using lcd display with arduino manufacturer

In this Instructables lesson, displaying texts and featuring them on a 16 by 2 LCD using Arduino is demonstrated. Let"s get started and I hope you enjoy!
Arduino is a device that is widely used by students for various robotics projects and sensors to detect heart-rate, temperature, air pressure ... Arduino is an open-source hardware and software company, project and user community that designs and manufactures single-board micro controllers and micro controller kits for building digital devices and interactive objects that can sense and control both physically and digitally. Basically Arduino is capable to store codes inserted from Arduino IDE using C and C++ coding languages from a computer to manipulate the functions that are assigned for the device to do. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screen is an electronic display module and find a wide range of applications. A 16x2 LCD display is very basic module and is very commonly used in various devices and circuits. A 16x2 LCD means it can display 16 characters per line and there are 2 such lines. The LCD has 16 pins. Starting from left to right, the first pin is GND (ground). The second pin is the VCC (5 volts) pin which is connected to the Arduino board. The third pin is the Vo (display contrast) pin which can be connected to a potentiometer to adjust the display contrast. Fourth pin is the RS (register select) pin used for selecting the commands/data sent to the LCD using methods defined in the Arduino Liquid Crystal packages. Fifth one is the R/W (read/write) pin which selects the mode whether we read or write on the LCD. Sixth pin is the E (enable) pin which enables writings to the registers. The next 8 pins are data pins D0 to D7 that registers are written in using binary numbers according to the ASCII Table. The fifteenth pin is the A (anode) , and the last one is K (cathode).
The IDE Now that we have a little undrestanding of what Arduino and the LCD are, let"s jump ahead into the Arduino IDE and install that on our computer. Arduino IDE can be downloaded from Or from the windows store on windows 8. The IDE is the place where coding takes place. Here, the codes are written in C and C++. After compiling the code and troubleshooting the mistakes, the complied code is sent to the Arduino Board using the USB 2 cable. After installing the IDE we implement the Liquid Crystal package as shown below. Liquid Crystal Package implementation... Installing LiquidCrystal package opens our access to use the methods and implementations defined in the specific package regarding to the LCD on our IDE to be compiled and stored into the Arduino board. After package installation, the setup and loop are written in the IDE. Follow the above and copy the parameters to make a connection between the board and the LCD.
Compiling and Storing the Code into the Arduino For the last step, connect the Arduino to the computer using a USB-2 cable. compile the code and select the Arduino UNO on the IDE and store the code into the Arduino by clicking on the horizontal arrow on the top left corner of the IDE.
The note "Arduino" should be appearing on your LCD. Congratulations !!! You have made your first text on the LCD... Now if you want to go the extra mile, www.arduino.cc has all the methods and explanations that can be used to use on your text for further design and change, move, personalize your own text. Above are some of the example codes found in the website. Try them yourself.
Liquid Crystal displays or LCDs have been used in electronics equipment since the late 1970s. LCD displays have the advantage of consuming very little current And they are ideal for your Arduino projects.
In this article and in the accompanying video I’ll show you how easy it is to add an LCD display to your next Arduino design. I’ll also show you a very popular Arduino Shield that has a keypad which you can use in your projects as well.
Today LCD displays are used in a variety of items from test equipment to televisions. They’re inexpensive and versatile, this makes them ideal for all sorts of designs.
LCD displays do not emit light. Instead they block the passage of light, like little windows which open and shut the let light through. The liquid crystals used inside LCD displays are sandwiched between two layers of polarized material. By changing the orientation of the liquid crystals they allow light to pass or they block the light entirely.
Because transmissive LCD displays (the type we will be using) work by blocking light they require a backlight. Several methods have been used to create back lights including electroluminescent panels and fluorescent tubes. these days the most common form of backlight is an LED, in fact so-called LED televisions are usually just LCD screens with an LED backlight system.
Another type of LCD display, the passive-matrix display, does not require a backlight, it works using reflected light. This type of display is often found in digital watches.
The principles of liquid crystals were discovered in the late 1880s but work on Modern LCD displays did not begin until the mid-1960s. a number of patents were filed in the early 1970s and in 1973 the Sharp Corporation introduced LCD displays for calculators.
The first color LCD displays were developed in the early 1980s but production units were not commonly available until the mid-1990s. By the late 1990s LCD displays were quite common.
A number of LCD displays are available for experimenters. These low-cost monochrome displays are ideal for use with microcontrollers like the Arduino and micro computers like the Raspberry Pi.
These displays are available in a number of different configurations. The part number for the display generally relates to the number of rows and columns in the display.
Common display configurations include 16 x 2, 16 x 4 and 20 x 4. All of these displays are used in a virtually identical fashion the only difference being the number of columns and rows they have.
The LCD1602 display module is a very popular and inexpensive LCD display. It is available in a number of different colors such as blue yellow and green and can easily be connected to an Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
In operation data is sent down the parallel data lines for the display. There are two types of data that can be sent to the display. The first type of data are the ASCII characters which are to be displayed on the display. The other type of data are the control characters that are used to activate the various display functions.
Brightness– This is the input for the brightness control voltage, which varies between 0 and 5 volts to control the display brightness. On some modules this pin is labeled V0.
Because the LCD module uses a parallel data input it requires 8 connections to the host microcontroller for the data alone. Add that to the other control pins and it consumes a lot of connections. On an Arduino Uno half of the I/O pins would be taken up by the display, which can be problematic if you want to use the I/O pins for other input or output devices.
We will begin our experiments by hooking up the LCD1602 to an Arduino Uno and running a few of the example sketches included with the Arduino IDE. This will allow you to get familiar with the display without needing to write any code.
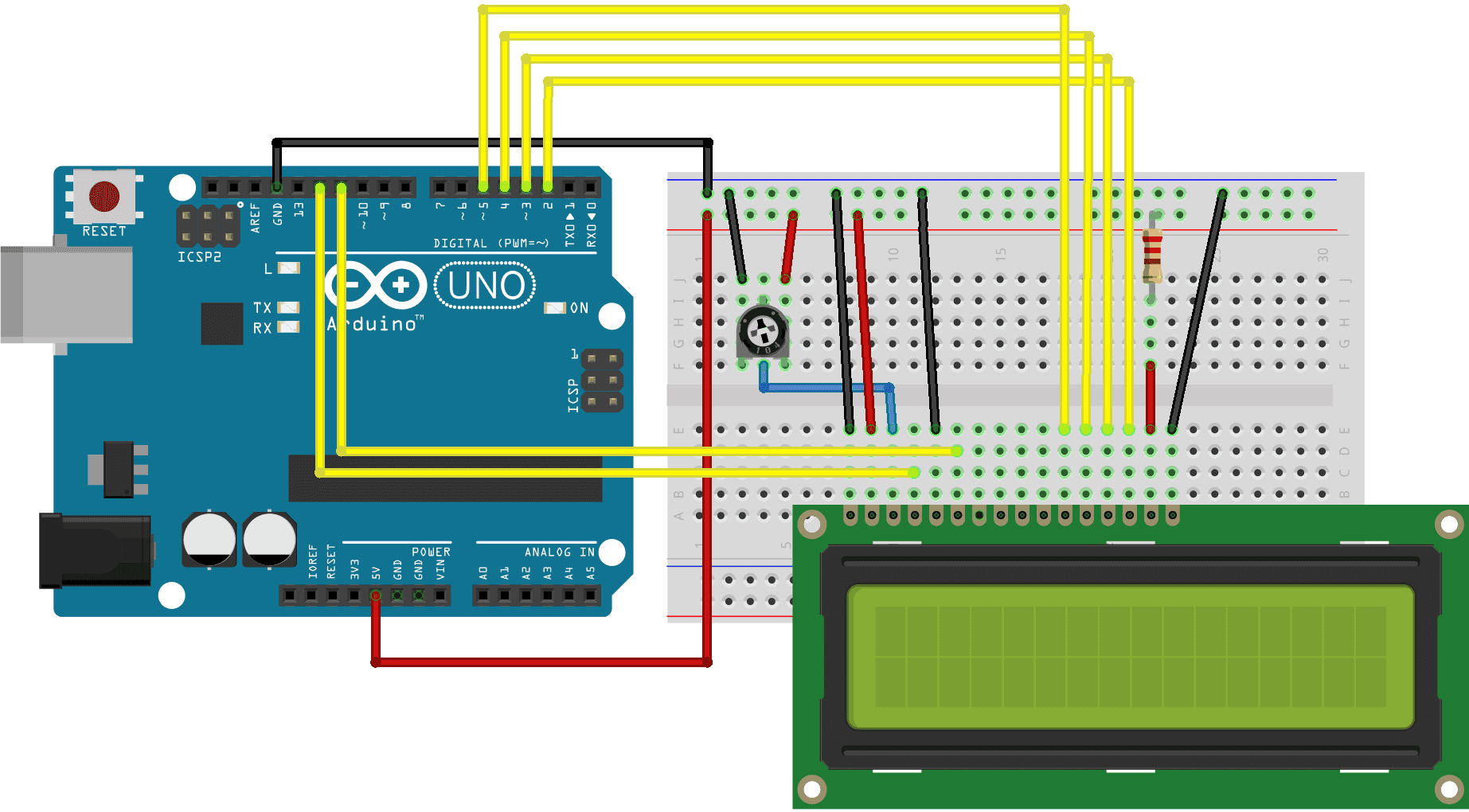
We need to hookup our LCD display to our Arduino. The display can use any of the Arduino digital I/O pins as it has no special requirements, but if you hook it up as I’ve illustrated here you can run the example sketches without needing to make any modifications.
In addition to the LCD1602 display ands the Arduino Uno you will need a 10K trimpot ot potentiometer, this is used a s a brightness control for the display. You’ll also need a 220 ohm resistor to drop the voltage for the displays LED backlight.
The Arduino IDE includestheLiquidCrystallibraryand this library has a number of example sketches. I’ll go over three of them here but you can also try the other ones.
The sketch starts with a number of credits and a description of the required hardware hookup. You’ll note that this is the same hookup you just performed on your Arduino and LCD module.
We then initialize an object that we call “lcd” using the pinouts of the LCD display. If you decide to hook up your display to different pins then you’ll need to modify this section.
In the beginning of the loop we set our cursor to the first position in the second row. Note that the row numbers start with zero so the second row is row 1.
That ends the loop, so we start back at the top of the loop and repeat. The result will be a counter on the second line that counts seconds from the htime the Arduino was last reset.
Load the sketch up to your Arduino and observe your display. If you don’t see anything try adjusting the brightness control that you wired to the display.
The second example we will try isthe Scroll sketch. Scrolling is a useful technique when you can’t get your text to fit on one line of the LCD display.
In the loop the code demonstrates the use of thescrollDisplayLeftandscrollDisplayRightfunctions. As their names imply they move the text in a left or right direction.
Finally the last counter moves the text 16 positions to the left again, which will restore it back to the center of the display. The loop then repeats itself.
Custom characters are useful when you want to display a character that is not part of the standard 127-character ASCII character set. Thi scan be useful for creating custom displays for your project.
A character on the display is formed in a 5 x 8 matrix of blocks so you need to define your custom character within that matrix. To define the character you’ll use thecreateCharfunctionof the LiquidCrystal library. You are limited to defining a maximum of eight characters.
To usecreateCharyou first set up an array of bytes with 8 elements. Each element in the array defines one row of the character in the 5 x 8 matrix. You then use createCharto assign a number from 0 to 7 to that array.
The Custom Character demonstration requires one additional component to be wired to the Arduino, a potentiometer (10K or greater) wired up to deliver a variable voltage to analog input pin A0.
As with the previous sketches we examined this one starts by loading theLiquidCrystallibrary and defining an object calledlcdwith the connection information for the display. It then moves on to define the custom characters.
Each character is defined as an array with 8 elements, the zeros and ones in the array indicate which elements in the character should be on and which ones should be off. Five arrays are defined, although the sketch actually only used four of them.
The last two arrays,amsUpandarmsDowndefine the shape of a little “stickman”, or “stickperson” if you want to be politically correct! This is done to show how we can animate a character on the display.
Then the five custom characters are assigned a unique integer using the createChar function. Remember, you can define a maximum of eight custom characters in a sketch.
Finally the setup routine ends by printing a line to the first row of the LCD display. The line makes use of two of the custom characters, the “heart” and the “smiley”.
We begin by reading the value of the voltage on pin A0 using the ArduinoanalogReadfunction. As the Arduino has a 10-bit analog to digital converter this will result in a reading ranging from 0 to 1023.
We then use an Arduinomapfunction to convert this reading into a range from 200 to 1000. This value is then assigned to an integer calleddelayTime, which as its name implies represents a time delay period.
One thing you may have noticed about using the LCD display module with the Arduino is that it consumes a lot of connections. Even in 4-wire mode there are still a total of seven connections made to the Arduino digital I/O pins. As an Arduino Uno has only 14 digital I/O pins that’s half of them used up for the display.
In other cases you would need to resort to using some of the analog pins as digital pins or even moving up to an Arduino Mega which has many more I/O pins.
But there is another solution. Use the I2C bus adapter for the LCD display and connect using I2C. This only consumes two I/O pins and they aren’t even part of the set of digital I/O pins.
The I2C or IIC bus is theInter Integrated Circuitbus. It was developed by Philips Semiconductors in 1982 for use in the television industry. The idea was to allow the integrated circuits in televisions to “talk” to one another using a standard bus.
The bus has evolved to be used as an ideal method of communicating between microcontrollers, integrated circuits, sensors and micro computers. You can use it to allow multiple Arduinos to talk to each other, to interface numerous sensors and output devices or to facilitate communications between a Raspberry Pi and one or more Arduinos.
In I2C communications there is the concept of Master and Slave devices. There can be multiples of each but there can only be one Master at any given moment. In most Arduino applications one Arduino is designated Master permanently while the other Arduinos and peripherals are the Slaves.
The Master transmits the clock signal which determines how fast the data on the bus is transferred. There are several clock speeds used with the I2C bus. The original design used 100 KHz and 400 KHz clocks. Faster rates of 3.4 MHz and higher are available on some I2C configurations.
Every device on the I2C bus has a unique address. When the Master wants to communicate with a Slave device it calls the Slaves address to initiate communications.
The I2C Adapter for the LCD display is a tiny circuit board with 16 male header pins soldered to it. These pins are meant to be connected directly to the 16-pin connection on the LCD1602 display (or onto other displays that use the same connection scheme).
The device also has a 4-pin connector for connection to the I2C bus. In addition there is a small trimpot on the board, this is the LCD display brightness control.
Most of these devices have three jumpers or solder pads to set the I2C address. This may need to be changed if you are using multiple devices on the same I2C bus or if the device conflicts with another I2C device.
Most Arduino Unos also have some dedicated pins for I2C, these are internally connected to A4 and A5 and are usually located above the 14 digital I/O pins. Some models of the Uno have additional I2C connectors as well.
Note how much easier it is to use the I2C connection, which does not consume any of the Arduino Unos 14 digital I/O pins. Since A4 and A5 are being used for the I2C bus they can’t be used as analog inputs in this configuration.
Nick has written a simple I2C scanner sketch that he’s put into the public domain. It scans your I2C bus and gives you back the address of every I2C device it finds. I’ve repeated Nick’s sketch here, it’s also in the ZIP file that you can download with all of the code for this article.
Load this sketch into your Arduino then open your serial monitor. You’ll see the I2C address of your I2C LCD display adapter. You can then make note of this address and use it in the sketches we’ll be looking at now.
In order to run the subsequent sketches you’ll need to install another library. This is theNewLiquidCrystallibrarywhich, as its name implies, is an improved version of the LiquidCrystal library packaged with your Arduino IDE.
The sketch starts by loading the ArduinoWirelibrary. This is the Arduino library that facilitates communications over I2C and it’s part of your Arduino IDE installation.
On the next line we define the connections to the LCD display module from the I2C Adapter,. Note that these are NOT the connections from the Arduino, they are the connections used by the chip on the adapter itself.
In setup we set the size of the display and then print “Hello world!” on the first line in the first position. After a short delay we print “How are you?” on the second line.
Load the sketch and run it on your Arduino. If you can’t get it to work check out the address and connection information to be sure you have it right.
We need to make a minor wiring adjustment to the hookup with our I2C adapter, specifically we will need to add a DHT22 temperature and humidity sensor into the circuit. The wiring is shown here:
As you can see the DHT22 is connected with its output tied to pin 7 of the Arduino. The other two connections are 5 volts and ground. Note that pin 3 of the DHT22 is not used.
This sketch also makes use of theDHTlibrary from Adafruit. We used this library in a previous article, “Using the HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Distance Sensor with Arduino” so you may want to take a look at that one in order to get it installed.
The key thing to note is that this library is dependant upon another Adafruit library, theirUnified Sensorlibrary. Both can be installed using the Library Manager in your Arduino IDE.
The sketch is similar to our demo sketch in that it creates an “lcd” object with the I2C and display connection information. It also defines a couple of parameters for the DHT22 sensor, as well as some floating variables to hold the temperature and humidity values.
Note that this displays the temperature in Celsius. If you want to change this to Fahrenheit its a simple matter of using some math. The formula( temp * 1.8 ) + 32will convert the results to Fahrenheit.
So far we have used the LCD1602 display module for all of our experiments. For our final demonstration we’ll switch to a popular Arduino shield that contains a LCD1602 along with some push buttons.
The LCD Keypad Shield is available from several different manufacturers. The device fits onto an Arduino Uno or an Arduino Mega and simplifies adding an LCD display to your project.
The Reset button is simply connected to the Arduino Reset pin and works just like the Reset button on the Arduino itself. This is common on many shields as the shields physically cover the Reset button.
Instead the buttons are connected to a resistor array that acts as a voltage divider. The entire array is connected to the Arduino’s analog A0 pin. One pin for five push buttons.
Note that the LCD is being used in 4-wire mode. The LCD itself is the same one used on the LCD1602 module, so all of the code for that module will work with the LCD Keypad Shield as well.
Now that you know how the LCD Keypad module works and which Arduino pins it uses all that remains is to install it onto your Arduino and load the demo sketch.
One thing – once the shield is installed on the Arduino you won’t have easy access to the unused I/O pins to connect any sensors or output devices you may want to use (although the demo sketch doesn’t need anything else connected). There are a couple of ways to get around this:
Use a shield that exposes the pins for prototyping before you install the LCD Keypad shield. In the video associated with this article I use a “Screw Shield” that brings all of the Arduino I/O pins out to a series of screw connectors. There are other similar shields. Using one of these shields is the easiest way to work with the LCD Keypad shield, as well as other Arduino shields.
The sketch begins by including theLiquidCrystallibrary. You can use the original one or the one includes with theNewLiquidCrystallibrary. We then set up an object with the LCD connections, note that these are just hard-coded as they won’t change.
Next we define a number of constants, one for each of the push buttons. Note that nothing is defined for the Reset button as it simply mimics the Arduino Reset button, however a constant is defined for the “none” condition.
After that we define a function calledread_LCD_buttons(). This function reads the value on analog port A0 and returns an integer corresponding to the button integers we defined earlier. Note that the function adds approximately 50 to each of the manufacturers specified values to account for intolerances in the resistors in the voltage divider.
We start the loop by placing the cursor 9 spaces over on the second line. We then use themillisfunction to display a counter that counts the time since the Arduino was reset. This is to test the Reset button.
We then call ourread_LCD_buttons()function and use it to display the value of the push button, right before the counter. Then we end the loop and do it again.
Load the code onto the Arduino and run it. You should see the value of each button as you press it, along with a counter that increments each second. If you press Reset the counter should reset itself back to zero.
As you can see LCD displays are pretty simple to use thanks to the availability of some excellent libraries for the Arduino. As these displays are also very inexpensive they will make an ideal addition to many of your Arduino projects.
And finally the LCD Keypad Shield is a convenient method of adding both a display and a simple keypad to your project, no wiring or soldering required.

If you’ve ever tried to connect an LCD display to an Arduino, you might have noticed that it consumes a lot of pins on the Arduino. Even in 4-bit mode, the Arduino still requires a total of seven connections – which is half of the Arduino’s available digital I/O pins.
The solution is to use an I2C LCD display. It consumes only two I/O pins that are not even part of the set of digital I/O pins and can be shared with other I2C devices as well.
True to their name, these LCDs are ideal for displaying only text/characters. A 16×2 character LCD, for example, has an LED backlight and can display 32 ASCII characters in two rows of 16 characters each.
If you look closely you can see tiny rectangles for each character on the display and the pixels that make up a character. Each of these rectangles is a grid of 5×8 pixels.
At the heart of the adapter is an 8-bit I/O expander chip – PCF8574. This chip converts the I2C data from an Arduino into the parallel data required for an LCD display.
If you are using multiple devices on the same I2C bus, you may need to set a different I2C address for the LCD adapter so that it does not conflict with another I2C device.
An important point here is that several companies manufacture the same PCF8574 chip, Texas Instruments and NXP Semiconductors, to name a few. And the I2C address of your LCD depends on the chip manufacturer.
So your LCD probably has a default I2C address 0x27Hex or 0x3FHex. However it is recommended that you find out the actual I2C address of the LCD before using it.
Connecting an I2C LCD is much easier than connecting a standard LCD. You only need to connect 4 pins instead of 12. Start by connecting the VCC pin to the 5V output on the Arduino and GND to ground.
Now we are left with the pins which are used for I2C communication. Note that each Arduino board has different I2C pins that must be connected accordingly. On Arduino boards with the R3 layout, the SDA (data line) and SCL (clock line) are on the pin headers close to the AREF pin. They are also known as A5 (SCL) and A4 (SDA).
After wiring up the LCD you’ll need to adjust the contrast of the display. On the I2C module you will find a potentiometer that you can rotate with a small screwdriver.
Plug in the Arduino’s USB connector to power the LCD. You will see the backlight lit up. Now as you turn the knob on the potentiometer, you will start to see the first row of rectangles. If that happens, Congratulations! Your LCD is working fine.
To drive an I2C LCD you must first install a library called LiquidCrystal_I2C. This library is an enhanced version of the LiquidCrystal library that comes with your Arduino IDE.
The I2C address of your LCD depends on the manufacturer, as mentioned earlier. If your LCD has a Texas Instruments’ PCF8574 chip, its default I2C address is 0x27Hex. If your LCD has NXP Semiconductors’ PCF8574 chip, its default I2C address is 0x3FHex.
So your LCD probably has I2C address 0x27Hex or 0x3FHex. However it is recommended that you find out the actual I2C address of the LCD before using it. Luckily there’s an easy way to do this, thanks to the Nick Gammon.
But, before you proceed to upload the sketch, you need to make a small change to make it work for you. You must pass the I2C address of your LCD and the dimensions of the display to the constructor of the LiquidCrystal_I2C class. If you are using a 16×2 character LCD, pass the 16 and 2; If you’re using a 20×4 LCD, pass 20 and 4. You got the point!
First of all an object of LiquidCrystal_I2C class is created. This object takes three parameters LiquidCrystal_I2C(address, columns, rows). This is where you need to enter the address you found earlier, and the dimensions of the display.
In ‘setup’ we call three functions. The first function is init(). It initializes the LCD object. The second function is clear(). This clears the LCD screen and moves the cursor to the top left corner. And third, the backlight() function turns on the LCD backlight.
After that we set the cursor position to the third column of the first row by calling the function lcd.setCursor(2, 0). The cursor position specifies the location where you want the new text to be displayed on the LCD. The upper left corner is assumed to be col=0, row=0.
There are some useful functions you can use with LiquidCrystal_I2C objects. Some of them are listed below:lcd.home() function is used to position the cursor in the upper-left of the LCD without clearing the display.
lcd.scrollDisplayRight() function scrolls the contents of the display one space to the right. If you want the text to scroll continuously, you have to use this function inside a for loop.
lcd.scrollDisplayLeft() function scrolls the contents of the display one space to the left. Similar to above function, use this inside a for loop for continuous scrolling.
If you find the characters on the display dull and boring, you can create your own custom characters (glyphs) and symbols for your LCD. They are extremely useful when you want to display a character that is not part of the standard ASCII character set.
As discussed earlier in this tutorial a character is made up of a 5×8 pixel matrix, so you need to define your custom character within that matrix. You can use the createChar() function to define a character.
CGROM is used to store all permanent fonts that are displayed using their ASCII codes. For example, if we send 0x41 to the LCD, the letter ‘A’ will be printed on the display.
CGRAM is another memory used to store user defined characters. This RAM is limited to 64 bytes. For a 5×8 pixel based LCD, only 8 user-defined characters can be stored in CGRAM. And for 5×10 pixel based LCD only 4 user-defined characters can be stored.
Creating custom characters has never been easier! We have created a small application called Custom Character Generator. Can you see the blue grid below? You can click on any 5×8 pixel to set/clear that particular pixel. And as you click, the code for the character is generated next to the grid. This code can be used directly in your Arduino sketch.
After the library is included and the LCD object is created, custom character arrays are defined. The array consists of 8 bytes, each byte representing a row of a 5×8 LED matrix. In this sketch, eight custom characters have been created.
In setup, a custom character is created using the createChar() function. This function takes two parameters. The first parameter is a number between 0 and 7 to reserve one of the 8 supported custom characters. The second is the name of the array.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

– Arduino is an open-source platform used for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of both a physical programmable microcontroller and a piece of software, or IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that runs on your computer, used to write and upload computer code to the physical board.
– The Arduino platform unlike most previous programmable circuit boards, the Arduino does not need a separate programmer to load new code onto the board — you can simply use a USB cable. Additionally, the Arduino IDE uses a simplified version of C++, making it easier to learn to program.
– The open sources and extensible language: Arduino IDE is based on open source tool. The programming language used can be extended through the C++ library.
– The open source and expandable hardware: Arduino is based on Atmel’s ATMEGA 8-bit microcontrollers and its SAM3X8E and SAMD21 32-bit microcontrollers. Development boards and modules are planned to be released under the premise of following the “Creative Commons License Agreement”, so experienced circuit designers can make their own modules and carry out corresponding expansions and improvements. Even users who are relatively inexperienced can make a trial version of the basic Uno development board, which is easy to understand the principle of its operation and save costs.
– The Arduino hardware and software were designed for artists, designers, hobbyists, hackers, newbies, and anyone interested in creating interactive objects or environments. Arduino can interact with buttons, LEDs, motors, speakers, GPS units, cameras, the internet, and even your smart-phone or your TV.
Arduino Leonardo: Arduino’s first development board to use one microcontroller with built-in USB. It is cheaper and simpler. The code libraries allow the board to emulate a computer keyboard, mouse, and more.
LCD means liquid crystal display. Basically, any displays can be used with Arduino, including alphanumeric character LCD display, monochrome graphic LCD display, color TFT LCD display, IPS LCD display. It can also be used for non LCD displays like: PMOLED display, AMOLED display, E-ink (E-paper) displays. Orient Display developed easy interface (SPI, I2C) displays which can be easily used with Arduino.
LCD displays were first used for watches and calculators. Now, LCD display technology dominants the display world, it can be found in wearables, smart homes, mobile phones, TVs, laptops, monitors, kiosks, aircraft cockpit, digital cameras, lab instrument, power grid etc.
LCD itself can emit light itself. It has to utilize outside light sources. LCD display module normally includes LCD glass (or LCD panel), LCD driving circuitry ( can be COG, COB or TAB) and a backlight.
A LCD display 16*2 is actually a basic and simple to use LCD module. It includes LCD glass, COB (Chip on PCB Board) LCD control board, backlight, zebra to connect LCD glass and control board and a bezel to hold everything together. 16×2 LCD display can display 16 characters per line and there are two lines. Each character has 5×7 dot matrix pixels and the cursor underneath. All 16×2 LCD display originally used standard Hitachi HD44780 driver. Of course the legendary HD44780 controller had EOL long time ago. All the 16×2 LCD displays use HD44780 compatible LCD controllers. Some of them are drop replacement, some of them need to modify the initialization code a little.
Pin5 (Read/Write/Control Pin): This pin toggles the display among the read or writes operation, and it is connected to a microcontroller unit pin to get either 0 or 1 (0 = Write Operation, and 1 = Read Operation).
Pins 7-14 (Data Pins): These pins are used to send data to the display. These pins are connected in two-wire modes like 4-bit mode and 8-bit mode. In 4-wire mode, only four pins are connected to the microcontroller unit like 0 to 3, whereas in 8-wire mode, 8-pins are connected to microcontroller unit like 0 to 7.
A 16×2 LCD has two registers like data register and command register. The RS (register select) is mainly used to change from one register to another. When the register set is ‘0’, then it is known as command register. Similarly, when the register set is ‘1’, then it is known as data register.
Command Register: The main function of the command register is to store the instructions of command which are given to the display. So that predefined tasks can be performed such as clearing the display, initializing, set the cursor place, and display control. Here commands processing can occur within the register.
Data Register: The main function of the data register is to store the information which is to be exhibited on the LCD screen. Here, the ASCII value of the character is the information which is to be exhibited on the screen of LCD. Whenever we send the information to LCD, it transmits to the data register, and then the process will be starting there. When register set =1, then the data register will be selected.
All of the code below uses the LiquidCrystal library that comes pre-installed with the Arduino IDE. A library is a set of functions that can be easily added to a program in an abbreviated format. In order to use a library, it needs be included in the program. Line 1 in the code below does this with the command #include
Now we’re ready to get into the programming! I’ll go over more interesting things you can do in a moment, but for now let’s just run a simple test program. This program will print “hello, world!” to the screen. Enter this code into the Arduino IDE and upload it to the board:
There are 19 different functions in the LiquidCrystal library available for us to use. These functions do things like change the position of the text, move text across the screen, or make the display turn on or off. What follows is a short description of each function, and how to use it in a program.
The LiquidCrystal() function sets the pins the Arduino uses to connect to the LCD. You can use any of the Arduino’s digital pins to control the LCD. Just put the Arduino pin numbers inside the parentheses in this order:
This function sets the dimensions of the LCD. It needs to be placed before any other LiquidCrystal function in the void setup() section of the program. The number of rows and number of columns are specified as lcd.begin(columns, rows). For a 16×2 LCD, you would use lcd.begin(16, 2), and for a 20×4 LCD you would use lcd.begin(20, 4).
This function clears any text or data already displayed on the LCD. If you use lcd.clear() with lcd.print() and the delay() function in the void loop() section, you can make a simple blinking text program.
Similar, but more useful than lcd.home() is lcd.setCursor(). This function places the cursor (and any printed text) at any position on the screen. It can be used in the void setup() or void loop() section of your program.
The cursor position is defined with lcd.setCursor(column, row). The column and row coordinates start from zero (0-15 and 0-1 respectively). For example, using lcd.setCursor(2, 1) in the void setup() section of the “hello, world!” program above prints “hello, world!” to the lower line and shifts it to the right two spaces:
This function creates a block style cursor that blinks on and off at approximately 500 milliseconds per cycle. Use it in the void loop() section. The function lcd.noBlink() disables the blinking block cursor.
This function turns on any text or cursors that have been printed to the LCD screen. The function lcd.noDisplay() turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD, without clearing it from the LCD’s memory.
This function takes anything printed to the LCD and moves it to the left. It should be used in the void loop() section with a delay command following it. The function will move the text 40 spaces to the left before it loops back to the first character. This code moves the “hello, world!” text to the left, at a rate of one second per character.
This function takes a string of text and scrolls it from right to left in increments of the character count of the string. For example, if you have a string of text that is 3 characters long, it will shift the text 3 spaces to the left with each step.
lcd.noAutoscroll() turns the lcd.autoscroll() function off. Use this function before or after lcd.autoscroll() in the void loop() section to create sequences of scrolling text or animations.
This function sets the direction that text is printed to the screen. The default mode is from left to right using the command lcd.leftToRight(), but you may find some cases where it’s useful to output text in the reverse direction.
This command allows you to create your own custom characters. Each character of a 16×2 LCD has a 5 pixel width and an 8 pixel height. Up to 8 different custom characters can be defined in a single program. To design your own characters, you’ll need to make a binary matrix of your custom character from an LCD character generator or map it yourself. This code creates a degree symbol (°).
The detailed LCD tutorial can be found in the article. ARDUINO LCD SET UP AND PROGRAMMING GUIDE or to check https://github.com/arduino-libraries/LiquidCrystal

Hello friend welcome to “Techno-E-Solution” in this article we are going to learn how to connect LCD display with Arduino Uno and print "Hello World!" on LCD using Arduino Uno. The 16x2 LCD is most popular LCD in electronics projects. In upcoming project we need this display in our project so it"s the beginners level tutorial learn this tutorial with fun. So friends let"s get started..........
A PCB Design Problems Detector, An Engineering Solution Provider Import the Gerber file with one click. No need for complicated file reading steps to review easily and improve efficiency.

This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

To establish a good communication between human world and machine world, display units play an important role. And so they are an important part of embedded systems. Display units - big or small, work on the same basic principle. Besides complex display units like graphic displays and 3D dispays, one must know working with simple displays like 16x1 and 16x2 units. The 16x1 display unit will have 16 characters and are in one line. The 16x2 LCD will have 32 characters in total 16in 1st line and another 16 in 2nd line. Here one must understand that in each character there are 5x10=50 pixels so to display one character all 50 pixels must work together. But we need not to worry about that because there is another controller (HD44780) in the display unit which does the job of controlling the pixels. (you can see it in LCD unit, it is the black eye at the back ).
In this tutorial, we are going to interface a 16x2 LCD with ARDUINO UNO. Unlike normal development boards interfacing an LCD to an ARDUINO is quite easy. Here we don’t have to worry about data sending and receiving. We just have to define the pin numbers and it will be ready to display data on LCD.
Note:We updated this tutorial and added some more additional information along with a step-by-step guide to interface 16x2 LCD withArduino. You can follow the below link for an updated tutorial.
In 16x2 LCD there are 16 pins over all if there is a back light, if there is no back light there will be 14 pins. One can power or leave the back light pins. Now in the 14 pins there are 8 data pins (7-14 or D0-D7), 2 power supply pins (1&2 or VSS&VDD or GND&+5v), 3rd pin for contrast control (VEE-controls how thick the characters should be shown), and 3 control pins (RS&RW&E).
In the circuit, you can observe I have only took two control pins, this gives the flexibility. The contrast bit and READ/WRITE are not often used so they can be shorted to ground. This puts LCD in highest contrast and read mode. We just need to control ENABLE and RS pins to send characters and data accordingly.
The ARDUINO IDE allows the user to use LCD in 4 bit mode. This type of communication enables the user to decrease the pin usage on ARDUINO, unlike other the ARDUINO need not to be programmed separately for using it in 4 it mode because by default the ARDUINO is set up to communicate in 4 bit mode. In the circuit you can see we have used 4bit communication (D4-D7).
First we need to enable the header file (‘#include
Second we need to tell the board which type of LCD we are using here. Since we have so many different types of LCD (like 20x4, 16x2, 16x1 etc.). Here we are going to interface a 16x2 LCD to the UNO so we get ‘lcd.begin(16, 2);’. For 16x1 we get ‘lcd.begin(16, 1);’.
In this instruction we are going to tell the board where we connected the pins. The pins which are connected need to be represented in order as “RS, En, D4, D5, D6, D7”. These pins are to be represented correctly. Since we have connected RS to PIN0 and so on as show in the circuit diagram, we represent the pin number to board as “LiquidCrystal lcd(0, 1, 8, 9, 10, 11);”. The data which needs to be displayed in LCD should be written as “ cd.print("hello, world!");”. With this command the LCD displays ‘hello, world!’.
As you can see we need not to worry about any thing else, we just have to initialize and the UNO will be ready to display data. We don’t have to write a program loop to send the data BYTE by BYTE here.
In this digital age, we come across LCDs all around us from simple calculators to smartphones, computers and television sets, etc. The LCDs use liquid crystals to produce images or texts and are divided into different categories based on different criteria like type of manufacturing, monochrome or colour, and weather Graphical or character LCD. In this tutorial, we will be talking about the 16X2 character LCD Modules.
The 16x2 LCDs are very popular among the DIY community. Not only that, but you can also find them in many laboratory and industrial equipment. It can display up to 32 characters at a time. Each character segment is made up of 40 pixels that are arranged in a 5x8 matrix. We can create alphanumeric characters and custom characters by activating the corresponding pixels. Here is a vector representation of a 16x2 LCD, in which you can see those individual pixels.
As the name indicates, these character segments are arranged in 2 lines with 16 characters on each line. Even though there are LCDs with different controllers are available, The most widely used ones are based on the famous HD44780 parallel interface LCD controller from Hitachi.
Vo / VEE Contrast adjustment; the best way is to use a variable resistor such as a potentiometer. The output of the potentiometer is connected to this pin. Rotate the potentiometer knob forward and backwards to adjust the LCD contrast.
The 16x2 LCD modules are popular among the DIY community since they are cheap, easy to use and most importantly enable us to provide information very efficiently. With just 6 pins, we can display a lot of data on the display.
The module has 16 pins. Out of these 16 pins, two pins are for power, two pins are for backlight, and the remaining twelve pins are for controlling the LCD.
If you look at the backside of the module you can simply see that there are not many components. The main components are the two controller chips that are under the encapsulation. There is an onboard current limiting resistor for the backlight. This may vary from different modules from different manufacturers. The only remaining components are a few complimentary resistors for the LCD controller.
In the module PCB, you may have noticed some unpopulated footprints. These footprints are meant for charge pump circuits based on switched capacitor voltage converters like ICL7660 or MAX660. You can modify your LCD to work with 3.3V by populating this IC and two 10uF capacitors to C1 and C2 footprint, removing Jumper J1 and adding jumper J3. This modification will generate a negative contrast voltage of around 2.5V. This will enable us to use the LCD even with a VCC voltage of 3.3V.
To test whether a 16x2 LCD works or not, connect the VDD, GND and backlight pins to 5v and GND. Connect the centre terminal of a 10K variable resistor to the VEE pin. Connect the other two terminals to VCC and GND. Simply rotate the variable resistor you will see that the contrast will be adjusted and small blocks are visible. If these rectangles are visible, and you were able to adjust the contrast, then the LCD is working
There are 16 pins on the display module. Two of them are for power (VCC, GND), one for adjusting the contrast (VEE), three are control lines (RS, EN, R/W), eight pins are data lines(D0-D7) and the last two pins are for the backlight (A, K).
The 16x2 LCD has 32 character areas, which are made up of a 5x8 matrix of pixels. By turning on or off these pixels we can create different characters. We can display up to 32 characters in two rows.
Yes, we can. We can store up to eight custom characters in the CGRAM (64 bytes in size) area. We can create load the matrix data for these characters and can recall when they need to be displayed.
Controlling the LCD module is pretty simple. Let’s walk through those steps. To adjust the contrast of the LCD, the Vo/ VEE pin is connected to a variable resistor. By adjusting the variable resistor, we can change the LCD contrast.
The RS or registry select pin helps the LCD controller to know whether the incoming signal is a control signal or a data signal. When this pin is high, the controller will treat the signal as a command instruction and if it’s low, it will be treated as data. The R/W or Read/Write pin is used either to write data to the LCD or to read data from the LCD. When it’s low, the LCD module will be in write mode and when it’s high, the module will be in reading mode.
The Enable pin is used to control the LCD data execution. By default, this pin is pulled low. To execute a command or data which is provided to the LCD data line, we will just pull the Enable pin to high for a few milliseconds.
To test the LCD module, connect the VDD, GND, and backlight pins to 5v and GND. Connect the center terminal of a 10K variable resistor to the VEE pin. Connect the other two terminals to VCC and GND as per the below connection diagram-
Simply rotate the variable resistor you will see that the contrast will be adjusted and small blocks are visible. If these rectangles are visible, and you were able to adjust the contrast, then the LCD is working.
Let’s see how to connect the LCD module to Arduino. For that first, connect the VSS to the GND and VDD to the 5V. To use the LCD backlight, connect the backlight Anode to the 5V and connect the backlight cathode to the GND through a 220Ωresistor. Since we are not using the read function connect the LCD R/W pin to the GND too. To adjust the contrast, connect the centre pin of a 10KΩ trimmer resistor to the VEE pin and connect the side pins to the VCC and GND. Now connect the registry select pin to D12 and Enable pin to D11.
Now let’s connect the data pins. The LCD module can work in two modes, 8-bit and 4-bit. 8-bit mode is faster but it will need 8 pins for data transfer. In 4-bit mode, we only need four pins for data. But it is slower since the data is sent one nibble at a time. 4-bit mode is often used to save I/O pins, while the 8-bit mode is used when speed is necessary. For this tutorial, we will be using the 4-bit mode. For that connect the D4, D5, D6 and D7 pins from the LCD to the D5, D4, D3 and D2 pins of the Arduino.
Here is the actual circuit. It is built as per the connection diagram provided. All the connections are made using standard male to male jumper wires.
The following Arduino 16x2 LCD code will print Hello, World! on the first line of the display and the time the Arduino was running in seconds on the second line.
Now let’s discuss the code. As usual, the sketch starts by including the necessary libraries. For this tutorial, we will be including the LiquidCrystal library from Arduino. This library is compatible with LCDs based on the Hitachi HD44780, or any compatible chipset. You can find more details about this library on the Arduino website.
Let’s create an object to use with the LiquidCrystal library. The following line of code will create an object called lcd. We will be using this object in the entire code to access the library functions. The object is initialized with the pin numbers.
Now let’s look at the setup()function. The lcd.begin function is used to initialize the LCD module. This function will send all the initialization commands. The parameters used while calling this function are the number of columns and the number of rows. And the next function is lcd.print. with this function, we have printed the word Circuit Digest! to the LCD. Since the LCD cursor is set to home position within the lcd.begin, we don’t need to set any cursor position. This text will stay there for two seconds. After that, the text will scroll from left to right until the entire text is out of the display. To scroll the display to the right, we have used the function lcd.scrollDisplayRight. After that, to clear display, we used lcd.clear, this will clear any characters on the display.
Now let’s look at theloop function. The for loop will count from 0 to 9, and when it reaches 9, it will reset the count and repeat the process all over again. lcd.setCursor is used to set the cursor position. lcd.setCursor(8, 1) will set the LCD cursor to the eighth position in the second row. In the LCD, the first row is addressed as 0 and the second row is addressed as 1. And the lcd.print(i) will print the count value stored in the variable i to the display.
Wrong characters are displayed: This problem occurs usually when the LCD is not getting the correct data. Make sure you are sending the correct ASCII value. If you are sending the correct ASCII characters, but still showing the wrong one on the LCD, check your connections for loose contact or short circuits.
Display shows Black boxes or does not show anything: First thing to do in these situations is to adjust the contrast voltage by rotating the variable resistor. This will correct the contrast value and will give you a visible readout.
Contrast is Ok, but still no display: Make sure to provide a sufficient time delay in between sending each character. Because if you don’t give enough time to process the data the display will malfunction.
Contrast and delay are ok, but still no display: Make sure you are powering the LCD from a 5V source. By default, these displays won’t work with a supply voltage below 5V. So if you are using the display with a 3.3V microcontroller make sure to power the display from 5V and use level shifters in between the display and the microcontroller.
In this project we will provide the input voice using Google Voice Keyboard via a Android App (BlueTerm) and print the text on 16x2 LCD using Raspberry Pi.
In this tutorial we are interfacing a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) module with the Raspberry Pi Pico using Micropython to display strings, and characters on the LCD.
We used some Python scripts to find the local IP address of your Raspberry Pi on the network and display it on the 16x2 LCD Screen. We also added the script in the Crontab so that it can be run on every 10 minutes and we will have the updated IP address every time.

An LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is a great way to display information in our Arduino Uno controller. We will be wiring and programming an alphanumeric, two rows with 16 characters on each row. The display has an LED (Light Emitting Diode) backlight with adjustable contrast.
This white and blue LCD will display “Hello World!” on the top line and temperature on the bottom line. The thermistor temperature circuit created last time will be displayed in both Celsius and Fahrenheit degrees. Let’s get started.
When you look at an LCD display, it is made up of a series of dots or pixels. Each of these pixels is a liquid crystal. If electricity flows through the liquid crystal it will change its structure and be more rigid. This rigidity will look darker than if no electricity is applied. If we use a light behind this LCD then the backlight will make the pixels more pronounced. So electricity on the pixel will block the light and no electricity will allow the light through. This contrast is what we see using an LCD display.
The LiquidCrystal.zip file came on the disk with the Arduino UNO R3 super starter kit. It can also be downloaded from the link below with the program. Select this library and then select open. This will add the library to the Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment).
This first part will set up the library and declare the variables for the LCD display unit. Using the Steinhart-Hart Equation we declare our variables and set the coefficients for the equation.
The LCD is set up with 16 characters and 2 lines. The cursor for the LCD display is set for the first character on the first line by default. We then print the message “ Hello, World!”.
The program will calculate the temperature in Celsius (T) and in Fahrenheit (TF). The LCD cursor is then set to the second row and column 0. We can then print our temperatures and units of measure.
You will see the ‘Hello World!’ and the current temperature in two units of measure displayed on the LCD. Hold the thermistor between your fingers to see how rapidly the temperature can be read.

Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is made use in various kinds of devices from small display screen in calculator to large screens in televisions. In case of a microcontroller based system the LCD is the most effective output device. Special kind of Liquid Crystal drivers are used with the commonly found LCD modules in microcontroller systems.The LCD module is very effective since it can display messages, values, clock etc. The LCD modules can display not only ASCII characters but custom characters also. The user can store the pixel array corresponding to the custom character in an LCD module. The stored custom character can be made to display by sending the corresponding value to the LCD module. The custom characters are used for the dynamic display in an LCD board.
The custom characters can be used to display various kinds of smileys in LCD display. Smileys are now a days very popular especially in SMS using mobile phones, online messenger applications etc. This particular project demonstrates how is it possible to create a smiley and display it in a 16x2 LCD. The project is done with the help of easy-prototyping platform Arduino.
The Arduino is an easy-prototyping platform where the hardware is very simple and the coding and IDE is veryeasy to start with. Since the basic Arduino board does not have a built –in LCD module to display data one should connect it externally to display data like strings, sensor values etc. The libraries in the Arduino IDE help in accessing the LCD module very easily.In this project the Arduino pro-mini board is used which is then programmed with the help of Arduino IDE version 1.0.3 on windows operating system. The image of the Arduino pro-mini board and the Arduino IDE is shown in the following;
This project makes use of the custom characters that can be generated in an LCD module. The LCD module has two or more controllers which helps in displaying the characters corresponding to the ASCII value which is send by the microcontroller. The ASCII character patterns are stored in the internal CGROM of the LCD controllers. The LCD modules also provide a CGRAM where the user can store the custom characters and display them. The method of generating custom characters is well explained in a previous project onhow to create custom characters in an LCD.
One has to work out the character of the custom character that needs to be displayed in the LCD screen as explained in the project onhow to create custom characters in an LCD. The custom characters which are displayed in this project are shown in the following image.
There are basically two symbols used in this project of which one is a smile symbol and another is a heart symbol. The bit patterns that need to be stored in the LCD to display those characters are find out using the method of drawing the pixel array and assuming the bit value for the pixel which is ON as 1and the pixel which is off as 0.
The Arduino IDE has a library called
The code written for this project has a function lcd.createChar() which helps to create the custom characters in an LCD screen. The details of the lcd.createChar() function are discussed in the following section.
The function lcd.createChar() can be used to write a custom character to the required location in the CGRAM. The function has two parameters in which the first parameter is the location in the CGRAM memory where the character array corresponding to the custom character need to be stored and the second parameter is the character array itself. For example if there is a custom character array called ‘cc’ and it need to be stored in the 5th location of CGRAM one can use the following statement;
The above statement writes the character array to the 5th location of the CGRAM of the LCD controller from where it can be displayed by calling the lcd.write() function discussed in the projects onhow to connect the LCD with the PCandhow to make an LCD scrolling display.
The code written for this project can store the smileys in the CGRAM of the LCD module and display them in the second line of the LCD module in such a way that the entire second line is filled with the two smileys.
Once done with the coding one can verify and upload the code to the Arduino board as explained in the projecthow to get started with the Arduinoand can find the smileys in the LCD module and also the blinking LED.

Liquid Crystal Display is made use in various kinds of devices from small display screen in calculator to large screens in televisions. There are lots of advantages in using the LCD displays in systems like power efficiency, thin size, low cost etc. LCD based small display modules are normally found in all kinds of embedded devices.The LCD even though looks simple, but it is actually difficult to make it work.
The LCD works with voltage pulses only and that with precise timing and voltage levels. Hence special kinds of LCD drivers are developed to drive the LCD. Two or more of this kind of driver ICs together with the LCD screen forms LCD modules which are normally found in embedded systems.The LCD module makes a system stand-alone which can take input and display the corresponding output. This particular project demonstrates how to interface a 16x2 LCD display with an Arduino board.
Any AVR microcontroller based board which follows the standard Arduino schematic and is flashed with the Arduinobootloadercan be called an Arduino board. There is no other tool available which helps in easy prototyping like the Arduino does. The Arduino board has all the required circuitary to get the built-in AVR microcontroller running. When it comes to programming the Arduino board anyone who have basic knowledge of c programming can quickly get started with the Arduino IDE. The tutorial onGetting started with Arduinoexplains about the steps required to get start with an Arduino board.The Arduino board used in this project is the Arduino pro-mini board and the IDE version of the Arduino is 1.0.3 for windows. The image of the Arduino pro-mini board and the Arduino IDE are shown below;
Since the Arduino pro-mini board has no circuitary for interfacing it with the serial port or the USB port of the PC, an external USB to TTL converter board is required to connect it with the PC. This hardware helps in programming the Arduino board and also helps in the serial communication with the USB port of the PC.
It is assumed that the reader has gone through the projectand tried out all the things discussed there.The Arduino IDE has so many functions which help one to interface the four bit LCD module. There are functions to initialize the LCD module and to write character characters in the LCD module. The functions used in the coding of this projects are lcd.begin(), and lcd.print(). The functions are available in the library
This function should be called to initialize the four bit LCD library and then only the library functions can be called in the code. The function has six parameters which should be provided during a function call as per the circuit connection with the Arduino board and the LCD module. The details of the function parameters are listed in the order below.
For example the following statement can be used to initialize an LCD library for the code written for the circuit in which the RS pin is connected to pin12, Enable pin to 11, and D4, D5, D6 and D7 to pins 5, 4,




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey