2.8 tft lcd shield tutorial pricelist
Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (2.8" diagonal) bright (4 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 attached by default and a optional capacitive touch panel with controller FT6206 attached by default, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen and doesn"t require pressing down on the screen with a stylus and has nice glossy glass cover.
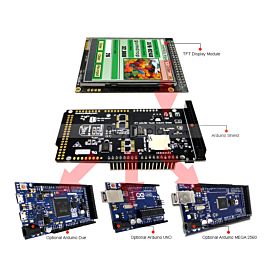
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (UNO/Due/Mega 2560).
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. You can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs.

ER-TFTM028IPS-4-IPS is 240x320 dots 2.8" color IPS tft lcd display with ILI9341 controller and board,superior display quality,super full viewing angle and easily controlled by MCU such as 8051, PIC, AVR, ARDUINO,ARM and Raspberry PI.It can be used in any embedded systems,industrial device,security and hand-held equipment which requires display in high quality and colorful image.
It supports 8080 8-bit /9-bit/16-bit /18-bit parallel ,3-wire,4-wire serial spi interface.Built-in optional microSD card slot, 2.8" 4-wire resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 and 2.8" capacitive touch panel with controller FT6206. It"s optional for font chip, flash chip and microsd card. We offer two types connection,one is pin header and the another is ZIF connector with flat cable mounting on board by default and suggested. Lanscape mode is also available.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!".Here is the link for 2.8"TFT Touch Shield with Libraries, EXxamples.Schematic Diagram for Arduino Due,Mega 2560 and Uno . For 8051 microcontroller user,we prepared the detailed tutorial such as interfacing, demo code and development kit at the bottom of this page.
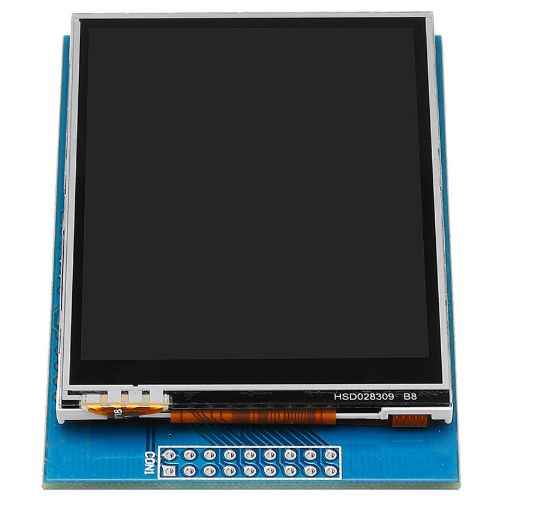

NMLCD-28240320-RTPis a colour active matrix LCD module incorporating amorphous silicon TFT (Thin Film Transistor). It is composed of a colour TFT-LCD panel, driver IC, FPC and a back light unit and with a Resistive Touch Panel (RTP). The module display area contains 240 x 320 pixels. This product accords with RoHS environmental criterion.
Shenzhen SLS Industrial Co.,ltd established in 2003, is a professional LCD module manufacturer and solution provider. We have 1 full-auto COG assembly line, 2 semi-auto assembly line, backlight assembly line, no dust TP bonding line and manufacturing tech support, we can provide unique, innovative and cost effective LCD module development and manufacturing. Our product range includes: middle-small size TFT LCD, industrial capacitive touch panel... Our LCD products have been widely used in communications, GPS, Equipment, electronic audio-visual, instrumentation, household appliances, PDA and other industries.

Add some sizzle to your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection and a capacitive touchscreen.
This TFT display is big (2.8" diagonal) bright (4 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. It has way more resolution than a black and white 128x64 display. As a bonus, this display has a capacitive touchscreen attached to it already, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen.
This shield is the capacitive version. This touchscreen doesn"t require pressing down on the screen with a stylus, and has a nice glossy glass cover. It is a single-touch display.
This shield uses SPI for the display and SD card and is easier to use with UNO, Mega & Leonardo Arduino"s. The capacitive touchscreen controller uses I2C but you can share the I2C bus with other I2C devices.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (UNO/Duemilanove/Diecimila). Solder three jumpers and you can use it at full speed on a Leonardo or Mega as well.
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. This shield needs fewer pins than our v1 shield, so you can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs: 5 SPI pins for the display, 2 shared I2C pins for the touchscreen controller and another pin for uSD card if you want to read images off of it.

This TFT display is big (2.8" diagonal) bright (4 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. It has way more resolution than a black and white 128x64 display. As a bonus, this display has a resistive touchscreen attached to it already, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino UNO. Solder three jumpers and you can use it at full speed on a Leonardo or Mega as well.
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. This shield needs fewer pins than our v1 shield, so you can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs: 5 SPI pins for the display, another pin for the SPI touchscreen controller and another pin for uSD card if you want to read images off of it.
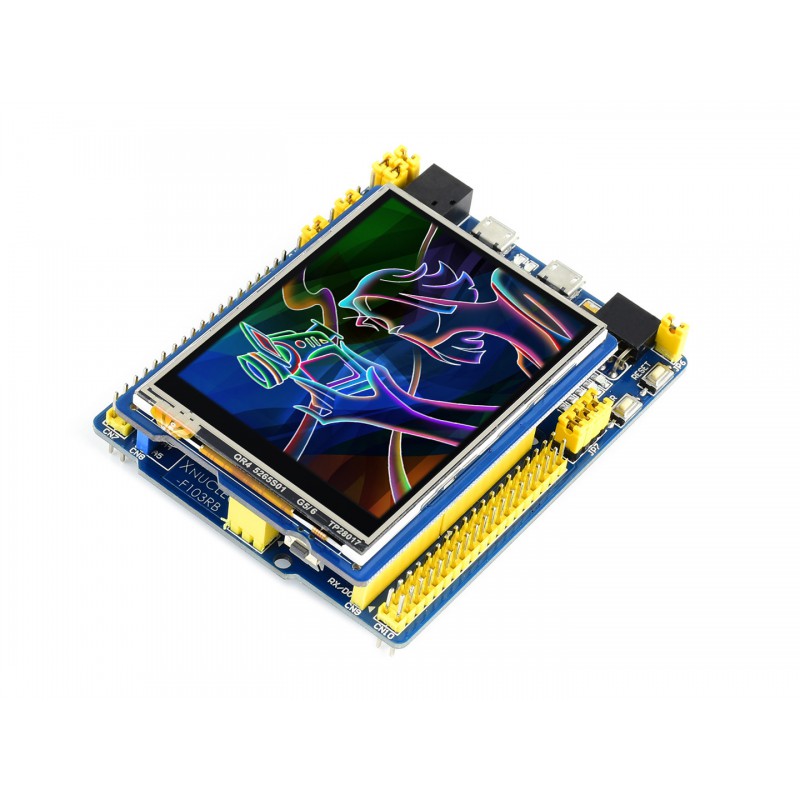

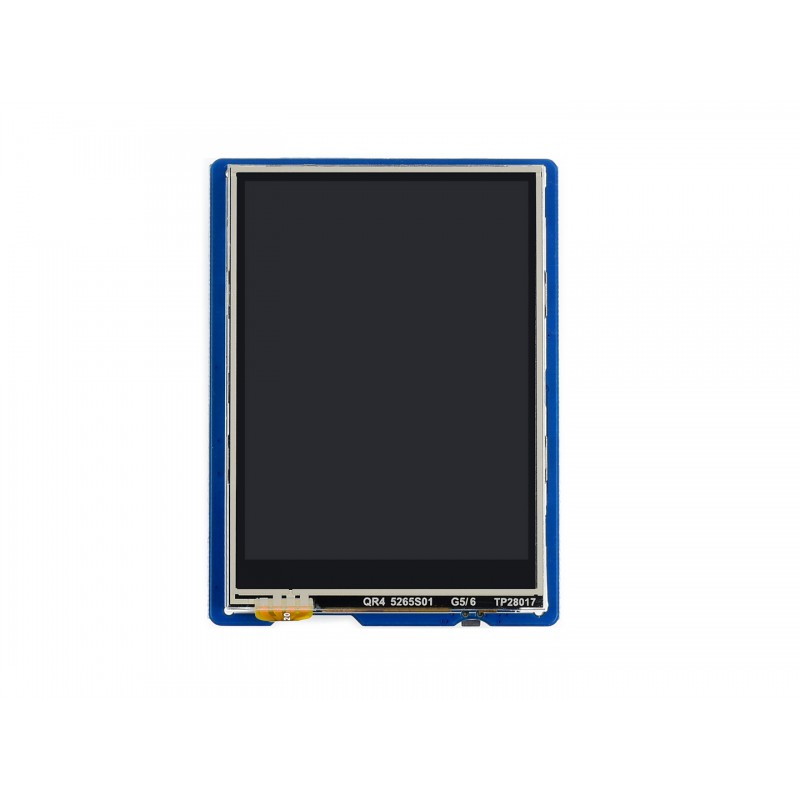
In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
For this tutorial I composed three examples. The first example is distance measurement using ultrasonic sensor. The output from the sensor, or the distance is printed on the screen and using the touch screen we can select the units, either centimeters or inches.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
Here’s that function which uses the ultrasonic sensor to calculate the distance and print the values with SevenSegNum font in green color, either in centimeters or inches. If you need more details how the ultrasonic sensor works you can check my particular tutorialfor that. Back in the loop section we can see what happens when we press the select unit buttons as well as the back button.
Ok next is the RGB LED Control example. If we press the second button, the drawLedControl() custom function will be called only once for drawing the graphic of that example and the setLedColor() custom function will be repeatedly called. In this function we use the touch screen to set the values of the 3 sliders from 0 to 255. With the if statements we confine the area of each slider and get the X value of the slider. So the values of the X coordinate of each slider are from 38 to 310 pixels and we need to map these values into values from 0 to 255 which will be used as a PWM signal for lighting up the LED. If you need more details how the RGB LED works you can check my particular tutorialfor that. The rest of the code in this custom function is for drawing the sliders. Back in the loop section we only have the back button which also turns off the LED when pressed.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:

We’ve done quite a number of tutorials on the use of several displays with Arduino boards and today we will add another tutorial to that list. We will look at the ILI9325 based 2.8″ touchscreen display shown below and how it can be used with the Arduino to deliver a better user experience for your projects.
For today’s tutorial, we will use the ILI9325 driver based, 2.8″ display from Geekcreit. The display comes as a shield so it’s ready to be used for Arduino based projects. It is an 18-bit color display with a total of 262,000 different color shades. The display has a resolution of 240 x 320 pixels with individual pixel control.
Today’s project involves some very simple tasks which we will use to demonstrate the capabilities of the display. We will create a button which when touched, will trigger the Arduino to display a message on the screen. At the end of today’s tutorial, we would have gone through how to create a user interface on the touchscreen, how to detect when the screen is touched and how to display data on the screen.
The Arduino Mega or any of the other Arduino board can be used for this project and the power bank comes in handy when the project is to be used in a standalone mode. As usual, the exact components used for this tutorial can be purchased via the links attached to each of them.
The 2.8″ TFT display used for this project comes as a shield with the form factor of the Arduino Uno. This makes it easy to connect the shield to boards like the Uno, Mega and Due, as all we need to do, is plug it directly into the board, eliminating all the mess made by wires. Plug the display to the Arduino as shown in the image below.
The fact that the display comes as a shield becomes a disadvantage when its used with the Arduino Uno as it occupies almost all the pins leaving just 2 digital pins and one analog pin for other uses. This can however, be overcome by using either the Arduino Mega or Due as they both work perfectly well with the display.
The code for this tutorial is heavily reliant on a modified version of Adafruit’s TFT LCD,GFX and touchscreen libraries. These libraries can be downloaded from the links attached to them.
As mentioned earlier, our focus for this tutorial will be to demonstrate, how UI can be created on the display and interpret touches to trigger actions. To achieve this, we will develop a simple sketch which displays a Youtube subscribe button. When the subscribe button is pressed, a text is displayed on the screen.
Next, we declare the colors to be used with their hexadecimal values and we create an object of the Adafruit TFTLCD library, indicating the variables used to represent the pins of the Arduino to which the display is connected.
We start by initializing the serial monitor and the display. After this, we set the orientation of the LCD and fill the screen with a black color to serve as the background.
That’s it for this tutorial guys. Feel free to expand this code for use in your projects and do not hesitate to let me know via the comment section if you have any questions.

Displaying a custom image or graphic on a LCD display is a very useful task as displays are now a premium way of providing feedback to users on any project. With this functionality, we can build projects that display our own logo, or display images that help users better understand a particular task the project is performing, providing an all-round improved User Experience (UX) for your Arduino or ESP8266 based project. Today’s tutorial will focus on how you can display graphics on most Arduino compatible displays.
The procedure described in this tutorial works with all color displays supported by Adafruit’s GFX library and also works for displays supported by the TFTLCD library from Adafruit with little modification. Some of the displays on which this procedure works include:
While these are the displays we have, and on which this tutorial was tested, we are confident it will work perfectly fine with most of the other Arduino compatible displays.
For each of the displays mentioned above, we have covered in past how to program and connect them to Arduino. You should check those tutorials, as they will give you the necessary background knowledge on how each of these displays works.
For this tutorial, we will use the 2.8″ ILI9325 TFT Display which offers a resolution of 320 x 340 pixels and we will display a bitmap image of a car.
As usual, each of the components listed above can be bought from the links attached to them. While having all of the displays listed above may be useful, you can use just one of them for this tutorial.
To demonstrate how things work, we will use the 2.8″ TFT Display. The 2.8″ TFT display comes as a shield which plugs directly into the Arduino UNO as shown in the image below.
Not all Arduino displays are available as shields, so when working with any of them, connect the display as you would when displaying text (we recommend following the detailed tutorial for the display type you use of the above list). This means no special connection is required to display graphics.
Before an image is displayed on any of the Arduino screens, it needs to be converted to a C compatible hex file and that can only happen when the image is in bitmap form. Thus, our first task is to create a bitmap version of the graphics to be displayed or convert the existing image to a bitmap file. There are several tools that can be used for creation/conversion of bitmap images including, Corel Draw and Paint.net, but for this tutorial, we will use the Paint.net.
Image2Code is an easy-to-use, small Java utility to convert images into a byte array that can be used as a bitmap on displays that are compatible with the Adafruit-GFX or Adafruit TFTLCD (with little modification) library.
To reduce the amount of code, and stress involved in displaying the graphics, we will use two wonderful libraries; The GFX library and the TFTLCD library from Adafruit.
As usual, we start writing the sketch by including the libraries required. For this procedure, we will use the TFTLCD library alone, since we are assuming you are using a display that is not supported by the GFX library.
The last section of the code is the drawBitmap function itself, as earlier mentioned, to use the drawbitmap() function with the Adafruit TFTLCD library, we need to copy the function’s code and paste into the Arduino sketch.
Plug in your screen as shown above. If you are using any other display, connect it as shown in the corresponding linked tutorial. With the schematics in place, connect the Arduino board to your PC and upload the code. Don’t forget the graphics file needs to be in the same folder as the Arduino sketch.
That’s it for this tutorial guys. The procedure is the same for all kinds of Arduino compatible displays. If you get stuck while trying to replicate this using any other display, feel free to reach out to me via the comment sections below.

Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (2.8" diagonal) bright (4 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 240x320 pixels with individual pixel control. It has way more resolution than a black and white 128x64 display. As a bonus, this display has a resistive touchscreen attached to it already, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen.
We"ve updated our original v1 shield to an SPI display - its a tiny bit slower but uses a lot less pins and is now much easier to use with Mega & Leonardo. We also include an SPI touchscreen controller so you only need one additional pin to add a high quality touchscreen controller. Even with all the extras, the price is lower thanks to our parts sourcing & engineering skillz!
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes!Works best with any classic Arduino (UNO/Duemilanove/Diecimila). Solder three jumpers and you can use it at full speed on a Leonardo or Mega as well.
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. This shield needs fewer pins than our v1 shield, so you can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs: 5 SPI pins for the display, another pin for the SPI touchscreen controller and another pin for uSD card if you want to read images off of it.

In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey