en la direcció vertical, sent la majoria incapaços de mostrar els 16.7 milions de colors (color veritable de 24 bits) disponibles de les targetes de gràfiques modernes. Aquests panells especials, amb 6 bits pel canal de color a diferència de 8, pot acostar-se al color de 24 bits usant un mètode de tramat que combina píxels adjacents per simular el to desitjat. També poden usar FRC (el control de rate de marc), el menys conspicu del dos. El FRC cicla moltes vegades ràpidament sobre els píxels per simular un to en particular. Aquests mètodes de simulació de color són perceptibles per a la majoria de les persones i angoixant per a altres. FRC tendeix a ser més notable en els tons més foscos. El motiu de tramat té la tendència de apareix com si els píxels individuals de la LCD estiguessin en realitat visibles. En general, la reproducció de color i angle de visió dels panells de tipus TN són pobres. Els defectes en la gamma de color de visualització (referència com uns percentatges de la 1953 gamma de color de NTSC sovint) també poden ser atribuïts a il·luminar des del fons la tecnologia. No és poc comú per a les visualitzacions amb CCFL (càtode llums fluorescents freds) fundat en encendre estendre 40% a 76% de la gamma de color de NTSC, mentre que visualitzacions que utilitzen blanc que LED il·lumina des del fons poden estendre 100% de la gamma de color de NTSC - una diferència poc perceptible a l"ull humà.
IPS (In-Plane Switching, alternança En-El-Pla) va ser desenvolupat per Hitachi el 1996 per superar els pobres angle de visió i reproducció de color dels panells TN. La majoria també suporta 8 bits de color reals. Aquestes millores van venir amb una pèrdua de temps de resposta, que estava inicialment en l"ordre dels 50ms. Els panells de IPS eren també summament costosos. IPS des de llavors ha estat reemplaçat per S-IPS (Super-IPS, Hitachi el 1998), que té tots els beneficis de la tecnologia d"IPS més un temps de refresc de píxel millorat. Encara que la reproducció de color s"apropa a la dels CRTs, el contrast és relativament pobre. La tecnologia S-IPS és àmpliament usada en els panells de 20 "i més. LG i Philips romanen com uns dels fabricants principals de panells basats en S-IPS.
AS-IPS (S-IPS Avançat), també desenvolupat per Hitachi el 2002, millora considerablement el contrast dels S-IPS tradicionals al punt de ser superats només per alguns S-PVAs. AS-IPS és també un terme usat per monitors NEC Corporation (per exemple, NEC LCD20WGX2) basats en tecnologia S-IPS, en aquest cas, desenvolupada per LG. Philips.
A-TW-IPS (IPS Blanc Real Avançat), desenvolupat per LG.Philips LCD per NEC, és un panell S-IPS personalitzat amb un filtre TW (Blanc Real) per fer que el blanc es vegi més natural i incrementar la gamma de color. Això s"utilitza en LCDs professionals o de fotografia.
H-IPS Llançat a finals de 2006, és una evolució del panell IPS que millora al seu predecessor, el panell S - IPS. El panell H - IPS pot veure al NEC LCD2690WUXi, Mitsubishi RDT261W 26 "LCD i en el més recent Apple iMac d"alumini de 24".
Una altra contra de la tecnologia IPS és que es pot veure afectada per un problema de contrallum, per les seves característiques. Deixa passar més llum a les zones fosques del que hauria, pel que en alguns angle de visió aguts, sobretot verticals, es pot veure que les zones negres deixen de ser-ho, transformant-se en una brillantor que el mateix monitor genera. Es va crear un filtre de polarització per solucionar-ho i que és incorporat en els IPS d"elevat cost.
MVA (Alineació Vertical Multidomini) va ser desenvolupat el 1998 per Fujitsu originalment com un punt intermedi entre TN i IPS. Va aconseguir una resposta de píxel ràpida (en el seu moment), amplis angle de visió, i el contrast alt, en detriment de la lluminositat i la reproducció de color. Els panells de MVA moderns poden brindar amplis angle de visió (només superats per la tecnologia S-IPS), bona profunditat de negre, bona reproducció i profunditat de color, i ràpids temps de resposta gràcies a l"ús de tecnologies RTC. Hi ha diverses tecnologies "de següent generació" basades en MVA, incloent P-MVA i A-MVA d"AU Optronics, com així també S-MVA de Chi Mei Optoelectronics. Els analistes van predir que MVA seria la tecnologia a seguir, però no obstant això TN ha dominat el mercat. Un factor contribuent era el major cost de MVA, conjuntament amb un temps de resposta més lent (que augmenta considerablement quan es donen canvis petits en la lluminositat). Els panells de MVA més econòmics també poden usar tramat i FRC.
PVA (Alineació Vertical per Patrons) i S-PVA (Super Alineació Vertical per Patrons) són les versions alternatives de la tecnologia de MVA ofertes per Samsung. Desenvolupat per separat, pateix del mateix problema que el MVA, però a canvi ofereix contrastos molt alts com 3000: 1. Els panells PVA econòmics també usen tramat i FRC. Tots els panells S-PVA són de 8 bits de color reals i no usen cap mètode de simulació de color. PVA i S-PVA poden brindar una bona profunditat de negre, amplis angle de visió i S-PVA pot oferir a més temps de resposta ràpids gràcies a modernes tecnologies de RTC.
PLS (Plane Line Switching) i S-PLS és una tecnologia actualment en desenvolupament per Samsung que permet angle de visió totals. Es pot considerar una millora del panell IPS, però amb millors angles, qualitat d"imatge, millor brillantor i un preu més baix. Els primers monitors amb aquesta tecnologia són els models S27A850 i S24A850 de Samsung, sortits a finals de 2011.
Els dispositius de visualització exteriors com una TFT LCD usen majoritàriament una connexió analògica VGA, mentre que la majoria dels nous models disposen d"una interfície digital, com DVI o HDMI. Dins d"un dispositiu de visualització extern hi ha una targeta controladora per convertir VGA, DVI, HDMI, CVBS, etc. a la resolució nativa digital RGB que el panell de pantalla pugui usar. En un portàtil el xip de gràfics directament produirà un senyal adequada per a la connexió TFT incorporada. El mecanisme de control de la llum de fons s"inclou normalment en la mateixa targeta controladora.
La interfície de baix nivell de STN, DSTN o panells de pantalla TFT usen tant el TTL 5V o TTL 3,3 V que transmet rellotge de píxels, sincronització horitzontal, sincronització vertical, vermell digital, verd digital, blau digital en paral·lel. Alguns models també tenen característiques d"entrada/pantalla activa, i escombrat de direcció horitzontal i vertical dels senyals de direcció.
Noves i grans (> 15 ") pantalles TFT solen utilitzar senyalització LVDS o TMDS que és la mateixa interfície paral·lela, però posarà control i bits RGB en el nombre de línies de sèrie de transmissió que són sincronitzades amb un rellotge en 1/3 de la taxa de bits de dades.
Els factors pels quals una pantalla d"un portàtil no pot ser reutilitzada directament amb una targeta de gràfics comú d"ordinador com la televisió, es deu principalment al fet que no té un equip rescaler (sovint l"ús d"alguna transformada de cosinus discreta) que pot canviar la mida de la imatge per adaptar-se a la resolució nativa del panell de pantalla. Amb senyals analògics com el controlador VGA de pantalla també ha de realitzar una conversió a alta velocitat d"analògica a digital. Amb senyals d"entrada digitals com DVI o HDMI alguns simples bits de farciment que es necessiten abans d"alimentar el rescalar si la resolució d"entrada no coincideix amb la resolució del panell de pantalla. Per CVBS o "TV" es necessita també l"ús d"un sintonitzador i un descodificador i transformador de color.
Els cristalls líquids de l"interior de la pantalla són extremadament tòxics. No han de ser ingerits, o tocats per la pell o la roba. Si es produeixen vessaments pel fet que la pantalla s"esquerda, renteu-vos immediatament amb aigua i sabó.
A causa de l"alt cost de construcció de les fàbriques de TFT, són pocs els principals proveïdors de panells OEM per a grans panells. Les principals proveïdores de panells de vidre són:
Els panells LCD TFT són habitualment classificats en les fàbriques en tres categories, en relació amb el nombre de píxels morts, llum de fons i la uniformitat de la llum de fons i la qualitat dels productes en general. A més, pot haver un màxim de ± 2 ms de diferència de temps de resposta entre els panells individuals que van arribar a la mateixa línia de muntatge en el mateix dia. Les pantalles més pobres es venen als venedors sense nom o utilitzant un «valor» dels monitors TFT (sovint marcades amb la lletra V darrere del tipus de nombre), les que es troben al mig s"orienten als jocs oa l"oficina a casa (de vegades marcades amb la lletra S), i les millors pantalles solen estar reservades per a un ús «professional» (marcat amb la lletra P o S després del seu tipus de nombre).
Actualment el mercat està acabant de desplaçar el CRT per les pantalles TFT i LCD, les quals estan sent el substitut tant a l"ordinador com a la televisió. Avui en dia, és pràcticament impossible trobar monitors d"una mida inferior a les 17 ", a més d"haver passat el seu format de 4:3 a format panoràmic 16:9. Les connexions que s"estan implantant s"estan desplaçant el vell VGA per obrir pas al DVI, al nou HDMI o al DisplayPort.
L"inconvenient actual és que la tecnologia encara no permet assolir la qualitat d"imatge (hi ha una sensació de sorra borrosa o pixelat en els TFT i LCD) i velocitat de resposta dels vells CRT (2 ms). Encara que a favor hi ha una interessant quantitat de millores, com és ara un menor mal a la vista (recordem que mirar un CRT és com clavar la vista a una bombeta), una resolució d"imatge inabastable (el famós FULL HD o 1080) i el que sempre va clamar al seu èxit, un pes i volum espacial considerablement petits, a més d"un consum reduït, especialment si la il·luminació és LED.
Our company specializes in developing solutions that arerenowned across the globe and meet expectations of the most demanding customers. Orient Display can boast incredibly fast order processing - usually it takes us only 4-5 weeks to produce LCD panels and we do our best to deliver your custom display modules, touch screens or TFT and IPS LCD displays within 5-8 weeks. Thanks to being in the business for such a noteworthy period of time, experts working at our display store have gained valuable experience in the automotive, appliances, industrial, marine, medical and consumer electronics industries. We’ve been able to create top-notch, specialized factories that allow us to manufacture quality custom display solutions at attractive prices. Our products comply with standards such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, QC 080000, ISO/TS 16949 and PPM Process Control. All of this makes us the finest display manufacturer in the market.
Customer service is another element we are particularly proud of. To facilitate the pre-production and product development process, thousands of standard solutions are stored in our warehouses. This ensures efficient order realization which is a recipe to win the hearts of customers who chose Orient Display. We always go to great lengths to respond to any inquiries and questions in less than 24 hours which proves that we treat buyers with due respect.

Asia has long dominated the display module TFT LCD manufacturers’ scene. After all, most major display module manufacturers can be found in countries like China, South Korea, Japan, and India.
In this post, we’ll list down 7 best display module TFT LCD manufacturers in the USA. We’ll see why these companies deserve recognition as top players in the American display module industry.
STONE Technologies is a leading display module TFT LCD manufacturer in the world. The company is based in Beijing, China, and has been in operations since 2010. STONE quickly grew to become one of the most trusted display module manufacturers in 14 years.
Now, let’s move on to the list of the best display module manufacturers in the USA. These companies are your best picks if you need to find a display module TFT LCD manufacturer based in the United States:
Planar Systems is a digital display company headquartered in Hillsboro, Oregon. It specializes in providing digital display solutions such as LCD video walls and large format LCD displays.
Microtips Technology is a global electronics manufacturer based in Orlando, Florida. The company was established in 1990 and has grown into a strong fixture in the LCD industry.
What makes Microtips a great display module TFT LCD manufacturer in the USA lies in its close ties with all its customers. It does so by establishing a good rapport with its clients starting from the initial product discussions. Microtips manages to keep this exceptional rapport throughout the entire client relationship by:
Displaytech is an American display module TFT LCD manufacturer headquartered in Carlsbad, California. It was founded in 1989 and is part of several companies under the Seacomp group. The company specializes in manufacturing small to medium-sized LCD modules for various devices across all possible industries.
The company also manufactures embedded TFT devices, interface boards, and LCD development boards. Also, Displaytech offers design services for embedded products, display-based PCB assemblies, and turnkey products.
Displaytech makes it easy for clients to create their own customized LCD modules. There is a feature called Design Your Custom LCD Panel found on their site. Clients simply need to input their specifications such as their desired dimensions, LCD configuration, attributes, connector type, operating and storage temperature, and other pertinent information. Clients can then submit this form to Displaytech to get feedback, suggestions, and quotes.
A vast product range, good customization options, and responsive customer service – all these factors make Displaytech among the leading LCD manufacturers in the USA.
Products that Phoenix Display offers include standard, semi-custom, and fully-customized LCD modules. Specifically, these products comprise Phoenix Display’s offerings:
Clients flock to Phoenix Display because of their decades-long experience in the display manufacturing field. The company also combines its technical expertise with its competitive manufacturing capabilities to produce the best possible LCD products for its clients.
True Vision Displays is an American display module TFT LCD manufacturing company located at Cerritos, California. It specializes in LCD display solutions for special applications in modern industries. Most of their clients come from highly-demanding fields such as aerospace, defense, medical, and financial industries.
The company produces several types of TFT LCD products. Most of them are industrial-grade and comes in various resolution types such as VGA, QVGA, XGA, and SXGA. Clients may also select product enclosures for these modules.
All products feature high-bright LCD systems that come from the company’s proprietary low-power LED backlight technology. The modules and screens also come in ruggedized forms perfect for highly-demanding outdoor industrial use.
LXD Incorporated is among the earliest LCD manufacturers in the world. The company was founded in 1968 by James Fergason under the name International Liquid Xtal Company (ILIXCO). Its first headquarters was in Kent, Ohio. At present, LXD is based in Raleigh, North Carolina.
We’ve listed the top 7 display module TFT LCD manufacturers in the USA. All these companies may not be as well-known as other Asian manufacturers are, but they are equally competent and can deliver high-quality display products according to the client’s specifications. Contact any of them if you need a US-based manufacturer to service your display solutions needs.
We also briefly touched on STONE Technologies, another excellent LCD module manufacturer based in China. Consider partnering with STONE if you want top-of-the-line smart LCD products and you’re not necessarily looking for a US-based manufacturer. STONE will surely provide the right display solution for your needs anywhere you are on the globe.

Monochrome character, graphic and static displays require different input voltages. All the different LCD voltage symbols can be confusing, but believe it or not, there is a system to the madness.
This LCD voltage terminology originated from the terminals of each type of transistor and their common connections in logic circuits. In other words, VCC is often applied to BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) collectors, VEE to BJT emitters, VDD to FET (Field-Effect Transistor) drains and VSS to FET sources. Most CMOS (Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor) IC data sheets now use VCC and GND to designate the positive and negative supply pins.
Pin three (3) is Vo and is the difference in voltage between VDD and VSS. This LCD voltage is adjusted to provide the sharpest contrast. The adjustment can be accomplished through a fixed resistor or a variable potentiometer. Many products have firmware that monitor the temperature and automatically adjust the contrast voltage.
In a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD), V0 is used to vary the screen brightness or contrast. Contrast, simply put is the ratio of the light areas to the dark areas in a LCD. This is usually done in a production setting with values which are optimized for most users. Temperature can have an undesirable effect on the display brightness and for this reason a varying resister or potentiometer is used to accommodate the desires of the user.
Below is a data sheet of a 16x2 Character LCD module that shows various recommended driving voltages. The LCD voltage can range from MIN (minimum) to TYP (Typical) to Max (maximum).
If the supplied LCD voltage drops too low, the display is ‘under-driven’ and will produce segments that are ‘grey’. The lower the LCD voltage falls below the acceptable threshold, the lower the contrast will be.
If the LCD is over-driven, you may see ghosting. This is where segments that should not be ‘on’ are gray. They are not as dark as the segments that should be on, but they can be seen and may cause confusion for the end user.
There are times when a customer needs to replace a display that has been discontinued or EOL (End-Of -Life) by their previous LCD supplier. The previous LCD’s pin-outs may be different than Focus’ standard, off-the-shelf display. This is not a large problem to overcome.
The third option is to pull power from pins one and two. This is the same location from which the LCD is pulling its power. Focus does not recommend this option and can modify the PCB for the customer to connect the backlight from a different location.
Many LCD Modules will require more than one internal voltage/current. This may make it necessary for the customer to supply the needed inputs. They may need to supply 3V, 5V, 9V, -12V etc.
The solution for this is to integrate a charge pump (or booster circuit) into the LCD circuitry. This solution works in most applications, but if the product will be operating in an intrinsic environment, care must be taken with layout of the circuit board.
Intrinsically-safe LCDs are Liquid Crystal Displays that are designed to operate in conditions where an arc or spark can cause an explosion. In these cases, charge pumps cannot be employed. In fact, the total capacitive value of the display needs to be kept to a minimum.
Focus Display Solutions does not build a display that is labeled ‘Intrinsically safe’ but we do design the LCD to meet the requirements of the engineer. In meeting the design engineer’s requirements, the display may need to contain two or three independent inputs. Focus can redesign the PCB and lay out the traces to allow for these additional inputs.

One of the industry’s leading oxide panel makers selected Astra Glass as its backplane glass substrate because it has the inherent fidelity to thrive in high-temperature oxide-TFT glass fabrication for immersive high-performance displays.
One of the industry’s leading oxide panel makers selected Astra Glass as its backplane glass substrate because it has the inherent fidelity to thrive in high-temperature oxide-TFT glass fabrication for immersive high-performance displays.

Estamos en un momento en el que damos mucha más importancia a la pantalla de los teléfonos inteligentes que a cualquier otra especificación. Además, el tamaño de la pantalla parece haber quedado relegado, ya que los usuarios están más interesados en la calidad real que proporciona la pantalla que en sus pulgadas.
Pasamos muchas horas delante de ellas: no nos vale cualquier cosa. Así pues, veamos por medio de un breve repaso los distintos tipos de pantalla que podemos encontrar en el mercado. Con sus pros y contras.
Vamos con un puñado de siglas: AMOLED es el acrónimo de Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Las pantallas AMOLED usan materiales orgánicos que emiten luz cuando se aplica electricidad.
Los AMOLED permiten mostrar imágenes brillantes, delgadas, flexibles y eficientes. Las pantallas AMOLED están siempre apagadas a menos que los píxeles individuales estén eléctricamente excitados. Esto significa que las pantallas AMOLED tienen negros mucho más puros y consumen menos energía cuando se muestran colores negros o más oscuros en la pantalla. Además, dado que son muy flexibles, pueden doblarse.
LCD significa pantalla de cristal líquido. Las pantallas LCD están formadas por una serie de cristales líquidos que se iluminan con una luz de fondo. Requieren menos energía y, por lo tanto, son muy populares en dispositivos portátiles como teléfonos móviles. Las pantallas LCD también tienden a funcionar bastante bien a la luz solar directa, ya que la iluminación del panel viene por detrás. Son ideales para muchos tipos de teléfonos inteligentes.
TFT significa "Transductor de película delgada", una versión avanzada de LCD que usa una matriz activa. La matriz activa significa que cada píxel está conectado a un transistor y condensador individualmente. La ventaja de tener pantallas TFT es que tienen una alta relación de contraste y un bajo costo de producción, lo que reduce el precio de su dispositivo. Sin embargo, no tienen buenos ángulos de visión e impresionante reproducción del color.
IPS significa In-Plane Switching (cambio en el plano) y es una mejora adicional en TFT LCD. De hecho, es un tipo específico de panel LCD que se creó para mejorar el TFT-LCD. La forma en que los cristales se excitan eléctricamente sobre ellos es diferente y la orientación de la matriz de cristal se rota. Este cambio de orientación mejora los ángulos de visión, la relación de contraste y la reproducción del color. El consumo de energía también se reduce en comparación con las pantallas LCD TFT. Debido a que los LCD IPS tienden a ser mejores que los LCD TFT, también son más caros cuando se los coloca en un teléfono inteligente.
La introducción de IPS redujo en gran medida muchas deficiencias de TFT-LCD. La reproducción del color mejoró mucho, el ángulo de visión aumentó y el tiempo de respuesta de la pantalla mejoró drásticamente.
IPS se ha convertido en una mejor opción para los jugadores debido a su tiempo de respuesta mínimo. Esto, a su vez, nos brinda una mejor respuesta táctil, mucho mejor que AMOLED y pantallas TFT-LCD normales.
Baja vida útil: los paneles OLED y AMOLED se degradan más rápido que el IPS LCD. La mayoría de las estimaciones indican 14,000 horas como tiempo de vida del panel. IPS fácilmente tiene una vida útil de hasta 60,000 horas. En el caso de los teléfonos inteligentes no es un problema importante. 14,000 horas es equivalente a 8 horas diarias durante 5 años. Pero en general, el color azul es el primero que comienza a degradarse en AMOLED. Los recientes avances en AMOLED han logrado una vida útil de 62,000 horas para el azul y 198,000 para el verde.
Necesita una luz de fondo fuerte: esto se traduce en un mayor consumo de energía, que es un punto débil en cualquier tipo de dispositivo. Esto da como resultado un drenaje de la batería mucho más rápido.
Terminales más gruesos: debido al requisito de retroiluminación, el fabricante tendrá que aumentar sus esfuerzos en la ingeniería interna o sacrificar algunos componentes para mantener la delgadez.
Una pantalla IPS, también conocida como panel de conmutación en el plano, es un tipo de tecnología de visualización de alta calidad que generalmente se implementan en monitores, tabletas y teléfonos inteligentes de computadora y portátiles de alto rendimiento.
IPS ofrece una mejor experiencia de usuario debido a su ángulo más amplio y calidad de color mejorada, características de visualización que han evolucionado bastante con el tiempo desde que se introdujeron las pantallas LCD con efecto TN y se utilizaron de forma ubicua en la década de 1990.
Si utilizas tu ordenador portátil o teléfono inteligente con fines creativos, para ver películas, chatear por video o cargar álbumes de fotos, querrá un IPS para obtener los mejores ángulos de visión y precisión del color.
Las tabletas y teléfonos inteligentes de alto rendimiento tienen esta tecnología de pantallas IPS porque estos productos nacieron para estas funciones: ver pelis, chatear por video, y almacenar y editar fotos. Las características mejoradas de la tecnología de ángulo y color proporcionan una mejor experiencia general para el usuario.
Tecnología como la Super IPS+ del nuevo Zenfone 4 rinden perfectamente bajo luz directa gracias a su límite lumínico de 600 nits, a que sumar la tecnología Splendid —que es capaz de ajustar la temperatura del color según las condiciones de la luz ambiente—
Y los profesionales creativos también se benefician de un monitor IPS: una pantalla IPS+ proporciona una gama de colores más amplia y mayores ángulos de visión, con los que obtener una mayor precisión estética y resultados más coherentes. Dicho de otro modo: lo que ven es una traducción sin artificios.

While there are many different manufacturers of LCD monitors, the panels themselves are actually only manufactured by a relatively small selection of companies. The three main manufacturers tend to be Samsung, AU Optronics and LG.Display (previously LG.Philips), but there are also a range of other companies like Innolux and CPT which are used widely in the market. Below is a database of all the current panel modules manufactured in each size. These show the module number along with important information including panel technology and a detailed spec. This should provide a detailed list of panels used, and can give you some insight into what is used in any given LCD display.

FPD (Flat Panel Display), LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), and TFT (Thin Film Transistor Display) - Flat panel displays are electronic viewing technologies used to enable people to see content in a range of entertainment, consumer electronics, personal computer, and mobile devices, and many types of medical, transportation and industrial equipment. A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronic visual display that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly. LCDs are used in a wide range of applications including computer monitors, televisions, instrument panels, aircraft cockpit displays, and indoor and outdoor signage. Small LCD screens are common in portable consumer devices such as digital cameras, watches, calculators, and mobile telephones, including smartphones. A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. TFT LCDs are used in appliances including television sets, computer monitors, mobile phones, handheld video game systems, personal digital assistants, navigation systems and projectors. TFT LCDs are also used in car instrument clusters because they allow the driver to customize the cluster, as well as being able to provide an analogue-like display with digital elements. The production of these panels utilize a variety of materials for testing, and handling including LCD Lift Pins made from Celazole® PBI, and Vespel® PI.

* Says unit plans to boost capital in JV for generation 11 TFT-LCD & AMOLED project by 21 billion yuan ($3.14 billion) in which Samsung Display will invest 2.1 billion yuan

In recent years, smartphone displays have developed far more acronyms than ever before with each different one featuring a different kind of technology. AMOLED, LCD, LED, IPS, TFT, PLS, LTPS, LTPO...the list continues to grow.
There are many display types used in smartphones: LCD, OLED, AMOLED, Super AMOLED, TFT, IPS and a few others that are less frequently found on smartphones nowadays, like TFT-LCD. One of the most frequently found on mid-to-high range phones now is IPS-LCD. But what do these all mean?
LCD means Liquid Crystal Display, and its name refers to the array of liquid crystals illuminated by a backlight, and their ubiquity and relatively low cost make them a popular choice for smartphones and many other devices.
LCDs also tend to perform quite well in direct sunlight, as the entire display is illuminated from behind, but does suffer from potentially less accurate colour representation than displays that don"t require a backlight.
Within smartphones, you have both TFT and IPS displays. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, an advanced version of LCD that uses an active matrix (like the AM in AMOLED). Active matrix means that each pixel is attached to a transistor and capacitor individually.
The main advantage of TFT is its relatively low production cost and increased contrast when compared to traditional LCDs. The disadvantage of TFT LCDs is higher energy demands than some other LCDs, less impressive viewing angles and colour reproduction. It"s for these reasons, and falling costs of alternative options, that TFTs are not commonly used in smartphones anymore.Affiliate offer
IPS technology (In-Plane Switching) solves the problem that the first generation of LCD displays experience, which adopts the TN (Twisted Nematic) technique: where colour distortion occurs when you view the display from the side - an effect that continues to crop up on cheaper smartphones and tablets.
The PLS (Plane to Line Switching) standard uses an acronym that is very similar to that of IPS, and is it any wonder that its basic operation is also similar in nature? The technology, developed by Samsung Display, has the same characteristics as IPS displays - good colour reproduction and viewing angles, but a lower contrast level compared to OLED and LCD/VA displays.
This is a very common question after "LED" TVs were launched, with the short answer simply being LCD. The technology used in a LED display is liquid crystal, the difference being LEDs generating the backlight.
One of the highlights from TV makers at the CES 2021 tradeshow, mini-LED technology seemed far removed from mobile devices until Apple announced the 2021 iPad Pro. As the name implies, the technique is based on the miniaturization of the LEDs that form the backlight of the screen — which still uses an LCD panel.
Despite the improvement in terms of contrast (and potentially brightness) over traditional LCD/LED displays, LCD/mini-LEDs still divide the screen into brightness zones — over 2,500 in the case of the iPad and 2021 "QNED" TVs from LG — compared to dozens or hundreds of zones in previous-generation FALD (full-array local dimming) displays, on which the LEDs are behind the LCD panel instead of the edges.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. While this may sound complicated it actually isn"t. We already encountered the active matrix in TFT LCD technology, and OLED is simply a term for another thin-film display technology.
OLED is an organic material that, as the name implies, emits light when a current is passed through it. As opposed to LCD panels, which are back-lit, OLED displays are "always off" unless the individual pixels are electrified.
This means that OLED displays have much purer blacks and consume less energy when black or darker colours are displayed on-screen. However, lighter-coloured themes on AMOLED screens use considerably more power than an LCD using the same theme. OLED screens are also more expensive to produce than LCDs.
Because the black pixels are "off" in an OLED display, the contrast ratios are also higher compared to LCD screens. AMOLED displays have a very fast refresh rate too, but on the downside are not quite as visible in direct sunlight as backlit LCDs. Screen burn-in and diode degradation (because they are organic) are other factors to consider.Affiliate offer
Super AMOLED is the name given by Samsung to its displays that used to only be found in high-end models but have now trickled down to more modestly specced devices. Like IPS LCDs, Super AMOLED improves upon the basic AMOLED premise by integrating the touch response layer into the display itself, rather than as an extra layer on top.
Speaking of pixel density, this was one of Apple"s highlights back in 2010 during the launch of the iPhone 4. The company christened the LCD screen (LED, TFT, and IPS) used in the smartphone as "Retina Display", thanks to the high resolution of the panel used (960 by 640 pixels back then) in its 3.5-inch display.
As a kind of consolation prize for iPhone XR and iPhone 11 buyers, who continued relying on LCD panels, Apple classified the display used in the smartphones with a new term, "Liquid Retina". This was later applied also to the iPad Pro and iPad Air models, with the name defining screens that boast a high range and colour accuracy, at least based on the company"s standards.
TFT(Thin Film Transistor) - a type of LCD display that adopts a thin semiconductor layer deposited on the panel, which allows for active control of the colour intensity in each pixel, featuring a similar concept as that of active-matrix (AM) used in AMOLED displays. It is used in TN, IPS/PLS, VA/PVA/MVA panels, etc.
LTPS(Low Temperature PolySilicon) - a variation of the TFT that offers higher resolutions and lower power consumption compared to traditional TFT screens, based on a-Si (amorphous silicon) technology.
IGZO(Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide) - a semiconductor material used in TFT films, which also allows higher resolutions and lower power consumption, and sees action in different types of LCD screens (TN, IPS, VA) and OLED displays
LTPO(Low Temperature Polycrystaline Oxide) - a technology developed by Apple that can be used in both OLED and LCD displays, as it combines LTPS and IGZO techniques. The result? Lower power consumption. It has been used in the Apple Watch 4 and the Galaxy S21 Ultra.
Among televisions, the long-standing featured technology has always been miniLED - which consists of increasing the number of lighting zones in the backlight while still using an LCD panel. There are whispers going around that smartphones and smartwatches will be looking at incorporating microLED technology in their devices soon, with it being radically different from LCD/LED displays as it sports similar image characteristics to that of OLEDs.
In the case of LCD displays, the main advantage lies in the low manufacturing cost, with dozens of players in the market offering competitive pricing and a high production volume. Some brands have taken advantage of this feature to prioritize certain features - such as a higher refresh rate - instead of adopting an OLED panel, such as the Xiaomi Mi 10T.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey