4 differences between crt and lcd monitors brands
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CRT-vs-LCD-monitor-cfe0b6f375b542928baf22a0478a57a3.jpg)
Following are the important differences between CRT and LCD.Sr. No.KeyCRTLCD1DefinitionCRT stands for Cathode Ray Tube.LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display.
CRT stands for Cathode Ray Tube and LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display area unit the kinds of display devices wherever CRT is employed as standard display devices whereas LCD is more modern technology. These area unit primarily differentiated supported the fabric they’re made from and dealing mechanism, however, each area unit alleged to perform identical perform of providing a visible variety of electronic media. Here, the crucial operational distinction is that the CRT integrates the 2 processes lightweight generation and lightweight modulation and it’s additionally managed by one set of elements. Conversely, the LCD isolates the 2 processes kind one another that’s lightweight generation and modulation.

Since the production of cathode ray tubes has essentially halted due to the cost and environmental concerns, CRT-based monitors are considered an outdated technology. All laptops and most desktop computer systems sold today come with LCD monitors. However, there are a few reasons why you might still prefer CRT over LCD displays.
While CRT monitors provide better color clarity and depth, the fact that manufacturers rarely make them anymore makes CRTs an unwise choice. LCD monitors are the current standard with several options. LCD monitors are smaller in size and easier to handle. Plus, you can buy LCD monitors in a variety of sizes, so customizing your desktop without all the clutter is easy.
The primary advantage that CRT monitors hold over LCDs is color rendering. The contrast ratios and depths of colors displayed on CRT monitors are better than what an LCD can render. For this reason, some graphic designers use expensive and large CRT monitors for their work. On the downside, the color quality degrades over time as the phosphors in the tube break down.
Another advantage that CRT monitors hold over LCD screens is the ability to easily scale to various resolutions. By adjusting the electron beam in the tube, the screen can be adjusted downward to lower resolutions while keeping the picture clarity intact. This capability is known as multisync.
The biggest disadvantage of CRT monitors is the size and weight of the tubes. An equivalently sized LCD monitor can be 80% smaller in total mass. The larger the screen, the bigger the size difference. CRT monitors also consume more energy and generate more heat than LCD monitors.
For the most vibrant and rich colors, CRTs are hard to beat if you have the desk space and don"t mind the excessive weight. However, with CRTs becoming a thing of the past, you may have to revisit the LCD monitor.
The biggest advantage of LCD monitors is the size and weight. LCD screens also tend to produce less eye fatigue. The constant light barrage and scan lines of a CRT tube can cause strain on heavy computer users. The lower intensity of the LCD monitors coupled with the constant screen display of pixels being on or off is easier on the eyes. That said, some people have issues with the fluorescent backlights used in some LCD displays.
The most notable disadvantage to LCD screens is the fixed resolution. An LCD screen can only display the number of pixels in its matrix. Therefore, it can display a lower resolution in one of two ways: using only a fraction of the total pixels on the display, or through extrapolation. Extrapolation blends multiple pixels together to simulate a single smaller pixel, which often leads to a blurry or fuzzy picture.
For those who are on a computer for hours, an LCD can be an enemy. With the tendency to cause eye fatigue, computer users must be aware of how long they stare at an LCD monitor. While LCD technology is continually improving, using techniques to limit the amount of time you look at a screen alleviates some of that fatigue.
Significant improvements have been made to LCD monitors over the years. Still, CRT monitors provide greater color clarity, faster response times, and wider flexibility for video playback in various resolutions. Nonetheless, LCDs will remain the standard since these monitors are easier to manufacture and transport. Most users find LCD displays to be perfectly suitable, so CRT monitors are only necessary for those interested in digital art and graphic design.

If you are shopping for a display, you may look to compare LCD vs CRT computer monitors. Some of the best computer monitors come in a wide variety of styles and design types. Keep reading to learn the difference between these two types of monitors.
CRT displays, however, are known for superior color rendering performance and for offering high refresh rates. We have a whole page dedicated to explaining what a CRT monitor is if you’re curious.
CRT monitors are bad for the environment, as they draw a whole lot of power during use. To help reduce humanity’s carbon footprint through tech products, there are opportunities for computer monitor recycling.
There are multiple distinctions to be made between LCD and CRT monitors, as well as LCD vs LED monitors, but that’s for another post. A liquid crystal display (LCD) has liquid crystals squeezed between two sheets of glass along with an electron gun that shoots an electron beam, while a CRT (cathode ray tube) monitor features a number of cathode-ray tubes. This overall difference in design leads to widely different use case scenarios, such as when you are comparing LCD vs LED monitors for gaming.
Despite being an older technology, CRT monitors are quite capable when it comes to rendering accurate colors. As a matter of fact, many creative professionals opt for expensive newly made CRT screens over LCD technology, LED screens, or even OLED displays for just this reason. Another advantage to the bright and vivid colors found with CRT displays is that they slightly reduce eye fatigue, which can be a handy bit of information if you are comparing LCD vs LED monitors for eye strain. The downside here is that CRT monitors are fragile, so this color accuracy will break down over time as the phosphor tubes degrade.
Another surprising feature of CRT monitors is their ultra-fast refresh rates. Due to the nature of the design, they offer higher refresh rates than LCD screens, as the light has a shorter route to travel.
There is no way around it. Cathode tubes are extremely large and extremely heavy, making CRT monitors an absolute beast to haul around and to place in your workspace. LCD screens, on the other hand, are light and portable, easily fitting just about anywhere.
In most cases, LCD monitors will offer a much larger field of view for viewing image and video than CRT displays, due to the nature of the design of the flat screen. Something like an LCD screen would come in handy as a gaming monitor. The larger the field of view with a CRT, the heavier and bulkier it will be.
CRT monitors are made from multiple materials that are relatively tough to source and they draw a whole lot of power during use. In other words, they are not too great for the environment.

Resolution on a CRT is flexible and a newer model will provide you with viewing resolutions of up to 1600 by 1200 and higher, whereas on an LCD the resolution is fixed within each monitor (called a native resolution). The resolution on an LCD can be changed, but if you’re running it at a resolution other than its native resolution you will notice a drop in performance or quality.
Both types of monitors (newer models) provide bright and vibrant color display. However, LCDs cannot display the maximum color range that a CRT can. In terms of image sharpness, when an LCD is running at its native resolution the picture quality is perfectly sharp. On a CRT the sharpness of the picture can be blemished by soft edges or a flawed focus.
A CRT monitor can be viewed from almost any angle, but with an LCD this is often a problem. When you use an LCD, your view changes as you move different angles and distances away from the monitor. At some odd angles, you may notice the picture fade, and possibly look as if it will disappear from view.
Some users of a CRT may notice a bit of an annoying flicker, which is an inherent trait based on a CRTs physical components. Today’s graphics cards, however, can provide a high refresh rate signal to the CRT to get rid of this otherwise annoying problem. LCDs are flicker-free and as such the refresh rate isn’t an important issue with LCDs.
Dot pitch refers to the space between the pixels that make up the images on your screen, and is measured in millimeters. The less space between pixels, the better the image quality. On either type of monitor, smaller dot pitch is better and you’re going to want to look at something in the 0.26 mm dot pitch or smaller range.
Most people today tend to look at a 17-inch CRT or bigger monitor. When you purchase a 17-inch CRT monitor, you usually get 16.1 inches or a bit more of actual viewing area, depending on the brand and manufacturer of a specific CRT. The difference between the “monitor size” and the “view area” is due to the large bulky frame of a CRT. If you purchase a 17″ LCD monitor, you actually get a full 17″ viewable area, or very close to a 17″.
There is no denying that an LCD wins in terms of its physical size and the space it needs. CRT monitors are big, bulky and heavy. They are not a good choice if you’re working with limited desk space, or need to move the monitor around (for some odd reason) between computers. An LCD on the other hand is small, compact and lightweight. LCDs are thin, take up far less space and are easy to move around. An average 17-inch CRT monitor could be upwards of 40 pounds, while a 17&-inch LCD would weigh in at around 15 pounds.
As an individual one-time purchase an LCD monitor is going to be more expensive. Throughout a lifetime, however, LCDs are cheaper as they are known to have a longer lifespan and also a lower power consumption. The cost of both technologies have come down over the past few years, and LCDs are reaching a point where smaller monitors are within many consumers’ price range. You will pay more for a 17″ LCD compared to a 17″ CRT, but since the CRT’s actual viewing size is smaller, it does bring the question of price back into proportion. Today, fewer CRT monitors are manufactured as the price on LCDs lowers and they become mainstream.

If you are looking for a new display, you should consider the differences between CRT and LCD monitors. Choose the type of monitor that best serves your specific needs, the typical applications you use, and your budget.
Require less power - Power consumption varies greatly with different technologies. CRT displays are somewhat power-hungry, at about 100 watts for a typical 19-inch display. The average is about 45 watts for a 19-inch LCD display. LCDs also produce less heat.
Smaller and weigh less - An LCD monitor is significantly thinner and lighter than a CRT monitor, typically weighing less than half as much. In addition, you can mount an LCD on an arm or a wall, which also takes up less desktop space.
More adjustable - LCD displays are much more adjustable than CRT displays. With LCDs, you can adjust the tilt, height, swivel, and orientation from horizontal to vertical mode. As noted previously, you can also mount them on the wall or on an arm.
Less eye strain - Because LCD displays turn each pixel off individually, they do not produce a flicker like CRT displays do. In addition, LCD displays do a better job of displaying text compared with CRT displays.
Better color representation - CRT displays have historically represented colors and different gradations of color more accurately than LCD displays. However, LCD displays are gaining ground in this area, especially with higher-end models that include color-calibration technology.
More responsive - Historically, CRT monitors have had fewer problems with ghosting and blurring because they redrew the screen image faster than LCD monitors. Again, LCD manufacturers are improving on this with displays that have faster response times than they did in the past.
Multiple resolutions - If you need to change your display"s resolution for different applications, you are better off with a CRT monitor because LCD monitors don"t handle multiple resolutions as well.
So now that you know about LCD and CRT monitors, let"s talk about how you can use two monitors at once. They say, "Two heads are better than one." Maybe the same is true of monitors!

You might have used a large bulk size of the computer monitor in your childhood; it is the CRT monitor. Nowadays you are seeing that those types of monitors are disappearing and some slim-looking monitors are taking their place; these are the LCD and LED monitors. It has become our reality due to a fast technological advancement during the last few decades. In today’s topic, we will analyze CRT vs LCD monitors; their relative comparison, and try to figure out the differences.
The full form of CRT is Cathode Ray Tube. The CRT monitor is one kind of display unit. It is one of the oldest types of monitor. Although the use of CRT monitors is becoming obsolete with the invention of smarter monitors and TVs, you can still find them on the market because it is still useful in many cases.
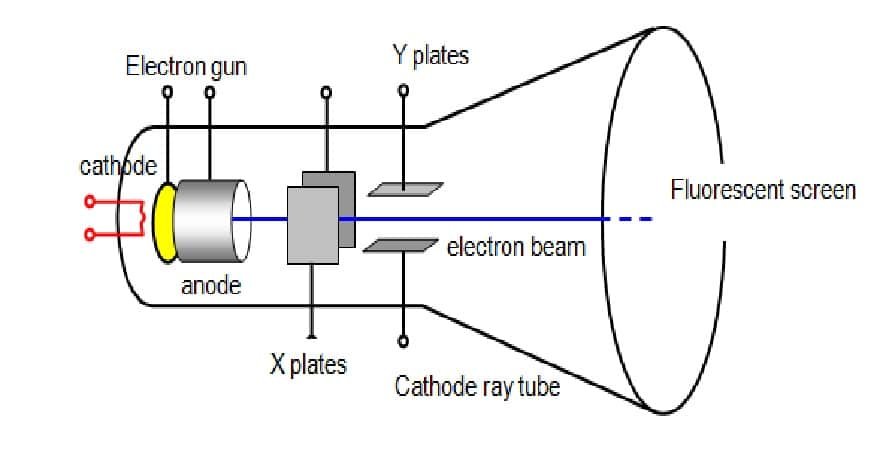
The CRT monitor has a coating of phosphor inside the tube. An electron gun is a crucial component of a CRT monitor. The black and white CRT monitor has got only one electron gun; on the other hand, the colored one has got three different electron guns- red, green, and blue. The electrons emitted from the electron guns strike on the phosphor dots; thus the dots become ablaze which in turn represent us as pictures.
The full form of LCD is Liquid Crystal Display. This kind of display unit uses transparent liquid crystals to produce pictures. The crystals are charged up electrically and we are able to watch the display. The LCD monitor is a flat one; hence also called a Flat Panel Monitor. Its refresh rate is also higher.
The LCD display is used on the calculator and digital watch. The laptop and netbook extensively use LCD monitors for the display unit. A flat-panel monitor is also available for desktop PC, but the price is quite high. It can generally be connected through DVI or HDMI cables. But what are the actual differences in terms of CRT vs LCD monitors? The next sections will clear your all questions.
The difference between the CRT monitor and LCD monitor is mainly based upon the technology used for the make-up of the two and also the user-friendliness. Both types of monitors have their pros and cons, different usability, and function-ability. In this section, we will try to explain CRT vs LCD keeping in mind these facts.
The CRT monitor is the older type of display unit; whereas the LCD monitor is more of a recent invention. Hence, we can easily say that the CRT monitor is more conventional than the LCD monitor.
CRT monitors function on the basis of electron beams originating from the electron beam and hitting the phosphor dots. On the other hand, the operation of LCD monitors is based upon liquid crystals being charged up electrically. Both the monitors’ ultimate goal is to produce pictures not only in the form of still images but also in the form of motion.
LCD monitors use up much less power than CRT monitors. In fact, an LCD monitor consumes 3 to 4 times less power than a CRT monitor. It is one of the biggest advantages of LCD monitors.
You may have found out that as technology advances, gadgets are becoming smaller and smaller. It is of course done for getting the advantages of portability. The same case has happened in the evolution of the monitor. CRT monitor being the older one possesses a sizable body structure; whereas the LCD displays are slim and very small in size.
The CRT monitor is very heavy because it has to carry a weighted electron gun. An average-sized CRT monitor weighs generally 20 to 25 kg. The LCD monitor has a great edge in this respect. An LCD monitor generally weighs 4 to 6 kg which makes it easy to handle.
Image flickering is the frame disturbances on the monitor; a series of frames can not appear flawlessly as a blank frame causes two frames to set apart. This annoys a viewer to a great extent. CRT monitors have more problems with image flickering than LCD monitors.
Image persistence or image retention is the nature of a picture remaining static for a period of time. The CRT monitor does not have image persistence which the LCD monitor does possess. Although being an old monitor, the CRT monitor has an edge over the LCD monitor in this regard.
A CRT monitor has got some extra space around the main display, and this extra space is totally useless. The LCD monitor covers almost the full display as the viewing area and thus making it more efficient.
CRT monitors are better for wide viewing; you can watch a CRT TV from different sections of your room in a much better way compared to the LCD monitors.
The refresh rate of a monitor is one of the most important things that must be considered. Most LCD monitors produce a minimum refresh rate of around 200Hz; whereas the refresh rate of CRT monitors ranges between 70 to 80 Hz on average. Therefore, the resolution of the LCD monitor is much higher than that of the CRT monitor. Also, the G-sync monitor made the viewing experience awesome.
All the television sets used to be made of CRT mechanism in the old times. Computer manufacturers were also making CRT monitors with the limitation of the technology. These monitors are still available, but their use is becoming less and less with time.
LCD monitors have taken the place of old CRT monitors. LCD monitors are extensively used for personal computers, laptops, netbooks, digital watches, calculators, television, and whatnot. You can easily set up dual monitor or triple monitor for convenient usage.
Both the CRT and LCD monitors have their advantages and disadvantages in several aspects. The newer technology will always replace the older ones; even the LED monitors are replacing the LCDs in recent times. No matter old or new; you should buy a monitor according to your need and choice. After reading the article, you should know all about CRT vs LCD monitors and their key differences.

CRT stands for cathode-ray tube, a TV or PC monitor that produces images using an electron gun. These were the first displays available, but they are now outdated and replaced by smaller, more compact, and energy-efficient LCD display monitors.
In contrast, a Liquid crystal display, or an LCD monitor, uses liquid crystals to produce sharp, flicker-free images. These are now the standard monitors that are giving the traditional CRTs a run for their money.
Although the production of CRT monitors has slowed down, due to environmental concerns and the physical preferences of consumers, they still have several advantages over the new-age LCD monitors. Below, we shed some light on the differences between CRT and LCD displays.
CRTLCDWhat it isAmong the earliest electronic displays that used a cathode ray tubeA flat-panel display that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals
CRTs boast a great scaling advantage because they don’t have a fixed resolution, like LCDs. This means that CRTs are capable of handling multiple combinations of resolutions and refresh rates between the display and the computer.
In turn, the monitor is able to bypass any limitations brought about by the incompatibility between a CRT display and a computer. What’s more, CRT monitors can adjust the electron beam to reduce resolution without affecting the picture quality.
On the other hand, LCD monitors have a fixed resolution, meaning they have to make some adjustments to any images sent to them that are not in their native resolution. The adjustments include centering the image on the screen and scaling the image down to the native resolution.
CRT monitors project images by picking up incoming signals and splitting them into audio and video components. More specifically, the video signals are taken through the electron gun and into a single cathode ray tube, through a mesh, to illuminate the phosphorus inside the screen and light the final image.
The images created on the phosphor-coated screen consist of alternating red, blue, and green (RGB) lights, creating countless different hues. The electron gun emits an electron beam that scans the front of the tube repetitively to create and refresh the image at least 100 times every second.
LCD screens, on the other hand, are made of two pieces of polarized glass that house a thin layer of liquid crystals. They work on the principle of blocking light. As a result, when light from a backlight shines through the liquid crystals, the light bends to respond to the electric current.
The liquid crystal molecules are then aligned to determine which color filter to illuminate, thus creating the colors and images you see on the screen. Interestingly, you can find color filters within every pixel, which is made up of three subpixels—red, blue, and green—that work together to produce millions of different colors.
Thanks to the versatility of pixels, LCD screens offer crisper images than CRT monitors. The clarity of the images is a result of the LCD screen’s ability to produce green, blue, and red lights simultaneously, whereas CRTs need to blur the pixels and produce either of the lights exclusively.
The diversity of the pixels also ensures LCD screens produce at least twice as much brightness as CRTs. The light on these screens also remains uninterrupted by sunlight or strong artificial lighting, which reduces general blurriness and eyestrain.
Over time, however, dead pixels negatively affect the LCD screen’s visual displays. Burnout causes these dead pixels, which affect the visual clarity of your screen by producing black or other colored dots in the display.
CRT monitors also have better motion resolution compared to LCDs. The latter reduces resolution significantly when content is in motion due to the slow pixel response time, making the images look blurry or streaky.
With CRTs, you don’t experience any display lag because the images are illuminated on the screen at the speed of light, thus preventing any delays. However, lag is a common problem, especially with older LCD displays.
CRTs are prone to flickeringduring alternating periods of brightness and darkness. LCDs don’t flicker as much thanks to the liquid pixels that retain their state when the screen refreshes.
CRTs have a thick and clunky design that’s quite unappealing. The monitor has a casing or cabinet made of either plastic or metal that houses the cathode ray tube. Then there’s the neck or glass funnel, coated with a conductive coating made using lead oxide.
Leaded glass is then poured on top to form the screen, which has a curvature. In addition, the screen contributes to about 65% of the total weight of a CRT.
LCDs feature low-profile designs that make them the best choice for multiple portable display devices, like smartphones and tablets. LCD displays have a lightweight construction, are portable, and can be made into much larger sizes than the largest CRTs, which couldn’t be made into anything bigger than 40–45 inches.
A German scientist called Karl Ferdinand Braun invented the earliest version of the CRT in 1897. However, his invention was not isolated, as it was among countless other inventions that took place between the mid-1800s and the late 1900s.
CRT technology isn’t just for displays; it can also be utilized for storage. These storage tubes can hold onto a picture for as long as the tube is receiving electricity.
Like the CRT, the invention of the modern LCD was not a one-man show. It began in 1888 when the Austrian botanist and chemist Friedrich Richard Kornelius Reinitzer discovered liquid crystals.
The invention of the cathode ray tube began with the discovery of cathode beams by Julius Plucker and Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Geissler in 1854. Interestingly, in 1855, Heinrich constructed glass tubes and a hand-crack mercury pump that contained a superior vacuum tube, the “Geissler tube.”
Later, in 1859, Plucker inserted metal plates into the Geissler tube and noticed shadows being cast on the glowing walls of the tube. He also noticed that the rays bent under the influence of a magnet.
Sir William Crookes confirmed the existence of cathode rays in 1878 by displaying them in the “Crookes tube” and showing that the rays could be deflected by magnetic fields.
Later, in 1897, Karl Ferdinand Braun, a German physicist, invented a cathode ray tube with a fluorescent screen and named it the “Braun Tube.” By developing the cathode ray tube oscilloscope, he was the first person to endorse the use of CRT as a display device.
Later, in 1907, Boris Rosing, a Russian scientist, and Vladimir Zworykin used the cathode ray tube in the receiver of a television screen to transmit geometric patterns onto the screen.
LCD displays are a much more recent discovery compared to CRTs. Interestingly, the French professor of mineralogy, Charles-Victor Mauguin, performed the first experiments with liquid crystals between plates in 1911.
George H. Heilmeier, an American engineer, made significant enough contributions towards the LCD invention to be inducted into the Hall of Fame of National Inventors. And, in 1968, he presented the liquid crystal display to the professional world, working at an optimal temperature of 80 degrees Celsius.
Many other inventors worked towards the creation of LCDs. As a result, in the 1970s, new inventions focused on ensuring that LCD displays worked at an optimal temperature. And, in the 1980s, they perfected the crystal mixtures enough to stimulate demand and a promotion boom. The first LCDs were produced in 1971 and 1972 by ILIXCO (now LXD Incorporated).
Although they may come in at a higher price point, LCD displays are more convenient in the long run. They last almost twice as long as CRTs are energy efficient, and their compact and thin size make them ideal for modern-day use.
LCDs are also more affordable compared to other display monitors available today. So, you can go for a CRT monitor for its ease of use, faster response rates, reduced flickering, and high pixel resolution. However, we don’t see why you should look back since there are so many new options that will outperform both CRTs and LCDs.

In today’s digital world we are very have seen different types of monitors. We spend most of our time sitting in front of many types of monitors, like playing games, watching movies, and many other things.
Have you wondered which types of monitor are you using to watch TV and playing games? Well, All the 5 types of monitors I have mentioned in this article for you look at which monitor you are using. Let’s get to know.
A good display can be very effective in the user experience. The properties of display devices have also improved a lot due to the innovation in Display Technologies. There are many types of computer monitors available right now, in the case of CRT monitor and plasma maybe not.
LCD is known for‘Liquid Crystal Display’made of liquid crystals. It is the most used monitor worldwide, as it requires less space, consumes less electricity, and produces relatively less heat than an old CRT monitor.
This display was first used in laptops,and later the manufacturers also being produced for Desktop Computers range from 17 inches to 60 inches. Being these monitors need less space and are light in weight, they do not create any trouble in transporting and moving them from one place to another.
Both LCD and LED monitors have considerably more adaptability for positioning the screen in the manner in which you need it. These monitors can turn, tilt up and down, and even rotate from landscape to portrait mode.
LED’s full form is ‘Light Emitting Diode’ is the latest innovation in the market today’s market competing with LCDs and Plasma Monitors. These types of monitors are slightly curved or flat panel displays that use light-emitting diodes for backlighting on the screen instead of cold cathode fluorescent (CCFL) for back-lighting.
LED displays are more bright with 4k resolution than other displays, due to which the user can be read or seen easily in daylight time. LED monitors use less power than LCDs as well as LEDs are widely used by gamers for playing high graphics and HD games.
The advantage of LEDs is that they produce images with higher contrastand vivid colors as well as don’t make a negative impact on the environment at the time of disposing of. In addition, the LEDs are more durable as compared to LCD and CRT Monitors.
The wavelength range of lights utilized is such that to give high quality. These LEDs screen delivers flicker-free image which lessens the eye strain and fatigue, and headaches.
These kinds of monitors have a long life expectancy, use less power, and are thinner greater contrast and more vivid colors, and have a less environmental impact than LCDs.
The price rate of LED monitors can be a little expensive than TVs even after same sized, so they are not affordable for some people at which they are available in the market.
OLED stands for “Organic Light Emitting Diode“. As the name suggests, it is made of organic material (such as carbon, plastic, wood, and polymers), that is used to convert electric current into light.
This is also the latest display technology used in displays of television, computer screen, game consoles, PDAs, or even in the latest smartphones. It can be thinner or lighter with a higher contrast ratio than LCDs
Since these LEDs are capable enough to produce a lot of different colored light, can be used directly to produce the correct color and there is no need for any backlight, which saves power also requires less space. The OLED display is considered great for watching movies.
OLED Monitors are considered the best display technology ever because of their characteristics like wide viewing angles, picture quality, outstanding contrast levels, No ghosting, fast response, and perfect contrast and brightness.
Also, you should protect the monitor from water as it can damage the OLED screen. The other disadvantages of the OLED monitor right now are its short life expectancy than LCDs and LEDs and the high price rate in the market currently.
The basic idea behind its invention is that it illuminates the tiny colored fluorescent lights that create image pixels. Each pixel is made of three fluorescent lights like a tiny neon light-red, green, and blue lights. that produces a superior contrast ratio, along with the intensity of these lights also vary accordingly.
In addition, it has the advantage of slimness, a plasma display is flat rather than slightly curved as an LCDs has. It cuts down image distortion and glare through its perfect flat screens.
A plasma display offers a good response, superior performance, time, and a much wide viewing angle as compared to LCDs. Plasma displays come in sizes up to 60 inches that can be considered the best home theater and HD television.
The major disadvantages of plasma monitors are their limited production and screen sizes. Plasma monitors are heavier in size a well as consume more electricity, on average than LCD monitors.
Here CRT means “Cathode Ray Tube”. Its main part is the Cathode Ray tube which is called the “Generally Picture tube”. The above image is of the CRT monitor and was used a few decades ago as a desktop computer or to watching TV.
CRT monitors are much heavier in size as compared to LCD and LED monitors. Due to being heavy, they have much trouble while moving and transporting from one place to another. Also, they need more space for installation.
As they now disappeared from the market quickly in the last few decades, because display manufacturers switched their production lines from CRT 4:3 displays to LCD 16:9 widescreen displays in order to survive the transition to the digital world widescreen television of LEDs or LCDs.
This monochrome is made up of two words Mono (Single) and Chrome (Color), hence it is called Single Color Display and it displays the monitor’s output in Black & White colors.
These Gray-scale display monitors are similar to monochrome but it displays in gray shades. These types of computer monitors are mostly used in portable and hand computers such as laptops.
Color monitor displays the output with the adjustment of RGB (Red-Green-Blue) radiations. The theory of such monitors is capable of displaying graphics in high-resolution it can be 4k.
Full FormLCD is known for"Liquid Crystal Display."LED"s full form is "Light Emitting Diode."OLED stands for "Organic Light Emitting Diode".Plasma also known as PDP stands for "Plasma Display Panel".CRT stands for "Cathode Ray Tube".
ContrastContrast Ratio ranges between 1000:1 to 4000:1 even more than this.It has higher contrast ratio over 100000:1.It has higher dynamic contrast ratio over 1000000:1.It has contrast ratio over 20000:1.It has contrast ratio over 15000:1.
Weight and SizeLCD monitors are compact in size and light in weight.LEDs are also compact in size and very light in weight.OLEDs are large in size and heavy in weight.Plasma monitors are also large in size and little bit heavy in weight.CRT monitors are bulky in size and very heavy in weight.
There are five types of monitors CRT(Cathode Ray tube), LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), LED (Liquid Emitting Diode), OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode), and Plasma Monitor all are used in televisions or computer desktops.
The following are the five types of monitor: 1. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), 2. LED (Liquid Emitting Diode), 3. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode), 4. CRT(Cathode Ray tube), and 5. Plasma Monitor.
LED displays are more bright with 4k resolution than other displays, due to which they can be read or seen easily in daylight time. LED monitors use less power than LCDs as well as LEDs are widely used by gamers for playing high graphics and HD games.
LCDs are much better than CRT monitors because they are much heavier in size as well as consume a lot of energy compared to LCD monitors. Due to being heavy, they have much trouble while moving and transporting from one place to another. Also, they need more space for installation.
Not at all, CRT monitors being older television sets. As they now disappeared from the market in the last few decades, because display manufacturers discontinued it and switched their production from CRT 4:3 displays to LCD 16:9 widescreen displays in order to survive the transition to the digital world widescreen television of LEDs or LCDs.
In this article, you have known the 5 different types of monitors with different qualities and works. I hope you have learned a new thing today, you can also share this post on social networks. Cheers!
Responsible for performing installations and repairs (motors, starters, fuses, electrical power to machine etc.) for industrial equipment and machines in order to support the achievement of Nelson-Miller’s business goals and objectives:
• Perform highly diversified duties to install and maintain electrical apparatus on production machines and any other facility equipment (Screen Print, Punch Press, Steel Rule Die, Automated Machines, Turret, Laser Cutting Machines, etc.).
• Provide electrical emergency/unscheduled diagnostics, repairs of production equipment during production and performs scheduled electrical maintenance repairs of production equipment during machine service.
Cathode Ray Tubes (CRT) were once the only way to convey pictures. They are large, bulky and consume a lot of power. Liquid Crystal Displays or more commonly known as LCDs are beginning to replace CRTs in most applications today. They are essentially the reverse of what CRTs are, light, thin, and energy efficient. Also, because of the high power consumption of CRT displays, it needs to dissipate a greater amount of energy which makes it run hotter compared to LCDs.
The only aspect where CRT wins over LCD in performance is in the response time. Older LCDs have been plagued with very slow response times that create ghosting effects on the screen whenever there is high speed motion. This made early LCD screens unsuitable for most gaming needs and even in viewing movies, but newer LCDs have improved on it and this is no longer such a big issue.
Understandably, LCDs cost significantly more compared to CRTs in displays of the same size due to the more complex production process that is needed to produce LCDs. But consumers often rationalize that the extra cost is recovered after a while due to the significantly lower power consumption. The physical dimensions of the LCD also meant that it is usable in so many applications where CRTs would simply be impractical to use. Aside from the usual TV screen or computer monitor, LCDs are also used in mobile phones, digital cameras, music players, GPS navigators, and so much more.
A problem that is unique to LCD screens is the dead pixel, which is unheard of in CRT screens. Since LCDs are a matrix of pixels, one or more of these pixels may not function due to irregularities in the production process. This leaves a small dot on the screen that doesn’t change with the display, appearing like a small piece of dirt stuck in there. Most manufacturers would accept and replace screens that have dead pixels in them but it is always best to inquire about the warranty and their dead pixel policy.

The article provides a detailed insight into the difference between CRT and LCD display type of PC monitors. Take time to read through to get awareness.

We often get asked, “should I replace my old CRT with a new LCD? What is the difference?” There are several factors to consider including price, resolution, energy savings and disposal. Listed below are some of the top reasons why the LCD may be a better choice.Size and Weight: The color LCD is thinner and much lighter. It is much easier to install into tight areas. The CRT can weigh up to 50 pounds and needs additional bracing and heavier supports.
Price: At first glance, the CRT wins here. It is older technology and the price is cheaper. However you give up all the features mentioned in this list. Also disposal costs and higher energy costs may negate any price savings.
Power: Energy savings on the LCD can make a big difference in companies having multiple units in production. Savings can be as much as 1/3 over the older CRT.
Summary: Based on price alone, you may choose to stay with the CRT. However, you must consider the energy cost savings to operate an LCD vs. CRT, plus the added cost of disposal for CRTs. In many instances, the CRT may actually cost more in the long run. With its large, high resolution screen and compact housing for easy installation, the LCD offers many advantages over the older CRT technology.

Monitors are the most important components of a computer. Without them, you could not read this article, play games (see top Fortnite monitors), or even watch movies.
So, what are the types of monitors? There are basically 6 types of monitors currently being sold by major manufacturers. They include LCD Monitor, LED Monitor, OLED Monitor, Plasma Monitor, CRT Monitor, and Touch Screen Monitors.
In this guide, I’ve discussed the different types of monitors that are available on the market, with details on their benefits and drawbacks, including screen size (see Dell"s 27-inch monitor), resolutions, refresh rates, technologies used, and more.
The history of computer monitors can be traced back to the Cathode Ray Tube, which was invented by Karl Ferdinand Braun in 1897. These types of monitors were bulky and consumed a lot of power.
As technology advanced, displays became less bulky and gained newer features, while resolutions increased. The CRT lasted all the way up until 1992 and since then we have seen a variety of monitors and display types such as Plasma monitors which lasted until 2014, and LCD and LED monitors take over as technology advanced.
An LCD monitor is a flat-panel display that uses liquid crystal technology to produce images. The image quality depends on the quality of the screen (the clarity) and not the size of the screen like with older CRT monitors.
Generally, LCD monitors offer crisp images and good contrast than their previous counterparts. These types of monitors are not as thin and lightweight as IPS monitors, but are also energy-efficient.
LCDs can offer higher resolution than other display technologies, including those that use cathode ray tubes (CRTs). The average price of LCD monitors ranges from $100 to $250. Top LCD monitors include monitors from LG, Samsung, and Boe.
An LCD monitor with flat-screen technology takes up less space with its slim design and it is more lightweight than normal CRT monitors. It does not require additional desktop space because the screen of the monitor is slim.
The LED monitor is the most energy-efficient available and it doesn"t take up much space at all. This is a great way to save some cash on your electric bills and still get the same crisp picture as the big TVs but in a smaller size.
IPS panels are now widely used in the manufacture of LCD monitors, due to their high-quality images, fast response times, and wide viewing angles. IPS panels are preferred over TN displays by web designers who require accurate color reproduction and good image quality for their work.
When compared to other LCD panel technologies such as inPlane Switching (IPS) and Vertical Alignment (VA), the twisted Nematic (TN) LCD panel technology delivers a higher faster response time making it the best panel type for monitors for games like League of Legends.
Vertical alignment (VA) panels are LCD technology that has many advantages over the existing TN displays. They are known for their high brightness, high contrast ratio, and ability to be viewed at many different angles.
An LED monitor is an advanced type of flat panel display that uses Light-Emitting Diodes for illumination. Compared to standard LCDs, an LED panel display is thinner and utilizes less power than LCD monitors. The benefits of LED monitors are also fully explained here.
This is particularly relevant for video editing (see also best editing monitors), graphic design enthusiasts, gamers, and PC users in general. They offer a wide array of other features and prices so anyone can choose the one that meets their needs. And, before you decide on a budget monitor bear in mind that some monitors prioritize different features or might have different aspects that will be useful to you. However, if you are not a PC user, don"t fret, but check out our earlier reviews of monitors for MacBook Pro.
The average price of LED pc monitor type is from $150 to $400. With some luck, you can pick up a nice high definition monitor for under 200 dollars, or for even less.
Just like the name suggests, an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) monitor is a type of flat panel display that produces its own light. OLED monitors gives you several advantages over traditional LCD monitors, including thinner panels and the use of less energy
Due to the fact it doesn"t produce any toxic waste products during use, OLED is also friendlier on the environment than an LCD or plasma display. QLED monitors (see QLED vs IPS review) though have tried to replicate the best picture quality features of OLED along with far superior brightness and colours..
They are ideal for video professional users who work in the fields of computer graphics design, animation, 3D animation, digital video editing, broadcasting, simulation, and home entertainment, etc, though monitors for music production may come with different features. Lastly, you can read the full guide to features and benefits of OLED in our artricle here.
Plasma monitors are flat-screen monitors that use phosphors gas to provide color. Because the picture is produced by gases instead of light bulbs or other heat sources, they are exceptionally thin and therefore can be mounted on walls.
Plasma monitors have exceptional brightness and color power. Millions of red, green, and blue cells light your screen with light so pure and bright, making them brighter than CRT monitors and LCD monitors.
This computer display type has the largest screens available such as 42 inches, 50 inches, and even 56 inches, and their bright colorful images can be viewed from virtually any angle. Plasma monitors also offer wide-angle views that create a cinematic effect that is perfect for watching sports, gaming, or viewing a video.
The cons of using a plasma monitor are that it is susceptible to burn-in due to the use of a phosphor screen. It also has a shorter lifespan because the gas wears out eventually and this reduces its brightness. The average price for plasma displays ranges from $50 for a 19-inch display to $500 for a 50 inch.
Various monitor brands that make plasma displays include Panasonic, Toshiba, and LG. Some monitor brands such as Samsung and LG have ceased making these types of monitors since they have been replaced by better technologies, such as LCD, LED, and OLED monitors.
An old-fashioned computer monitor, or CRT (cathode ray tube) display, is one of the main types of computer monitors. They are large and bulky monitors that come equipped with a bulky box that connects to the back of them.
This analog display was a popular display device before the invention of modern flat-screen monitors and TVs. The electron gun in the interior is the part that creates the image on the screen.
CRT monitors have been around since the late 1940s and were commonly used until the second decade of the 21st century. Now they are being replaced by newer technology monitors such as LCD or plasma screens, which offer clearer images and more flexibility in viewing angles.
These monitors are used in business and office environments mostly. They offer a more convenient method to access information and perform tasks without the hassle of a keyboard or mouse.
Each type has its own unique set of benefits—some offer better color accuracy than others, while some display deeper blacks. Since monitors have different uses and have different features, it is important to get a display that will serve your needs.
Business monitors; Business monitors are workstation-optimized, full-featured displays that meet the needs of your business from the desktop to the boardroom.
These monitors generally have higher resolution, high refresh rate, low response time, and more options than a typical home monitor, and are often made with energy efficiency in mind.
Gaming monitors; Gaming monitors like these for racing games are specifically designed for gamers because they feature fast response time, vivid graphics, and incredible refresh rate that goes up to 240Hz, all of which will improve a gaming experience. It could be argued though that 144hz monitors offer best of both worlds when it comes to performance and price, in addition to having a 1ms response time.
This is also where generally cheaper G-Sync monitors, developed by AMD and NVIDIA, come into equation with their linking of framerate and refresh rate to smooth out your visuals and enhance the gaming performance.
Ultrawide Monitors; these are super large monitors. They are an excellent choice for multitasking, with two or even three times the screen real estate of a standard monitor. Stay organized with multiple columns or spreadsheets or give your games an immersive feel with an ultra-wide computer monitor.
Work monitors; Work monitors are monitors that are designed for use in an office environment. Oftentimes, workstation monitors are special because they are very thin, have special features that will help the workspace, give you more room - especially curved monitors - and are optimized for tasks such as editing spreadsheets and word processing.
As technology advances, new devices emerge every now and then. Computer monitors are no different. LCDs replaced CRT monitors and plasma monitors, and then came along LED monitors.
LCD monitors are flat-panel monitors that use liquid crystal display technology to create the image displayed. These flat panels have replaced the bulky cathode ray tube monitors previously in use in most computer workstations.
This means that an LCD monitor like this by AOC is more portable, which makes it easier to transport from one location to another - see how they compare to other portable monitors such as this one from Asus or this one from Lenovo.
One of the biggest advantages of this type of PC display is probably their crystal-clear picture quality. An LCD monitor has a higher resolution and a sharper, crisper image than a CRT, and has far less glare than the latter.
One disadvantage with LCD monitors is that they are a bit expensive than other types of monitors such as plasma but are totally worth it because of their superior features.
This monochrome is made up of two words Mono (Single) and Chrome (Color), hence it is called Single Color Display and it displays the monitor’s output in Black & White colors.
These Gray-scale display monitors are similar to monochrome but it displays in gray shades. These types of computer monitors are mostly used in portable and hand computers such as laptops.
Color monitor displays the output with the adjustment of RGB (Red-Green-Blue) radiations. The theory of such monitors is capable of displaying graphics in high-resolution it can be 4k.
Computer monitors are such important PC components that are well worth spending time choosing the right model. If the display is the only piece of computer hardware you"re planning to upgrade this year, it"s imperative that you find a monitor that excels in all areas: image quality, color reproduction, connectivity options, and ergonomics.
This section will help you sort through all the available models and give sound advice on how to choose one, so you"ll learn exactly what makes one screen better than another.
If you are planning to buy one of the best monitors for your office or home, consider the size of a monitor. There are different sizes which are manufactured by different companies (see this 23.8 monitor by HP). Some are bigger while some are smaller in size like this 21.5"" monitor by HP. You can choose one according to your needs and requirements.
A large monitor will enable you to have more screen real estate for spreadsheets, documents and texts, programs (see monitors for programming), playing games, or watching movies.
An important factor to consider is the resolution of the monitor. Resolution determines how clear (sharp) or how vibrant (colorful) your monitor produces images and text on the screen.
If you are looking to get the best gaming experience from a monitor, I’d highly recommend you go for the highest possible resolution. However, if you do not game or use it for video or photo editing purposes, then I’d suggest you keep it simple by going with 1080p screens instead of spending extra on monitor with 4K resolution or higher.
If you are in the market for the best type of monitor for graphic design, there is one key feature that will help determine performance: color gamut. Color gamut is an indication of how many colors a screen can display. Top color performance and resolution, is also what most monitors for architects should come with. This also includes monitors for CAD.
While there are computer monitor screen types that use larger color gamuts than others, the most important thing to know is that wider color gamuts offer better picture quality than lower ones. They also allow more colors to be displayed on the screen at once, so images with many colors will appear richer and more vivid.
There are four connection types of monitors. Through these options, you can connect your video source, like game console, to a monitor for Xbox, for example. Monitor connection types include;A VGA connection
There are three different types of panels that are available in monitors today. One of the most popular monitor panel types is the Twisted Nematic (TN) monitor. The second monitor panel type is the Vertical Alignment (VA) monitor. Finally, there is the In-Plane Switching or IPS monitors.
The best monitor types are LCDs. With LCD computer displays, you have high-quality screens, which offer HD or higher resolution like QHD technology. They are thin and flat, have a high refresh rate, and wider color gamut unlike other types of monitors such as CRTs.
The most affordable monitor types will not be plasma or LCDs. It is actually CRTs or Cathode Ray Tubes. You can purchase one for approximately $30-$50. The price will depend on the size of the screen, and you can purchase a 19-inch screen for $30 -$50. They are available in sizes ranging from 13 inches to 24 inch monitors.
We all work on the computer, either for business or pleasure. So, it is important to have the best monitor for your eyes when working long hours behind the computer. The best monitors out there are these monitors from AOC that are flicker-free and blue light-free and include;AOC C27G2Z
LCD monitors are. Along with LED, LCD is the most common type of monitor you will find available currently. LCD monitors consist of two panes of glass with liquid in between and thousands of rows of pixels to organize said liquid.
TVs offer a PC Mode option, which removes the extra image processing and ensures the lowest possible input lag. The most important thing to consider when choosing a TV for PC monitor usage is the TV"s ability to display proper chroma 4:4:4 for clear text.
23/24-inch screen in 16:9 format: resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels (also known as Full-HD). 23/24-inch screens with a 16:10 aspect ratio are even better. This comes with a resolution of at least 1920 × 1200 pixels (WUXGA).

Glass substrate with ITO electrodes. The shapes of these electrodes will determine the shapes that will appear when the LCD is switched ON. Vertical ridges etched on the surface are smooth.
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directlybacklight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.seven-segment displays, as in a digital clock, are all good examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs can either be normally on (positive) or off (negative), depending on the polarizer arrangement. For example, a character positive LCD with a backlight will have black lettering on a background that is the color of the backlight, and a character negative LCD will have a black background with the letters being of the same color as the backlight. Optical filters are added to white on blue LCDs to give them their characteristic appearance.
LCDs are used in a wide range of applications, including LCD televisions, computer monitors, instrument panels, aircraft cockpit displays, and indoor and outdoor signage. Small LCD screens are common in LCD projectors and portable consumer devices such as digital cameras, watches, digital clocks, calculators, and mobile telephones, including smartphones. LCD screens are also used on consumer electronics products such as DVD players, video game devices and clocks. LCD screens have replaced heavy, bulky cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays in nearly all applications. LCD screens are available in a wider range of screen sizes than CRT and plasma displays, with LCD screens available in sizes ranging from tiny digital watches to very large television receivers. LCDs are slowly being replaced by OLEDs, which can be easily made into different shapes, and have a lower response time, wider color gamut, virtually infinite color contrast and viewing angles, lower weight for a given display size and a slimmer profile (because OLEDs use a single glass or plastic panel whereas LCDs use two glass panels; the thickness of the panels increases with size but the increase is more noticeable on LCDs) and potentially lower power consumption (as the display is only "on" where needed and there is no backlight). OLEDs, however, are more expensive for a given display size due to the very expensive electroluminescent materials or phosphors that they use. Also due to the use of phosphors, OLEDs suffer from screen burn-in and there is currently no way to recycle OLED displays, whereas LCD panels can be recycled, although the technology required to recycle LCDs is not yet widespread. Attempts to maintain the competitiveness of LCDs are quantum dot displays, marketed as SUHD, QLED or Triluminos, which are displays with blue LED backlighting and a Quantum-dot enhancement film (QDEF) that converts part of the blue light into red and green, offering similar performance to an OLED display at a lower price, but the quantum dot layer that gives these displays their characteristics can not yet be recycled.
Since LCD screens do not use phosphors, they rarely suffer image burn-in when a static image is displayed on a screen for a long time, e.g., the table frame for an airline flight schedule on an indoor sign. LCDs are, however, susceptible to image persistence.battery-powered electronic equipment more efficiently than a CRT can be. By 2008, annual sales of televisions with LCD screens exceeded sales of CRT units worldwide, and the CRT became obsolete for most purposes.
Each pixel of an LCD typically consists of a layer of molecules aligned between two transparent electrodes, often made of Indium-Tin oxide (ITO) and two polarizing filters (parallel and perpendicular polarizers), the axes of transmission of which are (in most of the cases) perpendicular to each other. Without the liquid crystal between the polarizing filters, light passing through the first filter would be blocked by the second (crossed) polarizer. Before an electric field is applied, the orientation of the liquid-crystal molecules is determined by the alignment at the surfaces of electrodes. In a twisted nematic (TN) device, the surface alignment directions at the two electrodes are perpendicular to each other, and so the molecules arrange themselves in a helical structure, or twist. This induces the rotation of the polarization of the incident light, and the device appears gray. If the applied voltage is large enough, the liquid crystal molecules in the center of the layer are almost completely untwisted and the polarization of the incident light is not rotated as it passes through the liquid crystal layer. This light will then be mainly polarized perpendicular to the second filter, and thus be blocked and the pixel will appear black. By controlling the voltage applied across the liquid crystal layer in each pixel, light can be allowed to pass through in varying amounts thus constituting different levels of gray.
The chemical formula of the liquid crystals used in LCDs may vary. Formulas may be patented.Sharp Corporation. The patent that covered that specific mixture expired.
Most color LCD systems use the same technique, with color filters used to generate red, green, and blue subpixels. The LCD color filters are made with a photolithography process on large glass sheets that are later glued with other glass sheets containing a TFT array, spacers and liquid crystal, creating several color LCDs that are then cut from one another and laminated with polarizer sheets. Red, green, blue and black photoresists (resists) are used. All resists contain a finely ground powdered pigment, with particles being just 40 nanometers across. The black resist is the first to be applied; this will create a black grid (known in the industry as a black matrix) that will separate red, green and blue subpixels from one another, increasing contrast ratios and preventing light from leaking from one subpixel onto other surrounding subpixels.Super-twisted nematic LCD, where the variable twist between tighter-spaced plates causes a varying double refraction birefringence, thus changing the hue.
LCD in a Texas Instruments calculator with top polarizer removed from device and placed on top, such that the top and bottom polarizers are perpendicular. As a result, the colors are inverted.
The optical effect of a TN device in the voltage-on state is far less dependent on variations in the device thickness than that in the voltage-off state. Because of this, TN displays with low information content and no backlighting are usually operated between crossed polarizers such that they appear bright with no voltage (the eye is much more sensitive to variations in the dark state than the bright state). As most of 2010-era LCDs are used in television sets, monitors and smartphones, they have high-resolution matrix arrays of pixels to display arbitrary images using backlighting with a dark background. When no image is displayed, different arrangements are used. For this purpose, TN LCDs are operated between parallel polarizers, whereas IPS LCDs feature crossed polarizers. In many applications IPS LCDs ha




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey