tft lcd display vs amoled display pricelist
Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.

When we purchase a new smartphone we go through a list of specifications that includes the processor, software, cameras, display type, battery, etc. The display of the smartphone is something which has always been a concern for people. And smartphone technology has advanced so much in the past decade that you get several display technology options to choose from.
Today, a smartphone is not just a means to send and receive calls and texts. It has become a general necessity, so choosing the right technology should be your main priority. Coming back to displays, as we said there are plenty of display types available right now.
Two of the main contenders for display technologies that are widely available are AMOLED and LCD. Here in this article, we will be comprising AMOLED vs LCD and find out which one is better for you.
Starting with the AMOLED first, it is a part of the OLED display technology but with some more advanced features. To completely know about it must understand its all three components. The first one is LED, “Light Emitting Diode”. Then we have “O” which stands for organic and makes the OLED.
It actually means that organic material is placed with two conductors in each LED, which helps to produce the light. And the “AM” in AMOLED means Active Matrix, it has the capability to increase the quality of a pixel.
The AMOLED display is similar to the OLED in various factors like high brightness and sharpness, better battery life, colour reproduction, etc. AMOLED display also has a thin film transistor, “TFT” that is attached to each LED with a capacitor.
TFT helps to operate all the pixels in an AMOLED display. This display might have a lot of positives but there are a few negatives too let’s point both of them out.
A major issue with these displays is of burning of pixels. After showing a specific image or colour for a longer period of time, the pixel can get burned. And if there is a problem with a single pixel it will affect the entire display.
Low outdoor visibility, usually the AMOLED Displays are quote not bright in direct sunlight and outdoor readability could be a problem for some devices but average screen brightness.
The LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display”, and this display produces colours a lot differently than AMOLED. LCD display uses a dedicated backlight for the light source rather than using individual LED components.
The LCD displays function pretty simply, a series of thin films, transparent mirrors, and some white LED lights that distributes lights across the back of the display.
As we have mentioned, an LCD display always requires a backlight and also a colour filter. The backlight must have to pass through a thin film transistor matrix and a polarizer. So, when you see it, the whole screen will be lit and only a fraction of light gets through. This is the key difference comparing AMOLED vs LCD and this is what differentiates these two display technologies.
The LCD displays are cheaper compared to the AMOLED as there is only one source of light which makes it easier to produce. Most budget smartphones also use LCD displays.
LCD displays have bright whites, the backlight emits lots of light through pixels which makes it easy to read in outdoors. It also shows the “Accurate True to Life” colours, which means it has the colours that reflect the objects of the real world more accurately than others.
LCDs also offer the best viewing angle. Although it may depend on the smartphone you have. But most high-quality LCD displays support great viewing angles without any colour distortion or colour shifting.
The LCD displays can never show the deep blacks like AMOLED. Due to the single backlight, it always has to illuminate the screen making it impossible to show the deep blacks.
The LCDs are also thicker than other displays because of the backlight as it needs more volume. So, LCD smartphones are mostly thicker than AMOLED ones.
Both of these display technologies have their own Pros and Cons. Taking them aside everything ends up with the user preferences as people might have different preferences among different colours and contrast profiles. However, a few factors might help you to decide which one fits perfectly for you.
Let’s start with the pricing. Most AMOLED display smartphones always cost more than an LCD smartphone. Although the trend is changing a bit. But still, if you want to get a good quality AMOLED display you have to go for the flagship devices.
The colors are also very sharp and vibrant with the AMOLED displays. And they look much better than any LCD display. The brightness is something where LCDs stood ahead of the AMOLED display. So using an LCD display outdoors gives much better results.
The last thing is battery consumption, and there is no one near the AMOLED displays in terms of battery. As of now, all smartphones feature a Dark Mode and most of the apps and UI are dark black with a black background. This dark UI on smartphones doesn’t require any other light, it gives the AMOLED displays a boost in battery performance.
Looking at all these factors and comparing AMOLED vs LCD displays, the AMOLED displays are certainly better than the LCDs. Also, the big display OEMs, like Samsung and LG are focusing more the OLED technologies for their future projects. So, it makes sense to look out for AMOLED displays. That being said, if we see further enhancements in the LCD technology in terms of battery efficiency and more, there is no point to cancel them at this moment.

AMOLED displays are popular for the pure blacks and energy efficient "glance" displays they enable. Thus they are seen as a premium option for smartphone and laptop users, and AMOLED panels are only seen in really high-end TVs. However, thanks to competition and demand spurring greater production, prices are starting to become more competitive with TFT LCD panels, reports IT industry journal DigiTimes.
According to the source report "The production cost for a 5.5-inch HD AMOLED panel has drifted to US$12.10 recently, compared to US$12.20 for a 5.5-inch HP LTPS LCD panel". This is a big change to the previous state of affairs where AMOLED panels had "much higher,"prices due to the increased production costs. Thanks to the levelling off of prices and demand it"s expected that AMOLED panels will be equipped on up to 50 per cent of smartphones by 2020.
In other recent AMOLED smartphone news, the Nikkei Asian Review asserts that Apple will "use OLED screens in all new iPhones launching in 2018". Industry sources say Apple is considering launching three smartphones in 2018 and all will come equipped with this type of display.
Later this year Apple will launch its first OLED iPhone - but only the premium version will get this type of display, in a design that eschews its iconic Home button. Two other iPhone models released this year will use TFT LCDs.
Back to the AMOLED panel pricing news, and there is hope that larger displays, not just those aimed at smartphones and tablets, will come down in price. LG Display"s E4-2 fab, its second production line for AMOLED displays for TVs, will enter volume production in H2 2017, says DigiTimes. Thanks to the new production line AMOLED TV display production is set to more than double to 1.5 million units, say sources. Furthermore, several Chinese panel makers have been investing in AMOLED production facilities with output set to increase fivefold (comparing 2016 output to that estimated to come on line in 2018).

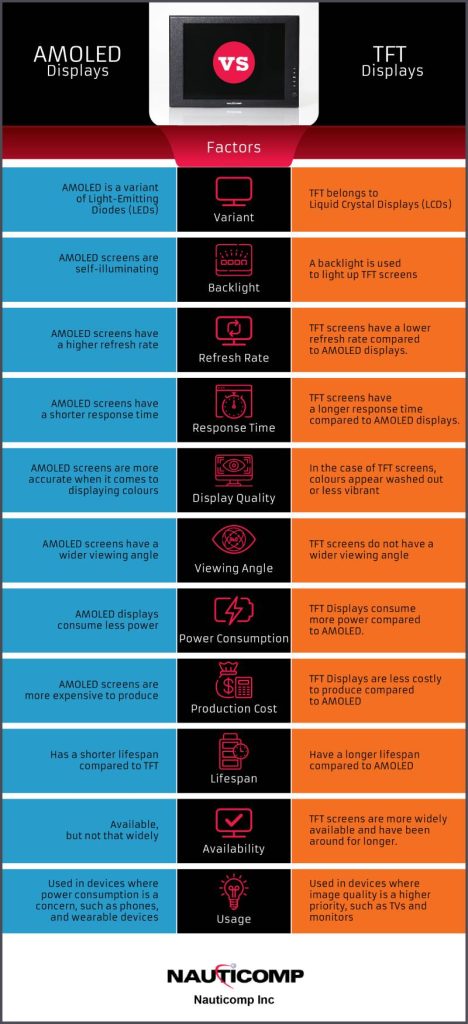
AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.
Nauticomp Inc.provides world-class fully customizable touchscreen displays for commercial and industrial settings. With features like sunlight readability, brightness adjustability, infrared lighting, full backlighting, all-weather capabilities, etc., our displays are second to none. Contact us today to learn more.

Samsung Electronics has been a driving force in this development as they dominate the Android market. Aside from last year’s smartwatch, Apple hasn’t been as enthusiastic in its adoption of the technology. Its biggest Android rival on the other hand, developed its very own Super AMOLED and has been supplying other gadget manufacturers with the display panels.
The report says that prices are likely to keep going down as Samsung is ramping up the game with new production facilities. If Samsung manages to keep up the demand for AMOLED displays, which seems likely if the price keeps going down, then the numbers keep falling. Consider it a positive loop.
Of course, there’s no guarantee that AMOLED will keep its position forever. If Apple decides to keep going for LCD displays, it will likely also limit how far down the AMOLED display prices reach.

A Thin Film Transistor (TFT) FT display is a form of Liquid Crystal Display with thin film transistors for controlling the image formation. The TFT technology works by controlling brightness in red, green and blue sub-pixels through transistors for each pixel on the screen. The pixels themselves do not produce light; instead, the screen uses a backlight for illumination. Discover our TFT Products
Standing for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, this type of display requires no backlight and can light up or turn off each of their pixels independently, meaning they offer better contrast and colour. As the name suggests they are made of organic material.
Otherwise knows as the IPS display, this superior version of the TFT provides all round viewing angles and exceptional contrast ratio, however this comes at a premium cost compared to standard TFT models. Read more here.
As with all display choice, knowing your intended audience, user requirements and environmental conditions, all form part of the initial design process, which will ultimately determine the best display at the right price for your application. Before you make your choice, why not speak with us and we will be happy to talk you through your options.

Over the years, there has been a steady growth in the use of smartphones. This has led to the growth of mobile display technologies. The names such as OLED, LCD, touchscreen, retina display, have been making rounds years. AMOLED is a technology derived from OLED, and it has gained immense attention in recent years. Each of the aforementioned technologies have made a big impact owing to their distinct advantages. This post focuses on an ongoing debate on AMOLED vs LCD.
For many people, both these display technologies look the same. The following points will help you understand the basic differences between LCD and AMOLED.
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) are thin-panel displays that are used in various computers, cell phones, and televisions. These displays use backlight for lighting, and they reproduce light differently than AMOLED. Thin-film transistor (TFT) and in-plane switching (IPS) are two important types of LCD displays used today.
Active-Matrix OLED (AMOLED) is a type of organic light emitting diode (OLED) display that does not require a backlight to assure power savings. These OLED display modules are commonly used for mobile phones and are emerging in the consumer tv market.
Brightness: The backlight on an LCD display helps light up pixels easily, thereby making it easier for users to read on their screens easily. Against this, AMOLED displays have low brightness levels.
Color Presentation: LCD screens are known to portray true to life colors on screen. This gives an actual idea of color to viewers who may not have seen certain things in real. However, AMOLED screens can produce vivid and bright colors with high contract ratios. AMOLED screens can produce true black colors. As no backlight is required, the display can easily power off pixels, which are required to highlight any black portions on the image. When compared, AMOLED display offers a large color gamut than other LCD displays. This is why they are available in warmer hues with a tint of red or yellow color, whereas LCD displays are blue. Yellow hues are soothing to eyes, however, blue lights will help see things in the dark. In short, AMOLED screens allow users to see vibrant colors than original, whereas LCD displays will provide real colors, thereby adding to their viewing experience.
Energy-efficient: LCD displays or screens utilize backlight for smooth operation, whereas AMOLED displays don’t require backlights. The backlight drains out battery life, and your phones may require regular recharging for proper functioning. However, AMOLED displays require no backlight, which makes them energy efficient. Also, you can use a black wallpaper to save energy on AMOLED displays.
Flexibility:AMOLED display modules are a lot more flexible among the two. Curved and circular AMOLED displays are used in many mobile phones and smart wearables. LCD displays cannot be molded or curved like AMOLED or OLED display modules, which limits their utilization in various applications.
Affordability: LCD display panels have been around for a long time, so its manufacturing has been perfected for the mobiles and other devices. Thus, mass volumes of modules can be produced at cheaper prices. However, AMOLED display module production is costlier because the technology is new, still in refinement phases. So, their manufacturing costs are higher than LCD counterparts.
As seen, each technology has its own benefits. After considering the majority of pros and cons it can be easily said that AMOLED displays are preferable than LCD panels if color presentation, battery life, and affordability are major concerns for your application. It is important that you partner with a reliable LCD or OLED display manufacturer like Microtips USA to source these modules. The company also provides custom OLED displays to meet various application

Typically, when scrolling through web pages and specs sheets of many smartphones, users are often faced with a number of confusing terminologies, particularly in the display department. While many smartphone enthusiasts and experts are familiar with these smartphone display technologies, many newbies aren’t.
There are more than four display types used on smartphones, and these displays are relative to the quality of images, colour quality, battery life, and even the price of the device. We explain the tech behind each known display types on smartphones.
LCD is an acronym that stands for Liquid Crystal Display and it is one of the most commonly used display by OEMs on their devices. LCD displays are further categorised into two types on the basis of the technology used to make them. The two types are IPS LCD and TFT LCDs.
TFT stands Thin-film Transistor and de facto, it really isn’t a type of display. TFT is only the technology used to produce LCD display panels. TFT LCD displays use an ‘Active Matrix Technology” where the display transistor and capacitor have individual pixels attached to them. In fact, each pixel can have as many as four transistors; for switching them off and on easily. TFT displays are widely known for having high contrast ratios, resolution and image quality. They are also cheaper to produce but not as cheap as IPS LCD.
IPS stands for In-Plane Switching and it is the most popularly used type of LCD panels for a number of reasons. First, compared to TFT, the crystal/pixel orientation on IPS LCD is different. This modification allows for improved colour reproduction, better viewing angles, and reduced energy consumption. This is why IPS LCD is preferred over TFT by most gadgets manufacturers.
Generally, LCDs are known as the “backlit displays” because the pixels on the display are powered by a polarized light engineered to the screen. The light passes through the (horizontal and vertical) filters which help determine the pixel’s brightness. Although the inclusion of a backlight makes LCD displays (and phones) thicker, pixels are generally more closely packed, colours are more natural, and images — sharper.
OLED stands for “Organic light-emitting diode”. OLED is one of the latest display innovation used in many gadgets and electronics like smartphones and TVs. Unlike LCD displays, OLED panels produce their own light and do not rely on a backlight. This self-emission is achieved when an electrical current passes through two conductors with an organic carbon-based film between them.
For every pixel in an OLED panel, this light emission process takes place, except when black is being displayed; the pixels are turned off instead. This makes OLED the best display that shows true black colour. The process of turning off pixels when displaying black is also a battery-wise feature of OLED panels.
Regarding quality, OLED are generally better at displaying blacks. They are also slimmer, dissipate less heat, and possess better contrast ratio when compared to LCDs. However, they are more expensive to produce and in turn lead to an increase in the price of smartphones they are used on. Shorter lifespan is also a downside to OLED displays.
AMOLED is an advanced type of OLED display that uses an “Active Matrix” technology. AMOLED is the acronym for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED). Like OLED, AMOLED pixels also emit their own light and further uses an active matrix system attached to a thin-film transistor (TFT) to exert more control over each pixels. This results to better visual experience; darker blacks, deeper brights, and higher refresh rates.
AMOLED panels are mostly used in big-sized smartphones as it supports almost any display size. One downside to AMOLED panels, though, is poor usability under sunlight.
Also called S-AMOLED, Super AMOLED is an upgrade of AMOLED panels. Unlike regular AMOLED, this upgrade uses almost the same technology but with architectural modifications that makes it better. In S-AMOLED, the touch sensor component have been integrated with the screen; both are separated in regular AMOLED.
This difference results in brighter display, reduced power consumption, reduced sunlight reflection, enhanced outdoor readability, and wider viewing angles. Super AMOLED is one the best displays out there and can be found on many flagship devices like the Samsung Galaxy A7 (2018) with three rear cameras, Samsung Galaxy Note9.
You can easily identify your smartphone’s screen type through a simple Google search of your phone specifications. You should see your device’s screen type under the display department. The image below shows the screen type (IPS LCD) of the Coolpad Note 5.

When you buy a smartphone and while reading the specifications of the phone, you often do not pay attention to the type of phone screen. Screen types abbreviations can be a bit confusing and most people don’t usually take them into consideration due to their ignorance. Don’t worry now we will give you everything you need to know about the main types of screens which are LCD, OLED and AMOLED.
Previously, there were only two main types in the smartphone industry, LCD and LED. But with the advancement in technology, many other types such as OLED, AMOLED, sAMOLED, and Retina have appeared. LCD screens are used in most mid-range phones from Xiaomi, Realme and other Chinese manufacturers and OLED in their top-end devices. Samsung uses AMOLED and sAMOLED displays, while Apple uses Retina displays. Let us discuss each of these types one by one.
LCD (abbreviation for Liquid Crystal Display). The oldest type of screen, it relied on backlighting as the only light source to illuminate the pixels. Also, LCD screens are brighter than most other types of screens, which makes them suitable for use in smartphones in bright sunlight. However, these screens suffer from less accurate colors. Smartphones use two main types of LCD screens:
TFTstands for Thin Film Transistor. TFT monitors are an advanced version of LCD monitors. While TFT has a relatively lower production cost and provides better image quality than previous generations of LCD monitors, it has higher power consumption, lower viewing angles and lower color representation.
IPSstands for In-Plane Switching. It is an improved version of TFT. Availability Provides better viewing angles and color representation by utilizing more powerful backlighting. It consumes less power than TFT, but its cost is higher overall.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode). The presence of this type is the main reason for the emergence of curved displays and foldable smartphones. Unlike LCD screens, which use backlighting, OLED screens do not require this because they contain a layer of organic matter that emits light when exposed to an electric current. OLED displays display more saturated and vibrant colors. Because of the luminance per pixel, OLED displays provide darker levels of black. Because the pixels that don’t get caught are in a sleep state, OLED screens usually use less power and give better battery life. These screens are of two main types:
AMOLEDstands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Similar to an OLED screen but has Thin Film Transistors (TFT) on the back panel. This ensures faster and more precise control as it can turn on or off any pixel individually, and it also has a storage capacitor which eliminates screen size limitations and provides the possibility of a larger screen. We will explain AMOLED screens in more detail due to their great popularity.
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). Improved OLED screens. The most important component of these displays is the TFT element that controls the flow in each pixel. With two TFTs per pixel, one to start and one to stop charging the storage capacitors this allows each LED to operate individually and generate light for itself. Due to its great flexibility it can be used in foldable phones.
You may have seen the term sAMOLED or Super AMOLED. These monitors were invented by Samsung and are available in their high-end models. This type provides a variety of colors with greater clarity. Super AMOLED displays can handle sunlight better than other AMOLED displays, while consuming less power.
Each of the above types of screens has its own advantages and disadvantages. In general, AMOLED is superior to LCD screens. Our primary comparison criteria are higher refresh rates, better color representation, and battery consumption. As for OLED versus AMOLED, we already mentioned that AMOLED is an improved version of OLED as it offers better image quality to battery consumption. Due to their low usability under sunlight, Super AMOLED screens are the best choices.
In the end, it all boils down to your needs and budget. If you’re on a tight budget, an LCD monitor isn’t a bad deal. But if your budget is good, you should definitely opt for the newer AMOLED screen especially for TVs.

The world of smartphones has been busy for the past few months. There have been numerous revolutionary launches with groundbreaking innovations that have the capacity to change the course of the smartphone industry. But the most important attribute of a smartphone is the display, which has been the focus for all prominent players in the mobile phone industry this year.
Samsung came up with its unique 18:5:9 AMOLED display for the Galaxy S8. LG picked up its old trusted IPS LCD unit for the G6’s display. These display units have been familiar to the usual Indian smartphone buyer. Honor, on the other hand, has just unveiled the new Honor 8 Pro for the Indian market that ships with an LTPS LCD display. This has led to wonder how exactly is this technology different from the existing ones and what benefits does it give Honor to craft its flagship smartphone with. Well, let’s find out.
The LCD technology brought in the era of thin displays to screens, making the smartphone possible in the current world. LCD displays are power efficient and work on the principle of blocking light. The liquid crystal in the display unit uses some kind of a backlight, generally a LED backlight or a reflector, to make the picture visible to the viewer. There are two kinds of LCD units – passive matrix LCD that requires more power and the superior active matrix LCD unit, known to people as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) that draws less power.
The early LCD technology couldn’t maintain the colour for wide angle viewing, which led to the development of the In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD panel. IPS panel arranges and switches the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules of standard LCD display between the glass substrates. This helps it to enhance viewing angles and improve colour reproduction as well. IPS LCD technology is responsible for accelerating the growth of the smartphone market and is the go-to display technology for prominent manufacturers.
The standard LCD display uses amorphous Silicon as the liquid for the display unit as it can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. This though restricts the display resolution and adds to overall device temperatures. Therefore, development of the technology led to replacing the amorphous Silicon with Polycrystalline Silicon, which boosted the screen resolution and maintains low temperatures. The larger and more uniform grains of polysilicon allow faster electron movement, resulting in higher resolution and higher refresh rates. It also was found to be cheaper to manufacture due to lower cost of certain key substrates. Therefore, the Low-Temperature PolySilicon (LTPS) LCD screen helps provide larger pixel densities, lower power consumption that standard LCD and controlled temperature ranges.
The AMOLED display technology is in a completely different league. It doesn’t bother with any liquid mechanism or complex grid structures. The panel uses an array of tiny LEDs placed on TFT modules. These LEDs have an organic construction that directly emits light and minimises its loss by eradicating certain filters. Since LEDs are physically different units, they can be asked to switch on and off as per the requirement of the display to form a picture. This is known as the Active Matrix system. Hence, an Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display can produce deeper blacks by switching off individual LED pixels, resulting in high contrast pictures.
The honest answer is that it depends on the requirement of the user. If you want accurate colours from your display while wanting it to retain its vibrancy for a longer period of time, then any of the two LCD screens are the ideal choice. LTPS LCD display can provide higher picture resolution but deteriorates faster than standard IPS LCD display over time.
An AMOLED display will provide high contrast pictures any time but it too has the tendency to deteriorate faster than LCD panels. Therefore, if you are after greater picture quality, choose LTPS LCD or else settle for AMOLED for a vivid contrast picture experience.

TFT is an abbreviation for Thin Film Transistor, a flat panel display used to improve the operation and utility of LCD screens. In order to portray an appearance to the audience, a liquid crystal display (LCD) utilizes a crystalline-filled fluid to modify rear lighting polarized origin through the use of an electromagnetic force among two relatively thin metal wires such as indium oxide (ITO). However, color TFT displays are associated with this method, which can be employed in both divided and pixelated display systems.
With motion pictures displayed on an LCD, the intrinsic sluggish rate of increase between liquid phases over a significant number of pixel components can be an issue due to capacitance impacts, which can create a blurring of the visuals. Placing a high-velocity LCD control device inside the formation of a thin-film transistor immediately next to the cell component just on a glass screen, the issue of LCD picture speed may be substantially improved, and image blur can be eliminated for all useful purposes entirely.
Organic light-emitting diodes (AMOLEDs) are a type of flat light-emitting advanced technologies that are created by interspersing a succession of organic thin sheets over two conducting conductors. An electrical charge causes a brilliant light to be produced when the current flows. AMOLED displays are light-emitting screens that do not require a backlight, making them thinner and more energy-efficient than liquid crystal displays (LCDs) (which will need a white backlight).
AMOLED displays are not only thin and fuel-intensive, but they also deliver the highest image quality available, so they can be made translucent, elastic, bendable, or even rollable and stretchy in the future, allowing for a variety of applications. AMOLEDs are a revolutionary technology in terms of display devices! It is possible to create an AMOLED by sandwiching a sequence of thin films across phase conductors. Electric charge causes a brilliant light to be emitted when the current flows through the coil.
The color display is fantastic. Color intensity, sharpness, and luminance settings that are second to none and can be customized to meet the needs of any application.
Half-Life has been expanded. TFT displays have a far longer half-life than its LED equivalents, and they are available in a number of sizes, which might have an effect on the device"s half-life based on the phone"s usage as well as other variables. Touch panels for TFT screens can be either resistant or capacitance in nature.
Due to the apparent glass panels, there is limited functionality. For instance, there are ineffective for outdoor use because the glass can display glares from its natural lighting)
They rely on backlight to give illumination rather than generating their own light. Hence they require constructed light-creating diodes (LEDs) in their backlit display framework to ensure enough brightness.
Backlighting is unnecessary for AMOLEDs. LCDs produce images by selectively blocking parts of the illumination, whereas AMOLEDs produce light. AMOLEDs utilize less energy than LCDs since they don"t need backlighting. This is critical for battery-powered devices such as phones.
While AMOLED light-emitting sheets are lightweight, the substrate can also be elastic rather than stiff. AMOLED films are not limited to glass-like LEDs and LCDs.
AMOLEDs offer 170-degree ranges of vision. LCDs operate by obscuring the light. Hence they have intrinsic viewing obstacles. In addition, AMOLEDs have a substantially wider viewing spectrum.
AMOLEDs outperform LEDs. Since AMOLED organic coatings are less than LED inorganic crystal levels, AMOLED conducting and particle emitters layers can just be multi-layered. Also, LEDs and LCDs need glass backing, which absorbs light. AMOLEDs don"t need it.
AMOLEDs seem to be simpler to implement and larger. AMOLEDs are constructed of polymers and may be produced into big sheets. It takes a lot of extra liquid crystals to build and set down.
While red and green AMOLED sheets have a greater lifespan (46,000 to 230,000 hours), azure compounds have significantly shorter longevity (up to roughly 14,000 hours).
Due to the fact that AMOLED displays inherently emit illumination, they do not need a backlight when used on a monitor screen. Conversely, LCDs require backlights since the liquid crystals themselves are incapable of producing light under their own. Direct light emission from AMOLED displays also allows for the developing of lightweight display devices than others using TFT LCDs.
LCD displays have a higher brightness than AMOLED panels. This is owing to the LCD"s usage of led backlight, which may provide a brilliant illumination of the entire display. Despite the fact that AMOLEDs produce high levels of brilliance from their illumination, they will never be able to match the intensity of LCD lighting.
LCD screens use less power than AMOLED displays, which provides a slight advantage. The amount of energy consumed by AMOLED displays is dependent on the intensity of the screen. Lowered luminance results in lower energy usage, however, it might not be the best solution because the contrast would suffer as a result of the decreased brightness. In some situations, such as when to use an AMOLED device in direct sunlight, it is not an optimal situation.
However, the backlit keys of TFT displays account for the majority of their power usage. TFT screens" efficiency is considerably improved when the backlight is set to a lesser brightness level than the default setting. For example, replacing the light of an LCD TV with just an Led flash will have no effect on the image quality, but will result in lower power usage than replacing the light of an AMOLED TV.
With the exception of phones, numerous other technologies make use of displays to allow customers to engage in direct communication with them. To determine whether or not TFT LCD will be able to withstand the development of AMOLED innovation, we should first review the benefits of LCD technology. The backlighting quality ensures that whites are strong and brightness is superb but will deplete a battery much more quickly than just an AMOLED display. Furthermore, the cost of LCD screens is a considerable consideration. In addition to being less expensive and more easily accessible, they are produced in standard industry sizes, allowing them to be purchased for innovative products with relative ease.

OLED64 * 48 dot matrix display module. The display module has blue light, white light, two color display, high brightness, self luminous, high contrast, ultra-thin, panorama view, storage operation temperature range, low power consumption, fast response and so on. It is widely used to display the display interface of electronic products.
Shenzhen SLS Industrial Co.,ltd established in 2003, is a professional LCD module manufacturer and solution provider. We have 1 full-auto COG assembly line, 2 semi-auto assembly line, backlight assembly line, no dust TP bonding line and manufacturing tech support, we can provide unique, innovative and cost effective LCD module development and manufacturing. Our product range includes: middle-small size TFT LCD, industrial capacitive touch panel... Our LCD products have been widely used in communications, GPS, Equipment, electronic audio-visual, instrumentation, household appliances, PDA and other industries.

Apple has used the Super AMOLED screen developed by Samsung since the iPhone X. If the original OLED is replaced after the warranty period of the mobile phone screen, the iPhone X and iPhone XS will cost $549. The high cost of replacing screens is not something that every consumer is willing to accept. Soft OLED and hard OLED replacement screens have gradually become hot selling products in mobile phone repair shops. Recently, the appearance of in cell LCD adapted to the iPhone X has broken this calm. It uses lower-cost LCD instead of OLED screens and enters the iPhone X repair industry with an absolute price advantage. What are the advantages and disadvantages of in cell LCD and OLED screen?
Take iFixit, a more authoritative website in the smartphone repair industry, and launched an in-cell LCD screen suitable for iPhone X / iPhone XS / iPhone XS Max. The prices are $75, $85, and $165.Its price is only half of OLED. The
In-cell LCD screen is darker than OLED, and the screen display color gamut and resolution are lower. When the mobile phone is in standby, the OLED screen can display pure black, while the LCD cannot.
The biggest advantage of the OLED screen is that the power consumption is small, the power consumption of the TFT LCD screen is larger than that of the OLED, and the standby time is shortened after the LCD screen is replaced.
In low-light environments, users who use OLED mobile phone screens are prone to eye pain. Because LCD can directly reduce the brightness of the screen, and OLED uses the method of adjusting the brightness and non-light duty cycle to deceive the brain to adjust the brightness. This means that in the dark light environment when the human pupil is naturally enlarged to allow more light to enter, the OLED actually enters the pupil at the highest brightness.
According to the iPhone customer experience feedback information, the LCD screen is more in line with the current user habits on the market. Apple is developing LCD screens for both the iPhone Xr and iPhone 11. Compared with OLED, iPhone in cell TFT LCD has a larger display effect than the original screen, and the price is much cheaper than OLED.

The smartphone display is today one of the most important elements of any new mobile device. With nearly all new phones using touchscreen technologies, the display is more than just a window full of words and pictures, it"s the way we interact with the technology we keep closest to ourselves.
If you are shopping for a new smartphone this year, there"s a good chance the quality of your new phone"s screen will be one of the deciding factors between competing models. Below we take a closer look at the main elements of today"s best smartphone displays.
Smartphone displays, like notebooks and tablets, are all based on LCD technologies. LCD has a fast refresh rate, which makes it great for mobile technologies that require bright displays with low power consumption.
TFT LCD — thin film transistor displays are easily the most common in smartphones at this time, though manufacturers are paving the way for newer, better performing screen technologies. TFT LCDs are often used in notebook displays as well.
AMOLED — active matrix organic light emitting diode is one of the prominent up and coming display technologies looking to take over from TFT displays.
AMOLED screens are visibly more colourful than TFT displays and have a lower power consumption with thanks to the intriguing fact that the colour black is produced by the OLED being switched off. AMOLED screens have been used by Samsung, HTC, Nokia and Dell to name a few, and continue to be in high demand.
Super AMOLED — Samsung has positioned itself at the forefront of mobile display technologies producing its "Super" variant on the AMOLED display. By combining the touch panel and the top layer of glass, Samsung has created a screen that is visibly more vibrant than previous AMOLED screens.
Super LCD — another contender for screen dominance is Super LCD. A variant of traditional LCD technologies, SLCD offers better contrast and warmer colours than older LCD displays, but is said to drain more power than AMOLED displays.
IPS — in-plane switching smartphone screens are characterised by vibrant colours and excellent off-axis viewing angles. IPS screens are typically more expensive, but the result is a screen you can see clearly from any angle. Apple recently employed IPS technology in the LCD display of the iPad and iPhone 4. This year, look out for LG to join Apple in producing smartphones with IPS screens.
Capacitive — the preferred technology, capacitive touchscreens, are almost always more responsive to user input and allow for the use of multi-touch technologies. Simply put, capacitive touchscreens transfer a small charge of energy from the display to the user"s finger when contact is made and the software calculates which specific area of the screen has changed its charge. For this reason only, parts of the human body (or similar materials) can be used on touchscreens, a restriction that can make character-based text input, like Asian languages, more difficult.
Resistive — this technology is comprised of two very thin layers of metal under the glass of a phone"s display which collect location data when they are pressed together. This requires the user to apply pressure and often results in a less responsive user experience.
Aside from the appearance of a screen, the two most important measurements to consider are the size (typically measured diagonally in inches) and the resolution, or how many pixels the screen displays. The resolution of a screen is often referred to as a variant of the classic VGA resolution (640x480 pixels), but we"re also seeing companies starting refer to resolution in terms of it as a fraction of full high definition, or 1920x1080 pixels.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey