arduino lcd module tutorial factory

The purpose of this guide is to get your 0.96″ color LCD display successfully operating with your Arduino, so you can move forward and experiment and explore further types of operation with the display. This includes installing the Arduino library, making a succesful board connection and running a demonstration sketch.
Although you can use the display with an Arduino Uno or other boad with an ATmega328-series microcontroller – this isn’t recommended for especially large projects. The library eats up a fair amount of flash memory – around 60% in most cases.
So if you’re running larger projects we recommend using an Arduino Mega or Due-compatible board due to the increased amount of flash memory in their host microcontrollers.
(As the display uses the ST7735S controller IC, you may be tempted to use the default TFT library included with the Arduino IDE – however it isn’t that reliable. Instead, please follow the instructions below).
The display uses the SPI data bus for communication, and is a 3.3V board. You can use it with an Arduino or other 5V board as the logic is tolerant of higher voltages.
In this digital age, we come across LCDs all around us from simple calculators to smartphones, computers and television sets, etc. The LCDs use liquid crystals to produce images or texts and are divided into different categories based on different criteria like type of manufacturing, monochrome or colour, and weather Graphical or character LCD. In this tutorial, we will be talking about the 16X2 character LCD Modules.
The 16x2 LCDs are very popular among the DIY community. Not only that, but you can also find them in many laboratory and industrial equipment. It can display up to 32 characters at a time. Each character segment is made up of 40 pixels that are arranged in a 5x8 matrix. We can create alphanumeric characters and custom characters by activating the corresponding pixels. Here is a vector representation of a 16x2 LCD, in which you can see those individual pixels.
As the name indicates, these character segments are arranged in 2 lines with 16 characters on each line. Even though there are LCDs with different controllers are available, The most widely used ones are based on the famous HD44780 parallel interface LCD controller from Hitachi.
The 16x2 has a 16-pin connector. The module can be used either in 4-bit mode or in 8-bit mode. In 4-bit mode, 4 of the data pins are not used and in 8-bit mode, all the pins are used. And the connections are as follows:
Vo / VEE Contrast adjustment; the best way is to use a variable resistor such as a potentiometer. The output of the potentiometer is connected to this pin. Rotate the potentiometer knob forward and backwards to adjust the LCD contrast.
The 16x2 LCD modules are popular among the DIY community since they are cheap, easy to use and most importantly enable us to provide information very efficiently. With just 6 pins, we can display a lot of data on the display.
The module has 16 pins. Out of these 16 pins, two pins are for power, two pins are for backlight, and the remaining twelve pins are for controlling the LCD.
If you look at the backside of the module you can simply see that there are not many components. The main components are the two controller chips that are under the encapsulation. There is an onboard current limiting resistor for the backlight. This may vary from different modules from different manufacturers. The only remaining components are a few complimentary resistors for the LCD controller.
In the module PCB, you may have noticed some unpopulated footprints. These footprints are meant for charge pump circuits based on switched capacitor voltage converters like ICL7660 or MAX660. You can modify your LCD to work with 3.3V by populating this IC and two 10uF capacitors to C1 and C2 footprint, removing Jumper J1 and adding jumper J3. This modification will generate a negative contrast voltage of around 2.5V. This will enable us to use the LCD even with a VCC voltage of 3.3V.
To test whether a 16x2 LCD works or not, connect the VDD, GND and backlight pins to 5v and GND. Connect the centre terminal of a 10K variable resistor to the VEE pin. Connect the other two terminals to VCC and GND. Simply rotate the variable resistor you will see that the contrast will be adjusted and small blocks are visible. If these rectangles are visible, and you were able to adjust the contrast, then the LCD is working
There are 16 pins on the display module. Two of them are for power (VCC, GND), one for adjusting the contrast (VEE), three are control lines (RS, EN, R/W), eight pins are data lines(D0-D7) and the last two pins are for the backlight (A, K).
The 16x2 LCD has 32 character areas, which are made up of a 5x8 matrix of pixels. By turning on or off these pixels we can create different characters. We can display up to 32 characters in two rows.
Controlling the LCD module is pretty simple. Let’s walk through those steps. To adjust the contrast of the LCD, the Vo/ VEE pin is connected to a variable resistor. By adjusting the variable resistor, we can change the LCD contrast.
The RS or registry select pin helps the LCD controller to know whether the incoming signal is a control signal or a data signal. When this pin is high, the controller will treat the signal as a command instruction and if it’s low, it will be treated as data. The R/W or Read/Write pin is used either to write data to the LCD or to read data from the LCD. When it’s low, the LCD module will be in write mode and when it’s high, the module will be in reading mode.
The Enable pin is used to control the LCD data execution. By default, this pin is pulled low. To execute a command or data which is provided to the LCD data line, we will just pull the Enable pin to high for a few milliseconds.
To test the LCD module, connect the VDD, GND, and backlight pins to 5v and GND. Connect the center terminal of a 10K variable resistor to the VEE pin. Connect the other two terminals to VCC and GND as per the below connection diagram-
Simply rotate the variable resistor you will see that the contrast will be adjusted and small blocks are visible. If these rectangles are visible, and you were able to adjust the contrast, then the LCD is working.
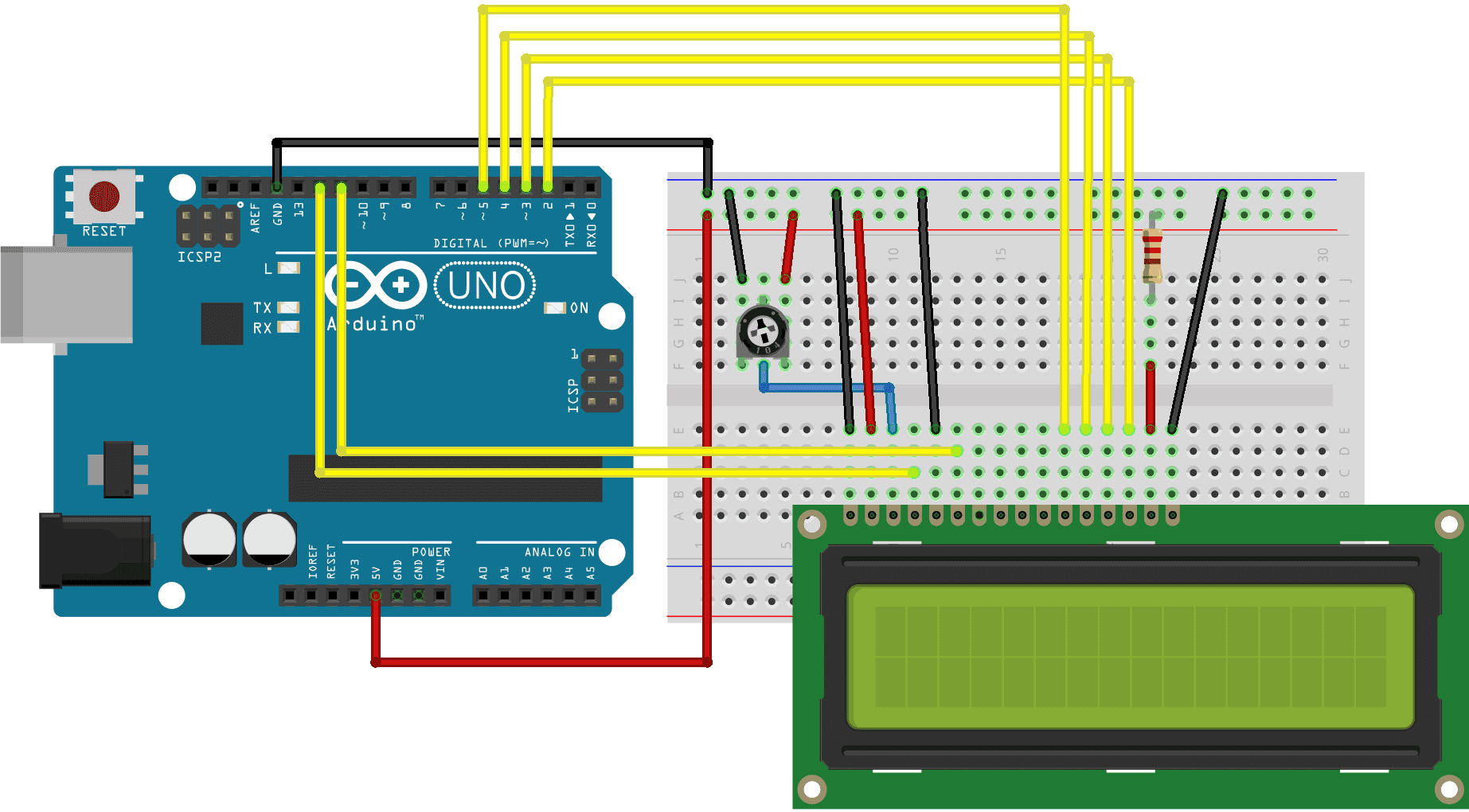
Let’s see how to connect the LCD module to Arduino. For that first, connect the VSS to the GND and VDD to the 5V. To use the LCD backlight, connect the backlight Anode to the 5V and connect the backlight cathode to the GND through a 220Ωresistor. Since we are not using the read function connect the LCD R/W pin to the GND too. To adjust the contrast, connect the centre pin of a 10KΩ trimmer resistor to the VEE pin and connect the side pins to the VCC and GND. Now connect the registry select pin to D12 and Enable pin to D11.
Now let’s connect the data pins. The LCD module can work in two modes, 8-bit and 4-bit. 8-bit mode is faster but it will need 8 pins for data transfer. In 4-bit mode, we only need four pins for data. But it is slower since the data is sent one nibble at a time. 4-bit mode is often used to save I/O pins, while the 8-bit mode is used when speed is necessary. For this tutorial, we will be using the 4-bit mode. For that connect the D4, D5, D6 and D7 pins from the LCD to the D5, D4, D3 and D2 pins of the Arduino.
The following Arduino 16x2 LCD code will print Hello, World! on the first line of the display and the time the Arduino was running in seconds on the second line.
Now let’s discuss the code. As usual, the sketch starts by including the necessary libraries. For this tutorial, we will be including the LiquidCrystal library from Arduino. This library is compatible with LCDs based on the Hitachi HD44780, or any compatible chipset. You can find more details about this library on the Arduino website.
Let’s create an object to use with the LiquidCrystal library. The following line of code will create an object called lcd. We will be using this object in the entire code to access the library functions. The object is initialized with the pin numbers.
Now let’s look at the setup()function. The lcd.begin function is used to initialize the LCD module. This function will send all the initialization commands. The parameters used while calling this function are the number of columns and the number of rows. And the next function is lcd.print. with this function, we have printed the word Circuit Digest! to the LCD. Since the LCD cursor is set to home position within the lcd.begin, we don’t need to set any cursor position. This text will stay there for two seconds. After that, the text will scroll from left to right until the entire text is out of the display. To scroll the display to the right, we have used the function lcd.scrollDisplayRight. After that, to clear display, we used lcd.clear, this will clear any characters on the display.
Now let’s look at theloop function. The for loop will count from 0 to 9, and when it reaches 9, it will reset the count and repeat the process all over again. lcd.setCursor is used to set the cursor position. lcd.setCursor(8, 1) will set the LCD cursor to the eighth position in the second row. In the LCD, the first row is addressed as 0 and the second row is addressed as 1. And the lcd.print(i) will print the count value stored in the variable i to the display.
Wrong characters are displayed: This problem occurs usually when the LCD is not getting the correct data. Make sure you are sending the correct ASCII value. If you are sending the correct ASCII characters, but still showing the wrong one on the LCD, check your connections for loose contact or short circuits.
Contrast and delay are ok, but still no display: Make sure you are powering the LCD from a 5V source. By default, these displays won’t work with a supply voltage below 5V. So if you are using the display with a 3.3V microcontroller make sure to power the display from 5V and use level shifters in between the display and the microcontroller.
In this project we will provide the input voice using Google Voice Keyboard via a Android App (BlueTerm) and print the text on 16x2 LCD using Raspberry Pi.
In this tutorial we are interfacing a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) module with the Raspberry Pi Pico using Micropython to display strings, and characters on the LCD.
We used some Python scripts to find the local IP address of your Raspberry Pi on the network and display it on the 16x2 LCD Screen. We also added the script in the Crontab so that it can be run on every 10 minutes and we will have the updated IP address every time.
Hello friend welcome to “Techno-E-Solution” in this article we are going to learn how to connect LCD display with Arduino Uno and print "Hello World!" on LCD using Arduino Uno. The 16x2 LCD is most popular LCD in electronics projects. In upcoming project we need this display in our project so it"s the beginners level tutorial learn this tutorial with fun. So friends let"s get started..........

Previous examples connect the white LED backlight to power. The following example is specifically for those using an LCD with a RGB LED backlight. The only difference between the connection is the LED"s backlight on pins 15-18.
Copy and paste the code below. Just make sure to select the correct board (in this case the Arduino/ Genuino Uno) and the COM port that the Arduino enumerated on. Then upload the code to your Arduino.
After uploading, you will notice the same "Hello, world!" and time since the Arduino was last reset in the first example. The only difference is that the current color of the backlight will be printed as it cycles through each of the primary, secondary, and tertiary colors. You should see something similar to the image below.

Open Arduino IDE, find TFT_eSPI in the file and example, the T-Display factory test program is located at TFT_eSPI -> FactoryTest, you can also use other sample programs provided by TFT_eSPI
3 In the Arduino IDE tool options, select the development board ESP32 Dev Module, select Disable in the PSRAM option, select 4MB in the Flash Size option, Other keep the default




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey