tft lcd arduino nano in stock

The TFT LCD Touch Screen Module for the Arduino is a version of a liquid crystal display(LCD) that uses thin film transistors(TFT) electronic that allows a user to create an interact-able interface between the user and the system. As the name may suggest, this screen module has the touch screen function.

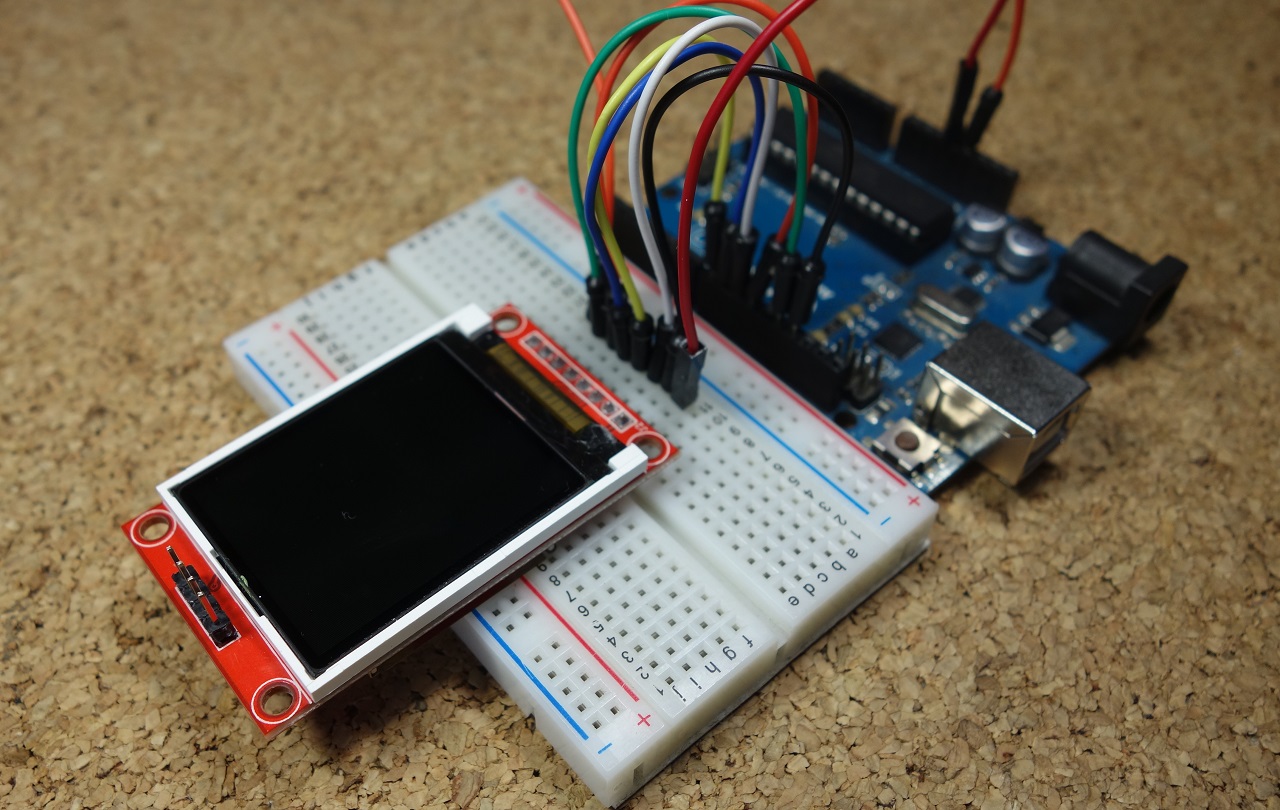
In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.

Connector for connecting a TFT display 320x240 (displays of various diagonals 2.4", 2.8" and 3.2" can be used, as well as connecting the display both on one side of the board and on the back).

Makerfocus shop provides many kinds of top brands about open source hardwares . Such as Raspberry Pi, Arduino, Nvidia, M5Stack, Orange Pi, ESP8266, ESP32, and other related electronic goodies from all around the globe!

In this article, you will learn how to use TFT LCDs by Arduino boards. From basic commands to professional designs and technics are all explained here.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
After choosing the right display, It’s time to choose the right controller. If you want to display characters, tests, numbers and static images and the speed of display is not important, the Atmega328 Arduino boards (such as Arduino UNO) are a proper choice. If the size of your code is big, The UNO board may not be enough. You can use Arduino Mega2560 instead. And if you want to show high resolution images and motions with high speed, you should use the ARM core Arduino boards such as Arduino DUE.
In electronics/computer hardware a display driver is usually a semiconductor integrated circuit (but may alternatively comprise a state machine made of discrete logic and other components) which provides an interface function between a microprocessor, microcontroller, ASIC or general-purpose peripheral interface and a particular type of display device, e.g. LCD, LED, OLED, ePaper, CRT, Vacuum fluorescent or Nixie.
The LCDs manufacturers use different drivers in their products. Some of them are more popular and some of them are very unknown. To run your display easily, you should use Arduino LCDs libraries and add them to your code. Otherwise running the display may be very difficult. There are many free libraries you can find on the internet but the important point about the libraries is their compatibility with the LCD’s driver. The driver of your LCD must be known by your library. In this article, we use the Adafruit GFX library and MCUFRIEND KBV library and example codes. You can download them from the following links.
You must add the library and then upload the code. If it is the first time you run an Arduino board, don’t worry. Just follow these steps:Go to www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software and download the software of your OS. Install the IDE software as instructed.
First you should convert your image to hex code. Download the software from the following link. if you don’t want to change the settings of the software, you must invert the color of the image and make the image horizontally mirrored and rotate it 90 degrees counterclockwise. Now add it to the software and convert it. Open the exported file and copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are sizes of image. you can change the color of the image in the last input.
Upload your image and download the converted file that the UTFT libraries can process. Now copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are size of the image.
In this template, We converted a .jpg image to .c file and added to the code, wrote a string and used the fade code to display. Then we used scroll code to move the screen left. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We used sin(); and cos(); functions to draw Arcs with our desired thickness and displayed number by text printing function. Then we converted an image to hex code and added them to the code and displayed the image by bitmap function. Then we used draw lines function to change the style of the image. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We added a converted image to code and then used two black and white arcs to create the pointer of volumes. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We added a converted image and use the arc and print function to create this gauge. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
while (a < b) { Serial.println(a); j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 255, 255)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
while (b < a) { j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 0, 0)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
In this template, We display simple images one after each other very fast by bitmap function. So you can make your animation by this trick. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We just display some images by RGBbitmap and bitmap functions. Just make a code for touchscreen and use this template. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.

In this blog I will show how to connect a 0.96" IPS color display that is 80x160 pixels to Arduino Nano. Then I will try the new Arduino Web Editor to create and later to share this project.
Sometimes it is handy to have a small screen in your Arduino project. The 0.96 inch IPS color diplay is perfect for this. You can get the original Adafruit Color TFT display with SD card readerfor this for $20 (excluding shipping costs), but you can also find a clone on Chinese reseller websites or eBay. Mine did not include a SD card reader, but it was $3 (including shipping).
Because everything happens now "In The Cloud". I have decided to try out the new Arduino Web Editor. Another reason you might want to create Arduino sketches online is if you want to share them.
To get it working follow the "Getting Started" steps on this page of the Arduino website. The steps include creating an account and installing a plugin, which will detect COM ports where your Arduinos are connected. It also works with Arduino clones. As a test I had an old Arduino Nano clone connected and it detected it flawlessly.
I was now able to create the breadboard diagram. Below you see the breadboard diagram created with Fritzing app of how to connect the display to Arduino Nano.
The display part is Adafruit based, but I have created a table on how to translate the Original Adafruit 0.96" 160x80 Color TFT Display to Chinese Clone IPS 0.96 inch 7P SPI ST7735 module
Now the transferring of that data is at the mercy of the SPI clock speed. How fast that can go depends on what the ST7735 can work at and the quality of your wiring (if it"s a shield you can almost discount the wiring). Assuming you can operate at the maximum 8MHz that the Arduino can run SPI at (which is probable) then you get:
That is the absolute maximum theoretical speed, and doesn"t take into account any work done by the Arduino to actually send the data. The SPI library is completely blocking in its operation and each pixel has to be sent separately as one blocking transaction. So you can expect about half that rate in reality, if not less, while it loops around and sends each pixel, then blocks waiting for the pixel to be sent.
TBH, though, a small Arduino is seldom a good choice to control a TFT screen. At the bare minimum you really need a chip with far more memory so you can draw graphics "off-screen" in a framebuffer, and then use DMA to transfer that off-screen buffer to the TFT screen over a 16-bit parallel connection at high speed while leaving the CPU free to do other jobs. Or even better a microcontroller with a built-in TFT controller to directly generate the correct drive signals for a TFT panel and store the whole screen image in internal RAM.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey