tft display vs super amoled in hindi price

आजकल बाज़ार में कई प्रकार के डिस्प्ले मौजूद हैं, जिस वजह से कुछ लोग कन्फ्यूजन में होते है कि किस प्रकार का Display वाला स्मार्टफोन लेना चाहिए, इन Displays का उपयोग बहुत से प्रोडक्ट्स में किया जाता है जैसे कि कंप्यूटर, मोबाइल स्मार्ट वाच आदि आदि.
AMOLED, OLED का ही Advanced Version है जिसका फुल-फॉर्म है Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. दोनों एक ही Machenism पर काम करते हैं इन Dispalys में Backlight नहीं होती इसके हर Pixels में खुद का एक Transister लगा होता है जिसकी वजह से Display के जिन जगहों पर Colours की जरुरत होती, Pixels वहीं की Light को ON करते है,
AMOLED डिस्प्ले मे रंग वास्तविक तो नहीं मिलते लेकिन थोड़ा Vibrant और Over Saturated Colour रहता है जो हमारे इंसानी आंखो को अत्यधिक प्रिय लगते है. ये Display बहुत ही लचीली होती है अतः जल्दी टूटती नहीं और कभी टूट गयी तो बनवाना थोड़ा महंगा पड़ जाता है।
OLED डिस्प्ले उपर के 3 Displays से अच्छे रंग दिखाता है इस वजह से कुछ महंगा है, OLED Display थोडा पतला होने के साथ साथ इसका View Angle भी अच्छा होता है,
पिछले कुछ वर्षों तक सारे Display, LCD टेक्नोलॉजी पर काम करते थे लेकिन इसका Machenism थोड़ा अलग है OLED में आपको कोई भी Backlight नहीं मिलती है जिसके कारण हल्का ओर पतला मिल जाता है।
किसी भी प्रकार के Display में इन तीन चीज़ों का होना अति आवश्यक होता है पहला - डिस्प्ले को रोशनी देने के लिए एक लाईट जिससे Display को देखा जा सके, दूसरा - कलर्स,आपको डिस्प्ले में रंग दिखाइ देगी अगर रंग ही नहीं होंगे तो पूरा डिस्प्ले सफेद दिखेगा या काला, अतः डिस्प्ले में रंगों का होना बहुत जरूरी है.
Tft display (Thin Film Transister) होता है इसको LCD Display का नया वर्शन माना जाता है क्योंकि TFT डिस्प्ले दुसरे Displays के मुकाबले सस्ता मिलता है और इसकी मोटाई भी कुछ ज्यादा होने के वजह से मोबाईल के आकर में भी फर्क आ जाता है अतःइस डिस्प्ले का इस्तेमाल पहले के Smartphones और आजकल के सस्ते Mobiles में किया जाता है,
चूंकि यह डिस्प्ले थोडा सस्ते में मिल जाता है अतः इसमें कुछ खामियां भी है रंगों और क्वालिटी के हिसाब से, अगर जब कभी आप नया फ़ोन लेने जाएँ तो ये सुनिश्चित कर लें कि मोबाइल tft डिस्प्ले वाला ना हो, क्योकि इसमें आपको थोड़ा फीका और विडियो का अनुभव ठीक से नहीं ले पाएंगे, साथ ही ये डिस्प्ले जल्दी टूट जाता है।
आईपीएस एलसीडी ये एलसीडी का ही एक रूप है इसमें भी वही टेक्नोलॉजी काम करती है जो एलसीडी डिस्प्ले में करती थी, यह डिस्प्ले आज के इस दौर में Trend में है क्योंकि ये AMOLED display के मुकाबले सस्ते और रंगों को बहुत Natural दिखाते है,
जबकि AMOLED डिस्प्ले मे Colours ज्यादा बूस्टेड और Over Saturated रहता है अगर आप भी अपने मोबाइल में एक्यूरेट कलर्स देखना चाहते है तो आपको IPS LCD Display के साथ ही जाइये.
इस Display में भी एक Backlight होता है जिसके कारण सूर्य की तेज किरणों में भी इस Display को बिना किसी दिक्कत के क्लियर देख पाएंगे, और View Angle को बढ़ाया गया है अर्थात आप जब Smartphone को कुछ Tilt भी करते है तो ठीक से देख पायेंगे,
यह Display भी AMOLED के मुकाबले सस्ती ओर TFT Display से महंगा मिल जाता है और AMOLED से कुछ कम ओर TFT से थोड़ा मोटा रहता है जिसके कारण Smartphones भी थोड़े भारी हो जाते है.
इस डिस्प्ले का Down Point ये है कि ये Backlight Technology पर काम करता है जिससे Battery भी ज्यादा खर्च होती है ओर Black Colour को Black के बजाए थोड़ा Grey Colour में दिखाता है।
बहुत से डिस्प्ले के बारे में जानने के बाद भी बहुत से लोग इसी Confusion में होंगे कि कौन सी Types of mobile display screen वाला मोबाइल लें, अगर आपके दिमाग में ये सवाल है तो फ़िक्र मत कीजिये हम आपको आपके Use के According सही डिस्प्ले की जानकारी देंगे,
अगर 3000-4000Rs.के अंदरथोड़े सस्ते मोबाइल चाहिए तो आप tft डिस्प्ले ही लें क्योंकि इस Price में किसी और Display का विकल्प ही नहीं है इसमें भी आपको अच्छा Experince मिलेगा,आपकी Budget 10K से उपर है तो आप IPS LCD का चुनाव करें क्योंकि इस कीमत में आपको AMOLED Display मुश्किल से ही मिल पाता है.
25K के उपर का बजट होगा तो AMOLED, Super AMOLED और Retina Display वाला Smartphone ले सकते है क्योंकि ये सभी Battery की खपत को कम करता है और Vibrant Colour दिखाता है जो इंसानी आंखो को अत्यधिक प्रिय लगते है ये सभी Display आंखो के लिए भी सेहतमंद होते है।
अब बारी आती है Display को सुरक्षित रखने की, एक अच्छी डिस्प्ले स्क्रीन वाला फोन ही काफी नहीं है हमें यह भी देख लेना चाहिए कि फोन में कौन सा Protector Glass लगा है, Market में आपको बहुत सारे Glass मिल जाएंगे लेकिन आज हम सिर्फ Gorilla GlassProtector ग्लास के बारे में जानकारी देंगे जो काफी कठोर ओर सबसे ज्यादा यूज़ किया जाता है.
इसका यूज़ सबसे पहले 2007 में iPhone में किया गया था, Gorilla Glass बनाने वाली Company Corning यहकभीनहीं बोलती की हमारे Glass में Scratch नहीं पड़ेगा ये जोग्लासहै वो काफी हद तक आपके Display में Scratch आने से बचाती है लेकिन एक भी Scratch ना आए ऐसा Possible नहीं है,
हमें उम्मीद है की आपको इस लेख Mobile Display Types - IPS, Retina, and AMOLED in Hindiसे काफी उपयोगी जानकारी मिली होगी. आपको हमारा यह लेख कैसा लगा हमें Comment में जरुर बताएं, साथ ही अगर लेख पसंद आया हो तो इसे Social साइट्स और दोस्तों के साथ Share करना ना भूलें

आपके स्मार्टफोन की डिस्प्ले के बारे में आप कितना जानते हैं? डिस्प्ले के नाम जैसे कि AMOLED, OLED, LCD, TFT के बारे में आप कितना विस्तार से जानते हैं? इनके नाम बहुत छोटे हैं, लेकिन इनमें से कौन-सा बेहतर है, किस रिफ्रेश रेट के साथ आता है, रेज़ॉल्यूशन कितना है इन सब सवालों को जानकर यदि आप अपने लिए स्मार्टफोन चुनना चाहते हैं तो आपके इन सभी प्रश्नों के उत्तर मिलेंगे यहाँ।
पिछले कुछ सालों में स्मार्टफोन की डिस्प्ले काफी बेहतर हुई हैं। लेकिन प्रत्येक स्मार्टफोन डिस्प्ले के साथ जो शार्ट-फॉर्म एक संक्षिप्त नाम जुड़ता है, जैसे कि AMOLED, LCD, इत्यादि वो केवल नाम नहीं बल्कि अपने आप में एक तकनीक है। स्मार्टफोन पर लगे पैनल AMOLED, OLED, LED, LCD, IPS, TFT, LTPS, इत्यादि होते हैं। ये सभी पूर्णत: अलग होते हैं।
पहले ही इतने टाइप के पैनल मौजूद हैं, ऐसे में स्मार्टफोन निर्माता द्वारा फैंसी नामों का इस्तेमाल जैसे कि Apple द्वारा Super Retina XDR और Samsung द्वारा Dynamic AMOLED ग्राहकों के बीच भ्रम या असमंजस को और बढ़ा देता है।
डिस्प्ले के टाइप तो बहुत सारे हैं जैसे कि TFT, LTPS, AMOLED, OLED, IPS, LCD इत्यादि। लेकिन इन दिनों TFT, LTPS जैसी डिस्प्ले काफी कम हो गयीं हैं। किफ़ायती दामों पर और मिड-रेंज में आने वाले फोनों में आपको IPS LCD डिस्प्ले मिलेगी। लेकिन इन सबका विस्तार से समझें, तो मतलब क्या है ?
अगर संक्षिप्त रूप से और आसान भाषा में समझें तो दो तरह की टेक्नोलॉजी- एलसीडी (LCD) और ओलेड (OLED) बाज़ार में आ रहीं हैं। प्रत्येक में कुछ विभिन्न प्रकार और जनरेशन हैं जो बाकी के स्क्रीन टाइप शार्ट फॉर्म को बनाती हैं। इसी तरह टेलीविज़न की दुनिया में भी अलग स्क्रीन टाइप उपलब्ध हैं जैसे कि LED, QLED, miniLED – ये सब दरसअल एलसीडी (LCD) तकनीक के ही अलग अलग रूप हैं जिनमें थोड़ी विविधताएं हैं।
LCD का मतलब या फुल फॉर्म है लिक्विड क्रिस्टल डिस्प्ले (Liquid Crystal Display)। इसमें लिक्विड क्रिस्टल्स की एक श्रंखला दी जाती है जिसके पीछे एक बैकलाइट होती है। इस डिस्प्ले टाइप का हर जगह आसानी से उपलब्ध होना और कम दामों में इसका निर्माण इसे स्मार्टफोनों के लिए एक प्रचलित विकल्प या पसंद बनाता है।
स्मार्टफोनों में आपको दोनों डिस्प्ले TFT और IPS मिलती हैं। TFT का फुल फॉर्म है – Thin Film Transistor, जो LCD का ही एक बेहतर या एडवांस्ड वर्ज़न है, जो एक एक्टिव मैट्रिक्स (active matrix) का इस्तेमाल करता है। active matrix का अर्थ है कि प्रत्येक पिक्सेल एक अलग ट्रांजिस्टर और कपैसिटर से जुड़ा होता है।
TFT डिस्प्ले का सबसे बड़ा फायदा यही है कि इसके प्रोडक्शन में तुलनात्मक कम खर्च होता है और इसमें असल LCD के मुकाबले ज्यादा कॉन्ट्रास्ट मिलता है। वहीं TFT LCD में नुकसान ये है कि इन्हें रेगुलर LCD प्रकारों के मुकबाले ज्यादा एनर्जी यानि बैटरी चाहिए, इनके व्यूिंग एंगल और रंग भी इतने अच्छे नहीं होते। इन्हीं सब कारणों से बाकी डिस्प्ले विकल्पों की गिरती कीमतों के कारण अब TFT डिस्प्ले का इस्तेमाल स्मार्टफोनों में नहीं किया जाता।
TFT(Thin Film Transistor) – ये भी LCD डिस्प्ले का ही एक प्रकार है जिसमें नीचे एक पतली सेमीकंडक्टर की परत होती है जो हर एक पिक्सल पर रंगों को नियंत्रित करने का काम करता है। इसका और AMOLED में आने वाले AM यानि कि active matrix का काम लगभग एक ही है।
LTPS(Low Temperature PolySilicon) – ये भी Si (amorphous silicon) तकनीक पर आधारित TFT का ही वैरिएंट है जिसमें आपको हाई रेज़ॉल्यूशन मिलता है और ऊर्जा यानि कि पॉवर साधारणत: TFT से कम लेता है।
IGZO(Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide) – ये भी एक सेमिकंडक्टर मैटेरियल है जो डिस्प्ले के नीचे लगी फिल्म में इस्तेमाल होता है और आजकल a semiconductor material used in TFT films, which also allows higher resolutions and lower power consumption, and sees action in different types of LCD screens (TN, IPS, VA) and OLED displays
LTPO( Low Temperature Polycrystaline Oxide) – इस टेक्नोलॉजी को Apple ने डेवेलप किया है और इसे वर्तमान समय में OLED और LCD दोनों तरह की स्क्रीन में इस्तेमाल किया जाता है। इसमें LTPS और IGZO दोनों तकनीकों का इस्तेमाल मिलाकर किया जाता है और नतीजा होता है – डिस्प्ले द्वारा पॉवर का कम इस्तेमाल। ये Apple Watch 4 और Galaxy S21 Ultra में आयी है।
IPS तकनीक को In-Plane Switching तकनीक कहते हैं। IPS टेक्नोलॉजी ने सबसे पहले आयी LCD डिस्प्ले में आने वाली समस्या को दूर किया जिसमें TN तकनीक का इस्तेमाल होता था और इसमें साइड से देखने पर रंग बहुत ख़राब नज़र आते थे। ये कमी ज़्यादातर सस्ते स्मार्टफोन और टैबलेटों में नज़र आया करती थी।
PLS (Plane to Line Switching) – PLS और IPS के नाम या उनके फुल फॉर्म लगभग एक ही जैसे लगते हैं। लेकिन इसमें आश्चर्य की कोई बात नहीं है क्योंकि इनका मुख्य कार्य भी एक समान ही है। PLS टेक्नोलॉजी को Samsung Display द्वारा बनाया गया है और IPS डिस्प्ले की ही तरह इसकी विशेषता भी डिस्प्ले पर अच्छे रंग दर्शाना और बेहतर व्यूइंग एंगल दिखाना ही हैं। लेकिन इसमें OLED और LCD/VA डिस्प्ले के मुकाबले कॉन्ट्रास्ट थोड़ा कम है।
Samsung Display का कहना है कि PLS पैनलों के उत्पादन में लागत कम लगती है, ब्राइटनेस लेवल अच्छा मिलता है और प्रतियोगी कंपनी LG Display के IPS पैनलों के मुकाबले व्यूइंग एंगल भी काफी अच्छे मिलते हैं। अंतत: PLS पैनल का उपयोग किया जाए या IPS पैनल का इस्तेमाल करें, ये पूरी तरह से स्मार्टफोन निर्माताओं पर निर्भर करता है।
AMOLED की फुल फॉर्म – एक्टिव मैट्रिक्स ऑर्गेनिक लाइट एमिटिंग डायोड (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) है। हालांकि ये सुनने में बहुत मुश्किल नाम लग रहा होगा, लेकिन ये है नहीं। हम पहले ही TFT LCD टेक्नोलॉजी में एक्टिव मैट्रिक्स के बारे में पढ़ चुके हैं और अब रहा OLED, तो ये केवल एक पतली फिल्म वाली डिस्प्ले तकनीक है और कुछ नहीं।
और क्योंकि OLED डिस्प्ले में काले पिक्सल बंद हो जाते हैं, उनमें करंट नहीं आता, इसीलिए कॉन्ट्रास्ट लेवल भी LCD डिस्प्ले के मुकाबले ज्यादा मिलता है। AMOLED डिस्प्ले में रिफ्रेश रेट तो ज़्यादा मिल जाता है, लेकिन वहीँ LCD डिस्प्ले को, AMOLED की तुलना में ज्यादा ब्राइट बनाया जा सकता है। क्योंकि ये एक ऑर्गेनिक मैटीरियल से बने होते हैं, एक लम्बे समय के इस्तेमाल के बाद इनकी ब्राइटनेस घटने लगती है जिससे कई बार स्क्रीन बर्न-इन जैसी समस्याएं भी आ सकती हैं। हालाँकि ये समस्या पुराने स्मार्टफोनों में ज्यादा आती थी, अब ऐसा ना के बराबर होता है।
वहीँ इसकी अच्छी बात ये है कि AMOLED डिस्प्ले LCD के मुकाबले पतली होती हैं क्योंकि इनमें अंदर बैकलिट की परत लगाने की ज़रुरत नहीं पड़ती और इन्हें फ्लेक्सिबल यानि कि लचीला भी बनाया जा सकता है।
OLED को- Organic Light Emitting Diode कहते हैं। एक OLED डिस्प्ले electroluminescent मैटीरियल की पतली शीट से बनी होती है, जिसका सबसे बड़ा फायदा यही है कि ये अपनी रौशनी खुद पैदा करते हैं और इन्हें बैकलाइट की ज़रुरत नहीं पड़ती, जिससे ऊर्जा या बिजली की ज़रुरत कम पड़ती है। यही OLED स्क्रीन जब स्मार्टफोन या टीवी के लिए उपयोग होती है तो इसे ज़्यादातर AMOLED डिस्प्ले के नाम से जाना जाता है।
जैसे कि हमने पहले भी बताया AMOLED में AM एक्टिव मैट्रिक्स (Active Matrix) के लिए इस्तेमाल होता है। हालाँकि ये पैसिव मैट्रिक्स (Passive Matrix) OLED से अलग होता है जिसे p-OLED कहा जाता है। ये स्मार्टफोनों में थोड़ा कम प्रचलित है।
वहीं Super AMOLED, दक्षिणी कोरियाई कंपनी Samsung द्वारा दिया गया है एक नाम है जो अब कंपनी के मिड-रेंज से प्रीमियम रेंज के स्मार्टफोनों में देखने को मिलता है। IPS LCD की ही तरह, Super AMOLED डिस्प्ले में साधारण AMOLED डिस्प्ले पर टच रिस्पांस लेयर को जोड़कर एक किया जाता है, इसमें अलग से एक परत नहीं लगाई जाती। और इसका नतीजा ये होता है कि Super AMOLED स्क्रीन सूरज की रौशनी या आउटडोर में AMOLED के मुकाबले बेहतर नज़र आती हैं और साथ ही ये पावर भी कम लेती हैं।
जैसे कि Samsung ने इस स्मार्टफोन डिस्प्ले टाइप का नाम -Super AMOLED रखा है। साधारण भाषा में ये AMOLED स्क्रीन का सुधार किया गया या कहें कि बेहतर वर्ज़न है। और ये केवल मार्केटिंग के लिए मारने वाली डींगें नहीं हैं, बल्कि कई उत्पादों की समीक्षा (review) करने बाद, तथ्य यही है कि Samsung की डिस्प्ले बाज़ार में सबसे उत्तम श्रेणी में आती हैं।
वहीँ इसकी तकनीक में किये गए सबसे नए विकास या सुधार को कंपनी ने Dynamic AMOLED का नाम दे दिया। . हालांकि Samsung ने इसके बारे में कभी विस्तार से नहीं बताया है लेकिन इतना साफ़ कर दिया है कि इस तरह की डिस्प्ले में HDR10+ सर्टिफिकेशन शामिल होता है जिसके साथ आपको स्क्रीन पर रंगों और कॉन्ट्रास्ट की एक वाइड रेंज मिलती है। साथ ही इसमें ब्लू लाइट कम होती जिससे ये डिस्प्ले आँखों के लिए ज्यादा आरामदायक हो।
ठीक इसी तरह OnePlus ने भी हाई-एंड स्मार्टफोनों के लिए नाम रखा है – Fluid AMOLED, जिसमें हाई रिफ्रेश रेट ही इसकी ख़ास बात है, इसमें कोई और अंतर नहीं होता। उदाहरण के लिए – डिस्प्ले अगर 120Hz रिफ्रेश रेट के साथ आएगी तो उसमें आपको और ज्यादा स्मूथ एनीमेशन मिलेगा।
पिक्सल डेंसिटी की बात करें तो, 2010 में iPhone 4 के लॉन्च के समय Apple का मुख्य आकर्षण यही था। इस स्मार्टफोन डिस्प्ले में कंपनी ने LCD डिस्प्ले का इस्तेमाल किया। इस LCD पैनल ((LED, TFT, और IPS) को हाई रेज़ॉल्यूशन (उस समय पर 960 X 640 पिक्सल्स) के साथ Retina Display का नाम दिया। इस फ़ोन में 3.5 इंच की डिस्प्ले थी।
उस समय पर Apple के मार्केटिंग डिपार्टमेंट ने Retina Display नाम इसलिए चुना क्योंकि कंपनी के अनुसार एक निश्चित दूरी से हमारी या किसी भी इंसान की आंखें अलग-अलग पिक्सल में फर्क नहीं कर पाती। iPhones के केस में, ये नाम तब इस्तेमाल होता था जब फ़ोन की डिस्प्ले पर 300 ppi (pixel per inch) से ज्यादा होती थी।
तब से, अन्य स्मार्टफोन बनाने वाली कंपनियों ने भी यही तरीका अपनाया और हाई रेज़ॉल्यूशन वाले पैनलों को अपनाना शुरू कर दिया। जबकि iPhone 12 Mini में 476 dpi और Sony Xperia 1 में 643 dpi मिलती है।
जब सबने हाई रेज़ॉल्यूशन के साथ डिस्प्ले लेना आरम्भ कर दिया, फिर Apple ने खुद को भीड़ में अलग करने के लिए अपने प्रीमियम स्मार्टफोनों में इस्तेमाल होने वाली OLED डिस्प्ले को “Super Retina” का नाम दे दिया। ये डिस्प्ले iPhone X और उसके बाद आने वाले फोनों में आयी है। ये डिस्प्ले हाई कॉन्ट्रास्ट रेट और डिस्प्ले पर रंगों की सटीकता के लिए जानी जाती है, और ऐसी ही स्क्रीन Samsung के S-सीरीज़ के स्मार्टफोनों में भी आप देख सकते हैं।
इसके बाद कंपनी ने iPhone 11 Pro के साथ डिस्प्ले का नया नाम भी लॉन्च किया – “Super Retina XDR”। इसमें भी वही OLED पैनल का उपयोग किया गया है, लेकिन इसे पैनल का निर्माण Samsung Display या LG Display द्वारा हुआ है। इसमें आपको 2,000,000:1 रेश्यो के साथ और भी बेहतर कॉन्ट्रास्ट लेवल और 1200 nits की ब्राइटनेस मिलते हैं और ये ख़ासकर HDR कंटेंट के लिए अनुकूल हैं।
वहीं iPhone XR और iPhone 11 के ग्राहकों को भी खुश रखने के लिए कंपनी ने इनमें आने वाले LCD पैनल को “Liquid Retina” का नाम दे दिया। बाद में यही डिस्प्ले कंपनी स्टैण्डर्ड के अनुसार बेहतर रेज़ॉल्यूशन और सही रंगों के साथ iPad Pro और iPad Air मॉडल में भी आया।
अंतरराष्ट्रीय प्रणाली या सिस्टम में Nit या कैंडेला प्रति वर्ग मीटर (candela per square meter), जलने या निकलने वाली रौशनी की तीव्रता या गहनता (intensity) को मापने की यूनिट है। अधिकतर स्मार्टफोन, टैबलेट, मॉनिटर के बारे में जब हम बात करते हैं तो ये यूनिट बताती है कि डिस्प्ले कितना ब्राइट है। इसकी वैल्यू जितनी ज्यादा होगा, डिस्प्ले पर पिछले से पड़ने वाली रौशनी की तीव्रता भी उतनी ही ज्यादा होगी।
टेलीविज़न की दुनिया में, miniLED के बारे में हम जान चुके हैं और ये फ़ीचर या तकनीक टीवी में हम देखते ही आ रहे हैं। इसमें बैकलाइट में लाइटिंग ज़ोन का नंबर बढ़ा दिया जाता है। लेकिन अब अफवाहों और कई ख़बरों के अनुसार स्मार्टफोनों और स्मार्टवॉच में भी कंपनियां microLED टेक्नोलॉजी जल्दी ही लेकर आ सकती हैं। ये टेक्नोलॉजी या पैनल LCD/LED से काफी अलग है क्योंकि ये OLED डिस्प्ले की तरह ही बारीकियों के साथ अच्छी पिक्चर क्वॉलिटी देती है।
microLED डिस्प्ले में हर एक सब-पिक्सल में एक अलग रौशनी देने वाला डायोड होता है – अधिकतर ये एक लाल, हरे और नीले डायोड का एक सेट होता है जो एक डॉट के लिए होता है । माना जा रहा है कि microLED में इस बार किसी तरह की अजैविक (inorganic) मैटेरियल का इस्तेमाल होगा जैसे कि gallium nitride (GaN)।
खुद अपनी रौशनी छोड़ने वाला पिक्सल यानि कि self-emitting light जैसी तकनीक अपनाने के साथ, microLED डिस्प्ले में भी बैकलाइट की ज़रूरत नहीं होती। इसमें भी आपको OLED जैसे ही हाई कॉन्ट्रास्ट के साथ पिक्चर देखने को मिलेंगी और साथ ही इसमें ऑर्गेनिक डायोड की तरह स्क्रीन बर्न-इन जैसी समस्याओं का डर भी नहीं है।
साथ ही दूसरी चुनौती ये है कि इनकी कीमत भी काफी ज्यादा होती है। उदाहरण के लिए – Samsung की microLED TVs (146 इंच से 292 इंच) की कीमत 3.5 करोड़ से 12 करोड़ है, जो कि बहुत ही ज़्यादा है।
जैसे कि हमने पहले भी कहा, OLED या AMOLED डिस्प्ले में सबसे बड़ा फ़ायदा है कि हर पिक्सल खुद को रौशनी देने का कार्य संभालता है और इससे कंट्रास्ट लेवल बढ़ता है। साथ ही दूसरा फ़ायदा है ज़्यादा और सटीक काला रंग, जो कि डिस्प्ले पर देखते समय अच्छी पिक्चर क्वालिटी के लिए बेहद महत्वपूर्ण है। साथ ही जिस समय स्क्रीन कोई गहरे (डार्क) रंग की तस्वीर दिखाती है तो ये ये ऊर्जा भी कम लेते हैं।
वहीँ इनकी ख़ामियों की बात करें तो, इनको बनाने में काफी ज़्यादा लागत लगती है और कॉम्पोनेन्ट की पूर्ती करने वाली कंपनियां भी सीमित ही हैं। इनमें Samsung Display, LG Display और तीसरे नंबर पर चीन की इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स कंपनी BOE और कुछ एक जो OLED की मांग को पूरा करते हैं। जबकि LCD पैनल बनाने वाली काफी कम्पनियां हैं।
इसके अलावा एक और बात जो हम यहां जोड़ना चाहते हैं, समय के साथ OLED स्क्रीन के ऑर्गेनिक डायोड अपनी चमक या कहें कि योग्यता खो देते हैं और ये तब होता है जब एक ही तस्वीर ज्यादा समय तक डिस्प्ले होती है। इसे कपनियां “burn-in” का नाम देती हैं।

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.
Over time, the purpose of using mobile phones or Smartphones has changed. Comparatively, it has now become a basic necessity of every individual. Smartphone has dramatically transformed the lives of individuals. It has now become a mini-computer that everyone carries in their pocket. Instead, you can have multiple things at your fingertips in a few seconds. While there are plenty of things to look for, AMOLED vs OLED is also a part of it.
Before purchasing any Smartphone, everyone goes through a list of specifications. This list includes display type, screen size, battery backup, supported operating system, total internal memory, and many others. Today, we have brought a comprehensive study of the significant display technologies available nowadays.
This article will introduce you to AMOLED vs OLED display technologies. Then, we will discuss the properties of both display technologies, followed by the difference between AMOLED vs OLED.
It stands for Natural Light-Emitting Diode, a type of LED technique that utilises LEDs wherein the light is of organic molecules that cause the LEDs to shine brighter. These organic LEDs are in use to make what are thought to be the best display panels in the world.
When you make an OLED display, you put organic films among two conductors to make them. As a result, a bright light comes out when electricity is used—a simple design with many advantages over other ways to show things.
OLEDs can be used to make emissive displays, which implies that each pixel can be controlled and emits its very own light. As a result, OLED displays have excellent picture quality. They have bright colours, fast motion, and most importantly, very high contrast. Most of all, “real” blacks are the most important. The simple design of OLEDs also makes it easy to create flexible displays that can bend and move.
PMOLED stands for Passive Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. The PMOLEDs are easy to find and much cheaper than other LEDs, but they cannot work for a long duration as their lifespan is very short. Therefore, this type of display is generally for small devices up to 3 inches.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. This type of display is generally for large platforms. It contains TFT, which further consists of a storage capacitor. It also works on the same principle as OLED displays.
AMOLED offers no restriction on the size of the display. The power consumption of AMOLED is much less than other display technologies. The AMOLED provides incredible performance. It is thinner, lighter, and more flexible than any other display technology like LED, or LCD technology.
The AMOLED display is widely used in mobiles, laptops, and televisions as it offers excellent performance. Therefore, SAMSUNG has introduced AMOLED displays in almost every product. For example, Full HD Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy S4 and Samsung Galaxy Note 3, Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy S3, HD Super AMOLED in Samsung Galaxy Note, and HD Super AMOLED Plus in Samsung Galaxy S3. Apart from this, it is also used in AMOLED vs OLED creating the following:
So far, we have discussed OLED and AMOLED display technologies. Now, we will look at some of the differences between OLED and AMOLED display technology:
OLED comprises thin layers of the organic component, which emits light when the current passes through it. In this technology, each pixel transmits its own light. On the other side, AMOLED consists of an additional layer of thin-film transistors (TFTs). In AMOLED, the storage capacitors are used to maintain the pixel states.
While the technology is different among various manufacturers, Samsung’s edge AMOLED displays use plastic substrates with poly-Si TFT technology similar to how LG uses it in their POLED technology. This technology is what makes the possibility to build curved displays using an active-matrix OLED panel.
OLED display much deeper blacks as compared to the AMOLED displays. You cannot see the screen in AMOLED display under direct sunlight. The AMOLED display quality is much better than the OLEDs as it contains an additional layer of TFTs and follows backplane technologies.
The OLED devices are simple solid-state devices consisting of a thin layer of organic compounds in an emissive electroluminescent layer where the electricity generates.
These organic compounds are present between the protective layers of glass or plastic. Comparatively, AMOLED comprises an active matrix of OLED pixels along with an additional layer of TFTs. This extra layer is responsible for controlling the current flow in each pixel.
The OLED display offers a high level of control over pixels. Hence, it can be turned off completely, resulting in an excellent contrast ratio compared to the AMOLED displays and less power consumption. On the other side, AMOLED has faster refresh rates than OLEDs. Also, they offer a tremendous artificial contrast ratio as each pixel transmits light but consumes more power than OLEDs.
OLED displays are comparatively much thinner compared to the LCDs. Hence, it provides more efficient and bright presentations. In addition, OLED offers support for large display sizes compared to the traditional LCDs. AMOLEDs remove the limitation of display sizes. one can fit it into any display size.
Putting all the points mentioned above in view, the key difference to understand appropriately is that POLED is an OLED display with a plastic substrate. On the other hand, AMOLED is Samsung’s word for its display technology which is mainly for marketing. Therefore, most phone manufacturers having AMOLED displays mean that they are using Samsung displays. It is as simple as that. To add to that, all the curved display technology is made possible because of the usage of plastic substrate.
So, based on the points mentioned above, the difference between OLED and AMOLED displays, you can choose any of the two display technology at your convenience. Both are good, offer excellent performance, and are customised according to your requirements.
The AMOLED display has a higher quality than OLEDs since it has an additional layer of TTs and uses backplane technologies. When compared to OLED screens, AMOLED displays are far more flexible. As a result, they are substantially more expensive than an OLED display.
Window to the digital world, the display is one of the first seen features when selecting a smartphone, so a show must be good, and an AMOLED display offers the same. Offering a great viewing experience, here are the top 3 AMOLED screen smartphones available in the market right now:
Realme 8 Pro features a 6.4-inch Super AMOLED display with 411 PPI and a 2.5D curved display. It runs on Snapdragon 720G, bundled with Adreno 618 and 6GB of RAM. On the rear, the Realme 8 Pro has a quad-camera setup with 108-megapixels primary sensor, 8-megapixel ultra-wide angle sensor, 2-megapixel macro sensor, and a 2-megapixel monochrome sensor.
Coming to the front, it has a 16-megapixel selfie camera housed in the punch-hole display. It comes with a 4,500 mAh battery that supports Super Dart fast charging, with 100 per cent coming in just 47 min. The Realme 8 Pro is one of the best segments with a Super AMOLED FHD+ display. Media lovers will enjoy this phone with its deep blacks and vibrant colours.
The Xiaomi Mi 11 Lite runs on Snapdragon 732G chipset bundled with Adreno 618 GPU and up to 8GB RAM. The display front comes with a 6.55-inch AMOLED display with HDR 10+ support and 402 PPI.
The cameras have a triple rear camera setup with a 64-megapixel primary sensor, 8-megapixel ultra-wide angle sensor, and a 5-megapixel macro sensor. In addition, it has a 16-megapixel selfie camera housed in the punch-hole display on the front. It has a 4,250 mAh battery with 33W fast charging with USB Type-C. With the support for HDR 10+, the AMOLED display on the Mi 11 Lite is a treat for all media enthusiasts.
OPPO has recently launched the Oppo Reno 6 Pro with MediaTek’s Density 1200 chipset coupled with Mali-G77 MC9 GPU and up to 12GB of RAM. In addition, it comes with a 6.55-inch curved AMOLED FHD+ display with support for HDR 10+ and an Oleophobic coating.
On the rear, it comes with a quad-camera setup with a 64-megapixel primary sensor, an 8MP ultra-wide angle sensor, a 2-megapixel macro sensor, and a 2-megapixel depth sensor. In addition, it has a 32-megapixel selfie camera integrated inside the punch-hole on display on the front. It comes with a 4,500 mAh battery that supports 65W Super VOOC fast charging and can charge the phone 100 per cent in just 31 minutes. Since it comes with an FHD+ curved AMOLED display on the display front, it is a treat for gamers and media consumption lovers.
Smartphone displays have advanced significantly in recent years, more so than most people realise in this technological age. Display screens are similar to windows in the mobile world, which has seen a tremendous transformation in innovative products in the last several years. People have gotten more selective when buying a phone in recent years, and although all of the functions are important, the display is always the most noticeable.
Major smartphone manufacturers attempt to provide their consumers with the most delicate devices possible that incorporate the most up-to-date technologies. In AMOLED vs OLED, AMOLED is a type of OLED and a more prominent example of both OLED and POLED, so there’s no debate about which is superior.
Click here if you’re looking tosell phone online, or want torecycle old phones, and Cashify will help you get the process completed right at your doorstep.

New Delhi: The technology used in mobile displays in the modern day smartphones has progressed significantly. In the era of touchscreen smartphones, the display technology has become one of its primary selling points, and certainly its most unique feature. Not only we want the touch screens to offer crisp text, vibrant images, blur-free video and enough brightness, we want them at low cost too.
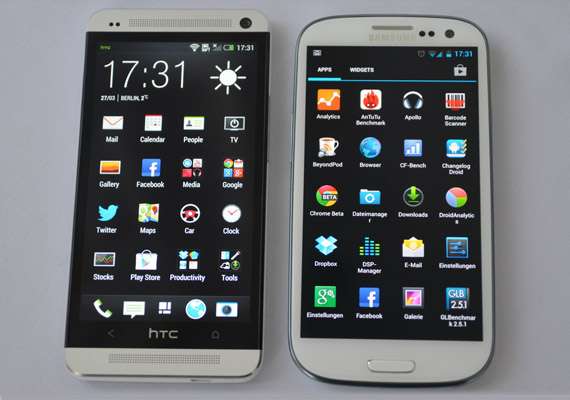
For instance, HTC One uses Super LCD3 tech, in its 4.7in screen which gives a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels, with pixel density of 469 pixels per inch (ppi). This results in super display in terms of crispness and colour reproduction. HTC says the SLCD technology gives the phone better power management, improved viewing angles and is easier to produce.
Here we"ve rounded up all the important information about different mobile screen types below, so you"ll know what to look out for on your next phone.
The Thin film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT LCD) technology is the most common display technology used in mobile phones. A variant of liquid crystal display (LCD), the technology uses TFT technology to enhance image quality. It offers better image quality and higher resolutions as compared to earlier generation LCD displays.
IPS LCD Stands for In Plane Switching liquid Crystal Display. This technology offers better display quality as compared to the TFT-LCD display. The good part about IPS LCD is that it offers better viewing angles and consumes less power. Due to higher costs, it is found only on high-end smartphones. Apple uses a high resolution (640x960 pixels) version of IPS LCD in its iPhone 4, which is also called Retina Display.
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) display technology is much better as compared to the LCD display technology because of its excellent colour reproduction, faster response times, wider viewing angles, higher brightness and extremely light weight designs.
OLEDs are brighter than LEDs and do not require backlighting like LCDs. Since OLEDs do not require backlighting, they consume much less power than LCDs.
Since these display forms are easier to produce, they can be made to larger sizes. Because OLEDs are essentially plastics, they can be made into large, thin sheets.
AMOLED stands for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode. A step ahead of OLED screens, the AMOLED screens can control each pixel individuality while maintaining the properties of an OLED panel. AMOLED screens use a different subpixel arrangement which can reduce the image quality a bit.
AMOLED screens have all the attributes of an OLED display like excellent colour reproduction, faster response times, wider viewing angles, higher brightness and extremely light weight designs.
Super AMOLED display technology is an advanced version of AMOLED display. Samsung uses this term for the AMOLED panels that they develop. Super AMOLED screens are built with capacitive touch sensors on the display itself. Super AMOLED display is much more responsive than an AMOLED display. Samsung top-of-the-line Galaxy SII comes engineered with Super AMOLED display technology. Samsung has already took it"s SMOLED screen to next levels by developing Super AMOLED+, HD Super AMOLED+ and FHD Super AMOLED+ screens.
It is a name given by Apple to the high-resolution screen technology introduced on the iPhone 4 in June 2010. Something is a Retina Display when it offers a density of pixels above 163 pixels per inch. The company calls it the Retina display because its pixels cannot be individually identified by a human eye, thus rendering a super sharp display, more crisp text and more clear pictures.
Retina Display is designed to smooth the jagged edges of pixels are provide a higher-quality image than previously available on mobile devices. Apple claims that its resolution is so good that it makes it impossible for the human eye to distinguish individual pixels. Its effects shows up in text, images and videos.
Color boost is simply Moto"s marketing term for their new display. Although it now uses LCD displays, the company fine-tuned its panels to match the saturation of OLED displays while maintaining the higher performance of LCD. It"s somewhere in the middle ground.

OLED displays have become increasingly common and accessible over the past few years. While they were once reserved for premium smartphones, you’ll now find OLED displays at every smartphone price point. Not every OLED display is equal, though – differences in materials and manufacturing processes can result in varying display qualities. In that vein, let’s explore the differences between POLED vs AMOLED, and what these acronyms mean in the real world.
Before differentiating between POLED and AMOLED, it’s worth understanding the fundamentals of OLED display technology. To that end, let’s ignore the P and AM prefixes for now.
If you look at an OLED display under a microscope, you’ll see these diodes arranged in various red, green, and blue configurations in order to produce a full range of colors. OLED has a key advantage over conventional LCDs – individual light emitters can be switched completely off. This gives OLED deep blacks and an excellent contrast ratio.
Naturally, light emitters in an OLED display need a power source in order to function. Manufacturers can use either a passive wiring matrix or an active wiring matrix. Passive matrix displays provide current to an entire row of LEDs, which isn’t ideal but it is cheap. An active matrix, on the other hand, introduces a capacitor and thin-film transistor (TFT) network that allows each pixel to be driven individually. This driving matrix is part of the panel that sits on top of a base substrate.
Today, virtually all high-resolution OLED displays use active-matrix technology. This is because a passive matrix requires higher voltages the more pixels you introduce. High voltage reduces LED lifetimes, making a passive matrix OLED impractical.
AMOLED simply refers to an Active Matrix OLED panel. The AMOLED branding has become synonymous with Samsung Display’s OLED panels over the years. However, all smartphone OLED panels, including those from Samsung’s rivals like LG Display use active-matrix technology too – they just aren’t marketed as such.
In case you’re wondering what Super AMOLED means, it’s another bit of branding to indicate the presence of an embedded touch-sensitive layer. Similarly, Dynamic AMOLED refers to a display with HDR capabilities, specifically support for Samsung’s favored HDR10+ standard.
Now that we know the layered structure of an OLED display, we can move on to the plastic part. While the first wave of OLED panels was built using glass substrates, the desire for more interesting form factors has seen manufacturers use more flexible plastic components. This is where the P in POLED comes from.
Glass is fixed and rigid, while plastic substrates can be more easily formed into new shapes. This property is absolutely essential for curved screens as well as foldable devices like Samsung’s Galaxy Fold series. Working with plastics is also much more cost-effective than glass.
Manufacturers have experimented with a range of plastics for flexible displays, including polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyethylene naphthalate (PEN). OLED manufacturers have settled on using polyimide plastics (PI) that can better withstand high TFT manufacturing temperatures. The type of substrate and heating process used also defines the flexibility of the display.
The somewhat confusing part is that Samsung’s AMOLED displays use plastic substrates. And as the name suggests, LG Display’s POLED technology clearly uses plastic as well. In summary, it’s absolutely possible to build a plastic substrate, active-matrix OLED panel. That’s exactly what both of the big two panel manufacturers are doing when it comes to mobile displays.
Even though LG and Samsung-made OLED panels qualify as both POLED and AMOLED simultaneously, the companies aren’t exactly producing identical panels. The quality of the TFT layer and plastic compound can make a difference to display performance, as can the type of emitters and sub-pixel layout.
Different color LEDs offer different brightnesses and shelf life. Blue emitters, for example, degrade the quickest. Panel manufacturers can therefore opt to use different LED materials – such as small-molecule, polymer, or phosphorescent – to optimize their designs. This may also necessitate different subpixel layouts in order to balance the panel white color, gamut, and resolution.
Over the years, we’ve seen OLED display manufacturers converge on a set of standard parameters. For example, both LG and Samsung use a diamond PenTile sub-pixel layout for smartphone displays. This just means that both should offer similar long-term reliability.
Even when it comes to other attributes like power consumption, brightness, low brightness performance, and panel uniformity, it’s unclear if one has an upper hand. That said, most smartphone makers — from Apple to OnePlus — turn to Samsung’s AMOLED panels for their flagship devices.
In the past, LG used POLED displays in its own flagship smartphones like the Velvet and Wing. However, these panels fell slightly short of the competition in certain aspects like peak brightness and color gamut coverage. These shortfalls led to speculations that Samsung has a leg up over the competition, but the accuracy of these claims is anyone’s guess.
So does that mean you should avoid POLED? Not quite — it’s still fundamentally OLED technology, which offers numerous advantages over IPS LCD. Moreover, you’ll mostly find POLED displays in mid-range and budget smartphones these days, where they should have no problem matching Samsung’s own lower-end AMOLED panels. As a relatively smaller player, LG may also offer more competitive pricing as compared to Samsung.
For most consumers, the choice of POLED vs AMOLED will be of little consequence. The underlying principle – an active-matrix OLED on a flexible plastic substrate – applies equally to both, after all. Despite the different names, LG Display and Samsung aren’t worlds apart in their approach to producing OLED panels for smartphones.

The world of smartphones has been busy for the past few months. There have been numerous revolutionary launches with groundbreaking innovations that have the capacity to change the course of the smartphone industry. But the most important attribute of a smartphone is the display, which has been the focus for all prominent players in the mobile phone industry this year.
Samsung came up with its unique 18:5:9 AMOLED display for the Galaxy S8. LG picked up its old trusted IPS LCD unit for the G6’s display. These display units have been familiar to the usual Indian smartphone buyer. Honor, on the other hand, has just unveiled the new Honor 8 Pro for the Indian market that ships with an LTPS LCD display. This has led to wonder how exactly is this technology different from the existing ones and what benefits does it give Honor to craft its flagship smartphone with. Well, let’s find out.
The LCD technology brought in the era of thin displays to screens, making the smartphone possible in the current world. LCD displays are power efficient and work on the principle of blocking light. The liquid crystal in the display unit uses some kind of a backlight, generally a LED backlight or a reflector, to make the picture visible to the viewer. There are two kinds of LCD units – passive matrix LCD that requires more power and the superior active matrix LCD unit, known to people as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) that draws less power.
The early LCD technology couldn’t maintain the colour for wide angle viewing, which led to the development of the In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD panel. IPS panel arranges and switches the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules of standard LCD display between the glass substrates. This helps it to enhance viewing angles and improve colour reproduction as well. IPS LCD technology is responsible for accelerating the growth of the smartphone market and is the go-to display technology for prominent manufacturers.
The standard LCD display uses amorphous Silicon as the liquid for the display unit as it can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. This though restricts the display resolution and adds to overall device temperatures. Therefore, development of the technology led to replacing the amorphous Silicon with Polycrystalline Silicon, which boosted the screen resolution and maintains low temperatures. The larger and more uniform grains of polysilicon allow faster electron movement, resulting in higher resolution and higher refresh rates. It also was found to be cheaper to manufacture due to lower cost of certain key substrates. Therefore, the Low-Temperature PolySilicon (LTPS) LCD screen helps provide larger pixel densities, lower power consumption that standard LCD and controlled temperature ranges.
The AMOLED display technology is in a completely different league. It doesn’t bother with any liquid mechanism or complex grid structures. The panel uses an array of tiny LEDs placed on TFT modules. These LEDs have an organic construction that directly emits light and minimises its loss by eradicating certain filters. Since LEDs are physically different units, they can be asked to switch on and off as per the requirement of the display to form a picture. This is known as the Active Matrix system. Hence, an Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display can produce deeper blacks by switching off individual LED pixels, resulting in high contrast pictures.
The honest answer is that it depends on the requirement of the user. If you want accurate colours from your display while wanting it to retain its vibrancy for a longer period of time, then any of the two LCD screens are the ideal choice. LTPS LCD display can provide hig




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey