tft lcd glass substrate brands
One of the industry’s leading oxide panel makers selected Astra Glass as its backplane glass substrate because it has the inherent fidelity to thrive in high-temperature oxide-TFT glass fabrication for immersive high-performance displays.
One of the industry’s leading oxide panel makers selected Astra Glass as its backplane glass substrate because it has the inherent fidelity to thrive in high-temperature oxide-TFT glass fabrication for immersive high-performance displays.
For its transparency, flat and smooth surface, and excellent heat resistance, this product is used as a substrate for various types of displays such as televisions, personal computers, smart phones, tablet devices, and in-vehicle infotainment. It is an alkali-free aluminosilicate glass that was developed by using the float process.
Recently, screen sizes of LCD TVs have become wider and larger. The glass substrates from AGC enable this trend of larger LCD TV sizes. Glass substrates also play a key role to reproduce clear and beautiful screen images as one of the core components of LCDs.
It is necessary for TFT-LCD glass to meet many strict quality requirements. Unlike window pane glass, glass for TFT-LCDs is not allowed to contain alkalis. This is because alkali-ions contaminate liquid crystal materials and even adversely affect the characteristics of the TFT. Additionally, the glass should not exhibit large sagging even though its thickness is just 0.3 to 0.7 mm and should have excellent heat resistance while assuring dimensional stability even after being heated at high temperature. The glass also should have properties that its composition does not dissolve during the fabrication process using chemicals. "AN100", non-alkali glass developed by us, is the one that has fulfilled those various requirements. Furthermore, since "AN100" does not contain hazardous materials such as arsenic or antimony, it has high reputation for being an environment-friendly glass. Our technologies are supporting the design of thin, large, and environmentally friendly LCD TVs.
An LCD has a layer of liquid crystal sandwiched between two sheets of glass. The most remarkable feature of liquid crystal is its optical characteristics of being both a liquid and a solid. Applying voltage to the layer of liquid crystal causes the orientation of the molecules in the liquid crystal to change relative to each other. This molecule rearrangement controls the light transmission from the backlight; the light passes through color filters of red, blue, and green, and eventually rich images appear on the screen.
Majority of LCDs in wide use now are TFT-LCDs. In a TFT-LCD, a layer of thin film that forms transistors is used as a device that applies voltage to the liquid crystal layer, and those transistors control the voltage supplied to each pixel. The advantages of a TFT-LCD are high resolution and quick response time that enables motion image to be fine and clear.
It is AGC’s display glass substrates, developed using its distinctive precision glass processing technologies, that support these higher resolution TVs.
Smartphones and tablets can now be considered life necessities, and the LCD screen is the most frequently used interface whenever such devices are used. Without the LCD display, it is not possible to send email or view pictures taken by the camera function.
Furthermore, LCDs play an important role in a variety of applications such as in-vehicle displays, e.g. navigation systems and center information displays, and digital signage.
Through production and supply of LCD glass substrates, which is a key material of LCDs, AGC helps create a more convenient and comfortable life through integrating various technologies within the Group.

In its display business, AGC holds the number-two global market share in glass substrates used for thin-film-transistor (TFT) liquid crystal displays (LCD) and OLEDs.

The global TFT LCD Glass Substrate market size is projected to reach multi million by 2028, in comparision to 2021, at unexpected CAGR during 2022-2028 (Ask for Sample Report).
The TFT LCD Glass Substrate has several applications, including: Television,Laptop & Tablet,Desktop Monitor,Automotive,Mobilphone,Other. Based on types these are segmented in Gen. 5,Gen. 6,Gen. 7,Gen. 8. The market for TFT LCD Glass Substrate is highly competitive. There are several major market players in the market, including Corning,AGC,NEG,Tunghsu Optoelectronic,AvanStrate,IRICO,LG Chem. The report provides an expansive market geographical regions analysis by covering areas like North America: United States, Canada, Europe: GermanyFrance, U.K., Italy, Russia,Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, South, India, Australia, China, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Latin America:Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Middle East & Africa:Turkey, Saudi, Arabia, UAE, Korea.
Key Benefits for Industry Participants & StakeholdersThis TFT LCD Glass Substrate research report provides an expansive market analysis of the desired sector by wrapping areas like growth drivers, trends persisting in the endeavor, regulatory framework prevalent in the sector as well as a comprehensive SWOT analysis.
The TFT LCD Glass Substrate Research Report focuses heavily on analyzing various segments of the market. The TFT LCD Glass Substrate Market is categorized by type, region, and Application.
Sections in TFT LCD Glass Substrate Market Report:Section 1 mainly consists of an overview and an introduction of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate company focusing on the important figures and statistics of the market.
Section 2 comprises multiple marketing transactions, sales generation, consistency key factors, and the overall growth of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate company.
Section 4 includes a key driver analysis for satisfaction and loyalty along with SWOT Analysis, considering the potential strengths, weaknesses, growth opportunities, and threats put forth by the TFT LCD Glass Substrate company..
Section 5 enlists the benefits of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate company, by providing a full overview of the feasible company verdicts which include an in-depth analysis of the product profiles, and corporate growth.
Section 6 chiefly covers the analysis of the effect of the impact of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate industry on the development and growth factors of the market across the globe.
Section 9 is the final section of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate market report that recaps and puts a full stop to all arguments and wrong interpretations by providing the right outcomes to the reader end.
The TFT LCD Glass Substrate Market Industry Research Report contains:The TFT LCD Glass Substrate market research report covers all topics of the company including marketing methodologies, analysis of the growth and performance, and interaction with real-time consumers.
It contains all the components of numerous market ideas, prototypes, product profiles, trends, and figures a user needs to evaluate the growth of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate company.
Another significant subject of this market report is the necessity to grade and evaluate the effectiveness of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate company in the global development of the firm.
In addition to this TFT LCD Glass Substrate research study, it aids in business marketing, business analysis, and overall performance concerning the competitive field.
The TFT LCD Glass Substrate Market Research Report says that the covid 19 pandemic has severely damaged not only human lives but also the global economy and global markets. Data information and statistics of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate report remained in flux, and government policies fluctuate to extremes, as the killer virus swept through nations, affecting production, disrupting supply chains, and unsettling the financial markets. The TFT LCD Glass Substrate Market Research Report aims to analyze the actions of competition authorities to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic and facilitate their recovery.
The TFT LCD Glass Substrate report gives insightful data about the TFT LCD Glass Substrate Market Share and the challenges within the industry. It discusses in detail theTFT LCD Glass Substrate Market Share to help businesses understand the areas of growth and the reasons slowing down the progress. The TFT LCD Glass Substrate Market Research also analyzes the future of the company and what are the challenges and risks that a company may face in the future.
This report helps to find information on how to boost sales of TFT LCD Glass Substrate in the overseas markets.The report offers detailed coverage of the TFT LCD Glass Substrate industry’s progress and main market trends with the impact of coronavirus.
The opportunities and threats that are ought to arise in the future for the key market players have also been emphasized in the TFT LCD Glass Substrate research report publication.
The research report also mentions the innovations, profound inventions, latest developments, marketing strategies, and branding techniques, present in the TFT LCD Glass Substrate market.
This TFT LCD Glass Substrate report additionally states import/export consumption, supply and demand figures, demographics, revenue, and gross margins alongside the features of different methodologies to upskill the company’s development.
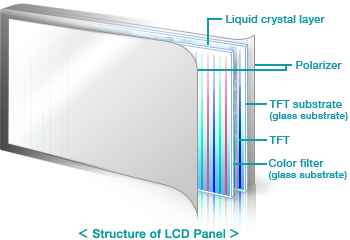
“LCD glass substrate” is a generic term for the special glass used for thin-film transistor (TFT) LCDs which form the display area of products including LCD televisions, personal computers and mobile phones. An LCD panel consists of various components stacked in a number of layers. These components include a polarizer, a color filter and a liquid crystal layer, with the glass substrate being the most important. Glass substrates are extremely thin – typically about 0.3-0.7 mm – and 8th-generation glass substrates (2,200 x 2,500 mm) are as large as three tatami mats in size.
In order to accurately display beautiful, high-definition images, LCD glass substrates must have super-smooth surfaces with irregularities reduced to the nano-level. It is also necessary to avoid the formation of internal bubbles and the intrusion of foreign matter (dust) too minute for the naked eye. Smooth and scratch-free glass substrates with the ultimate precision represent the maximum quality AvanStrate aims for.

The glass substrate is one of the core layers of TFT LCD. It influences fundamental features of the display in the resolution, light transmittance, thickness, weight, and viewing angle.
The glass substrate is the core component of the TFT LCD and plays a significant role in the upstream of the TFT LCD industry, similar to the silicon wafer in the semiconductor industry.
Since the quality of the glass substrate decides the features of the display in the resolution, light transmittance, thickness, weight, viewing angle, and other important parameters.
The fundamental structure of the TFT LCD is similar to a sandwich, two layers of “bread” (TFT substrate and color filter) sandwiched with “jam” (liquid crystal).
Considering the unique environment in the manufacturing process of TFT-LCD, such as high temperature, high pressure, and environment switching among acidic-neutral-alkaline, the following characteristics of the glass must meet the challenge and quality requirement.
In the manufacturing process, the maximum temperature can reach above 600 ℃, which requires the glass substrate to remain rigid without any sticking even at such a high temperature.
After the etching process, the glass substrate needs to remain with minimal changes, and can’t be left with visible residue and interference with film deposition.
In the process the mother glass is cut into pieces in the required size, with a thickness of only 0.5-0.7mm, the glass needs to have high mechanical strength and elastic modulus >70GPa.
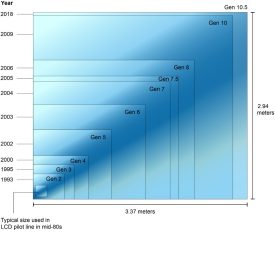
Usually, the size has doubled with each successive generation. From the initial generation 4 (G4) to the current G11, the size of the substrate has grown to 3000*3320mm.
In the global market of glass substrates for TFT-LCD, more than 90% are concentrated in several major manufacturers, such as Corning (America), Asahi Glass (Japan), Nippon Electric Glass (Japan), and AvanStrate (Taiwan).
However, there is still a gap and need for breakthroughs in the glass for high-generation LCD panel production lines and AMOLED alkali-free glass technology. It is hard to achieve high localization in a short time.
AGC has now decided to relocate a cutting-edge glass substrate production facility from within the AGC Group. This investment will significantly reduce the need for capital investment while maintaining the group"s total production capacity.
There has been a large increase in production of TFT-LCD panels in China in recent years which has resulted in an abrupt increase in demand for glass substrates. To accommodate demand growth, the AGC Group has established a supply system by setting up a processing facility in Kunshan, Jiangsu Province, and Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, and a furnace in Huizhou,Guangdong Province.
AGC has also decided to build an 11th generation dedicated glass substrate* furnace in order to address the anticipated growth in demand of TFT-LCD panels that will use similar-sized TFT-LCD glass substrates.

Recently, the Bengbu Glass Industry Design and Research Institute Holdings subsidiary, Chengdu Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd. production of the first ultra-thin 0.5mm the arsenic TFT-LCD glass substrate products passed the domestic core users - Tianma Microelectronics batch certification, and officially subsequent bulk purchases orders, successfully open up the market.

(Yicai Global) June 19 -- China National Building Material has built the country"s first production line capable of producing 8.5th-generation TFT-LCD glass substrates, making China one of few nations to master the technology.
The central state-owned firm"s Bengbu Glass Industry Design and Research built the facility after three years of research, Science and Technology Daily reported. The plant aims to obtain certifications that will allow it to manufacture for domestic display makers.
TFT-LCD, or thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal displays, are classified by the size of their glass substrate. Sixth-generation displays are now widely considered out-dated while 8.5th-gen tech is the most advanced. The newer technologies use larger substrates, which are more efficient to make and can be used in larger screens.
Demand for glass substrates in China reached 260 million square meters in 2018, with demand for 8.5th-gen components making up 233 million, according to the China Optics & Optoelectronics Manufacturers Association. But domestic production is only about 40 million square meters and all below 6th-gen. American and Japanese companies mostly dominate the more advanced segment of the market.

Flat-panel displays are thin panels of glass or plastic used for electronically displaying text, images, or video. Liquid crystal displays (LCD), OLED (organic light emitting diode) and microLED displays are not quite the same; since LCD uses a liquid crystal that reacts to an electric current blocking light or allowing it to pass through the panel, whereas OLED/microLED displays consist of electroluminescent organic/inorganic materials that generate light when a current is passed through the material. LCD, OLED and microLED displays are driven using LTPS, IGZO, LTPO, and A-Si TFT transistor technologies as their backplane using ITO to supply current to the transistors and in turn to the liquid crystal or electroluminescent material. Segment and passive OLED and LCD displays do not use a backplane but use indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent conductive material, to pass current to the electroluminescent material or liquid crystal. In LCDs, there is an even layer of liquid crystal throughout the panel whereas an OLED display has the electroluminescent material only where it is meant to light up. OLEDs, LCDs and microLEDs can be made flexible and transparent, but LCDs require a backlight because they cannot emit light on their own like OLEDs and microLEDs.
Liquid-crystal display (or LCD) is a thin, flat panel used for electronically displaying information such as text, images, and moving pictures. They are usually made of glass but they can also be made out of plastic. Some manufacturers make transparent LCD panels and special sequential color segment LCDs that have higher than usual refresh rates and an RGB backlight. The backlight is synchronized with the display so that the colors will show up as needed. The list of LCD manufacturers:
Organic light emitting diode (or OLED displays) is a thin, flat panel made of glass or plastic used for electronically displaying information such as text, images, and moving pictures. OLED panels can also take the shape of a light panel, where red, green and blue light emitting materials are stacked to create a white light panel. OLED displays can also be made transparent and/or flexible and these transparent panels are available on the market and are widely used in smartphones with under-display optical fingerprint sensors. LCD and OLED displays are available in different shapes, the most prominent of which is a circular display, which is used in smartwatches. The list of OLED display manufacturers:
LCDs are made in a glass substrate. For OLED, the substrate can also be plastic. The size of the substrates are specified in generations, with each generation using a larger substrate. For example, a 4th generation substrate is larger in size than a 3rd generation substrate. A larger substrate allows for more panels to be cut from a single substrate, or for larger panels to be made, akin to increasing wafer sizes in the semiconductor industry.
"Samsung Display has halted local Gen-8 LCD lines: sources". THE ELEC, Korea Electronics Industry Media. August 16, 2019. Archived from the original on April 3, 2020. Retrieved December 18, 2019.
"TCL to Build World"s Largest Gen 11 LCD Panel Factory". www.businesswire.com. May 19, 2016. Archived from the original on April 2, 2018. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
"Panel Manufacturers Start to Operate Their New 8th Generation LCD Lines". 대한민국 IT포털의 중심! 이티뉴스. June 19, 2017. Archived from the original on June 30, 2019. Retrieved June 30, 2019.
"Samsung Display Considering Halting Some LCD Production Lines". 비즈니스코리아 - BusinessKorea. August 16, 2019. Archived from the original on April 5, 2020. Retrieved December 19, 2019.
Herald, The Korea (July 6, 2016). "Samsung Display accelerates transition from LCD to OLED". www.koreaherald.com. Archived from the original on April 1, 2018. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
"China"s BOE to have world"s largest TFT-LCD+AMOLED capacity in 2019". ihsmarkit.com. 2017-03-22. Archived from the original on 2019-08-16. Retrieved 2019-08-17.
China"s first 8.5-generation tft-lcd glass substrate production line was successfully fired in bengbu, anhui province on Monday, entering the debugging stage of the equipment. The production is expected to reach mass production in September.
TFT-LCD glass substrate is the key strategic material of electronic information display industry.The 8.5 generation tft-lcd glass substrate has a size of 2.2m*2.5m and can be cut into 6 55-inch panels.At present, the 8.5 generation tft-lcd glass substrates for large-size LCD TVS in China are completely dependent on the technology and products of foreign companies, and they cannot be independently produced.
The ignition production line is the project result of the national key research and development program of ministry of science and technology "development and industrialization demonstration of core technology of high-generation electronic glass substrate and cover plate", which is led by China building materials bengbu glass industrial design and research institute.
According to the data of liquid crystal branch of China optical optoelectronics industry association, in 2018, the demand of glass substrate in mainland China is about 260 million square meters, among which the demand of 8.5 generation glass substrate is 233 million square meters, while the annual supply of domestic tft-lcd glass substrate is less than 40 million square meters, and all of them are 6 generation lines or below.
The 8.5 generation tft-lcd glass substrate production represents the high level of modern glass industry large-scale manufacturing, and its core technology has been monopolized by a few foreign enterprises for a long time.Supported by the national key research and development program, bengbu glass industry design and research institute of China building materials co., LTD., with years of accumulation and persistent research, has cooperated with several units to overcome the key technology of high-generation electronic glass, which will provide the key raw material guarantee for China"s LCD panel industry after mass production.
It is reported that after the project volume, China will become one of the few countries in the world to master the production technology of high-generation tft-lcd glass substrate.
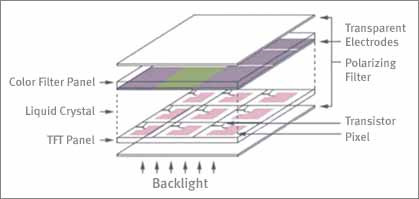
Today’s LCD displays are thinner and more immersive than ever. LCD technologyis continuously evolving to improve the touch response and quality of the display. Most displays are made of glass which is extremely thin in shape typically about 0.3-0.7 mm. In LCDs, a glass substrate is used to build the TFT (Thin-film transistors) layer that controls a color filter layer and liquid crystals.
For production efficiency, manufacturers are using large-sized substrates to cut into the appropriate size requirements of the product for instance LCD display panels are produced on top of a large substrate. The glass substrates that are the foundation of panels are called ‘Mother Glass’ and the generation is determined based on the size of the mother glass.
LCD glass substrate is a specialized glass used in thin-film transistors (TFTs) LCDs to form the display of various products such as personal computers, laptops, mobile phones, game consoles, automotive navigation systems, and digital cameras/camcorders. LCD glass substrate layers consist of liquid crystals, a color filter, a polarizer, TFT, and a TFT substrate.
The demand for high-resolution televisions is rapidly increasing as LCD technology is continuously growing. LCD glass substrates are widely used in televisions due to the usual size of televisions. Nowadays consumers are preferring bigger and wider televisions to enjoy vivid and fine pictures even in very large screen sizes.
TVs are usually bigger and wider compared to computers and laptops which results in increasing demand for LCD glass substrates for high-definition (HD) visuals and images.
New technological advancements in displays with higher resolution such as 4K and 8K TVs are being developed one after another which can create new pathways for the LCD glass substrates.
LCD Glass substrate enables high-resolution and rich color contrast for a better experience. The rapid growth in the television industry with large-sized screens and ultra-high definition (UHD) is likely to propel the demand for LCD glass substrates.
With this rapid growth in TV and laptop production, the globalLCD glass substrates market size was valued at USD 7879.5 million in 2020 and is anticipated to reach USD 10090 million by 2028, expanding at a CAGR of 4.2% during the forecast period, 2021–2028.
Corning Incorporated is a US-based multinational technology company that specializes in ceramics, specialty glass, and related materials and technologies including advanced optics, primarily for industrial and scientific applications.
This company has several products such as EAGLE XG Slim Glass which helps panel manufacturers to innovate for lighter, thinner, and more environmentally conscious display panels. These substrates offer smooth, clean, and flat surfaces.
Corning Astra Glass highly engineered glass substrate that enables high pixel density for high-performance displays for brighter, faster, and more realistic images. This glass offers an optimum blend of low total pitch variation (TPV), low total thickness variation (TTV), and low sag for high-performance panels.
Lotus NXT Glass is a premium glass solution designed to withstand high-temperature processing requirements with brighter, energy-efficient displays with higher resolutions while providing industry-leading levels of low total pitch variation.
Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd, is a Japanese glass manufacturing company. This company has several glass products based on the business such as display, consumer glass, glass fiber, electronic products, and thin film coatings.
OA-10G (Alkali-free Glass Substrate): It has excellent surface smoother because it is made by overflow technology and is widely used as a substrate for liquid crystal display and OLED display.
OA-11(Alkali-free Glass Substrate): OA-11 has particularly low deformation and deflection of gravity properties. This is both very thin and easy to handle and it is widely for OLED display and liquid crystal display, as well as a substrate for the formation of various thin films.
OA-31(High Heat-resistant and Low Thermal Compaction Glass Substrate): This is widely used in tablets and smartphones. It is suitable for OLED and LTPS displays.
LCD glass substrates are widely used in television, laptops, and automotive navigation system. Rising emerging economies and increasing technological & entertainment expenditures can produce new growth opportunities for the key players. Inventions such as the production of LCD screens using a single substrate and new upcoming substrate generations can drive market growth.

TFT-LCD was invented in 1960 and successfully commercialized as a notebook computer panel in 1991 after continuous improvement, thus entering the TFT-LCD generation.
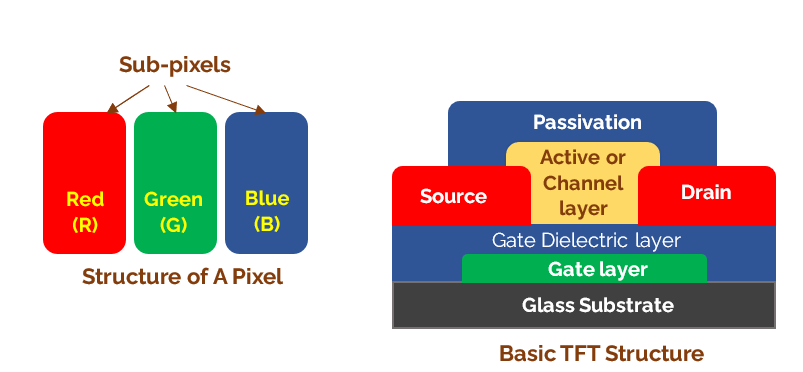
Simply put, the basic structure of the TFT-LCD panel is a layer of liquid crystal sandwiched between two glass substrates. The front TFT display panel is coated with a color filter, and the back TFT display panel is coated with a thin film transistor (TFT). When a voltage is applied to the transistor, the liquid crystal turns and light passes through the liquid crystal to create a pixel on the front panel. The backlight module is responsible for providing the light source after the TFT-Array panel. Color filters give each pigment a specific color. The combination of each different color pixel gives you an image of the front of the panel.
The TFT panel is composed of millions of TFT devices and ITO (In TI Oxide, a transparent conductive metal) regions arranged like a matrix, and the so-called Array refers to the region of millions of TFT devices arranged neatly, which is the panel display area. The figure below shows the structure of a TFT pixel.
No matter how the design of TFT display board changes or how the manufacturing process is simplified, its structure must have a TFT device and control liquid crystal region (if the light source is penetration-type LCD, the control liquid crystal region is ITO; but for reflective LCD, the metal with high reflection rate is used, such as Al).
The TFT device is a switch, whose function is to control the number of electrons flowing into the ITO region. When the number of electrons flowing into the ITO region reaches the desired value, the TFT device is turned off. At this time, the entire electrons are kept in the ITO region.
The figure above shows the time changes specified at each pixel point. G1 is continuously selected to be turned on by the driver IC from T1 to TN so that the source-driven IC charges TFT pixels on G1 in the order of D1, D2, and Dn. When TN +1, gATE-driven IC is selected G2 again, and source-driven IC is selected sequentially from D1.
Many people don’t understand the differences between generations of TFT-LCD plants, but the principle is quite simple. The main difference between generations of plants is in the size of glass substrates, which are products cut from large glass substrates. Newer plants have larger glass substrates that can be cut to increase productivity and reduce costs, or to produce larger panels (such as TFT display LCD TV panels).
The TFT-LCD industry first emerged in Japan in the 1990s, when a process was designed and built in the country. The first-generation glass substrate is about 30 X 40 cm in size, about the size of a full-size magazine, and can be made into a 15-inch panel. By the time Acer Technology (which was later merged with Unioptronics to become AU Optronics) entered the industry in 1996, the technology had advanced to A 3.5 generation plant (G3.5) with glass substrate size of about 60 X 72 cm.Au Optronics has evolved to a sixth-generation factory (G6) process where the G6 glass substrate measures 150 X 185 cm, the size of a double bed. One G6 glass substrate can cut 30 15-inch panels, compared with the G3.5 which can cut 4 panels and G1 which can only cut one 15-inch panel, the production capacity of the sixth generation factory is enlarged, and the relative cost is reduced. In addition, the large size of the G6 glass substrate can be cut into large-sized panels, which can produce eight 32-inch LCD TV panels, increasing the diversity of panel applications. Therefore, the global TFT LCD manufacturers are all invested in the new generation of plant manufacturing technology.
The TRANSISTor-LCD is an acronym for thin-film TFT Display. Simply put, TFT-LCD panels can be seen as two glass substrates sandwiched between a layer of liquid crystal. The upper glass substrate is connected to a Color Filter, while the lower glass has transistors embedded in it. When the electric field changes through the transistor, the liquid crystal molecules deflect, so as to change the polarization of the light, and the polarizing film is used to determine the light and shade state of the Pixel. In addition, the upper glass is fitted to the color filter, so that each Pixel contains three colors of red, blue and green, which make up the image on the panel.
– The Array process in the front segment is similar to the semiconductor process, except that thin-film transistors are made on glass rather than silicon wafers.
– The middle Cell is based on the glass substrate of the front segment Array, which is combined with the glass substrate of the color filter, and liquid crystal (LC) is injected between the two glass substrates.
-The rear module assembly process is the production operation of assembling the glass after the Cell process with other components such as backlight plate, circuit, frame, etc.
The organic light display can be divided into Passive Matrix (PMOLED) and Active Matrix (AMOLED) according to the driving mode. The so-called active driven OLED(AMOLED) can be visualized in the Thin Film Transistor (TFT) as a capacitor that stores signals to provide the ability to visualize the light in a grayscale.
Although the production cost and technical barriers of passive OLED are low, it is limited by the driving mode and the resolution cannot be improved. Therefore, the application product size is limited to about 5″, and the product will be limited to the market of low resolution and small size. For high precision and large picture, the active drive is mainly used. The so-called active drive is capacitive to store the signal, so when the scanning line is swept, the pixel can still maintain its original brightness. In the case of passive drive, only the pixels selected by the scan line are lit. Therefore, in an active-drive mode, OLED does not need to be driven to very high brightness, thus achieving better life performance and high resolution.OLED combined with TFT technology can realize active driving OLED, which can meet the current display market for the smoothness of screen playback, as well as higher and higher resolution requirements, fully display the above superior characteristics of OLED.
The technology to grow The TFT on the glass substrate can be amorphous Silicon (A-SI) manufacturing process and Low-Temperature Poly-Silicon (LTPS). The biggest difference between LTPS TFT and A-SI TFT is the difference between its electrical properties and the complicated manufacturing process. LTPS TFT has a higher carrier mobility rate, which means that TFT can provide more current, but its process is complicated.A-si TFT, on the other hand, although a-Si’s carrier movement rate is not as good as LTPS’s, it has a better competitive advantage in cost due to its simple and mature process.Au Optronics is the only company in the world that has successfully combined OLED with LTPS and A-SI TFT at the same time, making it a leader in active OLED technology.
Polysilicon is a silicon-based material about 0.1 to several um in size, composed of many silicon particles. In the semiconductor manufacturing industry, polysilicon should normally be treated by Low-Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition. If the annealing process is higher than 900C, this method is known as SPC. Solid Phase Deposition. However, this method does not work in the flat display industry because the maximum temperature of the glass is only 650C. Therefore, LTPS technology is specifically applied to the manufacture of flat displays.
The LTPS membrane is much more complex than a-SI, yet the LTPS TFT is 100 times more mobile than A-SI TFT. And CMOS program can be carried out directly on a glass substrate. Here are some of the features that p-SI has over A-SI:
2. Vehicle for OLED: High mobility means that the OLED Device can provide a large driving current, so it is more suitable for an active OLED display substrate.
3. Compact module: As part of the drive circuit can be made on the glass substrate, the circuit on the PCB is relatively simple, thus saving the PCB area.
LCD screens are backlit to project images through color filters before they are reflected in our eye Windows. This mode of carrying backlit LCD screens, known as “penetrating” LCD screens, consumes most of the power through backlit devices. The brighter the backlight, the brighter it will appear in front of the screen, but the more power it will consume.
Different from the traditional manufacturing process, COG technology directly assumes the drive IC on the glass substrate. The advantages of this technology include:

Panox Display provides a customized cover glass/touch panel service. We supply cover glass from Gorilla, AGC, and Panda, which all have excellent optical performance. We also supply driver ICs from Goodix and Focaltech.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey