lcd display comparison quotation

Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) screens are a staple in the digital display marketplace and are used in display applications across every industry. With every display application presenting a unique set of requirements, the selection of specialized LCDs has grown to meet these demands.
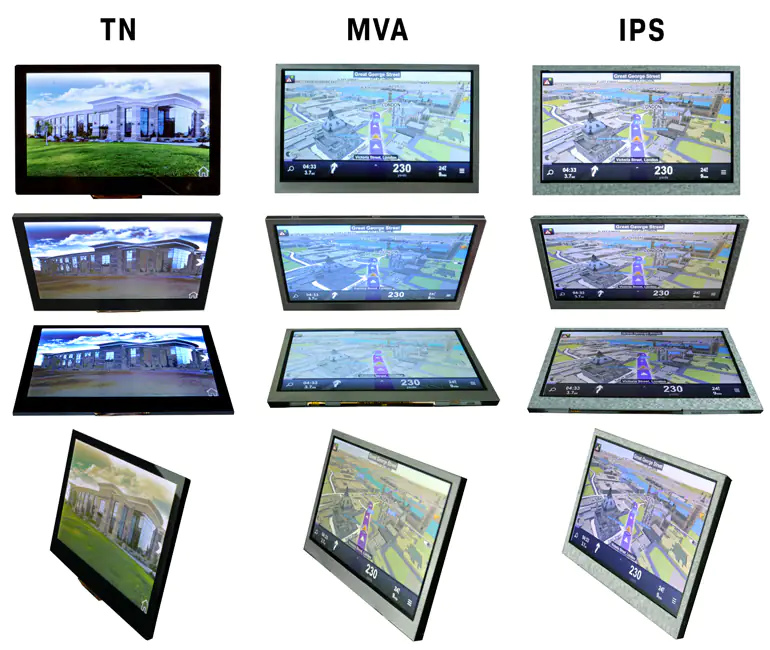
LCD screens can be grouped into three categories: TN (twisted nematic), IPS (in-plane switching), and VA (Vertical Alignment). Each of these screen types has its own unique qualities, almost all of them having to do with how images appear across the various screen types.
This technology consists of nematic liquid crystal sandwiched between two plates of glass. When power is applied to the electrodes, the liquid crystals twist 90°. TN (Twisted Nematic) LCDs are the most common LCD screen type. They offer full-color images, and moderate viewing angles.
TN LCDs maintain a dedicated user base despite other screen types growing in popularity due to some unique key features that TN display offer. For one,
VA, also known as Multi-Domain Vertical Alignment (MVA) dislays offer features found in both TN and IPS screens. The Pixels in VA displays align vertically to the glass substrate when voltage is applied, allowing light to pass through.
Displays with VA screens deliver wide viewing angles, high contrast, and good color reproduction. They maintain high response rates similar to TN TFTs but may not reach the same sunlight readable brightness levels as comparable TN or IPS LCDs. VA displays are generally best for applications that need to be viewed from multiple angles, like digital signage in a commercial setting.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) technology improves image quality by acting on the liquid crystal inside the display screen. When voltage is applied, the crystals rotate parallel (or “in-plane”) rather than upright to allow light to pass through. This behavior results in several significant improvements to the image quality of these screens.
IPS is superior in contrast, brightness, viewing angles, and color representation compared to TN screens. Images on screen retain their quality without becoming washed out or distorted, no matter what angle they’re viewed from. Because of this, viewers have the flexibility to view content on the screen from almost anywhere rather than having to look at the display from a front-center position.
IPS displays offer a slightly lower refresh rate than TN displays. Remember that the time for pixels to go from inactive to active is measured in milliseconds. So for most users, the difference in refresh rates will go unnoticed.
Based on current trends, IPS and TN screen types will be expected to remain the dominant formats for some time. As human interface display technology advances and new product designs are developed, customers will likely choose IPS LCDs to replace the similarly priced TN LCDs for their new projects.

A video wall is not a one-size-fits-all solution. There are many options to choose from when designing a commercial building video wall display: the size and shape of the digital canvas, what type of content will be displayed and the purpose of the video wall. Operationally, you may focus on desired reliability, maintenance and serviceability of the equipment. Hardware and technology decisions ensure the video wall will deliver both the desired viewing and ownership experience.
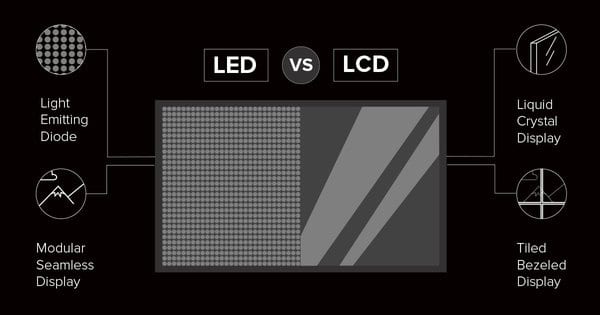
One of these choices is deciding between an LCD display or an LED video wall. Continue reading to find out more about the basics, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each solution.
Most people are familiar with LCD technology, which stands for Liquid Crystal Display. These types of displays have a massive presence in this world, used in living rooms to watch movies, fast-food restaurants to showcase menus, airports to show flight schedules, and everything in between. LCD technology was developed in the 1960s and has been used worldwide as a standard for roughly 20 years. It is a tried-and-true technology that has stood the test of time and will be around for the foreseeable future.
On an LCD screen, the panel is illuminated by a light source and works through reflection or transmission of light. Overall, LCD displays have better viewing angles and less glare than LED screens. This technology was designed to be energy efficient and tends to be lighter in weight.
An LCD video wall is made up of multiple LCD panel monitors mounted on a surface to create a digital canvas, which then work together to create a unified experience. They operate 24/7 at a high brightness and have thin bezels that help create a seamless look when the displays are placed next to one another.
Bezel thickness and the brightness rating are among key attributes to consider for an LCD video wall display. Here is what each of these means and why.
Bezel:Bezel thicknesses for video wall displays are measured in “bezel-to-bezel” thickness.This is the thickness of the bezel when two displays are placed next to one another. Displays can be either large bezel or thin bezel.
Nits:Brightness is measured in Nits. A higher Nit value means the display will be brighter. A brighter display is necessary in a room that sees plenty of direct sunlight, or if the intent is to draw in visitors from far away. With LCD video walls, the price of the hardware goes up as the display size and brightness increase, and the bezel width decreases.
The next item to consider is the type of content that will be displayed on your video wall. LCD displays have high resolution screens — modern 4K displays have over 8 million pixels! This means that the content being displayed is highly detailed and crystal-clear. A viewer could stand less than 1 foot away from the screen and be able to see exactly what is being shown on the screen.
Like previously mentioned with LCD video walls, an important consideration in the decision-making process is the type of content that will be displayed on the video wall. LED video walls suffer from image degradation and pixilation from up close, so fine details will be lost, and text will be illegible. If detail from up close is important, LCD displays are much better suited for that situation.Content examples that are well-suited for an LCD video wall:
Video walls are relatively new. But LCD technology has had decades of mainstream adoption, and with that comes both familiarity and lower costs. If those are important to you, then an LCD video wall is likely the right choice.
LED video walls are similar to LCD video walls, but the digital canvas is built using LED panels. Individual LED panels can be anywhere from 12”x12” to 36”x18”, which is much smaller than LCD displays. LED panels have a larger presence in this world than most might think—they are found indoors and outdoors at stadiums, arenas, concert venues, airports, and in use as large digital advertisements in iconic places such as Times Square.
The module is a small rectangular board that contains all the individual LEDs (light-emitting diodes).Unlike LCD, there is no glass or color filter on the LED video wall panels. The individual diodes that are placed on the modules produce both color and light.
One of the most impressive features of LED panels is that they can be combined to create almost any shape, without a bezel interrupting the digital canvas. LED video wall panels can be placed on curved surfaces, 90-degree edges, and other non-standard surfaces. The smaller size of the panels in relation to LCD video wall displays means they can fill more space on a surface—they aren’t limited to standard 46” and 55” sizes as are LCD video wall displays.
As is the case with an LCD video wall, an LED video wall will add exciting drama and premium value to showcase spaces. LED panel displays don’t enjoy the benefit of decades of mainstream adoption as do their LCD counterparts. However, the technology curve is increasing their availability and lowering their costs. At this time, an LED video wall will have higher upfront costs compared to an LCD video wall. If cost is the main concern, then an LED video wall system will not likely fit into your budget
Limitless shapes and sizes:the smaller size of LED panels allows them to be combined to create unique canvases, including curved, 90-degree edge, and other combinations not possible with LCD displays

Golden View Display wants you to make an informed choice among our LCD products. The tech center provides you with most of the information you will need to understand liquid crystal displays.
Here is a guideline to select a LCDs to meet your requirements in many aspects, such as cost, performance, and utility. We hope it can help you have a good understanding on the characteristics and properties of LCDs.
2) From TN to 240 twist STN, the response time become slower and slower, but the contrast gets better and better, and view cone gets wider and wider if the duty is determined, but the cost of LCD gets higher and higher as well.
The types and number of imaging data handled by hospitals are increasing as we witness improvements in medical technology. This is having an impact on the type of imaging you need to use, as well as the type of display you need to view and analyze images. As a result, you will see combined use of monochrome and color images to achieve the greatest diagnostic accuracy.
The choice between LCD Color and monochrome displays in diagnostic imaging is not a simple one. Each has some advantages over the other, and a comparison that considers the unique needs of your facility is warranted.
For example, both color and monochrome displays can use grayscale to view images. The grayscale that is used can impact the quality of the image and the accuracy of your diagnosis.
Which display you choose can determine how you use grayscale to view your images, whether you can switch from monochrome to color images, and whether images are converted manually by you, or through automated analysis.
Not only will these considerations influence the accuracy of your diagnoses, but the amount of time invested in achieving those outcomes. Display functionality can save you time or cost you time, depending on your priorities and choices.
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display. Today most monitors that radiologists use for reading studies are LCD. These displays look like flat panel televisions and computer monitors; however, medical-grade displays meet a higher level of standards, have greater functionality for medical imaging, and are more robust for your needs.
Most LCD monitors use Light-emitting diodes or LEDs as the backlight source. This is a change from past monitors, which used a Cathode Fluorescent Lamp (CCFL) technology. LEDs are slimmer than CCFLs, and this allows the display to be slimmer than those with CCFL tubes.
LED technology is a mercury-free source of light. While LED contains other dangerous metals, it doesn’t present the same health and environmental risk of mercury. LED and LCD life expectancy is greater than the old CCFL.
Traditionally, Monochrome medical-grade displays have been recommended in diagnostic radiology because they have a higher luminance. The higher luminance of monochrome displays makes it easier to see the entire grayscale in an image.
More specifically, monochrome displays have only one color of phosphor. Looking at the name, you can see that “Mono” means one and “chrome” means color. Everything (text and graphics) is displayed in that color.
If you perform a lot of imaging modalities such as chest CT, DR, and other imaging modalities that require higher brightness and contrast performance, then monochrome displays are a great solution for you.
Monochrome displays are significantly more expensive than LCD color displays. Less expensive monochrome displays are available. However, they come at a cost of reduced luminance which impacts image quality. Decreased image quality is a significant compromise when considering the impact on diagnostic accuracy.
Both monitors require calibration to maintain accurate functioning. Medical grade displays are usually equipped with controls to facilitate grayscale calibration. Monitors need to maintain calibration to the DICOM standard. Maintaining calibration is particularly important when images need to be compared to previous images of the same person and condition on a different display.
Both LCD Color and Monochrome displays should be medical grade because they are designed for high volume use and facilitate viewing radiological images with the detail needed for accurate diagnosis and efficient completion of the analysis.
There can be some variability in uses that are recommended; however, based on the general characteristics of LCD Color and Monochrome displays are recommended for several of the same modalities.
For example, looking at LCD color and monochrome displays used for mammography and tomography, both are recommended for Computed Radiology (CR), Computed Tomography (CT), Digital Radiography (DR), Ultrasound, PACS and Mammography.
They come in similar sizes with similar numbers of pixels and resolution. The viewing angle for these displays is not significantly different. There is no difference in palette, video inputs, dimensions, and weight, and both have external power supplies.
Monochrome displays have a much higher cost. The trade-off is the longer life span of the display. Also, they have higher luminance which facilitates efficiency and accuracy.
Color monitors have a lower maximum luminance compared to monochrome displays. This doesn’t necessarily mean that diagnostic accuracy will be decreased. The study by Geijer, et al.1, indicated that accuracy with color LCD and Monochrome monitors was not significantly different, but that the dwell time for color monitors was greater.
All displays can be windowed. However, color displays often need to be windowed to improve image quality for specific area you are analyzing. While a normal part of reading a digital image, it is more necessary in viewing on color displays, and this can reduce efficiency and limit the ability to compare objects in the window with those restricted from view.
Color and monochrome images should be viewed using different grayscales. Monochrome images are best viewed using the DICOM 14 Grayscale Standard Display Function (GSDF) while color images are best viewed using Gamma 2.2.
In addition to modalities recommended for both displays above, LCD color displays are recommended for Nuclear Medicine, 3D, Positron Emission Tomography (PET), and Tomosynthesis. LCD Color displays consume more power than monochrome.
An advantage of color displays is that they can show color information. As medical technology advances and more modalities use color, this is an important consideration. Modalities that already use color include Doppler ultrasound, 3D reconstructions in computed tomography (CT), functional magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, and nuclear medicine, including PET.
Displays now function to read images and adjust between color and monochrome, or to allow easy switching from one functionality to another. This makes the less expensive, LCD Color displays more attractive. However, there are circumstances when the monochrome display is the better choice.
Which display you choose will be influenced not only by cost, but also by the current and future needs of your hospital, which is determined by the types and numbers of modalities you perform as well as what you anticipate you might add to the modalities you perform during the life of the display.
Double Black Imaging understands the importance of displaying high quality images while containing costs. We can help you choose the best display options for your facility and your budget. We offer a range of options that are the best LCD Color and Monochrome displays on the market. Contact us today to set up a discussion about how we can help you with your next display purchase.
1 Geijer H, Geijer M, Forsberg L, Kheddache S, Sund P. Comparison of color LCD and medical-grade monochrome LCD displays in diagnostic radiology. J Digit Imaging. 2007 Jun;20(2):114-21. doi: 10.1007/s10278-007-9028-5. PMID: 17340227; PMCID: PMC3043910.
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. SMD refers to Surface Mounted Diode, a technology that utilizes a process of mounting each LED chip (pixel) directly to a printed circuit board (PCB). Mounting the diodes in this fashion allows displays to be thinner and sleeker than older LED technology. SMD also allows for finer pixel pitch. Simply put, pixel pitch refers to the distance between the diodes and is responsible for resolution. Fine pixel pitch translates into high resolution. Fine pixel pitch is what makes HD and UHD LED possible.
LCD panels are made of a layer of liquid crystal between two pieces of polarized glass. Liquid crystal can not emit light. Backlights are therefore used to illuminate the display. LCD panels are sleek in design, but typically limited to specific sets of dimensions.
LEDs are their own light source. This means that LED video walls are glare free and not subject to many of the problems ambient lighting creates for other video display types.
LED technology is modular in nature. This means that LED panels fit together seamlessly and can be used to make displays to fit any space. Custom cabinets can even be built to accommodate unusual shapes or dimensions.
LCD video walls on the other hand take on a tiled approach. This means that screens are jutted against one another. This approach creates bezels or seams and the final dimensions of the wall is directly dependent on the dimensions of the individual screens.
LED is a versatile display option. Thanks to various IP options, LED video walls can be displayed indoors or outdoors. LED video walls can be built with a variety of internal mechanisms as well. Quick refresh rates and dual power backup can ensure that LED video walls look great on camera. Various pixel pitches can ensure the proper resolution for the right context.
LCD is a more straightforward product and consumers are generally more familiar with LCD. LCD is used for cell phones, computer screens, and most TVs, but is it the best choice for video walls? Ultimately that choice is up to the consumer. LCD is cheaper, but generally less customizable. LCD does not work well for outdoor uses and is generally very limited in terms of size and shape.
Just like anything else, the best video wall product is largely dependant on context. If you like LED technology but are unsure of the process associated in obtaining a LED video wall read: How to Purchase a LED Video Wall Display.

On home appliances, it is often necessary to display numbers and words to convey information, such as the current time displayed on the clock, the current temperature information on the kettle… etc. The two most commonly used displays are LED displays and LCD displays, this article will compare the advantages and disadvantages of LED displays and LCD displays, and provide a two-step quick way to quickly determine whether this product is an LCD or LED display.
LCD displays are the most common displays in daily life, from your mobile phone screen to home appliances, you can use LCD displays, but whether it is a color or black and white LCD display, in fact, the principle is the same. There are two main components within the LCD display:Backlight module
Black-and-white LCD displays are widely used in a variety of low-cost products, and the picture above is a black-and-white LCD display used in science calculator.
Advantages of monochrome LCD displays:Can show very compact information.Each display point of the calculator as shown below is very close to each other, and high-resolution text can be displayed
Power savingBlack and white LCD displays can operated without a lot of power compared to full-color LCD, when products that do not require full-color demand and need to control power consumption are often used.
CheapIf you just want to display a set of numbers or a few ICONs, the price of using a black-and-white LCD display is much cheaper than that of a full-color LCD, and it is often used in a large number of consumer products.
Disadvantages of monochrome LCD displays:Small viewing angle, not easy to use for outdoor application.Usually black and white liquid crystal display in the front view, the display is the clearest, but due to the LCD panel characteristics, as long as the side view, the clarity will be declined, outdoor will be affected by strong light, the viewing angle is not large, the clarity is not enough, LED display due to the word luminescence characteristics, there is no viewing angle problem.
Can only be used in monochromeIf you need multi-color applications, you can only upgrade to a full-color LCD display that is many times more expensive, and the LED display can simply add different colors to the LED display without significantly increasing the cost
The structure and basic introduction of the display in this article this article, compared with LCD displays, self-illumination characteristics, so that LED displays in the outdoor visibility is high, high brightness, but also no viewing angle problem. LED displays are the same as black and white LCD liquid crystals, and the display information must be designed in advance and cannot be arbitrarily transformed. The price of LED displays is between full-color LCDs and monochrome LCDs, and if properly designed, they can save the cost of achieving display performance.
This article briefly introduces the basic principles and advantages and disadvantages of two common LCD displays, and provides two steps to quickly determine whether the display in hand is an LED display, and product designers can follow these two steps to understand which display the product is used when observing the product.

As a veteran manufacturer, we have accumulated rich display industry knowledge, including LCD display technology, OLED display technology, LED display technology, and so on. We want to share all these values here.
IPS (In-Plane Switching) lcd is still a type of TFT LCD, IPS TFT is also called SFT LCD (supper fine tft ),different to regular tft in TN (Twisted Nematic) mode, theIPS LCD liquid crystal elements inside the tft lcd cell, they are arrayed in plane inside the lcd cell when power off, so the light can not transmit it via theIPS lcdwhen power off, When power on, the liquid crystal elements inside the IPS tft would switch in a small angle, then the light would go through the IPS lcd display, then the display on since light go through the IPS display, the switching angle is related to the input power, the switch angle is related to the input power value of IPS LCD, the more switch angle, the more light would transmit the IPS LCD, we call it negative display mode.
The regular tft lcd, it is a-si TN (Twisted Nematic) tft lcd, its liquid crystal elements are arrayed in vertical type, the light could transmit the regularTFT LCDwhen power off. When power on, the liquid crystal twist in some angle, then it block the light transmit the tft lcd, then make the display elements display on by this way, the liquid crystal twist angle is also related to the input power, the more twist angle, the more light would be blocked by the tft lcd, it is tft lcd working mode.
A TFT lcd display is vivid and colorful than a common monochrome lcd display. TFT refreshes more quickly response than a monochrome LCD display and shows motion more smoothly. TFT displays use more electricity in driving than monochrome LCD screens, so they not only cost more in the first place, but they are also more expensive to drive tft lcd screen.The two most common types of TFT LCDs are IPS and TN displays.

Finding and choosing the right seven segment display can be very difficult and time-consuming. There are several technologies out there, with vastly different specifications, advantages, and disadvantages. Reading this article, will provide you new insights on what seven segment displays that will suit your project or product.
This post aims to give you a better understanding of what different 7 segment display technologies are available on the market and how they can be applied in various use-cases. We will cover the following seven segment display options:
* 2x2 cm^2 outer dimension of a 1x7 segment display, approximately equivalent to 1 cm2 active display area. The calculations are based on 100 display updates per day. The presented figures are the average energy consumption from multiple datasheets available online.
In this seven segment display comparison, we include both emissive displays and reflective displays. An emissive display versus a reflective display are significantly different when comparing factors such as energy consumption and optical performance. For instance, a reflective display cannot be used without ambient light, but an emissive display is close to impossible to read in direct sunlight. Additional factors that will be covered in this article include cost, form factor, electrical driving, connector options.
If you’re looking for an ultra-low-powered display technology, a segmented LED display is ruled out, and most likely, so is a backlit LCD display. What you need is a reflective display. This leaves us with three choices; reflective LCD, the E Ink display, and the Rdot display.
Reflective LCDs are less complex in terms of energy consumption. Our research indicates that the average power consumption for one square centimeter active display area will consume around 6.6 µW. This figure will not be significantly affected depending on the number of display updates you perform.
The E Ink display is close to fully bistable, which means that it will not consume any energy for static images. Close to all energy is consumed when the display content is changed. One display update is usually around 4mW during 1 second per 1 square centimeter. With 100 number changes per day, the total power consumption is approximately 4.6 µW/cm2.
The Rdot display has similar bistability characteristics as E Ink, but the screen will not retain the image as long as an E Ink display. The image retention time can be anywhere from 0 minutes up to 24 hours, depending on the use-case. For this example, we use a display with 15 minutes of image retention time. At 100 display updates per day, the Rdot display will consume around 1.2µW/cm2. One noteworthy feature to remember is that if the display is no longer powered, the current number on the seven segment display will naturally fade out during the next hour or so - you don’t have to actively turn it off.
The cost per unit will always influence the decision regarding which seven segment display technology to use. Before writing this article, a lot of work went into requesting offers from manufacturers worldwide to generate an average cost for all identified display technologies. The vast number of available variations, such as different types of liquid crystals, different connector types, different LED options, etc., makes it nearly impossible to end up at one generalized and representative number. For small one-digit seven segment displays in approximately 100 000 units per year, we are however able to draw the following conclusions:
The Rdot display is the only seven segment display that is bendable. The screen choice will therefore become very easy if your project requires a flexible display. The Rdot display is printed on a transparent plastic substrate that is bendable. The bend radius can be optimized to match your requirements simply through choosing the right thickness of the plastic substrate on which the display stack is printed upon.
Our preferred approach to evaluate the optical performance of various seven segment display types is to request samples from the producers. Seeing is believing. The very standard LCD and LED technologies will be easily accessible through multiple vendors. E Ink and Rdot have
My personal opinion is that the visual appearance of backlit and reflective LCDs, as well as segment LED displays, is not that appealing. One particular factor is that the segments in the unpowered state are still very visible in relation to the background. Another parameter is the viewing angle dependency. Most low-cost LCDs and LEDs are far from being perfectly non-angle dependent. Some are even impossible to read if you observe from only a 30° angle or more.
Both E Ink and the Rdot displays have close to no viewing angle dependency. E Ink has also managed to create very good black in the dark state, but still only 40% white reflection in the bright state which makes it fairly dark in poor light. The seven segment displays from Rdot will fade into the background color perfectly with accurate driving, which makes the Rdot display together with the E Ink display more visually appealing than the other options.
A robust display solution that can reliably work at least throughout the entire product lifetime is apparently a critical factor. From our perspective, the robustness can be broken down into three subparameters; lifetime, operating conditions, and ruggedness. We all know that seven segment displays have been around for a long time. Segment LCDs and LEDs are very mature and optimized. Typical operating conditions range from at least -40 °C to +85 °C, and the display lifetime will exceed almost all expected product lifetimes. Put simply, they are extremely robust. However, they do have one problem. They are fabricated on glass, meaning that they can crack or shatter. The typical solution to make them more rugged is through making the substrates thicker and also to add other safety measures in the display-device integration. This is the reason why there’s often a significant distance from the surface of the device to the display.
The Rdot display is fabricated on a flexible substrate that will not crack or shatter. E Ink also offers some flexible displays with similar properties. Both E Ink and Rdot will not yet compete on robustness in all environments. The operating temperature range spans from 0 °C to 50 °C for the majority of E Ink films, while the Rdot can guarantee -5 °C to 40 °C to this date. Lifetime is also slightly limited for the two seven segment technologies. The lifetime will depend on the number of display updates that are performed. E Ink suppliers communicate a lifetime number ranging from 1 million up to 10 million display updates. The Rdot display has a lifetime that is currently below 1 million updates.
The rdot display is most likely the best choice. It is very low cost, ultra low powered, and very environmentally friendly since it utilizes resource-efficient screen printing production and can be constructed with only organic materials.

If you’re in the market to rent a video wall, you’ve probably run into all sorts of confusing info. Here’s the lowdown on LCD vs. LED video walls so you can make the right choice for your next conference, trade show, or other event.
We’re about to throw a whole lot of info at you. So let’s first take a second to remember why both LED and LCD video walls are a good investment in the first place.
The old adage, “the bigger the better,” is definitely true when it comes to AV. A video wall immediately symbolizes your company is established, and sends a subconscious message that people should take your business seriously. Video walls help you stand out, and compete with all the other businesses who are investing in splashy, eye-catching displays.
Meanwhile, an LCD video wall is a large surface for video or images built from many LCD screens. You’ve interacted with an LCD screen before — they’re on your laptop, TV monitor, and more. However, the LCD video wall screens are designed to run longer and have thinner edges, called bezels.
Technicians use special hardware and tools to stack the LCD screens on top of one another, and calibrate the wall so that an image shows up across every screen. Temporary LCD walls can usually only be about five screens across and five screens high.
Temporary LCD walls can be configured to be in many different sizes and shapes, both large and small, but typically don’t go larger than five screens across and five screens high.
Our most popular LCD walls are about 16’ wide by 10’ tall. Also, when measuring your ceiling height, keep in mind that most walls don’t go all the way down to the floor. So you’ll need to add that into your total height need.
The image on an LCD wall will be sharper than on LED walls, especially while standing nearby, since it’s made from HD panels. Will have very thin seams between each LCD screen, called bezels.
Since an LCD Wall are basically fancy computer monitors, it’s typically easier to create content. If your content looks great on a standard computer monitor with a 16:9 aspect ratio, it will look good on an LCD wall. Your AV provider will give you dimensions and resolution requirements once you decide on the size you need, and can also help you determine where the seams (or “bezels”) will be so none of your image gets cut off.
Much lower than LCD — but you’ll still need to make sure your venue has enough power capabilities. Your video wall provider can tell you how much power you’ll need.
Imagine an LCD video wall is like a tray of lasagna. Reliable, beautiful, and sturdy — but you can only increase the size of a tray of lasagna so much. Affordable, but it has a limit in size.

Both DLP and LCD printers can print one full layer at a time, making them some of the fastest 3D printers available. An entry-level LCD printer costs $200 to $1,000. DLP printers start at $500 for entry-level printers and can go up to $100,000 for commercial use.
DLP is an older, more established technology than LCD printing. Though there are a lot of similarities between the two, the main difference is the light source used to cure the printing resin. DLP uses a high-intensity projector as a light source and directs it with thousands of tiny mirrors. LCD printers replace that setup with an LCD screen to mask the UV light which comes from an array of LED lights.
On the whole, LCD printers are constructed using cheaper components than DLP printers. However, LCD screens have shorter life spans than DLP mirror arrays. Plus, low-end screens tend to let light through in a less-than-uniform manner. This results in varying quality and precision from batch to batch and machine to machine.
DLP and LCD printers both employ liquid resin. DLP uses a high-power and higher-intensity light source that can operate on a wider range of resins. This gives DLP more options in terms of material quality. LCD printers, on the other hand, use low-intensity UV LEDs which require less viscous, fast-curing resins. This limits the types of material that can be used and impact the quality of the final product.
DLP is very accurate in narrow, small-scale prints. This makes it very useful for jewelry or dental implants, where precision is critical. LCD, on the other hand, is inexpensive and very accurate for the price point. This low price point makes it great for hobbyists. LCD is also ideal for when the price is more important than absolute precision. That can be valuable for industrial use, certain dental applications, and manufacturing.
DLP machines are available for hobbyists, professionals, and industrial applications that need large print volumes. LCD is a newer technology and has not caught on as much for industrial use. Therefore, large-volume LCD printers are not yet common, though this capability is gradually improving.
Less expensive versions of DLP and LCD systems can both have problems with surface finishes and print quality. DLP produces distortions on the edges of a print, especially in wide parts. LCD pieces can also come out imperfect due to inconsistencies in LEDs, especially with larger machines and larger prints. Both production methods must be followed by post-processing to finalize the parts’ surfaces. Generally, DLP parts come out with better surface finishes and print quality, especially with higher-end printers.
DLP and LCD are both available at affordable prices. An entry-level DLP printer can be purchased for as low as $500, while professional-grade types start at $2000. LCD printers, on the other hand, are available from $200 to $1,000.
There are a few technologies that are alternatives to both DLP and LCD printers. As an example:Stereolithography (SLA):SLA is a resin-based 3D printing technology known for its accuracy. It is similar to DLP and LCD in its use of photopolymer that is cured via UV light.
A 3D printing technology that shares similarities with LCD includes:LCD vs. SLS: SLS uses a laser to fuse powder into a 3D printed object. This is an established industrial technology that compares to LCD in terms of accuracy and printing speed.
When we purchase a new smartphone we go through a list of specifications that includes the processor, software, cameras, display type, battery, etc. The display of the smartphone is something which has always been a concern for people. And smartphone technology has advanced so much in the past decade that you get several display technology options to choose from.
Today, a smartphone is not just a means to send and receive calls and texts. It has become a general necessity, so choosing the right technology should be your main priority. Coming back to displays, as we said there are plenty of display types available right now.
Two of the main contenders for display technologies that are widely available are AMOLED and LCD. Here in this article, we will be comprising AMOLED vs LCD and find out which one is better for you.
Starting with the AMOLED first, it is a part of the OLED display technology but with some more advanced features. To completely know about it must understand its all three components. The first one is LED, “Light Emitting Diode”. Then we have “O” which stands for organic and makes the OLED.
The AMOLED display is similar to the OLED in various factors like high brightness and sharpness, better battery life, colour reproduction, etc. AMOLED display also has a thin film transistor, “TFT” that is attached to each LED with a capacitor.
TFT helps to operate all the pixels in an AMOLED display. This display might have a lot of positives but there are a few negatives too let’s point both of them out.
A major issue with these displays is of burning of pixels. After showing a specific image or colour for a longer period of time, the pixel can get burned. And if there is a problem with a single pixel it will affect the entire display.
Low outdoor visibility, usually the AMOLED Displays are quote not bright in direct sunlight and outdoor readability could be a problem for some devices but average screen brightness.
The LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display”, and this display produces colours a lot differently than AMOLED. LCD display uses a dedicated backlight for the light source rather than using individual LED components.
The LCD displays function pretty simply, a series of thin films, transparent mirrors, and some white LED lights that distributes lights across the back of the display.
As we have mentioned, an LCD display always requires a backlight and also a colour filter. The backlight must have to pass through a thin film transistor matrix and a polarizer. So, when you see it, the whole screen will be lit and only a fraction of light gets through. This is the key difference comparing AMOLED vs LCD and this is what differentiates these two display technologies.
The LCD displays are cheaper compared to the AMOLED as there is only one source of light which makes it easier to produce. Most budget smartphones also use LCD displays.
LCD displays have bright whites, the backlight emits lots of light through pixels which makes it easy to read in outdoors. It also shows the “Accurate True to Life” colours, which means it has the colours that reflect the objects of the real world more accurately than others.
LCDs also offer the best viewing angle. Although it may depend on the smartphone you have. But most high-quality LCD displays support great viewing angles without any colour distortion or colour shifting.
The LCD displays can never show the deep blacks like AMOLED. Due to the single backlight, it always has to illuminate the screen making it impossible to show the deep blacks.
The LCDs are also thicker than other displays because of the backlight as it needs more volume. So, LCD smartphones are mostly thicker than AMOLED ones.
Both of these display technologies have their own Pros and Cons. Taking them aside everything ends up with the user preferences as people might have different preferences among different colours and contrast profiles. However, a few factors might help you to decide which one fits perfectly for you.
Let’s start with the pricing. Most AMOLED display smartphones always cost more than an LCD smartphone. Although the trend is changing a bit. But still, if you want to get a good quality AMOLED display you have to go for the flagship devices.
The colors are also very sharp and vibrant with the AMOLED displays. And they look much better than any LCD display. The brightness is something where LCDs stood ahead of the AMOLED display. So using an LCD display outdoors gives much better results.
The last thing is battery consumption, and there is no one near the AMOLED displays in terms of battery. As of now, all smartphones feature a Dark Mode and most of the apps and UI are dark black with a black background. This dark UI on smartphones doesn’t require any other light, it gives the AMOLED displays a boost in battery performance.
Looking at all these factors and comparing AMOLED vs LCD displays, the AMOLED displays are certainly better than the LCDs. Also, the big display OEMs, like Samsung and LG are focusing more the OLED technologies for their future projects. So, it makes sense to look out for AMOLED displays. That being said, if we see further enhancements in the LCD technology in terms of battery efficiency and more, there is no point to cancel them at this moment.

Follow listed sections and review the LCD basic knowledge with us! Orient Display also has a friendly and knowledgeable team of technical support staff to help you with any specific questions you might have. Feel free to
In 1888, liquid crystals were first discovered in cholesterol extracted from carrots by Austrian botanist and chemist, Friedrich Reinitzer. In 1969, twisted-nematic (TN) mode of operation was discovered, which gave LCD the first commercial success. Learn more.
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Displays which are commonly used in TVs and Computer monitors. it is also used as mobile device screens such as laptops, tablets and smartphones. Learn more.
Liquid crystals were actually discovered over 100 years ago, but they did not find commercial applications until the invention of the twisted nematic (TN) LCD by Schadt and Helfrich in 1971 (Schadt and Helfrich, 1971).Learn more.
The biggest problem with early multiplexed LCDs was the reduction in contrast ratio with number of addressed lines. This problem was essentially eliminated with the invention of the film compensated super-twisted nematic (FSTN) LCD in the early 1980s. Learn more.
When selecting a Liquid Crystal Display Module or LCD Glass Panel, it is very important to identify the the range of its environmental temperature. Outlined in this section are the normal and wide temperature ranges of the LCD Modules and LCD panels offered by Orient Display. Learn more.
The display resolution of a LCD is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It is usually quoted as width × height, with the units in pixels. Learn more.
Is AMOLED technology ready to offer a better alternative to TFT-LCDs for industrial applications? Are advances in TFT keeping up with the clarity offered?Learn more.
Passive LCD, Active LCD and PMOLED , AMOLED are everywhere these days, but what’s the difference & which is better. Learn about the difference between Passive matrix LCD, Active matrix LCD and PMOLED, AMOLED, so next time you are starting a project, you know which one you need. Learn more.
![]()
Liquid crystal display (LCD) is a flat panel display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals. Liquid crystals do not produce light directly, instead using a backlight or reflector to produce images in colour or monochrome.

I always finding it interesting when a new customer of ours calls to let us know that they can find cheap LCD displays, the same LCD we supply, for almost half the price. After all, cheap LCD displays are the same no matter where you purchase it. Right?
Let me assure you that the phrase, ‘You get what you pay for’ is just as true for LCD displays as it is for insurance, fine jewelry, car repairs and open heart surgery. You will always be able to find a lower cost product or service, but many times you are not comparing apples to apples.
The word “cheap” is so polarized in that in one instance you can revel in the victory of finding that super low price and yet simultaneously it is no victory at all if someone looks at your product and says, “Wow, that looks cheap.” So, let’s talk about Cheap LCD displays.
The long and short of it is that LCD’s are in investment. In many cases, they are the most expensive component in your product, but you need to balance that with the fact that they are also what the customer looks at the most. If you are building a hand held device that measures the PH of pool water, it’s a safe bet that people will be looking at the display far more than the battery compartment on the back of the unit. The cheap LCD display may save you a fraction of what other suppliers are quoting, but what is it costing you? Return customers. Good online reviews. Word-of-mouth advertising.
There is a rule of thumb statistic that says it costs a company 7 times more money to earn a new customer, than it does to keep a current customer. So why would you save 20% or even 40% off the cost of an LCD and in return lose your current customers. The savings will not offset the increased advertising cost to bring in new customers.
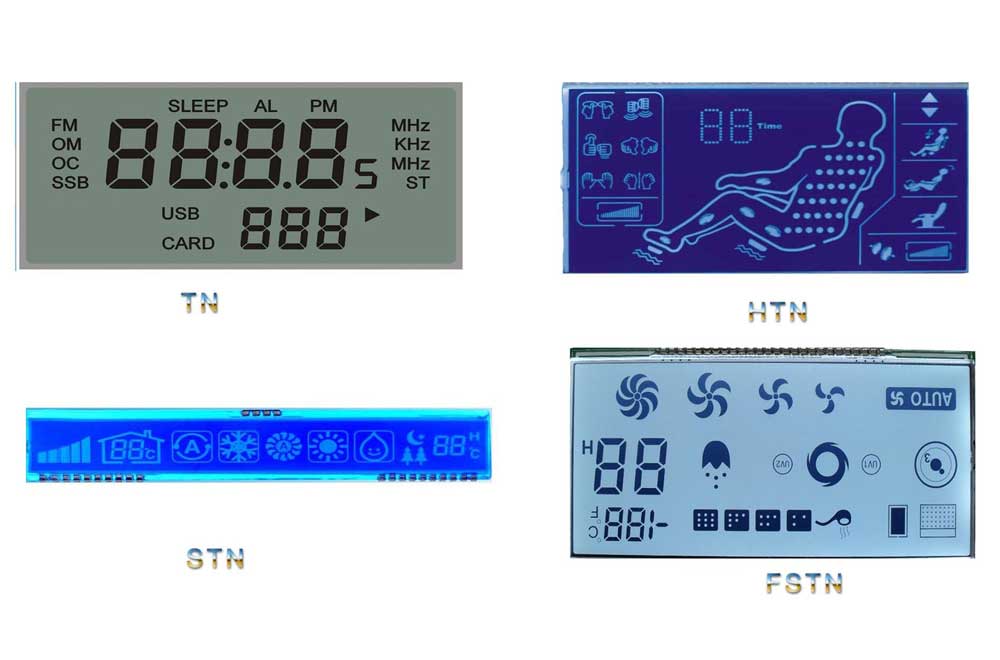
There are three main fluids used in a monochrome LCD module. They are TN, STN and FSTN. Each fluid has its own niche in which it operates well. One of the main factors impacted by the different fluids is acceptable viewing angle of the display.
TN, twisted nematic, is the lowest cost fluid and has the smallest viewing angle. That means that as you rotate the display farther from center, it will become harder to read. A mistake would be to assume that a TN display is junk; rather, it serves as an excellent unit for a very specific set of products.
An example of a TN display is the display found on gas pumps. You can easily read the gallons and dollars as they quickly fly by. Since most people see the display straight on, there is no need for a higher cost fluid. TN is the right choice and keeps the cost of the product down.
FSTN, film super-twisted nematic displays, are on the other end of the spectrum. They are more expensive than TN and STN, but it offers a sharper contrast and a much wider viewing angle. If you are building a portable device that measures radiation, you want to make sure you can see the numbers on the display from as wide of viewing able as possible. Using a TN in the application may save you as much as 15% on the cost of the display, but is this type of product an investment or expendable?
LCD displays are quite diverse when it comes to the temperatures in which they can operate well. Some even have as much and more than 100 degrees window of successful operation. There are three main temperature ranges of an LCD unit:Normal temperature (indoor temps—think of your living room)
Take for instance one customer of ours who needed the display to work properly on oil rigs near the North Pole. Their product monitors the safety equipment on the rig. Is it worth spending the extra $5 on a display that can survive working in all conditions? Is the LCD display an investment or expendable?
When a supplier is promising you the cheapest deal out there, you need to make sure that you are again dealing with an apples-to-apples comparison. Make sure that they aren’t saving you money by offering you a display that has the cheapest temperature range or the narrowest viewing angle, especially when those aren’t what will suit your product and your situation. They may just be choosing the cheapest alternatives of all the many options available, all to have you wind up with a unusable or inferior product. Then, you not only have a product you aren’t thrilled about but you face the problem of shipping the product back to the foreign country from which it came. This is not a convenient way to deal with the fallout from the “cheap” product! There is a real advantage to buying a product that has American support and part of that advantage is simply the convenience of speaking the same language and being within one shipping day apart from your customer support.
We understand that frustration and at Focus Display Solutions we offer uncompromising customer service and we provide it in a way that we would want to be served. We strive to pick up the phone on the first ring. We can talk to you about the products from a knowledge based on years of experience and not from a script that someone else wrote to troubleshoot only the most common problems. When you call us you talk to humans, not machines. We offer personal service to get the product right the first time and we do it in a way that works with your personal style.
The engineer took our price and specs and called back a few days later saying that another LCD vendor came in with a similar product that would cost in the low $5 range. Red flags immediately went up in my mind. Something was not right about this cheap LCD display. The display was similar, but upon inspection there were some ‘strings’ attached.
This is critical if you plan to build your product for the next few years. You will need to purchase more of these exact LCD displays in the future. When that time comes and you find out that the LCD modules are discontinued, you are in deep trouble. Your only option is to redesign your product for the current LCD.
Keep in mind that if you plan to repair your customer’s product, it is critical to have a supply of the original LCD. You cannot use a new LCD in an old product in the same way you cannot use a VHS tape (for those of you over the age of 20) in a blue ray player.
A simple tip is to do a little research on the product. Google can be your best friend. When someone offers you a screaming deal on a cheap LCD display, type in the part # and manufacture into Google; you may quickly find out why the prices are so cheap.
There are companies that contact us to buy our surplus/returns. These companies are providing a valuable service by keeping displays out of the landfills. If you need to be able to purchase the exact same LCD in the future, stay away from refurbished units. Once they are gone, there are no rain checks. Many of these displays can be found on eBay and other online auctions.
Focus Displays Solutions prefers to include the cost of the freight of those component parts from the Far East to Chandler, AZ. This way the customer only has to pay for the shipping from Arizona to their location.
That engineer quickly realized that asking the three critical questions makes all the difference in the price of the product! Getting cheap LCD displays is not always a mistake, just remember to ask questions and really think through whether this is an investment or an expendable item.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey