super amoled vs lcd display manufacturer
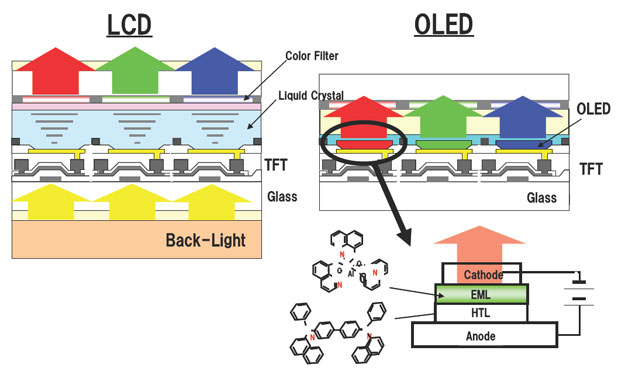
Mobile display technology is firmly split into two camps, the AMOLED and LCD crowds. There are also phones sporting OLED technology, which is closely associated with the AMOLED panel type. AMOLED and LCD are based on quite different underlying technologies, leading manufacturers to tout a number of different benefits depending on which display type they’ve opted for. Smartphone manufacturers are increasingly opting for AMOLED displays, with LCD mostly reserved for less expensive phones.
Let’s find out if really there’s a noticeable difference between these two display technologies, what sort of differences we can expect, and if the company marketing hype is to be believed.
We’ll start alphabetically with AMOLED, although to be a little broader we should probably start with a little background about OLED technology in general.
It’s hidden in the name, but the key component in these display types is a Light Emitting Diode (LED). Electronics hobbyists will no doubt have played around with these little lights before. In a display panel, these are shrunk down dramatically and arranged in red, green, and blue clusters to create an individual pixel that can reproduce white light and various colors, including red, green, and blue.
The arrangement of these sub-pixels alters the performance of the displays slightly. Pentile vs striped pixel layouts, for example, results in superior image sharpness, but lower pixel life spans due to the smaller pixel sizes.
Finally, the AM part in AMOLED stands in for Active Matrix, rather than a passive matrix technology. This tells us how each little OLED is controlled. In a passive matrix, a complex grid system is used to control individual pixels, where integrated circuits control a charge sent down each column or row. But this is rather slow and can be imprecise. Active Matrix systems attach a thin film transistor (TFT) and capacitor to each LED. This way, when a row and column are activated to access a pixel, the capacitor at the correct pixel can retain its charge in between refresh cycles, allowing for faster and more precise control.
One other term you will encounter is Super AMOLED, which is Samsung’s marketing term for a display that incorporates the capacitive touchscreen right into the display, instead of it being a separate layer on top of the display. This makes the display thinner.
The major benefits from OLED type displays come from the high level of control that can be exerted over each pixel. Pixels can be switched completely off, allowing for deep blacks and a high contrast ratio. Great if you want a display capable of playing back HDR content. Being able to dim and turn off individual pixels also saves on power ever so slightly. The lack of other layers on top of the LEDs means that the maximum amount of light reaches the display surface, resulting in brighter images with better viewing angles.
The use of LEDs and minimal substrates means that these displays can be very thin. Furthermore, the lack of a rigid backlight and innovations in flexible plastic substrates enables flexible OLED-based displays. Complex LCD displays cannot be built in this way because of the backlight requirement. Flexy displays were originally very promising for wearables. Today, premium-tier smartphones make use of flexible OLED displays. Although, there are some concerns over how many times a display can flex and bend before breaking.
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display and reproduces colors quite differently from AMOLED. Rather than using individual light-emitting components, LCD displays rely on a backlight as the sole light source. Although multiple backlights can be used across a display for local dimming and to help save on power consumption, this is more of a requirement in larger TVs.
Scientifically speaking, there’s no individual white light wavelength. White light is a mixture of all other visible colors in the spectrum. Therefore, LCD backlights have to create a pseudo white light as efficiently as possible, which can then be filtered into different colors in the liquid crystal element. Most LCDs rely on a blue LED backlight which is filtered through a yellow phosphor coating, producing a pseudo white light.
The really complicated part comes next, as light is then polarized and passed through a crystal element. The crystal can be twisted to varying degrees depending on the voltage applied to it, which adjusts the angle of the polarized light. The light then passes through a second polarized filter that is offset by 90 degrees compared with the first, which will attenuate the light based on its angle. Finally, a red, green, or blue color filter is applied to this light, and these sub-pixels are grouped into pixels to adjust colors across the display.
All combined, this allows an LCD display to control the amount of RGB light reaching the surface by culling a backlight, rather than producing colored light in each pixel. Just like AMOLED, LCD displays can either be active or passive matrix devices, but most smartphones are active these days.
This wide variation in the way that light is produced has quite a profound difference to the user experience. Color gamut is often the most talked-about difference between the two display types, with AMOLED providing a greater range of color options than LCD, resulting in more vibrant-looking images.
OLED displays have been known for additional green and blue saturation, as these tend to be the most powerful colors in the sub-pixel arrangement, and very little green is required for white light. Some observers find that this extra saturation produces results that they find slightly unnatural looking. Although color accuracy has improved substantially in the past few years and tends to offer better accuracy for wider color gamuts like DCI-P3 and BT-2020. Despite not possessing quite such a broad gamut, LCD displays typically offer 100% sRGB gamut used by most content and can cover a wide gamut and most of the DCI-P3 color space too.
As we mentioned before, the lack of a backlight and filtering layers weighs in favor of OLED over LCD. LCD displays often suffer from light bleed and a lower contrast ratio as the backlight doesn’t switch off even when pixels are supposed to be black, while OLED can simply switch off its pixels. LCD’s filtering layer also inherently blocks some light and the additional depth means that viewing angles are also reduced compared to OLED.
One downside of AMOLED is that different LEDs have different life spans, meaning that the individual RBG light components eventually degrade at slightly different rates. As well as the dreaded but relatively rare burn-in phenomenon, OLED display color balance can drift very slightly over time, while LED’s single backlight means that color balance remains more consistent across the display. OLED pixels also often turn off and on slower, meaning that the highest refresh rate displays are often LCD. Particularly in the monitor market where refresh rates exceed 120Hz. That said, plenty of OLED smartphones offer 90, 120, and even 144Hz support.
There are some pros and cons to both technologies and some reasonable user preferences between the different color and contrast profiles. Although the prevalence of multiple display modes available in modern smartphones makes this somewhat less of an issue these days. However, the falling production costs and additional benefits of OLED displays have made them a more popular choice than ever across a wide range of price segments. OLED dominates the high-end smartphone and TV spaces owing to its wider color gamut, superior contrast ratio, while still supporting decent refresh rates. Not to mention its flexible characteristics for brand new mobile form factors.
Major display manufacturers, such as LG Display and Samsung Display, are betting big on OLED technology for the future, making major investments into additional production facilities. Particularly when it comes to its use in flexible display technology. The AMOLED panel market is expected to be worth close to $30 billion in 2022, more than double its value in 2017 when this article was first published.
That said, developments in Quantum Dot and mini LED displays are closing the already small performance gap between LCD and OLED, so certainly don’t count LCD out of the race just yet.

Screen technology, quality, and visibility are just some of the most important factors to consider when choosing between AMOLED and LCD displays. Average consumers might not necessarily know the difference between these two types of devices or why one is preferable to the other. In this article, we’ll draw comparisons between LCD vs. AMOLED displays so you can decide which type of screen is the right choice for your personal or professional applications.
First, it’s important to note that AMOLED and Super AMOLEDs are both types of OLED display technology. OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. This is a type of thin-film display technology that’s built directly into the screen. The electroluminescent materials, also known as the light emitting diodes, immediately light up when they contact electricity.
AMOLED is an acronym that stands for active-matrix light-emitting diodes. This is a step up from traditional OLEDs. The basic concept of lighting up crystal diodes using electricity is the same, but the execution is slightly different. Each pixel inside of AMOLED displays consists of individual thin-film transistor strips that light up when an electrical current runs through them.
Super AMOLED devices are also descendants of the OLED technological display family. Commonly used for smartphones, AMOLEDs feature innovative touch technology integrated directly into the screen rather than including a separate thin film on top of the screen.
If you frequently use electronic devices, chances are very high that you’ve most likely come across an LCD (liquid crystal display) in some capacity. Common applications for LCDs include electronic billboards, computer and laptop monitors, digital cameras, portable electronic games, and the list goes on. LCDs are flat-panel displays. They consist of liquid crystal films that are sandwiched between two thin polarized glass layers. Backlighting is used to activate the crystals and illuminate the screen to present the desired image to the user.
– No backlighting means the display powers off pixels when showing the black portions of an image– Brighter overall picture quality, colours are true to life
Screen size and technology– AMOLEDs eliminate the need for a backlighting layer, so the screens can be made thinner– LCDs feature a backlighting layer, they require a thicker design, and will always be bulkier than AMOLEDs
Outdoor visibility and viewing angles– Side viewing angles aren’t ideal, better to view the device straight-on– Superior off-axis viewing angles and sunlight readability due to IPS technology
Display prices– Higher price point because they cost more to design and manufacture– Require more layers, but they use a slightly more affordable technology and have been around for years, which means all of the kinks have already been ironed out of the design and manufacturing process
That depends on what you need the device for and how much you are willing or able to spend. For basic and everyday applications, you’re probably better off purchasing a standard LCD device. But if you’re looking for enhanced picture quality with excellent colour contrast and have an expansive budget, then AMOLED is probably the right device for you.
At Nauticomp Inc., we’re always at the forefront of state-of-the-art commercial and industrial display design and manufacturing. Our devices are customizable and suitable for a wide range of applications from military ops to retail POS, and so much more. Contact us today to learn more.

There is a constant debate on Amoled vs LCD, which is a better display? Where Amoled display offers some remarkable colors with deep black eye-soothing contrast ratio, LCD displays offer much more subtle colors with better off-axis angles for viewing & offers a much brighter picture quality.
While purchasing a new smartphone we consider various specifications like software, camera, processor, battery, display type etc. Among all the specifications display is something that most people are concerned about. 2 of the major competitors of smartphone display are AMOLED and LCD. Often in the LCD vs Amoled comparison, people get confused about which one to choose. In this article, we have explained a clear comparison of the Amoled vs LCD screen to find out which is actually better.
Amoled display is nothing but a part of OLED display which comes with some extra features. The first component is Light Emitting Diode (LED) and the second component is "O", here "O" stands for organic & together they make OLED. The real meaning derived from it is organic material placed with 2 conductors in every LED. And this is how light is produced.
The OLED display can generate light out of individual pixels. AMOLED displays contain Thin Film Translator (TLT) which makes the overall procedure of sourcing current to the correct pixel much quicker and smoother. The TXT further helps grab control for operating different pixels at a time. For example, some pixels could be absolutely switched off though others remain on in Amoled displays. This produces a deep black color.
Speaking about LCDs, it is relatively pretty much commonly found in today"s smartphones. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) offers a devoted black light that is white or rather slightly blueish in color. Mostly here we get a blue light that is passed through some yellowish phosphor filter which brings out the white light. The white light is subsequently passed through multiple filters and thereafter the crystal elements are again passed through blue, red & green filters. Note that LCD displays have both passive and active matrix which depends on the cost and requirement involved.
Since the process involved in LCDs is much more complex than Amoled & requires extra steps, when compared to AMOLED displays, LCDs are less battery friendly. In the technological era where energy efficiency is the first priority, Amoled displays are certainly going to be the future of display technology. But both of them come with a separate set of pros and cons and it is only by knowing the pros and cons you will be able to choose the right one.
Amoled display technology is mostly used in smartphones, media players & digital cameras. Amoled is mostly used in low power, cost-effective & large application sizes.
Cost is one of the major factors that act as a differentiator between the two display types. Amoled displays are comparatively more expensive than LCD displays because LCD displays are much cheaper to manufacture. So while buying a low-budget smartphone, the probability to get a Amoled display is pretty less.
The quality of a display is mainly measured according to the colors and sharpness it offers. Also while comparing two displays, only technology comparison won"t work because often displays behave inversely even if a manufacturer is using the very same technology. If you consider colors especially contrasting colors such as blue, red or green, Amoled will serve better throughout the day. This happens mainly because in the case of AMOLED displays, as mentioned above, every pixel present in it emit its own light whereas in LCD light comes out of the backlight. Therefore Amoled displays offer high-end saturation and vibrant colors compared to LCD displays.
As Amoled displays put out vibrant colors, you will find Amoled displays to be warmer in nature compared to LCD displays which has a more neutral whitish tint. In short, the pictures seen on Amoled displays are more eye-soothing compared to LCD displays where the pictures appear more natural.
In the Amoled vs LCD screen display comparison, another thing to consider is the brightness offered by both of them. Compared to LCD displays, Amoled displays have lesser brightness levels. This is mainly because of the backlight in LCD displays which emits a higher brightness level. Therefore if you are a person who spends most of the time outdoors and mostly uses your smartphone under the sun, then LCD is the right choice for you. Although certain leading brands are working on the brightness level in Amoled displays.
The display is one such thing that sucks your phone"s battery to a great extent. In Amoled displays, the pixels can get absolutely switched off thereby saving a lot of battery. Whereas LCD displays remain dependent on the back light, as a result even if your screen is completely black, the backlight remain switched on throughout. This is why even though Amoled displays are more expensive than LCD displays as they consume much less battery than LCD displays.
In the battle between LCD display vs Amoled display both come with separate pros and cons. Well if battery consumption and color contrast or saturation is a concern then the Amoled display is going to win over LCD display anyway. While purchasing a smartphone, customers today mainly focus on two features- lesser battery consumption and a high-quality display. Amoled display offers both the benefits- high-end vibrant display and less battery consumption. The only criteria where LCD displays win over Amoled is the brightness level. But with brands coming with the latest technologies, Amoled is certainly going to catch up with the brightness level with LCD displays. Also, the brightness difference in current Amoled display smartphones that are available in the market is hardly noticeable.

Both screens are made up of Pixels. A pixel is made up of 3 sections called sub-pixels. The three sections are red, green and blue (primary colors for display tech).
The light is generated from a “backlight”. A series of thin films, transparent mirrors and an array of white LED Lights that shine and distribute light across the back of the display.
On some lower quality LCD screens, you can see bright spots in the middle or on the perimeters of screens. This is caused by uneven light distribution. The downside to using backlights, is that black is never true black, because no matter what, light has to be coming through, so it will never have as dark of a screen as an AMOLED screen. Its comparable to being able to slow a car down to 2 mph versus coming to a complete stop.
Each pixel is its own light source, meaning that no backlight is necessary. This allows the screen assembly to be thinner, and have more consistent lighting across the whole display.
When we purchase a new smartphone we go through a list of specifications that includes the processor, software, cameras, display type, battery, etc. The display of the smartphone is something which has always been a concern for people. And smartphone technology has advanced so much in the past decade that you get several display technology options to choose from.
Today, a smartphone is not just a means to send and receive calls and texts. It has become a general necessity, so choosing the right technology should be your main priority. Coming back to displays, as we said there are plenty of display types available right now.
Two of the main contenders for display technologies that are widely available are AMOLED and LCD. Here in this article, we will be comprising AMOLED vs LCD and find out which one is better for you.
Starting with the AMOLED first, it is a part of the OLED display technology but with some more advanced features. To completely know about it must understand its all three components. The first one is LED, “Light Emitting Diode”. Then we have “O” which stands for organic and makes the OLED.
It actually means that organic material is placed with two conductors in each LED, which helps to produce the light. And the “AM” in AMOLED means Active Matrix, it has the capability to increase the quality of a pixel.
The AMOLED display is similar to the OLED in various factors like high brightness and sharpness, better battery life, colour reproduction, etc. AMOLED display also has a thin film transistor, “TFT” that is attached to each LED with a capacitor.
TFT helps to operate all the pixels in an AMOLED display. This display might have a lot of positives but there are a few negatives too let’s point both of them out.
A major issue with these displays is of burning of pixels. After showing a specific image or colour for a longer period of time, the pixel can get burned. And if there is a problem with a single pixel it will affect the entire display.
Low outdoor visibility, usually the AMOLED Displays are quote not bright in direct sunlight and outdoor readability could be a problem for some devices but average screen brightness.
The LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display”, and this display produces colours a lot differently than AMOLED. LCD display uses a dedicated backlight for the light source rather than using individual LED components.
The LCD displays function pretty simply, a series of thin films, transparent mirrors, and some white LED lights that distributes lights across the back of the display.
As we have mentioned, an LCD display always requires a backlight and also a colour filter. The backlight must have to pass through a thin film transistor matrix and a polarizer. So, when you see it, the whole screen will be lit and only a fraction of light gets through. This is the key difference comparing AMOLED vs LCD and this is what differentiates these two display technologies.
The LCD displays are cheaper compared to the AMOLED as there is only one source of light which makes it easier to produce. Most budget smartphones also use LCD displays.
LCD displays have bright whites, the backlight emits lots of light through pixels which makes it easy to read in outdoors. It also shows the “Accurate True to Life” colours, which means it has the colours that reflect the objects of the real world more accurately than others.
LCDs also offer the best viewing angle. Although it may depend on the smartphone you have. But most high-quality LCD displays support great viewing angles without any colour distortion or colour shifting.
The LCD displays can never show the deep blacks like AMOLED. Due to the single backlight, it always has to illuminate the screen making it impossible to show the deep blacks.
The LCDs are also thicker than other displays because of the backlight as it needs more volume. So, LCD smartphones are mostly thicker than AMOLED ones.
Both of these display technologies have their own Pros and Cons. Taking them aside everything ends up with the user preferences as people might have different preferences among different colours and contrast profiles. However, a few factors might help you to decide which one fits perfectly for you.
Let’s start with the pricing. Most AMOLED display smartphones always cost more than an LCD smartphone. Although the trend is changing a bit. But still, if you want to get a good quality AMOLED display you have to go for the flagship devices.
The colors are also very sharp and vibrant with the AMOLED displays. And they look much better than any LCD display. The brightness is something where LCDs stood ahead of the AMOLED display. So using an LCD display outdoors gives much better results.
The last thing is battery consumption, and there is no one near the AMOLED displays in terms of battery. As of now, all smartphones feature a Dark Mode and most of the apps and UI are dark black with a black background. This dark UI on smartphones doesn’t require any other light, it gives the AMOLED displays a boost in battery performance.
Looking at all these factors and comparing AMOLED vs LCD displays, the AMOLED displays are certainly better than the LCDs. Also, the big display OEMs, like Samsung and LG are focusing more the OLED technologies for their future projects. So, it makes sense to look out for AMOLED displays. That being said, if we see further enhancements in the LCD technology in terms of battery efficiency and more, there is no point to cancel them at this moment.

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.

The world of mobile display technology is divided between those who prefer AMOLED screens and those who prefer LCD screens. OLED technology, closely related to AMOLED displays, is available on specific mobile devices. Since the two are based on fundamentally different technologies, distinct manufacturers will promote different advantages for their chosen display technology, AMOLED or LCD. AMOLED displays are becoming the standard for smartphones, whereas LCD screens are often kept for budget models.
First, let’s talk about AMOLED, similar to OLED displays but has a few more bells and whistles. One must be familiar with each of its three parts to grasp it fully. LED, short for “Light Emitting Diode,” is the first. The “O” in OLED refers to “organic,” which describes the material used to construct the device.
To put it another way, each LED has two conductors in which organic material is inserted to assist generate light. And the “AM” in AMOLED stands for Active Matrix, which may improve a pixel’s quality. High brightness and sharpness, improved battery life, accurate colour reproduction, etc., are all features shared by the AMOLED and OLED displays. A capacitor connects each LED in an AMOLED display to a thin film transistor (TFT).
TFT is used to control each pixel in an AMOLED screen. There are probably many benefits to this presentation, but because there are also some drawbacks, I’ll mention them.
The benefits of using best AMOLEDscreen include a higher contrast ratio and more vibrant colours, which contribute to a more satisfying video-viewing experience. Individual pixels may be activated or deactivated thanks to the included LEDs. The pixels in the black area of the picture will be disabled, revealing the most accurate black possible.
The use of individual LEDs improves the efficiency of the display. You may notice an increase in battery life as a result of the fact that specific pixels aren’t using any power at all.
LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display,” and its colour output differs from that of an AMOLED screen. Instead of employing separate LED lights for every pixel, an LCD screen has its own built-in backlight.
A backlight and colour filter are necessary components of every LCD panel, as we’ve discussed. A polarizer and a matrix of thin-film transistors are required stops for the backlight on its way to the display. This means that the whole screen will be illuminated, yet only a little amount of light will really reach the viewer. This is the main distinction between AMOLED and LCD, the two most common types of electronic displays now available.
Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) have lower production costs than AMOLEDs since they need less expensive light sources. LCD screens are also often seen in low-priced cell phones.
LCDs’ whites are so luminous because the backlight pumps so much illumination into each pixel that text on these screens can be read even in direct sunlight. Aside from that, it displays “Accurate True to Life” colours, which are most faithful to how things seem in the real world.
LCDs also provide the widest field of vision. This may be dependent on the kind of smartphone you use. However, most modern LCD screens have wide viewing angles with little colour shifting or distortion.
Let’s talk about the cost to begin. The cost of a smartphone with an AMOLED screen is often higher than that of a smartphone with an LCD screen. This, is despite the fact that the tide is beginning to turn. Even still,thebest AMOLED screen of sufficient quality are now available on only the most expensive flagship handsets. AMOLED screens also provide very crisp and vivid colours. Additionally, they surpass the visual quality of any LCD screen. Compared to an LCD, an AMOLED screen isn’t nearly as bright. Therefore, an LCD screen performs much better when used in the open air.
Finally, we look at battery life, and no other display technology comes close to AMOLEDs in this regard. All modern smartphones include a “Dark Mode,” where the screen and app icons are black. There is no need for additional lighting while using this dark user interface, which is great for smartphones with AMOLED screens.
AMOLED screens are superior to LCD displays when compared using these criteria. In addition, major display original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) like Samsung and LG emphasise OLED technology for their next endeavours. Therefore, it is prudent to keep an eye out for AMOLED screens. However, if we witness more LCD technology improvements in battery economy and more, there is no need to cancel them at this time.

Over the years, there has been a steady growth in the use of smartphones. This has led to the growth of mobile display technologies. The names such as OLED, LCD, touchscreen, retina display, have been making rounds years. AMOLED is a technology derived from OLED, and it has gained immense attention in recent years. Each of the aforementioned technologies have made a big impact owing to their distinct advantages. This post focuses on an ongoing debate on AMOLED vs LCD.
For many people, both these display technologies look the same. The following points will help you understand the basic differences between LCD and AMOLED.
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) are thin-panel displays that are used in various computers, cell phones, and televisions. These displays use backlight for lighting, and they reproduce light differently than AMOLED. Thin-film transistor (TFT) and in-plane switching (IPS) are two important types of LCD displays used today.
Active-Matrix OLED (AMOLED) is a type of organic light emitting diode (OLED) display that does not require a backlight to assure power savings. These OLED display modules are commonly used for mobile phones and are emerging in the consumer tv market.
Brightness: The backlight on an LCD display helps light up pixels easily, thereby making it easier for users to read on their screens easily. Against this, AMOLED displays have low brightness levels.
Color Presentation: LCD screens are known to portray true to life colors on screen. This gives an actual idea of color to viewers who may not have seen certain things in real. However, AMOLED screens can produce vivid and bright colors with high contract ratios. AMOLED screens can produce true black colors. As no backlight is required, the display can easily power off pixels, which are required to highlight any black portions on the image. When compared, AMOLED display offers a large color gamut than other LCD displays. This is why they are available in warmer hues with a tint of red or yellow color, whereas LCD displays are blue. Yellow hues are soothing to eyes, however, blue lights will help see things in the dark. In short, AMOLED screens allow users to see vibrant colors than original, whereas LCD displays will provide real colors, thereby adding to their viewing experience.
Energy-efficient: LCD displays or screens utilize backlight for smooth operation, whereas AMOLED displays don’t require backlights. The backlight drains out battery life, and your phones may require regular recharging for proper functioning. However, AMOLED displays require no backlight, which makes them energy efficient. Also, you can use a black wallpaper to save energy on AMOLED displays.
Flexibility:AMOLED display modules are a lot more flexible among the two. Curved and circular AMOLED displays are used in many mobile phones and smart wearables. LCD displays cannot be molded or curved like AMOLED or OLED display modules, which limits their utilization in various applications.
Affordability: LCD display panels have been around for a long time, so its manufacturing has been perfected for the mobiles and other devices. Thus, mass volumes of modules can be produced at cheaper prices. However, AMOLED display module production is costlier because the technology is new, still in refinement phases. So, their manufacturing costs are higher than LCD counterparts.
As seen, each technology has its own benefits. After considering the majority of pros and cons it can be easily said that AMOLED displays are preferable than LCD panels if color presentation, battery life, and affordability are major concerns for your application. It is important that you partner with a reliable LCD or OLED display manufacturer like Microtips USA to source these modules. The company also provides custom OLED displays to meet various application

The same picture often has different display effect in different material screens, especially in saturation and contrast. Also, there are some differences in the display effect of various materials under sunlight. When many people watch videos and pictures, the problem of the viewing angle of the screen will be visible. The larger the viewing angle of the screen, the better the viewing effect will be.
At present, Super AMOLED and IPS screens are the mainstream of smartphones in the market. Super AMOLED and IPS screens are common in the middle- high-grade product series. So what is the difference between the two monitors? We might as well verify it through actual testing.
First of all, we can see the effect of opening the same picture on three kinds of screens in full black indoor. After observation, we find that Super AMOLED and IPS screens have good performance in some display details, but in color, Super AMOLED screens are more abundant than IPS screens, because every pixel of Super AMOLED dazzling screen can be self-contained. Luminescent, can present more than 90% of Adobe RGB color range, so the Super AMOLED screen looks more comfortable.
For users, it is essential to have excellent color and more profound contrast, but for photos, we should pursue their authenticity more. Therefore, the author uses a daily SLR photograph, which is viewed on three screens and compares it with the original SLR image to see whose display effect is better. Close to the original performance.
Looking the two screens effects, it would be nice to take anyone out alone, but putting them together still shows the difference in color, especially in the small part of the sunlight shadow in the photo, because Super AMOLED has good contrast and broad color model. Weiwei, therefore, is more realistic in general and can express the original flavor of the original picture better.
In the aspect of visual angle display, we have selected several display screens which are common in the market. IPS and SuperAMOLED monitors have excellent performances. SLCD2 using AH-IPS technology inherits the high visual angle of IPS, while TFT screens still perform poorly in the visual aspect. Besides the problem of anti-whitening, the issue of color bias is more severe than other monitors.
Finally, we compare the two LCD screens in the sunshine. IPS and Super AMOLED have good display effect. They can see the main content of the screen display, but Super AMOLED is slightly better than IPS in picture details.
The quality of the LCD display will directly affect the user’s experience. To investigate how the LCD screen should proceed from the actual experience, the Super AMOLED screen has certain advantages in color reduction, color range, contrast, and visual angle range. In practical use, it is still excellent even under sunlight. For IPS technology that has been very mature, the high cost of Super AMOLED limits the popularity of products. With the promotion of OLED and the improvement of production technology, Super AMOLED will have more application space.

AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode, OLED display device technology. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescent material, and active matrix refers to the technology behind the addressing of pixels.
An AMOLED display consists of an active matrix of OLED pixels generating light (luminescence) upon electrical activation that have been deposited or integrated onto a thin-film transistor (TFT) array, which functions as a series of switches to control the current flowing to each individual pixel.
TFT backplane technology is crucial in the fabrication of AMOLED displays. In AMOLEDs, the two primary TFT backplane technologies, polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si) and amorphous silicon (a-Si), are currently used offering the potential for directly fabricating the active-matrix backplanes at low temperatures (below 150 °C) onto flexible plastic substrates for producing flexible AMOLED displays.
AMOLED was developed in 2006. Samsung SDI was one of the main investors in the technology, and many other display companies were also developing it. One of the earliest consumer electronics products with an AMOLED display was the BenQ-Siemens S88 mobile handsetiriver Clix 2 portable media player.Nokia N85 followed by the Samsung i7110 - both Nokia and Samsung Electronics were early adopters of this technology on their smartphones.
Manufacturers have developed in-cell touch panels, integrating the production of capacitive sensor arrays in the AMOLED module fabrication process. In-cell sensor AMOLED fabricators include AU Optronics and Samsung. Samsung has marketed its version of this technology as "Super AMOLED". Researchers at DuPont used computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software to optimize coating processes for a new solution-coated AMOLED display technology that is competitive in cost and performance with existing chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technology. Using custom modeling and analytic approaches, Samsung has developed short and long-range film-thickness control and uniformity that is commercially viable at large glass sizes.
The amount of power the display consumes varies significantly depending on the color and brightness shown. As an example, one old QVGA OLED display consumes 0.3 watts while showing white text on a black background, but more than 0.7 watts showing black text on a white background, while an LCD may consume only a constant 0.35 watts regardless of what is being shown on screen.
AMOLED displays may be difficult to view in direct sunlight compared with LCDs because of their reduced maximum brightness.Super AMOLED technology addresses this issue by reducing the size of gaps between layers of the screen.PenTile technology is often used for a higher resolution display while requiring fewer subpixels than needed otherwise, sometimes resulting in a display less sharp and more grainy than a non-PenTile display with the same resolution.
The organic materials used in AMOLED displays are very prone to degradation over a relatively short period of time, resulting in color shifts as one color fades faster than another, image persistence, or burn-in.
As of 2010, demand for AMOLED screens was high and, due to supply shortages of the Samsung-produced displays, certain models of HTC smartphones were changed to use next-generation LCD displays from the Samsung-Sony joint-venture SLCD in the future.
Flagship smartphones sold in 2020 and 2021 used either a Super AMOLED. Super AMOLED displays, such as the one on the Samsung Galaxy S21+ / S21 Ultra and Samsung Galaxy Note 20 Ultra have often been compared to IPS LCDs, found in phones such as the Xiaomi Mi 10T, Huawei Nova 5T, and Samsung Galaxy A20e.ABI Research, the AMOLED display found in the Motorola Moto X draws just 92 mA during bright conditions and 68 mA while dim.
"Super AMOLED" is a marketing term created by Samsung for an AMOLED display with an integrated touch screen digitizer: the layer that detects touch is integrated into the display, rather than overlaid on top of it and cannot be separated from the display itself. The display technology itself is not improved. According to Samsung, Super AMOLED reflects one-fifth as much sunlight as the first generation AMOLED.One Glass Solution (OGS).
Future displays exhibited from 2011 to 2013 by Samsung have shown flexible, 3D, transparent Super AMOLED Plus displays using very high resolutions and in varying sizes for phones. These unreleased prototypes use a polymer as a substrate removing the need for glass cover, a metal backing, and touch matrix, combining them into one integrated layer.
Also planned for the future are 3D stereoscopic displays that use eye-tracking (via stereoscopic front-facing cameras) to provide full resolution 3D visuals.
Kim, Yang Wan; Kwak, Won Kyu; Lee, Jae Yong; Choi, Wong Sik; Lee, Ki Yong; Kim, Sung Chul; Yoo, Eui Jin (2009). "40 Inch FHD AM-OLED Display with IR Drop Compensation Pixel Circuit". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. 40: 85. doi:10.1889/1.3256930. S2CID 110871831.
Lee, Myung Ho; Seop, Song Myoung; Kim, Jong Soo; Hwang, Jung Ho; Shin, Hye Jin; Cho, Sang Kyun; Min, Kyoung Wook; Kwak, Won Kyu; Jung, Sun I; Kim, Chang Soo; Choi, Woong Sik; Kim, Sung Cheol; Yoo, Eu Jin (2009). "Development of 31-Inch Full-HD AMOLED TV Using LTPS-TFT and RGB FMM". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. 40: 802. doi:10.1889/1.3256911. S2CID 110948118.
Hamer, John W.; Arnold, Andrew D.; Boroson, Michael L.; Itoh, Masahiro; Hatwar, Tukaram K.; Helber, Margaret J.; Miwa, Koichi; Levey, Charles I.; Long, Michael; Ludwicki, John E.; Scheirer, David C.; Spindler, Jeffrey P.; Van Slyke, Steven A. (2008). "System design for a wide-color-gamut TV-sized AMOLED display". Journal of the Society for Information Display. 16: 3. doi:10.1889/1.2835033. S2CID 62669850.
Lin, Chih-Lung; Chen, Yung-Chih (2007). "A Novel LTPS-TFT Pixel Circuit Compensating for TFT Threshold-Voltage Shift and OLED Degradation for AMOLED". IEEE Electron Device Letters. 28 (2): 129. Bibcode:2007IEDL...28..129L. doi:10.1109/LED.2006.889523. S2CID 11194344.
Reid Chesterfield, Andrew Johnson, Charlie Lang, Matthew Stainer, and Jonathan Ziebarth, "Solution-Coating Technology for AMOLED Displays Archived 16 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine", Information Display Magazine, January 2011.
Dong, Mian; Choi, Yung-Seok Kevin; Zhong, Lin (2009). "Power modeling of graphical user interfaces on OLED displays". Proceedings of the 46th Annual Design Automation Conference on ZZZ - DAC "09. p. 652. doi:10.1145/1629911.1630084. ISBN 9781605584973. S2CID 442526.
"AMOLED vs LCD: differences explained". Android Authority. 8 February 2016. Archived from the original on 27 December 2016. Retrieved 6 February 2017.
Tim Carmody (10 November 2010). "How Super AMOLED displays work". Wired. Wired.com. Archived from the original on 28 September 2012. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
Ashtiani, Shahin J.; Reza Chaji, G.; Nathan, Arokia (2007). "AMOLED Pixel Circuit With Electronic Compensation of Luminance Degradation". Journal of Display Technology. 38 (1): 36. Bibcode:2007JDisT...3...36A. doi:10.1109/JDT.2006.890711. S2CID 44204246.
"AMOLED vs LCD: Which screen is best for your phone?". digitaltrends.com. 29 August 2014. Archived from the original on 29 March 2018. Retrieved 6 May 2018.
S-AMOLED (super-active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) is a marketing term that refers to a display technology used in a variety of electronic devices. The "super" in its name distinguishes it from its older, less advanced versions (OLED and AMOLED).
S-AMOLED might also go by the name super amorphous organic light-emitting diode, or super amorphous OLED because it uses amorphous silicon technology.
Displays using organic light-emitting diodes (OLED) incorporate organic materials that light up when in contact with electricity. The active-matrix aspect of AMOLED sets it apart from OLED. AMOLED, then, is a kind of screen technology that includes not only a way to display light but also a method to detect touch (the "active-matrix" part). While it"s true that this method is a part of AMOLED displays as well, super-AMOLEDs are slightly different.
These displays are known for being able to render a deep black color when needed, a huge plus on any display and something you"ll notice right away when comparing with your standard IPS (in-plane switching) LCD. The benefit is obvious when watching a movie or viewing a picture that"s supposed to contain "true" black.
AMOLED technology includes a layer behind the OLED panel that gives light to each pixel instead of using a backlight as LCDs do. Because each pixel can be colored on an as-needed basis, pixels can be dimmed or turned off to make a true black instead of the pixels being blocked from receiving light (as with LCD).
This also means that AMOLED screens are great for displaying a huge range of color; the contrast against whites is infinite (because blacks are absolute black). On the other hand, this amazing ability makes it easier for images to be too vibrant or over saturated.
AMOLED is similar to Super-AMOLED in not only name, but also in function. In reality, Super-AMOLED is identical to AMOLED in all ways but one, but that"s what makes all the difference.
The two technologies are the same in that devices using them can incorporate light and touch sensors so the screen can be read and manipulated. The layer that detects touch (the digitizer, or capacitive touchscreen layer), however, is embedded directly into the screen in Super-AMOLED displays, while it"s an entirely separate layer on top of the screen in AMOLED displays.
This might not seem like a major difference, but Super-AMOLED displays carry many benefits over AMOLED displays because of the way these layers are designed:
Less power needs to be supplied to a Super-AMOLED screen because it doesn"t generate as much heat as older screen technologies. This is due, in part, to the fact that pixels are actually turned off and therefore not emitting light/using power when displaying black.
Manufacturing the technology behind Super-AMOLED displays is more expensive, however. Like most technology, this is likely to change as more manufacturers incorporate AMOLED into their TVs, smartphones, and other devices.
Organic materials eventually die, so AMOLED displays degrade faster than LED and LCD. Even worse, the materials used to create the individual colors have varying life spans, causing a noticeable difference in overall uniformity as the colors fade (e.g., blue OLED films don"t last as long as red or green).
Screen burn-in is a risk with AMOLED because of the non-uniform use of pixels. This effect is compounded as blue colors die out and leave red and green colors to take up the slack, leaving an imprint over time. That said, this issue doesn"t affect displays with high numbers of pixels per inch.
For example, HD Super-AMOLED is Samsung"s description of Super-AMOLED with a high-definition resolution of 1280x720 or greater. Motorola"s Super-AMOLED Advanced refers to displays that are brighter and of a higher resolution than Super-AMOLED screens. These displays use a technology called PenTile to sharpen the pixels. Others include Super-AMOLED Plus, HD Super-AMOLED Plus, Full HD Super-AMOLED, and Quad HD Super-AMOLED.
Dynamic-AMOLED displays are Super-AMOLED displays that also support HDR10+, which provides cinema-quality color and contrast. Dynamic-AMOLED displays are also certified for eye comfort by TUV Rheinland, so they emit less blue light than OLED displays.
Unlike Super-AMOLED displays that use LED, Retina displays use LCD. This screen type allows for higher resolution video than traditional AMOLEDs, but AMOLED displays offer superior contrast.
It"s a matter of personal preferences. When comparing Super-AMOLED and Super LCD (IPS-LCD), the former can display a wider range of colors. Super LCD, on the other hand, offers sharper images and is better for outdoor viewing.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey