lcd panel technology comparison supplier

Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) screens are a staple in the digital display marketplace and are used in display applications across every industry. With every display application presenting a unique set of requirements, the selection of specialized LCDs has grown to meet these demands.
LCD screens can be grouped into three categories: TN (twisted nematic), IPS (in-plane switching), and VA (Vertical Alignment). Each of these screen types has its own unique qualities, almost all of them having to do with how images appear across the various screen types.
This technology consists of nematic liquid crystal sandwiched between two plates of glass. When power is applied to the electrodes, the liquid crystals twist 90°. TN (Twisted Nematic) LCDs are the most common LCD screen type. They offer full-color images, and moderate viewing angles.
TN LCDs maintain a dedicated user base despite other screen types growing in popularity due to some unique key features that TN display offer. For one,
Displays with VA screens deliver wide viewing angles, high contrast, and good color reproduction. They maintain high response rates similar to TN TFTs but may not reach the same sunlight readable brightness levels as comparable TN or IPS LCDs. VA displays are generally best for applications that need to be viewed from multiple angles, like digital signage in a commercial setting.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) technology improves image quality by acting on the liquid crystal inside the display screen. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate parallel (or “in-plane”) rather than upright to allow light to pass through. This behavior results in several significant improvements to the image quality of these screens.
Based on current trends, IPS and TN screen types will be expected to remain the dominant formats for some time. As human interface display technology advances and new product designs are developed, customers will likely choose IPS LCDs to replace the similarly priced TN LCDs for their new projects.

The general consumer typically has very limited knowledge about the different types of LCD panels on the market and they take all of the information, specifications, and features printed on the packaging to heart. The reality is that advertisers tend to take advantage of the fact that most people conduct very minimal research before making big technological purchases—in fact, they depend on this to sell higher quantities of commercial monitors. With that in mind, how exactly do you know if you’re actually getting a good quality product that’ll suit your needs? Reading up on all of the different types of industrial LCD monitors is a good place to start!
LCD stands for liquid-crystal display. Over the years, LCD technology has become ubiquitous with various commercial and industrial screen manufacturing. LCDs are constructed of flat panels that contain liquid crystals with light modulating properties. This means that these liquid crystals use a backlight or reflector to emit light and produce either monochromatic or coloured images. LCDs are used to construct all sorts of displays from cellphones to computer screens to flat-screen TVs. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about the different types of LCD displays on the market.
Twisted Nematic LCDs are the most commonly manufactured and used types of monitors across a wide range of industries. They’re most commonly used by gamers because they’re inexpensive and boast faster response times than most of the other display types on this list. The only real downside to these monitors is that they possess low quality and limited contrast ratios, colour reproduction, and viewing angles. However, they suffice for everyday operations.
In Plane Switching displays are considered to be among the best of the best when it comes to LCD technology as they offer superior viewing angles, excellent image quality, and vibrant colour accuracy and contrast. They’re most commonly used by graphic designers and in other applications that require the highest possible standards for image and colour reproduction.
Vertical Alignment panels fall somewhere in the middle between TN and IPS panel technology. While they have much better viewing angles and higher quality colour reproduction features than TN panels, they also tend to have significantly slower response times. However, even their most positive aspects still don’t come anywhere close to holding a candle to IPS panels, which is why they’re much more affordable and suitable for everyday use.
AFFS LCDs offers far superior performance and a wider range of colour reproduction than even IPS panel technology. The applications involved in this type of LCD display are so advanced that they can minimize colour distortion without compromising on the extremely wide viewing angle. This screen is typically used in highly advanced and professional environments such as in the cockpits of commercial airplanes.
Nauticomp Inc. is the leading designer and manufacturer of high-quality LCD panels and displays. All of our touchscreen displays are made to order and customized according to your specific needs and applications. To learn more about our products, please contact us today.
Asia has long dominated the display module TFT LCD manufacturers’ scene. After all, most major display module manufacturers can be found in countries like China, South Korea, Japan, and India.
In this post, we’ll list down 7 best display module TFT LCD manufacturers in the USA. We’ll see why these companies deserve recognition as top players in the American display module industry.
STONE Technologies is a leading display module TFT LCD manufacturer in the world. The company is based in Beijing, China, and has been in operations since 2010. STONE quickly grew to become one of the most trusted display module manufacturers in 14 years.
Now, let’s move on to the list of the best display module manufacturers in the USA. These companies are your best picks if you need to find a display module TFT LCD manufacturer based in the United States:
Planar Systems is a digital display company headquartered in Hillsboro, Oregon. It specializes in providing digital display solutions such as LCD video walls and large format LCD displays.
Microtips Technology is a global electronics manufacturer based in Orlando, Florida. The company was established in 1990 and has grown into a strong fixture in the LCD industry.
What makes Microtips a great display module TFT LCD manufacturer in the USA lies in its close ties with all its customers. It does so by establishing a good rapport with its clients starting from the initial product discussions. Microtips manages to keep this exceptional rapport throughout the entire client relationship by:
Displaytech is an American display module TFT LCD manufacturer headquartered in Carlsbad, California. It was founded in 1989 and is part of several companies under the Seacomp group. The company specializes in manufacturing small to medium-sized LCD modules for various devices across all possible industries.
The company also manufactures embedded TFT devices, interface boards, and LCD development boards. Also, Displaytech offers design services for embedded products, display-based PCB assemblies, and turnkey products.
Displaytech makes it easy for clients to create their own customized LCD modules. There is a feature called Design Your Custom LCD Panel found on their site. Clients simply need to input their specifications such as their desired dimensions, LCD configuration, attributes, connector type, operating and storage temperature, and other pertinent information. Clients can then submit this form to Displaytech to get feedback, suggestions, and quotes.
A vast product range, good customization options, and responsive customer service – all these factors make Displaytech among the leading LCD manufacturers in the USA.
Products that Phoenix Display offers include standard, semi-custom, and fully-customized LCD modules. Specifically, these products comprise Phoenix Display’s offerings:
Clients flock to Phoenix Display because of their decades-long experience in the display manufacturing field. The company also combines its technical expertise with its competitive manufacturing capabilities to produce the best possible LCD products for its clients.
True Vision Displays is an American display module TFT LCD manufacturing company located at Cerritos, California. It specializes in LCD display solutions for special applications in modern industries. Most of their clients come from highly-demanding fields such as aerospace, defense, medical, and financial industries.
The company produces several types of TFT LCD products. Most of them are industrial-grade and comes in various resolution types such as VGA, QVGA, XGA, and SXGA. Clients may also select product enclosures for these modules.
All products feature high-bright LCD systems that come from the company’s proprietary low-power LED backlight technology. The modules and screens also come in ruggedized forms perfect for highly-demanding outdoor industrial use.
LXD Incorporated is among the earliest LCD manufacturers in the world. The company was founded in 1968 by James Fergason under the name International Liquid Xtal Company (ILIXCO). Its first headquarters was in Kent, Ohio. At present, LXD is based in Raleigh, North Carolina.
We’ve listed the top 7 display module TFT LCD manufacturers in the USA. All these companies may not be as well-known as other Asian manufacturers are, but they are equally competent and can deliver high-quality display products according to the client’s specifications. Contact any of them if you need a US-based manufacturer to service your display solutions needs.
We also briefly touched on STONE Technologies, another excellent LCD module manufacturer based in China. Consider partnering with STONE if you want top-of-the-line smart LCD products and you’re not necessarily looking for a US-based manufacturer. STONE will surely provide the right display solution for your needs anywhere you are on the globe.
NDSsi uses only “Grade A” LCD panels in all of its products, while many competitors use “Grade B” panels in order to save cost, and as a result compromise quality. In medical applications, it is important not to compromise the quality of the displayed image since it is often the basis for making clinical decisions. The following tables and images show the differences between “Grade A” and “Grade B” LCD panels in terms of different types of allowable defects.
There are essentially two different types of pixel defects, bright (stuck pixels) and dark (dead pixels).The table and images below show the differences between Grade A and Grade B LCD panels in terms of allowable pixel defects.

Many TVs use LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) panels that are lit by LED backlights. There are two popular types of LCD panels: In-Plane Switching (IPS) and Vertical Alignment (VA), and there are two main differences between each type. A VA panel usually has a high contrast ratio and narrow viewing angles. However, an IPS panel has low contrast and wide viewing angles. These are the main differences between each, and for the most part, panel type doesn"t affect other aspects of picture quality, like peak brightness, color gamut, or color accuracy.
For the purposes of this article, we"re going to compare two LED-backlit LCD TVs: the Sony X800H, which has an IPS panel, and the Hisense H9G, which has a VA panel. Due to their different panel types, there are three noticeable differences in picture quality: viewing angles, contrast, and black uniformity, so we"re going to look at each one.
Viewing angle refers to the angle at which you can watch the TV without seeing a noticeable drop in picture quality. IPS TVs are the clear winner here, as the image remains accurate when viewing from the side - you can see the differences in the videos above. This is their main advantage over VA panels. Most VA panel TVs have a noticeable loss in image accuracy when viewing from the side. The narrow viewing angle of VA-type TVs is also problematic when the TV is used as a PC monitor from up close since the edges of the display look washed out.
VA panels are far superior to IPS panels when it comes to this, so if you tend to watch movies in the dark, you likely want to get a TV with a VA panel. Most TVs use VA panels due to this main advantage, and high-end models may have a local dimming feature that further enhances black levels. On the other hand, IPS panels normally have low contrast, so blacks look closer to gray, but you may not notice the difference in contrast in bright environments.
Our black uniformity tests determine how well a TV displays a dark scene with a bright image in the center. Ideally, you want to see a completely black screen with the center cross being the only part that"s lit up, and this is important for people watching movies. No LED TV has perfect uniformity, and unlike viewing angles and contrast, the panel type doesn"t completely determine its black uniformity. However, most VA panels that we"ve tested have good black uniformity, while most IPS panels have sub-par black uniformity. This doesn"t mean that every VA panel TV has good uniformity, as this can change between units, and you can also improve uniformity using the local dimming feature.
LCDs function by having liquid crystals in little groups to form the pixels. These crystals react and change position when charged with electricity and, depending on their position, they allow a certain color of light to pass through.
There"s also another type of IPS panel, called Plane-to-Line Switching (PLS), which can be seen with the Sony X800H. This panel type was designed by Samsung and technically performs the same as an IPS panel. When you compare the pixels visually, IPS panels look like chevrons, VA looks like very straight rectangles, and PLS looks like round-edged capsules. You can learn more about pixels here.
The way the pixels are laid out can also affect text clarity. Many IPS panels, like the ones on the Sony X800H or the LG SK9000, use RGB sub-pixel layouts, while many VA panels have a BGR layout, like on the Hisense H9G. The sub-pixel layout doesn"t directly affect picture quality unless you"re using it as a PC monitor. Some applications may expect an RGB layout, so if you have a BGR sub-pixel layout, text may not look clear. You may need to increase the text scaling to read it properly, but this issue isn"t common with an RGB layout. You can learn more about it here.
Unlike LED TVs, OLEDs don"t use a backlight and instead have self-emitting pixels. This allows the pixels to individually turn on and off, resulting in perfect blacks. This means that they also have perfect black uniformity as there"s no blooming around bright objects like on some LED TVs. They also have wide viewing angles, sometimes even wider than some IPS panels, so OLEDs are a good choice for wide seating arrangements.
Samsung released quantum dot TVs in 2015, which they later labeled as QLED in 2017. These TVs include a quantum dot layer between the LED backlights and the LCD panel to achieve a wider color gamut. Other companies like Vizio and TCL also use this quantum dot technology on their TVs. Adding this extra quantum dot layer doesn"t change the characteristics of the panel type; the VA panel on the TCL 6 Series/S635 2020 QLED still has a high contrast ratio and narrow viewing angles. Although most QLED TVs use VA panels, you can easily use an IPS panel as well.
Manufacturers have tried different techniques to improve the viewing angles on VA panels over the years, aiming to produce a perfect LCD panel with both wide viewing angles and high contrast. While they have yet to achieve that goal, a few TVs have hit the market that try to combine the best of both panel types. The first TVs with this viewing angle technology came out in 2018, and only a few high-end models like the Samsung Q90/Q90T QLED and the Sony X950H had this technology in 2020. These TVs are a bit unique, delivering noticeably better viewing angles than their pure VA counterparts, but still worse than true IPS panels. This comes at the expense of a lower contrast ratio, as these TVs have worse native contrast than most VA panels, but they"re still better than IPS panels. Combined with their local dimming features, they still produce deep blacks.
Between IPS and VA panels, neither technology is inherently superior to the other as they both serve different purposes. In general, IPS TVs have wide viewing angles suitable for when you want to watch the big game or your favorite show in a large seating arrangement. They"re also beneficial for use as a PC monitor since the edges remain accurate if you sit up close. However, VA panels are a better choice for watching content in dark rooms, as their improved contrast allows them to display deep blacks. Choosing between the two is a series of trade-offs and qualities, so choosing the best TV for your needs depends on your usage.

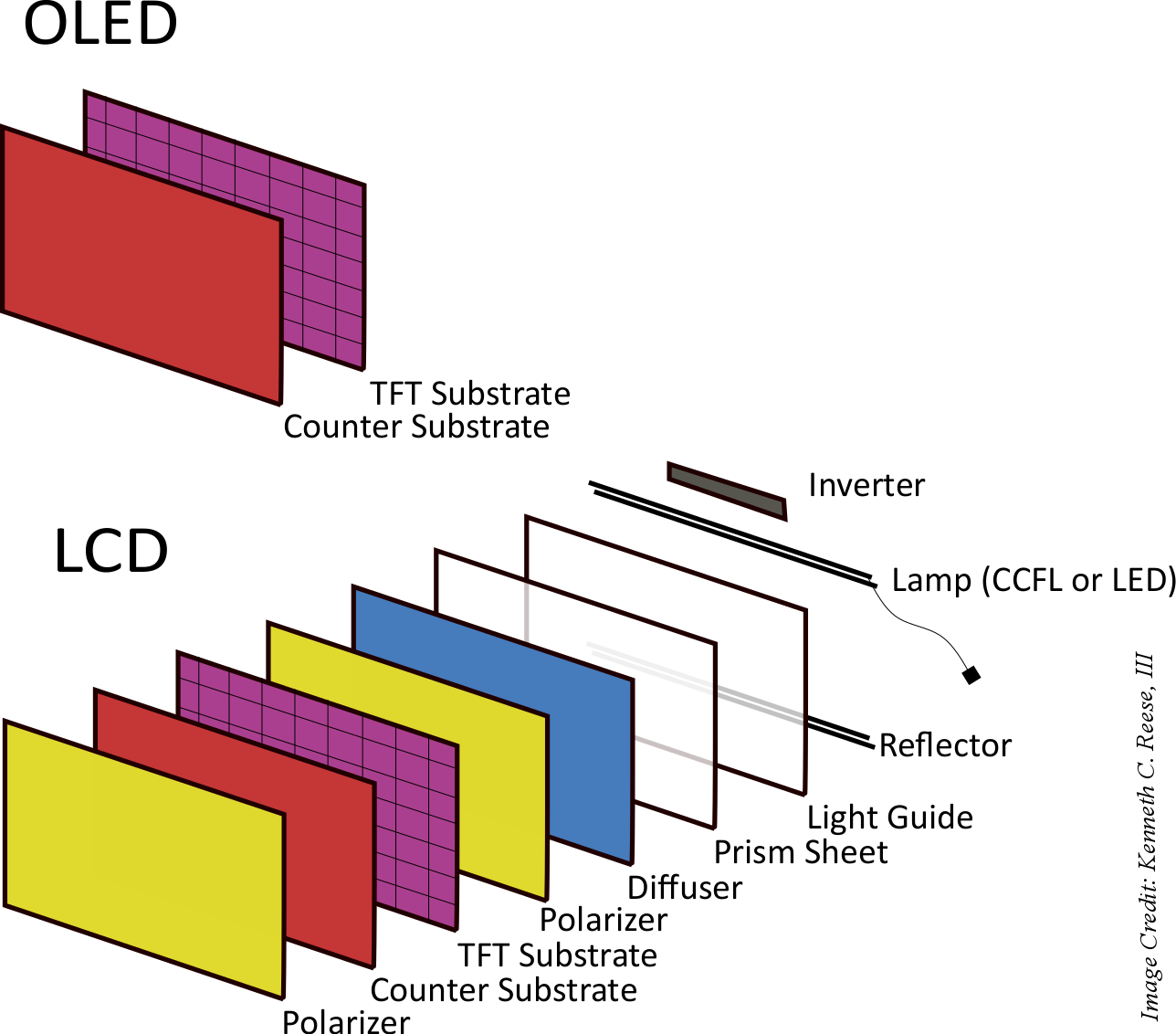
Flat-panel displays are thin panels of glass or plastic used for electronically displaying text, images, or video. Liquid crystal displays (LCD), OLED (organic light emitting diode) and microLED displays are not quite the same; since LCD uses a liquid crystal that reacts to an electric current blocking light or allowing it to pass through the panel, whereas OLED/microLED displays consist of electroluminescent organic/inorganic materials that generate light when a current is passed through the material. LCD, OLED and microLED displays are driven using LTPS, IGZO, LTPO, and A-Si TFT transistor technologies as their backplane using ITO to supply current to the transistors and in turn to the liquid crystal or electroluminescent material. Segment and passive OLED and LCD displays do not use a backplane but use indium tin oxide (ITO), a transparent conductive material, to pass current to the electroluminescent material or liquid crystal. In LCDs, there is an even layer of liquid crystal throughout the panel whereas an OLED display has the electroluminescent material only where it is meant to light up. OLEDs, LCDs and microLEDs can be made flexible and transparent, but LCDs require a backlight because they cannot emit light on their own like OLEDs and microLEDs.
Liquid-crystal display (or LCD) is a thin, flat panel used for electronically displaying information such as text, images, and moving pictures. They are usually made of glass but they can also be made out of plastic. Some manufacturers make transparent LCD panels and special sequential color segment LCDs that have higher than usual refresh rates and an RGB backlight. The backlight is synchronized with the display so that the colors will show up as needed. The list of LCD manufacturers:
Organic light emitting diode (or OLED displays) is a thin, flat panel made of glass or plastic used for electronically displaying information such as text, images, and moving pictures. OLED panels can also take the shape of a light panel, where red, green and blue light emitting materials are stacked to create a white light panel. OLED displays can also be made transparent and/or flexible and these transparent panels are available on the market and are widely used in smartphones with under-display optical fingerprint sensors. LCD and OLED displays are available in different shapes, the most prominent of which is a circular display, which is used in smartwatches. The list of OLED display manufacturers:
MicroLED displays is an emerging flat-panel display technology consisting of arrays of microscopic LEDs forming the individual pixel elements. Like OLED, microLED offers infinite contrast ratio, but unlike OLED, microLED is immune to screen burn-in, and consumes less power while having higher light output, as it uses LEDs instead of organic electroluminescent materials, The list of MicroLED display manufacturers:
LCDs are made in a glass substrate. For OLED, the substrate can also be plastic. The size of the substrates are specified in generations, with each generation using a larger substrate. For example, a 4th generation substrate is larger in size than a 3rd generation substrate. A larger substrate allows for more panels to be cut from a single substrate, or for larger panels to be made, akin to increasing wafer sizes in the semiconductor industry.
"Samsung Display has halted local Gen-8 LCD lines: sources". THE ELEC, Korea Electronics Industry Media. August 16, 2019. Archived from the original on April 3, 2020. Retrieved December 18, 2019.
"TCL to Build World"s Largest Gen 11 LCD Panel Factory". www.businesswire.com. May 19, 2016. Archived from the original on April 2, 2018. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
"Panel Manufacturers Start to Operate Their New 8th Generation LCD Lines". 대한민국 IT포털의 중심! 이티뉴스. June 19, 2017. Archived from the original on June 30, 2019. Retrieved June 30, 2019.
"TCL"s Panel Manufacturer CSOT Commences Production of High Generation Panel Modules". www.businesswire.com. June 14, 2018. Archived from the original on June 30, 2019. Retrieved June 30, 2019.
"Samsung Display Considering Halting Some LCD Production Lines". 비즈니스코리아 - BusinessKorea. August 16, 2019. Archived from the original on April 5, 2020. Retrieved December 19, 2019.
Herald, The Korea (July 6, 2016). "Samsung Display accelerates transition from LCD to OLED". www.koreaherald.com. Archived from the original on April 1, 2018. Retrieved April 1, 2018.
"China"s BOE to have world"s largest TFT-LCD+AMOLED capacity in 2019". ihsmarkit.com. 2017-03-22. Archived from the original on 2019-08-16. Retrieved 2019-08-17.
First, to be clear, there is no “best” panel type out of these, as all have their respective advantages and disadvantages over the others. The information here pertains to general characteristics, as even panels of the same panel type will have some variance in characteristics (power consumption, backlight bleed, etc.) depending on the luck of the draw. Manufacturer tuning can also impact display output, affording some differentiating leverage to manufacturers sourcing from panel suppliers (which is effectively all of them).
Nostalgia or riddance aside, there are still some valid reasons to use a CRT monitor. When compared to LCD panels, CRT monitors can have higher contrast ratio, very low response time (which leads to non-blurred pictures even with fast movement on screen), and very little input lag, although LCD input lag can be largely negated. The downsides of CRTs are apparent, though: they’re large, heavy, consume more power, produce flicker, can produce audible, high frequency noise (although age plays into whether one can hear them or not), produce slightly distorted images, and produce harmful electromagnetic waves (in the form of x-rays), which requires that toxic materials such as lead and barium must be used as shielding to prevent detrimental health effects. CRT monitors are also notoriously hazardous to repair, given their large, active electrical coils that can measure upwards of 50,000 volts of electricity.
CRT displays are sometimes still used in medical, simulation, military, and government fields that have embedded the displays into control panels and machinery.
CRT monitors have largely gone out of production, and are rarely sold new (finding a used CRT is fairly easy), but their advantages temporarily lent themselves to some special uses. In regards to gaming, CRT monitors have historically been advantageous to use when gaming competitively due to very little motion blur and very little input lag. That being said, these advantages have faded with the progressive march of TN panels.
TN panels now have low motion blur (especially with lightboost or a similar technology), offer high refresh rates, low response times (1ms GTG in many cases), and are more than adequate even in the world’s most competitive games.
Ultimately, for the vast majority of users, the disadvantages of CRTs aren’t worth their limited gains, especially when TN panels meant for gaming more than adequately satisfy the needs of even competitive gamers.
TN panels have many benefits over the previously popular CRT monitors: lower weight, lower cost to produce, lower power consumption, they’re much thinner, offer clearer pictures, have no realistically achievable resolution limits, offer flexibility in size and shape, and the ability to eliminate flicker.
That being said, TN panels weren"t and still aren’t perfect, and compared to the previously popular CRT monitors, they’ve suffered from limited viewing angles, uneven backlighting, worse motion blur, higher input lag, dead/stuck pixels, and poor display in sunlight.
To be clear, many of these issues have been improved upon, but due to the underlying science of LCD TN panels, cannot be completely resolved. In fact, many of these issues -- like uneven backlighting, motion blur, input lag, and dead/stuck pixels -- are inherent issues across all LCD panel types. Poor viewing angles become a more pressing issue with larger displays, since the viewing angle when viewed straight on increases towards the outside of the monitor, thus causing more color distortion. TN panels do have the advantages of lower response times and higher refresh rates than other panel types/CRTs. TN panels are generally from 60Hz to 144Hz, offering substantially greater fluidity of gameplay with higher frequencies.
TN panels provide a good compromise between CRTs and other LCD panels as their traditionally low response rates, input lag, and high refresh rate make them comparable to CRTs for accuracy; TN panels also have the advantages of offering sharper pictures, widescreen output, lower weight, smaller physical dimensions, and higher resolutions compared to CRTs.
Still, compared to other LCD panels, TN panels suffer from poor viewing angles and worse color reproduction. Ultimately, for most gamers playing somewhat competitively to very competitively, TN panels are a good choice, but for those looking for a prettier and improved color experience, another panel type may be worth considering.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) was created to address the shortcomings of TN panels. IPS panels seek to solve TN panels’ issues of poor color reproduction and viewing angles. In this regard, IPS panels have largely succeed. Not only do they offer a higher contrast ratio (superior blacks), high color accuracy (which leads to IPS panels also generally looking less “washed out”), but IPS panels also have very little color shift when changing the viewing angles.
The tradeoff to this is that IPS panels have slower response times, higher production costs, higher power consumption, and lower possible refresh rates. IPS panels have traditionally been 60Hz, although, as with all monitors, they can be overclocked (results will vary). There have been improvements to IPS panels over the years, and slightly different revisions in the form of E-IPS and H-IPS, but ultimately the differences between these versions are inconsequential to gamers and those not involved in graphic design as a job.
Due to their worse response rates and lower possible refresh rates, IPS panels are generally considered to be worse for competitive gameplay and used more often when color is important, such as graphic design. For gamers who don’t play competitively and prefer breathtaking strolls in Skyrim instead of sweeping scrubs in CS:GO, an IPS panel should be a consideration for the next monitor.
PLS (Plane to Line Switching) are quite similar to IPS panels, so much so that they have the same advantages and disadvantages, with a couple extra minor advantages. PLS is produced by Samsung, who claims that compared to IPS panels, PLS panels have better viewing angles, a 10% increase in brightness, 15% decrease in production costs, increased image quality, and allow for flexible panels. Samsung’s PLS panels have been known to overclock well in monitors such as the QNIX 2710 in particular. Overall, PLS is basically Samsung’s version of IPS, as it is very similar in functionality (and even name). AHVA is also very similar to IPS and PLS, and differentiation between them is rare, although it should not be confused with the next panel type.
VA (Vertical Alignment) panels offer a solid medium between TN and IPS panels. VA was created to combine the advantages of IPS and TN panels, and largely did, although they did so with some compromise. That seems to be a theme in the world of monitors.
Compared to IPS panels, VA panels have the advantage of higher possible refresh rates. Although most are currently 60Hz, there are a few that are above 60Hz. VA has more advantages over TN panels than IPS, with better color reproduction, higher maximum brightness, and better viewing angles. VA panels do have the best contrast ratios of all panel types mentioned, but they also have the worst response times of the monitor technologies covered here. This causes blurring in fast-moving pictures and is disadvantageous to gaming.
For the use of gaming, VA is not the greatest option due to generally higher response time in comparison to other panel types; this slower response causes more motion blur, effectively eliminating its deployment for fast-moving titles. For a general work monitor, VA panels provide high contrast ratios, brightness, refresh rates, good color reproduction, and good viewing angles.
TN panels are another good choice for competitive gamers, as they support higher refresh rates, low response times, decent input lag, and high resolutions. Their bad viewing angles, color reproduction, and slight blurring compared to CRT monitors (due to higher response times) are all disadvantages, ones which cannot be easily fixed.
IPS panels solve the issues of TN panels, with better color reproduction and viewing angles, but do so at the cost of refresh rate and response time. IPS panels are especially useful for those not wanting to play too competitively, but want a beautiful/immersive visual experience. PLS and AHVA are similar enough to IPS to usually not be differentiated.
VA panels provide a good middle ground with better-than-IPS refresh rates and contrast levels, but have worse viewing angles and color production, although generally still better than TN. Response times are VA’s largest downfall, though, being slower than IPS and its variants and TN.
What’s best for you will depend on all of these items. For those wanting to play at a competitive level and who favor FPS or racing games, TN panels are best. Those wanting a more impressive and immersive experience may want an IPS (or similar variant, such as PLS), especially if working on artistic endeavors. Finally, those wanting a general monitor for work might consider a VA panel, although due to their higher response times, they won’t be good for gaming.

For people that aren’t the most tech-savvy, it would seem that LCD monitors are all the same. But in reality, the opposite is true. There are four major types of LCD monitor panels, all with unique benefits and drawbacks depending on your needs. So, when shopping for an LCD screen, it’s important to consider how you’ll use it, and which type of computer monitor is best suited for that goal. To learn more about LCD, LED, QLED, and other monitor technology types, check out our guide on the types of monitors.
Technically, there are 11 different types of LCD panels, but they’re usually divided into three main categories — In-Plane Switching (IPS), Twisted Nematic (TN), and Vertical Alignment (VA). IPS is considered the top choice while VA is often associated with burn-in, a condition where pixels lose brightness over time and leave image silhouettes on the screen.
IPS panels tend to offer the best color accuracy, image quality, and viewing angles. As a result, these types are the best monitors for designers who demand better image quality to complete their graphic design work. In particular, IPS panels can provide fidelity at viewing angles as wide as 178 degrees.
However, these panels tend to be more expensive because of their enhanced image quality. Likewise, they don’t score as well for refresh rates, which makes them suboptimal for gamers.
IPS panels can be further divided into seven additional versions. While they’re all somewhat similar, how the pixels are structured is different. These include:S-IPS
Super PLS, or Plane to Line Switching, is another twist on IPS panels but is proprietary to Samsung. Their patented technology promises to offer wider viewing angles and 10% more brightness than standard IPS displays.
AHVA — not to be confused with VA panels — was developed by AOU and stands for Advanced Hyper-Viewing Angle. However, it still relies on IPS technology.
And Nano IPS was created by LG Electronics and promises to create a wider color range because of its use of nanoparticles instead of traditional pixels. Additionally, Nano IPS panels tend to have faster refresh rates.
Touchscreen monitors can be any panel variation, it depends on which one you need. However, if you can’t afford one, as they are expensive, then you’ll need to learn how to convert a monitor to touchscreen.
If you’re a budget shopper looking for an LCD screen, TN panels are going to be the most widely available option. While they’re wallet-friendly, this option has fantastic response times. Some TN-based LCDs can offer response times as low as one millisecond, which makes them ideal for gaming. However, TN panels aren’t as competitive when it comes to color accuracy. These panels are only six-bit instead of eight-bit like IPS panels and therefore can’t display all 16.7 million colors found in 24-bit true-color displays.
VA panels are a median choice for people who have a little bit more to spend but aren’t ready to invest in IPS panel technology. While they provide truer color than a TN panel and wider viewing angles, their response time isn’t as competitive. Additionally, VA viewing angles aren’t as wide as an IPS panel.
Although VA panels have higher contrast ratios for better black levels, they struggle with color shifting. This means that depending on your viewing angle, the brightness can vary. And especially for watching television, this can create a lack of detail in darker scenes. However, because of its affordability, this panel is incredibly popular with manufacturers and is often used in computer monitors and televisions. If you need something with closer to 100% of the sRGB color gamut, you’ll want a different option.
There are a few VA variations that you can find depending on your needs. These upgrades from the base VA versions are designed to offer better contrast and color reproduction as well as wider viewing angles. These newer advancements in VA technology are designed to rival IPS monitors while still being more affordable.P-MVA
This is going to depend on how you plan on using your LCD monitor, along with your budget. Remember that the lowest price isn’t always the best, especially when considering computer monitor lifespan. You want a monitor that will last you a while. And, also consider the different monitor sizes as well. But as a general rule, the three main panel categories are most compatible in the following ways.
IPS panels are ideal for professionals who need true color accuracy for their work. Gamers who are more concerned with image quality will also do well with this pick. Likewise, serious tech aficionados with exacting standards regarding color accuracy, want to avoid color shifting and maximize viewing angles will like IPS panels. Remember that IPS panels include a wide array of subcategories, many of which are proprietary to select electronics brands.
Budget-conscious shoppers that want a decent LCD monitor that won’t break the bank can’t go wrong with a TN panel LCD. Additionally, gamers who want faster response times will also like these panels. And, anyone who isn’t obsessed with technical specs and simply wants an affordable monitor for general use will like these LCDs.
Basic VA models are usually only recommended for general home or consumer use. Butif you’re open to upgrading to newer VA technology, these monitors are ideal for creatives such as photographers or content creators as well as gamers who are more focused on image quality.
Most of the new M+ technology was employed on 4K TV sets which led to a controversy after tests showed that the addition of a white sub pixel replacing the traditional RGB structure would reduce the resolution by around 25%. (source)

There’s a variety of display panel out there and even more on the way. But looking at all the different types of panels can be baffling. They come in various acronyms, and many of those acronyms are confusingly similar. How do LCD, LED and OLED compare? What about the different types of LCD panels? And how do these different technologies impact your viewing experience for things like gaming? To help, we’ve created this guide so you can gain a firm understanding of today’s display panel technology and which features really matter.
The first type of panels we’ll cover are LCD (liquid crystal display) panels. The main thing to understand about LCD panels is that they all use a white backlight (or sidelight, etc.). They work by shining a bright white light into your eyes, while the rest of the panel is for changing this backlight into individual pixels.
LED stands for light-emitting diode. You’ll often see LCD panels that are LED, but that doesn’t necessarily mean much when choosing an LCD. LED is just a different type of backlight compared to the old cold cathode backlights. While you could congratulate yourself on not using mercury, which is found in cathodes, at this point all LCDs use LED backlights anyway.
The second thing to understand is that LCDs take advantage of a phenomena known as polarization. Polarization is the direction in which the light wave is oscillating, or swinging back and forth at the same speed. Light comes out of the backlight unpolarized. It then passes through one polarizer, which makes all the light oscillate the same way.
Now you have an on and off (and between) switch for light. To produce color all that’s needed is three color filters, red, green and blue, that block all light other than that color from coming through. The difference between different types of LCD panels is mostly in how this in-between liquid crystal part works.
This design allows for fast response times (the time between the panel getting the frame it’s supposed to display and actually displaying it). It also allows for fast refresh rates. Consequently, TN panels are the only 240 hertz (Hz) gaming monitors available right now.
TN panels are cheap but suffer from poor viewing angles due to the “twist” only being aligned in one direction for viewing the panel straight on. They can also have poor color and contrast due to this twist mechanism not being the most precise or accurate.
VA stands for vertical alignment, again referring to the crystal alignment. These came about in the 1990s. Instead of using liquid crystals to twist a light’s polarization, a VA panel’s liquid crystals are aligned either perpendicular (vertical to) or parallel (horizontal to) the two polarizers. In the off state, the crystals are perpendicular to the two opposing polarizers. In the on state, the crystals begin to align horizontally, changing the polarization to match the second polarizer and allowing the light to go through the crystals.
This structure produces deeper blacks and better colors than TN panels. And multiple crystal alignments (shifted a bit off axis from each other) can allow for better viewing angles compared to TN panels.
However, VA panels come with a tradeoff, as they are often more expensive than TN panels and tend to have lower refresh rates and slower response times than TN panels. Consequently, you won’t see quite as many VA panel gaming monitors.
IPS stands for in-plane switching. These panels debuted after TN panels in the mid-1990s. The crystals are always horizontal to the two polarizers and twist 90° horizontally to go from off to on. Part of this design requires the two electrodes (which apply current to the liquid crystal to change its state) to be on the same glass substrate, instead of aligned with each other on the sandwiching glass substrates above and below the crystal (as in other types of LCDs). This, in turn, blocks a bit more light than both TN and VA panels.
IPS panels have the best viewing angles and colors of any LCD monitor type, thanks to its crystal alignment always lining up with the viewer. And while they don’t offer as fast a response time or refresh rate as TN panels, clever engineering has still gotten them to 144hz, and with nice viewing angles you’re not necessarily going wrong with an IPS gaming panel.
How do LCD panels go about reaching HDR brightness when incorrect polarization and color filters block so much light?The answer is quantum dots. These clever little things are molecules that absorb light and then re-emit that light in the color you engineered them to.
Today’s quantum dot layers usually go between a blue backlight and the polarization step, and are often used to produce red and green that more closely matches the color filters, so more light passes through them. This allows more of the backlight to come through instead of being blocked by the color filters, it can also reduce crosstalk, or colors slipping through the wrong subpixel, ensuring better colors of LCDs.
Other uses of quantum dots are being tried, however. One promising one is using QD molecules to replace the color filters entirely, allowing even more light through. Because LCD backlights produce more light than OLED panels (more on those below), this would allow LCDs to become the brightest displays around.
Motion blur/ghosting can be a result of how long an image takes to switch from one to another and how long an image is displayed on screen (persistence). But both of these phenomena differ greatly between individual LCD panels regardless of underlying LCD tech. And both are often better controlled by higher refresh rates, rather than clever panel engineering, at least for LCD displays.
Choosing an LCD panel based on underlying LCD tech should be more about cost vs desired contrast, viewing angles and color reproduction than expected blur, or other gaming attributes. Maximum refresh rate and response time should be listed in any respectable panel’s specs. Other gaming tech, such as strobe, which flashes the backlight on and off quickly to reduce persistence, may not be listed at all and is not part of the underlying type of LCD used. For that kind of info you’ll have to check the detailed reviews here on our site.
OLED, or organic light emitting diode, panels, are different from LCDs. There are no polarization tricks here. Instead, each pixel (or subpixel of red, green, or blue) lights itself up as a voltage is applied to a giant complex molecule called, yep, an organic light emitting diode. The color emitted is dependent on the molecule in question, and brightness is dependent on the voltage applied. OLEDs can reach HDR brightness because their molecules put out the right colors to begin with without being blocked.
Due to its approach to color and brightness, OLEDs have great contrast ratios. There’s no need to block a backlight, so there’s no worries about light bleeding through. Blacks are very black, and colors look great. OLEDs can also strobe, or flash off and on quickly to lower persistence. They can also use a trick called rolling scan.This turns blocks of the screen on and off one at a time, from top to bottom in a roll. This is all done as the image is sent to the screen, which cuts down on persistence blur a lot. This is why every major VR headset that can afford it uses OLED panels today.
Unfortunately, that’s where the advantages of OLED end. Refresh rates of OLED panels have never surpassed about 90Hz. And they’re quite expensive. A large part of that $1,000 iPhone X price is due to its OLED display. The current molecules used in OLEDs also degrade relatively quickly over time, especially those used for the color blue(opens in new tab), making the screen less and less bright.
OLEDs were also supposed to use less power than LCDs, but newer, giant OLED molecules that take less voltage to turn on have yet to appear. And while molecules covering the colors of the P3 HDR gamut are out today, those covering the larger BT.2020 gamut have yet to be found commercially. So OLEDs, while once promising and seemingly the future, have yet to live up to that promise.
A relevant question: If our fastest gaming displays are 240Hz TN panels now, just how fast do we need to go anyway? Well, a 2015 study places maximum human perception at 500Hz. So from that perspective, we’re halfway there. But that’s halfway there with today’s HDR, and not in lightfield 3D, or other possible advancements. And mobile devices could always use displays that take up less power.
In other words, in order to get fancy 3D effects, or much higher brightness, or any other desirable features, a different, new type of panel may be required. MicroLED tech is one such technology; think of it as OLED without the organic part and with the potential to improve contrast, response times and energy usage over standard LED panels. If you want to know more you can go here, but the real takeaway is that MicroLEDs work almost exactly like OLEDs.

In market, LCD means passive matrix LCDs which increase TN (Twisted Nematic), STN (Super Twisted Nematic), or FSTN (Film Compensated STN) LCD Displays. It is a kind of earliest and lowest cost display technology.
LCD screens are still found in the market of low cost watches, calculators, clocks, utility meters etc. because of its advantages of low cost, fast response time (speed), wide temperature range, low power consumption, sunlight readable with transflective or reflective polarizers etc. Most of them are monochrome LCD display and belong to passive-matrix LCDs.
TFT LCDs have capacitors and transistors. These are the two elements that play a key part in ensuring that the TFT display monitor functions by using a very small amount of energy without running out of operation.
Normally, we say TFT LCD panels or TFT screens, we mean they are TN (Twisted Nematic) Type TFT displays or TN panels, or TN screen technology. TFT is active-matrix LCDs, it is a kind of LCD technologies.
Actually, IPS technology is a kind of TFT display with thin film transistors for individual pixels. But IPS displays have superior high contrast, wide viewing angle, color reproduction, image quality etc. IPS screens have been found in high-end applications, like Apple iPhones, iPads, Samsung mobile phones, more expensive LCD monitors etc.
Both TFT LCD displays and IPS LCD displays are active matrix displays, neither of them can produce color, there is a layer of RGB (red, green, blue) color filter in each LCD pixels to make LCD showing colors. If you use a magnifier to see your monitor, you will see RGB color. With switch on/off and different level of brightness RGB, we can get many colors.
Neither of them can’t release color themselves, they have relied on extra light source in order to display. LED backlights are usually be together with them in the display modules as the light sources. Besides, both TFT screens and IPS screens are transmissive, it will need more power or more expensive than passive matrix LCD screens to be seen under sunlight. IPS screens transmittance is lower than TFT screens, more power is needed for IPS LCD display.

The most basic LCD introduced above is called passive matrix LCDs which can be found mostly in low end or simple applications like, calculators, utility meters, early time digital watches, alarm clocks etc. Passive matrix LCDs have a lot of limitations, like the narrow viewing angle, slow response speed, dim, but it is great for power consumption.
In order to improve upon the drawbacks, scientists and engineers developed active matrix LCD technology. The most widely used is TFT (Thin Film Transistor) LCD technology. Based on TFT LCD, even more modern LCD technologies are developed. The best known is IPS (In Plane Switching) LCD. It has super wide viewing angle, superior image picture quality, fast response, great contrast, less burn-in defects etc.
IPS LCDs are widely used in LCD monitors, LCD TVs, Iphone, pads etc. Samsung even revolutionized the LED backlighting to be QLED (quantum dot) to switch off LEDs wherever light is not needed to produce deeper blacks.
– Twisted Nematic Display: The TN (Twisted Nematic) LCDs production can be done most frequently and used different kinds of displays all over the industries. These displays are most frequently used by gamers as they are cheap & have quick response time as compared with other displays. The main disadvantage of these displays is that they have low quality as well as partial contrast ratios, viewing angles & reproduction of color. But, these devices are sufficient for daily operations.
– In-Plane Switching Display:IPS displays are considered to be the best LCD because they provide good image quality, higher viewing angles, vibrant color precision & difference. These displays are mostly used by graphic designers & in some other applications, LCDs need the maximum potential standards for the reproduction of image & color.
– Vertical Alignment Panel: The vertical alignment (VA) panels drop anywhere in the center among Twisted Nematic and in-plane switching panel technology. These panels have the best viewing angles as well as color reproduction with higher quality features as compared with TN type displays. These panels have a low response time. But, these are much more reasonable and appropriate for daily use.
– The structure of this panel generates deeper blacks as well as better colors as compared with the twisted nematic display. And several crystal alignments can permit for better viewing angles as compared with TN type displays. These displays arrive with a tradeoff because they are expensive as compared with other displays. And also they have slow response times & low refresh rates.
– Advanced Fringe Field Switching (AFFS): AFFS LCDs offer the best performance & a wide range of color reproduction as compared with IPS displays. The applications of AFFS are very advanced because they can reduce the distortion of color without compromising on the broad viewing angle. Usually, this display is used in highly advanced as well as professional surroundings like in the viable airplane cockpits.
– Passive and Active Matrix Displays: The Passive-matrix type LCDs works with a simple grid so that charge can be supplied to a specific pixel on the LCD. One glass layer gives columns whereas the other one gives rows that are designed by using a clear conductive material like indium-tin-oxide. The passive-matrix system has major drawbacks particularly response time is slow & inaccurate voltage control. The response time of the display mainly refers to the capability of the display to refresh the displayed image.
– Active-matrix type LCDs mainly depend on TFT (thin-film transistors). These transistors are small switching transistors as well as capacitors which are placed within a matrix over a glass substrate. When the proper row is activated then a charge can be transmitted down the exact column so that a specific pixel can be addressed, because all of the additional rows that the column intersects are switched OFF, simply the capacitor next to the designated pixel gets a charge.
LCD technologies have great advantages of light, thin, low power consumption which made wall TVs, laptops, smartphones, pad possible. On its way to progress, it wiped out the competition of many display technologies. We don’t see CRT monitors on our desks and plasma displays TV at our home anymore. LCD Technologies dominant the display market now. But any technology has the limitations.
LCD technologies have slow response times especially at low temperature, limited viewing angles, backlighting is needed. Focus on LCD drawbacks, OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diodes) technology was developed. Some high-end TV and mobile phones start to use AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes) displays.
This cutting-edge technology provides even better color reproduction, clear image quality, better color gamut, less power consumption when compared to LCD technology. Please note, OLED displays include AMOLED and PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diodes). What you need to choose is AMOLED for your TV and mobile phones instead of PMOLED.
One of the most important aspects of any display you can understand is the panel technology being used. Specifications alone won’t give you the full picture of a displays performance, and we all know that manufacturers can exaggerate specs on paper to suit their marketing. With an understanding of the panel technology being used you will get a feel for the overall performance characteristics of the display and how it should perform in real terms. Our extensive panel search database helps you identify the panel technology (and manufacturer and part number where known) of many screens in the market. This article which follows will help you understand what the different panel technologies can offer you. A lot of manufacturers now list the panel technology as well in their specs, something which wasn’t included a in the past.
TN Film panels are the mostly widely used in the desktop display market and have been for many years since LCD monitors became mainstream. Smaller sized screens (15″, 17″ and 19″) are almost exclusively limited to this technology in fact and it has also extended into larger screen sizes over the last 7 years or so, now being a popular choice in the 20 – 28″ bracket as well. The TN Film panels are made by many different manufacturers, with the big names all having a share in the market (Samsung, LG.Display, AU Optronics) and being backed up by the other companies including most notably Innolux and Chunghwa Picture Tubes (CPT). You may see different generations of TN Film being discussed, but over the years the performance characteristics have remained similar overall.
TN Film has always been so widely used because it is comparatively cheap to produce panels based on this technology. As such, manufacturers have been able to keep costs of their displays down by using these panels. This is also the primary reason for the technology to be introduced into the larger screen sizes, where the production costs allow manufacturers to drive down retail costs for their screens and compete for new end-users.
The other main reason for using TN Film is that it is fundamentally a responsive technology in terms of pixel latency, something which has always been a key consideration for LCD buyers. It has long been the choice for gaming screens and response times have long been, and still are today, the lowest out of all the technologies overall. Response times typically reach a limit of around 5ms at the ISO quoted black > white > black transition, and as low as 1ms across grey to grey transitions where Response Time Compensation (overdrive) is used. TN Film has also been incorporated into true 120Hz+ refresh rate desktop displays, pairing low response times with high refresh rates for even better moving picture and gaming experiences, improved frame rates and adding 3D stereoscopic content support. Modern 120Hz+ refresh rate screens normally also support NVIDIA 3D Vision 2 and their LightBoost system which brings about another advantage for gaming. You can use the LightBoost strobed backlight system in 2D gaming to greatly reduce the perceived motion blur which is a significant benefit. Some screens even include a native blur reduction mode instead of having to rely on LightBoost ‘hacks’, providing better support for strobing backlights and improving gaming experiences when it comes to perceived motion blur. As a result, TN Film is still the choice for gamer screens because of the low response times and 120Hz+ refresh rate support.
The main problem with TN Film technology is that viewing angles are pretty restrictive, especially vertically, and this is evident by a characteristic severe darkening of the image if you look at the screen from below. Contrast and colour tone shifts can be evident with even a slight movement off-centre, and this is perhaps the main drawback in modern TN Film panels. Some TN Film panels are better than others and there have been improvements over the years to some degree, but they are still far more restrictive with fields of view than other panel technologies. The commonly quoted 170/160 viewing angles are an unfair indication of the actual real-life performance really, especially when you consider the vertical contrast shifts. Where viewing angles are quoted by a manufacturer as 160/160 or 170/160 that is a clear sign that the panel technology will be TN Film incidentally.
Movie playback is often hampered by ‘noise’ and artifacts, especially where overdrive is used. Black depth was traditionally quite poor on TN Film matrices due to the crystal alignment, however, in recent years, black depth has improved somewhat and is generally very good on modern screens, often surpassing IPS based screens and able to commonly reach contrast ratios of ~1000:1. TN Film is normally only a true 6-bit colour panel technology, but is able to offer a 16.7 million colour depth thanks to dithering and Frame Rate Control methods (6-bit + FRC). Some true 8-bit panels have become available in recent years (2014 onwards) but given the decent implementation of FRC on other 6-bit+FRC panels, the real-life difference is not something to concern yourself with too much.
Most TN Film panels are produced with a 1920 x 1080 resolution, although some larger sizes have become available with higher resolutions. A new generation of Quad HD 2560 x 1440 27″ TN Film panels emerged in 2014. We’ve also seen the introduction of 28″ Ultra HD 3840 x 2160 resolution TN Film panels become available, and adopted in many of the lower cost “4k” models in the market. Where used, the Anti-Glare (AG) coating used on most TN Film panels is moderately grainy – not as grainy as some older IPS panel coatings, but not as light as modern IPS, VA or equivalents. Also at the time of writing there are no ultra-wide (21:9 aspect ratio) or curved format TN Film panels in production.
VA technology was first developed by Fujitsu in 1996. However the limited viewing angles were its main disadvantage, and so further investment focused on addressing this problem. It was eventually solved by dividing each pixel into domains which worked synchronously. This lead the birth of the following technologies:
MVA technology, was later developed by Fujitsu in 1998 as a compromise between TN Film and IPS technologies. On the one hand, MVA provided a full response time of 25 milliseconds (that was impossible at the time with IPS, and not easily achievable with TN), and on the other hand, MVA matrices had wide viewing angles of 160 – 170 degrees, and thus could better compete with IPS in that parameter. The viewing angles were also good in the vertical field (an area where TN panels suffer a great deal) as well as the horizontal field. MVA technology also provided high contrast ratios and good black depth, which IPS and TN Film couldn’t quite meet at the time.
In MVA panels, the crystals in the domains are oriented differently, so if one domain lets light pass through, the neighboring domain will have the crystals at an angle and will shutter the light (of course, save for the display of white color, in which case all the crystals are placed almost in parallel to the matrix plane).
As MVA developed over the years the problem became that the response times were not as good as TN film panels and was very difficult to improve. Sadly, the response time grows dramatically when there’s a smaller difference between the pixel’s initial and final states (i.e. the more common grey to grey transitions). Thus, such matrices were unsuitable for dynamic games. With the introduction of RTC and overdrive technologies, the manufacturers launched a new breed of MVA discussed in the following sections.
Premium MVA (P-MVA) panels were produced by AU Optronics, and Super MVA (S-MVA) panels by Chi Mei Optoelectronics (now Innolux) and Fujitsu from 1998 onwards. AU Optronics have since entered a more recent generation referred to as AMVA (see the next section) and S-MVA panels are rarely used in mainstream monitors nowadays. When they were launched they were able to offer improved response times across grey to grey (G2G) transitions which is a great improvement in the MVA market. While responsiveness was still not as fast as TN Film panels using similar RTC technologies, the improvement was obvious and quite drastic. This was really the first time that MVA matrices could be considered for gaming, and arrived at the time when overdrive was being more widely implemented in the market.
While some improvements have been made, the color-reproduction properties of these modern MVA technologies can still be problematic in some situations. Such panels give you vivid and bright colors, but due to the peculiarities of the domain technology many subtle color tones (dark tones often) are lost when you are looking at the screen strictly perpendicularly. When you deflect your line of sight just a little, the colors are all there again. This is a characteristic “VA panel contrast shift” (sometimes referred to as ‘black crush’ due to the loss of detail in dark colours) and some users pick up on this and might find it distracting. Thus, MVA matrices are somewhere between IPS and TN technologies as concerns color rendering and viewing angles. On the one hand, they are better than TN matrices in this respect, but on the other hand the above-described shortcoming prevents them from challenging IPS matrices, especially for colour critical work.
Traditionally M




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey