tft lcd without controller factory
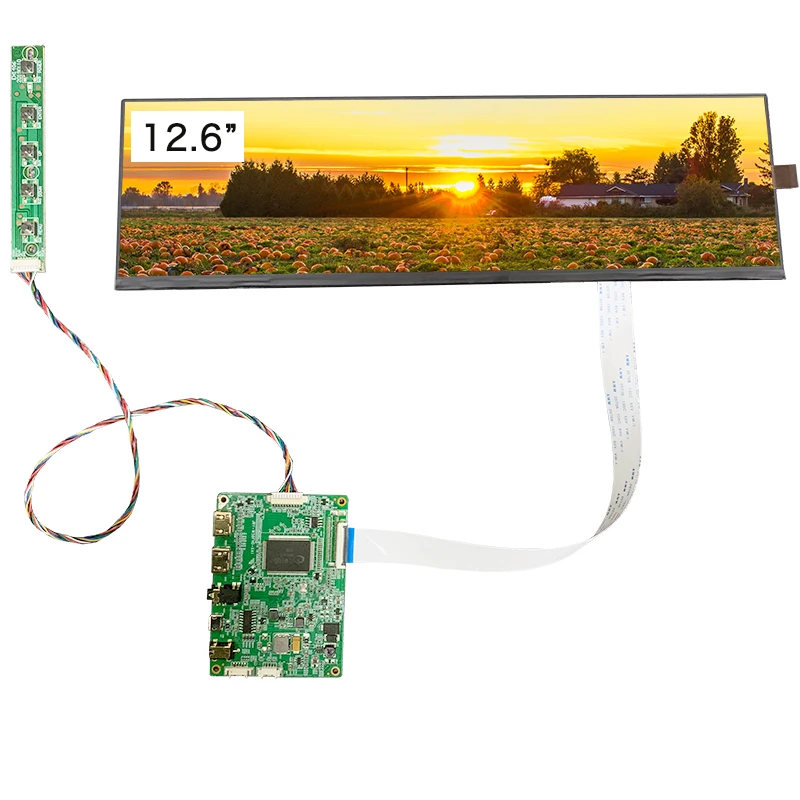
We always continually provide you with the most conscientious customer service, and the widest variety of designs and styles with finest materials. These efforts include the availability of customized designs with speed and dispatch for Industrial Tft-Lcd Panel, Mobile Lcd, Liquid Crystal Panel, Game Lcd Panel,Tft Lcd Backlight. We warmly welcome friends from all walks of life to seek mutual cooperation and create a more brilliant and splendid tomorrow. The product will supply to all over the world, such as Europe, America, Australia,Porto, Latvia,Niger, Kuwait.Our products are widely recognized and trusted by users and can meet continuously developing economic and social needs. We welcome new and old customers from all walks of life to contact us for future business relationships and achieving mutual success!

The 7.0 inch WF70QTIFGDBN0 TFT LCD (resolution 800x480) is built in with SSD1963 controller board plus a 36 pin-out connector on board. This model is available in 8080 family MPU 8bit/16bit options and already defined pin no. 33 ~ 36 as backlight supply; so there is no need to design extra backlight circuit. This display is with the module dimension of 165x100 mm and AA size of 154.08 x 85.92 mm.

Alibaba.com offers 190 tft lcd controller board slim products. About 81% % of these are lcd modules, 5%% are lcd touch screen, and 1%% are lcd boards & accessories.
A wide variety of tft lcd controller board slim options are available to you, You can also choose from original manufacturer, odm tft lcd controller board slim,As well as from tft, ips, and lcm.
LCD is the abbreviation for liquid crystal display. An LCD basically consists of two glass plates with a special liquid between them. The special attribute of this liquid is that it rotates or “twists” the plane of polarized light. This effect is influenced by the creation of an electrical field. The glass plates are thus each coated with a very thin metallic film. To obtain polarized light, you apply a polarization foil, the polarizer, to the bottom glass plate. Another foil must be applied to the bottom glass plate, but this time with a plane of polarization twisted by 90°. This is referred to as the analyzer.
In the idle state, the liquid twists the plane of polarization of the incoming light by 90° so that it can pass the analyzer unhindered. The LCD is thus transparent. If a specific voltage is applied to the metallic film coating, the crystals rotate in the liquid. This twists the plane of polarization of the light by another 90°, for example: The analyzer prevents the light getting through, and the LCD thus becomes opaque.TN, STN, FSTN, blue mode, yellow-green mode
However, the different colors occur only in displays that are either not lit or that are lit with white light. If there is any color in the lighting (e.g. yellow-green LED lighting), it overrides the color of the display. A blue-mode LCD with yellow-green LED lighting will always appear yellow-green.Static or multiplex driving method
Every LCD has a preferred angle of view at which the contrast of the display is at its optimum. Most displays are produced for the 6°° angle of view, which is also known as the bottom view (BV). This angle corresponds to that of a pocket calculator that is lying flat on a desktop.
LCDs without lighting are hard to imagine these days. However, since there are basically four different types of lighting, the type selected depends very much on the application. Here is a brief overview to clarify the situation:LED
Standard LCDs have a temperature range of 0 to +50°C. High-temperature displays are designed for operation in the range from -20 to +70°C. In this case, however, additional supply voltage is generally required. Since the contrast of any LCD is dependent on the temperature, a special temperature-compensation circuit is needed in order to use the entire temperature range, and this is particularly true for high-temperature displays (-20 to +70°C). Manual adjustment is possible but rather impractical for the user.
However, the storage temperature of a display should never be exceeded under any circumstances. An excessively high temperature can destroy the display very quickly. Direct exposure to the sun, for example, can destroy an LCD: This is because an LCD becomes darker (in positive mode) as it gets hotter. As it gets darker, it absorbs more light and converts it to heat. As a result, the display becomes even hotter and darker... In this way, temperatures of over 100°C can quickly be reached.Dot-matrix, graphics and 7-segment displays
The first LCDs were 7-segment displays, and they are still found today in simple pocket calculators and digital watches. 7 segments allow all of the digits from 0 to 9 to be displayed.
Text displays require what is known as a dot matrix, an area consisting of 5x7=35 dots, in order to display all of the letters in the alphabet as well as various special characters. Graphics displays have a similar structure to text displays. In this case, however, there are no spaces between the lines and characters.Display drivers and controllers
The semiconductor industry now offers a very large range of LCD drivers. We generally distinguish between pure display drivers without intelligence of their own, controllers with a display memory and possibly a character set, and micro-controllers with integrated LC drivers.
Pure display drivers work in a similar way to a shift register. They generally have a serial input. They require an external pulse, and in multiplex operation with high frequency they require new display data continuously in order to achieve a refresh frequency that is as high as possible (MSM5219, UPD7225, HD44100, LC7942, etc.). An example of a genuine controller is theHD44780 for dot-matrix displays: Once it has received the ASCII code, the controller manages its character set, memory and multiplexing entirely on its own. The following controllers are widely used for graphics displays: HD61202/3, HD61830, SED1520, SED1330, T6963.
Many ask themselves, "What is the difference between an LCD display and a TFT-display?" or "What is the difference between a TFT and an OLED display?". Here are these 3 sometimes extremely different display technologies briefly explained. LCD vs. TFT vs. OLED (comparison).
- The LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) is a passive display technology. The operation and the structure are described above. Passive means that an LCD can only darken or let out light. So it always depends on ambient light or a backlight. This can be an advantage because the power consumption of a LCD display is very, very low. Sometimes even less than the accumulated power consumption of an E-paper display, which in static operation requires absolutely no energy to maintain the content. To change the contents, however, a relatively large amount of power is required for an E-paper display.
LCDs can also be reflective, so they reflect incident light and are therefore legible even at maximum brightness (sunlight, surgical lighting). Compared to TFT and also OLED, they have an unbeatable advantage in terms of readability and power consumption :; the "formula" is: Sunlight = LCD.
- A TFT-display (of Thin-Film Transistor) is usually a color display (RGB). From the construction and the technology it corresponds to the LCD. It is also passive, so it needs a backlight. This is in any case necessary except for a few, very expensive constructions. However, a TFT needs much more light than the monochrome relatives, because the additional structures on the glass as well as the additional color filters "swallow" light. So TFTs are not particularly energy-efficient, but can display in color and at the same time the resolution is much higher.
- OLED displays (by Organic-Light-Emitting-Diode) are as the name implies active displays - every pixel or sign generates light. This achieves an extremely wide viewing angle and high contrast values. The power consumption is dependent on the display content. Here OLEDs to TFTs and LCDs differ significantly, which have a nearly constant power consumption even with different display contents. Unfortunately, the efficiency of converting the electric current into light energy is still very poor. This means that the power consumption of OLEDs with normal content is sometimes higher than that of a TFT with the same size. Colored OLEDs are increasingly used in consumer devices, but for the industry, due to their availability and lifetime, currently only monochrome displays are suitable (usually in yellow color).
In the reaction time, the OLEDs beat each TFT and LCD by worlds. Trise and Tfall are about 10μs, which would correspond to a theoretical refresh rate of 50,000 Hz. Possibly an advantage in very special applications.
Finally the question "What is better, LCD, OLED or TFT?" Due to the physical differences you can not answer that blanket. Depending on the application, there are pros and cons to each individual technology. In addition to the above differences, there are many more details in the design and construction that need to be individually illuminated for each device. Write us an e-mail or call us: we have specialists with some 20- and 30-year experience. We are happy to compare different displays together with you.AACS and IPS technology

INT070ATFT and INT070ATFT-TS are embedded display driver boards based on the Displaytech 7 inch 800 x 480 RGB resolution TFT display module. This embedded driver board includes a 7" standard or resistive touchscreen display. Mounted on the embedded board is the Solomon Systech SSD1963 LCD controller that supports common RAM-less LCD drivers and offers the following features and benefits:

We are going to introduce category of Raystar’s 7-inch TFT LCD modules, which includes resolutions of 800x480~1024x800, and has a variety of TFT module sizes/VA sizes/AA sizes. 7-inch displays have plenty of IC and interface combinations. You can also choose either module with capacitive touch (supports 1-10 point touch) or resistive touch. The brightness ranges from 250 cd/㎡ to high brightness 1100 cd/㎡. There are also options of 7-inch TFT LCD display with control panel. If you couldn’t find a suitable module on our page, we have more models that are not published on the website. You are welcome to click “contact us” button on the top of this page. We’re more than happy to serve you.
Let us start with the basics first; refresh the knowledge about TN and LCD displays in general, later we will talk about TFTs (Thin Film Transistors), how they differ from regular monochrome LCD displays. Then we will go on to the ghosting effect, so we will not only discuss the technology behind the construction of the TFT, but also some phenomena, like the ghosting effect, or grayscale inversion, that are important to understand when using an LCD TFT display.
Next, we will look at different technologies of the TFT LCD displays like TN, IPS, VA, and of course about transmissive and transflective LCD displays, because TFT displays also can be transmissive and transflective. In the last part we will talk about backlight.
Let us start with a short review of the most basic liquid crystal cell, which is the TN (twisted nematic) display. On the picture above, we can see that the light can be transmit through the cell or blocked by the liquid crystal cell using voltage. If you want to learn more about monochrome LCD displays and the basics of LCD displays, follow this link.
What is a TFT LCD display and how it is different from a monochrome LCD display? TFT is called an active display. Active, means we have one or more transistors in every cell, in every pixel and in every subpixel. TFT stands for Thin Film Transistor, transistors that are very small and very thin and are built into the pixel, so they are not somewhere outside in a controller, but they are in the pixel itself. For example, in a 55-inch TV set, the TFT display contains millions of transistors in the pixels. We do not see them, because they are very small and hidden, if we zoom in, however, we can see them in every corner of each pixel, like on the picture below.
On the picture above we can see subpixels, that are basic RGB (Red, Green, Blue) colors and a black part, with the transistors and electronic circuits. We just need to know that we have pixels, and subpixels, and each subpixel has transistors. This makes the display active, and thus is called the TFT display. TFT displays are usually color displays, but there are also monochrome TFT displays, that are active, and have transistors, but have no colors. The colors in the TFT LCD display are typically added by color filters on each subpixel. Usually the filters are RGB, but we also have RGBW (Red, Green, Blue, White) LCD displays with added subpixels without the filter (White) to make the display brighter.
Going a little bit deeper, into the TFT cell, there is a part inside well known to us from the monochrome LCD display Riverdi University lecture. We have a cell, liquid crystal, polarizers, an ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) layer for the electrodes, and additionally an electronic circuit. Usually, the electronic circuit consists of one transistor and some capacitors to sustain the pixel state when we switch the pixel OFF and ON. In a TFT LCD display the pixels are much more complicated because apart from building the liquid crystal part, we also need to build an electronic part.
That is why TFT LCD display technologies are very expensive to manufacture. If you are familiar with electronics, you know that the transistor is a kind of switch, and it allows us to switch the pixel ON and OFF. Because it is built into the pixel itself, it can be done very quickly and be very well controlled. We can control the exact state of every pixel not only the ON and OFF states, but also all the states in between. We can switch the light of the cells ON and OFF in several steps. Usually for TFT LCD displays it will be 8-bit steps per color, so we have 256 steps of brightness for every color, and every subpixel. Because we have three subpixels, we have a 24-bit color range, that means over 16 million combinations, we can, at least theoretically, show on our TFT LCD display over 16 million distinct colors using RGB pixels.
Now that we know how the TFT LCD display works, we can now learn some practical things one of which is LCD TFT ghosting. We know how the image is created, but what happens when we have the image on the screen for a prolonged time, and how to prevent it. In LCD displays we have something called LCD ghosting. We do not see it very often, but in some displays this phenomenon still exists.
Another issue present in TFT displays, especially TN LCD displays, is grayscale inversion. This is a phenomenon that changes the colors of the screen according to the viewing angle, and it is only one-sided. When buying a TFT LCD display, first we need to check what kind of technology it is. If it is an IPS display, like the Riverdi IPS display line, then we do not need to worry about the grayscale inversion because all the viewing angles will be the same and all of them will be very high, like 80, 85, or 89 degrees. But if you buy a more common or older display technology type, like the TN (twisted nematic) display, you need to think where it will be used, because one viewing angle will be out. It may be sometimes confusing, and you need to be careful as most factories define viewing direction of the screen and mistake this with the greyscale inversion side.
We know already that TN (twisted nematic) displays, suffer from grayscale inversion, which means the display has one viewing side, where the image color suddenly changes. It is tricky, and you need to be careful. On the picture above there is a part of the LCD TFT specification of a TN (twisted nematic) display, that has grayscale inversion, and if we go to this table, we can see the viewing angles. They are defined at 70, 70, 60 and 70 degrees, that is the maximum viewing angle, at which the user can see the image. Normally we may think that 70 degrees is better, so we will choose left and right side to be 70 degrees, and then up and down, and if we do not know the grayscale inversion phenomena, we may put our user on the bottom side which is also 70 degrees. The viewing direction will be then like a 6 o’clock direction, so we call it a 6 o’clock display. But you need to be careful! Looking at the specification, we can see that this display was defined as a 12 o’clock display, so it is best for it to be seen from a 12 o’clock direction. But we can find that the 12 o’clock has a lower viewing angle – 60 degrees. What does it mean? It means that on this side there will be no grayscale inversion. If we go to 40, 50, 60 degrees and even a little bit more, probably we will still see the image properly. Maybe with lower contrast, but the colors will not change. If we go from the bottom, from a 6 o’clock direction where we have the grayscale inversion, after 70 degrees or lower we will see a sudden color change, and of course this is something we want to avoid.
We will talk now about the other TFT technologies, that allow us to have wider viewing angles and more vivid colors. The most basic technology for monochrome and TFT LCD displays is twisted nematic (TN). As we already know, this kind of displays have a problem with grayscale inversion. On one side we have a higher retardation and will not get a clear image. That is why we have other technologies like VA (Vertical Alignment), where the liquid crystal is differently organized, and another variation of the TFT technology – IPS which is In-Plane Switching. The VA and IPS LCD displays do not have a problem with the viewing angles, you can see a clear image from all sides.
Apart from the different organization of the liquid crystals, we also organize subpixels a little bit differently in a VA and IPS LCD displays. When we look closer at the TN display, we will just see the subpixels with color filters. If we look at the VA or IPS display they will have subpixels of subpixels. The subpixels are divided into smaller parts. In this way we can achieve even wider viewing angles and better colors for the user, but of course, it is more complicated and more expensive to do.
The picture above presents the TN display and grayscale inversion. For IPS or VA technology there is no such effect. The picture will be the same from all the sides we look so these technologies are popular where we need wide viewing angles, and TN is popular where we don’t need that, like in monitors. Other advantages of IPS LCD displays are they give accurate colors, and wide viewing angles. What is also important in practice, in our projects, is that the IPS LCD displays are less susceptible to mechanical force. When we apply mechanical force to the screen, and have an optically bonded touch screen, we push the display as well as squeeze the cells. When we have a TN display, every push on the cell changes the image suddenly, with the IPS LCD displays with in-plane switching, different liquid crystals organization, this effect is lesser. It is not completely removed but it is much less distinct. That is another reason IPS displays are very popular for smartphones, tablets, when we have the touchscreens usually optically bonded.
Now, let us look at the backlight types. As we see here, on the picture above, we have four distinct types of backlight possible. The most common, 95 or 99 per cent of the TFT LCD displays on the market are the transmissive LCD display type, where we need the backlight from the back. If you remember from our Monochrome LCD Displays lecture, for transmissive LCD displays you need the backlight to be always on. If you switch the backlight off, you will not see anything. The same as for monochrome LCD displays, but less popular for TFT displays, we have the transflective LCD display type. They are not popular because usually for transflective TFT displays, the colors lack in brightness, and the displays are not very practical to use. You can see the screen, but the application is limited. Some transflective LCD displays are used by military, in applications where power consumption is paramount; where you can switch the backlight off and you agree to have lower image quality but still see the image. Power consumption and saving energy is most important in some kind of applications and you can use transflective LCD displays there. The reflective type of LCD displays are almost never used in TFT. There is one technology called Low Power Reflective Displays (LPRD) that is used in TFT but it is not popular. Lastly, we have a variation of reflective displays with frontlight, where we add frontlight to the reflective display and have the image even without external light.
Just a few words about Low Power Reflective Displays (LPRD). This kind of display uses environmental light, ambient light to reflect, and produce some colors. The colors are not perfect, not perfectly clear, but this technology is becoming increasingly popular because it allows to have color displays in battery powered applications. For example, a smartwatch would be a case for that technology, or an electrical bike or scooter, where we can not only have a standard monochrome LCD display but also a TFT LCD color display without the backlight; we can see the image even in
strong sunlight and not need backlight at all. So, this kind of TFL LCD display technology is getting more and more popular when we have outdoor LCD displays and need a low power consumption.
On the picture above, we have some examples of how transmissive and reflective LCD displays work in the sunlight. If we have a simple image, like a black and white pattern, then on a transmissive LCD display, even with 1000 candela brightness, the image probably will be lower quality than for a reflective LCD display; if we have sunlight, we have very strong light reflections on the surface of the screen. We have talked about contrast in more detail in the lecture Sunlight Readable Displays. So, reflective LCD displays are a better solution for outdoor applications than transmissive LCD displays, where you need a really strong backlight, 1000 candela or more, to be really seen outdoors.
To show you how the backlight of LCD displays is built, we took the picture above. You can see the edge backlight there, where we have LEDs here on the small PCB on the edge, and we have a diffuser that distributes the light to the whole surface of LCD screen.
In addition to the backlight, we have something that is called a frontlight. It is similar to backlight, it also uses the LEDs to put the light into it, but the frontlight needs to be transparent as we have the display behind. On the example on the picture above we can see an e-paper display. The e-paper display is also a TFT display variation, but it is not LCD (liquid crystal), it is a different technology, but the back of the display is the same and it is reflective. The example you see is the Kindle 4 eBook reader. It uses an e-paper display and a frontlight as well, so you can read eBooks even during the night.

LT7688 is a high-efficient graphic acceleration display controller. It integrated Levetop"s 32Bit MCU - LT32U02 and the core structure of TFT Graphic Accelerator - LT768. Its main function is to provide UART, USB communication, enable system"s MUC to send TFT screen displaying content to TFT driver via simple command. The chip support graphic acceleration, PIP, Geometric Drawing, and promote TFT display efficiency, and reduce the upper MCU processing time on graphic, it support 16/18bits RGB type TFT Panel from 320*240(QVGA) to 1280*1024 (SVGA).
The maximum of main frequency of LT7688 internal MCU is 72MHz, includes 64Kbytes Flash and 8Kbytes SRAM. Beside provides UART and USB serial communication, it also provides some analog input AIN, PWM and INT interrupt interfaces. These interfaces can also be set as general purpose IO interfaces. In order to achieve multi-layer, high resolution display effect,LT7680 has 128Mb built-in display memory to support 1bit/pixel to 18bit(262K)/pixel color display. It also owns built-in geometric drawing engine to support point drawing, line drawing, curve drawing, ellipse, triangle, rectangle, rounded rectangle drawing and so on. In addition, the chip has embedded hardware graphics processing unit to provide mandatory graphical operations like magic rotation, flip, reflect, PIP(picture in picture) , hybrid graphics and transparent display. If work with Levetop"s TFT module develop software will have better efficiency, and no need to upgrade MCU for TFT screen. The powerful performance of LT7688 is suitable for embedded systems with TFT-LCD display, such as home appliances, industrial control, electronic instruments, medical equipment, human-machine interface, industrial equipment, testing equipment, etc.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey