super amoled vs lcd display pricelist

When we purchase a new smartphone we go through a list of specifications that includes the processor, software, cameras, display type, battery, etc. The display of the smartphone is something which has always been a concern for people. And smartphone technology has advanced so much in the past decade that you get several display technology options to choose from.
Today, a smartphone is not just a means to send and receive calls and texts. It has become a general necessity, so choosing the right technology should be your main priority. Coming back to displays, as we said there are plenty of display types available right now.
Two of the main contenders for display technologies that are widely available are AMOLED and LCD. Here in this article, we will be comprising AMOLED vs LCD and find out which one is better for you.
Starting with the AMOLED first, it is a part of the OLED display technology but with some more advanced features. To completely know about it must understand its all three components. The first one is LED, “Light Emitting Diode”. Then we have “O” which stands for organic and makes the OLED.
It actually means that organic material is placed with two conductors in each LED, which helps to produce the light. And the “AM” in AMOLED means Active Matrix, it has the capability to increase the quality of a pixel.
The AMOLED display is similar to the OLED in various factors like high brightness and sharpness, better battery life, colour reproduction, etc. AMOLED display also has a thin film transistor, “TFT” that is attached to each LED with a capacitor.
TFT helps to operate all the pixels in an AMOLED display. This display might have a lot of positives but there are a few negatives too let’s point both of them out.
A major issue with these displays is of burning of pixels. After showing a specific image or colour for a longer period of time, the pixel can get burned. And if there is a problem with a single pixel it will affect the entire display.
Low outdoor visibility, usually the AMOLED Displays are quote not bright in direct sunlight and outdoor readability could be a problem for some devices but average screen brightness.
The LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display”, and this display produces colours a lot differently than AMOLED. LCD display uses a dedicated backlight for the light source rather than using individual LED components.
The LCD displays function pretty simply, a series of thin films, transparent mirrors, and some white LED lights that distributes lights across the back of the display.
As we have mentioned, an LCD display always requires a backlight and also a colour filter. The backlight must have to pass through a thin film transistor matrix and a polarizer. So, when you see it, the whole screen will be lit and only a fraction of light gets through. This is the key difference comparing AMOLED vs LCD and this is what differentiates these two display technologies.
The LCD displays are cheaper compared to the AMOLED as there is only one source of light which makes it easier to produce. Most budget smartphones also use LCD displays.
LCD displays have bright whites, the backlight emits lots of light through pixels which makes it easy to read in outdoors. It also shows the “Accurate True to Life” colours, which means it has the colours that reflect the objects of the real world more accurately than others.
LCDs also offer the best viewing angle. Although it may depend on the smartphone you have. But most high-quality LCD displays support great viewing angles without any colour distortion or colour shifting.
The LCD displays can never show the deep blacks like AMOLED. Due to the single backlight, it always has to illuminate the screen making it impossible to show the deep blacks.
The LCDs are also thicker than other displays because of the backlight as it needs more volume. So, LCD smartphones are mostly thicker than AMOLED ones.
Both of these display technologies have their own Pros and Cons. Taking them aside everything ends up with the user preferences as people might have different preferences among different colours and contrast profiles. However, a few factors might help you to decide which one fits perfectly for you.
Let’s start with the pricing. Most AMOLED display smartphones always cost more than an LCD smartphone. Although the trend is changing a bit. But still, if you want to get a good quality AMOLED display you have to go for the flagship devices.
The colors are also very sharp and vibrant with the AMOLED displays. And they look much better than any LCD display. The brightness is something where LCDs stood ahead of the AMOLED display. So using an LCD display outdoors gives much better results.
The last thing is battery consumption, and there is no one near the AMOLED displays in terms of battery. As of now, all smartphones feature a Dark Mode and most of the apps and UI are dark black with a black background. This dark UI on smartphones doesn’t require any other light, it gives the AMOLED displays a boost in battery performance.
Looking at all these factors and comparing AMOLED vs LCD displays, the AMOLED displays are certainly better than the LCDs. Also, the big display OEMs, like Samsung and LG are focusing more the OLED technologies for their future projects. So, it makes sense to look out for AMOLED displays. That being said, if we see further enhancements in the LCD technology in terms of battery efficiency and more, there is no point to cancel them at this moment.
Samsung Electronics has been a driving force in this development as they dominate the Android market. Aside from last year’s smartwatch, Apple hasn’t been as enthusiastic in its adoption of the technology. Its biggest Android rival on the other hand, developed its very own Super AMOLED and has been supplying other gadget manufacturers with the display panels.
The report says that prices are likely to keep going down as Samsung is ramping up the game with new production facilities. If Samsung manages to keep up the demand for AMOLED displays, which seems likely if the price keeps going down, then the numbers keep falling. Consider it a positive loop.
Of course, there’s no guarantee that AMOLED will keep its position forever. If Apple decides to keep going for LCD displays, it will likely also limit how far down the AMOLED display prices reach.

Super AMOLED is a more advanced version and it integrates touch-sensors and the actual screen in a single layer. Super AMOLED is even better at this with 20% brighter screen, 20% lower power consumption and 80% less sunlight reflection.
Most AMOLED display smartphones always cost more than an LCD smartphone. But still, if you want to get a good quality AMOLED display you have to go for the flagship devices. The colors are also very sharp and vibrant with the AMOLED displays. And they look much better than any LCD display.
AMOLED displays are designed for consumers not only because of their breathtaking appearance, but also because of they are one of the safest display technologies ever developed. Experts tell us that the human eye typically will perceive about 80% of the information that reaches our visual sensory system.
The display is one area where the iPhone 11 takes a noticeable step back from the Pro and many Android phones. Instead of the Pro’s high-resolution AMOLED, the iPhone 11 offers a 6.1-inch LCD with a resolution of 1,792 x 828. The display tends to look a bit washed out compared to other flagship devices.
Download the AMOLED test image If you see any light emanating from the phone—any light at all—your device has an LCD screen. Otherwise, if your screen is completely dark while displaying the test image at full brightness, you’ve got an AMOLED screen.
Most display experts and consumers agree that OLED displays are the world’s best smartphone displays. The best smartphone OLED displays are the Super AMOLED displays produced by Samsung Display, but other OLED producers (such as LG and BOE Display) are also producing high quality OLEDs.
Modern AMOLED displays also provide better viewing angles, surpassing IPS. However, since AMOLED is more difficult to produce than IPS, costs are higher and images aren’t quite as sharp. Since each “dot” is essentially its own colored light in an AMOLED display, colors are better and contrast is great!
It is a type of OLED display and is used in smartphones. Super AMOLED is an AMOLED display that has an integrated touch function: Instead of having a layer that recognizes touch on the top of the screen, the layer is integrated into the screen itself. Super AMOLED provides an exceptional viewing experience for you.
Super AMOLED displays are thinner and lighter as there are only two layers of glass between them. All the parts are spread uniformly, whereas the Amoled display is thicker and bulky due to the extra layer.
Active-matrix organic light-emitting diode (AMOLED) is a type of OLED display technology used in tablets, smartwatches, gaming consoles, digital cameras, portable music players and music production hardware. It uses a thin-film transistor (TFT), which comprises a storage capacitor for maintaining the line pixel states.
AMOLED screens consist of a thin layer of organic polymers that light up when zapped with an electric current. Due to this simple construction, AMOLED screens can be extremely thin and do not require a backlight.

Thanks for the display technology development, we have a lot of display choices for our smartphones, media players, TVs, laptops, tablets, digital cameras, and other such gadgets. The most display technologies we hear are LCD, TFT, OLED, LED, QLED, QNED, MicroLED, Mini LED etc. The following, we will focus on two of the most popular display technologies in the market: TFT Displays and Super AMOLED Displays.
TFT means Thin-Film Transistor. TFT is the variant of Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs). There are several types of TFT displays: TN (Twisted Nematic) based TFT display, IPS (In-Plane Switching) displays. As the former can’t compete with Super AMOLED in display quality, we will mainly focus on using IPS TFT displays.
OLED means Organic Light-Emitting Diode. There are also several types of OLED, PMOLED (Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). It is the same reason that PMOLED can’t compete with IPS TFT displays. We pick the best in OLED displays: Super AMOLED to compete with the LCD best: IPS TFT Display.
If you have any questions about Orient Display displays and touch panels. Please feel free to contact: Sales Inquiries, Customer Service or Technical Support.

Super AMOLED and Super LCD are two of the best and most popular screen technologies currently in use on phones, and are the display tech of choice for two of the most popular Android phones around.
HTC for example, packed its One flagship with a Super LCD screen (in fact, it"s one of the biggest customers of the tech by some way) while Samsung not only uses Super AMOLED, the company actually created it. But what"s the difference between them? And which is better?
To understand Super AMOLED you first need to understand its origins. It started with OLED, which stands for "organic light-emitting diode" and consists of a thin organic film with electrodes at either side. As soon as an electric current is applied to the film it emits light.
AMOLED is an "active-matrix organic light-emitting diode". It adds a layer of semiconducting film behind the OLED panel which allows it to more quickly activate each pixel. That increased speed makes it ideal for larger, higher definition displays with a lot of pixels. In fact it"s as much as 1000 times faster than LCD.
AMOLED screens also tend to have great contrast, as the light on the screen comes from each individual pixel rather than a backlight; when it needs to create a black colour it simply dims or turns off the relevant pixels, for a true, deep black.
Other advantages of AMOLED screens are that they have wide viewing angles and can even be made transparent or flexible, which makes them ideal for the curved handsets which are starting to hit the market, such as the Samsung Galaxy Round.
An AMOLED touchscreen usually has an extra, touch sensitive layer on top of the screen, but with Super AMOLED Samsung has been able to integrate touch sensitivity into the screen itself.
The result of this is that not only is the screen thinner, lighter, more touch sensitive and less power-hungry, but without that extra layer it"s also far less reflective than a typical AMOLED screen, making it easier to view in bright sunlight.
On the other hand Super AMOLED screens are quite susceptible to image burn in and sometimes use a PenTile matrix with fewer subpixels than their LCD companions, which can potentially lead to less sharp images or give the screen an unnatural colour tint.
For example there"s Super AMOLED Plus, which was used in the Samsung Galaxy S2 and has a standard RGB matrix rather than a PenTile matrix, meaning it has 50% more subpixels and therefore delivers clearer images, but it also degrades faster than a Super AMOLED display, which is why Samsung stopped using it in its flagships.
Then there"s HD Super AMOLED, which is just a 720 x 1280 Super AMOLED display and Full HD Super AMOLED, which, you guessed it, is Full HD 1080 x 1920.
Just as AMOLED was the predecessor to Super AMOLED, LCD was the predecessor to Super LCD. Unlike an AMOLED display which lights each pixel individually, an LCD (or liquid crystal display) has a backlight, so the whole screen is lit to some extent, even supposedly black areas.
In standard LCD displays there"s an air gap between the outer glass and the display element, but with Super LCD that gap is removed, which has similar benefits to Super AMOLED.
Glare is reduced, making it more easily viewable when outside and in bright sunlight, plus the screen is also thinner and uses less power than standard LCD.
Things get a bit more complicated when you consider that there"s also such a thing as Super LCD2 and Super LCD3, but really each numbered version is just an improvement on the last while working in much the same way.
Super LCD3 for example is brighter than Super LCD2, as well as having better viewing angles and a faster refresh rate to avoid blurring when watching videos.

By now you know that (one of) AMOLED"s Achilles" heel is readability in direct sunlight. But Samsung"s been working hard to fix that with its new Super AMOLED technology. Techblog took the display to task by pitting the Samsung Galaxy S (4-inch, 480 x 800 pixel Super AMOLED) against the HTC Desire (3.7-inch 480 x 800 pixel AMOLED) and Sony Ericsson XPERIA X10 (4-inch, 480 x 854 pixel TFT LCD). It"s clear from the video embedded after the break that the LCD still has the edge in the harsh Greek sun, but the Super AMOLED certainly makes a much stronger showing than its AMOLED sib. In fact, differences in visibility between the LCD and Super AMOLED are often indistinguishable, like the picture above. That"ll be good news for us just as soon as Samsung can start meeting demand... regardless of what Stevie J has to say. Check the video after the break and be sure to click the source for some more side-by-side pics, including a few taken indoors where that Super AMOLED display really shines.

A Super AMOLED Display Mobile has the ability to display vivid and bright colors. Moreover, it has a faster motion response time than LCD displays. This makes it more suitable for viewing multimedia content such as videos and images. The screen size on these phones is typically bigger than LCD displays which allow users to view content in greater detail.

When you buy a smartphone and while reading the specifications of the phone, you often do not pay attention to the type of phone screen. Screen types abbreviations can be a bit confusing and most people don’t usually take them into consideration due to their ignorance. Don’t worry now we will give you everything you need to know about the main types of screens which are LCD, OLED and AMOLED.
Previously, there were only two main types in the smartphone industry, LCD and LED. But with the advancement in technology, many other types such as OLED, AMOLED, sAMOLED, and Retina have appeared. LCD screens are used in most mid-range phones from Xiaomi, Realme and other Chinese manufacturers and OLED in their top-end devices. Samsung uses AMOLED and sAMOLED displays, while Apple uses Retina displays. Let us discuss each of these types one by one.
LCD (abbreviation for Liquid Crystal Display). The oldest type of screen, it relied on backlighting as the only light source to illuminate the pixels. Also, LCD screens are brighter than most other types of screens, which makes them suitable for use in smartphones in bright sunlight. However, these screens suffer from less accurate colors. Smartphones use two main types of LCD screens:
TFTstands for Thin Film Transistor. TFT monitors are an advanced version of LCD monitors. While TFT has a relatively lower production cost and provides better image quality than previous generations of LCD monitors, it has higher power consumption, lower viewing angles and lower color representation.
OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode). The presence of this type is the main reason for the emergence of curved displays and foldable smartphones. Unlike LCD screens, which use backlighting, OLED screens do not require this because they contain a layer of organic matter that emits light when exposed to an electric current. OLED displays display more saturated and vibrant colors. Because of the luminance per pixel, OLED displays provide darker levels of black. Because the pixels that don’t get caught are in a sleep state, OLED screens usually use less power and give better battery life. These screens are of two main types:
AMOLEDstands for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode. Similar to an OLED screen but has Thin Film Transistors (TFT) on the back panel. This ensures faster and more precise control as it can turn on or off any pixel individually, and it also has a storage capacitor which eliminates screen size limitations and provides the possibility of a larger screen. We will explain AMOLED screens in more detail due to their great popularity.
AMOLED (Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode). Improved OLED screens. The most important component of these displays is the TFT element that controls the flow in each pixel. With two TFTs per pixel, one to start and one to stop charging the storage capacitors this allows each LED to operate individually and generate light for itself. Due to its great flexibility it can be used in foldable phones.
You may have seen the term sAMOLED or Super AMOLED. These monitors were invented by Samsung and are available in their high-end models. This type provides a variety of colors with greater clarity. Super AMOLED displays can handle sunlight better than other AMOLED displays, while consuming less power.
Each of the above types of screens has its own advantages and disadvantages. In general, AMOLED is superior to LCD screens. Our primary comparison criteria are higher refresh rates, better color representation, and battery consumption. As for OLED versus AMOLED, we already mentioned that AMOLED is an improved version of OLED as it offers better image quality to battery consumption. Due to their low usability under sunlight, Super AMOLED screens are the best choices.
In the end, it all boils down to your needs and budget. If you’re on a tight budget, an LCD monitor isn’t a bad deal. But if your budget is good, you should definitely opt for the newer AMOLED screen especially for TVs.

Typically, when scrolling through web pages and specs sheets of many smartphones, users are often faced with a number of confusing terminologies, particularly in the display department. While many smartphone enthusiasts and experts are familiar with these smartphone display technologies, many newbies aren’t.
There are more than four display types used on smartphones, and these displays are relative to the quality of images, colour quality, battery life, and even the price of the device. We explain the tech behind each known display types on smartphones.
LCD is an acronym that stands for Liquid Crystal Display and it is one of the most commonly used display by OEMs on their devices. LCD displays are further categorised into two types on the basis of the technology used to make them. The two types are IPS LCD and TFT LCDs.
TFT stands Thin-film Transistor and de facto, it really isn’t a type of display. TFT is only the technology used to produce LCD display panels. TFT LCD displays use an ‘Active Matrix Technology” where the display transistor and capacitor have individual pixels attached to them. In fact, each pixel can have as many as four transistors; for switching them off and on easily. TFT displays are widely known for having high contrast ratios, resolution and image quality. They are also cheaper to produce but not as cheap as IPS LCD.
IPS stands for In-Plane Switching and it is the most popularly used type of LCD panels for a number of reasons. First, compared to TFT, the crystal/pixel orientation on IPS LCD is different. This modification allows for improved colour reproduction, better viewing angles, and reduced energy consumption. This is why IPS LCD is preferred over TFT by most gadgets manufacturers.
Generally, LCDs are known as the “backlit displays” because the pixels on the display are powered by a polarized light engineered to the screen. The light passes through the (horizontal and vertical) filters which help determine the pixel’s brightness. Although the inclusion of a backlight makes LCD displays (and phones) thicker, pixels are generally more closely packed, colours are more natural, and images — sharper.
OLED stands for “Organic light-emitting diode”. OLED is one of the latest display innovation used in many gadgets and electronics like smartphones and TVs. Unlike LCD displays, OLED panels produce their own light and do not rely on a backlight. This self-emission is achieved when an electrical current passes through two conductors with an organic carbon-based film between them.
For every pixel in an OLED panel, this light emission process takes place, except when black is being displayed; the pixels are turned off instead. This makes OLED the best display that shows true black colour. The process of turning off pixels when displaying black is also a battery-wise feature of OLED panels.
Regarding quality, OLED are generally better at displaying blacks. They are also slimmer, dissipate less heat, and possess better contrast ratio when compared to LCDs. However, they are more expensive to produce and in turn lead to an increase in the price of smartphones they are used on. Shorter lifespan is also a downside to OLED displays.
AMOLED is an advanced type of OLED display that uses an “Active Matrix” technology. AMOLED is the acronym for Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED). Like OLED, AMOLED pixels also emit their own light and further uses an active matrix system attached to a thin-film transistor (TFT) to exert more control over each pixels. This results to better visual experience; darker blacks, deeper brights, and higher refresh rates.
AMOLED panels are mostly used in big-sized smartphones as it supports almost any display size. One downside to AMOLED panels, though, is poor usability under sunlight.
Also called S-AMOLED, Super AMOLED is an upgrade of AMOLED panels. Unlike regular AMOLED, this upgrade uses almost the same technology but with architectural modifications that makes it better. In S-AMOLED, the touch sensor component have been integrated with the screen; both are separated in regular AMOLED.
This difference results in brighter display, reduced power consumption, reduced sunlight reflection, enhanced outdoor readability, and wider viewing angles. Super AMOLED is one the best displays out there and can be found on many flagship devices like the Samsung Galaxy A7 (2018) with three rear cameras, Samsung Galaxy Note9.
You can easily identify your smartphone’s screen type through a simple Google search of your phone specifications. You should see your device’s screen type under the display department. The image below shows the screen type (IPS LCD) of the Coolpad Note 5.

List of Super AMOLED Display Mobiles in India with price ranging from Rs. 11,490 to Rs. 57,900. We have found 724 phones. Here is the summary of the results:
Latest Super AMOLED Display Mobiles in India: Recent launches include Samsung Galaxy A53 5G 256GB, Samsung Galaxy M32 Prime Edition 128GB and Samsung Galaxy M32 Prime Edition.

When you purchase Smartphones or TV or a Desktop Monitor, you may notice after the resolution specs; the manufacturers mention the type of Display like LCD, OLED, AMOLED, SUPER-AMOLED, and Retina Display. In the last few years, we have seen a massive upgrade in display technology.
You may have been trying to understand the actual meaning of the different display technologies used to design smartphones and TV these days. In recent times, the most popular and trending is Amoled Display and OLED display. So what is the actual difference between these two display (Amoled vs Oled) technologies? Let’s find out.
OLED Full form Is -Organic Light-Emitting Diodes, is a flat light emitting technology, made by placing a series of organic thin films between two conductors. When an electrical current is applied, a bright light is emitted. OLEDs are emissive displays that do not require a backlight and so are thinner and more efficient than LCDs (which do require a white backlight). OLED displays are not just thin and efficient – they provide the best image quality ever and they can also be made transparent, flexible, foldable and even rollable and stretchable in the future. OLEDs represent the future of display technology.
To know in details, let’s start with the basics. Display screens are made up of Pixels. A pixel is made up of 3 sections called sub-pixels. The three sections are red, green and blue(primary colours for display tech). To make a certain colour, each pixel lets certain amounts of light through each pixel at different intensities, showing the colour on your screen.
Where you start seeing differences emerge, is how the light is generated in each screen. On LCD displays, the light is generated from a “backlight”. A series of thin films, transparent mirrors and an array of white LED Lights that shine and distribute light across the back of the display.
OLEDs on the other hand have the unusual property of being able to produce both light and colour from a single diode when they’re fed electricity. Because of this, OLED TVs don’t need a separate backlight. Each pixel you see is a self-contained source of colour and light.
AMOLED full form is Active-Matrix OLED. The “active-matrix” part refers to the driving electronics or the TFT layer. When you display an image, you actually display it line by line (sequentially) as you can only change one line at a time. An AMOLED uses a TFT which contains a storage capacitor that maintains the line pixel states, and so enables large size (and large resolution) displays.
AMOLED improves basic OLED technology for larger televisions, monitors and laptop displays by introducing a Thin Film Transistor (TFT) layer that enables greater control over the light emitted by the OLEDs. If TFT sounds familiar, it’s because the technology — which dedicates a current-controlling transistor to each pixel — is also important in conventional LED LCDs. The TFT layer provides an enhanced, “active matrix” of light control, accounting for the “AM” in AMOLED (although it’s important to note that even displays labelled simply “OLED” also likely feature an active matrix of some kind; it’s just not always mentioned).
It is an advanced version of AMOLED Display. SUPER AMOLED, also known as S-AMOLED (super-active-matrix organic light-emitting diode), is a marketing term that refers to a display technology used in a variety of electronic devices. The “super” in its name distinguishes it from its older, less advanced versions (OLED and AMOLED).
Super AMOLED is a more advanced version and it integrates touch-sensors and the actual screen in a single layer. Super AMOLED is even better at this with a 20% brighter screen, 20% lower power consumption and 80% less sunlight reflection.
OLED display emits light when current is passed through as it is made up of thin layers of the organic components and so each pixel transmits its light. An AMOLED display consists of thin-film transistors in which the storage capacitors are responsible for maintaining the pixel states.
OLED display offers deeper blacks when compared to the AMOLED displays. The display quality of AMOLED is much better and flexible than that of the OLEDs and so AMOLED is much expensive than the OLED display.
The OLED display offers an excellent contrast ratio as it has a high level of control over pixels. On the other side, the AMOLED display has faster refresh rates than OLEDs and so provides a great artificial contrast ratio in which each pixel transmits light resulting in a better display.
OLED provides more efficient and bright displays as these are comparatively thinner as compared to the LCDs, whereas AMOLED display can be fitted into any display size as it does not restrict with the limitation of display sizes.
In AMOLED, TFT(a Thin-film transistor) is responsible for supplying power and charge the pixel.In OLED, TFT is only responsible for supplying power to the organic light-emitting diodes.Difference between AMOLED and OLED
These were the simple differences between AMOLED and OLED displays. There’s not much difference, but now you know what they are. Both the screen types perform admirably, be it on any machine.
when it comes to choosing between these two, it’s absolutely a personal choice and budget. If you have the budget for AMOLED, then you can go with that. When it comes to phones, AMOLED displays rule while OLED is apt for televisions.
I hope you gained some information from this Amoled Vs OLED Blog. If you have any queries regarding the topic, leave them in the comment section below. will be happy to respond.
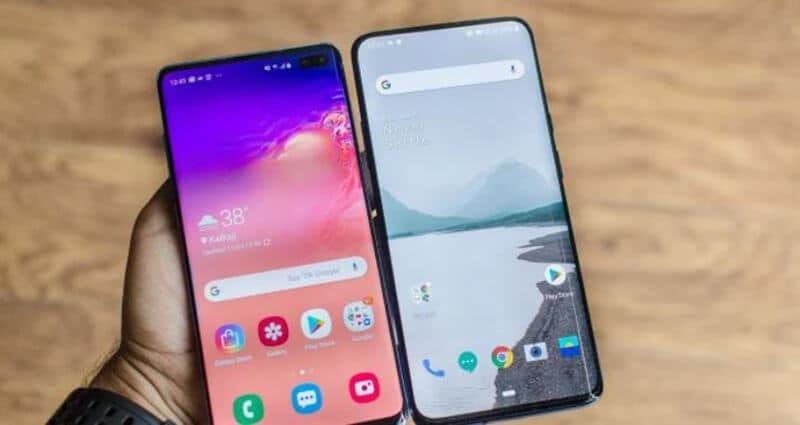

Over the years, there has been a steady growth in the use of smartphones. This has led to the growth of mobile display technologies. The names such as OLED, LCD, touchscreen, retina display, have been making rounds years. AMOLED is a technology derived from OLED, and it has gained immense attention in recent years. Each of the aforementioned technologies have made a big impact owing to their distinct advantages. This post focuses on an ongoing debate on AMOLED vs LCD.
For many people, both these display technologies look the same. The following points will help you understand the basic differences between LCD and AMOLED.
Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) are thin-panel displays that are used in various computers, cell phones, and televisions. These displays use backlight for lighting, and they reproduce light differently than AMOLED. Thin-film transistor (TFT) and in-plane switching (IPS) are two important types of LCD displays used today.
Active-Matrix OLED (AMOLED) is a type of organic light emitting diode (OLED) display that does not require a backlight to assure power savings. These OLED display modules are commonly used for mobile phones and are emerging in the consumer tv market.
Brightness: The backlight on an LCD display helps light up pixels easily, thereby making it easier for users to read on their screens easily. Against this, AMOLED displays have low brightness levels.
Color Presentation: LCD screens are known to portray true to life colors on screen. This gives an actual idea of color to viewers who may not have seen certain things in real. However, AMOLED screens can produce vivid and bright colors with high contract ratios. AMOLED screens can produce true black colors. As no backlight is required, the display can easily power off pixels, which are required to highlight any black portions on the image. When compared, AMOLED display offers a large color gamut than other LCD displays. This is why they are available in warmer hues with a tint of red or yellow color, whereas LCD displays are blue. Yellow hues are soothing to eyes, however, blue lights will help see things in the dark. In short, AMOLED screens allow users to see vibrant colors than original, whereas LCD displays will provide real colors, thereby adding to their viewing experience.
Energy-efficient: LCD displays or screens utilize backlight for smooth operation, whereas AMOLED displays don’t require backlights. The backlight drains out battery life, and your phones may require regular recharging for proper functioning. However, AMOLED displays require no backlight, which makes them energy efficient. Also, you can use a black wallpaper to save energy on AMOLED displays.
Flexibility:AMOLED display modules are a lot more flexible among the two. Curved and circular AMOLED displays are used in many mobile phones and smart wearables. LCD displays cannot be molded or curved like AMOLED or OLED display modules, which limits their utilization in various applications.
Affordability: LCD display panels have been around for a long time, so its manufacturing has been perfected for the mobiles and other devices. Thus, mass volumes of modules can be produced at cheaper prices. However, AMOLED display module production is costlier because the technology is new, still in refinement phases. So, their manufacturing costs are higher than LCD counterparts.
As seen, each technology has its own benefits. After considering the majority of pros and cons it can be easily said that AMOLED displays are preferable than LCD panels if color presentation, battery life, and affordability are major concerns for your application. It is important that you partner with a reliable LCD or OLED display manufacturer like Microtips USA to source these modules. The company also provides custom OLED displays to meet various application

The world of smartphones has been busy for the past few months. There have been numerous revolutionary launches with groundbreaking innovations that have the capacity to change the course of the smartphone industry. But the most important attribute of a smartphone is the display, which has been the focus for all prominent players in the mobile phone industry this year.
Samsung came up with its unique 18:5:9 AMOLED display for the Galaxy S8. LG picked up its old trusted IPS LCD unit for the G6’s display. These display units have been familiar to the usual Indian smartphone buyer. Honor, on the other hand, has just unveiled the new Honor 8 Pro for the Indian market that ships with an LTPS LCD display. This has led to wonder how exactly is this technology different from the existing ones and what benefits does it give Honor to craft its flagship smartphone with. Well, let’s find out.
The LCD technology brought in the era of thin displays to screens, making the smartphone possible in the current world. LCD displays are power efficient and work on the principle of blocking light. The liquid crystal in the display unit uses some kind of a backlight, generally a LED backlight or a reflector, to make the picture visible to the viewer. There are two kinds of LCD units – passive matrix LCD that requires more power and the superior active matrix LCD unit, known to people as Thin Film Transistor (TFT) that draws less power.
The early LCD technology couldn’t maintain the colour for wide angle viewing, which led to the development of the In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCD panel. IPS panel arranges and switches the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules of standard LCD display between the glass substrates. This helps it to enhance viewing angles and improve colour reproduction as well. IPS LCD technology is responsible for accelerating the growth of the smartphone market and is the go-to display technology for prominent manufacturers.
The standard LCD display uses amorphous Silicon as the liquid for the display unit as it can be assembled into complex high-current driver circuits. This though restricts the display resolution and adds to overall device temperatures. Therefore, development of the technology led to replacing the amorphous Silicon with Polycrystalline Silicon, which boosted the screen resolution and maintains low temperatures. The larger and more uniform grains of polysilicon allow faster electron movement, resulting in higher resolution and higher refresh rates. It also was found to be cheaper to manufacture due to lower cost of certain key substrates. Therefore, the Low-Temperature PolySilicon (LTPS) LCD screen helps provide larger pixel densities, lower power consumption that standard LCD and controlled temperature ranges.
The AMOLED display technology is in a completely different league. It doesn’t bother with any liquid mechanism or complex grid structures. The panel uses an array of tiny LEDs placed on TFT modules. These LEDs have an organic construction that directly emits light and minimises its loss by eradicating certain filters. Since LEDs are physically different units, they can be asked to switch on and off as per the requirement of the display to form a picture. This is known as the Active Matrix system. Hence, an Active Matrix Organic Light Emitting Diode (AMOLED) display can produce deeper blacks by switching off individual LED pixels, resulting in high contrast pictures.
The honest answer is that it depends on the requirement of the user. If you want accurate colours from your display while wanting it to retain its vibrancy for a longer period of time, then any of the two LCD screens are the ideal choice. LTPS LCD display can provide higher picture resolution but deteriorates faster than standard IPS LCD display over time.
An AMOLED display will provide high contrast pictures any time but it too has the tendency to deteriorate faster than LCD panels. Therefore, if you are after greater picture quality, choose LTPS LCD or else settle for AMOLED for a vivid contrast picture experience.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-975451056-a78e63853020468d97d2b5d19d2d9e3d.jpg)
Smartphone displays or displays, in general, have grown leaps and bounds over the years. There was a time when no matter how expensive a phone you would have, it would have the same display technology, that would be found in a mid-range phone - a basic LCD screen. Yes, the resolution and quality would be different, but the underlying technology would be the same.
Cut to 2022, most of your phones now come with some form of an OLED display. Not only have we seen the resolution of displays, especially in mobile phones, tablets and laptops go up drastically, but we have also seen the quality of the displays get a lot better over the years. Rich and vibrant colours, proper inky blacks, low response times, high contrast, and incredible brightness - we have OLED displays to thank for all of these boons.
OLED panels have been around since the 2000s when it was introduced in a car stereo system. Later, when it got a little mainstream, we saw it in some phones, but because it wasn’t cost-effective and did not look anything like the OLEDs of today, we soon got rid of them. After tons of improvements and development, it came to rule the best TVs that money could buy. Now, the display technology is finding its way back into our phones and personal devices, albeit in three distinct forms - OLED, AMOLED & P-OLED.
OLED or organic light-emitting diode is a display technology that runs a current through organic diodes on a glass substrate to create an image. The light-emitting pixels of an OLED display emits blue and yellow light. The yellow and blue light combine to form white light, which then passes through red, green, and blue subpixels in order to produce a single pixel. Unlike LCDs, OLED Panels do not need a separate backlight. This is one of the many reasons, why OLED displays consume much less energy, especially when they’re showing a dark image.
OLED displays have deep, inky blacks, and exceptionally good contrast. When no colour is displayed, there is no light emitted from that portion of the display. This also allows them to create “infinite contrast” or a contrast ratio of 1,000,000:1. That means, the darkest portion of the display, will be a million times darker than the portion that is the brightest. This gives us vivid colours and a better watching experience.
OLED panels, also have a much better response time, which, basically means, that each pixel responds to signal change much quicker than a traditional LCD. This is the refresh rate that manufacturers refer to. It basically means that an OLED panel will be able to change colours 120 times in a second. This gives the pictures that you watch a much more lucid, and smooth appeal.
OLED panels also take up a lot less space than your LCD panels, because they don’t use a panel for the backlight. This also makes them cheaper to make. And because they don’t need a backlight to work, OLED displays can be transparent at times. This has allowed manufacturers to develop in-display fingerprint readers and under-display cameras.
OLED Displays, however, are not perfect. They are prone to much faster degradation from age and UV exposure. Because the images and colours are very bright, on certain portions of the screen, one can often see the remnants or “ghosts” of an image, even when it is not being displayed. This is called burn-in, and it is the single biggest phenomenon that renders OLED panels useless, after a short period of constant use.
OLED panels are cheaper to manufacture, but because they are very thin, and fragile, in order to make a proper display out of it, as in a TV or a mobile phone, you need to use reinforced glass or metal frames. Also, at peak brightness, OLEDs draw more power than a regular LCD.
If you’re buying a premium smartphone with an OLED display, chances are, you’re actually buying an AMOLED Display. AMOLED is an acronym for "Active Matrix OLED," and modern OLED displays found in consumer electronics use an active matrix as opposed to passive matrices found in older OLED displays.
The active matrix or the thin-film transistor arrays used in AMOLED displays are more power efficient than most old OLED displays. Samsung dominates the market of AMOLED displays and has named the best of the best they produce as the Super AMOLED display. AMOLED displays usually combine the benefit of P-OLED displays and your regular OLED displays. They are very durable and versatile, and hence, tend to cost more.
P OLED displays replace glass substrates with ones that are made of polymers or plastic. This makes the panel more shock-resistant, and less prone to breaking. Depending on the kind of polymer being used, P OLED displays can also be flexible, so they can be used in foldable and rollable devices. Because polymer sheets can be manufactured within much higher tolerances than glass, Polymer OLEDs or P OLED displays can be much thinner.
P OLED displays have a few drawbacks. Usually, they aren’t as tack sharp as the modern OLED displays; with that being said, the difference can rarely be spotted. P OLED displays have a higher tendency to burn in




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey