arduino lcd display datasheet price

ERM1601SYG-2 is 16 characters wide,1 row character lcd module,SPLC780C controller (Industry-standard HD44780 compatible controller),6800 4/8-bit parallel interface,single led backlight with yellow green color included can be dimmed easily with a resistor or PWM,stn-lcd positive,dark blue text on the yellow green color,wide operating temperature range,rohs compliant,built in character set supports English/Japanese text, see the SPLC780C datasheet for the full character set. It"s optional for pin header connection,5V or 3.3V power supply and I2C adapter board for arduino.
It"s easily controlled by MCU such as 8051,PIC,AVR,ARDUINO,ARM and Raspberry Pi.It can be used in any embedded systems,industrial device,security,medical and hand-held equipment.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!".For 8051 microcontroller user,we prepared the detailed tutorial such as interfacing, demo code and Development Kit at the bottom of this page.
ERM4002FS-1 is 40 characters wide,2 rows character lcd module,SPLC780C controller (Industry-standard HD44780 compatible controller),6800 4/8-bit parallel interface,single led backlight with white color included can be dimmed easily with a resistor or PWM,fstn-lcd positive,black text on the white color,high contrast,wide operating temperature range,wide view angle,rohs compliant,built in character set supports English/Japanese text, see the SPLC780C datasheet for the full character set. It"s optional for pin header connection,5V or 3.3V power supply and I2C adapter board for arduino.
It"s easily controlled by MCU such as 8051,PIC,AVR,ARDUINO,ARM and Raspberry Pi.It can be used in any embedded systems,industrial device,security,medical and hand-held equipment.
Of course, we wouldn"t just leave you with a datasheet and a "good luck!".For 8051 microcontroller user,we prepared the detailed tutorial such as interfacing, demo code and Development Kit at the bottom of this page.

This tutorial includes everything you need to know about controlling a character LCD with Arduino. I have included a wiring diagram and many example codes. These displays are great for displaying sensor data or text and they are also fairly cheap.
The first part of this article covers the basics of displaying text and numbers. In the second half, I will go into more detail on how to display custom characters and how you can use the other functions of the LiquidCrystal Arduino library.
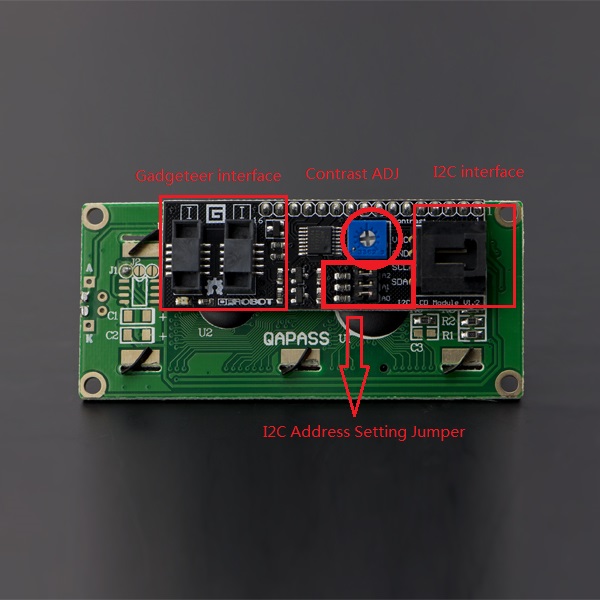
As you will see, you need quite a lot of connections to control these displays. I therefore like to use them with an I2C interface module mounted on the back. With this I2C module, you only need two connections to control the LCD. Check out the tutorial below if you want to use an I2C module as well:
These LCDs are available in many different sizes (16×2 1602, 20×4 2004, 16×1 etc.), but they all use the same HD44780 parallel interface LCD controller chip from Hitachi. This means you can easily swap them. You will only need to change the size specifications in your Arduino code.
For more information, you can check out the datasheets below. The 16×2 and 20×4 datasheets include the dimensions of the LCD and in the HD44780 datasheet you can find more information about the Hitachi LCD driver.
Most LCDs have a built-in series resistor for the LED backlight. You should find it on the back of the LCD connected to pin 15 (Anode). If your display doesn’t include a resistor, you will need to add one between 5 V and pin 15. It should be safe to use a 220Ω resistor, but this value might make your display a bit dim. You can check the datasheet for the maximum current rating of the backlight and use this to select an appropriate resistor value.
After you have wired up the LCD, you will need to adjust the contrast of the display. This is done by turning the 10 kΩ potentiometer clockwise or counterclockwise.
Plug in the USB connector of the Arduino to power the LCD. You should see the backlight light up. Now rotate the potentiometer until one (16×2 LCD) or 2 rows (20×4 LCD) of rectangles appear.
In order to control the LCD and display characters, you will need to add a few extra connections. Check the wiring diagram below and the pinout table from the introduction of this article.
We will be using the LCD in 4-bit mode, this means you don’t need to connect anything to D0-D3. The R/W pin is connected to ground, this will pull the pin LOW and set the LCD to WRITE mode.
To control the LCD we will be using the LiquidCrystal library. This library should come pre-installed with the Arduino IDE. You can find it by going to Sketch > Include Library > LiquidCrystal.
The example code below shows you how to display a message on the LCD. Next, I will show you how the code works and how you can use the other functions of the LiquidCrystal library.
After including the library, the next step is to create a new instance of the LiquidCrystal class. The is done with the function LiquidCrystal(rs, enable, d4, d5, d6, d7). As parameters we use the Arduino pins to which we connected the display. Note that we have called the display ‘lcd’. You can give it a different name if you want like ‘menu_display’. You will need to change ‘lcd’ to the new name in the rest of the sketch.
In the loop() the cursor is set to the third column and first row of the LCD with lcd.setCursor(2,0). Note that counting starts at 0, and the first argument specifies the column. If you do not specify the cursor position, the text will be printed at the default home position (0,0) if the display is empty, or behind the last printed character.
Next, the string ‘Hello World!’ is printed with lcd.print("Hello World!"). Note that you need to place quotation marks (” “) around the text. When you want to print numbers or variables, no quotation marks are necessary.
The LiquidCrystal Arduino library has many other built-in functions which you might find useful. You can find an overview of them below with explanation and some code snippets.
Clears the LCD screen and positions the cursor in the upper-left corner (first row and first column) of the display. You can use this function to display different words in a loop.
This function turns off any text or cursors printed to the LCD. The text/data is not cleared from the LCD memory. This means it will be shown again when the function display() is called.
Scrolls the contents of the display (text and cursor) one space to the left. You can use this function in the loop section of the code in combination with delay(500), to create a scrolling text animation.
This function turns on automatic scrolling of the LCD. This causes each character output to the display to push previous characters over by one space. If the current text direction is left-to-right (the default), the display scrolls to the left; if the current direction is right-to-left, the display scrolls to the right. This has the effect of outputting each new character to the same location on the LCD.
The following example sketch enables automatic scrolling and prints the character 0 to 9 at the position (16,0) of the LCD. Change this to (20,0) for a 20×4 LCD.
With the function createChar() it is possible to create and display custom characters on the LCD. This is especially useful if you want to display a character that is not part of the standard ASCII character set.
Technical info: LCDs that are based on the Hitachi HD44780 LCD controller have two types of memories: CGROM and CGRAM (Character Generator ROM and RAM). CGROM generates all the 5 x 8 dot character patterns from the standard 8-bit character codes. CGRAM can generate user-defined character patterns.
/* Example sketch to create and display custom characters on character LCD with Arduino and LiquidCrystal library. For more info see www.www.makerguides.com */
After including the library and creating the LCD object, the custom character arrays are defined. Each array consists of 8 bytes, 1 byte for each row. In this example 8 custom characters are created.
In this article I have shown you how to use an alphanumeric LCD with Arduino. I hope you found it useful and informative. If you did, please share it with a friend that also likes electronics and making things!
I would love to know what projects you plan on building (or have already built) with these LCDs. If you have any questions, suggestions, or if you think that things are missing in this tutorial, please leave a comment down below.
LCD Display Modules└ LEDs, LCDs & Display Modules└ Electronic Components & Semiconductors└ Electrical Equipment & Supplies└ Business & IndustrialAll CategoriesAntiquesArtBabyBooks & MagazinesBusiness & IndustrialCameras & PhotoCell Phones & AccessoriesClothing, Shoes & AccessoriesCoins & Paper MoneyCollectiblesComputers/Tablets & NetworkingConsumer ElectronicsCraftsDolls & BearsMovies & TVEntertainment MemorabiliaGift Cards & CouponsHealth & BeautyHome & GardenJewelry & WatchesMusicMusical Instruments & GearPet SuppliesPottery & GlassReal EstateSpecialty ServicesSporting GoodsSports Mem, Cards & Fan ShopStampsTickets & ExperiencesToys & HobbiesTravelVideo Games & ConsolesEverything Else

16x2 LCD modules are very commonly used in most embedded projects, the reason being its cheap price, availability, programmer friendly and available educational resources.
16×2 LCD is named so because; it has 16 Columns and 2 Rows. There are a lot of combinations available like, 8×1, 8×2, 10×2, 16×1, etc. but the most used one is the 16×2 LCD. So, it will have (16×2=32) 32 characters in total and each character will be made of 5×8 Pixel Dots. A Single character with all its Pixels is shown in the below picture.
Now, we know that each character has (5×8=40) 40 Pixels and for 32 Characters we will have (32×40) 1280 Pixels. Further, the LCD should also be instructed about the Position of the Pixels. Hence it will be a hectic task to handle everything with the help of MCU, hence an Interface IC like HD44780is used, which is mounted on the backside of the LCD Module itself. The function of this IC is to get the Commands and Data from the MCU and process them to display meaningful information onto our LCD Screen. You can learn how to interface an LCD using the above mentioned links. If you are an advanced programmer and would like to create your own library for interfacing your Microcontroller with this LCD module then you have to understand the HD44780 IC working and commands which can be found its datasheet.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey