tft display arduino calculator using gfx tftlcd quotation

Arduino development boards always help us to build a project easily and make it look more attractive. Programming an LCD with touch functionality may sound like a complicated task, but it can be made very easy by using Arduino libraries and extension modules. In this project, we will use a 3.5" Arduino TFT LCD to build an Arduino touchscreen calculator that can perform all basic calculations such as addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication.
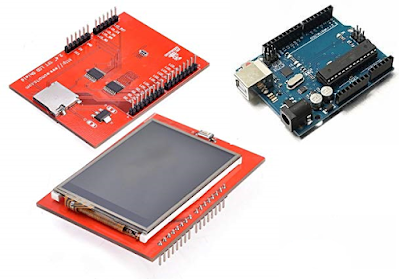
Before we dive into the project, it is important to understand how this 3.5" TFT LCD module works and the model number used. Let"s take a look at the pinout of this 3.5" TFT LCD module.
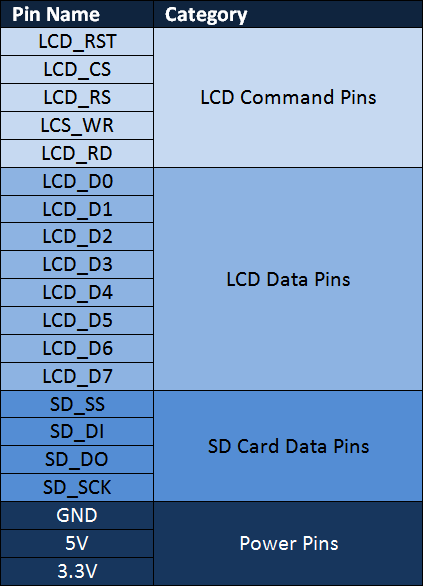
As you can see, the module has 28 pins and fits perfectly into any Arduino Uno / Arduino Mega development board. The table below gives a description of these pins.
As you can see, the module pins can be divided into four main categories, namely LCD command pins, LCD data pins, SD card pins and power pins, we don"t need to know the details of how these pins work because they will be implemented by the Arduino library.
You can also find an SD card slot on the bottom of the module shown above. This slot can be used to load an SD card with bmp image files, which can be displayed on our TFT LCD screen using the Arduino program.
Another important thing to keep in mind is your interface IC. there are many types of TFT modules on the market from Adafruit TFT LCD modules to cheap Chinese clones. A program that fits an Adafruit expansion board may not be the same for a Chinese expansion board. Therefore, it is very important to know which type of LCD LCD you are holding. This detail must be obtained from the supplier. If you have a cheap clone like mine, then it most likely uses driver IC ili9341. You can follow the official Arduino tutorial to try some basic example programs to get familiar with this LCD.
If you intend to use the touch screen function of a TFT LCD module, it must be calibrated to work properly. An LCD screen that is not calibrated is unlikely to work properly; for example, you may touch in one place and the TFT may think it is touching somewhere else. These calibration results are not the same for all boards, so you will have to do this work yourself.
The 3.5" TFT LCD is a great Arduino expansion board. You can push the LCD directly onto the top of the Arduino Uno and have it match the pins perfectly and slide them in. However, for safety reasons, the programming terminals of the Arduino UNO must use small insulating tape in case the terminals come into contact with your TFT LCD screen. the LCD assembled to the UNO development board looks like the following.
We use the SPFD5408 library to ensure that the arduino calculator code works properly. This is a modified Adafruit library that works seamlessly with our LCD TFT module. You can view the full program at the end of this article.
Now, open the Arduino IDE and select Sketch -> Include Librarey -> Add .ZIP library. a browser window will open to navigate to the ZIP file and click "OK". If successful, you should notice "Library added to your Libraries" in the bottom left corner of your Arduino.
Now you can use the following code in the Arduino IDE and upload it to Arduino UNO to get the touchscreen calculator working. Further down the page, I"ll explain the code in small segments.
As we know, TFT LCD screens can display many colors, all of which must be entered as hexadecimal values. To make it more readable, we assign these values to a variable as shown below.
Okay, now we can move on to the programming part. This program involves three parts. One is to create a user interface for the calculator using buttons and displays. Then, detect the buttons based on user touch and finally calculate the results and display them. Let"s go through them one by one.
Here you can get creative to design the user interface of the calculator. I simply made the basic layout of the calculator with 16 buttons and a display unit. You must build the design as if you were drawing something on an MS drawing board. The added libraries will allow you to draw lines, rectangles, circles, characters, strings and more in any of the preferred colors. You can learn about the available features from this article.
Another challenging task is to detect the user"s touch. Every time the user touches something, we are able to know the X and Y position of the pixel he touched. This value can be displayed on the serial monitor using println, as shown below.
The final step is to calculate the results and display them on the TFT LCD screen. The arduino calculator can only perform two numeric operations. These two numbers are named as variables "Num1" and "Num2". The variable "Number" is given and taken from Num1 and Num2, and the result is obtained.
The process of working with this Arduino touch screen calculator is very simple. You need to upload the following code to the Arduino development board and then power it up. At this point, a calculator will be displayed on the LCD screen.

In this Arduino touch screen tutorial we will learn how to use TFT LCD Touch Screen with Arduino. You can watch the following video or read the written tutorial below.
For this tutorial I composed three examples. The first example is distance measurement using ultrasonic sensor. The output from the sensor, or the distance is printed on the screen and using the touch screen we can select the units, either centimeters or inches.
The next example is controlling an RGB LED using these three RGB sliders. For example if we start to slide the blue slider, the LED will light up in blue and increase the light as we would go to the maximum value. So the sliders can move from 0 to 255 and with their combination we can set any color to the RGB LED, but just keep in mind that the LED cannot represent the colors that much accurate.
The third example is a game. Actually it’s a replica of the popular Flappy Bird game for smartphones. We can play the game using the push button or even using the touch screen itself.
As an example I am using a 3.2” TFT Touch Screen in a combination with a TFT LCD Arduino Mega Shield. We need a shield because the TFT Touch screen works at 3.3V and the Arduino Mega outputs are 5 V. For the first example I have the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, then for the second example an RGB LED with three resistors and a push button for the game example. Also I had to make a custom made pin header like this, by soldering pin headers and bend on of them so I could insert them in between the Arduino Board and the TFT Shield.
Here’s the circuit schematic. We will use the GND pin, the digital pins from 8 to 13, as well as the pin number 14. As the 5V pins are already used by the TFT Screen I will use the pin number 13 as VCC, by setting it right away high in the setup section of code.
I will use the UTFT and URTouch libraries made by Henning Karlsen. Here I would like to say thanks to him for the incredible work he has done. The libraries enable really easy use of the TFT Screens, and they work with many different TFT screens sizes, shields and controllers. You can download these libraries from his website, RinkyDinkElectronics.com and also find a lot of demo examples and detailed documentation of how to use them.
After we include the libraries we need to create UTFT and URTouch objects. The parameters of these objects depends on the model of the TFT Screen and Shield and these details can be also found in the documentation of the libraries.
So now I will explain how we can make the home screen of the program. With the setBackColor() function we need to set the background color of the text, black one in our case. Then we need to set the color to white, set the big font and using the print() function, we will print the string “Arduino TFT Tutorial” at the center of the screen and 10 pixels down the Y – Axis of the screen. Next we will set the color to red and draw the red line below the text. After that we need to set the color back to white, and print the two other strings, “by HowToMechatronics.com” using the small font and “Select Example” using the big font.
Next is the distance sensor button. First we need to set the color and then using the fillRoundRect() function we will draw the rounded rectangle. Then we will set the color back to white and using the drawRoundRect() function we will draw another rounded rectangle on top of the previous one, but this one will be without a fill so the overall appearance of the button looks like it has a frame. On top of the button we will print the text using the big font and the same background color as the fill of the button. The same procedure goes for the two other buttons.
Now we need to make the buttons functional so that when we press them they would send us to the appropriate example. In the setup section we set the character ‘0’ to the currentPage variable, which will indicate that we are at the home screen. So if that’s true, and if we press on the screen this if statement would become true and using these lines here we will get the X and Y coordinates where the screen has been pressed. If that’s the area that covers the first button we will call the drawDistanceSensor() custom function which will activate the distance sensor example. Also we will set the character ‘1’ to the variable currentPage which will indicate that we are at the first example. The drawFrame() custom function is used for highlighting the button when it’s pressed. The same procedure goes for the two other buttons.
In order the code to work and compile you will have to include an addition “.c” file in the same directory with the Arduino sketch. This file is for the third game example and it’s a bitmap of the bird. For more details how this part of the code work you can check my particular tutorial. Here you can download that file:

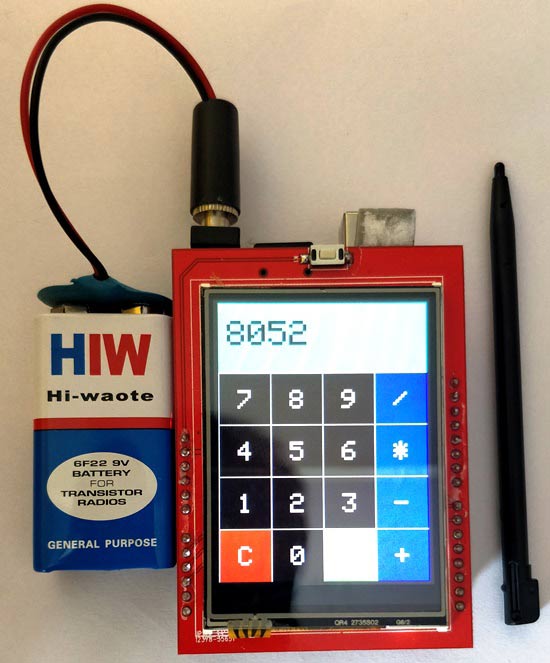
In this tutorial we are going to learn how to make Arduino Calculator with TFT Display. Our calculator’s precision is up to two decimal points and you can add, subtract, multiply or divide up to 4 digit per number. Obviously you can add more number of digits if you want.
You have to just add number by touching on screen, maximum digits per number allowable is 4 and then select operator and add again second number, press on equal. Finally, you got the result on screen, Congratulation you have made your own Arduino Calculator with TFT Display.

Displays are one of the best ways to provide feedback to users of a particular device or project and often the bigger the display, the better. For today’s tutorial, we will look on how to use the relatively big, low cost, ILI9481 based, 3.5″ Color TFT display with Arduino.
This 3.5″ color TFT display as mentioned above, is based on the ILI9481 TFT display driver. The module offers a resolution of 480×320 pixels and comes with an SD card slot through which an SD card loaded with graphics and UI can be attached to the display. The module is also pre-soldered with pins for easy mount (like a shield) on either of the Arduino Mega and Uno, which is nice since there are not many big TFT displays that work with the Arduino Uno.
The module is compatible with either of the Arduino Uno or the Arduino Mega, so feel free to choose between them or test with both. As usual, these components can be bought via the links attached to them.
One of the good things about this module is the ease with which it can be connected to either of the Arduino Mega or Uno. For this tutorial, we will use the Arduino Uno, since the module comes as a shield with pins soldered to match the Uno’s pinout. All we need to do is snap it onto the top of the Arduino Uno as shown in the image below, thus no wiring required.
This ease of using the module mentioned above is, however, one of the few downsides of the display. If we do not use the attached SD card slot, we will be left with 6 digital and one analog pin as the module use the majority of the Arduino pins. When we use the SD card part of the display, we will be left with just 2 digital and one analog pin which at times limits the kind of project in which we can use this display. This is one of the reasons while the compatibility of this display with the Arduino Mega is such a good news, as the “Mega” offers more digital and analog pins to work with, so when you need extra pins, and size is not an issue, use the Mega.
To easily write code to use this display, we will use the GFX and TFT LCD libraries from “Adafruit” which can be downloaded here. With the library installed we can easily navigate through the examples that come with it and upload them to our setup to see the display in action. By studying these examples, one could easily learn how to use this display. However, I have compiled some of the most important functions for the display of text and graphics into an Arduino sketch for the sake of this tutorial. The complete sketch is attached in a zip file under the download section of this tutorial.
As usual, we will do a quick run through of the code and we start by including the libraries which we will use for the project, in this case, the Adafruit GFX and TFT LCD libraries.
With this done, the Void Setup() function is next. We start the function by issuing atft.reset() command to reset the LCD to default configurations. Next, we specify the type of the LCD we are using via the LCD.begin function and set the rotation of the TFT as desired. We proceed to fill the screen with different colors and display different kind of text using diverse color (via the tft.SetTextColor() function) and font size (via the tft.setTextSize() function).
Next is the void loop() function. Here we basically create a UI to display the youtube subscribe button, using some of the same functions we used under the void setup() function.
The Adafruit library helps reduce the amount of work one needs to do while developing the code for this display, leaving the quality of the user interface to the limitations of the creativity and imagination of the person writing the code.

Arduino has always helped to build projects easily and make them look more attractive. Programming an LCD screen with touch screen option might sound as a complicated task, but the Arduino libraries and shields had made it really easy. In this project we will use a 2.4” Arduino TFT LCD screen to build our own Arduino Touch Screen calculator that could perform all basic calculations like Addition, Subtraction, Division and Multiplication.
Before we actually dive into the project it is important to know, how this 2.4” TFT LCD Module works and what are the types present in it. Let us take a look at the pinouts of this 2.4” TFT LCD screen module.
As you can see there are 28 pins which will perfectly fit into any Arduino Uno / Arduino Mega Board. A small classification of these pins is given in the table below.
As you can see the pins can be classified in to four main classifications such as LCD Command Pins, LCD Data Pins, SD Card Pins and Power Pins, We need not know much about the detailed working of these pins since they will be take care by our Arduino Library.
You can also find an SD card slot at the bottom of the module shown above, which can be used to load an SD card with bmp image files, and these images can be displayed in our TFT LCD screen using the Arduino Program.
Another important thing to note is your Interface IC. There are many types of TFT modules available in the market starting from the original Adafruit TFT LCD module to cheap Chinese clones. A program which works perfectly for your Adafruit shield might not work the same for Chinese breakout boards. So, it is very important to know which types of LCD display your are holding in hand. This detail has to be obtained from the vendor. If you are having a cheap clone like mine then it is most probably using the ili9341 driver IC.You can follow this TFT LCD interfacing with Arduino tutorial to try out some basic example programs and get comfortable with the LCD screen. Also check out our other TFT LCD projects with Arduino here:
If you planning to use the touch screen function of your TFT LCD module, then you have to calibrate it to make it work properly. A LCD screen without calibration might work unlikely, for instance you might touch at one place and the TFT might respond for a touch at some other place. These calibrations results will not be similar for all boards and hence you are left on your own to do this.
The 2.4” TFT LCD screen is a perfect Arduino Shield. You can directly push the LCD screen on top of the Arduino Uno and it will perfectly match with the pins and slid in through. However, as matters of safety cover the Programming terminal of your Arduino UNO with a small insulation tape, just in case if the terminal comes in contact with your TFT LCD screen. The LCD assembled on UNO will look something like this below.
We are using the SPFD5408 Library to get this arduino calculator code working. This is a modified library of Adafruit and can work seamlessly with our LCD TFT Module. You can check the complete program at the end of this Article.
Now, open Arduino IDE and select Sketch -> Include Librarey -> Add .ZIP library. A browser window will open navigate to the ZIP file and click “OK”. You should notice “Library added to your Libraries” on the bottom-left corner of Arduino, if successful. A detailed guide to do the same is given in the Interfacing Tutorial.
Now, you can use the code below in your Arduino IDE and upload it to your Arduino UNO for the Touch Screen Calculator to work. Further down, I have explained the code into small segments.
As we know the TFT LCD screen can display a lot of colours, all these colours have to be entered in hex value. To make it more human readable we assign these values to a variable as shown below.
Okay now, we can get into the programming part. There are three sections involved in this program. One is creating a UI of a calculator with buttons and display. Then, detecting the buttons based on the users touch and finally calculating the results and display them. Let us get through them one by one.
This is where you can use a lot of your creativity to design the User Interface of calculator. I have simply made a basic layout of a calculator with 16 Buttons and one display unit. You have to construct the design just like you will draw something on MS paint. The libraries added will allow you to draw Lines, Rectangle, Circles, Chars, Strings and lot more of any preferred colour. You can understand the available functions from this article.
I have used the line and box drawing abilities to design an UI which looks very similar to the 90’s calculator. Each box has a width and height of 60 pixels.
Another challenging task is detecting the user touch. Every time the user touches somewhere we will able to how where the X and Y position of the pixel he touched. This value can be displayed on the serial monitor using the println as shown below.
The final step is to calculate the result and display them on TFT LCD Screen. This arduino calculator can perform operation with 2 numbers only. These two numbers are named as variables “Num1” and “Num2”. The variable “Number” gives and takes value from Num1 and Num2 and also bears the result.
The working of this Arduino Touch Screen Calculator is simple. You have to upload the below given code on your Arduino and fire it up. You get the calculator displayed on your LCD screen.

After uploading the code you"ll able to see the calculator running in your display as mine and now you can perform basic mathematics calculations on this. So have fun making your own calculator with Arduino UNO.
It is basicly the CPU of the calculator as amongst other things, it will get instructions from the ROMs and execute them to perform the required tasks.
You also have to provide the code with the appropriate values of each key press, the position of the Run/PRGM switch, decode the 7 segment display digits and provide access to each of the operating registers and memory.
After the first - very wiggely - steps of a bloody novice like me to bring this thing into life (one issue is ATM I can just upload a sketch if I unplug the shield from the MEGA - very annoying and also dangerous to the TFT) that thing runs now as it should. I am very happy. :)

Draw buttons for digits and operators and the display field of the calculator. All digits and operator buttons have the same size. So, the co-ordinates of each button can be calculated in the program.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The liquid crystal displays used in calculators and other devices with similarly simple displays have direct-driven image elements, and therefore a voltage can be easily applied across just one segment of these types of displays without interfering with the other segments. This would be impractical for a large display, because it would have a large number of (color) picture elements (pixels), and thus it would require millions of connections, both top and bottom for each one of the three colors (red, green and blue) of every pixel. To avoid this issue, the pixels are addressed in rows and columns, reducing the connection count from millions down to thousands. The column and row wires attach to transistor switches, one for each pixel. The one-way current passing characteristic of the transistor prevents the charge that is being applied to each pixel from being drained between refreshes to a display"s image. Each pixel is a small capacitor with a layer of insulating liquid crystal sandwiched between transparent conductive ITO layers.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
In 2004, Hydis Technologies Co., Ltd licensed its AFFS patent to Japan"s Hitachi Displays. Hitachi is using AFFS to manufacture high end panels in their product line. In 2006, Hydis also licensed its AFFS to Sanyo Epson Imaging Devices Corporation.
Less expensive PVA panels often use dithering and FRC, whereas super-PVA (S-PVA) panels all use at least 8 bits per color component and do not use color simulation methods.BRAVIA LCD TVs offer 10-bit and xvYCC color support, for example, the Bravia X4500 series. S-PVA also offers fast response times using modern RTC technologies.
A technology developed by Samsung is Super PLS, which bears similarities to IPS panels, has wider viewing angles, better image quality, increased brightness, and lower production costs. PLS technology debuted in the PC display market with the release of the Samsung S27A850 and S24A850 monitors in September 2011.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
The bare display panel will only accept a digital video signal at the resolution determined by the panel pixel matrix designed at manufacture. Some screen panels will ignore the LSB bits of the color information to present a consistent interface (8 bit -> 6 bit/color x3).
With analogue signals like VGA, the display controller also needs to perform a high speed analog to digital conversion. With digital input signals like DVI or HDMI some simple reordering of the bits is needed before feeding it to the rescaler if the input resolution doesn"t match the display panel resolution.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
Brody, T. Peter; Asars, J. A.; Dixon, G. D. (November 1973). "A 6 × 6 inch 20 lines-per-inch liquid-crystal display panel". 20 (11): 995–1001. Bibcode:1973ITED...20..995B. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1973.17780. ISSN 0018-9383.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Kim, Sae-Bom; Kim, Woong-Ki; Chounlamany, Vanseng; Seo, Jaehwan; Yoo, Jisu; Jo, Hun-Je; Jung, Jinho (15 August 2012). "Identification of multi-level toxicity of liquid crystal display wastewater toward Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa". Journal of Hazardous Materials. Seoul, Korea; Laos, Lao. 227–228: 327–333. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.059. PMID 22677053.
I can see this kind of thing very easily added to some of the students designs in our 4th year project course. The usual 16×2 LCD displays only provide so much functionality, and as you can guess, there’s usually a heap of dead laptops to harvest LCDs out of




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey