thin-film transistor tft display in stock

Manufacturer of standard & custom touch screen displays & thin film transistor touchscreen monitors. Features include 17 in. to 23 in. LCD, rugged steel & aluminum construction, optional resistive or capacitive touch-screens, light textured powder coated black color, contrast filters, transmissive daylight modification, hard coated vandal shields, 16.7 million display colors, anti-glare hard coating, analog RGB input, weight ranging 13 lbs to 24 lbs & 1280 x 1024 SXGA or 1600 x 1200 UXGA resolution. Applications include use for rack, wall, panel or kiosk installations in commercial, military & broadcast industries. One year limited warranty. RoHS compliant. Meet NEMA & Military Spec.

TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) Displays are active-matrix LCDs with full RGB color screens. These screens feature bright, vivid colors and have the ability to show fast animations, complex graphics and crisp custom fonts.
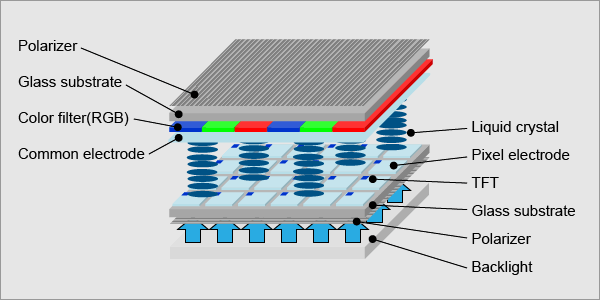
Orient Display sunlight readable TFT displays can be categorized into high brightness TFT displays, high contrast IPS displays, transflective TFT displays, Blanview TFT displays etc.
The brightness of our standard high brightness TFT displays can be from 700 to 1000 nits. With proper adding brightness enhancement film (BEF) and double brightness enhancement film (DBEF) and adjustment of the LED chips, Orient Display high brightness TFT products can achieve 1,500 to 2,000 nits or even higher luminance. Orient Display have special thermal management design to reduce the heat release and largely extend LED life time and reduce energy consumption.
Our high contrast and wide viewing angle IPS displays can achieve contrast ratio higher than 1000:1 which can make readability under strong sunlight with lower backlight luminance. High brightness IPS displays have been widely accepted by our customers with its superb display quality and it has become one of the best sellers in all our display category.Transflective display is an old monochrome display technology but it has been utilized in our color TFT line for sunlight readable application. Orient Display has 2.4” and 3.5” to choose from.
Blanview TFT displays are the new technology developed by Ortustech in Japan. It can provide around 40% of energy consumption for TFT panels which can use smaller rechargeable or disposable batteries and generate less heat. The price is also lower than traditional transflective TFT displays. Orient Display is partnering with the technology inventor to provide 4.3” and 5.0”.
Orient Display can also provide full customized or part customized solutions for our customers to enhance the viewing experience. Orient Display can provide all the different kinds of surface treatments, such as AR (Anti-reflection); AG (Anti-glare), AF (Anti-finger print or Anti-smudge); AS (Anti-smashing); AM (Anti-microbial) etc. Orient Display can also provide both dry bonding (OCA, Optical Clear Adhesive), or wet bonding (OCR, Optical Clear Resin and OCG, Optical Clear Glue) to get rid of light reflective in air bonding products to make the products much more readable under sunlight and be more robust.
Touch panels have been a much better human machine interface which become widely popular. Orient Display has been investing heavy for capacitive touch screen sensor manufacturing capacity. Now, Orient Display factory is No.1 in the world for automotive capacitive touch screen which took around 18% market share in the world automotive market.
Based on the above three types of touch panel technology, Orient Display can also add different kinds of features like different material glove touch, water environment touch, salt water environment touch, hover touch, 3D (force) touch, haptic touch etc. Orient Display can also provide from very low cost fixed area button touch, single (one) finger touch, double finger (one finger+ one gesture) touch, 5 finger touch, 10 points touch or even 16 points touch.
Considering the different shapes of the touch surface requirements, Orient Display can produce different shapes of 2D touch panel (rectangle, round, octagon etc.), or 2.5D touch screen (round edge and flat surface) or 3D (totally curved surface) touch panel.
Considering different strength requirements, Orient Display can provide low cost chemical tampered soda-lime glass, Asahi (AGC) Dragontrail glass and Corning high end Gorilla glass. With different thickness requirement, Orient Display can provide the thinnest 0.5mm OGS touch panel, to thickness more than 10mm tempered glass to prevent vandalizing, or different kinds of plastic touch panel to provide glass piece free (fear) or flexible substrates need.
Of course, Orient Display can also offer traditional RTP (Resistive Touch Panel) of 4-wire, 5-wire, 8-wire through our partners, which Orient Display can do integration to resistive touch screen displays.
Engineers are always looking for lower cost, faster, more convenient interfaces to transmit signals and to accept data and commands. The numbers of available interfaces available in the market can be dazzling. Orient Display follows market trends to produce various kind of interfaces for our customers to choose.
Genetic Interfaces: Those are the interfaces which display or touch controller manufacturers provide, including parallel, MCU, SPI(,Serial Peripheral Interface), I2C, RGB (Red Green Blue), MIPI (Mobile Industry Processor Interface), LVDS (Low-Voltage Differential Signaling), eDP ( Embedded DisplayPort) etc. Orient Display has technologies to make the above interface exchangeable.
High Level Interfaces: Orient Display has technologies to make more advanced interfaces which are more convenient to non-display engineers, such as RS232, RS485, USB, VGA, HDMI etc. more information can be found in our serious products. TFT modules, Arduino TFT display, Raspberry Pi TFT display, Control Board.

Global Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Display Market, By Technology (Plasma Display (PDP), Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED), Other), Type (Twisted Nematic, In-Plane Switching, Advanced Fringe Field Switching, Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment, Advanced Super View, Cell Technology), Panel Type (A_MVA, ASV, MVA, S_PVA, P-IPS), End Use (Domestic Use, Industrial Use) – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2029
Liquid crystal are considered highly light valves or electo-optic transducers. These thin film transistors are known to be simple electronic control devices widely fabricated on a large transparent substrates. They enable fabrication of electronic display.
Global Thin Film Transistor (TFT) Display Market was valued at USD 270.26 million in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 968.64 million by 2029, registering a CAGR of 17.30% during the forecast period of 2022-2029. Twisted Nematic accounts for the largest type segment in the respective market owing to its low cost. The market report curated by the Data Bridge Market Research team includes in-depth expert analysis, import/export analysis, pricing analysis, production consumption analysis, and pestle analysis.
A thin-film-transistor display refers to a form of LCD that uses TFT technology for enhancing image quality including addressability and contrast. These displays are commonly utilized in mobile phones, handheld video game systems, projectors, computer monitors, television screens, navigation systems and personal digital assistants.
Technology (Plasma Display (PDP), Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED), Other), Type (Twisted Nematic, In-Plane Switching, Advanced Fringe Field Switching, Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment, Advanced Super View, Cell Technology), Panel Type (A_MVA, ASV, MVA, S_PVA, P-IPS), End Use (Domestic Use, Industrial Use)
Panasonic Corporation (Japan), LG Display Co., Ltd (South Korea), HannStar Display Corporation (Taiwan), AU Optronics Corp. (Taiwan), Chi Mei Corporation. (Taiwan), SAMSUNG (South Korea), SHARP CORPORATION (Japan), Schneider Electric (France), Siemens (Germany), Mitsubishi Electric Corporation (Japan), SONY INDIA. (India), FUJITSU (Japan), Chunghwa Picture Tubes, LTD. (Taiwan), Barco.(Belgium), BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd. (China), Innolux Corporation (Taiwan), Advantech Co., Ltd (Taiwan), among others.
The increase in the smartphone and tablet proliferation acts as one of the major factors driving the growth of thin film transistor (TFT) display market. Technological advancements are leading a radical shift from traditional slow, bulky and imprecise resistive mono touch to highly sensitive multi-touch capacitive screen have a positive impact on the industry.
The rise in number of electronic readers and growing demand for on-the-move information accelerate the market growth. The development of easy-to-use display devices drives the growth of the market.
The increase in application areas of large e thin film transistor (TFT) display due to the advantages offered by these paper displays in terms of user experience, manufacturing cost, readability, and energy consumption further influence the market.
Additionally, rapid urbanization, change in lifestyle, surge in investments and increased consumer spending positively impact the thin film transistor (TFT) display market.
On the other hand, high cost associated with the manufacturing is expected to obstruct market growth. Also, lack of awareness and low refresh rate are projected to challenge the thin film transistor (TFT) display market in the forecast period of 2022-2029.
This thin film transistor (TFT) display market report provides details of new recent developments, trade regulations, import-export analysis, production analysis, value chain optimization, market share, impact of domestic and localized market players, analyses opportunities in terms of emerging revenue pockets, changes in market regulations, strategic market growth analysis, market size, category market growths, application niches and dominance, product approvals, product launches, geographic expansions, technological innovations in the market. To gain more info on thin film transistor (TFT) display market contact Data Bridge Market Research for an Analyst Brief, our team will help you take an informed market decision to achieve market growth.
The COVID-19 has impacted thin film transistor (TFT) display market. The limited investment costs and lack of employees hampered sales and production of electronic paper (e-paper) display technology. However, government and market key players adopted new safety measures for developing the practices. The advancements in the technology escalated the sales rate of the thin film transistor (TFT) display as it targeted the right audience. The increase in sales of devices such as smart phones and tablets across the globe is expected to further drive the market growth in the post-pandemic scenario.
The thin film transistor (TFT) display market is segmented on the basis of technology, type, panel type and end-use. The growth amongst these segments will help you analyze meager growth segments in the industries and provide the users with a valuable market overview and market insights to help them make strategic decisions for identifying core market applications.
The thin film transistor (TFT) display market is analysed and market size insights and trends are provided by country, technology, type, panel type and end-use as referenced above.
The countries covered in the thin film transistor (TFT) display market report are U.S., Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Rest of South America, Germany, Italy, U.K., France, Spain, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Turkey, Russia, Rest of Europe, Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, Rest of Asia-Pacific, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E, South Africa, Egypt, Israel, Rest of Middle East and Africa (MEA).
North America dominates the thin film transistor (TFT) display market because of the introduction of advanced technology along with rising disposable income of the people within the region.
The thin film transistor (TFT) display market competitive landscape provides details by competitor. Details included are company overview, company financials, revenue generated, market potential, investment in research and development, new market initiatives, global presence, production sites and facilities, production capacities, company strengths and weaknesses, product launch, product width and breadth, application dominance. The above data points provided are only related to the companies" focus related to thin film transistor (TFT) display market.

Besides, the report also helps analyze and identify emerging trends and changing dynamics along with essential drivers, opportunities, challenges, and restraints in the global Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display (TFT-LCD) market. The report includes the conceptual analysis of the products, applications, end-user, and regions.
The report on the Global Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display (TFT-LCD) market helps to inspect the market based on market share, market description, and size of the market.
The report on the Global Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display (TFT-LCD) market helps to analyze the market based on product type, application, and end-users.
A detailed assessment of all risks and opportunities of the Global Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display (TFT-LCD) market is mentioned in the report.

A thin film transistor (TFT) is a type of field-effect transistor that is usually used in a liquid crystal display (LCD). These are simple electronic control devices that are fabricated on a large transparent substrates. These thin film transistor display are used widely in flat-panel displays, television screens, computer monitors, mobile phones, projectors and personal digital assistants. TFT-based displays have a transistor for each pixel on the screen. This allows the electrical current that illuminates the display to be turned on and off at a faster rate, which makes the display brighter and shows motion smoother. A thin film transistor is also known as active matrix display technology which is more responsive to change. The Thin Film Transistors (TFT) market is expected to expand at a higher growth rate in the forecast period owing to the increasing demand of compact size, low price, reduced weight, and low power consumption displays in consumer electronic goods and rising disposable incomes and change in preference of consumers towards high definition picture quality. The continuous innovation in technology has increased the demand for global thin film transistor displays. However, high cost of manufacturing and less availability of high resolutions TFTs for professional applications are some factors which hinders the growth of the market. Efforts are being taken by many companies to upgrade their research and development activities to analyze further application that is expected to generate profitable growth opportunities for the market in the forecast period. Most of the companies are in process to develop Organic TFT technology, which makes it possible to have flexible display surfaces.
The global Thin Film Transistors (TFT) market is segmented on the basis of material type, product type, application, end-user and region. On the basis of material type, the market has been segmented into organic and inorganic material. By product type, the market has been segmented into liquid crystal display, electronic paper display, LED, AMOLED, and others. On the basis of application, the market is segmented into television screens, computer/laptops monitors, mobile phones, wearable devices, and others. Television and computer/laptop monitors is expected to the largest application segment owing to its high demand for advanced high definition monitors and televisions from consumers. On the basis of end-user, the market has been segmented into automotive, consumer electronics, industrial, healthcare, BFSI and others. The consumer electronics segment witnesses a rising need for advanced TFT display, which has created a demand for Organic and advanced TFT display. Consumer electronics is expected to hold a major share of the global thin film transistor market.
In the region wise study, the global Thin Film Transistors (TFT) market has been segmented into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America. Asia Pacific which comprises China, India, South Korea, Australia and other rising economies captured significant market share followed by North America and Europe in 2016. Asia Pacific showed the fastest growth rate during the forecast period due to the emerging economies. China represents huge potential for the Thin Film Transistors (TFT) with the low cost of raw materials and huge production facilities in the country. The U.S. and India are expected to be the second largest market after China.
The global Thin Film Transistors (TFT) market is highly fragmented with number of companies operating in the segment. Leading players are currently focusing on providing cost competitive products to the customers. Some of the key players engaged in Thin Film Transistors (TFT) market include various manufacturers such as Sony Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, LG Display, Samsung Group, Fujitsu Limited, AU Optronics Corp, Sharp Corporation, Chunghwa Picture Tubes, Ltd., Barco NV, BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd., Chi Mei Corporation, Innolux Corp, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Advantech Co. among others.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The liquid crystal displays used in calculators and other devices with similarly simple displays have direct-driven image elements, and therefore a voltage can be easily applied across just one segment of these types of displays without interfering with the other segments. This would be impractical for a large display, because it would have a large number of (color) picture elements (pixels), and thus it would require millions of connections, both top and bottom for each one of the three colors (red, green and blue) of every pixel. To avoid this issue, the pixels are addressed in rows and columns, reducing the connection count from millions down to thousands. The column and row wires attach to transistor switches, one for each pixel. The one-way current passing characteristic of the transistor prevents the charge that is being applied to each pixel from being drained between refreshes to a display"s image. Each pixel is a small capacitor with a layer of insulating liquid crystal sandwiched between transparent conductive ITO layers.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
In 2004, Hydis Technologies Co., Ltd licensed its AFFS patent to Japan"s Hitachi Displays. Hitachi is using AFFS to manufacture high end panels in their product line. In 2006, Hydis also licensed its AFFS to Sanyo Epson Imaging Devices Corporation.
A technology developed by Samsung is Super PLS, which bears similarities to IPS panels, has wider viewing angles, better image quality, increased brightness, and lower production costs. PLS technology debuted in the PC display market with the release of the Samsung S27A850 and S24A850 monitors in September 2011.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
The bare display panel will only accept a digital video signal at the resolution determined by the panel pixel matrix designed at manufacture. Some screen panels will ignore the LSB bits of the color information to present a consistent interface (8 bit -> 6 bit/color x3).
With analogue signals like VGA, the display controller also needs to perform a high speed analog to digital conversion. With digital input signals like DVI or HDMI some simple reordering of the bits is needed before feeding it to the rescaler if the input resolution doesn"t match the display panel resolution.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
Brody, T. Peter; Asars, J. A.; Dixon, G. D. (November 1973). "A 6 × 6 inch 20 lines-per-inch liquid-crystal display panel". 20 (11): 995–1001. Bibcode:1973ITED...20..995B. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1973.17780. ISSN 0018-9383.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Kim, Sae-Bom; Kim, Woong-Ki; Chounlamany, Vanseng; Seo, Jaehwan; Yoo, Jisu; Jo, Hun-Je; Jung, Jinho (15 August 2012). "Identification of multi-level toxicity of liquid crystal display wastewater toward Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa". Journal of Hazardous Materials. Seoul, Korea; Laos, Lao. 227–228: 327–333. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.059. PMID 22677053.
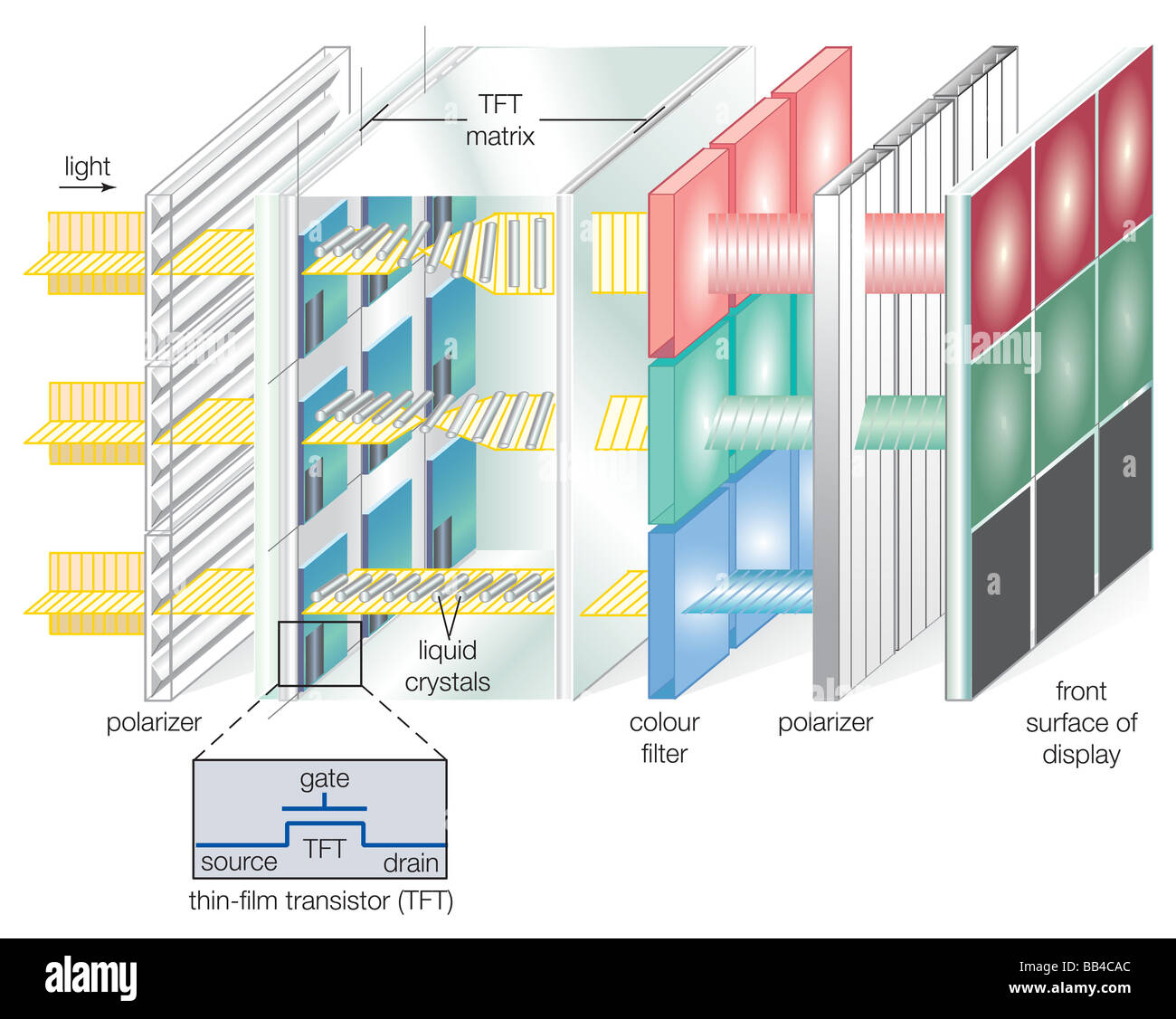
Thin-film transistors are built by layering the thin films of an active semiconductor, hence the name, as well as a dielectric layer and some metallic contacts on a glass substrate. Glass is used because it is nonconductive with excellent optical clarity; it is also nonreactive to the chemicals used in semiconductor processing. In contrast, in the construction of a typical transistor, the substrate used is a semiconductor material, usually a silicon wafer.
Thin-film transistors are primarily used in LCD displays, which is why glass is used as the substrate. TFT technology is also used in both direct and indirect capture digital radiography detectors used in medical radiography. Active-matrix organic light-emitting diode (AMOLED) screens also have a TFT layer.

Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Displays are gaining popularity due to the increasing size availability, user interface customization, end user appeal and continual R&D. At Polytronix we offer standard industry sizes, and continually adding standard sizes to our list. All of our TFT standards can be modified to fit your specification with some examples shown below.
Our development board is designed and preprogrammed to work in conjunction with selected standard TFT modules. For your convenience we have included a preloaded micro-SD card which can easily be loaded with your own custom image(s) as well as a user-friendly instuction manual.

RM2D5EKBE–Visual Phone VP-210, equipped with a 2-inch TFT LCD (thin film transistor liquid crystal display) and 110,000 pixel CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor), is shown off at a news conference in Tokyo May 17 as Kyocera Corp announced it had developed the new personal handy phone system (PHS) able to transmit and receive colour images. The Visual Phone can be used as the world"s first cellular colour television phone as device which can transmit or receive two frame per second along with voice, Kyocera said. The company plans to market the new PHS device at end-July in Japan




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey