revolution of the tft lcd technology pricelist

At present, TFT LCD touch panel prices rebounded, after six months of continuous decline, TFT LCD touch panel prices began to rebound at the end of July. Global TFT LCD panel prices have rebounded since August, according to Displaysearch, an international market-research firm. The price of a 17-inch LCD touch panel rose 6.6% to $112 in August, up from $105 in July, and fell from $140 in March to $105 in July. At the same time, 15 – inch, 19 – inch LCD touch panel prices also showed a different range of recovery. The price of a 17-inch LCD touch panel rose 5.8 percent, to $110, from $104 in late July, according to early August quotes from consulting firm with a view. Analysts believe the rebound will continue through the third quarter; LCDS will see seasonal growth in the third quarter, driven by back-to-school sales in us and the completion of inventory liquidation in the first half of the year. Dell and Hewlett-Packard (HPQ) started placing orders for monitors in the third quarter, and display makers Samsungelectronics (SXG) and TPV (TPV) are expected to increase production by 25% and 18% respectively.
It seems that due to the increasing demand in the market, the production capacity of the display panel production line has been released. Domestic TFT-LCD touch panel makers boe and Shanghai guardian said their production schedules have been set for September, and their production capacity may reach full capacity by the end of the year. Jd will produce 85,000 glass substrates per month (with a designed capacity of 90,000), according to boe and Shanghai guardian. Previously, panel makers have been hit by falling prices, with boe, SFT, and even international panel giant LG Philips all reporting losses. If the rebound continues into the fourth quarter, boe, Shanghai radio and television and other panel makers will use the rebound to reverse the decline, according to industry analysts.
It is understood that the first quarter of the boe financial results show that the company’s main business income of 2.44 billion yuan, a loss of 490 million yuan.Jd.com attributed the loss to a drop in the price of 17-inch TFT-LCD displays made by its Beijing TFT-LCD fifth-generation production line of Beijing boe photoelectric technology co., LTD., a subsidiary. Boe has issued the announcement of pre-loss in the first half of the year in April. Due to the influence of the off-season of TFT-LCD business operation in the first quarter of 2006, the company has suffered a large operating loss, and the low price in the TFT-LCD market has continued till now. Therefore, it is expected that the operating loss will still occur in the first half of 2006.LG Philips, the world’s largest TFT LCD maker, reported a won322bn ($340m) loss in July, compared with a won41.1bn profit a year earlier.LG Philips attributed the loss to fierce price competition and market demand did not meet expectations.

The introduction of flat panel displays that are fabricated with thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal displays (TFT LCDs) has changed human"s lifestyle very significantly. Traditionally, the revolution of the TFT LCD technology has been presented by the timeline of product introduction. Namely, it first started with audio/video (AV) and notebook applications in the early 1990s, and then began to replace cathode-ray tubes (CRTs) for monitor and TV applications. Certainly, TFT LCDs will continue…Expand

Recently, there is a lot of buzz about whether Apple will choose Mini-LEDover OLED, for the next round of iPads, MacBooks and other products. Regardless of the fascination analyzing current product releases, or one specific consumer-product company, the more significant movement over the last 5~10 years, has been the steep upwards ramp in Micro-LED Startups, IP, investments and acquisitions by: Apple, Facebook, and Google. And from the chip makers themselves such as Intel, Global-Foundries, in Startups such as Luxview, InfiniLED, Plessey, Aledia, Compound Photonics and more.
For an industry that is literally in the business of visualization, the display industry often seems rather opaque, mysterious, and even geo-politically contentious (refer: Foxconn"s LCD Fab in Wisconsin). These articles will cover aspects not well-elaborated in popular analysis, and also provide an update to the material presented 5yrs ago at the Bay-Area SID (Society for Information Displays), on why this technology, is so different, so disruptive, and how it will reach far beyond even the wildest market projections. But for a background on the basics of how & why, vision, the brain and displays work, recommend an easy to digest, and popular, book by Mark Changizi: The Vision Revolution. There are also excellent industry analysts, who cover displays professionally, and in much finer-grain detail, such as Yole Development (thanks to Eric Virey for source graphics) and DSCC (thanks to Ross Young & team for references, and feedback).
Firstly, to be clear: the flat-panel display industry is a semiconductor industry. This is the critical "border", where electrons of digital information, are turned into photons of visual information. And the pixels you see, while reading this article, are driven by transistors - Thin-Film Transistors (TFT) - somewhere between 3 and 12 transistors per pixel, depending on the type of display (OLED needs more than LCD), and the maker. The Transistor, Resistor, Capacitor circuits are built by nano-scale material deposition processes, on a glass substrate (the backplane), via semiconductor manufacturing equipment, from suppliers including US"s Applied Materials, Japan"s Canon Tokki, Korea"s SNU Precision, Wonik IPS and more. Yet it has not attracted the same strategic interest from within the US, as other semiconductor industry segments e.g. processor chips. While there is a drive to increase the number of (existing) semiconductor chip fabs on US soil, the fact is that the US has no significant domestic display manufacturing capability at all, effectivelyzero. And the same is true for most of the technology ingredients comprising the display, such as the film layers, LED’s & OLED and their ingredient materials, and the controller & driver chips - which is dominated entirely by non-US companies you probably never heard of, such as Taiwan Novatek (the 13th largest semi maker, worldwide), Taiwan Himax, Taiwan Parade, and Japan"s Renesas. That is, until one of them has a problem.
So if the geopolitical semiconductor war gets any rougher, you might be wondering, where is this chip (that Biden is holding) going to display it"s output ? On an etch-sketch ? (perhaps the only display device still made in the US ?)
Since more than 40% of our brain is devoted to vision, more than all of the other senses combined, this would seem an important gap. After all, light, color and contrast are the fundamentals of art, literature, civilization, as well as your next Zoom virtual meeting. Of course we need to see the results of the computation of AI, CPU, Memory, GPU, Network, 5G ... processors, appear on some display eventually, right ? So this article also aims to provide some more insights on key factors in the previous transition, what"s going on now, why it"s important, and how it may matter in real-life terms.
Secondly, (and this an easy bet) you’re more likely reading this article on an LCD flat-panel Display, rather than OLED or ePaper. But all 3 have been transformational technologies of the 21st century. Could modern society continue to communicate effectively, presenting a person in front of you from anywhere/anytime, productivity continuing virtually, during a Global Pandemic ? What would it have been like if we were still sharing the 20th century family’s TV ? (recap for millennials: the Cathode Ray Tube TV was a 50 ~ 100 lb, X-Ray-emitting, monster appliance, using electron beam scanning technology from the 1920"s, and with coarse interlaced video rendering designed to save 6MHz (3 Mbit/s by modern standards) of precious radio-frequency bandwidth). Even the 12yr old iPhone 3GS could muster more than that, on a bad day.
As for myself, am writing this article across two of my favorite consumer flat-panel devices: a newer 15” Retina MacBook Pro and an older 17” MacBook Pro. Partly because both are still the best, un-compromised, example of the portability & performance enabled by the Hybrid Graphics technology, a Display & GPU technology, drove across the laptop industry while working at NVIDIA. But mostly because Apple consistently aims for excellence in their displays. Am enjoying a large, bright, 300 “nit” (candela/meter2) LCD screen, an excellent 900~1000:1 contrast ratio, a full DCI-P3 color gamut, and sharp 220 ppi "retina" resolution that renders crisp text and beautiful images. The recurring theme: light, color, contrast.
However, at the 2019, 2020 and 2021 CES, Micro-LED and Mini-LED began appearing across more and more applications (e.g. TV, AR, Monitors, Digital Signage), and demo"s like the Samsung Wall and Sony MicroLED continue to attract the largest, most excited crowds, have ever seen at CES (before it went virtual). Back in 2017, I wrote this article about Micro-LED & Mini-LED"s, talking about potential applications, and specifically about the key challenges to this visual revolution, that PixelDisplay set out to solve: in the color conversion material needed to more economically create Red & Green from the high efficiency Blue. In November 2020, PixelDisplay publicly disclosed details of NanoBright™solution, at the Phosphor & QD Summit, and is now offered for sale on PixelDisplay.com
In the Mini-LED ecosystem, the role of NanoBright is often used the same as per regular white LED"s, which in 2018 PixelDisplay estimated to be worth $750m/yr, but this market is now projected to be worth $5b, for Mini-LED"s overall, by 2025. The color converter can be simply coated on the Mini-LED and surrounding backplane (providing a high efficiency, bright-contrast, High-Dynamic-Range with DCI-P3 wide-color gamut), but there are more interesting benefits e.g. eliminating existing LCD films to make thinner, borderless and more efficient.
But to put this in larger perspective, here"s the role NanoBright™fills in the Micro-LED ecosystem, as described in DSCC"s ( @Guillaume Chansin) excellent LinkedIn article.
But why should this Micro-LED technology be of any broader importance ? Why is it any different than OLED, or LCD ? How is it a disrupting technology ? What difference does it have from any of the other opaque display industry machinations that means it will have significant impact in our lives? It"s a great test to ask: "would my mother care ?".
To start with how it"s different, and how it is disruptive, we need to recap on how we got here on the glass backplane of LCD and OLED. And to fully appreciate the magnitude of the disruption represented by the Micro-LED revolution, we have to also understand the scale of the investment behind the commercializing flat-panel glass, and to the display TFT semiconductor industry.
Am not going to cover the long sordid history of display technologies, nor the detailed lineage of LCD, or OLED. But it is worth noting that both technologies were born in the US, the LCD from RCA, and the OLED from Kodak - and ironically, both pioneering companies are now just brands - non practicing entities. But there are other pioneers, such as UDC, who have persisted, and remain necessary ingredients in the ecosystem (we"ll touch on "why ?" later). But instead, will identify two key elements from the 1990"s, that were the major accelerators flat-panel displays to escape velocity in 2000"s, launched the FPD revolution into orbit, and led to the proliferation of what we enjoy today:
1) TFT follows Square-Rule Growth:To understand the explosion in the economics of producing glass flat panel displays covered in TFT pixels, we can start with the size increases of the glass processing fabrication itself. The term, "Gen" refers to the size generation, the capability of the TFT panel fab, by the dimensions of the glass sheet that it can process, which typically entails creating deposition layers stacked layer-by-layer, to build the TFT pixels - whether OLED or LCD, it starts with TFT pixels on a sheet of glass. In the late 90’s, massive government investments spurred the creation of ever larger display fabrication facilities, with ever larger deposition equipment based on the successful A-Si (amorphous Silicon) process, which grew quickly from Gen 3.5 (0.62 x 0.75m) to Gen 5 (1.1 x 1.3m) to Gen 6 (1.5 x 1.85m) glass substrates, in just a handful of years. Every sheet of glass processed in an LCD production line is cut into smaller panels, making TV’s, Monitors, laptops, tablets and phones.
But unlike Moore’s Law (which doubles transistors every 18months), the glass panel area increase (width x height) results in a faster, power-of-2 square-rule, increase in the number of pixels, and thus the number of TFT transistors. In fact, the number of semiconductor transistors on glass TFT was increasing at 2.5x Moore’s Law, during the last decade. While it took 10 years to go from 5mil transistors in Intel’s Pentium Pro 1995, to 169 mil transistors in the Prescott CPU 2005 – the LCD display industry made the same increase in the number of TFT transistors for 8K resolution, in roughly 5 years (from the PixelDisplay presentation at the 2018 DSCC Future Display Technology Conference).
By early 2000"s, Plasma was beyond hope, the transition from CRT"s was in full-swing, the IBM Thinkpad was a staple of corporate life, and laptops had crossed the 8hr battery-life mark thanks to display efficiency improvements (as we"ll discuss later the display is the key enabler of longer battery-life). The LCD plants were pumping out everything from laptop screens, to LCD monitors, to 60" large-screen LCD TV"s, at lower-and-lower price-points - from fabs based in Japan, then Taiwan, and Korea. By the late 2000"s, the Fab-depreciation (eff. cost of borrowed capital) was the most significant component of the LCD panel prices, and panel makers squeezed the margins out of everyone in the supply chain including films, LED, controller and driver chips. Major winners were the materials suppliers: Corning Inc (the Glass), Merck (the LCD material itself), Nichia (the backlight LED"s), and Canon Tokki & Applied Materials (TFT-glass deposition equipment).
Meanwhile in the US, Intel made a huge bet in 2001, that LCD would not scale, and that LCOS would provide solutions, and enable larger-screen, like the earlier (CRT-based TV) projection displays. But in just 3~4 years, it became clear the LCD square-rule economies were different, ever-larger ever-cheaper LCD panels seemed to be viral, ramping to fill the large-screen TV market. The LCOS & DLP were relegated to the projector market, and Intel exited LCOS in late 2004. It"s worth noting Intel has gradually become more active in the display industry, and Intel Capital has made multiple investments in the Micro-LED partnerships for GaN-on-Si (and we"ll come back to that later).
Outside the US, the display industry has been the target of massive strategic investments for Asia for over 3 decades. Starting with Japan government forcing the collaboration of Sony, Hitachi and Toshiba to create JDI (which made the first iPhone and iPad screens), and the INCJ (a government investment consortium) of Japan, then Korea and Taiwan Governments, and then China. Today this industry is dominated by China, as per the reports from analysts e.g. this one from Display Supply Chain Consultants. The government of China and private investors, aggressively funded the rise of China from sub 10% a decade ago, to owning more than 63% of the world’s display production. By 2017, the Taiwan government had publicly stated they were no longer going to invest in more LCD fabs, and in 2018 the chairman of LG got up in front of the entire company taking a sledge hammer to smash an LCD TV, in a symbolic communication of the company"s shift in focus to the highly profitable OLED (not facing competition from China) - the fate of LCD flat-panels was sealed.
One example of China"s investment in display leadership is Beijing Opto Electronics (BOE). And I have visited BOE’s Gen 6, 8.5, and 10.5 (2.9m x 3.4m) fabs in HeFei and Beijing. This picture below is a panorama I took standing outside one of the older (smaller, older) Gen 8.5 Fab"s from a visit to the BOE facility in HeFei. At the time, they had built a Gen 10 behind it, and building another beside that.
But when you’re outside looking at a factory that is literally over 1.3 kilometer per side, the staggering magnitude of China"s investment in display leadership, is simply breathtaking. The first Gen 10.5 fab located in Sakai Japan, was also Japan"s last one. But at last count there are seven (7) Gen 10.5 fabs in Mainland China, and still more are being built. There is no questioning China’s intent to seize control over the majority of eye-balls, from the source.
2) Inorganic Solid-State gives 4x increase in efficiency: The second important innovation was the In/GaN-based Blue LED. Invented in Japan (ironically, US-based CREE had a blue LED earlier, but failed to productize until much later), from which Nichia made White LED’s, by adding yellow-emitting YAG:Ce inorganic phosphor, they had left over from their CRT phosphor business. It was a cheap trick to synthesize something that looked White, from a psycho-visual hack of using two complementary colors: Blue + Yellow. But in short, the poor color was an acceptable tradeoff for higher-efficiency, smaller size, more robust inorganic solid-state solution. LED backlights quickly transformed the industry from (thicker, bulky, and very fragile) fluorescent tube (CCFL) backlights, into thin/efficient LED backlights, in the early-mid 2000"s. And the lead inventors, including Shuji Nakamora of Nichia, won the 2014 Nobel prize for the work on GaN LED.
This was an important step forward in the story. Originally, the CCFL backlit display was 70~80% of the total power consumption of an idle Laptop. In fact, back in 2001 while at Intel, together with Ying Cui we invented and implemented Intel’s Backlight Modulation Technology (called DPST(tm)) which was like an inverse-High-Dynamic Range, it proportionally increased pixel contrast, in order to allow decreasing the CCFL backlight brightness and provide huge system power-savings. That was the star feature of Intel’s EBL (Extended Battery Life) initiative, saving more system power than other, more publicized, Intel CPU features (e.g. Geyserville aka "SpeedStep"). For me, that was a first introduction to the value and importance of the flat-panel display technology, as the essential ingredient in portable platforms. But LED"s further helped enable the "implosion" of visual-compute portability into sub-8lb / sub-1inch Laptops. And the displays that appeared in Phones and Tablets, were using LED"s that are only 0.4~0.6 mm tall, fitting in the edge of the panel.
Today, LED efficiency is over 200 lm/W (4x the efficiency of older CCFL), but efficiency improvements in processor and memory technology means the display is still typically 50~70% of total system power for phone or laptop, and this is worse for OLED (than LCD) because of how poorly OLED technology handles mostly-white backgrounds (e.g. of browsers, text & productivity applications).
The LED industry has also been a source of massive investment and deeply geopolitical rifts as Japan (e.g. Nichia) vs Korea (e.g. Seoul Semi Conductor) vs Taiwan (e.g. Foxconn/AOT, LiteOn, Epistar) vs China (e.g. CSOT, SanAn). Initially dominated by IP held by Nichia, CREE and Osram, those players now have diminished roles, but it has remained a complex ecosystem.
Tiny efficient LED"s enable 2D-array backlighting on LCD to achieve HDR (High-Dynamic-Range). Higher-end LCD TV"s were the first consumer displays to use LED"s with better R-G Phosphors to create a wider DCI-P3 color gamut. Firstly, arranging the Edge-Backlight LED"s to control 1-Dimensional regions, from along the edge. And then advancing into 2D-array of LED"s, to create active-region backlight. This enabled LCD"s to increase the contrast ratio beyond 1000:1, and peak brightness beyond traditional edge illumination, creating the High-Dynamic Range (HDR) experience first popularized by BrightSide (later acquired by Dolby, to form DolbyVision, and which is now licensed-technology on the iPhone). Today HDR content leverages individual screen-region lighting, to create brighter highlights, and the deeper-blacks to create a more realistic and dynamic experience. In summary, HDR LCD TV with 2D backlight became commercially practical as a result of small (less than 3.0 x 3.0 mm) LED"s with over 220 Lm/W efficiency - 13x more efficient than incandescent bulbs Brightside originally used, which had required huge exotic water cooling solution.
Challenges of the "Crystal Cycle":the size of these glass-processing fab investments is so large, and the equipment CapEx expenditures are so huge, that this leads to massive disconnect between supply and demand, causing large cyclical swings in pricing, which became known as the "Crystal Cycle"
To ride the economies of scale requires increasing the glass handling size, which requires ever larger investments, just as the second of Moore’s Laws predicts. For example, BOE’s invested US$7 billion to make a Gen 10.5 fab. And in an interesting geopolitical twist, after the Taiwan (once a former colony of Japan) government declared they were not investing anymore in the LCD business, Terry Guo (Taiwan Foxconn CEO), acquired a majority of Sharp, and their huge LCD display production lines in Kameyama (which made the innovative IGZO-based LCD panels, which enabled the thinner/more-efficient iPhone 6, and iPad Air), and Japan’s only Gen 10.5 plant in Sakai, which is making 8K TV’s (was spun-off into Sakai Display Corporation). Foxconn was already a large player in the display industry owning Taiwan’s #2 maker, Innolux Optoelectronics. Far beyond merely being “the sport of king’s”, the display industry has been “the sport of nations”.
OLED is doubly challenged: and it has not become progressively cheaper with economies-of-scale as many expected. In LCD only a tiny current is needed to flip a pixel, all of the light is produced from a thin string of backlight LED"s. Whereas in OLED, every pixel is itself a light emitting organic-LED, with many orders of magnitude higher current required at every pixel. The high contrast emissive pixel design of OLED displays provides excellent contrast, but typically requires the use of the more expensive and complex LTPS (low-temperature polycrystalline silicon) process to produce the active TFT driving backplane. LTPS involves a more complex 11-step process, with much higher-temperatures that only a few materials (glass, clear polyamide) can sustain. LTPS requires a high-power excimer laser to anneal the surface, forming the layer of polycrystalline silicon - this is slow, and does not scale well into larger sizes. The OLED fabs have thus been limited to Gen 6 (1.5 x 1.85m) or smaller, in glass size. Even though this is big enough to make a few TV"s, the smaller starting glass size means the cost-curve is sub-optimal, unless partitioned into many smaller panels e.g. the higher-cost has lower impact for smaller smartphone screen. While an oxide deposition process called LTPO (a simpler Oxide process, borrowing from the IGZO process that delivered LCD efficiency improvements in iPhone 6 & iPad Air), offers some hope in the future, there’s another additional challenge.
The complexities of driving a large number of emitters from a thin layer on glass backplane has also meant limits on full-screen brightness, and limited ability to address higher resolutions. A full screen of white does not occur often on a OLED TV, as it does on an Tablet or Laptop, but if you do witness a larger amount of white (as in productivity apps on a Laptop) you"d notice the whole OLED screen goes dimmer, this is done in order to limit the total current across the thin conductor traces that feed the pixels on the glass.
Unlike LCD TFT (which only requires a single transistor and storage capacitor), a typical OLED driving circuit can have 3~6 transistor (and similar number of capacitors) per color i.e. 9~18 transistors per pixel. This driving complexity also limits the net active emitting area of the pixel, versus the inactive driving circuit, also called the "Fill-Ratio". And that"s part of the reason why the Oculus and Samsung Gear VR headsets look like watching everything through a thick fly-screen mesh - the amount of non-emitting "dark-area" per pixel is huge (much larger than LCD). Laying out complex circuits naturally extends the non-emitting pixel-area, horizontally outwards in width & length, that is of course a limitation of thin deposition layers on glass. This limits both the ability to go into finer pitch (>1000ppi and 40Kx16K resolution is the ultimate goal for x-Reality displays), and also to create larger emitters for higher brightness.
Furthermore, the front-plane of an OLED panel requires ultra-precise patterning with emissive organic phosphor materials, with tightly controlled size & depth-tolerances. This has switched from vapor deposition, to inkjet patterning to save some cost, but because of the non-uniformity it is limited in ability to go into very fine pitch, retina-quality displays. But either way, the OLED materials themselves remain very expensive, with Universal Display Corp (UDC) maintaining a tight grip on the materials supply chain, thanks to a portfolio of significant & early IP. The alternatives to UDC patents, such as HF (Hyper fluorescence e.g. KyuLux) or TADFL (thermally activated delayed fluorescence e.g. Cynora) are really 5~10yrs out, and merging QD on OLED aka "QD-OLED (e.g. Nanosys & Samsung) has consistently missed every promised demo/roll-out, and feels more like either a science project, or a ploy for negotiating UDC pricing.
But since OLED breaks-down with age, and even faster with moisture, heat, and higher-energy blue/uv photons (reminder, the “O” in OLED, stands for Organic), the use of glass (or expensive polyamide materials) with low gas & moisture permeability remains a requirement, since lifetime & brightness remain the bigger issues for OLED. In the phone industry, key manufacturers came to embrace OLED since it looks fantastic but wears out - after-all consumers are more motivated to buy a new phone, if it looks noticeably brighter and sharper, than the worn-out 2-year-old one in hand. While higher production costs, aging and burn-in problems of OLED have been acceptable (even desirable) in the phone business, they have hampered the progression of OLED into IT and Automotive applications. And while OLED came with the promise of more freedoms than LCD, in creating foldable and flexible displays, the fact remains: it lasts longer when hermetically encapsulated in glass the best barrier protecting from oxygen and moisture.
While OLED has not enjoyed the same cost-reduction curve, as in the LCD proliferation, the higher-end and visually-satisfying (initial) experience continue to feed hope & investment. Glass TFT has both enabled, and limited OLED"s ability to achieve higher brightness, and higher resolution. There"s frequently news of better OLED solution coming down the research pipeline, and we"ve already touched on the bigger ones (e.g. Hyperfluorescence, Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence, Quantum Dot on OLED), but the reality has fallen far short, nor is there anything helping to break-free from the most expensive TFT processes. OLED is very likely to continue to service the small display markets, products that have a shorter life expectancy, and only need a lower-brightness display (e.g. TV"s, which only need 100nits of brightness).
The industry is ripe for disruption from a brighter, more robust inorganic solution, that comes with a better (near-term) ability to reduce cost as it scales.
Unmet needs, in important niche markets: is the essential formula, for the beginning of disruption, as outlined by Clayton Christensen. Who described the formula for disruption as essentially: a niche market (of future importance) with unmet needs, that can afford to adopt a more expensive solution, where that solution has an ability to scale and leverage the niche-win to expand into broader markets, displacing incumbent technologies. Some example display niche markets:Automotive and Smartwatches displays have been over 1,000 nits for some time, but need much more to compete with typical daylight glare.
Autonomous vehicles (e.g. robo-taxis) are on the horizon, but pause for a moment to consider how they will visually communicate to passengers & pedestrians, when no human is present ? No driver to confirm name or usher in passenger, or gesticulate with body language to other less-patient human drivers. The solutions are being developed right now (and PixelDisplay is involved), they of course need to operate in bright daylight, and be colorful & robust as the painted bumper panel or shatter-resistant safety-glass, they"ll be integrated-into.
When the HDR standards were formed, they included a high peak-brightness of 10,000 nits (far beyond wildest dreams of OLED and Quantum Dots), and real-world contrast ratio"s (>10x that available on LCD with edge backlight). And studio-grade content-authoring displays can do well over 4,000 nits, but need constant recalibration to account for non-uniformity from wear, and sometimes replaced after only a year. We can expect this to migrate into more consumer displays over the next 5yrs, and the Gaming/TV/Video/Movie content standards (BluRay-UHD, VESA DisplayHDR and the Hollywood UHD-Alliance) already integrated that support.
These are markets that will pay for a more expensive solution, that can deliver unmet needs of bright, high (HDR) contrast, deep-black and defined shadows, and crisp-rich colors (like OLED), in a thin form-factor, but with higher brightness and longer lifetime (like LED-backlit LCD).
The value of the Flat Panel Display: the industry is worth over $120 billion (3x the value of the GPU market), and is project to grow to well over $200 billion by 2025. Yearly production (rough numbers): over 1.8 billion smartphone panels, 300 million laptop and tablet panels. This thin, complex, glass-stack, in the flat-panel module, still represents the single most expensive component in the phone & tablet (and many laptops also).
In the iPhone BOM, the display has, at times, been more than 2~3x the cost of the SoC (CPU & GPU) and RF BaseBand chips, combined. And in the iPhone 12, the new OLED display is responsible for 35% of the BOM cost increase vs iPhone 11. It should then, be unsurprising that Apple (unlike Intel, NVIDIA, AMD, DELL or any other OEM that I know), has multiple (large) divisions devoted just to display technology - one in each of their business verticals. Staffed with display architects, and engineers refining technologies, sourcing core materials (even the phosphors), creating new designs. Even custom-designing the display controller and driver chips, for the panel makers to insert inside displays made - exclusively for Apple - that are not available to any other panel customers. Perhaps because it is the most critical border of the Visual Information Age, and obviously because it is necessary to control the border to control your future, right ?
In summary,during this pandemic we"re able to adapt and continue our communications visually; collaborating, pitching, working efficiently, and remotely from anywhere; thanks to the internet, wireless connectivity, and the glass flat-panel visual interface. Long Zoom sessions can be taxing, but imagine if this had happened in the 1950"s, 1970"s or 1990"s ? Would our children have been able to engage in school remotely ? Would we have remained as connected, and as productive ?
The technology innovations may have US origins, but the major enablers of the last visual revolution were: a) execution driven by massive investments in manufacturing & commercialization from: Japan, Taiwan, Korea and China in flat-panel display leadership, b) faster than Moore’s Law growth in the economies-of-scale of glass-substrate TFT pixels, and c) the shift to cheaper/smaller/robustsolid-state In/GaN semiconductor LED technology.
Now there’s a another shift happening. With the Micro-LED & Mini-LED generation, there"s a new, and very different, formula. Unlike the past display technologies: Micro-LED are innately decoupled from the glass backplane, and that changes everything.
In the next article,more details of how this visual revolution is progressing, firstly re-igniting LCD 2.0 with Mini-LED"s, and breaking through the glass-barrier with Micro-LED"s, and what displays of the future will look like.

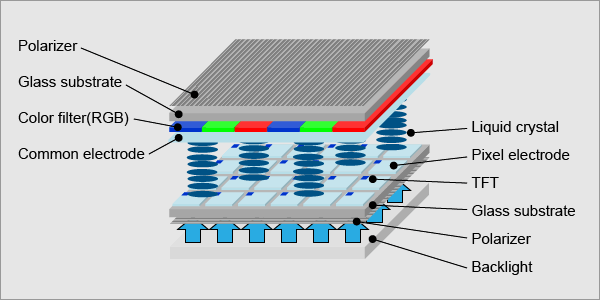
TFT (Thin Film Transistor) LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)technology is currently dominant in the display world right now due to its lightweight, low power consumption, low manufacturing cost, etc. But LCDs do have several generic drawbacks. A narrow viewing angle is one of the main issues compared with other display technologies, such asOLED (Organic Light Emitting Diodes), CRT(Cathode-Ray Tube), Plasma, VFD(Vacuum Fluorescent Display), and most recent SamsungMicroLEDdisplays. They also don’t have a response time issue.
LCD scientists and engineers took more than 30 years of effort to improve the TFT LCD viewing angle which has made TFT screens widely applicable in different applications ranging from automotive, home appliances, medical, military, industrial, consumer, etc. The following is a summary of the different TFT wide viewing angle technologies.
When we talk about TFT LCD, we normally mean TN LCD. Thetwisted nematic effect(TN-LCD) takes advantage of the ability of the nematic substance to rotate the polarization of light beams passing through it. Two polarizing filters, parallel planes of glass with their polarizing lines oriented at right angles with respect to each other, are positioned on either side of the liquid crystal. When light enters the display, it is polarized by the input filter. In the absence of an electric field, all the incoming light is transmitted. This is because the light polarization is rotated 90 degrees by the nematic liquid crystal, and the light, therefore, passes easily through the output filter, which is oriented to match the 90-degree shift. With the application of a voltage, an electric field is produced in the nematic liquid crystal. Under these conditions, the polarization effect is reduced. If the voltage is large enough, the polarization effect disappears altogether, and the light is blocked by the output polarizing filter. Refer to Fig.1
In this case, when the display is observed from a vertical direction to the substrate, the display shows a dark state, because the optical axis of the liquid crystal is perpendicular to the substrate. However, when the display is observed from the tilted direction, the display does not show completely a dark state because light leaks due to the birefringence. The birefringence becomes predominant with an increase in the voltage. At different viewing angles, the birefringence is different and the transmission is different in each direction. This is the reason for the poor viewing angle of TFT LCDs. See Fig.3.
The most cost-effective and common way is to use a wide viewing angle polarizer. Of course, the improved viewing angle is not wide enough for some applications. Another limitation is that the wide viewing angle polarizer will not be able to change the Gray Scale Inversion shown at the bottom photo in Fig.3.
O-Film is an optical film that is applied to the TN TFT LCD and redirects light, providing all round viewing angles to any TN TFT LCD to which it is applied. It is easy to apply and relatively low cost.
The best advantage of O Film is to eliminate grayscale inversion. The drawback is to reduce the contrast and brightness. With the wider adoption of IPS, O Film gradually fell out of favor with the market.
The VA (Vertically Aligned) method combines the vertically aligning film and nematic liquid crystal with negative dielectric anisotropy. Contrary to the conventional TN method, a very high
This article is an original piece of content written by the engineering and technical support team atOrient Display. We are an LCD and display technology provider with over two decades of industry experience in delivering cutting edge display solutions. Please browse ourknowledge baseif you would like to learn more about LCDs!

The world of smartphones has been busy for the past few months. There have been numerous revolutionary launches with groundbreaking innovations that have the capacity to change the course of the smartphone industry. But the most important attribute of a smartphone is the display, which has been the focus for all prominent players in the mobile phone industry this year.
Samsung came up with its unique 18:5:9 AMOLED display for the Galaxy S8. LG picked up its old trusted IPS LCD unit for the G6’s display. These display units have been familiar to the usual Indian smartphone buyer. Honor, on the other hand, has just unveiled the new Honor 8 Pro for the Indian market that ships with an LTPS LCD display. This has led to wonder how exactly is this technology different from the existing ones and what benefits does it give Honor to craft its flagship smartphone with. Well, let’s find out.
The LCD technology brought in the era of thin displays to screens, making the smartphone possible in the current world. LCD displays are power efficient and work on the principle of blocking light. The liquid crystal in the display unit uses some kind of a backlight, generally a LED backlight or a reflector, to make the picture visible to the viewer. There are two kinds of LCD units – passive matrix LCD that requires more power and the superior active matrix LCD unit, known to people as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) that draws less power.
The early LCD technology couldn’t maintain the colour for wide angle viewing, which led to the development of the In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD panel. IPS panel arranges and switches the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules of standard LCD display between the glass substrates. This helps it to enhance viewing angles and improve colour reproduction as well. IPS LCD technology is responsible for accelerating the growth of the smartphone market and is the go-to display technology for prominent manufacturers.
The standard LCD display uses amorphous Silicon as the liquid for the display unit as it can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. This though restricts the display resolution and adds to overall device temperatures. Therefore, development of the technology led to replacing the amorphous Silicon with Polycrystalline Silicon, which boosted the screen resolution and maintains low temperatures. The larger and more uniform grains of polysilicon allow faster electron movement, resulting in higher resolution and higher refresh rates. It also was found to be cheaper to manufacture due to lower cost of certain key substrates. Therefore, the Low-Temperature PolySilicon (LTPS) LCD screen helps provide larger pixel densities, lower power consumption that standard LCD and controlled temperature ranges.
The AMOLED display technology is in a completely different league. It doesn’t bother with any liquid mechanism or complex grid structures. The panel uses an array of tiny LEDs placed on TFT modules. These LEDs have an organic construction that directly emits light and minimises its loss by eradicating certain filters. Since LEDs are physically different units, they can be asked to switch on and off as per the requirement of the display to form a picture. This is known as the Active Matrix system. Hence, an Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display can produce deeper blacks by switching off individual LED pixels, resulting in high contrast pictures.
The honest answer is that it depends on the requirement of the user. If you want accurate colours from your display while wanting it to retain its vibrancy for a longer period of time, then any of the two LCD screens are the ideal choice. LTPS LCD display can provide higher picture resolution but deteriorates faster than standard IPS LCD display over time.
An AMOLED display will provide high contrast pictures any time but it too has the tendency to deteriorate faster than LCD panels. Therefore, if you are after greater picture quality, choose LTPS LCD or else settle for AMOLED for a vivid contrast picture experience.

The TFT-LCD (Flat Panel) Antitrust Litigationclass-action lawsuit regarding the worldwide conspiracy to coordinate the prices of Thin-Film Transistor-Liquid Crystal Display (TFT-LCD) panels, which are used to make laptop computers, computer monitors and televisions, between 1999 and 2006. In March 2010, Judge Susan Illston certified two nationwide classes of persons and entities that directly and indirectly purchased TFT-LCDs – for panel purchasers and purchasers of TFT-LCD integrated products; the litigation was followed by multiple suits.
TFT-LCDs are used in flat-panel televisions, laptop and computer monitors, mobile phones, personal digital assistants, semiconductors and other devices;
In mid-2006, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) Antitrust Division requested FBI assistance in investigating LCD price-fixing. In December 2006, authorities in Japan, Korea, the European Union and the United States revealed a probe into alleged anti-competitive activity among LCD panel manufacturers.
The companies involved, which later became the Defendants, were Taiwanese companies AU Optronics (AUO), Chi Mei, Chunghwa Picture Tubes (Chunghwa), and HannStar; Korean companies LG Display and Samsung; and Japanese companies Hitachi, Sharp and Toshiba.cartel which took place between January 1, 1999, through December 31, 2006, and which was designed to illegally reduce competition and thus inflate prices for LCD panels. The companies exchanged information on future production planning, capacity use, pricing and other commercial conditions.European Commission concluded that the companies were aware they were violating competition rules, and took steps to conceal the venue and results of the meetings; a document by the conspirators requested everybody involved "to take care of security/confidentiality matters and to limit written communication".
This price-fixing scheme manipulated the playing field for businesses that abide by the rules, and left consumers to pay artificially higher costs for televisions, computers and other electronics.
Companies directly affected by the LCD price-fixing conspiracy, as direct victims of the cartel, were some of the largest computer, television and cellular telephone manufacturers in the world. These direct action plaintiffs included AT&T Mobility, Best Buy,Costco Wholesale Corporation, Good Guys, Kmart Corp, Motorola Mobility, Newegg, Sears, and Target Corp.Clayton Act (15 U.S.C. § 26) to prevent Defendants from violating Section 1 of the Sherman Act (15 U.S.C. § 1), as well as (b) 23 separate state-wide classes based on each state"s antitrust/consumer protection class action law.
In November 2008, LG, Chunghwa, Hitachi, Epson, and Chi Mei pleaded guilty to criminal charges of fixing prices of TFT-LCD panels sold in the U.S. and agreed to pay criminal fines (see chart).
The South Korea Fair Trade Commission launched legal proceedings as well. It concluded that the companies involved met more than once a month and more than 200 times from September 2001 to December 2006, and imposed fines on the LCD manufacturers.
Sharp Corp. pleaded guilty to three separate conspiracies to fix the prices of TFT-LCD panels sold to Dell Inc., Apple Computer Inc. and Motorola Inc., and was sentenced to pay a $120 million criminal fine,
Chunghwa pleaded guilty and was sentenced to pay a $65 million criminal fine for participating with LG and other unnamed co-conspirators during the five-year cartel period.
In South Korea, regulators imposed the largest fine the country had ever imposed in an international cartel case, and fined Samsung Electronics and LG Display ₩92.29 billion and ₩65.52 billion, respectively. AU Optronics was fined ₩28.53 billion, Chimmei Innolux ₩1.55 billion, Chungwa ₩290 million and HannStar ₩870 million.
Seven executives from Japanese and South Korean LCD companies were indicted in the U.S. Four were charged with participating as co-conspirators in the conspiracy and sentenced to prison terms – including LG"s Vice President of Monitor Sales, Chunghwa"s chairman, its chief executive officer, and its Vice President of LCD Sales – for "participating in meetings, conversations and communications in Taiwan, South Korea and the United States to discuss the prices of TFT-LCD panels; agreeing during these meetings, conversations and communications to charge prices of TFT-LCD panels at certain predetermined levels; issuing price quotations in accordance with the agreements reached; exchanging information on sales of TFT-LCD panels for the purpose of monitoring and enforcing adherence to the agreed-upon prices; and authorizing, ordering and consenting to the participation of subordinate employees in the conspiracy."
On December 8, 2010, the European Commission announced it had fined six of the LCD companies involved in a total of €648 million (Samsung Electronics received full immunity under the commission"s 2002 Leniency Notice) – LG Display, AU Optronics, Chimei, Chunghwa Picture and HannStar Display Corporation.
On July 3, 2012, a U.S. federal jury ruled that the remaining defendant, Toshiba Corporation, which denied any wrongdoing, participated in the conspiracy to fix prices of TFT-LCDs and returned a verdict in favor of the plaintiff class. Following the trial, Toshiba agreed to resolve the case by paying the class $30 million.
On March 29, 2013, Judge Susan Illston issued final approval of the settlements agreements totaling $1.1 billion for the indirect purchaser’ class. The settling companies also agreed to establish antitrust compliance programs and to help prosecute other defendants, and cooperate with the Justice Department"s continuing investigation.

The functions of our boards include, but are not limited to, adjustment of brightness, sound output, touch interface, extra data transmission, and gyroscope.
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

Here you can compare Jivi Revolution TnT3 and Zen Admire Unity. Comparing Jivi Revolution TnT3 vs Zen Admire Unity on Smartprix enables you to check their respective specs scores and unique features. It would potentially help you understand how Jivi Revolution TnT3 stands against Zen Admire Unity and which one should you buy The current lowest price found for Jivi Revolution TnT3 is ₹2,550 and for Zen Admire Unity is ₹3,650. The details of both of these products were last updated on Jan 15, 2023.SpecificationJivi Revolution TnT3Zen Admire UnityRAM1 GB1 GB




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey