tft display vs ips quotation

IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

If you want to buy a new monitor, you might wonder what kind of display technologies I should choose. In today’s market, there are two main types of computer monitors: TFT LCD monitors & IPS monitors.
The word TFT means Thin Film Transistor. It is the technology that is used in LCD displays. We have additional resources if you would like to learn more about what is a TFT Display. This type of LCDs is also categorically referred to as an active-matrix LCD.
These LCDs can hold back some pixels while using other pixels so the LCD screen will be using a very minimum amount of energy to function (to modify the liquid crystal molecules between two electrodes). TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These two elements play a key part in ensuring that the TFT display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy while still generating vibrant, consistent images.
Industry nomenclature: TFT LCD panels or TFT screens can also be referred to as TN (Twisted Nematic) Type TFT displays or TN panels, or TN screen technology.
IPS (in-plane-switching) technology is like an improvement on the traditional TFT LCD display module in the sense that it has the same basic structure, but has more enhanced features and more widespread usability.
Both TFT display and IPS display are active-matrix displays, neither can’t emit light on their own like OLED displays and have to be used with a back-light of white bright light to generate the picture. Newer panels utilize LED backlight (light-emitting diodes) to generate their light hence utilizing less power and requiring less depth by design. Neither TFT display nor IPS display can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red, green, blue) color filter in each LCD pixels to produce the color consumers see. If you use a magnifier to inspect your monitor, you will see RGB color in each pixel. With an on/off switch and different level of brightness RGB, we can get many colors.
Winner. IPS TFT screens have around 0.3 milliseconds response time while TN TFT screens responds around 10 milliseconds which makes the latter unsuitable for gaming
Winner. the images that IPS displays create are much more pristine and original than that of the TFT screen. IPS displays do this by making the pixels function in a parallel way. Because of such placing, the pixels can reflect light in a better way, and because of that, you get a better image within the display.
As the display screen made with IPS technology is mostly wide-set, it ensures that the aspect ratio of the screen would be wider. This ensures better visibility and a more realistic viewing experience with a stable effect.
Winner. While the TFT LCD has around 15% more power consumption vs IPS LCD, IPS has a lower transmittance which forces IPS displays to consume more power via backlights. TFT LCD helps battery life.
Normally, high-end products, such as Apple Mac computer monitors and Samsung mobile phones, generally use IPS panels. Some high-end TV and mobile phones even use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) displays. This cutting edge technology provides even better color reproduction, clear image quality, better color gamut, less power consumption when compared to LCD technology.
This kind of touch technology was first introduced by Steve Jobs in the first-generation iPhone. Of course, a TFT LCD display can always meet the basic needs at the most efficient price. An IPS display can make your monitor standing out.

Before you get a new monition for your organization, comparing the TFT display vs IPS display is something that you should do. You would want to buy the monitor which is the most advanced in technology. Therefore, understanding which technology is good for your organization is a must. click to view the 7 Best Types Of Display Screens Technology.
That is why it is important to break it down and discuss point by point so that you can understand it in a layman’s language devoid of any technical jargon. Therefore, in this very article, let’s discuss what exactly TFT LCDs and IPS LCDs are, and what are their differences? You will also find out about their pros and cons for your organization.
The word TFT means Thin-Film-Translator. Click to view: what is TFT LCD, It is the technology that is used in LCD or Liquid Crystal Display. Here you should know that this type of LCD is also categorically referred to as active-matrix LCDs. It tells that these LCDs can hold back some pixels while using other pixels. So, the LCD will be using a very minimum amount of energy to function. TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
Now, it is time to take a look at its features that are tailored to improve the experience of the monitor users significantly. Here are some of the features of the TFT monitor;
The display range covers the application range of all displays from 1 inch to 40 inches as well as the large projection plane and is a full-size display terminal.
Display quality from the simplest monochrome character graphics to high resolution, high color fidelity, high brightness, high contrast, the high response speed of a variety of specifications of the video display models.
No radiation, no scintillation, no harm to the user’s health. In particular, the emergence of TFT LCD electronic books and periodicals will bring humans into the era of a paperless office and paperless printing, triggering a revolution in the civilized way of human learning, dissemination, and recording.
It can be normally used in the temperature range from -20℃ to +50℃, and the temperature-hardened TFT LCD can operate at low temperatures up to -80 ℃. It can not only be used as a mobile terminal display, or desktop terminal display but also can be used as a large screen projection TV, which is a full-size video display terminal with excellent performance.
The manufacturing technology has a high degree of automation and good characteristics of large-scale industrial production. TFT LCD industry technology is mature, a mass production rate of more than 90%.
TFT LCD screen from the beginning of the use of flat glass plate, its display effect is flat right angles, let a person have a refreshing feeling. And LCDs are easier to achieve high resolution on small screens.
The word IPS refers to In-Plane-Switching which is a technology used to improve the viewing experience of the usual TFT displays. You can say that the IPS display is a more advanced version of the traditional TFT LCD module. However, the features of IPS displays are much more advanced and their applications are very much widespread. You should also know that the basic structure of the IPS LCD is the same as TFT LCD if you compare TFT LCD vs IPS.
As you already know, TFT displays do have a very quick response time which is a plus point for it. But, that does not mean IPS displays a lack of response time. In fact, the response time of an IPS LCD is much more consistent, stable, and quick than the TFT display that everyone used to use in the past. However, you will not be able to gauge the difference apparently by watching TFT and IPS displays separately. But, once you watch the screen side-by-side, the difference will become quite clear to you.
The main drawback of the TFT displays as figured above is the narrow-angle viewing experience. The monitor you buy for your organization should give you an experience of wide-angle viewing. It is very much true if you have to use the screen by staying in motion.
So, as IPS displays are an improved version of TFT displays the viewing angle of IPS LCDs is very much wide. It is a plus point in favor of IPS LCDs when you compare TFT vs IPS. With a TFT screen, you cannot watch an image from various angles without encountering halo effects, blurriness, or grayscale that will cause problems for your viewing.
It is one of the major and remarkable differences between IPS and TFT displays. So, if you don’t want to comprise on the viewing angles and want to have the best experience of viewing the screen from wide angles, the IPS display is what you want. The main reason for such a versatile and wonderful viewing angle of IPS display is the screen configuration which is widely set.
Now, when you want to achieve wide-angle viewing with your display screen, you need to make sure it has a faster level of frequency transmittance. It is where IPS displays overtake TFT displays easily in the comparison because the IPS displays have a much faster and speedier transmittance of frequencies than the TFT displays.
Now the transmittance difference between TFT displays and IPS displays would be around 1ms vs. 25ms. Now, you might think that the difference in milliseconds should not create much of a difference as far as the viewing experience is concerned. Yes, this difference cannot be gauged with a naked eye and you will find it difficult to decipher the difference.
However, when you view and an IPS display from a side-by-side angle and a TFT display from a similar angle, the difference will be quite evident in front of you. That is why those who want to avoid lagging in the screen during information sharing at a high speed; generally go for IPS displays. So, if you are someone who is looking to perform advanced applications on the monitor and want to have a wider viewing angle, then an IPS display is the perfect choice for you.
As you know, the basic structure of the IPS display and TFT displays are the same. So, it is quite obvious that an IPS display would use the same basic colors to create various shades with the pixels. However, there is a big difference with the way a TFT display would produce the colors and shade to an IPS display.
The major difference is in the way pixels get placed and the way they operate with electrodes. If you take the perspective of the TFT display, its pixels function perpendicularly once the pixels get activated with the help of the electrodes. It does help in creating sharp images.
But the images that IPS displays create are much more pristine and original than that of the TFT screen. IPS displays do this by making the pixels function in a parallel way. Because of such placing, the pixels can reflect light in a better way, and because of that, you get a better image within the display.
As the display screen made with IPS technology is mostly wide-set, it ensures that the aspect ratio of the screen would be wider. This ensures better visibility and a more realistic viewing experience with a stable effect.
As you already know the features of both TFT and IPS displays, it would be easier for you to understand the difference between the two screen-types. Now, let’s divide the matters into three sections and try to understand the basic differences so that you understand the two technologies in a compressive way. So, here are the difference between an IPS display and a TFT display;
Now, before starting the comparison, it is quite fair to say that both IPS and TFT displays have a wonderful and clear color display. You just cannot say that any of these two displays lag significantly when it comes to color clarity.
However, when it comes to choosing the better display on the parameter of clarity of color, then it has to be the IPS display. The reason why IPS displays tend to have better clarity of color than TFT displays is a better crystal oriental arrangement which is an important part.
That is why when you compare the IPS LCD with TFT LCD for the clarity of color, IPS LCD will get the nod because of the better and advanced technology and structure.
IPS displays have a wider aspect ratio because of the wide-set configuration. That is why it will give you a better wide-angle view when it comes to comparison between IPS and TFT displays. After a certain angle, with a TFT display, the colors will start to get a bit distorted.
But, this distortion of color is very much limited in an IPS display and you may see it very seldom after a much wider angle than the TFT displays. That is why for wide-angle viewing, TFT displays will be more preferable.
When you are comparing TFT LCD vs. IPS, energy consumption also becomes an important part of that comparison. Now, IPS technology is a much advanced technology than TFT technology. So, it is quite obvious that IPS takes a bit more energy to function than TFT.
Also, when you are using an IPS monitor, the screen will be much larger. So, as there is a need for much more energy for the IPS display to function, the battery of the device will drain faster. Furthermore, IPS panels cost way more than TFT display panels.
1. The best thing about TFT technology is it uses much less energy to function when it is used from a bigger screen. It ensures that the cost of electricity is reduced which is a wonderful plus point.
2. When it comes to visibility, the TFT technology enhances your experience wonderfully. It creates sharp images that will have no problems for older and tired eyes.
1. One of the major problems of TFT technology is that it fails to create a wider angle of view. As a result, after a certain angle, the images in a TFT screen will distort marring the overall experience of the user.
Although IPS screen technology is very good, it is still a technology based on TFT, the essence of the TFT screen. Whatever the strength of the IPS, it is a TFT-based derivative.
Finally, as you now have a proper understanding of the TFT displays vs IPS displays, it is now easier for you when it comes to choose one for your organization. Technology is advancing at a rapid pace. You should not be surprised if you see more advanced display screens in the near future. However, so far, TFT vs IPS are the two technologies that are marching ahead when it comes to making display screens.
STONE provides a full range of 3.5 inches to 15.1 inches of small and medium-size standard quasi TFT LCD module, LCD display, TFT display module, display industry, industrial LCD screen, under the sunlight visually highlight TFT LCD display, industrial custom TFT screen, TFT LCD screen-wide temperature, industrial TFT LCD screen, touch screen industry. The LCD module is very suitable for industrial control equipment, medical instruments, POS system, electronic consumer products, vehicles, and other products.

As you might already be aware, there’s a large variety of versatile digital display types on the market, all of which are specifically designed to perform certain functions and are suitable for numerous commercial, industrial, and personal uses. The type of digital display you choose for your company or organization depends largely on the requirements of your industry, customer-base, employees, and business practices. Unfortunately, if you happen to be technologically challenged and don’t know much about digital displays and monitors, it can be difficult to determine which features and functions would work best within your professional environment. If you have trouble deciphering the pros and cons of using TFT vs. IPS displays, here’s a little guide to help make your decision easier.
TFT stands for thin-film-transistor, which is a variant of liquid crystal display (LCD). TFTs are categorized as active matrix LCDs, which means that they can simultaneously retain certain pixels on a screen while also addressing other pixels using minimal amounts of energy. This is because TFTs consist of transistors and capacitors that respectively work to conserve as much energy as possible while still remaining in operation and rendering optimal results. TFT display technologies offer the following features, some of which are engineered to enhance overall user experience.
The bright LED backlights that are featured in TFT displays are most often used for mobile screens. These backlights offer a great deal of adaptability and can be adjusted according to the visual preferences of the user. In some cases, certain mobile devices can be set up to automatically adjust the brightness level of the screen depending on the natural or artificial lighting in any given location. This is a very handy feature for people who have difficulty learning how to adjust the settings on a device or monitor and makes for easier sunlight readability.
One of the major drawbacks of using a TFT LCD instead of an IPS is that the former doesn’t offer the same level of visibility as the latter. To get the full effect of the graphics on a TFT screen, you have to be seated right in front of the screen at all times. If you’re just using the monitor for regular web browsing, for office work, to read and answer emails, or for other everyday uses, then a TFT display will suit your needs just fine. But, if you’re using it to conduct business that requires the highest level of colour and graphic accuracy, such as completing military or naval tasks, then your best bet is to opt for an IPS screen instead.
Nonetheless, most TFT displays are still fully capable of delivering reasonably sharp images that are ideal for everyday purposes and they also have relatively short response times from your keyboard or mouse to your screen. This is because the pixel aspect ration is much narrower than its IPS counterpart and therefore, the colours aren’t as widely spread out and are formatted to fit onto the screen. Primary colours—red, yellow, and blue—are used as the basis for creating brightness and different shades, which is why there’s such a strong contrast between different aspects of every image. Computer monitors, modern-day HD TV screens, laptop monitors, mobile devices, and even tablets all utilize this technology.
IPS (in-plane-switching) technology is almost like an improvement on the traditional TFT display module in the sense that it has the same basic structure, but with slightly more enhanced features and more widespread usability. IPS LCD monitors consist of the following high-end features.
IPS screens have the capability to recognize movements and commands much faster than the traditional TFT LCD displays and as a result, their response times are infinitely faster. Of course, the human eye doesn’t notice the difference on separate occasions, but when witnessing side-by-side demonstrations, the difference is clear.
Wide-set screen configurations allow for much wider and versatile viewing angles as well. This is probably one of the most notable and bankable differences between TFT and IPS displays. With IPS displays, you can view the same image from a large variety of different angles without causing grayscale, blurriness, halo effects, or obstructing your user experience in any way. This makes IPS the perfect display option for people who rely on true-to-form and sharp colour and image contrasts in their work or daily lives.
IPS displays are designed to have higher transmittance frequencies than their TFT counterparts within a shorter period of time (precisely 1 millisecond vs. 25 milliseconds). This speed increase might seem minute or indecipherable to the naked eye, but it actually makes a huge difference in side-by-side demonstrations and observations, especially if your work depends largely on high-speed information sharing with minimal or no lagging.
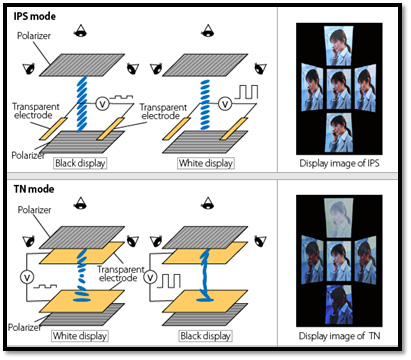
Just like TFT displays, IPS displays also use primary colours to produce different shades through their pixels. The main difference in this regard is the placement of the pixels and how they interact with electrodes. In TFT displays, the pixels run perpendicular to one another when they’re activated by electrodes, which creates a pretty sharp image, but not quite as pristine or crisp as what IPS displays can achieve. IPS display technologies employ a different configuration in the sense that pixels are placed parallel to one another to reflect more light and result in a sharper, clearer, brighter, and more vibrant image. The wide-set screen also establishes a wider aspect ratio, which strengthens visibility and creates a more realistic and lasting effect.
When it comes to deciphering the differences between TFT vs. IPS display technologies and deciding which option is best for you and your business, the experts at Nauticomp Inc. can help. Not only do we offer a wide variety of computer displays, monitors, and screen types, but we also have the many years of experience in the technology industry to back up our recommendations and our knowledge. Our top-of-the-line displays and monitors are customized to suit the professional and personal needs of our clients who work across a vast array of industries. For more information on our high-end displays and monitors, please contact us.
IPS, also known as In-Plane Switching, is a type of monitor display and screen technology that uses a voltage to control the alignment of liquid crystals, similar to TN technology. However, IPS displays use a different crystal orientation where the crystals are parallel to the glass substrates, hence the term ‘in-plane’. Rather than ‘twisting’ the crystals to modify the amount of light let through, IPS crystals are essentially rotated, which has a range of benefits. IPS displays offer the best color reproduction as well as the widest viewing angles compared to other LCD technologies.
While TN LCD’s support high refresh rates with low response times, they do come with sub-optimal viewing angles, and slightly diminished color reproduction. IPS panels address these downfalls with 80 degree viewing angles that eliminate color inversion and contrast diminishment. IPS technology is ideal for a wide array of applications such as medical, industrial, HVAC, Pool/Spa due to the ability to use the displays in both landscape and portrait mode while maintaining uniform viewing angles. This also allows for displays to be seen from different angles and heights, ideal for jacuzzi controls and thermostats that tend to require consideration of dynamic user parameters.

Technology can be confusing because it evolves quickly, and there are complex acronyms for almost everything. If you are thinking ofbuildinga monitor or want to learn about the technology, you will encounter the term TFT Monitor at some point.
A lot goes on behind the glass surface, and we will look at this in comparison to other technologies to paint a clear picture of what TFT is and how it evolved.
TFT is an acronym for Thin Film Transistor, and it is a technology used in Liquid Crystal Display screens. It came about as an improvement to passive-matrix LCDs because it introduced a tiny, separate transistor for each pixel. The result? Such displays could keep up with quick-moving images, which passive-matrix LCDs could not do.
Also, because the transistors are tiny, they have a low power consumption and require a small charge to control each one. Therefore, it is easy to maintain a high refresh rate, resulting in quick image repainting, making a TFT screen the ideal gaming monitor.
The technology improved on the TN (Twisted Nematic) LCD monitor because the shifting pattern of the parallel, horizontal liquid crystals gives wide viewing angles. Therefore, IPS delivers color accuracy and consistency when viewed at different angles.
Both TFT and IPS monitors are active-matrix displays and utilize liquid crystals to paint the images. Technically, the two are intertwined because IPS is a type of TFT LCD. IPS is an improvement of the old TFT model (Twisted Nematic) and was a product of Hitachi displays, which introduced the technology in 1990.
The monitors can create several colors using the different brightness levels and on/off switches. But unlike OLED, both TFT and IPS do not emit light, so most have bright fluorescent lamps or LED backlights to illuminate the picture. Also, neither of them can produce color, so they have an RGB color filter layer.
Easy to Integrate and Update: By combining large-scale semiconductor IC and light source technology, TFTs have the potential for easy integration and updating/development.
Wide Application Range: TFTs are suitable for mobile, desktop screens, and large-screen TVs. Additionally, the technology can operate at a temperature range of -20°C to +50°C, while the temperature-hardened design can remain functional at temperatures not exceeding -80°C.
Impressive Display Effect: TFT displays use flat glass plates that create an effect of flat right angles. Combine this with the ability of LCDs to achieve high resolutions on small screen types, and you get a refreshing display quality.
Good Environmental Protection: The raw materials used to make TFT displays produce zero radiation and scintillation. Thus, the technology does not harm the user or the environment.
Mature Manufacturing Technology: TFT technology came into existence in the 60s. Over time, its manufacturing technology has matured to have a high degree of automation, leading to cheaper, large-scale industrial production.
Wide View Angle: One of the main advantages of IPS screens is their wide viewing angle due to the horizontal liquid crystals. They do not create halo effects, grayscale, or blurriness, but these are common flaws with TFTs.
Better Color Reproduction and Representation: The pixels in TFTs function perpendicularly after activation with the help of electrodes. However, IPS technology makes the pixels function while parallel horizontally. Thus, they reflect light better and create a more original and pristine image color.
Faster Frequency Transmittance: Compared to TFT, IPS screens transmit frequencies at about 25ms, which is 25x faster. This high speed is necessary to achieve wide viewing angles.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a front panel display that utilizes liquid crystals held between two layers of polarized glass to adjust the amount of blocked light. The technology does not produce light on its own, so it needs fluorescent lamps or white LEDs.
As explained earlier, TFT improved on the passive-matrix LCD design because it introduces a thin film transistor for each pixel. The technology reducescrosstalkbetween the pixels because each one is independent and does not affect the adjacent pixels.
LED screens are like the new kids on the block in the display market, and they operate very differently from LCDs. Instead of blocking light, LEDs emit light and are thinner, provide a faster response rate, and are more energy-efficient.
Since IPS is a type of TFT, when comparing the two, we are essentially looking at the old Thin-Film Transistor technology (Twisted Nematic) vs. the new (IPS). Even though TN is relatively old, this digital display type has its advantages, a vital one being the fast refresh rate. This feature makes such screens the preferred option by competitive gamers. If you have any inquiries about the technology,contact usfor more information.

TFT displays are full color LCDs providing bright, vivid colors with the ability to show quick animations, complex graphics, and custom fonts with different touchscreen options. Available in industry standard sizes and resolutions. These displays come as standard, premium MVA, sunlight readable, or IPS display types with a variety of interface options including HDMI, SPI and LVDS. Our line of TFT modules include a custom PCB that support HDMI interface, audio support or HMI solutions with on-board FTDI Embedded Video Engine (EVE2).

We offer a wide range of In-Plane Switching (IPS) TFT LCD displays with a variety of touchscreen and module options. IPS displays deliver the best contrast, truest color reproduction, and widest viewing angles of any LCD. They also feature high brightness backlights for direct sunlight visibility. Learn more about IPS

If driving the backlight of the C version display with 12 Volts and a series resistor, substituting a D version display will not work since the four LEDs need more than 12 Volts to get the same current flowing.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The liquid crystal displays used in calculators and other devices with similarly simple displays have direct-driven image elements, and therefore a voltage can be easily applied across just one segment of these types of displays without interfering with the other segments. This would be impractical for a large display, because it would have a large number of (color) picture elements (pixels), and thus it would require millions of connections, both top and bottom for each one of the three colors (red, green and blue) of every pixel. To avoid this issue, the pixels are addressed in rows and columns, reducing the connection count from millions down to thousands. The column and row wires attach to transistor switches, one for each pixel. The one-way current passing characteristic of the transistor prevents the charge that is being applied to each pixel from being drained between refreshes to a display"s image. Each pixel is a small capacitor with a layer of insulating liquid crystal sandwiched between transparent conductive ITO layers.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
Initial iterations of IPS technology were characterised by slow response time and a low contrast ratio but later revisions have made marked improvements to these shortcomings. Because of its wide viewing angle and accurate color reproduction (with almost no off-angle color shift), IPS is widely employed in high-end monitors aimed at professional graphic artists, although with the recent fall in price it has been seen in the mainstream market as well. IPS technology was sold to Panasonic by Hitachi.
Most panels also support true 8-bit per channel color. These improvements came at the cost of a higher response time, initially about 50 ms. IPS panels were also extremely expensive.
IPS has since been superseded by S-IPS (Super-IPS, Hitachi Ltd. in 1998), which has all the benefits of IPS technology with the addition of improved pixel refresh timing.
In 2004, Hydis Technologies Co., Ltd licensed its AFFS patent to Japan"s Hitachi Displays. Hitachi is using AFFS to manufacture high end panels in their product line. In 2006, Hydis also licensed its AFFS to Sanyo Epson Imaging Devices Corporation.
Less expensive PVA panels often use dithering and FRC, whereas super-PVA (S-PVA) panels all use at least 8 bits per color component and do not use color simulation methods.BRAVIA LCD TVs offer 10-bit and xvYCC color support, for example, the Bravia X4500 series. S-PVA also offers fast response times using modern RTC technologies.
A technology developed by Samsung is Super PLS, which bears similarities to IPS panels, has wider viewing angles, better image quality, increased brightness, and lower production costs. PLS technology debuted in the PC display market with the release of the Samsung S27A850 and S24A850 monitors in September 2011.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
The bare display panel will only accept a digital video signal at the resolution determined by the panel pixel matrix designed at manufacture. Some screen panels will ignore the LSB bits of the color information to present a consistent interface (8 bit -> 6 bit/color x3).
With analogue signals like VGA, the display controller also needs to perform a high speed analog to digital conversion. With digital input signals like DVI or HDMI some simple reordering of the bits is needed before feeding it to the rescaler if the input resolution doesn"t match the display panel resolution.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
Brody, T. Peter; Asars, J. A.; Dixon, G. D. (November 1973). "A 6 × 6 inch 20 lines-per-inch liquid-crystal display panel". 20 (11): 995–1001. Bibcode:1973ITED...20..995B. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1973.17780. ISSN 0018-9383.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Kim, Sae-Bom; Kim, Woong-Ki; Chounlamany, Vanseng; Seo, Jaehwan; Yoo, Jisu; Jo, Hun-Je; Jung, Jinho (15 August 2012). "Identification of multi-level toxicity of liquid crystal display wastewater toward Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa". Journal of Hazardous Materials. Seoul, Korea; Laos, Lao. 227–228: 327–333. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.059. PMID 22677053.

Do you need a display with beautiful graphics and touch capabilities in a tough environment? This resistive touch IPS EVE TFT module is a fantastic choice. The BT817 EVE chip helps simplify sending complex graphics to the display and also handles the touchscreen sensing and communication to the host. Read more about the benefits of an EVE module.

This square 4" IPS TFT is great for displaying information indoors. It would make an excellent display for an Internet of Things (IoT) application. The square form factor helps make the final product look modern and clean. Plus, with 16 million colors, this display supports vivid eye-catching graphics.

ASI-T-17711A1SPN/D is a 1.77 inch transflective TFT with a resolution of 160 x 128, SPI interface and with a brightness of 110 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight.
ASI-T-20043A5PMN/AY is a 2.0 inch TFT with a resolution of 480 x 360, 3W SPI+16 bit RGB or MIPI interface, IPS all view, with a high brightness of 500 Nits.
ASI-T-240DA8BN/D is a 2.4 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 240 X 320, CPU 16-bit interface and with a brightness of 800 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight.
ASI-T-240DA10SMN/AQ is a 2.4 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 240 x 320, SPI & MCU interface, IPS all-angle view and with a brightness of 1000 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight. It also features an extra wide operating temperatures of -30 to +80C; perfect for extreme environmental applications.
ASI-T-240DAKBN/D is a 2.4 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 240 x 320, MCU interface and with a brightness of 1000 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight.
ASI-T-283DAKCRN/A is a 2.83 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 240 x 320, CPU, RGB, SPI interface and with a brightness of 1000 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight
ASI-T-3501RA1EN/A is a 3.5 inch TFT with a resolution of 480 x 640, 18 bit RGB, All View interface and with a brightness of 120 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight
ASI-T-3501RA1EN/D is a 3.5 inch TFT with a resolution of 480 x 640, 18-bit DBI Type B, All View interface and with a brightness of 120 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight
ASI-T-350EA8RCY6/A is a 3.5 inch high brightness TFT with a resolution of 320 x 240, 24-bit Parallel RGB/Serial RGB/CCIR/YUV interface and with a brightness of 850 Nits; viewable in direct sunlight with Capacitive Touch Panel
ASI-T-350EA10SRN/A is a 3.5 inch TFT with a resolution of 320 x 240, SPI & RGB interface and with a high brightness of 1,000 Nits and wide temperature range of -30 - +85 C.
.jpg)
The lower the response time the better. Be aware of ISO response time figures and grey to grey (G2G) transition figures as you will need to understand the difference. Screens with a G2G quoted response time use ‘Response Time Compensation’ (RTC) technologies, sometimes referred to as overdrive. These technologies are used to boost pixel response times and in practice can make quite a lot of difference. This is particularly important with non-TN Film panels (i.e. IPS, PVA, MVA etc)
The wider the viewing angles the better. Be wary of how they calculate their figures. Sometimes they will try sneaking things like listed them when CR > 5 instead of when CR > 10 to inflate their numbers. Again real life performance might not match quoted specs. You will normally see TN Film panels listed with a 170/160 viewing angle (a classic indication that the screen is using TN Film technology by the way). IPS-type and VA-type panels will normally feature a 178/178 viewing angle spec, but in reality the performance does vary.
If you’re a gamer then look out for Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) technologies which will significantly improve fluidity in gaming and avoid stuttering, tearing or lag associated with older Vsync technologies. At the moment your choice depends on your graphics card vendor, either AMD FreeSync or NVIDIA G-sync.
A. very important thing to consider is what panel technology the screen uses you are interested in buying. While specs may look similar on paper, performance may vary quite considerably between the models due to the underlying panel technology used. The most common technologies used in the desktop monitor market are TN Film, IPS-type (and similar variants like PLS and AHVA) and VA -type. These are all produced by a range of panel manufacturers and offer a variety of strengths and weaknesses. There is a reasonable amount of talk about panel technologies with many people quick to jump on a bandwagon and claim one is superior to another. To be honest, they all still have their place in the modern market, and due to their different characteristics, can play a key part in finding the right monitor for your use.
PLS (Plane to Line Switching)= S-PLS, a Samsung technology exclusive to them and very similar to LG.Display’s IPS in performance and can therefore be called an “IPS-type” technology
AHVA (Advanced Hyper-Viewing Angle) = developed by AU Optronics as another alternative to LG.Display’s IPS, very similar again and so can be called “IPS-type”
Colour gamut – don’t assume that a higher colour gamut is better! The gamut represents the colour space that the backlighting unit of the monitor allows the screen to display. You need to understand that most normal content is based on a certain colour space (sRGB) and that there can be issues if you view this using a wide gamut screen. See here for more information.
A. Generally nowadays with all the ultra-low response time models available, ghosting caused by slow pixel response times is just not an issue for the majority of users. Performance has improved significantly over the years and blurring and ghosting has been largely eliminated on the faster displays. The use of RTC technologies (overdrive) significantly helps improve response times and speed up pixel transitions. This is particularly important on IPS/VA type displays which can be very slow where RTC is not used. Look out for response time specs quoted with a “G2G” (grey to grey) response time as that should indicate the use of overdrive technologies.
Nowadays screens supporting high refresh rates (120Hz+) input frequencies are becoming more and come common, and these can help reduce motion blur and ghosting and improve gaming performance considerably. They are also able to support higher frame rates than traditional 60Hz displays and some are also capable of supporting 3D stereoscopic content through active shutter glasses. Do be careful of assuming that a screen advertised as supporting 3D is in fact able to support 120Hz though, as some 3D models do not support this and instead use passive methods to produce the 3D effect (see here for more info on 3D technologies). Refresh rate of the panel does have a direct impact on motion clarity and for optimal gaming performance you will want to consider those high refresh rate displays above 60Hz.
Ghosting and motion blur perception may also depend on how susceptible you are as a user, as one person may see no ghosting, another may see lots on the same panel. The best bet is to try and see a TFT in action in a shop and see for yourself, if that’s not possible you will have to settle for the opinions of other users and take the plunge! Also be careful to get an idea of real life performance in practice, and don’t just rely on quoted specs. While they are often a good rough guide to the gaming performance, they are not always reliable.
One area which cannot be eliminated fully through response time improvements is perceived motion blur. This is related to how the human eye tracks movement on hold-type displays like LCD’s. In recent years several methods have been used to help provide improved motion blur for users. Models featuring LightBoost backlights for 3D gaming were found to be “hackable” to bring about motion blur benefits through the use of their strobed backlight system. Other displays have now introduced native strobed backlights to offer similar benefits. Look out for models with Motion Blur Reduction backlights like the BenQ XL2420Z / XL2720Z (Blur Reduction mode), Eizo Foris FG2421 (Turbo 240) and Asus ROG Swift PG278Q (ULMB) for instance. ULMB as a feature is common on NVIDIA G-sync enabled displays where high refresh rate is used.
Have a read here about response times if you are unsure about what specs mean or want more information. Generally modern TN Film panels will offer the fastest response times, and often also support 120Hz input frequencies for 3D support / extended frame rates. Look out for models with a quoted “G2G” response time indicating they also use overdrive which can really help in practice. Modern IPS-type panels can also be very fast where overdrive is applied well, so again look for “G2G” figures. High refresh rate IPS panels are also becoming more common which helps improve motion clarity further. Other technologies like PVA and MVA are unfortunately quite slow in practice by modern standards, even where overdrive or high refresh rates are used. Check reviews to be sure of an individual screens performance wherever possible.
A. As a rule of thumb, it would normally be best to use the digital video connection end to end to connect your device to your monitor. For a PC, this would commonly be DisplayPort, HDMI or DVI which offer a pure digital end to end connection between the graphics card and the monitor. DisplayPort is needed to run the high resolution/high refresh rate panels so you will need to ensure your graphics card has a DP output. Some screens or cards use Mini DP instead of the full size version, but that is simply a different size connection and can be easily inter-changed with “normal” DisplayPort. Cables which are DP at one end, and Mini DP at the other are common and simple to use.
HDMI and DisplayPort are also common digital connections now being offer, but unlike DVI are also capable of carrying audio as well as video. The picture quality should not be any different between DVI, HDMI and DisplayPort in theory as long as no additional video “enhancements” are applied when using one over the other. Bandwidth requirements will vary so this might influence which type you need to use depending on the screen resolution and refresh rate.
Converting between DVI and HDMI is easy and cables are readily available to offer that if needed (keeping in mind you will lose the sound transmission when it reaches the DVI). Converting between DVI/HDMI and DisplayPort is far more tricky and not simple to achieve. It is very hit and miss and working active adapters are expensive. We would advise avoiding the attempt to convert DP to HDMI/DVI if you can.
A. There is a lot of talk about colour depth on TFT screens, now more than ever with the emergence of 6-bit IPS and VA panels. At one time TN Film was the main 6-bit technology but today that is no longer the case. It’s important to put this into perspective though, and not jump on the bandwagon of 8-bit being much, much better than 6-bit. Or even 10-bit being much better than 8-bit.
An 8-bit display would offer a colour palette of 16.7 million colours. They offer a ‘true’ colour palette, and are generally the choice of manufacturers for colour critical displays over 6-bit panels. On the other hand modern 6-bit screens use a range of Frame Rate Control (FRC) technologies to extend the colour palette from 262,144 colours to around 16.7m. In fact on many modern panels these FRC are very good and in practice you’d be hard pressed to spot any real difference between a 6-bit + FRC display and a true 8-bit display. Colour range is good, screens show no obvious gradation of colours, and they show no FRC artefacts or glitches in normal everyday use. Most average users would never notice the difference and so it is more important to think about the panel technology and your individual uses than get bogged down worrying about 6-bit vs. 8-bit arguments.
Manufacturers use 6-bit panels (+FRC) to help keep costs lower. As a result, a modern range of IPS and VA panels is also now produced which use 6-bit colour depth (+FRC) instead of true 8-bit colour depths. At the other end of the scale there are also some panels which can offer support of 10-bit colour depth. Again these come in two flavours, being either a true 10-bit panel (quite rare and expensive) offering 1.07 billion colours or an 8-bit panel with an additional FRC stage added (1.07 billion colours produced through FRC). The 8-bit +FRC panels are of course more common and will often be used to offer “10-bit” support in desktop displays. With 10-bit colour though there is also an additional consideration which is whether you would ever even be able to use this in your work. You can also only make use of this 10-bit support if you have a full end-to-end 10-bit workflow, including a supporting software, graphics card and operating system which is still very rare and expensive for most users. So for many people the use of a 10-bit capable panel is rather meaningless.
While a larger colour space might sound like a good idea, it’s not always for everyone. You need to keep in mind what content you will be viewing on the screen, and what colour space that content is based on. Since sRGB is very common and the standard for many things like Windows and the internet, viewing sRGB content on an extended gamut screen can cause oversaturation of colours and an unrealistic ‘stretching’ of the colours. Reds and greens in particular can appear quite ‘neon’ and some users do not like this. The smaller colour space of the content is, as a very crude description, ‘stretched’ over the larger colour space of the monitor. On the other hand, some applications are colour space aware (e.g. Adobe Photoshop) and so if you are working with extended gamut content, you will prefer an extended gamut screen. I’d certainly recommend reading more into this as it is only a brief summary here. Where a screen has an extended gamut, they sometimes provide an sRGB emulation mode which work to varying degrees. Handy if you might need to use it, but make sure the screen offers a decent performance when in this mode and that it works. At the end of the day, the choice of monitor might very well depend on the colour space you want to work with. For most average users a standard CCFL or W-LED backlit display with a standard sRGB gamut would probably be preferred.
A. The simplest and cheapest way to clean a TFT screen is with a slightly damp cloth; wipe off the left behind water with a towel or similar then smooth/dry completely with a yellow polishing cloth. Be careful not to use products such as toilet paper and kitchen roll as they contain lint and can leave scratches on your beloved screen! Cleaning solution from opticians and lint free clothes for lens cleaning are also very good.
A. Unfortunately dead pixels can be an issue on TFT screens as they are often developed during the manufacturing stage. For retail costs to be kept low the companies cannot afford to make all screens defect-free and check for dead pixels all the time. Pixels can be described in the following ways:
If you want to ensure that you receive a pixel perfect screen (and who wouldn’t at the kind of prices you are paying for the TFT!?!) then you can often pay for pixel checks from some online retailers. Beware though! Never buy a TFT from retailers who offer the pixel check without having the check done as you can be sure the screens they find to be non-perfect will be winging their way to the customers who don’t have the check! The only other option to ensure you get a pixel perfect screen is to check out the panel in a shop in person, then you can see for yourself…..
If you find you have a dead pixel there is not a lot you can do unfortunately. If you have a certain number of dead pixels (usually at least 3 or a certain number centrally on the panel) then the manufacturer will replace the TFT for you, but the number of dead pixels needed before this happens varies between each manufacturer, so check with them before you order if you’re concerned.
If you still have a dead pixel problem, can’t bring it back to life and can’t RMA it under warranty then you can sometimes return it to the stockist if you purchased it online. If you bought online you can take advantage of the “Distance Selling Act” which entitles you to return any item within 7 days as you were not present at the time of purchase. If you are not happy with your TFT you can return it at your cost of postage and often claim a refund or exchange. However, be aware that a lot of places will try and charge you restocking fees and they will almost certainly specify the goods must be packaged and in the same condition as when you received it, so be careful to package it back up nicely. Legally, if the stocker accepts the TFT back as a return governed by the Distance Selling Act, then they are NOT allowed to charge you a restocking fee as covered in the Government Regulations. This selling act is not widely advertised by retailers, but does exist if you really need to use it. You should only have to pay for postage to send it back to them.

Quote: This display uses the NT57860 driver IC. I"m using the TC358860 eDP-to-MIPIDSI bridge chip, but I"m not sure whether it can drive this display panel. Is it possible to share the datasheet of this NT57860 driver IC? That way I"m able to verify that. Thanks in advance, With kind regards




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey