4 differences between crt and lcd monitors for sale
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CRT-vs-LCD-monitor-cfe0b6f375b542928baf22a0478a57a3.jpg)
CRT stands for Cathode Ray Tube and LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display area unit the kinds of display devices wherever CRT is employed as standard display devices whereas LCD is more modern technology. These area unit primarily differentiated supported the fabric they’re made from and dealing mechanism, however, each area unit alleged to perform identical perform of providing a visible variety of electronic media. Here, the crucial operational distinction is that the CRT integrates the 2 processes lightweight generation and lightweight modulation and it’s additionally managed by one set of elements. Conversely, the LCD isolates the 2 processes kind one another that’s lightweight generation and modulation.
Since the production of cathode ray tubes has essentially halted due to the cost and environmental concerns, CRT-based monitors are considered an outdated technology. All laptops and most desktop computer systems sold today come with LCD monitors. However, there are a few reasons why you might still prefer CRT over LCD displays.
While CRT monitors provide better color clarity and depth, the fact that manufacturers rarely make them anymore makes CRTs an unwise choice. LCD monitors are the current standard with several options. LCD monitors are smaller in size and easier to handle. Plus, you can buy LCD monitors in a variety of sizes, so customizing your desktop without all the clutter is easy.
The primary advantage that CRT monitors hold over LCDs is color rendering. The contrast ratios and depths of colors displayed on CRT monitors are better than what an LCD can render. For this reason, some graphic designers use expensive and large CRT monitors for their work. On the downside, the color quality degrades over time as the phosphors in the tube break down.
Another advantage that CRT monitors hold over LCD screens is the ability to easily scale to various resolutions. By adjusting the electron beam in the tube, the screen can be adjusted downward to lower resolutions while keeping the picture clarity intact. This capability is known as multisync.
The biggest disadvantage of CRT monitors is the size and weight of the tubes. An equivalently sized LCD monitor can be 80% smaller in total mass. The larger the screen, the bigger the size difference. CRT monitors also consume more energy and generate more heat than LCD monitors.
For the most vibrant and rich colors, CRTs are hard to beat if you have the desk space and don"t mind the excessive weight. However, with CRTs becoming a thing of the past, you may have to revisit the LCD monitor.
The biggest advantage of LCD monitors is the size and weight. LCD screens also tend to produce less eye fatigue. The constant light barrage and scan lines of a CRT tube can cause strain on heavy computer users. The lower intensity of the LCD monitors coupled with the constant screen display of pixels being on or off is easier on the eyes. That said, some people have issues with the fluorescent backlights used in some LCD displays.
The most notable disadvantage to LCD screens is the fixed resolution. An LCD screen can only display the number of pixels in its matrix. Therefore, it can display a lower resolution in one of two ways: using only a fraction of the total pixels on the display, or through extrapolation. Extrapolation blends multiple pixels together to simulate a single smaller pixel, which often leads to a blurry or fuzzy picture.
For those who are on a computer for hours, an LCD can be an enemy. With the tendency to cause eye fatigue, computer users must be aware of how long they stare at an LCD monitor. While LCD technology is continually improving, using techniques to limit the amount of time you look at a screen alleviates some of that fatigue.
Significant improvements have been made to LCD monitors over the years. Still, CRT monitors provide greater color clarity, faster response times, and wider flexibility for video playback in various resolutions. Nonetheless, LCDs will remain the standard since these monitors are easier to manufacture and transport. Most users find LCD displays to be perfectly suitable, so CRT monitors are only necessary for those interested in digital art and graphic design.

Distinguish, differentiate, compare and explain what is the differences between CRT and LCD Monitor. Comparison and Difference. As the technology has improved and the prices have come down, LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) monitors have rapidly been replacing CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) monitors on desktops around the world. ComputerWorld first reported that LCD sales would surpass CRT sales for the first time in 2003, a lead that it didnt hold for good. But according to DisplaySearch, a flat panel display market research and consulting company, the sales of LCD monitors regained the lead over CRT sales in the third quarter of 2004, a lead that it should eventually hold for good.

Following are the important differences between CRT and LCD.Sr. No.KeyCRTLCD1DefinitionCRT stands for Cathode Ray Tube.LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display.

There are two primary types of computer monitors in use today: LCD monitors and CRT monitors. Nearly every modern desktop computer is attached to an LCD monitor. This page compares the pros and cons of both the CRT type displays and LCD or flat-panel type displays. You"ll quickly discover that the LCD or flat-panel displays pretty much sell themselves and why they are the superior display used today.
LCD monitors are much thinner than CRT monitors, being only a few inches in thickness (some can be nearly 1" thick). They can fit into smaller, tighter spaces, whereas a CRT monitor can"t in most cases.
Although a CRT can have display issues, there is no such thing as a dead pixel on a CRT monitor. Many issues can also be fixed by degaussing the monitor.
LCD monitors have a slightly bigger viewable area than a CRT monitor. A 19" LCD monitor has a diagonal screen size of 19" and a 19" CRT monitor has a diagonal screens size of about 18".
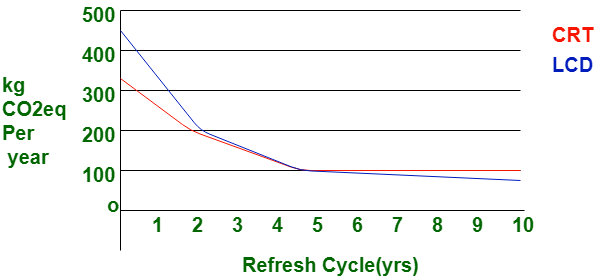
If you are looking for a new display, you should consider the differences between CRT and LCD monitors. Choose the type of monitor that best serves your specific needs, the typical applications you use, and your budget.
Require less power - Power consumption varies greatly with different technologies. CRT displays are somewhat power-hungry, at about 100 watts for a typical 19-inch display. The average is about 45 watts for a 19-inch LCD display. LCDs also produce less heat.
Smaller and weigh less - An LCD monitor is significantly thinner and lighter than a CRT monitor, typically weighing less than half as much. In addition, you can mount an LCD on an arm or a wall, which also takes up less desktop space.
More adjustable - LCD displays are much more adjustable than CRT displays. With LCDs, you can adjust the tilt, height, swivel, and orientation from horizontal to vertical mode. As noted previously, you can also mount them on the wall or on an arm.
Less eye strain - Because LCD displays turn each pixel off individually, they do not produce a flicker like CRT displays do. In addition, LCD displays do a better job of displaying text compared with CRT displays.
Better color representation - CRT displays have historically represented colors and different gradations of color more accurately than LCD displays. However, LCD displays are gaining ground in this area, especially with higher-end models that include color-calibration technology.
More responsive - Historically, CRT monitors have had fewer problems with ghosting and blurring because they redrew the screen image faster than LCD monitors. Again, LCD manufacturers are improving on this with displays that have faster response times than they did in the past.
Multiple resolutions - If you need to change your display"s resolution for different applications, you are better off with a CRT monitor because LCD monitors don"t handle multiple resolutions as well.
So now that you know about LCD and CRT monitors, let"s talk about how you can use two monitors at once. They say, "Two heads are better than one." Maybe the same is true of monitors!
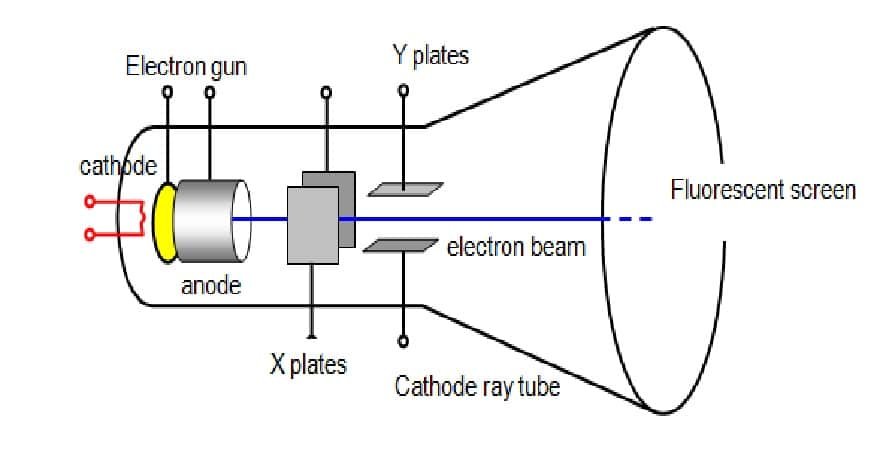
You might have used a large bulk size of the computer monitor in your childhood; it is the CRT monitor. Nowadays you are seeing that those types of monitors are disappearing and some slim-looking monitors are taking their place; these are the LCD and LED monitors. It has become our reality due to a fast technological advancement during the last few decades. In today’s topic, we will analyze CRT vs LCD monitors; their relative comparison, and try to figure out the differences.
The full form of CRT is Cathode Ray Tube. The CRT monitor is one kind of display unit. It is one of the oldest types of monitor. Although the use of CRT monitors is becoming obsolete with the invention of smarter monitors and TVs, you can still find them on the market because it is still useful in many cases.
The CRT monitor has a coating of phosphor inside the tube. An electron gun is a crucial component of a CRT monitor. The black and white CRT monitor has got only one electron gun; on the other hand, the colored one has got three different electron guns- red, green, and blue. The electrons emitted from the electron guns strike on the phosphor dots; thus the dots become ablaze which in turn represent us as pictures.
The full form of LCD is Liquid Crystal Display. This kind of display unit uses transparent liquid crystals to produce pictures. The crystals are charged up electrically and we are able to watch the display. The LCD monitor is a flat one; hence also called a Flat Panel Monitor. Its refresh rate is also higher.
The LCD display is used on the calculator and digital watch. The laptop and netbook extensively use LCD monitors for the display unit. A flat-panel monitor is also available for desktop PC, but the price is quite high. It can generally be connected through DVI or HDMI cables. But what are the actual differences in terms of CRT vs LCD monitors? The next sections will clear your all questions.
The difference between the CRT monitor and LCD monitor is mainly based upon the technology used for the make-up of the two and also the user-friendliness. Both types of monitors have their pros and cons, different usability, and function-ability. In this section, we will try to explain CRT vs LCD keeping in mind these facts.
The CRT monitor is the older type of display unit; whereas the LCD monitor is more of a recent invention. Hence, we can easily say that the CRT monitor is more conventional than the LCD monitor.
CRT monitors function on the basis of electron beams originating from the electron beam and hitting the phosphor dots. On the other hand, the operation of LCD monitors is based upon liquid crystals being charged up electrically. Both the monitors’ ultimate goal is to produce pictures not only in the form of still images but also in the form of motion.
LCD monitors use up much less power than CRT monitors. In fact, an LCD monitor consumes 3 to 4 times less power than a CRT monitor. It is one of the biggest advantages of LCD monitors.
You may have found out that as technology advances, gadgets are becoming smaller and smaller. It is of course done for getting the advantages of portability. The same case has happened in the evolution of the monitor. CRT monitor being the older one possesses a sizable body structure; whereas the LCD displays are slim and very small in size.
The CRT monitor is very heavy because it has to carry a weighted electron gun. An average-sized CRT monitor weighs generally 20 to 25 kg. The LCD monitor has a great edge in this respect. An LCD monitor generally weighs 4 to 6 kg which makes it easy to handle.
Image flickering is the frame disturbances on the monitor; a series of frames can not appear flawlessly as a blank frame causes two frames to set apart. This annoys a viewer to a great extent. CRT monitors have more problems with image flickering than LCD monitors.
Image persistence or image retention is the nature of a picture remaining static for a period of time. The CRT monitor does not have image persistence which the LCD monitor does possess. Although being an old monitor, the CRT monitor has an edge over the LCD monitor in this regard.
A CRT monitor has got some extra space around the main display, and this extra space is totally useless. The LCD monitor covers almost the full display as the viewing area and thus making it more efficient.
CRT monitors are better for wide viewing; you can watch a CRT TV from different sections of your room in a much better way compared to the LCD monitors.
The refresh rate of a monitor is one of the most important things that must be considered. Most LCD monitors produce a minimum refresh rate of around 200Hz; whereas the refresh rate of CRT monitors ranges between 70 to 80 Hz on average. Therefore, the resolution of the LCD monitor is much higher than that of the CRT monitor. Also, the G-sync monitor made the viewing experience awesome.
All the television sets used to be made of CRT mechanism in the old times. Computer manufacturers were also making CRT monitors with the limitation of the technology. These monitors are still available, but their use is becoming less and less with time.
LCD monitors have taken the place of old CRT monitors. LCD monitors are extensively used for personal computers, laptops, netbooks, digital watches, calculators, television, and whatnot. You can easily set up dual monitor or triple monitor for convenient usage.
Both the CRT and LCD monitors have their advantages and disadvantages in several aspects. The newer technology will always replace the older ones; even the LED monitors are replacing the LCDs in recent times. No matter old or new; you should buy a monitor according to your need and choice. After reading the article, you should know all about CRT vs LCD monitors and their key differences.

A cathode-ray tube monitor is a display device used in television sets and computer monitors. It is a kind of vacuum tube which contains one or more electron guns, electrostatic deflection plates and a phosphor target which is located at the back of the glass screen.
In computer or in a television set, images and color are produced by shooting and controlling the electrons beams representing each additive color light (red, blue and green) using the video signal as the reference. The brightness, color and persistence of the illumination can be varied using different kinds of phosphor.
Cathode ray tubes (CRTs) have an electron gun at the end of the monitor tube. The electron gun emits electron beam that strikes the phosphors dots on the monitor screen.

Responsible for performing installations and repairs (motors, starters, fuses, electrical power to machine etc.) for industrial equipment and machines in order to support the achievement of Nelson-Miller’s business goals and objectives:
• Perform highly diversified duties to install and maintain electrical apparatus on production machines and any other facility equipment (Screen Print, Punch Press, Steel Rule Die, Automated Machines, Turret, Laser Cutting Machines, etc.).
• Provide electrical emergency/unscheduled diagnostics, repairs of production equipment during production and performs scheduled electrical maintenance repairs of production equipment during machine service.

In today’s digital world we are very have seen different types of monitors. We spend most of our time sitting in front of many types of monitors, like playing games, watching movies, and many other things.
Have you wondered which types of monitor are you using to watch TV and playing games? Well, All the 5 types of monitors I have mentioned in this article for you look at which monitor you are using. Let’s get to know.
A good display can be very effective in the user experience. The properties of display devices have also improved a lot due to the innovation in Display Technologies. There are many types of computer monitors available right now, in the case of CRT monitor and plasma maybe not.
LCD is known for‘Liquid Crystal Display’made of liquid crystals. It is the most used monitor worldwide, as it requires less space, consumes less electricity, and produces relatively less heat than an old CRT monitor.
This display was first used in laptops,and later the manufacturers also being produced for Desktop Computers range from 17 inches to 60 inches. Being these monitors need less space and are light in weight, they do not create any trouble in transporting and moving them from one place to another.
Both LCD and LED monitors have considerably more adaptability for positioning the screen in the manner in which you need it. These monitors can turn, tilt up and down, and even rotate from landscape to portrait mode.
LED’s full form is ‘Light Emitting Diode’ is the latest innovation in the market today’s market competing with LCDs and Plasma Monitors. These types of monitors are slightly curved or flat panel displays that use light-emitting diodes for backlighting on the screen instead of cold cathode fluorescent (CCFL) for back-lighting.
LED displays are more bright with 4k resolution than other displays, due to which the user can be read or seen easily in daylight time. LED monitors use less power than LCDs as well as LEDs are widely used by gamers for playing high graphics and HD games.
The advantage of LEDs is that they produce images with higher contrastand vivid colors as well as don’t make a negative impact on the environment at the time of disposing of. In addition, the LEDs are more durable as compared to LCD and CRT Monitors.
The wavelength range of lights utilized is such that to give high quality. These LEDs screen delivers flicker-free image which lessens the eye strain and fatigue, and headaches.
These kinds of monitors have a long life expectancy, use less power, and are thinner greater contrast and more vivid colors, and have a less environmental impact than LCDs.
The price rate of LED monitors can be a little expensive than TVs even after same sized, so they are not affordable for some people at which they are available in the market.
OLED stands for “Organic Light Emitting Diode“. As the name suggests, it is made of organic material (such as carbon, plastic, wood, and polymers), that is used to convert electric current into light.
This is also the latest display technology used in displays of television, computer screen, game consoles, PDAs, or even in the latest smartphones. It can be thinner or lighter with a higher contrast ratio than LCDs
Since these LEDs are capable enough to produce a lot of different colored light, can be used directly to produce the correct color and there is no need for any backlight, which saves power also requires less space. The OLED display is considered great for watching movies.
OLED Monitors are considered the best display technology ever because of their characteristics like wide viewing angles, picture quality, outstanding contrast levels, No ghosting, fast response, and perfect contrast and brightness.
Also, you should protect the monitor from water as it can damage the OLED screen. The other disadvantages of the OLED monitor right now are its short life expectancy than LCDs and LEDs and the high price rate in the market currently.
The basic idea behind its invention is that it illuminates the tiny colored fluorescent lights that create image pixels. Each pixel is made of three fluorescent lights like a tiny neon light-red, green, and blue lights. that produces a superior contrast ratio, along with the intensity of these lights also vary accordingly.
In addition, it has the advantage of slimness, a plasma display is flat rather than slightly curved as an LCDs has. It cuts down image distortion and glare through its perfect flat screens.
A plasma display offers a good response, superior performance, time, and a much wide viewing angle as compared to LCDs. Plasma displays come in sizes up to 60 inches that can be considered the best home theater and HD television.
The major disadvantages of plasma monitors are their limited production and screen sizes. Plasma monitors are heavier in size a well as consume more electricity, on average than LCD monitors.
Here CRT means “Cathode Ray Tube”. Its main part is the Cathode Ray tube which is called the “Generally Picture tube”. The above image is of the CRT monitor and was used a few decades ago as a desktop computer or to watching TV.
CRT monitors are much heavier in size as compared to LCD and LED monitors. Due to being heavy, they have much trouble while moving and transporting from one place to another. Also, they need more space for installation.
As they now disappeared from the market quickly in the last few decades, because display manufacturers switched their production lines from CRT 4:3 displays to LCD 16:9 widescreen displays in order to survive the transition to the digital world widescreen television of LEDs or LCDs.
This monochrome is made up of two words Mono (Single) and Chrome (Color), hence it is called Single Color Display and it displays the monitor’s output in Black & White colors.
These Gray-scale display monitors are similar to monochrome but it displays in gray shades. These types of computer monitors are mostly used in portable and hand computers such as laptops.
Color monitor displays the output with the adjustment of RGB (Red-Green-Blue) radiations. The theory of such monitors is capable of displaying graphics in high-resolution it can be 4k.
Full FormLCD is known for"Liquid Crystal Display."LED"s full form is "Light Emitting Diode."OLED stands for "Organic Light Emitting Diode".Plasma also known as PDP stands for "Plasma Display Panel".CRT stands for "Cathode Ray Tube".
ContrastContrast Ratio ranges between 1000:1 to 4000:1 even more than this.It has higher contrast ratio over 100000:1.It has higher dynamic contrast ratio over 1000000:1.It has contrast ratio over 20000:1.It has contrast ratio over 15000:1.
Weight and SizeLCD monitors are compact in size and light in weight.LEDs are also compact in size and very light in weight.OLEDs are large in size and heavy in weight.Plasma monitors are also large in size and little bit heavy in weight.CRT monitors are bulky in size and very heavy in weight.
There are five types of monitors CRT(Cathode Ray tube), LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), LED (Liquid Emitting Diode), OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode), and Plasma Monitor all are used in televisions or computer desktops.
The following are the five types of monitor: 1. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), 2. LED (Liquid Emitting Diode), 3. OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode), 4. CRT(Cathode Ray tube), and 5. Plasma Monitor.
LED displays are more bright with 4k resolution than other displays, due to which they can be read or seen easily in daylight time. LED monitors use less power than LCDs as well as LEDs are widely used by gamers for playing high graphics and HD games.
LCDs are much better than CRT monitors because they are much heavier in size as well as consume a lot of energy compared to LCD monitors. Due to being heavy, they have much trouble while moving and transporting from one place to another. Also, they need more space for installation.
Not at all, CRT monitors being older television sets. As they now disappeared from the market in the last few decades, because display manufacturers discontinued it and switched their production from CRT 4:3 displays to LCD 16:9 widescreen displays in order to survive the transition to the digital world widescreen television of LEDs or LCDs.
In this article, you have known the 5 different types of monitors with different qualities and works. I hope you have learned a new thing today, you can also share this post on social networks. Cheers!
![]()
Summary: Difference Between CRT and LCD is that CRTis a desktop/pc monitor that contains a cathode-ray tube. A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a large, sealed glass tube.
Picture slightly less natural and “filmlike” than plasmas; slower refresh rate; limited viewing angle; blacks are brighter; susceptible to burn-out and image persistence; dead or stuck pixels may appear
The obsolescence of CRT monitors requires replacing stimulators used for eliciting VEPs with new monitors. Currently, LCD monitors are the only suitable alternative, however other technologies, like OLED, may become a viable option [23]. So far, the ISCEV extended protocol for VEP methods of estimation of visual acuity recommends ensuring luminance artifacts caused by non-CRT stimulators [9], which can be achieved by reducing the stimulus contrast [23]. However, this may not be possible without falling below the minimum contrast values recommended for VEP [1, 23]. Since LCD stimulators have been shown to result in mostly a delay in the VEP responses [2,3,4, 23] but seem not to affect the size of the amplitudes [2], we expected no difference between the estimated visual acuity by using LCD or CRT monitors used as a stimulator for the sweep VEP.
The results of the first experiment show statistically significant effects of the monitor type on the time-to-peak after stimulus onset and the peak-to-trough amplitude (Table 1). The mean delay of the time-to-peak after stimulus onset between recordings obtained using the LCD and the CRT monitor was about 60 ms, which is quite high and possibly caused by the relatively old LCD monitor used. Accordingly, statistically significant effects on the time-to-peak after stimulus onset and the peak-to-trough amplitude were found for the monitor/contrast combination in the results of the second experiment (Table 4). Surprisingly, the mean delay of the time-to-peak after stimulus onset of the CRT monitors with high contrast was with up to 151 ms, longer (Table 5) than that of the LCD monitors (with low and high contrast), although one would expect modern monitors to have shorter or even no delays [24, 25]. Additionally, a statistically significant interaction between the spatial frequency and the monitor type was revealed in both experiments, causing an increased time delay for the intermediate spatial frequencies (1.4–10.3 cpd) with LCD stimulation (Fig. 2, top left) in the first experiment and an almost linear increase with the spatial frequencies in the second experiment (Fig. 2, bottom left). This may be explained by the semi-manual cursor placement, which is necessary because the amplitudes are less pronounced at frequencies below and above this frequency band. Another cause might be an input lag resulting from the time required by the monitor to prepare the image data to be displayed. This could be caused by, e.g., internal scaling for non-native resolutions, which may even be present when using the monitor’s native resolution. In the worst case, this leads to nonlinearities of the response timing of the LCD monitor when presenting patterns of low or high frequency [26, 27]. In doubt, the precise duration of the input lag should be measured using a photodiode attached to the display [28] and in case of being constant, the delay could then be subtracted from the respective time-to-peak values. Finally, the higher latencies may also be caused by the different software used for generating the stimuli: whereas in the first experiment, a custom-developed Java-based software was used, in the second experiment, the Python-based PsychoPy was employed. Nevertheless, these differences seem not to affect the estimated visual acuity. The mean peak-to-trough amplitude using the LCD monitor in the first experiment is reduced by about 0.9 µV with a confidence interval from − 1.6 to − 0.2 µV compared to the CRT stimulator, but increased by about 2.6 µV (confidence interval from 1.2 to 4.0 µV) when comparing the new LCD monitor with the CRT monitor (both with high contrast) in the second experiment (Table 5). However, these differences were, despite being statistically significant, within the expected standard deviation from about 0.5 to 7 µV of the P100 amplitude found in the literature [29,30,31] and therefore probably of no clinical relevance (Fig. 2, right). Interestingly, the results of Nagy et al. [2] suggest a similar reduction in the peak-to-trough amplitude when using an LC display for stimulation. In the first experiment, no statistically significant interaction between monitor type and spatial frequency on peak-to-trough amplitude was found but a tendency to smaller amplitudes at intermediate frequencies (Table 1), whereas in the second experiment, the effect of the interaction of stimulator and spatial frequency was statistically significant (Table 4). It has to be taken into account that the residuals of the models were heteroscedastic and therefore the statistical significance of the effects may be overestimated [32].
In the first experiment, the difference between the subjective visual acuity and that estimated by the second-order polynomial method, or by the modified Ricker function, was not statistically significant from a hypothetical assumed value of 0 logMAR (Table 2). Neither were the variances between CRT and LCD statistically different. Accordingly, the linear mixed-effects models revealed no statistically significant effects of neither the monitor type, the recording cycle, nor their interaction on the difference between subjective and estimated visual acuity for both estimation methods (Table 3).
In contrast in the second experiment, the differences between subjective visual acuity determined using FrACT and the visual acuities estimated using the modified Ricker function along with the conversion formula used in the first experiment were significantly different from the hypothesized difference of 0 logMAR for both, the new gaming LCD monitor and the old LCD monitor, at high and low contrast, but not for the CRT monitor. After using an individually adjusted conversion formula for each monitor/contrast combination, no statistically significant difference from the hypothesized difference of 0 logMAR was found (Table 7). However, one should keep in mind that using the results to calculate the conversion formula used to predict the results is circular reasoning. Nevertheless, it indicates, that using individual established conversion formulas calculated from a sufficiently large number of normative data will minimize the error between true visual acuity and estimated visual acuity.
Table 6 lists the signal-to-noise ratio calculated from the fitted Ricker model for the different combinations of monitors and contrasts. The highest SNR was found for the CRT monitor using high contrast. The LCDs showed lower SNR values. The on average higher amplitudes obtained using LCD monitors (Table 5) indicate that more noise is present when stimulating using LCDs. However, this effect could be caused by the different software used for the stimulus presentation and the lower number of sweeps recorded for averaging compared to the recordings using the CRT monitor. Nevertheless, none of the differences between the SNR values obtained from the different monitor types was statistically significant (Table 6), which corresponds to the findings of Fox et al. [28].
We want to point out the limitations of the current study: We included only healthy participants, so the possible effects of LCD stimulators on patients with reduced visual acuity remain unclear and should be further investigated, especially since we found a statistically significant, albeit not clinically relevant, effect of the monitor/contrast combination on peak-to-trough amplitude and time-to-peak after stimulus onset in the second experiment (Tables 4, 5). Further limitations are that the participants were not stratified by age and that the subjective visual acuity in the first experiment was determined using an eye chart projector, in contrast to the second experiment, where FrACT was used, limiting the accuracy of the estimated value. Finally, this study compared only three specific monitors; therefore, the results are not universally valid.
In conclusion, based on the results of this study, LCD monitors may substitute CRT monitors for presenting the stimuli for the sweep VEP to objectively estimate visual acuity. Newer LCD screens, especially with low response times in the range of 1–2 ms, therefore, allow for a reduction in luminance artifacts at required contrast levels [23], albeit the luminance artifact may not have a large effect on the recorded signals [28]. New technologies like OLED displays [23] may even be better suited, since one the one hand, the onset will be the same for the whole pattern, and on the other hand, LCDs and OLEDs provide a constant luminance level during stimulation, whereas CRTs need a constants pulses to keep the phosphor lit up, causing fast local luminance flashes all the time [28]. Therefore, in contrast to CRTs, LCD and OLED stimulators, e.g., may allow for recording true offset responses [33]. However, caution should be taken when leveraging modern displays for stimulation, since their in-built electronics perform all kinds of sophisticated image-enhancing procedures including color-correction, brightness boosting, contrast enhancement by real-time adjustments of the colors or the backlight, or eyestrain-reducing blue light filtering, with the aim to improve the users’ experience, or to increase the monitors lifetime. This applies in particular to consumer electronics like TVs. Gaming monitors, in addition, use special acceleration drivers, which shut down the backlight, insert black frames (Black Frame Insertion, BFI), or employ variable refresh rates (e.g., Nvidia G-SYNC or AMD FreeSync) to clean the retained image from the eye. Therefore, one should disable any image processing or enhancing functionality in the monitor settings, before using the monitor as stimulator for electrophysiological experiments. Finally, it is advisable to perform a calibration with healthy volunteers using best-corrected and artificially reduced visual acuity and to collect normative data for the employed setup, as always recommended by ISCEV [34], in order to establish an individual conversion formula between the sweep VEP outcome and the estimated visual acuity.

If you are shopping for a display, you may look to compare LCD vs CRT computer monitors. Some of the best computer monitors come in a wide variety of styles and design types. Keep reading to learn the difference between these two types of monitors.
CRT displays, however, are known for superior color rendering performance and for offering high refresh rates. We have a whole page dedicated to explaining what a CRT monitor is if you’re curious.
CRT monitors are bad for the environment, as they draw a whole lot of power during use. To help reduce humanity’s carbon footprint through tech products, there are opportunities for computer monitor recycling.
There are multiple distinctions to be made between LCD and CRT monitors, as well as LCD vs LED monitors, but that’s for another post. A liquid crystal display (LCD) has liquid crystals squeezed between two sheets of glass along with an electron gun that shoots an electron beam, while a CRT (cathode ray tube) monitor features a number of cathode-ray tubes. This overall difference in design leads to widely different use case scenarios, such as when you are comparing LCD vs LED monitors for gaming.
Despite being an older technology, CRT monitors are quite capable when it comes to rendering accurate colors. As a matter of fact, many creative professionals opt for expensive newly made CRT screens over LCD technology, LED screens, or even OLED displays for just this reason. Another advantage to the bright and vivid colors found with CRT displays is that they slightly reduce eye fatigue, which can be a handy bit of information if you are comparing LCD vs LED monitors for eye strain. The downside here is that CRT monitors are fragile, so this color accuracy will break down over time as the phosphor tubes degrade.
Another surprising feature of CRT monitors is their ultra-fast refresh rates. Due to the nature of the design, they offer higher refresh rates than LCD screens, as the light has a shorter route to travel.
There is no way around it. Cathode tubes are extremely large and extremely heavy, making CRT monitors an absolute beast to haul around and to place in your workspace. LCD screens, on the other hand, are light and portable, easily fitting just about anywhere.
In most cases, LCD monitors will offer a much larger field of view for viewing image and video than CRT displays, due to the nature of the design of the flat screen. Something like an LCD screen would come in handy as a gaming monitor. The larger the field of view with a CRT, the heavier and bulkier it will be.
CRT monitors are made from multiple materials that are relatively tough to source and they draw a whole lot of power during use. In other words, they are not too great for the environment.

We all are familiar with the computer monitors. We spend time sitting in front of them for hours working, gaming or watching movies. A monitor is used to display the output of any computer system. A good display makes all the difference and no doubt enhances the user experience. The innovation in the display technologies has improved the quality of the display devices including monitors. Now the desktop computers are available with a variety of displays ranging from technologically obsolete CRT monitors to latest slim LCD, LED or OLED monitors.
A computer monitor, technically termed as visual display unit is an output device that presents the information from the CPU on the screen working as an interface between CPU and the user. A cable connects the monitor to a video adaptor or video card which is set up on the motherboard of the computer. The CPU (Central Processing Unit) sends instruction to the video adaptor telling what needs to be displayed on the screen. The video adaptor converts the instructions into a set of corresponding signals and sends to the monitor. Monitor contains a circuitry that generates the picture on the screen from the set of signals.
The major parameters that measure the performance of a monitor are luminance, contrast ratio, resolution, dot pitch, response time, refresh rate and power consumption. The common problem that arises in monitors is dead pixels, blurred screen, phosphor-burn, etc.
which were the boxy Video Display Terminals (VDTs). VDTs were monochrome monitors which used CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) technology. They were capable of working with any type of computer by connecting through a serial interface.
IBM’s CRT– IBM launched its first computer also known as a ‘three piece computer’ in 1981. It had three different units – CPU, monitor and keyboard separately. By 1984, IBM introduced the new CRT monitor with enhanced Color Graphics Adaptor (CGA) with 16 colors and a resolution of 640 x 350 pixels. In 1987 IBM started offering the Video Graphics Array as part of its new PCs which allowed 256 different colors and a resolution of 640 x 480 pixels.
XGA and UXGA– A new technology named Enhanced Graphics Array or XGA was introduced in 1990 which allowed 16.8 million colors with a resolution of 800 x 600 pixels. The new monitors were now offering true colors that matched the human eye (human eye can detect 10 million different colors). Later the technology extended as UXGA, Ultra Extended Graphics Array which allowed 1600 x 1200 pixels.
In the 90s the LCD monitors came in the scene and gradually started competing with the CRT monitors. By the end of the 20th century, the CRT era was declining with the increasing popularity of Liquid Crystal Technology (LCD). This technology produces sharper images than the CRT monitors and the LCD monitors are significantly thinner having lower radiation emissions.
Few years’ back, LED displays came in the scene and they are gradually making its space in the market. LED technology has various advantages over LCD technology like better image quality, low power consumption, etc.
Since the beginning of computer era, there have been a number of technologies used for the display of output. The major technologies are CRT, LCD, Plasma, LED and OLED displays.
signals through a cable and the signal is decoded by the display controller which finally appears on a phosphor screen. The detailed working is as following:
As shown in the image CRTs have a conical shape and there is an electron gun or cathode ray gun at the back end of the monitor and a phosphor screen in the front. The electron gun fires a stream of electrons towards the display screen through a vacuum tube. This stream of electrons is also known as cathode rays. At the middle of the monitor, there are magnetic anodes which are magnetized in accordance with the instruction from the display controller. When electrons (cathode rays) pass through the magnetic anodes, they are pushed or pulled in one direction or other depending on the magnetic field on the anodes. This directs the electrons towards the correct part of phosphor coating inside the display glass. When electrons strikes the phosphor coated screen passing through a mesh (shadow mask or aperture grill), the phosphor lights up making a displayable dot on the computer screen. There are three different colored phosphors (Red, Green and Blue) for each pixel and the color of the pixel depends on the phosphor on which the electrons strike.
has three different phosphors for each pixel. A cathode ray strikes to one or more of these phosphors and the corresponding colored pixel appear on the screen. However high quality monitors use individual electron gun for each color which improves the image quality. Distance for two same colored phosphors (for single electron gun monitors) is known as dot pitch. Lesser the dot pitch higher is the quality of monitors.
brightness on the screen. Shadow mask is an obsolete technology in which there is a metal sheet with millions of holes to pass electrons in order to hit the phosphor coating. The shadow mask covers the entire screen thereby protecting the phosphors from stray ions (due to vacuum) and also limits the strength of the rays reducing the brightness on the monitor.
What is the resolution of the screen?–Resolution of a monitor tells how densely pixels are arranged on the screen. A combination of dot pitch and the viewable image area defines the maximum resolution of the screen. For example if a 21 inch monitor screen with a viewable area of 401mm x 298mm has a dot pitch of 0.26 mm, then its resolution is 1843 x 1370 pixels derived from a formula.
currently. LCD monitors are lightweight, compact, occupy less space, consume low power and are available in a reasonable price. Currently there are two types of LCD technology in use – Active matrix LCD technology or TFT and Passive matrix technology. The TFT technology is more reliable with better image quality while the passive matrix technology has a slower response and gradually becoming outdated.
As the name indicates, liquid crystals are the key elements of the display screen. By manipulating the crystal we can change the way they interacts with the light. There is a display controller in the monitor which receives the display signals from the video adaptor in the motherboard. The display controller controls two things – the electric signals to the liquid crystals and the back light. Structure of an LCD is shown in the below images (Also see how LCD works).
The liquid crystals used in the LCD are Twisted Nemantic (TN), a type of liquid crystals that are twisted at 90owith the surface. In this state, crystals allow the light to pass through the polarizer but on applying a voltage, they get untwisted and block the light to passing through the polarizer. The display controller starts the backlight that passes through the first piece of the glass. At the same time the display controller also send the electrical currents to the liquid crystal molecules to align and allowing the varying level of light to pass through the second piece of glass, forming the desired picture on the screen. In color monitors, each pixel is made of three liquid crystal cells fronted with red, green and blue filters. The light passing through the filtered screen forms the color what you see on the monitor. A wide range of colors are formed by varying the intensity of colored pixels.
The backlight is made of cathodes, and depending on the quality of the monitor, there may be a single cathode at the top or one at the top and one at the bottom, or two at the top and two at the bottom to improve the brightness and clarity of the monitor. These cathodes are diffused through a layer of plastic and diffusing materials.
Resolution– Unlike the CRT monitors there is no complex equation for the dot pitch and the resolution. The resolution of a monitor is simply the number of pixels contained in the matrix. Typically a 17 inch monitor has a resolution of 1280 x 1024 pixels.
In the below video Bill Hammack explains how a TFT monitor works, how it uses liquid crystals, thin film transistors and polarizers to display information.
In this field. LED monitors use light emitting diodes that acts as a performance booster in the monitors. Basically LED monitors are the LCD monitors with a LED backlight to power up the LCD panel. It means that LEDs are placed behind or around the LCD panel to enhance the luminosity and video definition of the monitor screen.
As we have seen in the above section of LCD monitors, they use a cold cathode light as backlight. In the LED monitors all the concepts are same except this backlight, which is replaced by LEDs.
There are three different types of LED monitors available based on the manner how the diodes are arranges in the monitor. These are – Direct LEDs, Edge LEDs and RGB LEDs. Both Edge and Direct LED display monitors use white diodes that are used to illuminate the LCD panel to produce the improved picture quality. The arrangement of LEDs in the monitor is shown in the below image:
In the Direct LEDs display, white diodes are placed all over the panel to produce higher quality image while the Edge LEDs display uses LEDs only on the borders of the LCD panel. Direct LEDs are generally used in the production of high definition TV whereas the Edge LEDs is mainly used in the production of computer screens. RGB LEDs display is better among the three types of LED monitors as it uses red, green and blue diodes to produce the lifelike images with amazing contrast ratio.
Both types of monitors work on the same technology. LED monitors are LCD monitors with replaced cold cathode backlight to LED backlight. Here are the differences that make the LED displays better than the LCDs
Contrast and Black level of the LED screen is better than the LCD screens because the liquid crystals cannot stop 100% of the backlight from cold cathode backlight and hence when the black screen is to be shown on the monitor, it is not completely black (as shown in the below image). But Edge LED screens perfectly show the black screen as there is no backlight at all.
illuminate tiny colored fluorescent lights to create image pixels. Each pixel is made of three such fluorescent lights – red, green and blue lights. To create a wide range of colors, intensity of these lights is varied accordingly.
There are millions of tiny cells filled with the gas like xenon and neon. They are positioned between two plates of glass known as front plate glass and rear plate glass. Two transparent electrodes covered by an insulating dielectric material and a magnesium oxide protective layer are also sandwiched between the glass plates on both sides of the cells on the entire screen.
When the CPU sends the signals to the Plasma monitor, the corresponding electrodes are charged which ionizes the gas in the intersecting cells by passing an electric current. Due to the collisions between the gas ions they release energy in the form of the photons of light which illuminate the respective cells. This process occurs thousands of times in a small fraction of second making the display faster. The released ultraviolet photons strike the phosphor material coated on the inner wall of the cell and hence phosphor electrons jump to the higher energy level. When the electron falls back to its normal state, it releases the energy as a visible light photon. Every pixel on the screen is made of three different colored phosphors – red, green and blue.
are some organic material (containing carbon, like wood, plastic or polymers.) that is used to convert the electric current into light. Since the LEDs are capable of producing different colored light, they are directly used to produce the correct color and there is no need of a backlight which saves power and space. With fast response time, wide viewing angles, outstanding contrast levels and perfect brightness, OLED displays are surely better than the existing other display technologies.
The heart of the OLED display is a stack of thin organic layers which is sandwiched between two conductors – a transparent anode and a metallic cathode, which in turn are sandwiched between two glass plates known as seal and substrate. The organic layer consists of a hole-injection layer, a hole-transport layer, an emissive layer and an electron-transport layer. When an appropriate voltage is applied, an electric current flows from cathode to anode through the organic layers. The cathode give electrons to the emissive layer of organic molecules while the anode takes equivalent electrons from the conducting layer of organic molecules. At the boundary of emissive and conductive layers, electrons and the holes are gathered. Here electrons are recombined with the holes by releasing energy in the form of photon of light. Hence the organic layer emits the light to produce the display. The color of the light depends on the type of organic molecules while the brightness depends on the amount of the current applied. By maximizing the recombination process in the emissive layer the output light can be improved in OLED devices. Thus the emissive layer is slightly doped with highly fluorescent molecules to enhance the electro-luminescent efficiency and control of color.
·Comparing it with the LCD devices, OLED displays can be viewed from different angles as they are “emissive” devices i.e. they emit light rather than modulating transmitted or reflected light.

Whether you want one for nostalgia sake or because you need a monitor that"s compatible with your classic computer, a monochrome monitor could be what you"re looking for. Take a look on eBay for a wide variety of monochrome monitors.Which brands made monochrome monitors?
Some common brands of monitors include:IBM: This company started in the early 1900s as a Computing-Tabulating-Recording company, and it has gone on to make computer hardware and software.
The first thing you will need to consider is your intended purposes. Some screens are intended for medical use while other screens are intended for use with a personal computer. Deciding if you want an LCD or CRT screen will be another factor. LCD screens create sharper images, but you can find used CRT screens at a lesser price. You will also want to consider what kind of computer you intend to hook it up to if you are buying for a personal computer. Also, check to see if it is refurbished, new, or used. Refurbished means that the monitor has been checked and anything that is broken has been fixed. If a monitor is labeled as "used," then it hasn"t been tested, so you"re taking more of a chance on how well it will work.What is the difference between LCD and CRT monitors?
LCD stands for "Liquid Crystal Display." It"s often used in laptops and flat-panel computer screens, and it produces clearer images than CRT screens. In an LCD screen, liquid crystals rotate polarized light to create the image. CRT stands for "Cathode Ray Tube." It was often used in computer monitors and televisions screens until the LCD and plasma screens replaced them. This type of screen creates images by sending electrons from the back of the tube to the phosphors at the front of the tube.

We often get asked, “should I replace my old CRT with a new LCD? What is the difference?” There are several factors to consider including price, resolution, energy savings and disposal. Listed below are some of the top reasons why the LCD may be a better choice.Size and Weight: The color LCD is thinner and much lighter. It is much easier to install into tight areas. The CRT can weigh up to 50 pounds and needs additional bracing and heavier supports.
Price: At first glance, the CRT wins here. It is older technology and the price is cheaper. However you give up all the features mentioned in this list. Also disposal costs and higher energy costs may negate any price savings.
Power: Energy savings on the LCD can make a big difference in companies having multiple units in production. Savings can be as much as 1/3 over the older CRT.
Summary: Based on price alone, you may choose to stay with the CRT. However, you must consider the energy cost savings to operate an LCD vs. CRT, plus the added cost of disposal for CRTs. In many instances, the CRT may actually cost more in the long run. With its large, high resolution screen and compact housing for easy installation, the LCD offers many advantages over the older CRT technology.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey