difference between tft lcd and oled factory
TFT stands for ‘Thin Film Transistor’ – it is a type of LCD that gives higher resolution and better image quality than standard LCDs. These are usually coloured, but Mono is becoming more popular and therefore more readily available.
OLED stands for ‘Organic Light Emitting Diode’. It has a layer of organic compound that emits its own light eliminating the requirement for a backlight. They are super thin, have a really wide viewing angle with exceptional contrast ratios. Some can also be curved, creating all sorts of interesting new applications for example LG’s new ‘wallpaper TV’.
This depends on the application and what you want to achieve, this is a very subjective question. LCDs can be very cheap – the older green and black ones (think calculators for example) can be extremely cheap, but they are not as colourful or easy to read as newer technologies. TFTs will give you full colour and a higher solution than an LCD, but they are more difficult to drive and tend to be more expensive. OLED is a relatively new technology. OLEDs are lower power than TFT and offer very good viewing, but have lifetime issues and are only available in smaller sizes.
Capacitive touch is most commonly used in products such as smartphones. It’s used in all sorts of applications currently but it’s difficult to get working. Capacitive is a lot more expensive than resistive but it does enable nice gesture features and has the ability to have a cover lens. Resistive touch screens are much cheaper and easier to drive, but do suffer from a mottled effect over the display and can be damaged easily as there is no cover lens.
OLEDs currently range from 1” to 6” – Please note manufacturers such as LG have much bigger OLED televisions but these are a different technology to those available in the industrial market.
For LCD and TFT displays, most power is consumed by the backlight. If you turn the backlight off on a standard LCD, the display itself can run from batteries for many days.
Nearly all TFTs need to have their backlight on to be able to work, which is why your tablet or phone shuts down the backlight quickly when it detects you are not using it. There are some TFTs that can work with no backlight, but they are unique and expensive.
An OLED is self-emitting, so has no backlight. With an OLED, power consumption is controllable by the user – if you want the battery to last longer then dim the display, or show fewer dots as each dot consumes power.
An LCD will work very well in direct sunlight. We actually use the sunlight as the backlight, as it bounces off the rear and becomes part of the display.
We can also achieve this in TFT by adding special films - it does decrease the overall brightness of the display but enables it to be run in direct sunlight.
We all use and handle TFTs in our daily lives with phones, monitors, laptops etc. All of these use TFT displays, but they are very different to TFTs we may use in industrial applications. Why is this?
Consumer electronics have a different specification requirement to those of us in the industrial world. From the outside, they may well look the same with the same TFT cell and white LED backlights, but the differences then start to show. Laptop screens for example are designed to be as thin and lightweight as possible – often just 3mm thick and very susceptible to physical damage, not something you would want in an industrial application.
Consumer TFTs are also designed for typically one product, and when the next one is launched their specification will change to meet the requirements of that next generation, often meaning things like mounting holes and connector positions have changed in the space of a few months.
Interfaces to consumer displays also tend to use protocols designed for highly integrated systems like mobile phones and the ability to drive them requires you to use the latest mobile platform’s chipset.
Industrial displays have been designed and developed to overcome all of these issues. They use fixed rigid mounting holes, the interfaces are industry standard and most importantly they have a guaranteed lifetime of at least 5 years, so you can guarantee you will not have to redesign your own product due to TFT changes.
Intelligent Display Solutions (IDS) has recently introduced a whole family of industrial TFTs into RS Components, all incorporating the latest technology and all available for 5 years minimum.
Integrated cap touch screens and controllers, mean integration into your software platform is seamless with easy recognition for Windows, Linux and embedded platforms.
All of this, with the latest high resolutions and bright backlights, means these displays are the best you can currently buy as an industrial product.
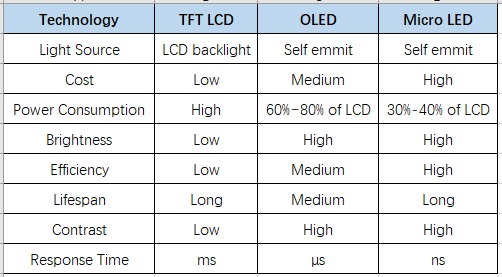
A new form of display technology called Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) is sweeping the display world today. Let’s take a look at what TFT display VS OLED display and how it stacks up to TFTs.
OLED display uses a light-emitting diode (LED) that features an organic compound as its emissive electroluminescent layer. Electric current is applied to the diode, activating the organic compound film and giving off light as a result. The organic compound film is typically situated between two electrodes, one of which is transparent.
OLEDs are mostly used in smartphones and limited releases of high-end smart televisions. It can also be used in computer monitors and handheld game consoles.
OLED displays naturally emit light, so using them on a display panel doesn’t require a backlight. Meanwhile, LCDs need backlights because the liquid crystals cannot create light on their own. OLED’s natural light emission also paves the way for creating lighter screen devices than those using TFT LCD display.
LCD displays are brighter than OLED. This is due to the LCD’s use of backlights that can brightly light up the entire screen. While OLEDs emit good brightness levels from their light, they can never match the brightness that LCD backlights have.
OLED wins in the black levels feature. It’s because OLEDs can perfectly turn off a pixel, causing it to become completely black. LCDs can’t create perfect black screens even with their full-array local dimming feature. LCDs are also prone to blooming, where a bright part spoils the darkness of an adjacent black area.
OLED screens have better viewing angles than LCDs display. Some LCDs improve their viewing angles by using in-plane switching panels (IPS). However, the clarity of images and videos can’t match that of OLEDs when viewed from extreme side angles. This is because LCDs inherently block light due to their filtering layers, and that creates added depth which makes LCD viewing angles limited.
LCD displays are a bit more energy-efficient than OLEDs. Energy consumption in OLED displays depends on the screen brightness. Less brightness used means lower power consumption, but this may not be ideal because the contrast ratio will suffer when brightness is reduced. This is not ideal if, for instance, you’re using an OLED smartphone under bright sunlight.
Meanwhile, the backlights form the bulk of power consumption in TFT displays. Putting the backlight to a lower setting significantly improves the energy efficiency of TFT displays. For instance, reducing the backlight brightness of an LCD TV with a LED backlight won’t affect the picture quality but will draw less power consumption than an OLED TV.
Both OLED and LCD create high-quality images with a wide color gamut on a screen. OLED display wins over TFT display regarding blackness levels and viewing angle. However, the TFT display takes the cake for brightness and energy efficiency.
AMOLED is another emerging display technology lately. It stands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. AMOLED is a type of OLED display used in several smartphones, digital cameras, televisions, and media players.
Thin film transistors (TFTs) and capacitors are attached to each pixel LED component of the panel. At least two TFTs are attached to one pixel – one to control the capacitor’s charging and another to give a voltage source.
The voltage source allows continuous, constant current to the pixel. Hence, there is a better level of control exerted over pixels, allowing you to quickly dim or turn off and on individual pixels.
AMOLED displays have better color accuracy than LCDs. What makes the color more accurate in AMOLED displays is largely due to the precise pixel control achieved by AMOLED panels.
Whites and blacks appear perfect in AMOLED displays. Whites produced by LCDs may carry a bluish tint due to the backlight. Blacks don’t completely appear dark in LCDs, too.
AMOLED provides a greater color gamut than LCDs. AMOLEDs (and all OLED displays in general) have additional blue and green saturation. While these hues greatly widen AMOLED’s color options, some people find the resulting colors a bit unnatural to look at.
Meanwhile, LCDs have subdued greens and quite compelling red hues. Its color gamutmay not be as wide as AMOLED’s, but many people still find it satisfying. That’s because LCD’s color range closely matches the Standard RBG color gamut profile, the one most utilized in videos and images.
LCD’s backlights help maintain the color balance of the entire screen. The backlights ensure that color balance remains consistent across the display. Meanwhile, AMOLED tends to suffer from very slight color balance drifts because of variances in the diodes’ light-emitting capacity over time.
LCDs often have a lower contrast ratio and are prone to light bleeds. That’s due to the backlights remaining open even if light has been blocked and the pixels are supposed to show black color. This is not a problem with AMOLED displays because the panel can simply switch off the pixel to create a pure black color. AMOLEDs have a better contrast ratio as exhibited by their pure black and white levels.
Since AMOLED displays do not require filtering layers and backlights, they’re more suited for use in handheld mobile devices such as smartphones and gaming consoles. LCD may be used in mobile devices as well, but the filtering layers and backlights tend to add a slight bulk to the device. Hence, many manufacturers are now switching to thinner and lighter AMOLED displays.
To sum up this part, AMOLED displays fare better than LCDs in terms of color gamut, accuracy, contrast, and mobile device suitability. However, LCDs have the potential for longer lifespans and carry a better color balance across the display device.
Display P3 is an Apple-developed color space heavily used in American films and digital movie projection. It allows devices to display richer, vibrant, and more lifelike colors that are demanded in videos and movies. It’s also created for adapting to computer displays.
If you compare color LCD vs Display P3, you’ll find a significantly wider color range in Display P3 than the typical sRGB used in color LCDs. LCD monitors, especially those used in computers and laptops, are configured to accurately represent the sRGB gamut as precisely as possible. Meanwhile, Display P3 has been consistently used in Apple products since 2015, starting with the iMac desktop.
Display P3 is not limited to Apple devices, though. Several devices have been configured to support Display P3 as well. These include smartphones from Samsung, OnePlus, Google, and HTC. Even Windows-based laptops from Acer and Asus support Display P3 color gamut.
That’s all the basic information you need to know about LCD display screens. And the difference between TFT Display VS OLED Display. Now, you know How LCD Works, its possible lifespan, components, and how it compares to other display technologies.
Armed with this information, you can better appreciate and take care of your LCD display devices. And in case you’re planning to add display devices to your business, the information you’ve learned will help you make educated choices regarding the display technologies you’ll utilize.

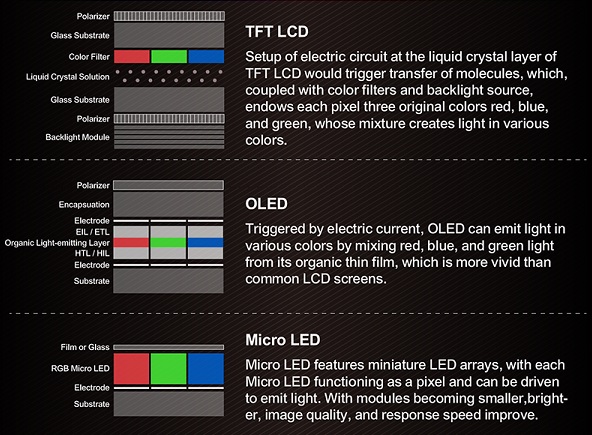
TFT LCD is a mature technology. OLED is a relatively new display technology, being used in more and more applications. As for Micro LED, it is a new generation technology with very promising future. Followings are the pros and cons of each display technology.
TFT Liquid Crystal Display is widely used these days. Since LCD itself doesn"t emit light. TFT LCD relies on white LED backlight to show content. This is an explanation of how TFT LCD works.
Relatively lower contrast:Light needs to pass through LCD glasses, liquid crystal layer, polarizers and color filters. Over 90% is lost. Also, LCD can not display pure black.
Organic Light-Emitting Diode is built from an electro-luminescent layer that contains organic compounds, which emit light in response to an electric current. There are two types of OLED, Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) and Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED). These driving methods are similar to LCD"s. PMOLED is controlled sequentially using a matrix addressing scheme, m + n control signals are required to address a m x n display. AMOLED uses a TFT backplane that can switch individual pixels on and off.
Low power consumption and flexible: OLED doesn"t rely on backlight and consumes less power. OLED is essentially created on plastic film. It is bendable and easy to process.
High contrast and vivid color: OLED emits light itself, can produce very bright image with beautiful color. And because OLED can be turned off, it can produce true black.
Stroboscopic effect: most OLED screen uses PWM dimming technology. Some people who are easy perceive stroboscopic frequency may have sore eyes and tears.
Micro LED, sometimes called μLED is made up of tiny LED, measure less than 100μm. Another way of looking at this is that MicroLEDs are simply traditional LEDs shrunk down and placed into an array.
Replacing organic material with inorganic GaN material eliminates the need of polarizing and encapsulation layer, found in OLED. Micro LED is smaller and thinner, consumes less power.

TFT displays are also known as an “Active Matrix TFT LCD module” and have an array of thin film transistors fabricated on the glass that makes the LCD. There is one of these transistors for each pixel on the LCD. See our blog post RGB and Color Depth for more on how TFTs show color.
LCDs use voltage applied to a field of microscopic liquid crystals to change the crystal’s orientation. The orientation of the crystals changes the polarization of the liquid crystal creating light or dark pixels on the display.
These pixels are arranged to create characters or graphic images. This type of display may be sunlight-readable and may have a backlight, which allows it to be viewed in dark areas.
Beautiful, complex images: All of our TFT modules are full-color graphic displays. Unlike standard monochrome character displays, you can create complex images for an imaginative user experience.
Thin and light: These are ideal display modules for handheld devices, communications equipment, information displays, and test and measurement equipment.
Single Supply: Most of the TFTs use an integrated controller with built-in voltage generation so only a single 3.3v supply is needed for both the panel power and logic voltage.
Many of our character LCD modules use a standard HD44780 compatible controller, so they can be quickly integrated into a new product or used as a replacement in your existing products.
Many of the LCD controllers on board our graphic LCD display modules also include a CGROM (character generator ROM) which allows for easy character information as well as full bit-mapped graphic information to be shown.
Some of the graphic LCD displays have the ability to render graphics in grayscale, enabling you to show images and elements of your UI (user interface) with more depth and definition.
Because OLEDs are emissive, these displays can always be used in dark environments. There is usually a software command or hardware setting that will allow OLEDs to be dimmed.
Some OLED displays are bright enough to be sunlight readable–these models will typically take more current and may have a shorter rated lifetime. Additionally, OLEDs have extremely wide viewing angles.
What makes OLEDs useful for display construction is that they can be fabricated in bulk. Using OLED fabrication techniques, all the diodes can be made at the same time, at a much lower cost. OLEDs also come in a wide variety of colors.
If you have any questions, we can be reached at support@crystalfontz.com, we also provide chat and telephone support Monday through Friday during our open hours.
We love to hear about your projects! Find us around the web (YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter, Forum) and let us know what you’re working on.

In market, LCD means passive matrix LCDs which increase TN (Twisted Nematic), STN (Super Twisted Nematic), or FSTN (Film Compensated STN) LCD Displays. It is a kind of earliest and lowest cost display technology.
LCD screens are still found in the market of low cost watches, calculators, clocks, utility meters etc. because of its advantages of low cost, fast response time (speed), wide temperature range, low power consumption, sunlight readable with transflective or reflective polarizers etc. Most of them are monochrome LCD display and belong to passive-matrix LCDs.
TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the TFT display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
Normally, we say TFT LCD panels or TFT screens, we mean they are TN (Twisted Nematic) Type TFT displays or TN panels, or TN screen technology. TFT is active-matrix LCDs, it is a kind of LCD technologies.
TFT has wider viewing angles, better contrast ratio than TN displays. TFT display technologies have been widely used for computer monitors, laptops, medical monitors, industrial monitors, ATM, point of sales etc.
Actually, IPS technology is a kind of TFT display with thin film transistors for individual pixels. But IPS displays have superior high contrast, wide viewing angle, color reproduction, image quality etc. IPS screens have been found in high-end applications, like Apple iPhones, iPads, Samsung mobile phones, more expensive LCD monitors etc.
Both TFT LCD displays and IPS LCD displays are active matrix displays, neither of them can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red, green, blue) color filter in each LCD pixels to make LCD showing colors. If you use a magnifier to see your monitor, you will see RGB color. With switch on/off and different level of brightness RGB, we can get many colors.
Neither of them can’t release color themselves, they have relied on extra light source in order to display. LED backlights are usually be together with them in the display modules as the light sources. Besides, both TFT screens and IPS screens are transmissive, it will need more power or more expensive than passive matrix LCD screens to be seen under sunlight. IPS screens transmittance is lower than TFT screens, more power is needed for IPS LCD display.

It"s an organic light-emitting display. OLED display technology is different from the traditional LCD display mode, without backlight. It uses a very thin coating of organic materials and a glass substrate, which emit light when an electric current passes through. Moreover, OLED screen module can be made lighter and thinner, with larger viewing angle, and can significantly save power.
AMOLED is panel-self luminous. The TFT is illuminated on the LCD panel by backlight. AMOLED effect is more colorful and brighter. The screen can be seen clearly outside during the day. The most important is that the power consumption of AMOLED is much lower. AMOLED screen is more expensive than TFT LCD touch screen. The life of AMOLED screens is also longer.
AMOLED, after all, is a new technology, which has a bright future. TFT LCD touch screen can be thinned, and LTPS technology is still relatively stable. AMOLED module has low qualified rate and long lead time. So if the size and resolution are the same, buy the cheapest one.
Kingtech LCD is one of the leading TFT LCD OEM / ODM LCD display manufacturers in China. Customizing industrial equipment, medical, POS, logistics equipment, smart home applications and other projects is allowed.

OLED relies on its own light to display images, does not need to use backlight, and is not affected by the surrounding light. Its general life is about 5000 times. TFT is an active matrix liquid crystal, and needs to use the brightness of backlight to display images, which is affected by the surrounding light, and its general life is about 20000 times.
OLED display is essentially different from traditional LCD display, that is, it does not need backlight. It uses very thin organic material coating and glass substrate. When there is current, these organic materials will emit light. Therefore, OLED LCD screen can be made lighter and thinner, with a larger viewing angle and more power saving at the same time. However, it has a short service life and can"t make the screen bigger. OLED is mostly used for folding mobile phone screen.
TFT thin film transistor (TFT) is the current material LCD screen. It belongs to the active matrix type LCD screen. There is a special lamp on the back, which can "actively" control each independent pixel on the screen. This is what we often call active matrix TFT. The reaction time is relatively fast, about 80 ms, and the visual angle is large, usually about 130 degrees, It is used in some high-end models. Because the arrangement of TFT LCD has memory, it will not recover immediately after the current disappears, which effectively improves the ability of playing dynamic pictures. The disadvantages are power consumption and high manufacturing cost.
OLED color screen is 30% more expensive than TFT color screen of the same size! The big difference between true color OLED screen and TFT screen is that OLED true color screen has high screen contrast and fuller color restoration, and OLED true color screen is better than TFT screen in backlight and brightness.

If you’re designing a display application or deciding what type of TV to get, you’ll probably have to choose between an OLED or LCD as your display type.
Not sure which one will be best for you? Don’t worry! We’re here to help you figure out the right display for your project or application. In this post we’ll break down the pros and cons of these display types so you can decide which one is right for you.
LCDs utilize liquid crystals that produce an image when light is passed through the display. OLED displays generate images by applying electricity to organic materials inside the display.OLED and LCD Main Difference:
These different technological approaches to display technology have big impact in some features including contrast, brightness, viewing angles, lifespan, black levels, image burn-in, and price.
Everything from the environment your display will be used in, your budget, to the lighting conditions and the required durability will play a part in this decision.
Contrast refers to the difference between the lightest and darkest parts of an image. High contrast will produce sharper images and more easily readable text. It’s a crucial quality for high fidelity graphics and images or to make sure that a message on a display is very visible.
graphics and images visible. This is the reason you’re still able to see light coming through on images that are meant to be dark on an LCD monitor, display, or television.
OLEDs by comparison, deliver a drastically higher contrast by dynamically managing their individual pixels. When an image on an OLED display uses the color black, the pixel shuts off completely and renders a much higher contrast than that of LCDs.OLED vs LCD - Who is better at contrast?
Having a high brightness level is important if your display is going to be used in direct sunlight or somewhere with high ambient brightness. The display"s brightness level isn"t as important if it’s going to be used indoors or in a low light setting.OLED vs LCD - Who is better at Brightness?
Have you ever looked at a screen from an angle and noticed that the images became washed out or shadowy? The further away you get from the “front and center” view, the worse the image appears to be. This is an example of viewing angles in action – the wider the viewing angle, the better the images on screen will appear as you view them from different vantage points.
This means the display is much thinner than LCD displays and their pixels are much closer to the surface of the display, giving them an inherently wider viewing angle.
You’ll often notice images becoming distorted or losing their colors when tilting an LCD or when you view it from different angles. However, many LCDs now include technology to compensate for this – specifically In-Plane Switching (IPS).
LCDs with IPS are significantly brighter than standard LCDs and offer viewing angles that are on-par with OLEDs.OLED vs LCD - Who is better at Viewing Angles?
LCDs have been on the market much longer than OLEDs, so there is more data to support their longevity. On average LCDs have proven to perform for around 60,000 hours (2,500) days of operation.
With most LCDs you can expect about 7 years of consistent performance. Some dimming of the backlight has been observed but it is not significant to the quality of the display.
OLEDs are a newer technology in the display market, which makes them harder to fully review. Not only does OLED technology continue to improve at a rapid pace, but there also hasn’t been enough time to thoroughly observe their performance.
You must also consider OLED’s vulnerability to image burn-in. The organic material in these displays can leave a permanent afterimage on the display if a static image is displayed for too long.
So depending on how your OLED is used, this can greatly affect its lifespan. An OLED being used to show static images for long periods of time will not have the same longevity as one displaying dynamic, constantly moving images.OLED vs LCD - Which one last longer?
There is not yet a clear winner when it comes to lifespans between LCD and OLED displays. Each have their advantages depending on their use-cases. It’s a tie!
For a display application requiring the best colors, contrast, and viewing angles – especially for small and lightweight wearable devices – we would suggest an OLED display.

Engineers should choose TFT vs OLED for new designs…and here’s why. OLED (organic light-emitting diode) technology continues to increase in popularity, but its growth has really exploded in the last few months due to such large-scale mass production of consumer products such as: e-cigarettes (personal vaporizers), smart-watches, cell phones and other wearables.
But these advantages have worked against OLEDs in new products as more and more new designs have incorporated OLEDs, increasing demand, while the supply side of this technology has failed to keep pace.
“There are only a handful of factories here in Shenzhen that produce OLED screens,” says Alex Liu, President of EC Supply Inc., a leading distributor of vape and electronic cigarette products. “These factories are extremely understaffed for the tens of millions of OLED screens that are in demand, yet everyone wants to jump on board the wearable technology craze. These factories simply lack the work force and raw materials to keep up with production of wearables, let alone fulfill relatively small orders for the vape industry in time for the holiday season.”
Adding to the OLED supply nightmare is the labor shortage in China coupled with many OEM customers increasing their order quantities in a race to beat the Chinese New year shut down.
“I strongly recommend customers purchase any MODs with OLED screens through a trusted source that can guarantee inventory.” – Alex Liu, President of EC Supply Inc.
TFT technology has been in production for several years and is here to stay. There are several TFT glass suppliers to support current demand and they have a great deal of capacity for increased demand.
Focus Displays carries TFT Displays as a standard stock item and can be shipped the same day from our online store as well as from distributor: Allied Electronics

LCD: liquid crystal display. Works by adjusting the amount of light blocked. Usually has a backlight but might not (clocks, calculators, Nintendo Gameboy). The green-black ones can be very cheap and are a mature technology. Response time can be slow.
TFT: is a type of LCD with a thin film transistor attached to each pixel. All computer LCD screens are TFT since early 2000s; older ones had slower response times and poorer colour. Cost is now very good; power consumption is fairly good but dominated by the backlight. Has to be manufactured out of glass.
LED: light emitting diode. As the name suggests, emits light rather than blocking it like LCD. Used for red/green/blue/white indicator lights everywhere.
Some manufacturers advertise "LED" displays that are TFT screens with a white LED backlight, which is just confusing. Ones that are real LED screens are usually OLED.
OLED: organic LED (rather than silicon or germanium based like regular LEDs). Comparatively recent technology, so cost still quite variable and not available in really large sizes. In theory can be printed on plastic, resulting in lighter flexible displays with good brightness, good power consumption and good response time.

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
Both technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages. So, how do you know which one is best for your needs? We compare these two technologies below.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.
Nauticomp Inc.provides world-class fully customizable touchscreen displays for commercial and industrial settings. With features like sunlight readability, brightness adjustability, infrared lighting, full backlighting, all-weather capabilities, etc., our displays are second to none. Contact us today to learn more.

Reports suggest that Apple is getting closer to implementing MicroLED in its future product releases, including the Apple Watch, with the display technology potentially offering a number of benefits compared to other methods. AppleInsider explains how the current TFT and OLED display technologies work, and how MicroLED differs.
MicroLED shows promise as a display technology, potentially offering power savings and a reduced screen thickness when put beside current-generation display panels. Apple has recognized the potential, and has invested heavily into developing the technology over the last few years, with a view to using it in the company"s future products.
To understand fully how MicroLED can benefit Apple, it is worth understanding how the commonly-used display technologies work in the first place, before examining how different MicroLED really is in a comparison.
The most common display technology used by consumer products today, and the oldest of the technologies examined in this article, TFT"s full name of TFT LCD stands for Thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display. This technology is extensively used by Apple in its products, found in iPads, iPhones, MacBooks, and iMac lines.
The LCD part relates to the concept of defining small translucent or transparent areas in a thin and flexible liquid crystal-filled panel, like the displays used in calculators. Passing current through the segment changes the molecular properties of the defined segment area, allowing it to switch between being see-through or opaque.
TFT takes this a stage further, by effectively covering an entire panel with a grid of isolated liquid crystal segments, which again can vary between opaque and transparent based on the level of electrical current. In this case, there are far more segments needed to make up the display than with a normal calculator.
Three neighboring segments can be used to create a single pixel, with color filters used to change the light passing through to red, blue, or green. By varying the charge applied to each liquid crystal segment, the three combined can be used to generate a wide variety of colors and at different brightnesses.
Polarizing filters on either side of the TFT display sandwich are used to prevent light from passing through directly, with the liquid crystal reaction of each segment affecting polarized light passing through the first filter to go through the second.
Sometimes these types of display are known as "LED," but this somewhat of a misnomer, as this actually refers to the use of Light Emitting Diodes as a light source. The LED backlight shines light through the various layers making up the TFT LCD.
Displays that use collections of LEDs as individual pixels do exist, but it isn"t usually found in consumer products. LED screens are commonly used for billboards, in attractions, and as a large-scale display for events.
TFT LCD screens continue to be widely used in production for a number of reasons. Manufacturers have spent a long time perfecting the production of the display panels to make it as cheap as possible, while its high usage allows it to benefit from economies of scale.
Used in consumer devices in a similar way to TFT LCD, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a display technology that is similar in the basic concept, but differs considerably in its execution. Again, the idea is for a thin panel to be divided up into segments, with charge applied to each section to alter its molecular properties, but that"s where the techniques diverge.
As the name implies, OLED uses an organic compound film that is put between two electrodes, which are used to provide charge. Instead of the charge changing how light passes through, the current instead causes the emissive electroluminescent layer to emit light, without the need for a rear light source.
These self-emitting pixels gives OLED a considerable advantage over LCD-based systems in a number of areas. Most obviously, by not needing a backlight, OLED panels can be made far thinner than an equivalent LCD-based display, allowing for the production of thinner devices or more internal area for other components, like a larger battery.
The power efficiency of OLED panels can be far greater, as while a TFT screen requires an always-on backlight, the brightness of OLED pixels themselves determine power usage, with a black pixel consuming no power at all. OLED screens are also faster to respond than LCD displays, making them more useful for VR displays, where response time needs to be as rapid as possible.
This also allows OLED to provide superior contrast ratios compared to TFT, as the lack of backlight bleed-through that occurs in TFT simply doesn"t happen in OLED.
OLED also can be produced on plastic substrates instead of glass, allowing it to be used to create flexible displays. While this is currently embodied in curved and other non-flat screens in some devices, it has the potential to be employed in foldable smartphones or rolled up for storage, an area Apple is also allegedly examining.
Despite the advantages, OLED is still lagging behind TFT in terms of adoption. The cost of production is far higher, in part due to the need for extremely clean environments, as a single speck of dust can potentially ruining a display during fabrication.
OLED panels are also affected by the presence of water, both in production and in use. Small amounts of water contacting the organic substrate can cause immediate damage to the display, rendering parts of the screen useless.
So far, Apple"s usage of OLED consists of the premium iPhone X and the Apple Watch. As the cost of production drops down, it is plausible for Apple to use OLED in more future products, providing a better screen for customers to use.
Thought to be the next big thing in display technology, MicroLED basically takes the idea of using LEDs for pixels in a large stadium-style screen and miniaturizes it all.
Using extremely small LEDs, three MicroLEDs are put together to create each pixel, with each subpixel emitting a different color from the usual red, blue, and green selection. As each LED emits light, there is no need for a backlight as used in TFT screens.
MicroLED doesn"t use an organic compound to produce light, making it less susceptible to failure compared to OLED. Just like OLED, it can be applied onto a flexible material, allowing it to be used for curved displays or non-stationary components, like a watch strap, and can result in an extremely thin display panel.
MicroLED offers the same lower power consumption and high contrast ratio benefits as OLED when compared to TFT. However, MicroLED is also capable of producing a far brighter image than OLED, up to 30 times brighter, and is in theory more efficient in converting electricity into light.
As a relatively new and in-development technology, the cost of MicroLED production is extremely high in comparison to the more established OLED and TFT mass production lines, in part due to lower than required yields. Manufacturing equipment vendors have produced hardware for MicroLED production that cuts defects in half and reduces deposition deviance from 3 nanometers down to 1 nanometer, but it is unclear if this is enough to help mass production move forward.
While MicroLED is an attractive proposition for Apple, it is not the only technology under development by the company"s engineers. Apple has previously filed patent applications for a technology described as "Quantum Dot LED and OLED Integration for High Efficiency Displays."
Quantum Dots are photoluminescent particles included in an LED-backed TFT display that can produce brighter and more vibrant colors, with the colors produced depending on their size. While available in current QLED televisions, the technology is only really being used to enhance the backlight, rather than being used to illuminate individual pixels.
Under Apple"s implementation, thought to be a "true quantum dot" (QD) system, the dot will emit light on demand without needing a backlight. For true QD, the photoluminescent dots are instead replaced by electroluminescent nanoparticles which are capable of such emissions.
The technology in theory can create an even thinner display than OLED, along with a more streamlined manufacturing process. True QD displays are also capable of high pixel densities of up to 1,000ppi, multiple times the density required to be called a Retina-quality display, and based on Apple"s hybrid invention, will also boast the response times of OLED technology.
As is usually the case, Apple does produce a considerable number of patent applications every week that are filed with the US Patent and Trademark Office, and not everything it files will be fully commercialized.
The QD patent application certainly shows Apple is thinking about display technology in multiple ways, and how it can be applied to future devices, but short of getting firm supply chain information or an official announcement from Apple directly, it is difficult to confirm which direction it will be heading.
Apple has been interested in using the technology for some time now, with the first notable sign being its acquisition of LuxVue in May 2014, alongside assorted related patents. A MicroLED specialist, LuxVue was rumored to have been the display producer for the ill-fated Google Glass headset, but was also the holder of assorted patents in the LED display field, including MicroLED.
At the time, the acquisition was thought to be an attempt by Apple to bring part of its display technology development in-house, with suggestions the MicroLED technology would be used in another rumored-at-the-time device, the Apple Watch. A more recent report suggests Apple is working with TSMC to make small panels for a future premium Apple Watch, potentially starting mass production by the end of the year.
Apple has also reportedly set up a secret facility just 15 minutes away from Apple Park, believed to be used for developing MicroLED. The 62,000 square-foot facility is thought to house around 300 engineers on a project named "T159," relating directly to the technology"s development.
The facility is also claimed to be sufficient in size to perform small scale manufacturing of display panels, allowing the company to keep development and testing in-house without involving third-parties. Considering Apple"s previous history in developing technologies before issuing information to manufacturing partners, it is possible that Apple is trying to work out the kinks in production before suppliers even attempt to make MicroLED panels.
The rumored small screen production may be for the Apple Watch now, but it may also benefit another often-rumored device, namely the VR or AR headset. This type of hardware relies on light components to keep the weight off the user"s head and neck, as well as displays with a high refresh rate and as close to perfect color reproduction as possible.
Reports from last year also suggest Apple"s investment in MicroLED was a cause for concern for Samsung, LG, and other South Korean suppliers who provide display panels for the company"s products. Owning the process for MicroLED manufacturing could allow Apple to migrate away from its existing display suppliers in the coming years, reducing revenues and profits.
Aside from Apple"s development, there has been little in the way of announcements from other firms for products using the technology that could be bought by consumers in the coming months. The exception is Samsung, Apple"s main rival in the mobile marketplace and a major supplier of display panels, but its usage of MicroLED is not aimed at producing smaller screens.
At CES 2018, Samsung introduced The Wall, a 148-inch TV claimed to be the "world"s first consumer modular MicroLED" television. According to the South Korean electronics giant, The Wall"s modularity meant consumers would be able to customize their television"s size and shape to suit their needs.
Samsung claimed at the show it will be available to buy from August, but declined to advise how much it will cost. Given the technology"s allegedly expensive production using current methods, and the usual high cost associated with the company"s televisions headlining at the tradeshow, it will probably be prohibitive for the vast majority of potential buyers.
The impending use of the technology in a high-priced consumer product could be considered proof that MicroLED display technology is maturing enough for use in devices. If the reports claiming Apple is getting close to mass producing panels is true, the inclusion of MicroLED in the Apple Watch could end up being the first mainstream usage of the technology.
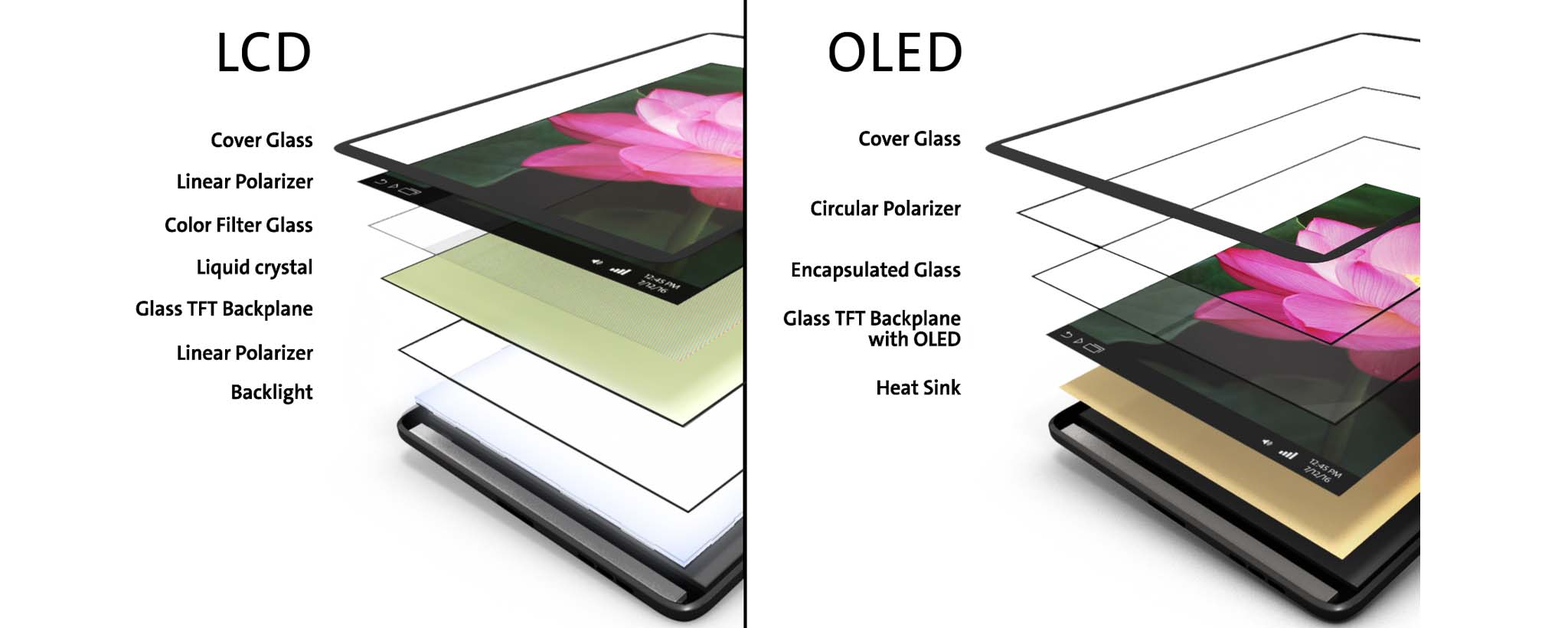
Have you ever wonder where TFT derive from? Why is TFT referred to as LCD? The phenomenon started in early days, when bulky CRT displays were thing of the past and LCD was its replacement, but as time progresses, there were still room for improvement, which leads to the birth of TFT’s.
TFT is a variant of an LCD which uses thin film transistor technology to improve an image quality, while an LCD is class of displays that uses modulating properties of liquid crystals to form what we call an LCD (liquid crystals display) which in fact does not emits light directly.
Even though LCDs were very energy efficient, light weight and thin in nature, LCD were falling behind to the CRT display, which then leads to a change in LCD manufacturing, where performance became a big problem.
For example, having a 2001 Mustang vs a 2014 Mustang, the dimensions and engine of the 2014 has been redesign for performance reasons, not mentioning user friendly, so does the LCD to TFT.
As the birth of TFT, the elements are deposited directly on the glass substrate which in fact the main reason for the switch was because TFTs are easier to produce, better performance in terms of adjusting the pixels within the display to get better quality.
LCDs became ineffective over a period of time, almost all aspect of watching a TV, playing video games or using a handheld device to surf the net became daunting, this phenomenon is known as high response time with low motion rate.
Another problem with LCD was crosstalking, in terms of pixelating, this happens when signals of adjacent pixels affects operations or gives an undesired effect to the other pixel.
As TFT’s become very popular throughout the century due to its elaborate low charge associate and outstanding response time, LCDs became a thing of the past, and TFT became the predominant technology with their wider viewing angles and better quality this technology will be around for a long time.

OLED, an acronym for Organic Light Emitting Diode, is often identified as the modern-age display. Many companies are still using LCDs, but the growing demand for OLEDs overshadows the market of LCDs.
Traditional LCDs use CCFL or cold-cathode fluorescent lamps backlight whereas OLEDs use organic material to emit light in different combinations of colors without using any backlight. In LCDs, the light emitted by the LED backlight passes through a layer of crystal material.
Since LCDs exhibit full-screen brightness with their LED backlights, they get a competitive edge over OLEDs in this parameter. However, in the modern-age displays, brightness is not given much importance in terms of image clarity and light output.
The standard contrast ratio of LCDs of computers may value 1000:1, whereas the contrast ratio of LCD TV displays may go around 4000:1. The contrast ratio of the OLED displays can go as high as 1,000,000:1. The more the contrast ratio is, the better your device’s picture quality will be.
The contrast ratio is the difference between the brightest and darkest visual of a display. Since OLEDs have true black where the pixels turn off when they show black color, which is not the case with LCDs, the OLEDs become a better option for contrast and picture quality.
The number of times a display presents a new image every second is called refresh rate. The OLEDs switch images far faster than LCDs. Today’s OLED displays have a 120Hz refresh rate far more than the 60Hz refresh rate of traditional LCDs. Despite being ahead of LCD, the OLEDs exhibit motion blur, which is a challenge for aspiring electronic equipment manufacturers of today.
Unlike LCDs that always need the backlight to illuminate their pixels, OLEDs use organic material to emit light and create an image. Having true black is another crucial reason why OLEDs consume less power than the contending LCDs. We can say that it is more about the brightness of the image being displayed. The less the light is emitted, the module will consume less energy. It means if we keep the LED backlight of LCDs low, it is possible to make them more energy-efficient than OLEDs.
Viewing angle is one of the most crucial parameters where OLEDs win over LCDs. If you sit off-axis in front of an LCD, you may not consider the image in its actual appearance as the visuals would fade away, which is not the case with OLED displays.
In all the parameters we have discussed here, OLEDs seem more advantageous. Moreover, OLEDs are easier to manufacture. Many OLED displays are offering bendable, foldable, and rollable OLED displays. From small-scale applications such as smartwatches to large-scale applications such as smartphones and TV displays, OLEDs are finding across more and more use cases.

OLED displays have higher contrast ratios (1 million : 1 static compared with 1,000 : 1 for LCD screens), deeper blacks and lower power consumption compared with LCD displays. They also have greater color accuracy. However, they are more expensive, and blue OLEDs have a shorter lifetime.
OLED displays offer a much better viewing angle. In contrast, viewing angle is limited with LCD displays. And even inside the supported viewing angle, the quality of the picture on an LCD screen is not consistent; it varies in brightness, contrast, saturation and hue by variations in posture of the viewer.
There are no geographical constraints with OLED screens. LCD screens, on the other hand, lose contrast in high temperature environments, and lose brightness and speed in low temperature environments.
Blue OLEDs degrade more rapidly than the materials that produce other colors. Because of this, the manufacturers of these displays often compensate by calibrating the colors in a way that oversaturates the them and adds a bluish tint to the screen.
With current technology, OLED displays use more energy than backlit LCDs when displaying light colors. While OLED displays have deeper blacks compared with backlit LCD displays, they have dimmer whites.
LCDs use liquid crystals that twist and untwist in response to an electric charge and are lit by a backlight. When a current runs through them, they untwist to let through a specific amount of light. They are then paired with color filters to create the display.
AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) is a different form of OLED used in some mobile phones, media players and digital cameras. It offers higher refresh rates with OLEDs and consume a lot less power, making them good for portable electronics. However, they are difficult to view in direct sunlight. Products with AMOLED screens include Galaxy Nexus, Galaxy S II, HTC Legend and PlayStation Vita.
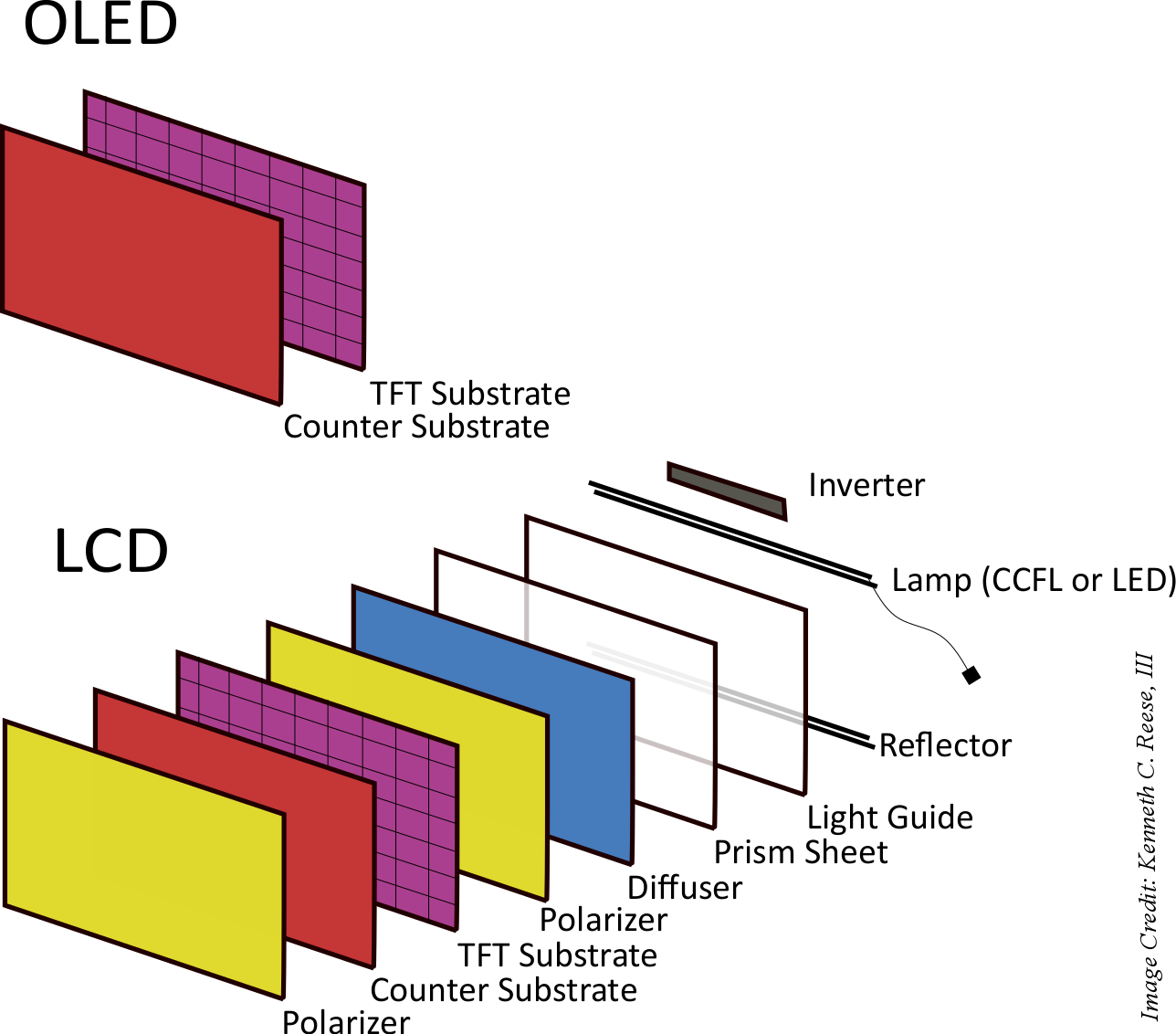
OLED vs. IPS LCD is a topic that comes up whenever consumers upgrade to a newer TV or a smartphone. Should you buy a TV that uses an IPS LCD display or should you pick up a TV with an OLED screen? Well, the answer isn’t so straightforward because they both have their advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will explain how these screen technologies work and which one you should opt for while buying a TV.
IPS LCD (In-Plane Switching Liquid Crystal Display) and OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) are the two most commonly used screen technologies. Older technologies, such as TN (Twisted Nematic) and PLS (Plane-to-Line Switching) displays, have almost disappeared (except in the world of PC monitors and budget laptops) because IPS LCD and OLED are clearly better in almost all aspects. Other technologies such as Mini-LED, MicroLED, and QNED technologies are extremely new and they won’t become mainstream for a few years.
So, when you are finally deciding which TV to buy, the real battle is between OLED and IPS LCD. So where do these stand? Which is better for you? Which one should you pick for your new home theatre? Read on for more information on the OLED vs IPS LCD battle.
IPS LCD displays are perhaps the most common display type days, especially in TVs and laptops. Laptops, entry-level and mid-range smartphones, and most TVs use LCD displays. So, how do IPS displays work? IPS displays use an array of LCD pixels that shift colour as required. However, they don’t emit light on their own. That’s the reason they need a backlight made up of LEDs (Light-Emitting Diodes). The backlight can be arranged in various layouts: towards the edges, spread across the whole display, or separated into different sections.
IPS screens display the black colour by changing the alignment of LCDs so that pixels block the transmission of light, but some light still gets through. That’s the reason IPS LCD displays can’t display true deep black colour. Instead, they display dark grey and there is some ‘backlight bleed’.
To reduce the backlight bleed, a feature called Local Dimming is used. The feature requires the backlight to be compartmentalized into different matrices, and only those sections are turned on which need to display non-black colours. Other sections of the backlight are turned off, offering true blacks. However, active zones still display some backlight bleed.
OLED displays have traditionally been restricted to high-end devices. Even today, only high-end TVs and laptops feature OLED displays. In the world of smartphones, though, OLED technology has been democratised and even mid-range smartphones these days use OLED displays with high brightness and high refresh rates.
In a nutshell, OLED displays don’t use separate backlight sources. Instead, every pixel can reproduce its own light (also known as self-emissive displays). So, there’s no need for an additional backlight and each pixel can be turned on or off as needed. Since there is no need for a separate backlight plane, OLED displays are much thinner than LCD displays. They also offer a much better contrast ratio and viewing angles. However, the organic material used in OLED pixels tends to “burn” over the years that results in ghosting. Moreover, they can’t be as bright as LCD, Mini-LED, or Micro-LED displays.
We have given you a brief overview of IPS and OLED technologies. But which one is better? And which of these will be right for you? Here’s a list of pros and cons to help you in your purchase decision, where it is for smartphones or TVs.
OLEDs have a quicker response time: OLEDs individually-lit pixels can switch on/off or change colour faster. This makes for lower ghosting during fast-and-frenetic action scenes or while playing games. Ghosting refers to when the image on the screen seems to be following itself around or is blurry at the edges.
OLED TVs are slimmer and flexible: As we mentioned earlier, OLED displays don’t need a bulky backlight plane, so OLED TVs are really slim. The next wave of display technologies – foldable and rollable displays – will also be powered by OLED.
IPS LCD TVs offer higher brightness: IPS LCD TVs use a powerful backlight which also lets them get much brighter than their OLED counterparts. This can make for better HDR and even offer a better viewing experience if your TV room gets a lot of sunlight.
IPS TVs suffer from backlight bleed and blooming: This is less of an issue with high-end IPS TVs, but some cheaper models may suffer from glow (bright, greyish areas near the corners of the screen) or backlight bleed (patches or leaks of light, usually around the edges).
OLED TVs can suffer burn-in: OLED displays are at risk of burn-in, a condition in which a static image left on for too long can get permanently ‘burned’ onto the display and may appear like a ghostly dark patch.
OLEDs may get dimmer with age: OLEDs use organic substances which tend to decay over time. So, OLED displays lose brightness with age. It is quite slow and modern OLED TVs are not as affected by this as older OLED TVs, and this really shouldn’t be an issue, but you need to be aware of this.
IPS TVs are much cheaper: OLED is a relatively newer technology and is more expensive to manufacture. Currently, very few companies make OLED display panels. LG Display makes most of the OLED panels found on OLED TVs, while Samsung Display, CSOT, LG Display, and BOE make OLED screens for smartphones and smaller products. Most manufacturers also tend to restrict OLED tech to their largest, most feature-packed range, fueling the perception of OLED being expensive.
Follow Onsitego on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and YouTube to get the latest news, reviews, maintenance tips, and videos about your favourite gadgets and appliances.

OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode and is made up of individual image elements called pixels comprised of organic chemical compounds which emit light when an electric current is applied between a anode and cathode of each pixel. This process is similar in operation to a standard LED operation where light emission is through the recombination of electrons and holes from the cathode and anode.
OLEDs and LCDs are used in display devices but are very different in how they present their display information. An OLED is an emissive type of display meaning it’s self-illuminating. An LCD, however, presents information via transmissive or transflective methods, which means that image illumination is supplied with methods such as a backlight and room light or the sun.
PMOLED stands for Passive Matrix OLED and is fabricated of emitting OLED pixel arrays configured in columns and rows with each pixel intersecting at a column row. These OLED pixels are arranged where their anodes are current driven by an electronic controller chip which also controls the cathode turn on to produce the desired display image.
The controller electronic continually scans the entire OLED column and row array at a set frame rate to produce an image. Because of this, the most power efficient display designs are best in smaller display sizes of 3” or less.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix OLED and is fabricated similarly to a TFT display with each individual pixel element being addressable unlike the row and column design of a PMOLED. PMOLED displays are good for displaying text but fall short when displaying moving images due to the time needed to scan the rows and columns which can cause a perceived ghosting.
On the contrary, with an AMOLED, each individual OLED pixel can be turned on individually without the need to scan an entire array making them far superior for moving images. This allows the AMOLED to produce an image without any ghosting. This individually pixel design also allows for better illumination control for a brighter, higher contrast, more power efficient display. AMOLED displays are much faster the LCDs which makes them more attractive for video displays.
OLED displays have an advantage over other displays such as TFT LCDs since they are a self emitting light source and do not need a separate external light source in order to display an image. Therefore, they are more efficient. This self-illumination allows OLED displays to be much thinner than other technologies and can even be used in flexible displays as well. Some other advantages are:
The current production processes make it difficult and costly to p




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey