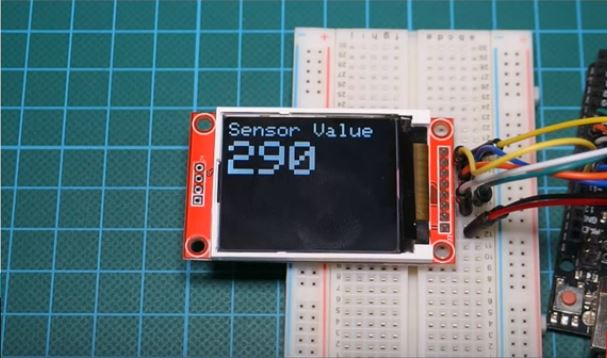
make images for 1.8 tft display free sample

In this guide we’re going to show you how you can use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino. You’ll learn how to wire the display, write text, draw shapes and display images on the screen.
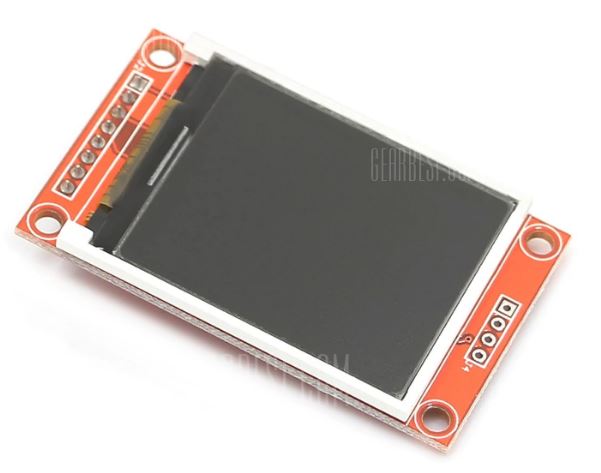
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back. The following figure shows the screen front and back view.
This module uses SPI communication – see the wiring below . To control the display we’ll use the TFT library, which is already included with Arduino IDE 1.0.5 and later.
The TFT display communicates with the Arduino via SPI communication, so you need to include the SPI library on your code. We also use the TFT library to write and draw on the display.
In which “Hello, World!” is the text you want to display and the (x, y) coordinate is the location where you want to start display text on the screen.
The 1.8 TFT display can load images from the SD card. To read from the SD card you use the SD library, already included in the Arduino IDE software. Follow the next steps to display an image on the display:
Note: some people find issues with this display when trying to read from the SD card. We don’t know why that happens. In fact, we tested a couple of times and it worked well, and then, when we were about to record to show you the final result, the display didn’t recognized the SD card anymore – we’re not sure if it’s a problem with the SD card holder that doesn’t establish a proper connection with the SD card. However, we are sure these instructions work, because we’ve tested them.
In this guide we’ve shown you how to use the 1.8 TFT display with the Arduino: display text, draw shapes and display images. You can easily add a nice visual interface to your projects using this display.
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.
Electronics has transited from a work meant for well-trained engineers to something which is dabbled into by people in other fields especially in Arts and related fields. The introduction of platforms like Arduino (which was created for reasons like this), has been one of the main facilitators of this trend which has produced diverse forms of electronics embedded art pieces, from interactive paintings to animatronic sculptures. For today’s tutorial, we will build our own work of “art” – a digital Photo Frame. Photoframes are used to display pictures or artworks and are made from wood, metal and several synthetic material. They were created to hold just one picture/artwork but with digital photo frames, you could have more than one picture stored on the photo frame, switching between them at desired intervals.
Digital Photo frames are usually made up of four main components; a display/screen, a storage device, a microcontroller or microprocessor, and a power supply. For today’s tutorial, we will use the 1.8″ ST7735 based, color TFT as our display and the Arduino nano as the microcontroller. The TFT display is a 1.8″ display with a resolution of 128×160 pixels and can display a wide range of colors ( full 18-bit color, 262,144 shades!). The display uses the SPI protocol for communication and has its own pixel-addressable frame buffer which means it can be used with all kinds of microcontrollers and you only need 4 IO pins. The display module also comes with an SD card slot which we will use as the storage device for this project.
Beside just building the digital photo frame, at the end of this tutorial, you would have also learned how to use the SD card slot on the 1.8″ TFT display module for other projects.
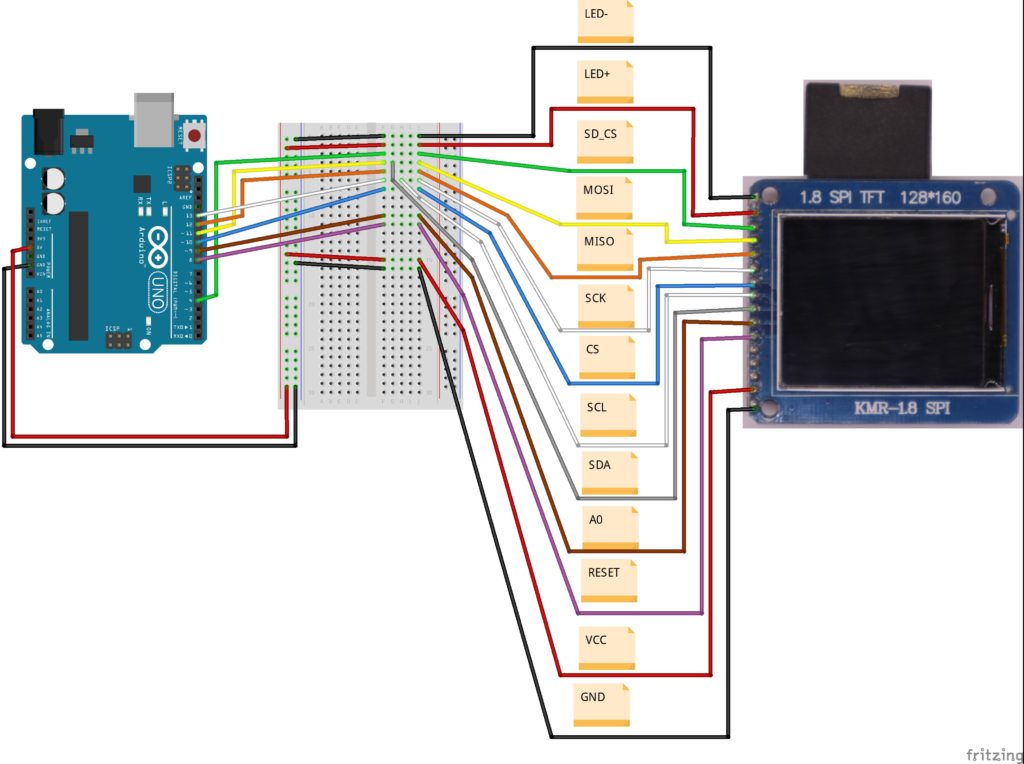
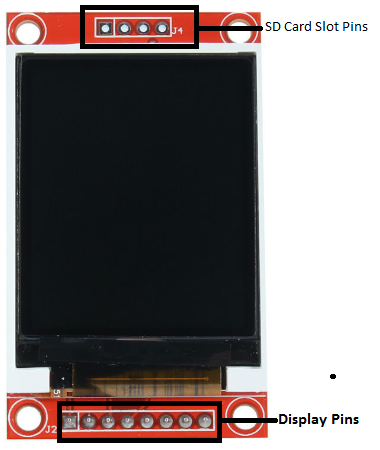
The ST7735 1.8″ TFT display is made up of two set of header pins. The first one at the top consists of 4 pins and are used to interface the SD card slot at the back of the display.
The second set of headers below the screen represent the pins for driving the display itself. However, the SD card slot and the display, both use the SPI protocol for communications with the MCU so they will be connected to the same pins on the Arduino nano. The only difference will be the CS/SS pin as each of them will be connected to a different pin.
For this schematic, we used the Fritzing model of the ST7735 1.8″ TFT display and the arrangement of the pins is slightly different from that of our display. This model has the pins of the SD card slot and the display merged together breaking out only their CS/SS pins.
Go over the schematics one more time to be sure everything is as it should be. More on the use of the 1.8″ TFT display was covered in a previous tutorial here.
The images that will be displayed on the TFT has to be in a bitmap format, thus before the images are copied to the SD card, we need to convert them to the recognizable bitmap form. To do this, I used the free Paint.net software (for windows) but you can use any other image editing software.
Load the images into the software one by one and use the resize tool to reduce its resolution and size to that (160×128 pixels) of the 1.8″ TFT display.
The code for this project is a slightly modified version of the SPI TFT bitmap example shipped with the ST7735 library by Adafruit. Thus the code for this tutorial is heavily reliant on the Adafruit ST7735 and GFX libraries.
With this done, we declare the pins of the Arduino to which the CS pins of the SD card slot and the TFT are connected and also create an object of the Adafruit ST7735 library with the declared pins passed on as arguments.
Next is thevoid setup() function. We start by initializing serial communication which will be used to debug our code. After this, we initialize the TFT and the SDcard, setting the rotation of the TFT to landscape (represented by 1).
Next is the void loop function. Here we simply invoke the bmpDraw function for each of the images we will like to display, setting a suitable delay time between each of the pictures. The bmpDraw function makes it super easy to display images on the TFT. All we need to do is to provide the name of the .bmp file, starting coordinates and it will use that information to fetch the image from the SD card and display on the screen.
Ensure your connections are correct, then upload the code to your Arduino. After a while, you should see the pictures being displayed like a slideshow on the TFT.
The possibilities attached to the concept shared in this tutorial are limitless. You could make the pictures change based on weather, time of the day or gesture.
That’s it for this tutorial. Do let me know if you have any question about it via the comment section. Feel free to also share ideas on cool modifications and additions that could make the project bigger and more useful.
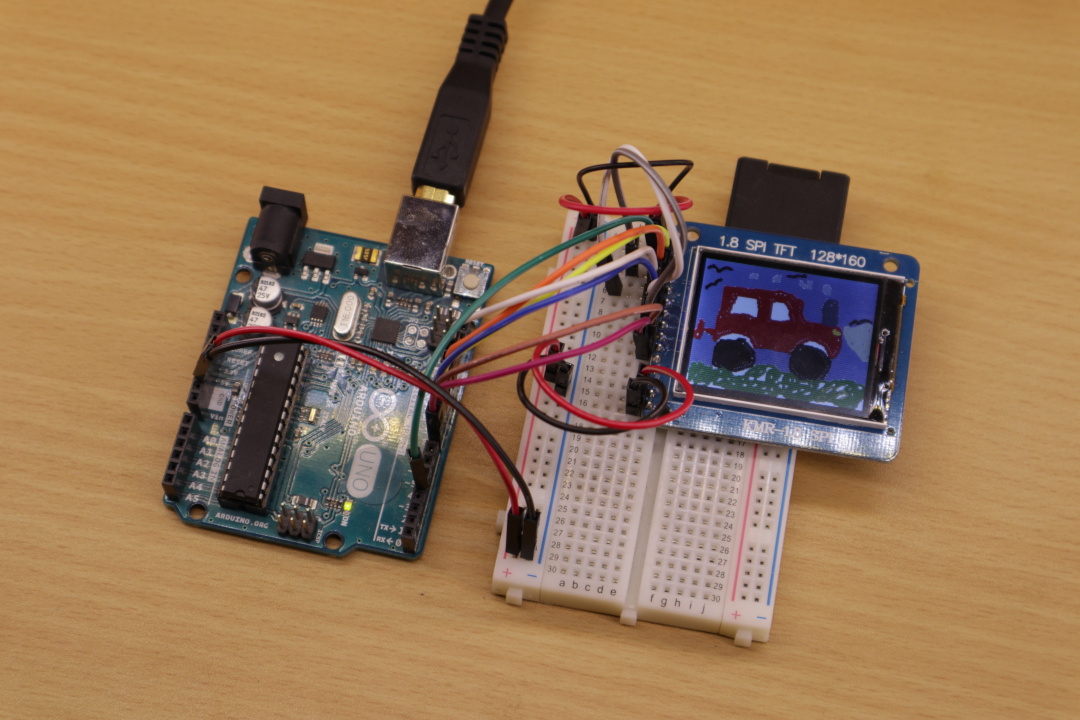
Recently, I had the idea to make a digital picture frame—one of these kinds which load images from SD cards and show each image for some time. I was remembering myself that I already own a small TFT display, the KMR-1.8 SPI, that works out of the box with an Arduino Uno. When I digged up my KMR-1.8 SPI, I realized that it has also an in-built SD card reader. Moreover, I looked up the Internet and found ready-to-use libraries for the in-built SD card reader as well as showing images on the TFT display. For these reasons, I thought making such an digital picture frame will turn out very easy.
When I started to implement my first lines of codes and started to connect my Arduino Uno to the KMR-1.8 SPI, I ran into two major problems. First, the colors of my image file did not match to the colors displayed by the KMR-1.8 (red and blue were interchanged). Second, my first prototypes stopped to work after about 5 minutes. The application started to freeze and showed the same image forever instead of displaying the next image after a chosen time.
I did some research on the Internet and I found out that many people ran into similar problems. The second problem seemed to be caused by some memory leaks in the code. Nevertheless, I did not came across any example code that worked out of the box for my setup. Therefore, I want to share how I made it work.
There exists various versions of so-called “1.8 TFT displays” from different manufacturers. Not all of them are 100% compatible to each other. Therefore, if you own a TFT display and want to use my tutorial to make it work, please check if your TFT display really matches the version I used in this tutorial:
The source code relies on three header files (and libraries): SPI.h (Link), SD.h (Link) and TFT.h (Link). Please make sure that all of them are correctly installed before trying out my source code (In Arduino IDE: Tools -> Manage Libraries…).
I overcame the first problem by not using the default initialization method (“TFTscreen.begin();”) of the TFT library. Instead, I looked up whats inside the “begin”-method. I found a method called “initR” which has a parameter that allows to perform the initialization for a specific chip. Here, the parameter value “INITR_BLACKTAB” worked for me as the colors were then shown correctly. In addition, I call the method “setRotation” with parameter value “1” in order to be conform to the default initialization method. In the end, the code for the setting up the TFT library object looks like this:// ...
I solved the second problem (application freezes after some time) by avoiding any possible memory leak, i.e. to “free” every bit of memory that was reserved before as soon as it is not needed anymore. Therefore, you will find a lot of “close”-method calls as well as some weird string handling. When I wrote the code, I thought I could simplify a few things. However, the memory leak problems came back. So, the code might look weird but it works :)
The code looks for image files (*.BMP) on the SD card and shows each image for 60 seconds. You can change the display time by setting “DELAY_IMAGE_SWAP” to a new value.
Important Note: The image files on the SD card must be stored as BMP with a resolution of 160x128 pixels (width x height). Moreover, long file names and special characters must be avoided.
This new library is a standalone library that contains the TFT driver as well as the graphics functions and fonts that were in the GFX library. This library has significant performance improvements when used with an UNO (or ATmega328 based Arduino) and MEGA.
Examples are included with the library, including graphics test programs. The example sketch TFT_Rainbow_one shows different ways of using the font support functions. This library now supports the "print" library so the formatting features of the "print" library can be used, for example to print to the TFT in Hexadecimal, for example:
The larger fonts are now Run Length Encoded (RLE) so that they occupy less FLASH space, this frees up space for the rest of the sketch. A byproduct of the RLE approach is that the font drawing is also speeded up so it is a win-win situation.
To use the F_AS_T performance option the ILI9341 based display must be connected to an MEGA as follows:MEGA +5V to display pin 1 (VCC) and pin 8 (LED) UNO 0V (GND) to display pin 2 (GND)
TFT_ILI9341 library updated on 1st July 2015 to version 12, this latest version is attached here to step 8:Minor bug when rendering letter "T" in font 4 without background fixed
Anyway now I commented that line, beacuse I am not interested in speed right now. But now the problem seems to be the programation code. the error message is as follows: ( I am using Arduino 1.8.7)
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:101:37: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:106:42: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:118:39: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:121:42: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:151:40: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:163:39: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:176:37: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:183:38: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:188:38: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:193:38: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:198:38: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:205:39: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:210:39: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:215:39: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]
C:\Users\ADMIRAL\Videos\arduino\Libraries\Adafruit_ILI9341_AS\examples\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2\ILI9341_draw_bitmap_v2.ino:220:39: warning: ISO C++ forbids converting a string constant to "char*" [-Wwrite-strings]

To do this, we will useLCD image converter.You can find it here :https://sourceforge.net/projects/lcd-image-converter/Resize your imageto the size of your screen (240x240)

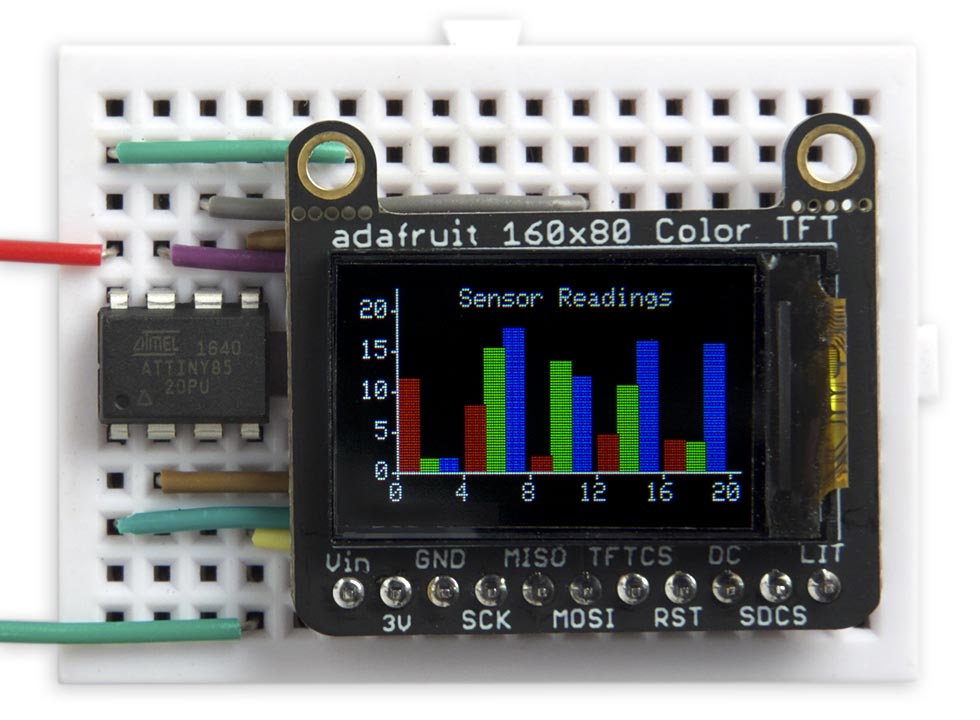
This is a graphics library for the family of small colour TFT displays based on the ST7735 and ST7789 driver chips. These are really nice displays; bright, colourful, available in a variety of useful sizes, and available at low cost from suppliers like Adafruit, AliExpress, or Banggood:
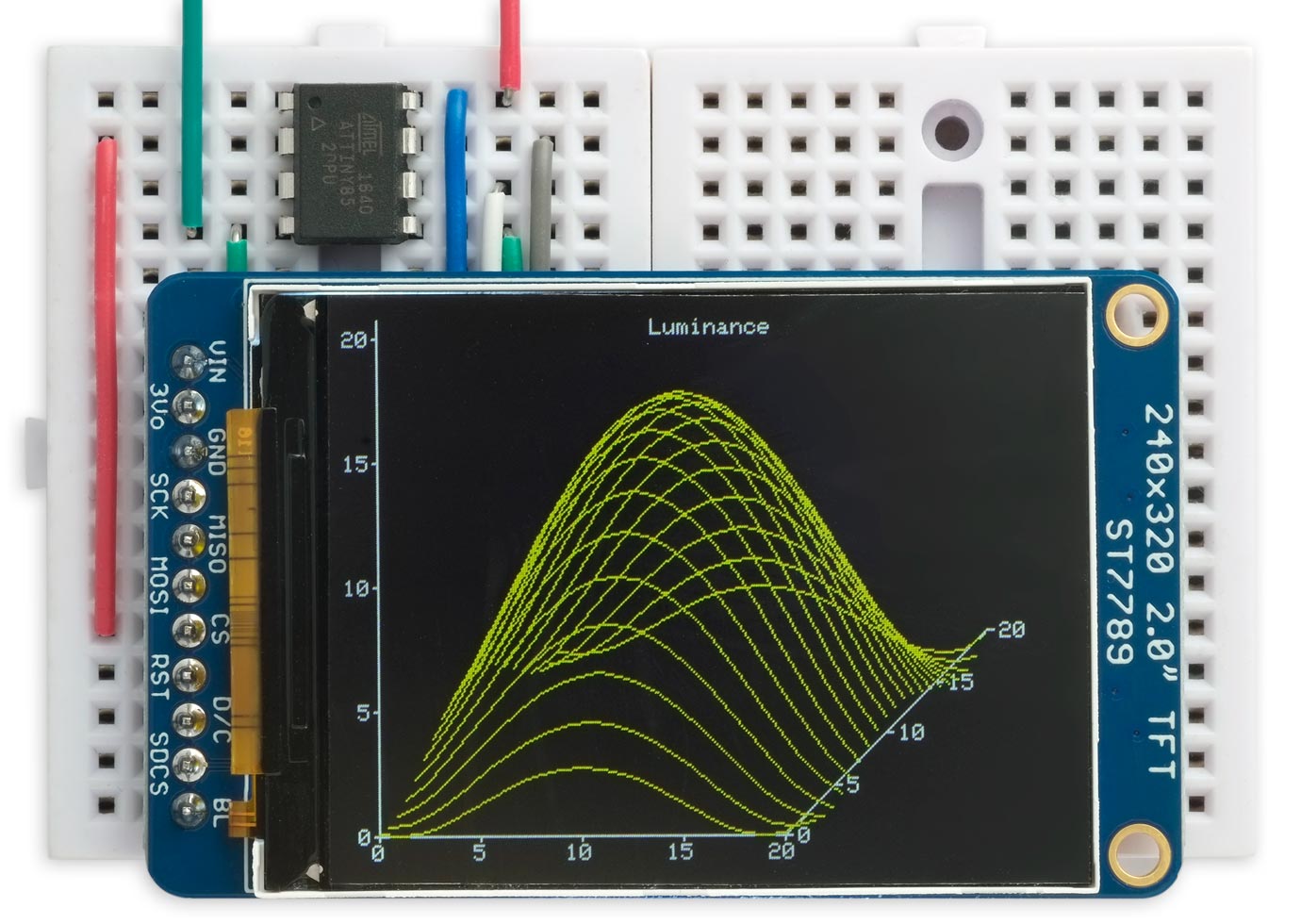
This library allows you to plot points, draw lines, draw filled rectangles, and plot text with an optional scale factor. I"ve included a demo histogram-plotting program that adjusts itself to fit each of the displays I"ve supported.
Unlike most other TFT display libraries this one doesn"t require a memory buffer, allowing it to be run on any processor down to an ATtiny85. The displays are SPI and require four pins to drive the display, leaving one pin free on an ATtiny85 to interface to another device, such as a temperature sensor. If you need more pins choose a larger chip, such as the ATtiny84; see Using the library with other AVR chips at the end of the article for information about how to convert the code for different chips.
I started developing this library for another project that I hope to write about at a later date; in the meantime I thought it would be useful to write it up as a stand-alone article.
I"ve published a library for a colour OLED display in a previous article: Colour Graphics Library. The main difference between the colour TFT displays and the colour OLED displays is that the TFT displays are not self-illuminating, and so need a backlight; they therefore have a slightly higher power consumption. However, they are exceedingly cheap, and they are available in larger sizes than the colour OLED displays.
I wrote an initial version of this library in uLisp, my Lisp interpreter for microcontrollers, which made it easy to experiment with different approaches. I then converted it to C to run on an ATtiny85. I can publish the uLisp version if anyone"s interested.
This library will work with displays based on the ST7735 which supports a maximum display size of 132 (H) x 162 (V), or the similar ST7789 which supports a maximum display size of 240 (H) x 320 (V).
The display driver interfaces to the displays with the longer side as the vertical dimension, which is why the rectangular displays are usually listed with the longer dimension second. My library allows you to rotate the image for any desired orientation.
All the Adafruit breakout boards for these displays include level-shifting circuitry, so they will work with either 5V or 3.3V microcontroller boards. They also include an SD card socket, if that"s of interest to you. The Adafruit boards have pullups on the backlight and reset pins, so the display will work if you leave these pins unconnected.
The pullup resistor from the display"s CS pin is optional; it holds the chip select high to prevent the display from being affected by the ISP signals while programming the ATtiny85.
The different displays are catered for by six constants which specify the size of the display, the offsets relative to the area supported by the display driver, whether the display is inverted, and the rotation value; for example:
Note that on some displays you may also have to change the xoff or yoff value when rotating the display. For example, to rotate the image on the 240x240 displays by 180° use the settings:
To check or adjust the values for each display I ran this program, which draws a one-pixel border around the display area, and plots an "F" to show the orientation:
The ATtiny85 and other AVR processors supports toggling of one or more bits in a port, so provided you set all the pins to their disabled state at startup, for speed the display access routines can simply toggle the appropriate pins to enable or disable them.
The InitDisplay() routine first defines the four display pins as outputs, and takes the SCK, DC, and CS pins high (inactive). It then sends the essential configuration commands to the display.
The display memory stores 18 bits per pixel: 6 bits per colour. However, you can write to the display in three alternative modes, with 12, 16, or 18 bits per pixel. I chose the 16 bit mode, which assigns 5 bits to red, 6 bits to green, and 5 bits blue. It"s the most convenient one to work with as you simply send two bytes to define the colour of each pixel.
The foreground and background colours are defined by the two global variables fore and back. Initially these are set to 0xFFFF, white, and 0, black, respectively:
To clear the display the ClearDisplay() routine sends the appropriate number of zero bytes. The routine temporarily switches to 12-bit colour mode, which reduces the time to clear the display by 25%:
The library includes basic graphics routines for plotting points and drawing lines. These work on a conventional coordinate system with the origin at lower left. For example, on the 80x160 display:
My first version of PlotChar() plotted characters by calling PlotPoint() for each pixel. However, I then tried the following alternative approach which defines an area of the display using the CASET (Column Address Set) and RASET (Row Address Set) commands, and then sends a stream of the appropriate bytes to define the character. This turned out to be over three times faster!
The default value of scale is 1, but you can change it to plot larger characters. After plotting a character PlotChar() moves the plot position to the start of the next character to make it easy to plot several characters in a row without needing to callMoveTo().
By default the ATtiny85 runs at 1MHz. Choose Burn Bootloader to set the fuses for 8MHz operation, or your graphics will run rather slowly, then upload the program using ISP (in-system programming).
14th January 2020: Tested the program with the Adafruit 1.3" 240x240 TFT display, and updated the program to correct a problem when rotating the image on that display.
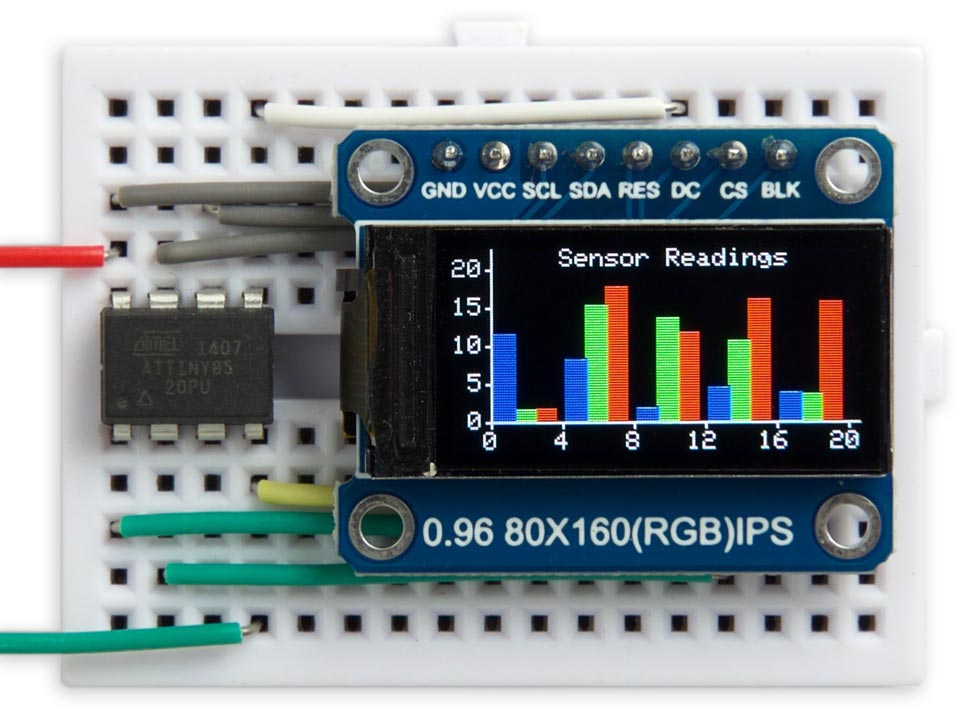
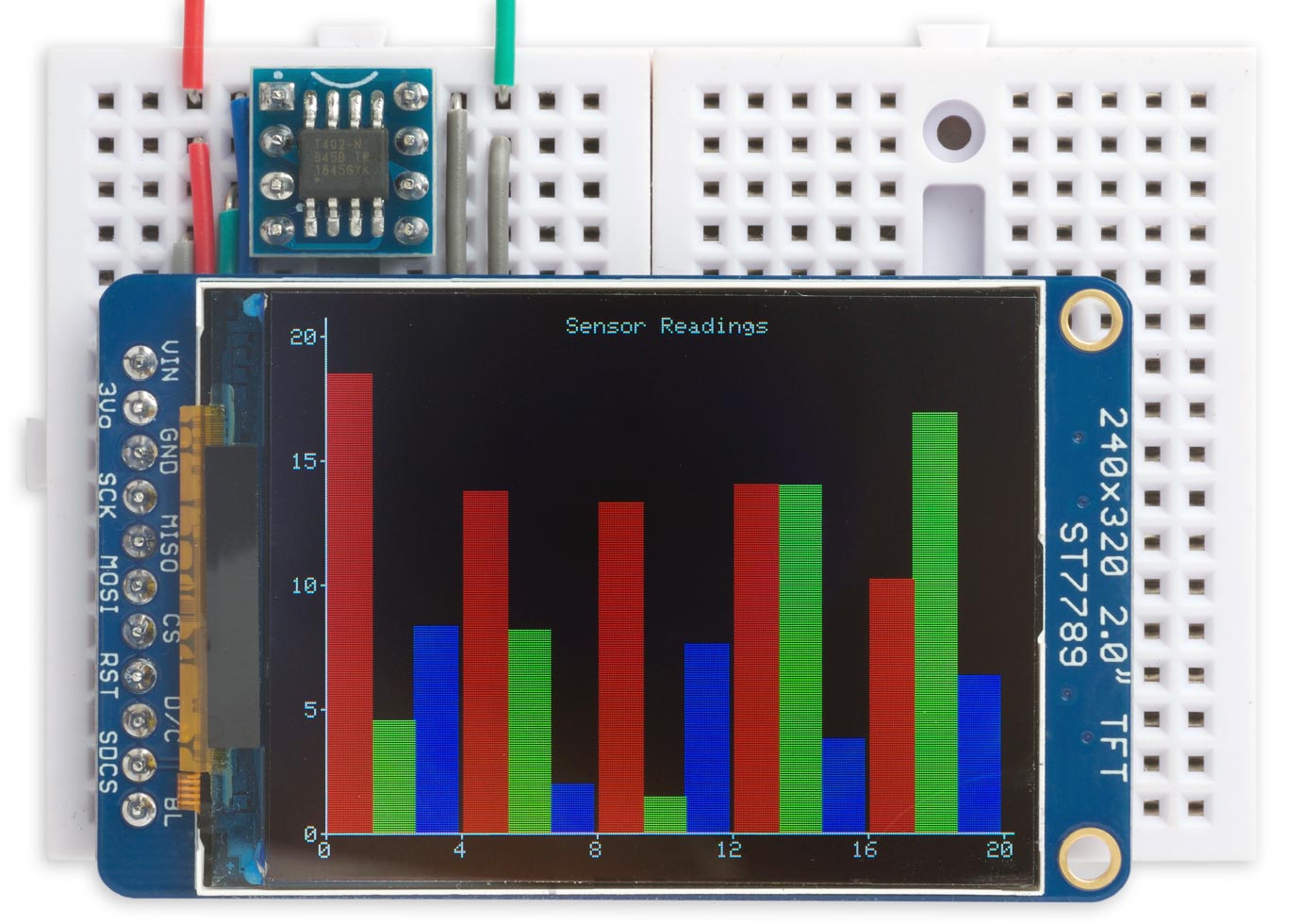
This is a small graphics library, specifically aimed at ATtiny microcontrollers, for the variety of small colour TFT displays available at low cost from suppliers like Adafruit, AliExpress, or Banggood:
It"s an updated version of my Tiny TFT Graphics Library. This latest version of the library supports both the classic ATtiny processors, such as the ATtiny85, and the new 0-series, 1-series, and 2-series ATtiny processors, such as the ATtiny402. Like the original library it allows you to plot points, draw lines, draw filled rectangles, and plot characters and text with an optional scale factor, in 16-bit colour.
This version adds the ability to plot outline rectanges, and outline and filled circles. I"ve included demo curve-plotting and histogram-plotting programs that adjust to fit any display.
This library supports TFT displays that use an SPI interface and require four pins to drive the display. This leaves one pin free on an 8-pin chip such as the ATtiny85 or ATtiny402. If you need more pins choose a larger chip, such as the ATtiny84 or ATtiny404.
Unlike my Compact TFT Graphics Library which uses standard Arduino SPI calls, this library uses direct I/O pin manipulations. This means that you can use any assignment of pins to the four I/O lines needed by the display, and makes it about twice as fast as one using SPI calls. I"ve also added support for some additional displays, so it now supports 16 different TFT displays.
On the classic ATtiny processors, such as the ATtiny85, the library uses the feature that you can toggle one or more bits in a port by writing to the PINB register; for example, to enable or disable the chip-select signal:
So provided you set all the pins to their disabled state at startup, the display routines can simply toggle the appropriate pins to enable or disable them.
The differences between each family of processors are handled by constants to define the pin assignments, and preprocessor macros to define the bit manipulations. If you use the circuits given below you won"t need to change anything, apart from specifying which display you"re using.
The ClearDisplay() routine has been optimised further by realising that we don"t need to keep setting the mosi bit, since to clear the display it is always zero, so the routine only needs to toggle the sck bit the appropriate number of times. I"m grateful to Thomas Scherer for suggesting this.
This library will work with displays based on the ST7735 which supports a maximum display size of 162x132, or the ST7789 and ILI9340/1 which support a maximum display size of 320x240. It includes parameters for the following colour TFT displays:
* These Adafruit displays conveniently all have the same edge-connector layout, so you can make a prototyping board or PCB that will take any of them, such as my Universal TFT Display Backpack.
Some of the AliExpress displays include a LDO 3.3V regulator, but not logic-level translation, so I recommend only interfacing them to a processor running from 3.3V.
The Adafruit displays all include an LDO 3.3V regulator and logic-level translation, so can be safely interfaced to processors powered from either 5V or 3.3V.
On the AliExpress red 160x128 display you need to connect the backlight pin to Vcc to turn it on. This doesn"t seem to be necessary with the other displays.
The library will probably support other TFT displays that use the same ST7735, ST7789, ILI9340/1 driver chips, but you may need to experiment with the parameters to get the image scaled and centered correctly.
The display needs to be connected to the microcontroller via four I/O lines: MOSI, SCK, CS, and DC. You can use any pins for these, but they should all be in the same port. You need to specify the port pin numbers of the pins you are using at the start of the Tiny TFT Graphics Library listing.
The 33kΩ pullup resistor from the display"s CS pin is optional; it is only needed on the AliExpress displays, and holds the chip select high to prevent the display from flickering while programming the ATtiny85.
The different displays are catered for by seven constants which specify the size of the display, the offsets relative to the area supported by the display driver, whether the display is inverted, the rotation value, and the order of the colours; for example:
By default the parameters give the correct orientation assuming you"re using the display with the header pins along the top, except in the case of the larger displays which have the header pins along the shorter edge, in which case the header pins are assumed to be on the left.
To check or adjust the values for each display you can run the TestChart() program, which draws a one-pixel border around the display area, and plots a red "F" to show the orientation:
The library will probably support other TFT displays that use the same driver chips, but you may need to experiment with the parameters to get the image scaled and centered correctly.
The foreground and background colours are defined by the two global variables fore and back. Initially these are set to White (0xFFFF) and Black (0) respectively:
The library includes basic graphics routines for plotting points and drawing lines. These work on a conventional coordinate system with the origin at lower left. For example, on the 80x160 display:
DrawRect() draws an outline rectangle andFillRect() draws a filled rectangle in the foreground colour with width w and height h, and the bottom left corner at the current drawing position:
DrawCircle() draws an outline circle andFillCircle() draws a filled circle in the foreground colour with radius radius, and the centre at the current drawing position:
You can plot larger characters by setting the global variable scale, default value 1. After plotting a character PlotChar() moves the drawing position to the start of the next character to make it easy to plot several characters in a row without needing to call MoveTo().
By default the ATtiny85 runs at 1MHz. Choose Burn Bootloader to set the fuses for 8MHz operation, or your graphics will run rather slowly, then upload the program using an ISP (in-system programming) programmer such as Sparkfun"s Tiny AVR Programmer Board

The ST7789 TFT module contains a display controller with the same name: ST7789. It’s a color display that uses SPI interface protocol and requires 3, 4 or 5 control pins, it’s low cost and easy to use. This display is an IPS display, it comes in different sizes (1.3″, 1.54″ …) but all of them should have the same resolution of 240×240 pixel, this means it has 57600 pixels. This module works with 3.3V only and it doesn’t support 5V (not 5V tolerant).
The ST7789 display module shown in project circuit diagram has 7 pins: (from right to left): GND (ground), VCC, SCL (serial clock), SDA (serial data), RES (reset), DC (or D/C: data/command) and BLK (back light).
As mentioned above, the ST7789 TFT display controller works with 3.3V only (power supply and control lines). The display module is supplied with 3.3V (between VCC and GND) which comes from the Arduino board.
To connect the Arduino to the display module, I used voltage divider for each line which means there are 4 voltage dividers. Each voltage divider consists of 2.2k and 3.3k resistors, this drops the 5V into 3V which is sufficient.
The first library is a driver for the ST7789 TFT display which can be installed from Arduino IDE library manager (Sketch —> Include Library —> Manage Libraries …, in the search box write “st7789” and install the one from Adafruit).
The TFT module is the heart of this product -- it contains all the subsystems that are required to make an image show up. Starting with one of the most obvious features; the LCD screen is a glass panel with small little cells of liquid crystal (LC) material that can be shifted from opaque to clear with an electronic signal (more on how LCDs work). For each of the 128x160 pixels in the screen there are three LC cells and each cell has either a red, green, or blue filter in it to color the light. A pixel gets colored when white light from the LED backlight passes through the filtered cells in varying amounts.
The amount of light passed through is controlled by the signal applied to the liquid crystal cells, but the sheer number of pins and complexity of those signals is totally impractical to control directly with a microcontroller. Fortunately some really smart cookies created a dedicated driver Integrated Circuit (IC) that stores pixel data and puts it on the screen for us. Connections to the driver, as well as the backlight, are broken out along a flexible flat printed circuit (FPC) cable - and that"s where we take over.
The FPC connector is convenient for two reasons. First, it"s extremely simple to (re)connect the display to the breakout board. Second, production of this product is made easier because all soldering can be done in our normal surface mount process.
To disconnect the TFT module just flip up the black locking bar with a finger or pair of tweezers and then gently pull the cable straight out from the connector. To put the cable back in, first make sure that the polarity indicators on the cable (1, 40) match up with those on the board and that the black locking bar is flipped up. Next push the cable in evenly for about 2mm.
The microSD card holder is there to relieve your microcontroller"s poor memory due to having to store hundreds of images of cats, or really whatever you want to keep there. The SD card is connected to the same SPI bus as the display, which in turn keeps the required pin count low.
Out of the box, the TFT will come with a large backing PCB that makes it easy to securely mount the display in a project. If you need a more flexible solution you can remove the display module, snap off half the backing board, and then re-insert the display module. When this is done you"ll be left with the bare minimum frame around the display to more seamlessly integrate with your project.
The pinout of this breakout includes the standard SPI interfaces for both the TFT and the microSD card as well as a few specialty pins. You can power the breakout with either 5V or 3.3V thanks to the onboard voltage regulator and level shifter.
D/C : This is a special signal found in many display controllers. When it is high the incoming data is interpreted as data as opposed to commands when it is low.
TE : Tearing Effect is an optional output from the display to synchronize data writes - to avoid the "Tearing Effect" that is seen when data is changed halfway through a screen refresh

An excellent new compatible library is available which can render TrueType fonts on a TFT screen (or into a sprite). This has been developed by takkaO and is available here. I have been reluctant to support yet another font format but this is an amazing library which is very easy to use. It provides access to compact font files, with fully scaleable anti-aliased glyphs. Left, middle and right justified text can also be printed to the screen. I have added TFT_eSPI specific examples to the OpenFontRender library and tested on RP2040 and ESP32 processors, however the ESP8266 does not have sufficient RAM. Here is a demo screen where a single 12kbyte font file binary was used to render fully anti-aliased glyphs of gradually increasing size on a 320x480 TFT screen:
The following is now deprecated due to the number of issues it can cause in certain circumstances. For ESP32 ONLY, the TFT configuration (user setup) can now be included inside an Arduino IDE sketch providing the instructions in the example Generic->Sketch_with_tft_setup are followed. See ReadMe tab in that sketch for the instructions. If the setup is not in the sketch then the library settings will be used. This means that "per project" configurations are possible without modifying the library setup files. Please note that ALL the other examples in the library will use the library settings unless they are adapted and the "tft_setup.h" header file included. Note: there are issues with this approach, #2007 proposes an alternative method.
Support has been added in v2.4.70 for the RP2040 with 16 bit parallel displays. This has been tested and the screen update performance is very good (4ms to clear 320 x 480 screen with HC8357C). The use of the RP2040 PIO makes it easy to change the write cycle timing for different displays. DMA with 16 bit transfers is also supported.
Support for the ESP32-S2, ESP32-S3 and ESP32-C3 has been added (DMA not supported at the moment). Tested with v2.0.3 RC1 of the ESP32 board package. Example setups:
Smooth fonts can now be rendered direct to the TFT with very little flicker for quickly changing values. This is achieved by a line-by-line and block-by-block update of the glyph area without drawing pixels twice. This is a "breaking" change for some sketches because a new true/false parameter is needed to render the background. The default is false if the parameter is missing, Examples:
New anti-aliased graphics functions to draw lines, wedge shaped lines, circles and rounded rectangles. Examples are included. Examples have also been added to display PNG compressed images (note: requires ~40kbytes RAM).
Frank Boesing has created an extension library for TFT_eSPI that allows a large range of ready-built fonts to be used. Frank"s library (adapted to permit rendering in sprites as well as TFT) can be downloaded here. More than 3300 additional Fonts are available here. The TFT_eSPI_ext library contains examples that demonstrate the use of the fonts.
Users of PowerPoint experienced with running macros may be interested in the pptm sketch generator here, this converts graphics and tables drawn in PowerPoint slides into an Arduino sketch that renders the graphics on a 480x320 TFT. This is based on VB macros created by Kris Kasprzak here.
The RP2040 8 bit parallel interface uses the PIO. The PIO now manages the "setWindow" and "block fill" actions, releasing the processor for other tasks when areas of the screen are being filled with a colour. The PIO can optionally be used for SPI interface displays if #define RP2040_PIO_SPI is put in the setup file. Touch screens and pixel read operations are not supported when the PIO interface is used.
The use of PIO for SPI allows the RP2040 to be over-clocked (up to 250MHz works on my boards) in Earle"s board package whilst still maintaining high SPI clock rates.
DMA can now be used with the Raspberry Pi Pico (RP2040) when used with both 8 bit parallel and 16 bit colour SPI displays. See "Bouncy_Circles" sketch.
The library now supports the Raspberry Pi Pico with both the official Arduino board package and the one provided by Earle Philhower. The setup file "Setup60_RP2040_ILI9341.h" has been used for tests with an ILI9341 display. At the moment only SPI interface displays have been tested. SPI port 0 is the default but SPI port 1 can be specifed in the setup file if those SPI pins are used.
The library now provides a "viewport" capability. See "Viewport_Demo" and "Viewport_graphicstest" examples. When a viewport is defined graphics will only appear within that window. The coordinate datum by default moves to the top left corner of the viewport, but can optionally remain at top left corner of TFT. The GUIslice library will make use of this feature to speed up the rendering of GUI objects (see #769).
An Arduino IDE compatible graphics and fonts library for 32 bit processors. The library is targeted at 32 bit processors, it has been performance optimised for RP2040, STM32, ESP8266 and ESP32 types, other processors may be used but will use the slower generic Arduino interface calls. The library can be loaded using the Arduino IDE"s Library Manager. Direct Memory Access (DMA) can be used with the ESP32, RP2040 and STM32 processors with SPI interface displays to improve rendering performance. DMA with a parallel interface (8 and 16 bit parallel) is only supported with the RP2040.
For other processors only SPI interface displays are supported and the slower Arduino SPI library functions are used by the library. Higher clock speed processors such as used for the Teensy 3.x and 4.x boards will still provide a very good performance with the generic Arduino SPI functions.
"Four wire" SPI and 8 bit parallel interfaces are supported. Due to lack of GPIO pins the 8 bit parallel interface is NOT supported on the ESP8266. 8 bit parallel interface TFTs (e.g. UNO format mcufriend shields) can used with the STM32 Nucleo 64/144 range or the UNO format ESP32 (see below for ESP32).
The library supports some TFT displays designed for the Raspberry Pi (RPi) that are based on a ILI9486 or ST7796 driver chip with a 480 x 320 pixel screen. The ILI9486 RPi display must be of the Waveshare design and use a 16 bit serial interface based on the 74HC04, 74HC4040 and 2 x 74HC4094 logic chips. Note that due to design variations between these displays not all RPi displays will work with this library, so purchasing a RPi display of these types solely for use with this library is NOT recommended.
A "good" RPi display is the MHS-4.0 inch Display-B type ST7796 which provides good performance. This has a dedicated controller and can be clocked at up to 80MHz with the ESP32 (125MHz with overclocked RP2040, 55MHz with STM32 and 40MHz with ESP8266). The MHS-3.5 inch RPi ILI9486 based display is also supported, however the MHS ILI9341 based display of the same type does NOT work with this library.
Some displays permit the internal TFT screen RAM to be read, a few of the examples use this feature. The TFT_Screen_Capture example allows full screens to be captured and sent to a PC, this is handy to create program documentation.
The library supports Waveshare 2 and 3 colour ePaper displays using full frame buffers. This addition is relatively immature and thus only one example has been provided.
The library includes a "Sprite" class, this enables flicker free updates of complex graphics. Direct writes to the TFT with graphics functions are still available, so existing sketches do not need to be changed.
A Sprite is notionally an invisible graphics screen that is kept in the processors RAM. Graphics can be drawn into the Sprite just as they can be drawn directly to the screen. Once the Sprite is completed it can be plotted onto the screen in any position. If there is sufficient RAM then the Sprite can be the same size as the screen and used as a frame buffer. Sprites by default use 16 bit colours, the bit depth can be set to 8 bits (256 colours) , or 1 bit (any 2 colours) to reduce the RAM needed. On an ESP8266 the largest 16 bit colour Sprite that can be created is about 160x128 pixels, this consumes 40Kbytes of RAM. On an ESP32 the workspace RAM is more limited than the datasheet implies so a 16 bit colour Sprite is limited to about 200x200 pixels (~80Kbytes), an 8 bit sprite to 320x240 pixels (~76kbytes). A 1 bit per pixel Sprite requires only 9600 bytes for a full 320 x 240 screen buffer, this is ideal for supporting use with 2 colour bitmap fonts.
One or more sprites can be created, a sprite can be any pixel width and height, limited only by available RAM. The RAM needed for a 16 bit colour depth Sprite is (2 x width x height) bytes, for a Sprite with 8 bit colour depth the RAM needed is (width x height) bytes. Sprites can be created and deleted dynamically as needed in the sketch, this means RAM can be freed up after the Sprite has been plotted on the screen, more RAM intensive WiFi based code can then be run and normal graphics operations still work.
Drawing graphics into a sprite is very fast, for those familiar with the Adafruit "graphicstest" example, this whole test completes in 18ms in a 160x128 sprite. Examples of sprite use can be found in the "examples/Sprite" folder.
If an ESP32 board has SPIRAM (i.e. PSRAM) fitted then Sprites will use the PSRAM memory and large full screen buffer Sprites can be created. Full screen Sprites take longer to render (~45ms for a 320 x 240 16 bit Sprite), so bear that in mind.
The "Animated_dial" example shows how dials can be created using a rotated Sprite for the needle. To run this example the TFT interface must support reading from the screen RAM (not all do). The dial rim and scale is a jpeg image, created using a paint program.
The XPT2046 touch screen controller is supported for SPI based displays only. The SPI bus for the touch controller is shared with the TFT and only an additional chip select line is needed. This support will eventually be deprecated when a suitable touch screen library is available.
The library supports SPI overlap on the ESP8266 so the TFT screen can share MOSI, MISO and SCLK pins with the program FLASH, this frees up GPIO pins for other uses. Only one SPI device can be connected to the FLASH pins and the chips select for the TFT must be on pin D3 (GPIO0).
The library contains proportional fonts, different sizes can be enabled/disabled at compile time to optimise the use of FLASH memory. Anti-aliased (smooth) font files in vlw format stored in SPIFFS are supported. Any 16 bit Unicode character can be included and rendered, this means many language specific characters can be rendered to the screen.
The library is based on the Adafruit GFX and Adafruit driver libraries and the aim is to retain compatibility. Significant additions have been made to the library to boost the speed for the different processors (it is typically 3 to 10 times faster) and to add new features. The new graphics functions include different size proportional fonts and formatting features. There are lots of example sketches to demonstrate the different features and included functions.
Configuration of the library font selections, pins used to interface with the TFT and other features is made by editing the User_Setup.h file in the library folder, or by selecting your own configuration in the "User_Setup_Selet,h" file. Fonts and features can easily be enabled/disabled by commenting out lines.
Anti-aliased (smooth) font files in "vlw" format are generated by the free Processing IDE using a sketch included in the library Tools folder. This sketch with the Processing IDE can be used to generate font files from your computer"s font set or any TrueType (.ttf) font, the font file can include any combination of 16 bit Unicode characters. This means Greek, Japanese and any other UCS-2 glyphs can be used. Character arrays and Strings in UTF-8 format are supported.
The .vlw files must be uploaded to the processors FLASH filing system (SPIFFS, LittleFS or SD card) for use. Alternatively the .vlw files can be converted to C arrays (see "Smooth Font -> FLASH_Array" examples) and stored directly in FLASH as part of the compile process. The array based approach is convenient, provides performance improvements and is suitable where: either use of a filing system is undesirable, or the processor type (e.g. STM32) does not support a FLASH based filing system.
It would be possible to compress the vlw font files but the rendering performance to a TFT is still good when storing the font file(s) in SPIFFS, LittleFS or FLASH arrays.
Anti-aliased fonts can also be drawn over a gradient background with a callback to fetch the background colour of each pixel. This pixel colour can be set by the gradient algorithm or by reading back the TFT screen memory (if reading the display is supported).
The common 8 bit "Mcufriend" shields are supported for the STM Nucleo 64/144 boards and ESP32 UNO style board. The STM32 "Blue/Black Pill" boards can also be used with 8 bit parallel displays.
Unfortunately the typical UNO/mcufriend TFT display board maps LCD_RD, LCD_CS and LCD_RST signals to the ESP32 analogue pins 35, 34 and 36 which are input only. To solve this I linked in the 3 spare pins IO15, IO33 and IO32 by adding wires to the bottom of the board as follows:
If the display board is fitted with a resistance based touch screen then this can be used by performing the modifications described here and the fork of the Adafruit library:
If you load a new copy of TFT_eSPI then it will overwrite your setups if they are kept within the TFT_eSPI folder. One way around this is to create a new folder in your Arduino library folder called "TFT_eSPI_Setups". You then place your custom setup.h files in there. After an upgrade simply edit the User_Setup_Select.h file to point to your custom setup file e.g.:
You must make sure only one setup file is called. In the custom setup file I add the file path as a commented out first line that can be cut and pasted back into the upgraded User_Setup_Select.h file. The ../ at the start of the path means go up one directory level. Clearly you could use different file paths or directory names as long as it does not clash with another library or folder name.
You can take this one step further and have your own setup select file and then you only need to replace the Setup.h line reference in User_Setup_Select.h to, for example:
The library was intended to support only TFT displays but using a Sprite as a 1 bit per pixel screen buffer permits support for the Waveshare 2 and 3 colour SPI ePaper displays. This addition to the library is experimental and only one example is provided. Further examples will be added.
This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks. The action you just performed triggered the security solution. There are several actions that could trigger this block including submitting a certain word or phrase, a SQL command or malformed data.

The display is driven by a ST7735R controller ( ST7735R-specifications.pdf (2.1 MB) ), can be used in a “slow” and a “fast” write mode, and is 3.3V/5V compatible.
Adafruit_ST7735 is the library we need to pair with the graphics library for hardware specific functions of the ST7735 TFT Display/SD-Card controller.
In the file dialog select the downloaded ZIP file and your library will be installed automatically. This will automatically install the library for you (requires Arduino 1.0.5 or newer). Restarting your Arduino software is recommended as it will make the examples visible in the examples menu.
The easiest way to remedy this is by extracting the GitHub ZIP file. Place the files in a directory with the proper library name (Adafruit_GFX, Adafruit_ST7735 or SD) and zip the folder (Adafruit_GFX, Adafruit_ST7735.zip, SD.zip). Now the Arduino software can read and install the library automatically for you.
Basically, besides the obvious backlight, we tell the controller first what we are talking to with the CS pins. CS(TFT) selects data to be for the Display, and CS(SD) to set data for the SD-Card. Data is written to the selected device through SDA (display) or MOSI (SD-Card). Data is read from the SD-Card through MISO.
So when using both display and SD-Card, and utilizing the Adafruit libraries with a SainSmart display, you will need to connect SDA to MOSI, and SCL to SCLK.
As mentioned before, the display has a SLOW and a FAST mode, each serving it’s own purpose. Do some experiments with both speeds to determine which one works for your application. Of course, the need of particular Arduino pins plays a role in this decision as well …
Note: Adafruit displays can have different colored tabs on the transparent label on your display. You might need to adapt your code if your display shows a little odd shift. I noticed that my SainSmart display (gree tab) behaves best with the code for the black tab – try them out to see which one works best for yours.
Low Speed display is about 1/5 of the speed of High Speed display, which makes it only suitable for particular purposes, but at least the SPI pins of the Arduino are available.
After connecting the display in Low Speed configuration, you can load the first example from the Arduino Software (“File” “Example” “Adafruit_ST7735” – recommend starting with the “graphictest“).
Below the code parts for a LOW SPEED display (pay attention to the highlighted lines) – keep in mind that the names of the pins in the code are based on the Adafruit display:
The SD-Card needs to be FAT-16 or FAT-32 formatted, single partition, and the BMP file needs to be placed in the root (ie. not in a directory or anything like that).
You can name your BMP file “parrot.bmp” or modify the Sketch to have the proper filename (in “spitftbitmap” line 70, and in “soft_spitftbitmap” line 74).
#define SD_CS 4 // Chip select line for SD card#define TFT_CS 10 // Chip select line for TFT display#define TFT_DC 9 // Data/command line for TFT#define TFT_RST 8 // Reset line for TFT (or connect to +5V)
#define SD_CS 4 // Chip select line for SD card#define TFT_CS 10 // Chip select line for TFT display#define TFT_DC 9 // Data/command line for TFT#define TFT_RST 8 // Reset line for TFT (or connect to +5V)
As you have seen before the Adafruit_GFX library (supported by the Adafruit_ST7735 library) makes this easy for us – More information can be found at the GFX Reference page.
To use this in your Arduino Sketch: The first 2 characters represent RED, the second set of two characters is for GREEN and the last 2 characters represent BLUE. Add ‘0x’ in front of each of these hex values when using them (‘0x’ designates a hexadecimal value).
This function is used to indicate what corner of your display is considered (0,0), which in essence rotates the coordinate system 0, 90, 180 or 270 degrees.
However, if your application needs your screen sideways, then you’d want to rotate the screen 90 degrees, effectively changing the display from a 128×160 pixel (WxH) screen to a 160×128 pixel display. Valid values are: 0 (0 degrees), 1 (90 degrees), 2 (180 degrees) and 3 (270 degrees).
tft.print("Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Curabitur adipiscing ante sed nibh tincidunt feugiat. Maecenas enim massa, fringilla sed malesuada et, malesuada sit amet turpis. Sed porttitor neque ut ante pretium vitae malesuada nunc bibendum. Nullam aliquet ultrices massa eu hendrerit. Ut sed nisi lorem. In vestibulum purus a tortor imperdiet posuere. ");

In this article, you will learn how to use TFT LCDs by Arduino boards. From basic commands to professional designs and technics are all explained here.
In electronic’s projects, creating an interface between user and system is very important. This interface could be created by displaying useful data, a menu, and ease of access. A beautiful design is also very important.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
In this article, we have used libraries and advanced technics to display data, charts, menu, etc. with a professional design. This can move your project presentation to a higher level.
In electronic’s projects, creating an interface between user and system is very important. This interface could be created by displaying useful data, a menu, and ease of access. A beautiful design is also very important.
There are several components to achieve this. LEDs, 7-segments, Character and Graphic displays, and full-color TFT LCDs. The right component for your projects depends on the amount of data to be displayed, type of user interaction, and processor capacity.
TFT LCD is a variant of a liquid-crystal display (LCD) that uses thin-film-transistor (TFT) technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.
In Arduino-based projects, the processor frequency is low. So it is not possible to display complex, high definition images and high-speed motions. Therefore, full-color TFT LCDs can only be used to display simple data and commands.
In this article, we have used libraries and advanced technics to display data, charts, menu, etc. with a professional design. This can move your project presentation to a higher level.
Size of displays affects your project parameters. Bigger Display is not always better. if you want to display high-resolution images and signs, you should choose a big size display with higher resolution. But it decreases the speed of your processing, needs more space and also needs more current to run.
After choosing the right display, It’s time to choose the right controller. If you want to display characters, tests, numbers and static images and the speed of display is not important, the Atmega328 Arduino boards (such as Arduino UNO) are a proper choice. If the size of your code is big, The UNO board may not be enough. You can use Arduino Mega2560 instead. And if you want to show high resolution images and motions with high speed, you should use the ARM core Arduino boards such as Arduino DUE.
In electronics/computer hardware a display driver is usually a semiconductor integrated circuit (but may alternatively comprise a state machine made of discrete logic and other components) which provides an interface function between a microprocessor, microcontroller, ASIC or general-purpose peripheral interface and a particular type of display device, e.g. LCD, LED, OLED, ePaper, CRT, Vacuum fluorescent or Nixie.
The display driver will typically accept commands and data using an industry-standard general-purpose serial or parallel interface, such as TTL, CMOS, RS232, SPI, I2C, etc. and generate signals with suitable voltage, current, timing and demultiplexing to make the display show the desired text or image.
The LCDs manufacturers use different drivers in their products. Some of them are more popular and some of them are very unknown. To run your display easily, you should use Arduino LCDs libraries and add them to your code. Otherwise running the display may be very difficult. There are many free libraries you can find on the internet but the important point about the libraries is their compatibility with the LCD’s driver. The driver of your LCD must be known by your library. In this article, we use the Adafruit GFX library and MCUFRIEND KBV library and example codes. You can download them from the following links.
By these two functions, You can find out the resolution of the display. Just add them to the code and put the outputs in a uint16_t variable. Then read it from the Serial port by Serial.println(); . First add Serial.begin(9600); in setup().
First you should convert your image to hex code. Download the software from the following link. if you don’t want to change the settings of the software, you must invert the color of the image and make the image horizontally mirrored and rotate it 90 degrees counterclockwise. Now add it to the software and convert it. Open the exported file and copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are sizes of image. you can change the color of the image in the last input.
Upload your image and download the converted file that the UTFT libraries can process. Now copy the hex code to Arduino IDE. x and y are locations of the image. sx and sy are size of the image.
In this template, We converted a .jpg image to .c file and added to the code, wrote a string and used the fade code to display. Then we used scroll code to move the screen left. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We used sin(); and cos(); functions to draw Arcs with our desired thickness and displayed number by text printing function. Then we converted an image to hex code and added them to the code and displayed the image by bitmap function. Then we used draw lines function to change the style of the image. Download the .h file and add it to the folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We created a function which accepts numbers as input and displays them as a pie chart. We just use draw arc and filled circle functions.
while (a < b) { Serial.println(a); j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 255, 255)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
while (b < a) { j = 80 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i = 80 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); j2 = 50 * (sin(PI * a / 2000)); i2 = 50 * (cos(PI * a / 2000)); tft.drawLine(i2 + 235, j2 + 169, i + 235, j + 169, tft.color565(0, 0, 0)); tft.fillRect(200, 153, 75, 33, 0x0000); tft.setTextSize(3); tft.setTextColor(0xffff); if ((a/20)>99)
In this template, We display simple images one after each other very fast by bitmap function. So you can make your animation by this trick. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
In this template, We just display some images by RGBbitmap and bitmap functions. Just make a code for touchscreen and use this template. Download the .h file and add it to folder of the Arduino sketch.
The speed of playing all the GIF files are edited and we made them faster or slower for better understanding. The speed of motions depends on the speed of your processor or type of code or size and thickness of elements in the code.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey