tft display working factory
When compared to the ordinary LCD, TFT LCD gives very sharp and crisp picture/text with shorter response time. TFT LCD displays are used in more and more applications, giving products better visual presentation.
TFT is an abbreviation for "Thin Film Transistor". The colorTFT LCD display has transistors made up of thin films of Amorphous silicon deposited on a glass. It serves as a control valve to provide an appropriate voltage onto liquid crystals for individual sub-pixels. That is why TFT LCD display is also called Active Matrix display.
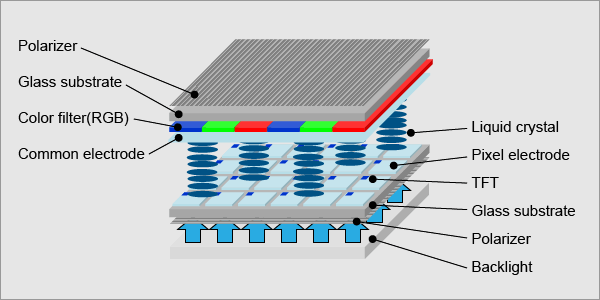
A TFT LCD has a liquid crystal layer between a glass substrate formed with TFTs and transparent pixel electrodes and another glass substrate with a color filter (RGB) and transparent counter electrodes. Each pixel in an active matrix is paired with a transistor that includes capacitor which gives each sub-pixel the ability to retain its charge, instead of requiring an electrical charge sent each time it needed to be changed. This means that TFT LCD displays are more responsive.
To understand how TFT LCD works, we first need to grasp the concept of field-effect transistor (FET). FET is a type of transistor which uses electric field to control the flow of electrical current. It is a component with three terminals: source, gate, and drain. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source.
Using FET, we can build a circuit as below. Data Bus sends signal to FET Source, when SEL SIGNAL applies voltage to the Gate, driving voltage is then created on TFT LCD panel. A sub-pixel will be lit up. A TFT LCD display contains thousand or million of such driving circuits.
Topway started TFT LCD manufacturing more than15 years ago. We produce color TFT LCD display from 1.8 to 15+ inches with different resolutions and interfaces. Here is some more readings about how to choose the right TFT LCD.

There’re more than 300 procedures to produce TFT LCD. The most advanced LCD, in which the array and cell process are highly automatic. Technically, every step in the process can lead to defects, and most of the defects have been eliminated through the development of TFT LCD technology.
Point defect is a kind of defect that some point on your screen don’t display correctly. There are mainly three situations: the point keeps displaying black or whitewhen the screen is working or the point can only display a single color.
For the first two situations, that’s because the circuit on the TFT and CF controlling that defective pixel point is shorted or broken. While the third situation is caused by damaged color pixel.
You may notice there are some screens have uneven display, which means some white area appears in dark picture or vice versa. We call this ‘mura’, a word originated from Japanese.
Mura is very common but it doesn’t affect the screen function severely, however it still bring bad look. Hence, many high end display manufacturers have their own standards of mura, and the displays without mura are of the best quality.

For many years, TFT displays have been the dominating technology in visualization. TFT LCDs are all around in our daily lives — in consumer and automotive applications, in our business environments, in healthcare, and within communication devices, home appliances, and factory automation products. While there are many LCD products available today, they’re not all suitable for every application. This is especially the case for industrial LCD monitors. To determine the best LCD display for your application, it’s important to understand your target market and its unique design issues.
The vast majority of LCD displays are designed for consumer devices such as smartphones, cameras, tablet computers, and gaming devices. But they have very different requirements than those for industrial applications. Due to very competitive pricing and quick production cycles, consumer display modules don’t always incorporate the durability, reliability, and advanced features required to survive in an industrial environment. Product life cycles are also typically much shorter in consumer applications. Screens manufactured for these applications are generally only available for one, in best case two years.
In contrast, display modules for industrial applications require Long product life cycles— often up to ten years or more. Plus, when an industrial module is discontinued by the manufacturer, a successor product should be backward-compatible so as to fit into the existing enclosure without requiring a redesign of the entire system.
The ability to withstand temperature variations as well as shock and vibration is also a key consideration when selecting displays for today’s industrial applications. They must be resilient enough to withstand frequent bumps or jiggles by machine operators and surrounding equipment, and also must be able to handle various operating temperatures.
Industrial displays are typically housed in an enclosure as part of a larger piece of equipment. In these situations, the heat generated by the surrounding equipment gets trapped within the enclosure, which can be detrimental to many displays. Therefore, it’s important to keep the real storage and operating temperature requirements in mind when choosing a display. While measures can be taken to dissipate the generated heat — such as using fans within the enclosure — the most efficient way to ensure compliance with the storage and operating temperature requirements is to select a display that is optimized for these types of environments. Fortunately, improvements in liquid-crystal materials have made it possible to extend the operating temperature ranges of LCDs from –30 to 80°C presently.
It’s important that displays used in industrial applications support clear and precise viewing from multiple angles under a variety of ambient light conditions. The brighter the environment, the more difficult it can be to read a standard transmissive LCD display with a typical brightness of 250 to 300 cd/m2. NVD has developed displays that can perform in the 800-cd/m2-and-higher range by implementing high-efficiency LEDs for the backlight unit– if necessary, in combination with special brightness enhancement films.
Increasing the display’s contrast ratio is another effective way that display manufacturers can improve display readability in bright environments. Typical contrast ratios for non-industrial displays are in the range of 200:1 to 300:1, which may not be sufficient when a machine operator is viewing the display from a distance. Displays with contrast ratios around 500:1 or greater are better suited for industrial environments. Another benefit of this method is that it doesn’t increase power consumption.
Multi-angle readability is another key selection factor. In a typical industrial environment, a machine operator is more likely to be positioned at an off-angle rather than right in front of the screen. Implementing a display designed for consumer applications typically doesn’t work well in this situation, as there is image distortion and color shifting when viewed at an angle. But, a number of technologies have been employed to improve off-angle viewing in displays, making them suitable for industrial applications. Some film-based technologies yield viewing angles of 160º horizontally and 140º vertically, but in some cases, this is still not sufficient. In-plane switching technology (IPS), multi-domain vertical alignment (MVA), and fringe field switching (FFS)offer alternatives. These proprietary technologies are able to achieve viewing angles of almost 90-degrees into all four directions without any color shift.
Size and resolution also play a role in overall readability. Displays between 2 and 15-inch diagonal sizes are used most often in industrial applications. These sizes provide sufficient area to view figures, waveforms, and other graphical data without taking up too much real estate on a piece of equipment.
From an aspect ratio 4:3 initially, industrial displays are now shifting to wide formats with WVGA to WXGA resolutions. The wide-aspect format enables users to view longer waveforms and more data on a single display. These display modules can also be designed to incorporate touch-key functions, allowing equipment manufacturers to skip physical switches and buttons and design HMIs based more on software than hardware.
New Vision Display’s experts are prepared to assist in defining appropriate solutions for all applications and in helping find the right balance between manufacturing cost and performance.

The TFT LCD screen display, for the general masses, is no longer a difficult noun. And it is another after semiconductor could create a large number of emerging technology products of the business turnover, more because of its features, thin so it than using the application scope of the cathode ray tube (CRT, cathode ray tube) display made by wider. Today, I’m going to talk about how the TFT LCD Touch Screen Display Works.
As I mentioned earlier, liquid-crystal displays (LCDs) refer to a bunch produced by using the TFT screen LCD display. Now for LCD displays the name is directed mostly used in notebook computers, or desktop computer applications display. Is the thin film transistor TFT LCD display. Abbreviation of TFT LCD. This kind of display form has two main characteristics, one is a thin film transistor, the other is TFT LCD itself. Let’s talk about the TFT screen itself.
This type of TFT LCD screen was first discovered, had been spent more than one hundred years ago. In 1888 AD, the Austrian botanist Friedrich Reinitzer, found in the observation from the plant refined out of benzoic acid cholesterol (cholesteryl benzoate) found that when the melting behavior of the compound heated to 145.5 ℃, Solid can melt, presents a kind of solid phase and liquid phase between the half gonorrhea melt flow of the liquid. This situation will always maintain ℃ temperature rise to 178.5 degrees, to form a clear isotropic liquid (isotropic liquid).
Its structure is composed of TFT LCD molecules stick together, forming a layer structure. It’s every layer of the molecular long axis direction parallel to each other. And the long axis direction for each layer plane is vertical or a tilt Angle. Due to its structure is very similar to crystals, so they are called phase. The order parameter S (the order parameter) tend to be 1. Type in layered crystal layer and interlayer bonding can fracture because of temperature, so the layer and interlayer sliding more easily. But each layer within the molecular bonding is stronger, so it is not easy to be interrupted. Therefore in the context of the monolayer, Its arranged orderly and viscosity is bigger. If we use the macroscopic phenomenon to describe the physical properties of liquid crystal, we can make a group of regional average points as the liquid crystal molecules are pointing in the direction of the arrow (director), which is the direction of a group of liquid crystal molecules regional average. And with lamellar liquid crystal, because of its structure, the TFT LCD molecules will cambium-like so can point to a vector of different classification of the different lamellar liquid crystal again. When the long axis of the liquid crystal molecules are vertical stand, Call it “Sematic A phase.” if stand long axis direction of the TFT LCD molecules have some Angle of tilt (tilt), call it “Sematic C phase”. In A, C and other letters to name, which was discovered in accordance with the order to address, and so on, there should be A “Semantic phase B is.” but later found A deformation phase B is C phase, And the liquid crystal molecules in the structure layer by layer, in addition to each layer of TFT LCD molecules have tilt Angle, the tilt Angle between layer by layer will form a helical structure.
Nematic is a Greek word, the word mean in the thread is the same as in English. Mainly because with the naked eye to observe the liquid crystal, it looks like a silk pattern. The LCD screen molecules on the space of the regular arrangement of one dimension, all rod long axis of the liquid crystal molecules will choose a particular direction (that is, pointing vector) as the main shaft and arranged parallel to each other. And don’t like lamellar liquid crystal has a layered structure. Compared with the layer column type liquid crystal alignment is no order, That is to say, its order parameter S is smaller than the lamellar liquid crystal, and its viscosity is smaller, so it is easier to flow (its flow mainly comes from the free movement of molecules in the long axis direction). Linear liquid crystal is the common TFT LCD display screen TN(Twisted nematic) type liquid crystal.
If we are according to the molecular weight of high and low points can be divided into liquid crystal polymer (polymer liquid crystal, the polymer in many of the liquid crystal molecules) and low molecular liquid crystal. This kind of classification of TFT LCD belongs to the application of the low molecular liquid crystal. If the reasons for the formation of liquid crystal state, because it can be divided into type temperature formation of liquid crystal state to a liquid crystal (thermotropic), and because of the concentration and the formation of a liquid crystal state type lyotropic liquid crystal (lyotropic).
The solution so types lyotropic TFT screen molecules in the appropriate solvents reaches a certain critical concentration, the formation of liquid crystal state. Type lyotropic liquid crystal is one of the best examples that is soap. When soap bubbles in the water will not be at once into a liquid, and the bubble in the water for a long time, after the formation of white matter, is its liquid crystal state.
Due to the structure of the liquid crystal molecules for different parties (Anisotropic), so caused by the photoelectric effect will vary because of a different direction, in short, that is, the liquid crystal molecules in the dielectric coefficient and refractive index, and so on photoelectric properties have different sex, so we can use these properties to change the intensity of the incident light, so that the formation of gray-scale, to apply on the display component. We’ll discuss below, is one of the characteristics of liquid crystal belongs to the optical and electrical related, about the following items:
Our dielectric coefficient can be separated into two directions respectively is epsilon / / (and point to parallel component) and epsilon coming (a component perpendicular to the pointing vector). When the epsilon / / > epsilon coming then called the dielectric coefficient of different parts of LCD, can be used in parallel coordination. And epsilon / / < epsilon is called the dielectric coefficient of the different part coming negative type of TFT screen, only can be used in vertical coordination will need the photoelectric effect. When the applied electric field, the liquid crystal molecules will vary with dielectric coefficient is positive or negative, To determine whether the orientation of the liquid crystal molecules is parallel or perpendicular to the electric field, to determine whether the light penetrates. Now on most commonly used type TN LCD TFT LCD that belongs to the dielectric coefficient are type liquid crystal. When the dielectric coefficient of square difference Δ epsilon (= epsilon / / – epsilon) comes, the greater the LCD of the critical voltage (threshold voltage) will be smaller. So the LCD can be in the low voltage operation.
For example, the elastic constant (kappa 11, kappa 22, kappa 33) contains the three most important constants: kappa 11 is the elastic constant at splay, kappa 22 is the elastic constant at the twist. Kappa 33 refers to predominating the elastic constants of bending (bend). The other as the coefficient of viscosity (viscosity coefficients and eta), will affect the rotational speed of the liquid crystal molecules with reaction time (response time), its value as small as possible. But this feature is affected by temperature is the largest. In addition to magnetic susceptibility (magnetic susceptibility), but also because of liquid crystals of different sex, Divided into c / / c coming. And the difference of magnetic susceptibility is defined as Δ c = c / / – c coming. In addition to the conductance coefficient (conductivity), and so on the photoelectric properties. Liquid crystal properties of the most important are the dielectric coefficient and refractive index of liquid crystal. The dielectric coefficient is determined liquid crystal under the influence of the electric field to the characteristics of the liquid crystal molecules, while the refractive index is liquid crystal in the light of its important parameters influencing the light path. The LCD is in using the liquid crystal itself of these features, the appropriate use of voltage, to control the rotation of the TFT LCD molecules, in turn, affect the direction of the light, to form different grayscale, a tool for displaying images. Of course, LCD itself is not alone as the monitor, also need other materials to help, Below, we will introduce the composition of various materials and operating principle of TFT LCD display.
I remember in high school physics class, when to teach the relevant physical properties of light, to do a lot of physical experiments, the purpose is to prove that light is a wave. And the marching direction of light waves, and the electric field and magnetic field perpendicular to each other. Light itself of the electric field and magnetic field component at the same time also is perpendicular to each other. That is to say with the electric field and magnetic field component direction, each other is two parallel to each other. (see figure 7) and the role of the polarizing film is like a fence, usually will be cut off a component perpendicular to the fence, With a fence parallel component only permitted through. So if we picked up a piece of the light polarization slabs, feel like wearing sunglasses, the light became dark. But if the two pieces of polarizing film ideas together, it won’t be the same. When you rotate the two pieces of the relative Angle of the polarizing film, you will find that as the relative Angle is different, the brightness of the light will be more and darker. When two polaroids fence Angle perpendicular to each other, Light was completely failing. (see figure 8) and a liquid crystal display is to use this feature. Use upper and lower two pieces of fences between perpendicular slant plate, filled with liquid crystal, recycle electric field control liquid crystal rotation, to change the direction of light, so that different electric field sizes, can form different gray-scale brightness.
The upper and lower two layers of glass are mainly to grip the LCD with. Below the glass layer with Thin film transistor (thin film transistor, TFT screen), while the layer above the glass with a Color filter (Color filter). If you notice (see figure 3), these two pieces of glass are in contact with the side of the LCD screen, not smooth, but with jagged grooves. The main purpose of the groove with the hope of a long rod, liquid crystal molecules will line up along the grooves. In this way, Liquid crystal molecules are arranged neatly. Because if it is smooth and flat, the arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules will not neat, causing light scattering, forming a light-leaking phenomenon. In fact, this is just a theory that told us to put the glass and LCD interface, complete processing so that the arrangement of liquid crystal has a certain order. But in the actual manufacturing process, and can not be with such a groove, the distribution of glass is made usually in glass coating on the surface layer of the PI (polyimide), and then a cloth to do the action of friction (rubbing), In order to make the surface molecules of PI no longer be scattered and arranged in a fixed and uniform direction, this layer of PI is called the coordination membrane, and its function is just like the grooves in the glass in FIG. 3, which provides the interface conditions for the uniform arrangement of liquid crystal molecules and allows the liquid crystals to be arranged in a predetermined order.
The STN LCD and TN LCD are very similar in structure, the main difference between TN LCD, the arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules, the rotation angle from top to bottom. A total of 90 degrees and type the STN LCD liquid crystal molecules are arranged, the rotation angle will be greater than 180 degrees, usually is 270 degrees. (see figure 12) because of its rotation Angle is different, its characteristics different. We from figure 13 TN type and type the STN LCD voltage of the transmittance curve can know, when the voltage is low, the light penetration rate is very high. With a high voltage, the light of the penetration rate is very low. So they belong to the Normal White polaroids configuration. When the voltage in the middle position, the change of type TN LCD curve is flat, and the change of the STN LCD type curve is steep. So in TN type LCD, when transmittance change from 90% to 10%, corresponding to the voltage difference is larger than the STN LCD. We mentioned before, in the liquid crystal display, The different characteristics of TN and STN will result in TN type LCD, which has more grayscale changes than STN type LCD, so generally TN type LCD has 6~8 bits of changes. It is 64 ~ 256 gray-scale changes. Type the STN LCD for a maximum of 4 bits are only 16 orders of gray-scale changes. In addition, the STN type and TN LCD has a different place is the reaction time (response time) general type the STN LCD it’s response time to type in more than 100 ms and TN LCD its response time is 30 ~ 50 ms as shown in the image change quickly for the STN LCD type ghosting effect phenomenon is easy to happen.
TFT LCD Chinese translation of the name is called a thin film transistor liquid crystal display, from the beginning, we mentioned LCD voltage control is needed to produce gray. And the use of a thin-film transistor to generate the voltage, to control the transition of liquid crystal display, is called a TFT LCD. From the point of the cross-section structure of figure 8, between upper and lower two layers of glass, with LCD, will form a parallel plate capacitor, we call it the CLC (capacitor of liquid crystal). Its size is about 0.1 m3, But on the practical application, the capacitance and unable to keep the voltage to the next time to update the data in the picture.
That is to say, when TFT is good to the capacitor charging power, it is impossible to maintain voltage, until the next TFT this point charge again. (in general of 60 Hz screen update frequency, need time to keep about 16 ms.) as a result, there were changes in voltage, displayed gray scale is not correct. Therefore generally on the design of the panel, we will add a storage capacitor CS (storage capacitor is about 0.5 pF). So charged electric voltage can keep until the next update screen. But the right, long on the glass TFT itself, just use a transistor to make the switch. Its main work is to determine the LCD source voltage on the driver whether to charge to this point. As for this point more charge to high voltage, so as to show how the gray-scale. It is outside of the LCD source driver.
If you have a chance, take a magnifying glass, close to the LCD screen. You will find that as shown in figure 9 shows. We know that red, blue and green, are the so-called primary colors. That is to say, using the three kinds of color, can produce a variety of different colors. In a lot of flat-panel displays, this principle is used to show the color. We put the RGB 3 kinds of color, is divided into independent three points, each has different gray-scale changes, then the three neighboring RGB display point, as the basic unit of a display, Pixel is that this a pixel, and can have different color changes. Then for a need for a 1024 * 768 resolution display screen, we just let the composition of the flat panel display with 1024 * 768 pixels, can show a picture of the right. In figure 9, each point between the Black part of RGB is called the Black matrix. We can find that looking back on it in figure 8Black matrix is mainly used to cover do not intend to previous to light part. Such as some ITOs walk the line, or Cr/Al walk the line or are part of a TFT. This is why we in figure 9, the highlight of each RGB, it seems, is not a rectangle, and also on the top left corner is a piece of black matrix cover part, this part of a black missing Angle is the location of the TFT.
The CRT screen, it is using a high-speed electron gun that emits electrons, hits the phosphors on the silver screen, so as to produce the light, to show the picture. LCD itself, however, can only control the brightness of the light through, no glowing function itself. Therefore, a liquid crystal display must be combined with a backplate, to provide high brightness, brightness, and uniform distribution of the light source. We can see in figure 14, of the backplate of the main parts are CCFL (cold cathode tube), reflex plate, guide plate, prism sheet, Diffuser plate, and so on. Tubes are the main light-emitting parts, by a light guide, everywhere. The light distribution and baffle will be limited only to the TFT LCD light direction. Finally, by prism sheet and help diffuser, the light evenly distributed to all areas, provide TFT LCD a bright light. While TFT LCD is borrowed by the rotation of the voltage-controlled liquid crystal, control through the brightness of the light, so as to form different grayscale.
A very important specification of LCD is brightness, and the most important factor to determine the brightness is the opening rate. What is the opening rate? Is simple light can pass through the effective area proportion. 17, let’s look at the picture to the left of figure 17 is an LCD display from directly above or below the past structure. When the light is emitted through the backplate, not all of the light can be through the panel, like for LCD source driver chip and the gate driver chip signal line, and TFT itself, the stored voltage is the use of storage capacity, etc. These places besides incomplete pervious to light, but also because the light through these places is not under voltage control, to display the correct gray-scale, so have to use the black matrix to cover, in order to avoid interference to other correct brightness of the light area. So the effective area of the previous to light, it’s just like figure 17 shows area on the right. This piece of the effective area of the previous to light and the ratio of the total area is called the opening rate.
STONE is industrial screen manufacturers, provide a full range of 3.5 inches to 15.1 inches of small and medium-size standard quasi TFT LCD module, TFT screen module, TFT display module, display industry, industrial LCD screen, under the sunlight visually highlight TFT LCD display, industrial custom TFT screen, TFT LCD screen-wide temperature, industrial TFT LCD screen, touch screen industry. The TFT LCD module is very suitable forindustrial control equipment, medical instruments, POS system, electronic consumer products, vehicles, and other products.

Important technical improvements of LCD, such as LED backlighting and wide viewing Angle, are directly related to LCD. And account for an LCD display 80% of the cost of the LCD panel, enough to show that the LCD panel is the core part of the entire display, the quality of the LCD panel, can be said to directly determine the quality of an LCD display.
The production of civil LCD displays is just an assembly process. The LCD panel, the main control circuit, shell, and other parts of the main assembly, basically will not have too complex technical problems.
In addition, there is a driving IC and printed circuit board beside the LCD panel, which is mainly used to control the rotation of LCD molecules in the LCD panel and the transmission of display signals. The LCD plate is thin and translucent without electricity. It is roughly shaped like a sandwich, with an LCD sandwiched between a layer of TFT glass and a layer of colored filters.
First of all, the motion and arrangement of LCD molecules need electrons to drive them. Therefore, on the TFT glass, the carrier of LCD, there must be conductive parts to control the motion of LCD. In this case, we use ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) to do this.ITO is transparent and also acts as a thin-film conductive crystal so that it doesn’t block the backlight.
The different arrangement of LCD molecules and the rapid motion change can ensure that each pixel displays the corresponding color accurately and the image changes accurately and quickly, which requires the precision of LCD molecule control.ITO film needs special treatment, just like printing the circuit on the PCB board, drawing the conductive circuit on the whole LCD board.
First, the ITO film layer needs to be deposited on the TFT glass, so that there is a smooth and uniform ITO film on the whole TFT glass. Then, using ionized water, the ITO glass is cleaned and ready for the next step.
This completes the previous Array process. It is not difficult to see from the whole process that ITO film is deposited, photoresist coated, exposed, developed, and etched on TFT glass, and finally, ITO electrode pattern designed in the early stage is formed on TFT glass to control the movement of LCD molecules on the glass. The general steps of the whole production process are not complicated, but the technical details and precautions are very complicated, so we will not introduce them here. Interested friends can consult relevant materials by themselves.
The glass that the LCD board uses makes a craft also very exquisite. (The manufacturing process flow of the LCD display screen)At present, the world’s largest LCD panel glass, mainly by the United States Corning, Japan Asahi glass manufacturers, located in the upstream of the production of LCD panel, these manufacturers have mastered the glass production technology patents. A few months ago, the earthquake caused a corning glass furnace shutdown incident, which has caused a certain impact on the LCD panel industry, you can see its position in the industry.
As mentioned earlier, the LCD panel is structured like a sandwich, with an LCD sandwiched between the lower TFT glass and the upper color filter. The terminal Cell process in LCD panel manufacturing involves the TFT glass being glued to the top and bottom of a colored filter, but this is not a simple bonding process that requires a lot of technical detail.
After the TFT glass substrate is cleaned, a sealant coating is applied to allow the TFT glass substrate to be bonded to the color filter and to prevent LCD outflow.
Finally, the conductive adhesive is applied to the frame in the bonding direction of the glass of the color filter to ensure that external electrons can flow into the LCD layer. Then, according to the bonding mark on the TFT glass substrate and the color filter, two pieces of glass are bonded together, and the bonding material is solidified at high temperatures to make the upper and lower glasses fit statically.
When making LCD panel, must up and down each use one, and presents the alternating direction, when has the electric field and does not have the electric field, causes the light to produce the phase difference and to present the light and dark state, uses in the display subtitle or the pattern.
The rear Module manufacturing process is mainly the integration of the drive IC pressing of the LCD substrate and the printed circuit board. This part can transmit the display signal received from the main control circuit to the drive IC to drive the LCD molecules to rotate and display the image. In addition, the backlight part will be integrated with the LCD substrate at this stage, and the complete LCD panel is completed.
Next is the drive IC press. The main function of the drive IC is to output the required voltage to each pixel and control the degree of torsion of the LCD molecules. The drive IC is divided into two types. The source drive IC located in the X-axis is responsible for the input of data. It is characterized by high frequency and has an image function. The gate drive IC located in the Y-axis is responsible for the degree and speed of torsion of LCD molecules, which directly affects the response time of the LCD display. However, there are already many LCD panels that only have driving IC in the X-axis direction, perhaps because the Y-axis drive IC function has been integrated and simplified.
LCD (LC) is a kind of LCD, which has the properties of light transmission and refraction of solid Crystal, as well as the flow property of Liquid. It is because of this property that it will be applied to the display field.
However, LCD does not emit light autonomously, so the display equipment using LCD as the display medium needs to be equipped with another backlight system.
First, a backplate is needed as the carrier of the light source. The common light source for LCD display equipment is CCFL cold cathode backlight, but it has started to switch to an LED backlight, but either one needs a backplate as the carrier.
At the top of the diffusion plate, there will be 3~4 diffuser pieces, constantly uniform light to the whole surface, improve the uniformity of light, which is directly related to the LCD panel display effect. Professional LCD in order to better control the brightness uniformity of the screen, panel procurement, the later backlight control circuit, will make great efforts to ensure the quality of the panel.

In this article, we’ll be covering how TFT displays work, the main differences between TFT and LCD, their typical display specifications and also outline a list of common applications where TFT displays are used.
If you’ve ever purchased a computer monitor or a television, then you’ll likely have heard of the terms TFT and LCD. They stand for thin-film-transistor and liquid-crystal display respectively and are the most common display technologies used in not just monitors and televisions, but also in cameras, GPS devices, tablets, medical equipment and even aircraft computers.
Groups of these molecules form a pixel, a word invented from the term “picture element”. It’s a unit of programmable colour on an LCD display that varies in size depending on a number of conditions, such as the current resolution of the display. Pixels contain red, green and blue colour filters and the molecules are twisted to release a certain amount of each light to create millions of different colour combinations.
Early LCD displays used a matrix of pixels known as passive matrix. This means that each individual pixel is controlled by sending an electrical charge to the row and column that it’s found in. Unfortunately, images on LCD displays were often blurry when the pixels needed to be switched often, such as during high-action scenes, due to the limited number of electrical charges that could be sent in a single second. In addition, the electrical charge would often interfere with adjacent pixels, causing a defect known as crosstalk.
In contrast, LCD displays today use an active matrix of pixels which contains a sheet of thin-film transistors. Each pixel in an active matrix is paired with a transistor that includes capacitors that give each subpixel the ability to retain their charge instead of requiring an electrical charge sent each time it needed to be changed. This means that TFT displays are more responsive than regular LCD monitors. TFT displays are often called TFT-LCD monitors because the two technologies are used together to produce a clear and non-blurry image.
Due to the use of an active matrix of pixels, TFT displays have faster response times which means clearer pictures and less blurring, and also provide more vibrant colours that can be controlled with precision thanks to the thin-film transistors.
TFT displays from GSR Technology come in various different designs and specifications. Here is a list of specifications that are typically listed and their definitions:
Size or format is used to describe the physical distance between opposite corners of a display, usually expressed in inches and often referred to as the physical image size.
Refresh rate is expressed in Hertz and is often included at the end of the resolution specification. Commonly referred to as vertical refresh rate, it is used to measure the number of times a second that the display can update its buffer. Normal displays operate at 60 Hz.
Brightness or luminance is a measurement of luminance and is expressed in nits. Between 200 and 300 nits is where an average display sits, whereas 700 nits offer far greater contrast, resulting in sharper picture quality.
Display resolution will drastically affect the image quality of the display but also require more processing power in order to update the buffer at the optimal refresh rate offered by the panel. Resolution does not necessarily affect the size of the panel itself. However, larger panels with lower resolutions tend to have visible pixels and will create a blurrier image if high-resolution images are displayed. Here are some of the most common display resolutions and their aspect ratios:
Another factor in TFT displays is the range of operating temperatures it can cope with. This is especially important in industrial and automotive uses where equipment surrounding the TFT display can affect the picture quality. Since heat from electrical currents is used to change the orientation of the molecules in each subpixel, outside heat sources can turn the liquid crystals inside a TFT-LCD display into a real liquid due to their sensitivity to temperature changes.

A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a variant of a liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technologyactive matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments.
In February 1957, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA implemented Wallmark"s ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium sulfide. The idea of a TFT-based liquid-crystal display (LCD) was conceived by Bernard Lechner of RCA Laboratories in 1968. In 1971, Lechner, F. J. Marlowe, E. O. Nester and J. Tults demonstrated a 2-by-18 matrix display driven by a hybrid circuit using the dynamic scattering mode of LCDs.T. Peter Brody, J. A. Asars and G. D. Dixon at Westinghouse Research Laboratories developed a CdSe (cadmium selenide) TFT, which they used to demonstrate the first CdSe thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD).active-matrix liquid-crystal display (AM LCD) using CdSe TFTs in 1974, and then Brody coined the term "active matrix" in 1975.high-resolution and high-quality electronic visual display devices use TFT-based active matrix displays.
The liquid crystal displays used in calculators and other devices with similarly simple displays have direct-driven image elements, and therefore a voltage can be easily applied across just one segment of these types of displays without interfering with the other segments. This would be impractical for a large display, because it would have a large number of (color) picture elements (pixels), and thus it would require millions of connections, both top and bottom for each one of the three colors (red, green and blue) of every pixel. To avoid this issue, the pixels are addressed in rows and columns, reducing the connection count from millions down to thousands. The column and row wires attach to transistor switches, one for each pixel. The one-way current passing characteristic of the transistor prevents the charge that is being applied to each pixel from being drained between refreshes to a display"s image. Each pixel is a small capacitor with a layer of insulating liquid crystal sandwiched between transparent conductive ITO layers.
The circuit layout process of a TFT-LCD is very similar to that of semiconductor products. However, rather than fabricating the transistors from silicon, that is formed into a crystalline silicon wafer, they are made from a thin film of amorphous silicon that is deposited on a glass panel. The silicon layer for TFT-LCDs is typically deposited using the PECVD process.
Polycrystalline silicon is sometimes used in displays requiring higher TFT performance. Examples include small high-resolution displays such as those found in projectors or viewfinders. Amorphous silicon-based TFTs are by far the most common, due to their lower production cost, whereas polycrystalline silicon TFTs are more costly and much more difficult to produce.
The twisted nematic display is one of the oldest and frequently cheapest kind of LCD display technologies available. TN displays benefit from fast pixel response times and less smearing than other LCD display technology, but suffer from poor color reproduction and limited viewing angles, especially in the vertical direction. Colors will shift, potentially to the point of completely inverting, when viewed at an angle that is not perpendicular to the display. Modern, high end consumer products have developed methods to overcome the technology"s shortcomings, such as RTC (Response Time Compensation / Overdrive) technologies. Modern TN displays can look significantly better than older TN displays from decades earlier, but overall TN has inferior viewing angles and poor color in comparison to other technology.
Most TN panels can represent colors using only six bits per RGB channel, or 18 bit in total, and are unable to display the 16.7 million color shades (24-bit truecolor) that are available using 24-bit color. Instead, these panels display interpolated 24-bit color using a dithering method that combines adjacent pixels to simulate the desired shade. They can also use a form of temporal dithering called Frame Rate Control (FRC), which cycles between different shades with each new frame to simulate an intermediate shade. Such 18 bit panels with dithering are sometimes advertised as having "16.2 million colors". These color simulation methods are noticeable to many people and highly bothersome to some.gamut (often referred to as a percentage of the NTSC 1953 color gamut) are also due to backlighting technology. It is not uncommon for older displays to range from 10% to 26% of the NTSC color gamut, whereas other kind of displays, utilizing more complicated CCFL or LED phosphor formulations or RGB LED backlights, may extend past 100% of the NTSC color gamut, a difference quite perceivable by the human eye.
In 2004, Hydis Technologies Co., Ltd licensed its AFFS patent to Japan"s Hitachi Displays. Hitachi is using AFFS to manufacture high end panels in their product line. In 2006, Hydis also licensed its AFFS to Sanyo Epson Imaging Devices Corporation.
A technology developed by Samsung is Super PLS, which bears similarities to IPS panels, has wider viewing angles, better image quality, increased brightness, and lower production costs. PLS technology debuted in the PC display market with the release of the Samsung S27A850 and S24A850 monitors in September 2011.
TFT dual-transistor pixel or cell technology is a reflective-display technology for use in very-low-power-consumption applications such as electronic shelf labels (ESL), digital watches, or metering. DTP involves adding a secondary transistor gate in the single TFT cell to maintain the display of a pixel during a period of 1s without loss of image or without degrading the TFT transistors over time. By slowing the refresh rate of the standard frequency from 60 Hz to 1 Hz, DTP claims to increase the power efficiency by multiple orders of magnitude.
Due to the very high cost of building TFT factories, there are few major OEM panel vendors for large display panels. The glass panel suppliers are as follows:
External consumer display devices like a TFT LCD feature one or more analog VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort interface, with many featuring a selection of these interfaces. Inside external display devices there is a controller board that will convert the video signal using color mapping and image scaling usually employing the discrete cosine transform (DCT) in order to convert any video source like CVBS, VGA, DVI, HDMI, etc. into digital RGB at the native resolution of the display panel. In a laptop the graphics chip will directly produce a signal suitable for connection to the built-in TFT display. A control mechanism for the backlight is usually included on the same controller board.
The low level interface of STN, DSTN, or TFT display panels use either single ended TTL 5 V signal for older displays or TTL 3.3 V for slightly newer displays that transmits the pixel clock, horizontal sync, vertical sync, digital red, digital green, digital blue in parallel. Some models (for example the AT070TN92) also feature input/display enable, horizontal scan direction and vertical scan direction signals.
New and large (>15") TFT displays often use LVDS signaling that transmits the same contents as the parallel interface (Hsync, Vsync, RGB) but will put control and RGB bits into a number of serial transmission lines synchronized to a clock whose rate is equal to the pixel rate. LVDS transmits seven bits per clock per data line, with six bits being data and one bit used to signal if the other six bits need to be inverted in order to maintain DC balance. Low-cost TFT displays often have three data lines and therefore only directly support 18 bits per pixel. Upscale displays have four or five data lines to support 24 bits per pixel (truecolor) or 30 bits per pixel respectively. Panel manufacturers are slowly replacing LVDS with Internal DisplayPort and Embedded DisplayPort, which allow sixfold reduction of the number of differential pairs.
The bare display panel will only accept a digital video signal at the resolution determined by the panel pixel matrix designed at manufacture. Some screen panels will ignore the LSB bits of the color information to present a consistent interface (8 bit -> 6 bit/color x3).
With analogue signals like VGA, the display controller also needs to perform a high speed analog to digital conversion. With digital input signals like DVI or HDMI some simple reordering of the bits is needed before feeding it to the rescaler if the input resolution doesn"t match the display panel resolution.
Kawamoto, H. (2012). "The Inventors of TFT Active-Matrix LCD Receive the 2011 IEEE Nishizawa Medal". Journal of Display Technology. 8 (1): 3–4. Bibcode:2012JDisT...8....3K. doi:10.1109/JDT.2011.2177740. ISSN 1551-319X.
Brody, T. Peter; Asars, J. A.; Dixon, G. D. (November 1973). "A 6 × 6 inch 20 lines-per-inch liquid-crystal display panel". 20 (11): 995–1001. Bibcode:1973ITED...20..995B. doi:10.1109/T-ED.1973.17780. ISSN 0018-9383.
K. H. Lee; H. Y. Kim; K. H. Park; S. J. Jang; I. C. Park & J. Y. Lee (June 2006). "A Novel Outdoor Readability of Portable TFT-LCD with AFFS Technology". SID Symposium Digest of Technical Papers. AIP. 37 (1): 1079–82. doi:10.1889/1.2433159. S2CID 129569963.
Kim, Sae-Bom; Kim, Woong-Ki; Chounlamany, Vanseng; Seo, Jaehwan; Yoo, Jisu; Jo, Hun-Je; Jung, Jinho (15 August 2012). "Identification of multi-level toxicity of liquid crystal display wastewater toward Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa". Journal of Hazardous Materials. Seoul, Korea; Laos, Lao. 227–228: 327–333. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.05.059. PMID 22677053.

Assume full responsibility to satisfy all needs of our clients; achieve continual advancements by endorsing the expansion of our purchasers; turn into the final permanent cooperative partner of clientele and maximize the interests of clients for Industrial Tft-Lcd Panel, Active Matrix Monitor, Tft Widescreen Display, Lcd Panel Camera,Touch Screen Monitor. We appreciate your enquiry and it"s our honor to work with every friend worldwide. The product will supply to all over the world, such as Europe, America, Australia,Moldova, Hamburg,Milan, Bolivia.If any item be of interest to you, please let us know. We will try our best to satisfy your requirements with high quality products, the best prices and prompt delivery. Please feel free to contact us at any time. We will reply you when we receive your inquiries. Please note that samples are available before we start our business.

We have thousands of standard products that are in stock and available from our Seattle, WA and Hong Kong warehouses to support fast product development and preproduction without MOQ. The stock covers TN, STN LCD display panels, COB, COG character LCD display, graphic LCD display, PMOLED, AMOLED display, TFT display, IPS display, high brightness and transflective, blanview sunlight readable display, super high contrast ratio display, lightning fast response displays, efficient low power consumption display, extreme temperature range display, HMI display, HDMI display, Raspberry Pi Display, Arduino display, embedded display, capacitive touch screen, LED backlight etc. Customers can easily purchase samples directly from our website to avoid time delays with setting up accounts and credit terms and shipping within 24 hours.
Many of our customers require customized OEM display solutions. With over two decades of experience, we apply our understanding of available display solutions to meet our customer’s requirements and assist from project concept to mass production. Using your ideas and requirements as a foundation, we work side by side with you to develop ideas/concepts into drawings, build prototypes and to final production seamlessly. In order to meet the fast changing world, we can provide the fastest turnaround in the industry, it takes only 3-4 weeks to produce LCD panels samples and 4-6 weeks for LCD display module, TFT LCD, IPS LCD display, and touch screen samples. The production time is only 4-5 weeks for LCD panels and 5-8 weeks for LCD display module, TFT LCD, IPS LCD display, and touch screen.

TFT displays are full color LCDs providing bright, vivid colors with the ability to show quick animations, complex graphics, and custom fonts with different touchscreen options. Available in industry standard sizes and resolutions. These displays come as standard, premium MVA, sunlight readable, or IPS display types with a variety of interface options including HDMI, SPI and LVDS. Our line of TFT modules include a custom PCB that support HDMI interface, audio support or HMI solutions with on-board FTDI Embedded Video Engine (EVE2).

A liquid crystal display (LCD) has liquid crystal material sandwiched between two sheets of glass. Without any voltage applied between transparent electrodes, liquid crystal molecules are aligned in parallel with the glass surface. When voltage is applied, they change their direction and they turn vertical to the glass surface. They vary in optical characteristics, depending on their orientation. Therefore, the quantity of light transmission can be controlled by combining the motion of liquid crystal molecules and the direction of polarization of two polarizing plates attached to the both outer sides of the glass sheets. LCDs utilize these characteristics to display images.
An LCD consists of many pixels. A pixel consists of three sub-pixels (Red/Green/Blue, RGB). In the case of Full-HD resolution, which is widely used for smartphones, there are more than six million (1,080 x 1,920 x 3 = 6,220,800) sub-pixels. To activate these millions of sub-pixels a TFT is required in each sub-pixel. TFT is an abbreviation for "Thin Film Transistor". A TFT is a kind of semiconductor device. It serves as a control valve to provide an appropriate voltage onto liquid crystals for individual sub-pixels. A TFT LCD has a liquid crystal layer between a glass substrate formed with TFTs and transparent pixel electrodes and another glass substrate with a color filter (RGB) and transparent counter electrodes. In addition, polarizers are placed on the outer side of each glass substrate and a backlight source on the back side. A change in voltage applied to liquid crystals changes the transmittance of the panel including the two polarizing plates, and thus changes the quantity of light that passes from the backlight to the front surface of the display. This principle allows the TFT LCD to produce full-color images.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey