amoled vs tft display pricelist

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
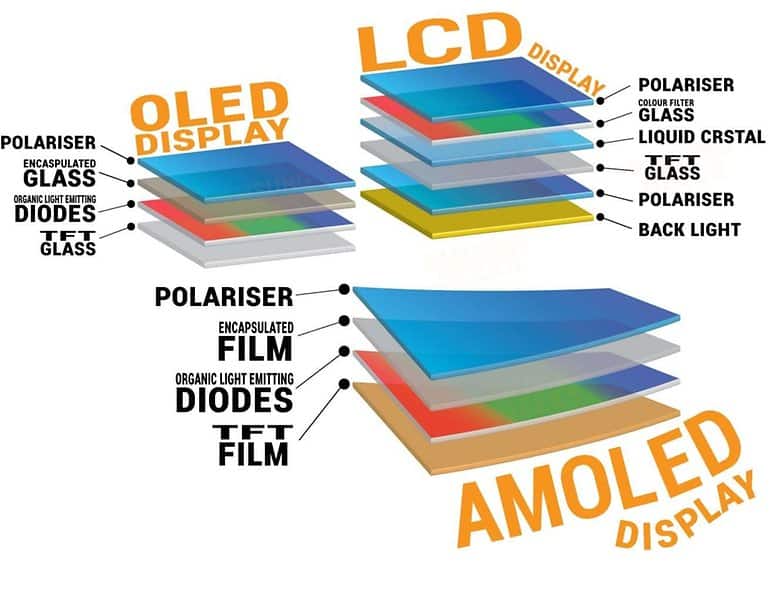
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.

A Thin Film Transistor (TFT) FT display is a form of Liquid Crystal Display with thin film transistors for controlling the image formation. The TFT technology works by controlling brightness in red, green and blue sub-pixels through transistors for each pixel on the screen. The pixels themselves do not produce light; instead, the screen uses a backlight for illumination. Discover our TFT Products
Standing for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode, this type of display requires no backlight and can light up or turn off each of their pixels independently, meaning they offer better contrast and colour. As the name suggests they are made of organic material.
Otherwise knows as the IPS display, this superior version of the TFT provides all round viewing angles and exceptional contrast ratio, however this comes at a premium cost compared to standard TFT models. Read more here.
As with all display choice, knowing your intended audience, user requirements and environmental conditions, all form part of the initial design process, which will ultimately determine the best display at the right price for your application. Before you make your choice, why not speak with us and we will be happy to talk you through your options.

AMOLED and TFT are two types of display technology used in smartphones. AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays are made up of tiny organic light-emitting diodes, while TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) displays use inorganic thin-film transistors.
AMOLEDs are made from organic materials that emit light when an electric current is passed through them, while TFTs use a matrix of tiny transistors to control the flow of electricity to the display.
What Are the Main Differences between AMOLED and TFT Displays?Backlight: One of the main differences between AMOLED and TFT displays is how they are lit up. A backlight is used to light up TFT screens, while AMOLED screens are self-illuminating. This means that TFT displays require more power to operate than AMOLED displays.
Refresh Rate: Another key difference between AMOLED and TFT displays is the refresh rate. The refresh rate is how often the image on the screen is updated. AMOLED screens have a higher refresh rate than TFT screens, which means that they can display images more quickly and smoothly.
Response Time: The response time is how long it takes for the pixels to change from one colour to another. AMOLED screens have a shorter response time than TFT screens..
Colour Accuracy/Display Quality: AMOLED screens are more accurate when it comes to displaying colours. This is because each pixel on an AMOLED screen emits its own light, which means that the colours are more pure and true to life. TFT screens, on the other hand, use a backlight to illuminate the pixels, which can cause the colours to appear washed out or less vibrant.
Viewing Angle: The viewing angle is the angle at which you can see the screen. AMOLED screens have a wider viewing angle than TFT screens, which means that you can see the screen from more angles without the colours looking distorted.
Power Consumption: One of the main advantages of AMOLED displays is that they consume less power than TFT displays. This is because the pixels on an AMOLED screen only light up when they need to, while the pixels on a TFT screen are always illuminated by the backlight.
Production Cost: AMOLED screens are more expensive to produce than TFT screens. This is because the manufacturing process for AMOLED screens is more complex, and the materials used are more expensive.
Availability: TFT screens are more widely available than AMOLED screens and have been around for longer. They are typically used in a variety of devices, ranging from phones to TVs.
Usage: AMOLED screens are typically used in devices where power consumption is a concern, such as phones and wearable devices. TFT screens are more commonly used in devices where image quality is a higher priority, such as TVs and monitors.
AMOLED and TFT are two different types of display technology. AMOLED displays are typically brighter and more vibrant, but they are more expensive to produce. TFT displays are cheaper to produce, but they are not as bright or power efficient as AMOLED displays.
The display technology that is best for you will depend on your needs and preferences. If you need a screen that is bright and vibrant, then an AMOLED display is a good choice. If you need a screen that is cheaper to produce, then a TFT display is a good choice. However, if you’re worried about image retention, then TFT may be a better option.
Nauticomp Inc.provides world-class fully customizable touchscreen displays for commercial and industrial settings. With features like sunlight readability, brightness adjustability, infrared lighting, full backlighting, all-weather capabilities, etc., our displays are second to none. Contact us today to learn more.

When we purchase a new smartphone we go through a list of specifications that includes the processor, software, cameras, display type, battery, etc. The display of the smartphone is something which has always been a concern for people. And smartphone technology has advanced so much in the past decade that you get several display technology options to choose from.
Today, a smartphone is not just a means to send and receive calls and texts. It has become a general necessity, so choosing the right technology should be your main priority. Coming back to displays, as we said there are plenty of display types available right now.
Two of the main contenders for display technologies that are widely available are AMOLED and LCD. Here in this article, we will be comprising AMOLED vs LCD and find out which one is better for you.
Starting with the AMOLED first, it is a part of the OLED display technology but with some more advanced features. To completely know about it must understand its all three components. The first one is LED, “Light Emitting Diode”. Then we have “O” which stands for organic and makes the OLED.
It actually means that organic material is placed with two conductors in each LED, which helps to produce the light. And the “AM” in AMOLED means Active Matrix, it has the capability to increase the quality of a pixel.
The AMOLED display is similar to the OLED in various factors like high brightness and sharpness, better battery life, colour reproduction, etc. AMOLED display also has a thin film transistor, “TFT” that is attached to each LED with a capacitor.
TFT helps to operate all the pixels in an AMOLED display. This display might have a lot of positives but there are a few negatives too let’s point both of them out.
A major issue with these displays is of burning of pixels. After showing a specific image or colour for a longer period of time, the pixel can get burned. And if there is a problem with a single pixel it will affect the entire display.
Low outdoor visibility, usually the AMOLED Displays are quote not bright in direct sunlight and outdoor readability could be a problem for some devices but average screen brightness.
The LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display”, and this display produces colours a lot differently than AMOLED. LCD display uses a dedicated backlight for the light source rather than using individual LED components.
The LCD displays function pretty simply, a series of thin films, transparent mirrors, and some white LED lights that distributes lights across the back of the display.
As we have mentioned, an LCD display always requires a backlight and also a colour filter. The backlight must have to pass through a thin film transistor matrix and a polarizer. So, when you see it, the whole screen will be lit and only a fraction of light gets through. This is the key difference comparing AMOLED vs LCD and this is what differentiates these two display technologies.
The LCD displays are cheaper compared to the AMOLED as there is only one source of light which makes it easier to produce. Most budget smartphones also use LCD displays.
LCD displays have bright whites, the backlight emits lots of light through pixels which makes it easy to read in outdoors. It also shows the “Accurate True to Life” colours, which means it has the colours that reflect the objects of the real world more accurately than others.
LCDs also offer the best viewing angle. Although it may depend on the smartphone you have. But most high-quality LCD displays support great viewing angles without any colour distortion or colour shifting.
The LCD displays can never show the deep blacks like AMOLED. Due to the single backlight, it always has to illuminate the screen making it impossible to show the deep blacks.
The LCDs are also thicker than other displays because of the backlight as it needs more volume. So, LCD smartphones are mostly thicker than AMOLED ones.
Both of these display technologies have their own Pros and Cons. Taking them aside everything ends up with the user preferences as people might have different preferences among different colours and contrast profiles. However, a few factors might help you to decide which one fits perfectly for you.
Let’s start with the pricing. Most AMOLED display smartphones always cost more than an LCD smartphone. Although the trend is changing a bit. But still, if you want to get a good quality AMOLED display you have to go for the flagship devices.
The colors are also very sharp and vibrant with the AMOLED displays. And they look much better than any LCD display. The brightness is something where LCDs stood ahead of the AMOLED display. So using an LCD display outdoors gives much better results.
The last thing is battery consumption, and there is no one near the AMOLED displays in terms of battery. As of now, all smartphones feature a Dark Mode and most of the apps and UI are dark black with a black background. This dark UI on smartphones doesn’t require any other light, it gives the AMOLED displays a boost in battery performance.
Looking at all these factors and comparing AMOLED vs LCD displays, the AMOLED displays are certainly better than the LCDs. Also, the big display OEMs, like Samsung and LG are focusing more the OLED technologies for their future projects. So, it makes sense to look out for AMOLED displays. That being said, if we see further enhancements in the LCD technology in terms of battery efficiency and more, there is no point to cancel them at this moment.

Mobile screen technology is split into two peaks, both the AMOLED Vs LCD audiences. Additionally, phones are sporting OLED branding, which is the same technology as AMOLED.
AMOLED and LCD derive from the very different underlying technology, leading producers to tout many distinct advantages depending on which screen type they have chosen for. Smartphone makers are opting for AMOLED displays, together with LCD, mostly earmarked for significantly less expensive telephones.
Let Colorfy find out if there is a noticeable difference between AMOLED and LCD technologies if there’s what type of difference we could anticipate. In the event, the business promoting hype is to be considered.
AMOLED is a version of the renowned OLED screen technologies. To begin with, LED stands for Light Emitting Diode along with the O here constitutes as Organic LED. Further, AM is an abbreviation for Active Matrix, which helps to light a specific pixel when required.
As its name implies, OLED displays create light from pixels. To put it differently, each LED pixel once provided sufficient present can light up for itself. Further, all AMOLED screens additionally have a TFT (Thin Film Transistor), making the entire process of sending the gift to the ideal pixel a whole lot smoother and faster. Further, obtaining an Active Matrix set up, the TFT helps to catch the perfect control to operate a variety of pixels. By way of instance, in AMOLED displays, a few pixels may be completely switched off while some are around, so, producing deep blacks.
Amoled Screens has very vibrant colors – Ever need your pictures or pictures to pop up as though they have not previously? AMOLED displays can make that occur with unusual comparison ratios (distance in color from darkest to lightest).
Adaptive, Curvable, Adaptable – Adaptable AMOLED Displays exist from the Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge. The Galaxy Gear Fit utilizes a curved screen, and almost any other smart wearable uses a round AMOLED display. LCDs might not have the ability to operate in one of these scenarios. AMOLED is your display technician for wearables (Apple Watch, Moto 360, Gear S3, etc.. )
Pricey – Right now, the regular price on the repair marketplace for an AMOLED display is double that of a similar (in some scenarios, it could be more). That is tied to high production expenses, and that the tech is younger and less elegant in comparison with their LCD counterparts.
Less Durable – substantially like older strings of Christmas lights, even if one pixel is ruined, it may cause the whole screen to quit displaying entirely. Often, the AMOLED screen will crack or split before the Gorilla Glass in addition to its will.
Burn-in – This is a problem that was current on older Plasma Televisions. With the time the pixels may get “stuck,” revealing a particular picture or color, meaning over time since the display gets old, it may demonstrate a shadow of the icon. A fantastic way to do that is to maneuver your icons around every once in a while.
Cheap – LCD Technology’s been in existence for quite a while. The production process was perfected in the mobile world, enabling vast quantities of displays to be produced at very cost-effective prices.
LCDs cannot reach deep blacks – The existence of an always-on backlight to light up a display irrespective of how much of this display is black signifies it won’t ever get as dim as an AMOLED display may.
LCDs can’t be made elastic – The Galaxy Notice Edge turned heads in 2014 when Samsung introduced a curved AMOLED screen. LCDs are stiff and cannot be flexed or bent into a curved design, restricting the kind factors it could fit into.
Thickness – Since the LCD also requires a backlight behind it, the display will always occupy a more inner volume of a telephone, restricting how light and thin designs could be.
The very first difference that I wish to highlight is that the price of the technology. The probability of you finding an AMOLED screen on your budget smartphone is a lot less than LCD screens. This is mostly because LCD screens are inexpensive to manufacture and procure while AMOLED or OLED screens, in particular, demand a higher price.
An AMOLED screen, each pixel produces its own mild while at an LCD, the mild is sourced by a backlight. To put it differently, AMOLED displays set more vivid colors and hit high pubs in saturation.
Pixels on an AMOLED screen can be shut off, so obviously, it conserves more juice when you’re working on a black backdrop as the pixels to get that component of these screens will be changed off.
On the other hand, the LCD screen is based upon a dedicated backlight which still stays switched on even when you’re on an entirely black screen. That is why features such as Always On Screen or Lively Display on smartphones create much more awareness on an AMOLED screen while it’s going to influence your battery stats onto an LCD screen undoubtedly. So think twice before utilizing the always On’ screen feature in your LCD screen smartphones.
It is not possible to say one screen is far better than another. Not all LCD screens look the same, just like not all AMOLED screens look the same. Finally, it comes down to user preference. Some people today adore the punchy color of AMOLED, other men and women despise. The same can be stated for LCD.
People might argue about what technology is exceptional, but at the close of the day, all that matters is that which seems better for the eyes. The fantastic news is that there are excellent alternatives for both. Samsung makes excellent AMOLED displays. LG and HTC have mobiles with incredible LCD screens. Android is about choice, so pick that you like best and love.

TFT and LCD are two different types of electronic displays used in computers, TVs, and smartphones. However, they are not as different as you might think. Let’s start with what those abbreviations mean.
A key weakness of TFT panels is that they do not have wide viewing angles, so they are better suited to displays that require you to view head-on. This can be a good or a bad thing, depending on your needs. For example, the narrower viewing angles mean people sitting or standing around you are less likely to be able to snoop on what you are doing on your mobile phone.
TFT panels are cheaper to manufacture, but they also consume much more power than regular LCD panels. Lastly, they have poorer sunlight visibility. You will find TFT displays on feature phones, smart feature phones, and low-end Android phones.
LCD: This is an abbreviation for “liquid crystal display”. It is a flat panel display with wider viewing angles compared to TFT. They also have lower power consumption and so deliver much better battery life than their TFT counterparts.
In summary, while TFT panels have some distinct advantages, they fall short in other areas and so their use have been limited to low end phones, from feature phones to entry-level Android phones. Plastic feels inferior to touch than glass, which means that TFT screens don’t get to feature much on mid-range and premium devices.
As we see improvements to TFT technology, we will see them deployed on higher end devices over time. In 2022, Samsung used TFT displays in its mid-range Galaxy A13 and Galaxy A23. Perhaps those improvements are happening already.
For now, LCD is the most widely used display type in modern smartphones. At the very top end, we have premium flagships using OLED and AMOLED displays.
TFT displays are higher quality components than regular LCD displays. TFT displays are sharper, brighter, and refresh better than LCD panels. However, they have weaknesses that make them unsuitable for higher end phones.
AMOLED panels have all the benefits of OLED screens, which means they are better than LCD panels. They are expensive though, and so are used in high-end smartphones only.
These are improved versions of AMOLED screens and were developed by Samsung. They are also thinner. The name explains it: think of Super AMOLED as AMOLED on steroids.

Display technologies are advancing every day. All the major tech giants like Apple, Samsung, One Plus use one among these technologies for building the displays of their Apple phones or Galaxy Notes. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. So which one is better? Is it the AMOLED favored mostly by Samsung? Or is it the IPS LCD favored by Apple for their iPhones? Let us take a detailed look at the features of AMOLED vs IPS display technologies.
AMOLED stands for Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode is a type of display used mainly in mobile phones. You might have seen the AMOLED display mentioned in the specifications for smart devices, especially mobile phones. They are also used in smartwatches, laptops, and even televisions. Let’s see what the terms in AMOLED mean.
The Active Matrix technology came about as an improvement on the existing passive matrix technology that used passive components like wires which were arranged vertically and horizontally to control each pixel. The color and brightness of the pixels and thereby the picture can be altered by varying the electrical charge at the given joint of vertical and horizontal wires. The newer Active Matrix uses active electrical components like transistors and capacitors to carry out the same purpose. Instead of varying current at the intersection of wires to control the pixels, this latest technology uses a grid or matrix of thin-film transistors commonly referred to as TFTs and capacitors.
You might be familiar with the giant LED bulbs used at parties or even as indicators on televisions showing the on/off state. These same LED lights are used in AMOLEDs, but of course in the smallest size possible. The LEDs used are in the primary shades namely Red, Blue, and Green, and are grouped in triangle-shaped pixelated forms.
The Organic Light Emitting Diode is commonly referred to as OLED. It is pronounced as “oh-led”. OLED is a type of display in which each LED lights up one at a time. When you light them up together in different intensities, you will get more colors in the spectrum. So all LEDs switched on at the same time give you white color and similarly switching off all the LEDs together gives black color. An OLED display is comprised of a substrate, an anode, a conductive layer, an emissive layer, a cathode, and the cover. The substrate is either plastic or glass that supports the display panel.
Compared to the LCD and LED displays, the diodes in the OLED display produce light individually meaning they do not need a backlight like their predecessors. OLEDs use lesser electricity and are thinner compared to LEDs. They are also bendable and may even be curved. However, they are much more expensive than LED displays. Hence in the earlier days, it was majorly used for displays for
Now the technologies mentioned above combine to give the AMOLED displays. Here an OLED display is driven with an active matrix control scheme. The TFTs (thin-film transistors) turn on/off each pixel one at a time. The other scheme where the OLEDs are controlled by a passive matrix requires each grid ( rows and lines) to be controlled together. The advanced AMOLED displays allow for higher resolution display with a much bigger physical size.
AMOLEDs have deep black lights. The blacks are darker than LEDs and LCDs because parts of the screen can be switched off altogether. AMOLEDs are also thinner and lighter than LCDs. This feature especially stands out in a dark theater room where OLED displays give a higher contrast ratio compared to LCDs making for an excellent visual experience. This feature of OLED which can work with no backlight makes it better than LCDs whether or not they have an LED backlight.
Since they use Active Matrix technology over the passive matrix version, AMOLEDs have a faster response time. They are up to a millisecond faster and extract less power from your mobile phone’s battery. Extended battery life means major advantages in the portability department. This adding to its high display features leads to them being extensively used. They are preferred over the other versions by major companies like Samsung. Speaking of power, the amount consumed by an OLED display varies according to the brightness and color of the picture displayed.
AMOLEDs have impressive contrast ratios. The contrast ratio is the ratio of the luminance of white color to the black color of a display unit. The high contrast of AMOLEDs is because when the LEDs are off, it gives complete black and since no backlight is used in LEDs, we get deep blacks.
One of the disadvantages the AMOLED had over LCD was the blurriness caused in sunlight which is a result of its lowered peak-brightness values. This issue was corrected in the advanced Super AMOLEDs. In the Super AMOLEDs, the size of gaps between the various layers of the screen namely the cathode layer, anode layer, organic active layer, TFT layer is made narrower than before.
Another problem associated with the AMOLEDs is that the organic materials used in the emissive layer and the conductive layer suffer degradation. This happens comparatively in a short amount of time. As a result, various display problems arise including image persistence, burn-in, etc which are essentially screen burn type problems and color shifts where some colors fade quicker than others. Burn-in is essentially the pixel quality becoming trash after a while because of the degradation of the organic molecules.
Most flagship models of major companies like Samsung, Apple, and One Plus use either super AMOLED or IPS panel premium LCDs. So what exactly is an IPS display? and how does it feature against like the likes of super AMOLEDs?
First, let us understand the basics of a standard LCD. Simply put, when you apply current to some crystals, they may or may not let through the light which comes from a backlight that covers the whole display. In addition to this, there are polarization and color filters present in LCDs which finally give the primary colors Red, Blue, and Green.
Before we get into detailed explanations, you have to keep in mind that for the final end-product that ends up on the market, the quality of the display does not solely depend on whether it is IPS or AMOLED. The companies usually put their tweaks on top of the existing technology before making them available in the market. AMOLEDs are a newer technology than IPS LCD and improve on it in some areas while still lagging in others.
The IPS LCD stands for In-Plane Switching Liquid Crystal Displays. It emerged onto the scene as an improvement on the existing and vulnerable Thin Film Transistor LCD technology commonly referred to as the TFT. Samsung was the leading manufacturer to employ Super AMOLEDs. The IPS display is mainly being used in Apple iPhones. Apple beginning with the iPhone X is switching to AMOLED displays with contrast ratios of 1000000 to 1
As said before, an IPS display is an improved version of the regular TFT LCDs. Here, the difference comes in the way the anode and the cathode are arranged. They are planted as strip electrodes on one of the two glass substrates.
The IPS display scores big time when it comes to offering better viewing angles compared to the other LCD technologies like Twisted Nematic LCD (TN) and Vertical Alignment LCD (VA). The IPS display can be viewed without any color degradation or blurriness at flimsy shallow angles compared to TN and VA displays.
The consistency of colors and clarity of pictures at wider viewing angles is the major advantage of an LCD. IPS displays have higher resolution. They also can display a wide range of colors. These features also make the IPS displays costlier than TN and VA LCDs. Normally IPS monitors allow up to 178 degrees of viewing angles. These displays almost guarantee absolute color accuracy.
For other LCD models, the color and the brightness of an image vary when viewed from different angles. Compared with them, IPS displays are more suited for someone working as a visual/graphic artist. As a regular television, all LCD models are mostly considered equally good. This is because the viewers would mostly be sitting right in front of the screen where these differences between the models do not matter.
IPS displays are capable of displaying a wider spectrum of colors. Considering no monitors can display the entire color spectrum visible to the human eye, IPS LCD panels are the closest things to a perfect display monitor far better than TN and VA LCDs
Image retention is a problem often associated with LCDs. This happens because of the crystal which gets into a particular position for the light to go through stays in that same spot without falling back into its original position. This leads to some parts of the image being left on the screen. This is, however, a temporary problem. The crystal will eventually twist back into the position when the current is applied to it again. When it comes to color accuracy, the previous generation of LCDs was no match for the AMOLED. They had the highest color accuracy among mobile phones. But recent versions of the LCDs have fared much better versus their counterparts.
Large-sized IPS monitors are not affordable for the average customer. They should be avoided since they offer nothing impressive over other LCDs considering the price range. However, if you are a visual artist or a photographer, IPS displays provide the best color accuracy in the market. It would be more beneficial to you compared to an ordinary TN display unit.
AMOLEDs and IPS LCDs are two sides of the same coin in a sense. They both got their advantages and disadvantages. Their disadvantages are mostly overshadowed by the many tweaks installed by the parent companies to ensure customer satisfaction. From high power consumption to ugly blacks, the flaws are minimized in every newer version.

According to an analysis done by IHS Technology, AMOLED screen production cost is now lower than that of LCD screens. Production costs in the first quarter of the year for a 5" 1080p display amount to $14.30 for an AMOLED panel compared to $14.60 for an LCD one.
However, it"s yet to see if this trend will keep on. In Q4 2015, an AMOLED panel cost $17.10 to make, while an LCD one was cheaper at $15.70. IHS notes that the numbers apply for the production cost of a LTPS LCD (Low Temperature Poly-Silicon Liquid Crystal Display), which is the most efficient type of TFT LCD.

By now you know that (one of) AMOLED"s Achilles" heel is readability in direct sunlight. But Samsung"s been working hard to fix that with its new Super AMOLED technology. Techblog took the display to task by pitting the Samsung Galaxy S (4-inch, 480 x 800 pixel Super AMOLED) against the HTC Desire (3.7-inch 480 x 800 pixel AMOLED) and Sony Ericsson XPERIA X10 (4-inch, 480 x 854 pixel TFT LCD). It"s clear from the video embedded after the break that the LCD still has the edge in the harsh Greek sun, but the Super AMOLED certainly makes a much stronger showing than its AMOLED sib. In fact, differences in visibility between the LCD and Super AMOLED are often indistinguishable, like the picture above. That"ll be good news for us just as soon as Samsung can start meeting demand... regardless of what Stevie J has to say. Check the video after the break and be sure to click the source for some more side-by-side pics, including a few taken indoors where that Super AMOLED display really shines.

When you buy a smartphone and while reading the specifications of the phone, you often do not pay attention to the type of phone screen. Screen types abbreviations can be a bit confusing and most people don’t usually take them into consideration due to their ignorance. Don’t worry now we will give you everything you need to know about the main types of screens which are LCD, OLED and AMOLED.
Previously, there were only two main types in the smartphone industry, LCD and LED. But with the advancement in technology, many other types such as OLED, AMOLED, sAMOLED, and Retina have appeared. LCD screens are used in most mid-range phones from Xiaomi, Realme and other Chinese manufacturers and OLED in their top-end devices. Samsung uses AMOLED and sAMOLED displays, while Apple uses Retina displays. Let us discuss each of these types one by one.
LCD (abbreviation for Liquid Crystal Display). The oldest type of screen, it relied on backlighting as the only light source to illuminate the pixels. Also, LCD screens are brighter than most other types of screens, which makes them suitable for use in smartphones in bright sunlight. However, these screens suffer from less accurate colors. Smartphones use two main types of LCD screens:
TFTstands for Thin Film Transistor. TFT monitors are an advanced version of LCD monitors. While TFT has a relatively lower production cost and provides better image quality than previous generations of LCD monitors, it has higher power consumption, lower viewing angles and lower color representation.
IPSstands for In-Plane Switching. It is an improved version of TFT. Availability Provides better viewing angles and color representation by utilizing more powerful backlighting. It consumes less power than TFT, but its cost is higher overall.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode). The presence of this type is the main reason for the emergence of curved displays and foldable smartphones. Unlike LCD screens, which use backlighting, OLED screens do not require this because they contain a layer of organic matter that emits light when exposed to an electric current. OLED displays display more saturated and vibrant colors. Because of the luminance per pixel, OLED displays provide darker levels of black. Because the pixels that don’t get caught are in a sleep state, OLED screens usually use less power and give better battery life. These screens are of two main types:
AMOLEDstands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Similar to an OLED screen but has Thin Film Transistors (TFT) on the back panel. This ensures faster and more precise control as it can turn on or off any pixel individually, and it also has a storage capacitor which eliminates screen size limitations and provides the possibility of a larger screen. We will explain AMOLED screens in more detail due to their great popularity.
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). Improved OLED screens. The most important component of these displays is the TFT element that controls the flow in each pixel. With two TFTs per pixel, one to start and one to stop charging the storage capacitors this allows each LED to operate individually and generate light for itself. Due to its great flexibility it can be used in foldable phones.
You may have seen the term sAMOLED or Super AMOLED. These monitors were invented by Samsung and are available in their high-end models. This type provides a variety of colors with greater clarity. Super AMOLED displays can handle sunlight better than other AMOLED displays, while consuming less power.
Each of the above types of screens has its own advantages and disadvantages. In general, AMOLED is superior to LCD screens. Our primary comparison criteria are higher refresh rates, better color representation, and battery consumption. As for OLED versus AMOLED, we already mentioned that AMOLED is an improved version of OLED as it offers better image quality to battery consumption. Due to their low usability under sunlight, Super AMOLED screens are the best choices.
In the end, it all boils down to your needs and budget. If you’re on a tight budget, an LCD monitor isn’t a bad deal. But if your budget is good, you should definitely opt for the newer AMOLED screen especially for TVs.

The world of smartphones has been busy for the past few months. There have been numerous revolutionary launches with groundbreaking innovations that have the capacity to change the course of the smartphone industry. But the most important attribute of a smartphone is the display, which has been the focus for all prominent players in the mobile phone industry this year.
Samsung came up with its unique 18:5:9 AMOLED display for the Galaxy S8. LG picked up its old trusted IPS LCD unit for the G6’s display. These display units have been familiar to the usual Indian smartphone buyer. Honor, on the other hand, has just unveiled the new Honor 8 Pro for the Indian market that ships with an LTPS LCD display. This has led to wonder how exactly is this technology different from the existing ones and what benefits does it give Honor to craft its flagship smartphone with. Well, let’s find out.
The LCD technology brought in the era of thin displays to screens, making the smartphone possible in the current world. LCD displays are power efficient and work on the principle of blocking light. The liquid crystal in the display unit uses some kind of a backlight, generally a LED backlight or a reflector, to make the picture visible to the viewer. There are two kinds of LCD units – passive matrix LCD that requires more power and the superior active matrix LCD unit, known to people as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) that draws less power.
The early LCD technology couldn’t maintain the colour for wide angle viewing, which led to the development of the In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD panel. IPS panel arranges and switches the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules of standard LCD display between the glass substrates. This helps it to enhance viewing angles and improve colour reproduction as well. IPS LCD technology is responsible for accelerating the growth of the smartphone market and is the go-to display technology for prominent manufacturers.
The standard LCD display uses amorphous Silicon as the liquid for the display unit as it can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. This though restricts the display resolution and adds to overall device temperatures. Therefore, development of the technology led to replacing the amorphous Silicon with Polycrystalline Silicon, which boosted the screen resolution and maintains low temperatures. The larger and more uniform grains of polysilicon allow faster electron movement, resulting in higher resolution and higher refresh rates. It also was found to be cheaper to manufacture due to lower cost of certain key substrates. Therefore, the Low-Temperature PolySilicon (LTPS) LCD screen helps provide larger pixel densities, lower power consumption that standard LCD and controlled temperature ranges.
The AMOLED display technology is in a completely different league. It doesn’t bother with any liquid mechanism or complex grid structures. The panel uses an array of tiny LEDs placed on TFT modules. These LEDs have an organic construction that directly emits light and minimises its loss by eradicating certain filters. Since LEDs are physically different units, they can be asked to switch on and off as per the requirement of the display to form a picture. This is known as the Active Matrix system. Hence, an Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display can produce deeper blacks by switching off individual LED pixels, resulting in high contrast pictures.
The honest answer is that it depends on the requirement of the user. If you want accurate colours from your display while wanting it to retain its vibrancy for a longer period of time, then any of the two LCD screens are the ideal choice. LTPS LCD display can provide higher picture resolution but deteriorates faster than standard IPS LCD display over time.
An AMOLED display will provide high contrast pictures any time but it too has the tendency to deteriorate faster than LCD panels. Therefore, if you are after greater picture quality, choose LTPS LCD or else settle for AMOLED for a vivid contrast picture experience.

AMOLED displays are popular for the pure blacks and energy efficient "glance" displays they enable. Thus they are seen as a premium option for smartphone and laptop users, and AMOLED panels are only seen in really high-end TVs. However, thanks to competition and demand spurring greater production, prices are starting to become more competitive with TFT LCD panels, reports IT industry journal DigiTimes.
According to the source report "The production cost for a 5.5-inch HD AMOLED panel has drifted to US$12.10 recently, compared to US$12.20 for a 5.5-inch HP LTPS LCD panel". This is a big change to the previous state of affairs where AMOLED panels had "much higher,"prices due to the increased production costs. Thanks to the levelling off of prices and demand it"s expected that AMOLED panels will be equipped on up to 50 per cent of smartphones by 2020.
In other recent AMOLED smartphone news, the Nikkei Asian Review asserts that Apple will "use OLED screens in all new iPhones launching in 2018". Industry sources say Apple is considering launching three smartphones in 2018 and all will come equipped with this type of display.
Later this year Apple will launch its first OLED iPhone - but only the premium version will get this type of display, in a design that eschews its iconic Home button. Two other iPhone models released this year will use TFT LCDs.
Back to the AMOLED panel pricing news, and there is hope that larger displays, not just those aimed at smartphones and tablets, will come down in price. LG Display"s E4-2 fab, its second production line for AMOLED displays for TVs, will enter volume production in H2 2017, says DigiTimes. Thanks to the new production line AMOLED TV display production is set to more than double to 1.5 million units, say sources. Furthermore, several Chinese panel makers have been investing in AMOLED production facilities with output set to increase fivefold (comparing 2016 output to that estimated to come on line in 2018).
Looking out for best Super Amoled Display Phones Price list? Well, your search ends here. The Top Super Amoled Display Phones across India geography and most popular among these models are Apple iPhone 12 (₹ 48,999), Vivo V15 Pro (₹ 23,999), Vivo S1 Pro (₹ 19,499), Vivo V17 Pro (₹ 28,990), Vivo V19 (₹ 22,500).
For all the customers looking for best Super Amoled Display Phones , check out the list below and you can click on any model to read out the Specifications, Reviews, Features, FAQs, User Ratings and Images for any model. The list of Super Amoled Display Phones with the best price in India was generated on November 2022.
The best Super Amoled Display Phones is Apple iPhone 12 which is priced at ₹ 48,999 which is powered by Apple A14 Bionic (5 nm) processor and comes with 4 GB of RAM and 64 GB of storage. Apple iPhone 12 has 12mp primary rear camera and 12 MP of front camera.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey