3 5 zoll tft display free sample

Displays are one of the best ways to provide feedback to users of a particular device or project and often the bigger the display, the better. For today’s tutorial, we will look on how to use the relatively big, low cost, ILI9481 based, 3.5″ Color TFT display with Arduino.
This 3.5″ color TFT display as mentioned above, is based on the ILI9481 TFT display driver. The module offers a resolution of 480×320 pixels and comes with an SD card slot through which an SD card loaded with graphics and UI can be attached to the display. The module is also pre-soldered with pins for easy mount (like a shield) on either of the Arduino Mega and Uno, which is nice since there are not many big TFT displays that work with the Arduino Uno.
This ease of using the module mentioned above is, however, one of the few downsides of the display. If we do not use the attached SD card slot, we will be left with 6 digital and one analog pin as the module use the majority of the Arduino pins. When we use the SD card part of the display, we will be left with just 2 digital and one analog pin which at times limits the kind of project in which we can use this display. This is one of the reasons while the compatibility of this display with the Arduino Mega is such a good news, as the “Mega” offers more digital and analog pins to work with, so when you need extra pins, and size is not an issue, use the Mega.
To easily write code to use this display, we will use the GFX and TFT LCD libraries from “Adafruit” which can be downloaded here. With the library installed we can easily navigate through the examples that come with it and upload them to our setup to see the display in action. By studying these examples, one could easily learn how to use this display. However, I have compiled some of the most important functions for the display of text and graphics into an Arduino sketch for the sake of this tutorial. The complete sketch is attached in a zip file under the download section of this tutorial.
As usual, we will do a quick run through of the code and we start by including the libraries which we will use for the project, in this case, the Adafruit GFX and TFT LCD libraries.
With this done, the Void Setup() function is next. We start the function by issuing atft.reset() command to reset the LCD to default configurations. Next, we specify the type of the LCD we are using via the LCD.begin function and set the rotation of the TFT as desired. We proceed to fill the screen with different colors and display different kind of text using diverse color (via the tft.SetTextColor() function) and font size (via the tft.setTextSize() function).
Next is the void loop() function. Here we basically create a UI to display the youtube subscribe button, using some of the same functions we used under the void setup() function.
The Adafruit library helps reduce the amount of work one needs to do while developing the code for this display, leaving the quality of the user interface to the limitations of the creativity and imagination of the person writing the code.
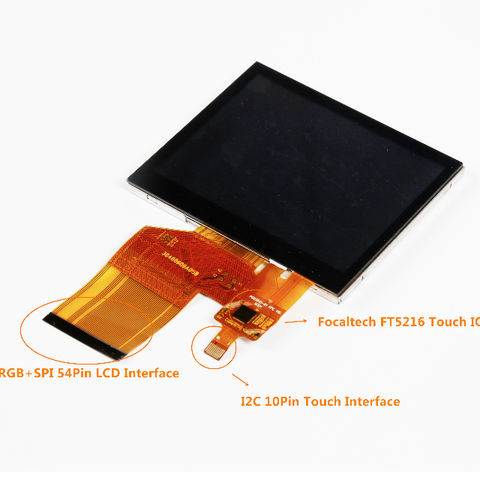

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
The next example is controlling an RGB LED using these three RGB sliders. For example if we start to slide the blue slider, the LED will light up in blue and increase the light as we would go to the maximum value. So the sliders can move from 0 to 255 and with their combination we can set any color to the RGB LED, but just keep in mind that the LED cannot represent the colors that much accurate.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
Ok next is the RGB LED Control example. If we press the second button, the drawLedControl() custom function will be called only once for drawing the graphic of that example and the setLedColor() custom function will be repeatedly called. In this function we use the touch screen to set the values of the 3 sliders from 0 to 255. With the if statements we confine the area of each slider and get the X value of the slider. So the values of the X coordinate of each slider are from 38 to 310 pixels and we need to map these values into values from 0 to 255 which will be used as a PWM signal for lighting up the LED. If you need more details how the RGB LED works you can check my particular tutorialfor that. The rest of the code in this custom function is for drawing the sliders. Back in the loop section we only have the back button which also turns off the LED when pressed.

i had the same issues with this 3,5" TFT LCD and wiring it to an ESP32 and making the TouchScreen work. However i managed to find a solution to the problem. Lets start with the wiring:
Next lets focus on the software side. In bodmers awesome library you have to comment/uncomment the right sections. The User_Setup.h file is pretty straight forward. My display used the ILI9488 processor and is run in 8 Bit parallel mode:
When it came to the touchscreen i faced some difficulties. Since the display with 8 bit there is no dedicated "Touch Pin" like other displays use. I decided to use a different library than @Bodmer (no front, still love you and the library <3). I used the ADAFRUIT Touchscreen library in extend:

In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
In which “Hello, World!” is the text you want to display and the (x, y) coordinate is the location where you want to start display text on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
Note: some people find issues with this display when trying to read from the SD card. We don’t know why that happens. In fact, we tested a couple of times and it worked well, and then, when we were about to record to show you the final result, the display didn’t recognized the SD card anymore – we’re not sure if it’s a problem with the SD card holder that doesn’t establish a proper connection with the SD card. However, we are sure these instructions work, because we’ve tested them.
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.
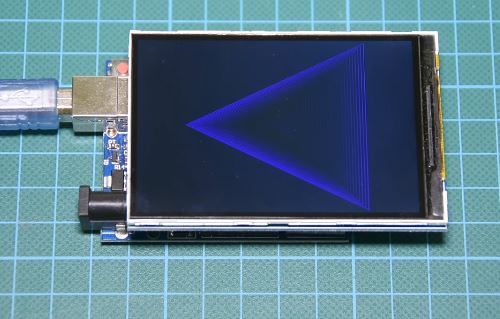
Spice up your Arduino project with a beautiful large touchscreen display shield with built in microSD card connection. This TFT display is big (3.5" diagonal) bright (6 white-LED backlight) and colorful (18-bit 262,000 different shades)! 320x480 pixels with individual pixel control. As a bonus, this display has a optional resistive touch panel with controller XPT2046 attached by default and a optional capacitive touch panel with controller FT6236 attached by default, so you can detect finger presses anywhere on the screen and doesn"t require pressing down on the screen with a stylus and has nice glossy glass cover.
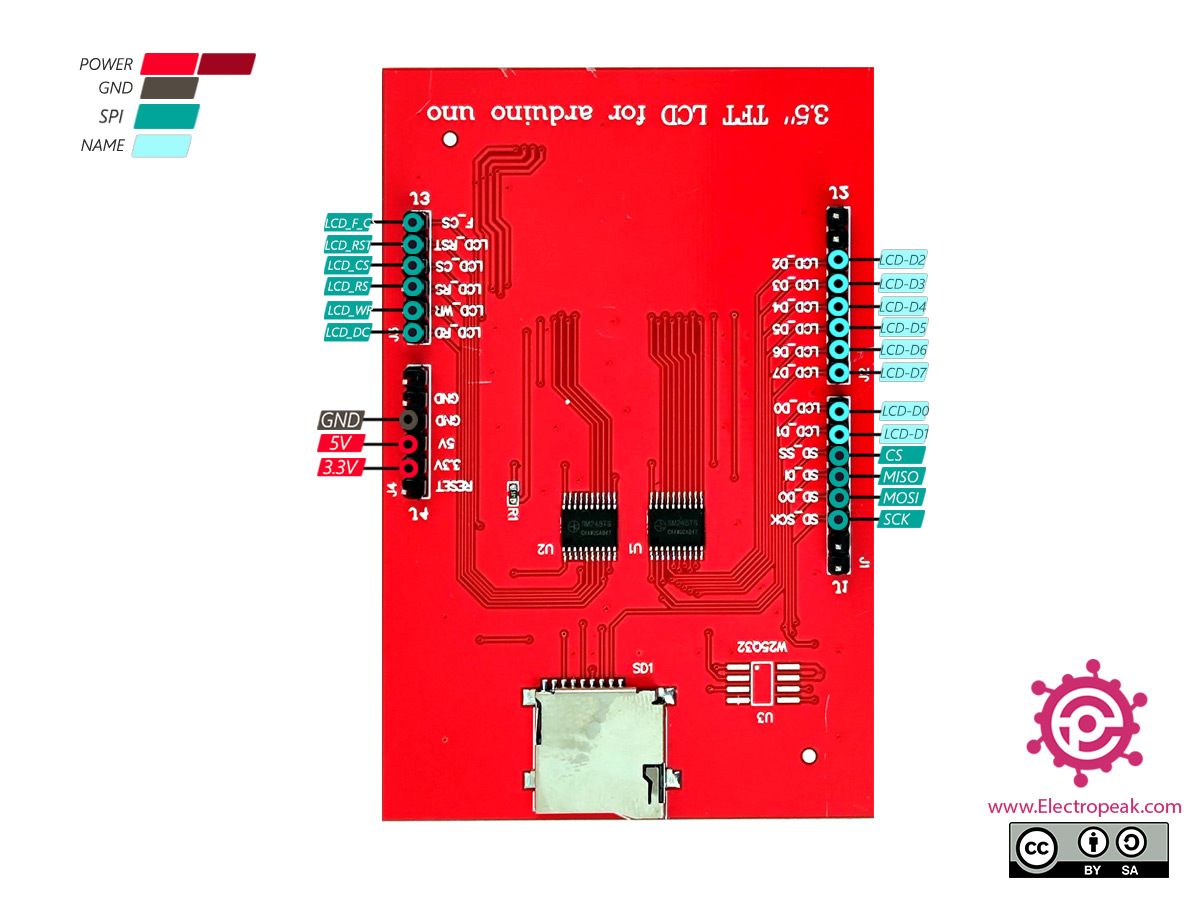
The pin32 (SDO) of 3.5 display module is also used by touch panel or SD card SPI interface, so we must cut off this pin to avoid conflict with the touch panel or SD card.
The shield is fully assembled, tested and ready to go. No wiring, no soldering! Simply plug it in and load up our library - you"ll have it running in under 10 minutes! Works best with any classic Arduino (Due/Mega 2560).
This display shield has a controller built into it with RAM buffering, so that almost no work is done by the microcontroller. You can connect more sensors, buttons and LEDs.
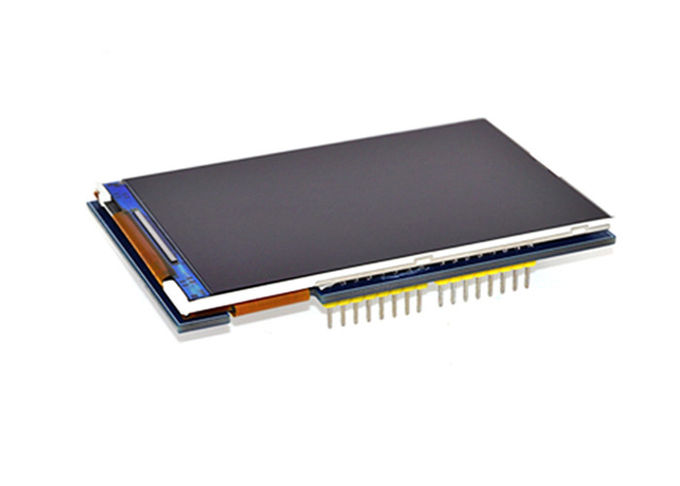

This module is a 3.5-inch TFT LCD module with “320X480” resolution and 65K color display. It is suitable for Arduino Uno and Mega2560 development boards, and also supports SD card expansion function. It uses 8-bit parallel port communication, and the driver IC is ILI9486.
The 3.5-inch display is a ready-made shield for Arduino Uno, which can also be placed on the Arduino Mega. The pins of this shield are designed to be easily installed on the Arduino. The bad point about these modules is that they use all Arduino Uno pins.
my_lcd.Fill_Triangle(x_spec+i*side_len-1,y_spec+(5-i)*h_len-1,x_spec+side_len/2+i*side_len-1,y_spec+(4-i)*h_len-1,x_spec+(i+1)*side_len-1,y_spec+(5-i)*h_len-1);
my_lcd.Draw_Line(2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34));
my_lcd.Draw_Rectangle(2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34));
my_lcd.Draw_Round_Rectangle(2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34),5);
my_lcd.Draw_Triangle(2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34),2+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()-4),17+random(my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()-34));
my_lcd.Fill_Round_Rectangle(my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()/2-1-120+1, my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()/2-1-60+1, my_lcd.Get_Display_Width()/2-1+120-1, my_lcd.Get_Display_Height()/2-1+60-1,5);

Rotating the screen to the proper orientation proved challenging. The config.txt rotate commands don’t work with the raspberry pi4. I couldn’t get the xorg configuration to rotate the display. When I added kernel commandline parameters to rotate the display, that worked for the initial verbose boot screen… but once KlipperScreen loaded, it was the wrong orientation.

The display driver is able to display predefined setups of text or user defined text. To display text using DisplayText set DisplayMode to 0, or set DisplayMode to 1 for the HT16K33 dot-matrix display.
To use the seven-segment-specific TM1637, TM1638 and MAX7219 Display- commands, set DisplayMode to 0. Parameter LCD Display OLED Display TFT Display 7-segment Display (TM163x and MAX7219) 0 DisplayText DisplayText DisplayText All TM163x Display- functions
The DisplayText command is used to display text as well as graphics and graphs on LCD, OLED and e-Paper displays (EPD). The command argument is a string that is printed on the display at the current position. The string can be prefixed by embedded control commands enclosed in brackets [].
In order to use the DisplayText command the DisplayMode must be set to 0 (or optional 1 on LCD displays) or other modes must be disabled before compilation with #undef USE_DISPLAY_MODES1TO5.
In the list below p stands for parameter and may be a number from 1 to n digits. On monochrome graphic displays things are drawn into a local frame buffer and sent to the display either via the d command or automatically at the end of the command.
fp = set font (1=12, 2=24,(opt 3=8)) if font==0 the classic GFX font is used, if font==7 RA8876 internal font is used, if font==4 special 7 segment 24 pixel number font is used, a ram based font is selected if font==5
Pfilename: = display an rgb 16-bit color (or jpg on ESP32) image when file system is present, Scripteditor contains a converter to convert jpg to special RGB16 pictures See ScriptEditor Ffilename: = load RAM font file when file system is present. the font is selected with font Nr. 5, these fonts are special binary versions of GFX fonts of any type. they end with .fnt. an initial collection is found in Folder BinFonts
Draw up to 16 GFX buttons to switch real Tasmota devices such as relays or draw Sliders to dimm e.g. a lamp Button number + 256 - a virtual touch toggle button is created (MQTT => TBT)
When a file system is present you may define displaytext batch files. If a file named "display.bat" is present in the file system this batch file is executed. The file may contain any number of diplaytext cmds, one at a line. You may have comment lines beginning with a ;
While computers and web design are generally using a 24-bit RGB888 color code built from a byte-triplet such as (255, 136, 56) or #FF8038, small color panels often use a more compact code 16-bit RGB565 color code. This means that the R, G and B coefficient are coded on less number of bits: Red on 5 bits = 0..31
E-Paper displays have 2 operating modes: full update and partial update. While full update delivers a clean and sharp picture, it has the disadvantage of taking several seconds for the screen update and shows severe flickering during update. Partial update is quite fast (300 ms) with no flickering but there is the possibility that erased content is still slightly visible. It is therefore useful to perform a full update in regular intervals (e.g., each hour) to fully refresh the display.
The typical specifications for the lifetime of an OLED when permanently on is about 10000 hours (416 days). Dimming to 50% expands the lifetime to about 25000 hours.
The data sheets of the TFT and OLED displays mention burn-in effects when a static display is shown for extended periods of time. You may want to consider turning on the display on demand only.
The EPD font contains 95 characters starting from code 32, while the classic GFX font contains 256 characters ranging from 0 to 255. Custom characters above 127 can be displayed. To display these characters, you must specify an escape sequence (standard octal escapes do not work). The ~character followed by a hex byte can define any character code.
The I2C address must be specified using DisplayAddress XX, e.g., 60. The model must be specified with DisplayModel, e.g., 2 for SSD1306. To permanently turn the display on set DisplayDimmer 100. Display rotation can be permanently set using DisplayRotate X (x = 0..3).
E-Paper displays are connected via software 3-wire SPI (CS, SCLK, MOSI). DC should be connected to GND , Reset to 3.3 V and busy may be left unconnected. The jumper on the circuit board of the display must be set to 3-wire SPI.
The ILI9488 is connected via hardware 3-wire SPI (SPI_MOSI=GPIO13, SPI_SCLK=GPIO14, CS=GPIO15) and must also be connected to the backlight pin The SSD1351 may be connected via hardware 3-wire SPI or 4-wire SPI with support for dimmer. The ILI9341 is connected via hardware 4-wire SPI, Backlight and OLEDRESET (dimmer supported on ESP32) Wiring
The RA8876 is connected via standard hardware 4-wire SPI (SPI_MOSI=GPIO13, SPI_SCLK=GPIO14, RA_8876_CS=GPIO15, SSPI_MISO=GPIO12). No backlight pin is needed, dimmer supported, on ESP32 gpio pins may be freeley defined (below gpio 33).
Waveshare has two kinds of display controllers: with partial update and without partial update. The 2.9 inch driver is for partial update and should also support other Waveshare partial update models with modified WIDTH and HEIGHT parameters. The 4.2 inch driver is a hack which makes the full update display behave like a partial update and should probably work with other full update displays.
In black and white displays, a local RAM buffer must be allocated before calling the driver. This must be set to zero on character or TFT color displays.
Universal Display Driver or uDisplay is a way to define your display settings using a simple text file and easily add it to Tasmota. uDisplay is DisplayModel 17. It supports I2C and hardware or software SPI (3 or 4 wire).
Initial register setup for the display controller. (IC marks that the controller is using command mode even with command parameters) All values are in hex. On SPI the first value is the command, then the number of arguments and the the arguments itself. Bi7 7 on the number of arguments set indicate a wait of 150 ms. On I2C all hex values are sent to I2C.
rotation pseudo opcode for touch panel, in case of RGB panel use only these entries the appropriate coordinate convervsions are defined via pseudo opcodes 0 = no conversion 1 = swap and flip x 2 = flipx, flip y 3 = swap and flip y 4 = flip x 5 = flip y bit 7 = swap x,y
bit 2: enable async DMA, 0 wait for DMA to complete before returning, 4 run DMA async in the background. This later mode is only valid if the SPI bus is not shared between the display and any other SPI device like SD Card Reader.
# Scripter is the nost convenient way to edit and develop a uDisplay driver. On every scripter save the display is reinitialized and you immediately see results of your changes.
There are also many variants of each display available and not all variants may be supported. #define directive Description USE_DISPLAY Enable display support. Also requires at least one of the following compilation directives
The two controllers are in the attached photo are HC245, the seller sent me the sample code, but only this code works, I can do no other work, the following code that works:

The Transmissive polarizer is best used for displays that run with the backlight on all the time. This polarizer provides the brightest backlight possible. If you have a need for a bright backlight with lower power drain, transmissive is a good choice for this TFT LCD.
Focus LCDs can provide many accessories to go with your display. If you would like to source a connector, cable, test jig or other accessory preassembled to your LCD (or just included in the package), our team will make sure you get the items you need.Get in touch with a team member today to accessorize your display!
Focus Display Solutions (aka: Focus LCDs) offers the original purchaser who has purchased a product from the FocusLCDs.com a limited warranty that the product (including accessories in the product"s package) will be free from defects in material or workmanship.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey