size of vr lcd panel in stock

By continuing to use AliExpress you accept our use of cookies (view more on our Privacy Policy). You can adjust your Cookie Preferences at the bottom of this page.

In a talk titled ‘High-PPI Fast-Switch Display Development for Oculus Quest 2 VR Headsets’, Meta display engineer Cheon Hong Kim detailed the headset’s display architecture and discussed the design challenges of using LCD for VR.
It’s essential that displays used in VR headsets only illuminate the pixels for a small fraction of each frame – a technique called Low Persistence. That’s because each frame represents an exact moment in time, whereas in real life as you rotate or move your head the light arriving to your eyes will continuously change. If the pixels were constantly illuminated, your eyes would be receiving light for the original position even as your head turned, and your brain perceives this as motion blur. The original Oculus Rift Development Kit shipped in 2013 had this problem, and it was solved in Development Kit 2 in 2014.
LCD displays were originally thought unsuitable for VR, given the much longer response time. But since the release of the Windows MR headsets in 2017, a new type of LCD panels called ‘fast switch’ have become available. These panels illuminate the backlight for a fraction of the frame, after waiting for the liquid crystal to “settle down”. Quest 2, like Oculus Go and Rift S before it, use such a panel.
The 1920×3664 resolution and 120 Hz max refresh rate were already publicly known, but the talk revealed the panel’s exact 5.46 inch size and density: 773 pixels per inch.
It’s also noteworthy that Meta revealed the panel’s brightness – 100 nits. Keep in mind that figure is when using low persistence, so it would likely be much brighter if used outside a headset.
Meta also revealed some interesting physical properties of the display. Since Quest 2 has three IPD settings and two lenses but only one panel, only a subsection of the panel is used at once. And because the lenses are closer to circular than square, the very corner of the display is never needed – so it was simply cut out to save space.
This approach of using a single panel with an active area subsection means each eye actually gets fewer than the 1832×1920 pixels listed in the Quest 2 specifications on the Meta Store – roughly 1720×1890.
These factors are important considerations when specifying and sourcing panels for VR headsets, but Cheon acknowledged Quest 2 has some of the issues outlined here. Meta still hasn’t released a headset fully free from the screen door effect.
In the conclusions slide, the key display resolution spec of Quest 2 was revealed, the angular resolution measured in pixels per degree. Meta says Quest 2 has 21 pixels per degree. The generally accepted figure for “retinal” human eye resolution is 60 pixels per degree. While VR headsets have been making solid advancements – the Oculus Rift had roughly 14 pixels per degree – there’s still clearly a long way to go.
Finally, Cheon alluded to Meta’s future research and development priorities – to reach the human perceptual limit of 60 pixels per degree using “high PPI micro displays” and “various foveation technologies”.
The size of current VR headsets is primarily dictated by what field of view current lenses can achieve (without uncorrectable distortion) with a given panel size. The smaller the panel, the more difficult this is.
The Oculus Quest, Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, HTC Vive Pro, and HTC Vive Cosmos all use dual panels between 3.4 and 3.6 inches diagonal. Other headsets like PlayStation VR and Oculus Rift S use a single panel, but these panels occupy essentially the same total space.
The company statesthat it is “used in VR glasses that have already been introduced to the market”. Given the above size, resolution, and panel type (and that the refresh rate is within the max) the only known headset on the market this could be is Huawei VR Glass.
These smaller panels, alongside pancake lenses (a fundamentally different design to all other headsets currently on the market), enable the incredibly small size of the Huawei VR Glass.
However, keep in mind that that product doesn’t have built in positional tracking or cameras. If these panels are used for a position tracked PC VR headset the size would likely be larger. And of course if they were used in an Oculus Quest competitor it would need to be much larger to house a battery and compute hardware.
The relatively standard resolution and use of LCD may make this panel significantly cheaper than high resolution OLED microdisplay alternatives like what Panasonic showed at CES. Huawei’s product is only officially available in China, for the equivalent of roughly $430.
It’s important to note, however, that when we tried Huawei VR Glass at CES we noted that it has a narrower field of view than typical. It may require a larger design to solve this.
Most current VR headsets are not comfortable to wear for extended periods of time. For some, they are even uncomfortable after a matter of minutes. This can be because they push a relatively heavy weight against the sinuses, where humans are particularly sensitive to pressure.
The weight’s fundamental cause is the the size of the panels currently available and the lenses used with them. Smaller panels of the same resolution are more difficult to produce, and more difficult to magnify over a large field of view. But JDI appears to have solved the first hurdle and Huawei demonstrated that the second can be shipped too (with a few tradeoffs).
With smaller panels, and suitable pancake lenses, VR could soon start to become a more comfortable medium that people can spend hours in without wanting the bulky heavy box off their face. Current VR might one day be looked back on like we look at the earliest cellular telephones or CRT monitors.
Whether this display system paradigm will stay in the realm of media viewers or come to gaming focused headsets is yet to be seen, but we’ll keep a close eye on JDI and companies likely to use its new panels.

The Chinese company TCL announced two tiny new LCD displays featuring impressive resolutions and striking pixel density per inch. If the displays are equal to their description these LCD panels will enable smaller and higher-resolution standalone VR headsets.
The first is a 2.1-inch LCD panel. Incidentally, the same size as HTC Vive FLOW, currently acting as the smallest display size on the market. However, where the FLOW delivers a resolution of 1600×1600, the new display prototype from TCL features a 2280×2280 resolution with a 120 Hz refresh rate.
Even more impressive, TCL showcased this first display in a standalone VR HMD: illustrating that such a small-sized LCD panel could enable powerful standalone virtual reality headsets to be created.
The second display that TCL teased as a prototype is only 1.77 inches, making it the smallest display engine for a VR headset on the market. This display has a resolution of 2160×2160, meaning it is lower than the other display, however, the loss of resolution compared to the reduction in size makes it very attractive.
TCL plans to make a big splash in the virtual reality industry with its upcoming LCD displays. Both TCL displays have impressive resolution densities and sizes, enabling crystal clear VR HMDs to be developed for a lower price than if OLED display engines are employed.All in all, with such high resolutions and pixel densities, cramped into such small form factors, TCL may power the next generation of stand-alone virtual reality headsets.

Panox Display provides a customized cover glass/touch panel service. We supply cover glass from Gorilla, AGC, and Panda, which all have excellent optical performance. We also supply driver ICs from Goodix and Focaltech.
The functions of our boards include, but are not limited to, adjustment of brightness, sound output, touch interface, extra data transmission, and gyroscope.
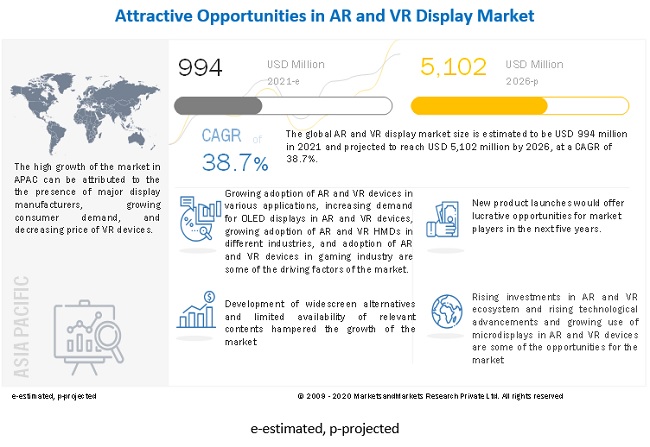
The global AR and VR display market attained a value of nearly USD 736 million in 2020. The market is further expected to grow in the forecast period of 2023-2028 at a CAGR of 36%.
Augmented reality and virtual reality have been extensively used in the healthcare industry for pain management and medical training. The coronavirus pandemic has significantly accelerated the use of AR and VR displays to foster a connection between healthcare professionals and patients while providing them a personalised treatment. They are increasingly used in operating rooms and classrooms to prepare medical professionals for efficient surgery and deliver complex care. Hence, the extensive use of AR and VR display is impacting the market growth positively. Moreover, the rising prevalence of virtual training in many industries is also fuelling the growth of the AR and VR display industry.
Technological advancements, including edge-computing and artificial intelligence (AI), are expected to provide personalised, accessible, and well-designed experiences, which are anticipated to further augment the market growth. Additionally, the advent of the 5G network is increasing the use of AR and VR displays in various applications, including entertainment, gaming, and training. The surging popularity of online gaming and e-sports, which require live immersive experience, is also increasing owing to the high-bandwidth and low-latency network capabilities of 5G. Hence, the growing deployment of the 5G network is providing further impetus to the market growth.
AR display, variously known as augmented reality display, is a display that presents an enhanced version of the physical world achieved through digital visual elements, any sensory stimuli, or sound by the use of technology. VR display or virtual reality display presents a computer-generated environment with the use of stimulation that enables users to interact with the 3D virtual world.
The EMR report looks into the regional markets of AR and VR display like North America, Europe, the Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East and Africa.
The use of augmented reality display, especially head-up display (HUD), in the automotive industry to make the drivers aware of potential hazards and redirect the driver’s focus on the road is expected to boost the market growth for AR and VR display. Moreover, mixed reality displays are used to present virtual objects to drivers while preparing them for potential hazards. Also, they can be used for marketing to enable consumers to experience their automobile in virtual reality. These are anticipated to propel the market growth for AR and VR displays in the forecast period.
The rising use of AR and VR technology in the education sector is further strengthening the market growth. It is widely used to provide personalised education, enhance the learning experience, and increase interaction via immersive technology, which is consequently invigorating the market growth. Moreover, research and development (R&D) by the leading companies to develop advanced displays and turn smartphones into AR and VR displays is accelerating the growth of the AR and VR display industry. In addition, the increasing adoption of AR technology in the gaming industry to provide an interactive experience to the viewers is also catalysing the market growth.
The report presents a detailed analysis of the following key players in the global AR and VR display market, looking into their capacity, market shares, and latest developments like capacity expansions, plant turnarounds, and mergers and acquisitions:
The comprehensive report looks into the macro and micro aspects of the industry. The EMR report gives an in-depth insight into the market by providing a SWOT analysis as well as an analysis of Porter’s Five Forces model.
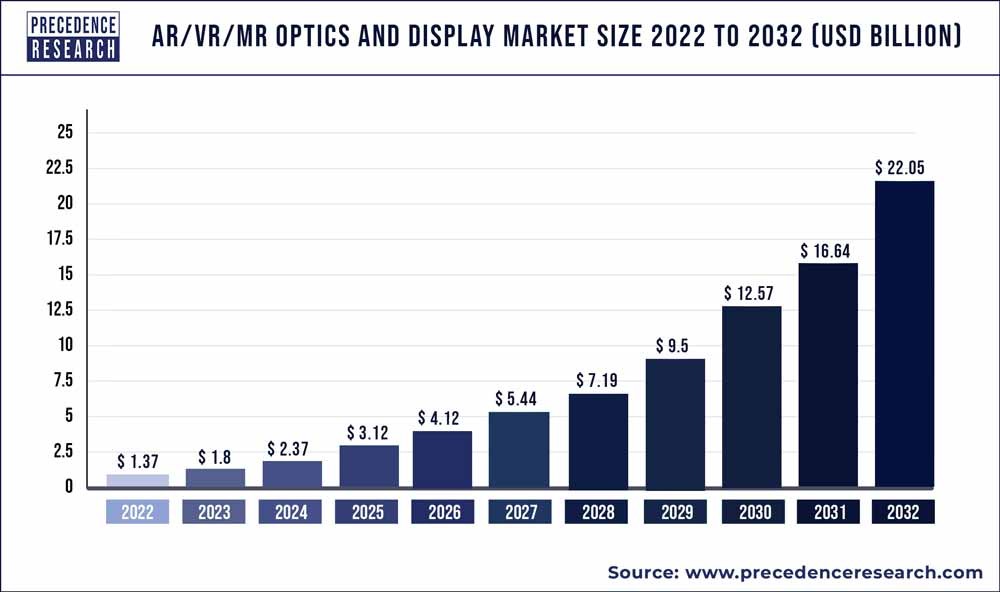
The AR/VR/MR optics and display market encircles the entire sector of optics and display technologies which are utilized in spatial reality products. Within VR devices, the prime optics are Fresnel lenses.The way the experience of a consumer is made engaging is defined by their first hand experience and after it has become an unforgettable experience, it provides a high possibility that they will stick to use the device to continue their elite experience.
Unlike the other industries the augmented reality and virtual reality market had seen a faster growth during the pandemic which proved to be a challenge for the other developing technologies. The pandemic has provided a much needed push to the adoption of this technology across the globe. The strict lockdowns across the globe made people look for new solutions in order to meet their daily needs. There was an extensive use of online platforms for purchasing of groceries and getting the food delivered at the doorstep. Online platforms were helpful in providing the medical requirements and serving the products needed for the educational purposes. Pandemic has been the major factor for the development of many new technologies. The health care sector the education sectors the tourism sector and the retail sector has used these technologies for their business. There has been a major behavioral change after the pandemic that instigated the market.
VR has showcased a significant impact in the form of a training facility, it proves to be an enhancer of telepresence and provides a method for design or visualization and is not considered to be described as the future of gaming. The pandemic has shifted the main focus on this socially interactive hands-free technological system. It is foreseen that this focus will remain fixed for a significant period of time. There will be a requirement for this advanced technology in numerous new events, which before this did not need hands-free, or remote functioning. The utilization of this advanced technology permits other clinicians to locate themselves in a separate room, and while using Microsoft Teams, they can observe a live video streaming of the physician who is tackling with the COVID-19 patients. This is done by using the remote assistance features which have been previously used by Hololens users for producing, maintenance, and other similar purposes. By utilizing this technology, the staff has cut down the duration of time they were required to spend by being physically present in a high-risk area by around 83%.
Moreover, they are making less use of PPE, pertaining to the fact that only a few physicians are present in the high risk zone during patient care. The utilization of AR/MR systems for directing skilled individuals, maintaining operating layouts in front of surgeons and substituting the smart devices for data consumption is considerably growing. In the moments to come, these advanced technologies are predicted to revolutionize the techniques with which we function and communicate with each other.
Within the VR headsets, advanced, unconventional lens options are used so that there is increasing usage to solve the shortcomings of the Fresnel lens-based architectures that have been serving us until now. For AR/MR, an entire department of specialized, usually fabless, optics firms has sprung up, which provides a huge range of advanced technologies to headset producers that are as per the demands in these present market situations. There is a strong demand from many industries like the automotive industry and the health care industry as it provides automation virtual propel the market growth. Many new opportunities will be provided to the major market players due to the significant demand for augmented reality and virtual reality in the manufacturing industries across the globe. Augmented reality and virtual reality market has seen dominant growth in the recent years. Increasing utilization of these capabilities for the corporate communications and the accomplishment of the gains will lead to the growth of the market in the forecast period.
Blippar, Google LLC, EON Reality Inc., Hewlett-Packard Company, awe.org Pty Ltd (buildar.com), Zapper Limited, Virtalis Limited, Samsung Group, Facebook Inc., Terminal Eleven (SkyView), Wikitude GmbH, Sony Corporation, Microsoft Corporation
Depending upon the organization size, the large enterprises segment is expected to have the highest revenue share in 2021. This segment is expected to maintain its dominance in the coming years due to an increase in the application of augmented and virtual reality in different industries. There is an increased use of augmented and virtual reality in the manufacturing industry, automotive industry, extract the windows tree aircraft industry, construction industry, education industry, law enforcement industry and the real estate industry.
The small and medium sized enterprises segment will also witness a good growth during the forecast. The small and medium enterprises segment have benefited in the recent years due to the augmented reality and virtual reality technology. The use of augmented reality and virtual reality in the small and medium enterprises provides benefits like reduction in the costs acquired for the training of the Staffs, less time required for repairs, and increased customer satisfaction due to the use of these technologies.
On the basis of application, the consumer segment had the largest market share in the augmented reality and virtual reality market during the forecast period. The consumer segment is expected to maintain its dominance. Due to an increase in the number of enterprises the enterprise segment will also have a good amount of growth. The gaming and other consumer entertainment sub sectors are also expected to see a substantial growth during the forecast period. Many industries are adopting and testing the augmented reality and virtual reality technologies for many work related applications. Gaming and entertainment form a major part of the total revenue produced by this market. The need for high resolution displays that are essential to have a top notch experience while gaming have been fulfilled by this latest technology.
The entertainment sector has also provided a great opportunity pertaining to the increasing number of shows displayed on the screens. The healthcare sector has also provided a boost to the market pertaining to get requirement of high resolution displays while performing orthopedic surgeries, neurological procedures and cardiac surgeries. The accuracy of the displays helps to have a maximum success rate. The education sector provides a great scope to the market owing to he increasing shift of the system to smart devices and techniques which are adopted by the institutions. Military and defense service a make use of these technologies and obtain accurate coordinates and pictures through the satellites, thus proving to be an inevitable equipment in the defense system.
Automotive and manufacturing sector have also contributed to the market growth due to the heavy use of digital products in the recent vehicles. Retail industry is another potential sector for the growth of this market during the forecast period. Other applications include the increasing use of smart devices and technology in the households and commercial spaces that may propel the market growth in the near future.
On the basis of display type, the Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) segment has garnered largest market share in 2021. Liquid Crystal Displays (LCD) screens have been using this advanced technology for the production of precise visual displays for a seamless experience to the consumers.
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED) are used for manufacturing display screens which guarantees low energy consumption while providing top notch experience to the consumers. Other display types which are manufactured also use this latest technology to produce reasonable outputs with high resolution while consumption of less energy is taken into consideration.
The North American region leads the market and it will maintain its market position continuously throughout the forecast period. The factors that are proving to be helpful for the growth of this market are the presence of major market players in the North American region. Google Microsoft and Facebook are the major market players in the augmented reality and virtual reality market that are helping in the growth of the North American region. The growing industrial sector is also driving the market growth in the North American region. Due to the increasing demand for connected devices and advancements in technologies of the augmented reality the market is expected to grow.
Europe is the second significant market for this technology. Due to the increasing adoption of augmented reality and virtual reality technologies in the media and entertainment industry, education, healthcare industry and the increasing use of mobile phones and play stations will help in the growth of the market. There is an increasing demand from the healthcare industry and the manufacturing industries for the use of augmented reality and virtual reality. In the European region the countries that contribute to the growth of this market are Germany, Italy, Spain, France etc.
In the Asia Pacific region the augmented reality and virtual reality market is expected to grow due to its use in various industry verticals. The adoption of augmented reality and virtual reality market solutions for 3D animation, 3D modeling and virtualization applications is driving the growth of this market. There"s a continuous rise in the demand for this technology and the government in the Asia Pacific region is making significant investments to offer innovative solutions. The major market players are also investing a significant amount to offer new solutions in the healthcare segment retail segment and the ecommerce segment. In the Asia Pacific region China is the largest augmented reality on virtual reality market. China has an increased demand for augmented reality and virtual reality technologies in the industrial sectors and the infrastructural sectors. It is expected that in China there shall be a rise of 65% CAGR during the forecast period.
UK-based Micro LED display developer Plessey Company plc is focusing on AR/MR display application and it announced that it is collaborating with FB in the month of March 2020. It is ready to assist in forming a prototype for future use in reality space.
New York, US, Oct. 25, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- According to a comprehensive research report by Market Research Future (MRFR), “AR and VR Hardware Market Research Report: Information By hardware type, By application, By industry vertical and Region - Forecast Till 2030, the market is anticipated to acquire a valuation of approximately USD 3,89,066.4 million by the end of 2030. The reports further predict the market to flourish at a robust CAGR of over 37.8% during the assessment timeframe.
The surge in the usage of tablets and smartphones for AR & VR will offer lucrative opportunities for this market in the forecast period. Users are still downloading VR & AR content for their cellphones from Oculus, Google Play, and other retailers, particularly for AR-capable mobile devices. 5G, as well as mobile apps, will have a huge impact on both AR and VR, particularly AR. AR and VR, particularly VR, have inherent requirements for virtual image production, processing, and high data transfer. This will improve when more mobile and Internet devices support 5G connectivity.
The components required for the proper application of immersive display technology are still in the works. The two key problems impeding market growth are limited battery life and picture latency difficulties. Due to image delay difficulties, such as decreased interpupillary distance to prevent generating blurry images, existing AR VR-based displays confront a significant hurdle. Similarly, the commercially available display devices have a limited battery life.
COVID-19 has had a significant influence on and disrupted supply chain hubs all over the world. China, one of the key manufacturing hubs, has seen a 14% decrease in production capacity and a 40% decrease in worldwide electronic component shipments. COVID-19 has infected the Global Value Chain hub, with China playing a key role in raw material supply, product assembly, and final delivery. Textile raw materials, textiles and apparel accessories, mechanical and electrical products, automatic data processing systems, central processing units, electrical equipment, and vehicles have all experienced major declines in export. Furthermore, as per a survey conducted by the National Association of Manufacturers to assess the economic effect of COVID-19 on manufacturers, 78% predict a financial hit, roughly 51% anticipate a change in operations, and nearly 35% anticipate supply chain disruptions.
The North American augmented reality & virtual reality hardware market is separated into two countries: the United States and Canada. Growing AR and VR technology development, combined with a large number of AR and VR technology players in North America, is predicted to generate a high CAGR during the projection period. Several educational institutions, for example, plan to launch digital twin campuses to give students access to learning options in the metaverse, according to VictoryXR, a provider of augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) content for schools and educational institutions, which has announced the launch of ten "Metaversities" in the US this fall. Furthermore, the increased demand for consumer-electronics-based VR applications and end-user awareness of immersive reality systems has prompted enterprises operating in the region to constantly reinvent and rebrand old goods in order to enhance the level of quality and unique design. For example, Meta (formerly Facebook) intends to produce four new virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (MR) devices by 2024. Later this year, the business hopes to introduce a web version of Horizon, allowing consumers to access metaverse experiences from a variety of devices, even those without a headset.
The Asia-Pacific AR/VR market is being driven by rising spending on augmented reality & virtual reality (AR/VR) technology, as well as increased adoption of the wireless-first strategy among corporations, industries, and public sector organizations. Vendors will enhance VR headsets, AR for smart glasses and phones, and disrupt augmented audio technologies, creating good growth possibilities for the consumer market. Businesses" need for a new immersive experience in how they conduct business and interact with customers and employees is driving the spectacular market growth for AR/VR technologies. However, vendors must respond to consumer AR/VR applications as well if they want to capitalize on prospects with high growth in the future years. Professional services, healthcare, discrete manufacturing, education, and healthcare will be the largest spending sectors over the projection period.
AR/VR in Aviation Market Research Report: Information by Technology, Function, Product , Component, Application, Vertical and Region - Forecast till 2030
Market Research Future (MRFR) is a global market research company that takes pride in its services, offering a complete and accurate analysis regarding diverse markets and consumers worldwide. Market Research Future has the distinguished objective of providing the optimal quality research and granular research to clients. Our market research studies by products, services, technologies, applications, end users, and market players for global, regional, and country level market segments, enable our clients to see more, know more, and do more, which help answer your most important questions.CONTACT: Contact Market Research Future (Part of Wantstats Research and Media Private Limited) 99 Hudson Street, 5Th Floor New York, NY 10013 United States of America +1 628 258 0071 (US) +44 2035 002 764 (UK) Email: sales@marketresearchfuture.com Website: https://www.marketresearchfuture.com

New York, Aug. 29, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Reportlinker.com announces the release of the report "AR/VR Display Market Research Report by Technology, Device, Display Technology, End User, Application, Region - Global Forecast to 2027 - Cumulative Impact of COVID-19" - https://www.reportlinker.com/p06297897/?utm_source=GNW
The Global AR/VR Display Market size was estimated at USD 3,064.59 million in 2021 and expected to reach USD 3,584.65 million in 2022, and is projected to grow at a CAGR 17.52% to reach USD 8,073.63 million by 2027.
COVID-19 is an incomparable global public health emergency that has affected almost every industry, and the long-term effects are projected to impact the industry growth during the forecast period. Our ongoing research amplifies our research framework to ensure the inclusion of underlying COVID-19 issues and potential paths forward. The report delivers insights on COVID-19 considering the changes in consumer behavior and demand, purchasing patterns, re-routing of the supply chain, dynamics of current market forces, and the significant interventions of governments. The updated study provides insights, analysis, estimations, and forecasts, considering the COVID-19 impact on the market.
We continuously monitor and update reports on political and economic uncertainty due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Negative impacts are significantly foreseen globally, especially across Eastern Europe, European Union, Eastern & Central Asia, and the United States. This contention has severely affected lives and livelihoods and represents far-reaching disruptions in trade dynamics. The potential effects of ongoing war and uncertainty in Eastern Europe are expected to have an adverse impact on the world economy, with especially long-term harsh effects on Russia.This report uncovers the impact of demand & supply, pricing variants, strategic uptake of vendors, and recommendations for AR/VR Display market considering the current update on the conflict and its global response.
The Competitive Strategic Window analyses the competitive landscape in terms of markets, applications, and geographies to help the vendor define an alignment or fit between their capabilities and opportunities for future growth prospects. It describes the optimal or favorable fit for the vendors to adopt successive merger and acquisition strategies, geography expansion, research & development, and new product introduction strategies to execute further business expansion and growth during a forecast period.
The FPNV Positioning Matrix evaluates and categorizes the vendors in the AR/VR Display Market based on Business Strategy (Business Growth, Industry Coverage, Financial Viability, and Channel Support) and Product Satisfaction (Value for Money, Ease of Use, Product Features, and Customer Support) that aids businesses in better decision making and understanding the competitive landscape.
The Market Share Analysis offers the analysis of vendors considering their contribution to the overall market. It provides the idea of its revenue generation into the overall market compared to other vendors in the space. It provides insights into how vendors are performing in terms of revenue generation and customer base compared to others. Knowing market share offers an idea of the size and competitiveness of the vendors for the base year. It reveals the market characteristics in terms of accumulation, fragmentation, dominance, and amalgamation traits.
The Competitive Scenario provides an outlook analysis of the various business growth strategies adopted by the vendors. The news covered in this section deliver valuable thoughts at the different stage while keeping up-to-date with the business and engage stakeholders in the economic debate. The competitive scenario represents press releases or news of the companies categorized into Merger & Acquisition, Agreement, Collaboration, & Partnership, New Product Launch & Enhancement, Investment & Funding, and Award, Recognition, & Expansion. All the news collected help vendor to understand the gaps in the marketplace and competitor’s strength and weakness thereby, providing insights to enhance product and service.
The report profoundly explores the recent significant developments by the leading vendors and innovation profiles in the Global AR/VR Display Market, including AU Optronics Corp., Augmedics, Barco N.V., BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd., eMagin Corporation, Google LLC by Alphabet Inc., Innolux Corporation, Kopin Corporation, Kura Technologies, Lenovo Group Limited, Lg Display Co., Ltd., Magic Leap, Inc., Meta Platforms, Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Sony Group Corporation, STMicroelectronics N.V., Upskill, Virtual Realities, LLC, Vuzix Corporation, and Wave Optics Limited.
4. Competitive Assessment & Intelligence: Provides an exhaustive assessment of market shares, strategies, products, certification, regulatory approvals, patent landscape, and manufacturing capabilities of the leading players

Riel, H. et al. Tuning the emission characteristics of top-emitting organic light-emitting devices by means of a dielectric capping layer: an experimental and theoretical study. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 5290–5296 (2003).
Cheng, D. W. et al. Design of an optical see-through head-mounted display with a low f-number and large field of view using a freeform prism. Appl. Opt. 48, 2655–2668 (2009).
Benitez, P. et al. Advanced freeform optics enabling ultra-compact VR headsets. In Proc. SPIE 10335, Digital Optical Technologies (SPIE, Germany, 2017)
Gagnon, H. C. et al. Gap affordance judgments in mixed reality: testing the role of display weight and field of view. Front. Virtual Real. 2, 654656 (2021).
Chang, K. D. et al. A hybrid simulated method for analyzing the optical efficiency of a head-mounted display with a quasi-crystal OLED panel. Opt. Express 22, A567–A576 (2014).
Käläntär, K. A directional backlight with narrow angular luminance distribution for widening the viewing angle for an LCD with a front-surface light-scattering film. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 20, 133–142 (2012).
Hoffman, D. M., Stepien, N. N. & Xiong, W. The importance of native panel contrast and local dimming density on perceived image quality of high dynamic range displays. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 24, 216–228 (2016).
Kikuchi, S. et al. Thin mini-LED backlight using reflective mirror dots with high luminance uniformity for mobile LCDs. Opt. Express 29, 26724–26735 (2021).
Song, S. J. et al. Deep-learning-based pixel compensation algorithm for local dimming liquid crystal displays of quantum-dot backlights. Opt. Express 27, 15907–15917 (2019).
Deng, M. Y. et al. Reducing power consumption of active-matrix mini-LED backlit LCDs by driving circuit. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 68, 2347–2354 (2021).
Chang, C. L. et al. Toward the next-generation VR/AR optics: a review of holographic near-eye displays from a human-centric perspective. Optica 7, 1563–1578 (2020).
Isomae, Y. et al. Design of 1-μm-pitch liquid crystal spatial light modulators having dielectric shield wall structure for holographic display with wide field of view. Opt. Rev. 24, 165–176 (2017).
Isomae, Y. et al. Alignment control of liquid crystals in a 1.0-μm-pitch spatial light modulator by lattice-shaped dielectric wall structure. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 27, 251–258 (2019).
Moser, S., Ritsch-Marte, M. & Thalhammer, G. Model-based compensation of pixel crosstalk in liquid crystal spatial light modulators. Opt. Express 27, 25046–25063 (2019).
Persson, M., Engström, D. & Goksör, M. Reducing the effect of pixel crosstalk in phase only spatial light modulators. Opt. Express 20, 22334–22343 (2012).
Shi, L. et al. Near-eye light field holographic rendering with spherical waves for wide field of view interactive 3D computer graphics. ACM Trans. Graph. 36, 236 (2017).
Lavrentovich, M. D., Sergan, T. A. & Kelly, J. R. Switchable broadband achromatic half-wave plate with nematic liquid crystals. Opt. Lett. 29, 1411–1413 (2004).
He, Z., Nose, T. & Sato, S. Diffraction and polarization properties of a liquid crystal grating. Japanese Journal of Applied. Physics 35, 3529–3530 (1996).
Yi, Y. et al. Alignment of liquid crystals by topographically patterned polymer films prepared by nanoimprint lithography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 163510 (2007).
Schadt, M., Seiberle, H. & Schuster, A. Optical patterning of multi-domain liquid-crystal displays with wide viewing angles. Nature 381, 212–215 (1996).
Lee, Y. H., Zhan, T. & Wu, S. T. Enhancing the resolution of a near-eye display with a Pancharatnam–Berry phase deflector. Opt. Lett. 42, 4732–4735 (2017).
Martínez-Corral, M. & Javidi, B. Fundamentals of 3D imaging and displays: a tutorial on integral imaging, light-field, and plenoptic systems. Adv. Opt. Photonics 10, 512–566 (2018).
Chigrinov, V. G., Kozenkov, V. M. & Kwok, H. S. Photoalignment of Liquid Crystalline Materials: Physics and Applications (Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2008).
Schadt, M. et al. Surface-induced parallel alignment of liquid crystals by linearly polymerized photopolymers. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 31, 2155–2164 (1992).
Bai, B. F. et al. Optimization of nonbinary slanted surface-relief gratings as high-efficiency broadband couplers for light guides. Appl. Opt. 49, 5454–5464 (2010).
Äyräs, P., Saarikko, P. & Levola, T. Exit pupil expander with a large field of view based on diffractive optics. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 17, 659–664 (2009).
Gu, Y. C. et al. Holographic waveguide display with large field of view and high light efficiency based on polarized volume holographic grating. IEEE Photonics J. 14, 7003707 (2022).
Shi, Z. J., Chen, W. T. & Capasso, F. Wide field-of-view waveguide displays enabled by polarization-dependent metagratings. In Proc. SPIE 10676, Digital Optics for Immersive Displays. 1067615 (SPIE, France, 2018).

Reality Labs is a business of Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook Inc.) that produces virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) hardware and software, including virtual reality headsets such as Quest, and online platforms such as Horizon Worlds. Reality Labs is the corporate successor to Oculus, a company that was founded in 2012 by Palmer Luckey, Brendan Iribe, Michael Antonov and Nate Mitchell to develop a VR headset for video gaming known as the Oculus Rift. Before the acquisition, Oculus raised over $2.4 million for the project via a crowdfunding campaign on Kickstarter—nearly ten times the original goal of $250,000.
Oculus was acquired by Facebook in March 2014. The company partnered with Samsung Electronics to release the Gear VR accessory for Samsung Galaxy smartphones in 2015. In March 2016, Oculus released the first consumer version of the Rift headset. In 2017, the company released a standalone mobile headset known as Oculus Go, produced by Xiaomi. In 2019, it released a high-end standalone headset known as Oculus Quest (which, since a software update, is capable of operating as both a standalone and PC headset), and Oculus Rift S, a follow-up to the original Oculus Rift manufactured by Lenovo. In 2020, the Oculus Quest 2 was released.
Oculus ceased operating as an autonomous subsidiary of Facebook in 2018, and became a brand of Facebook Technologies, LLC (marketed as Oculus from Facebook)—a subsidiary that includes other Facebook-developed hardware such as Portal. The Oculus team was later amalgamated into Facebook Reality Labs, a business of Facebook dedicated to VR and AR. In October 2021, Facebook announced that Reality Labs would begin to report its revenue separately from the Facebook "Family of Apps". Facebook subsequently announced that it would change its corporate name to Meta, and the Oculus brand was replaced on current and existing products by the "Meta" (hardware) and "Horizon" (online communities) brands.
Under Facebook ownership, Oculus products have been increasingly integrated with Facebook and its social networking platforms: since October 2020, all new users, and any user of Facebook-produced VR hardware released since then (beginning with Oculus Quest 2) must log in with a Facebook account in order to use their headsets. Support for standalone Oculus accounts was announced as ending in January 2023, but ultimately in October 2021, it was stated that "new ways to log into Quest that won’t require a Facebook account" were being developed. This requirement has faced criticism due to digital privacy concerns and Facebook"s real-name policy, and prompted Facebook to suspend sales of all Oculus products in Germany due to concerns from regulators over its compliance with the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
As a head-mounted display (HMD) designer at the University of Southern California Institute for Creative Technologies, Palmer Luckey earned a reputation for having the largest personal collection of HMDs in the world and was a longtime moderator in Meant to be Seen (MTBS)"s discussion forums.
Palmer created a series of new technologies that resulted in a VR headset that was both higher performance than what was currently on the market and was also inexpensive for gamers. To develop the new product, Luckey founded Oculus VR with Scaleform co-founders Brendan Iribe and Michael Antonov,
Coincidentally, John Carmack of id Software had been doing his research on HMDs and happened upon Palmer"s developments. After sampling an early unit, Carmack favored Luckey"s prototype, and just before the 2012 Electronic Entertainment Expo (E3), id Software announced that the
During the convention, Carmack introduced a duct-taped head-mounted display, based on Palmer"s Oculus Rift prototype, which ran Carmack"s software. The unit featured a high-speed IMU and a 5.6-inch (14 cm) LCD, visible via dual lenses that were positioned over the eyes to provide a 90 degree horizontal and 110 degree vertical stereoscopic 3D perspective.Chief technology officer.
The Oculus Rift prototype was demonstrated at E3 in June 2012. On August 1, 2012, the company announced a Kickstarter campaign to further develop the product. Oculus announced that the "dev kit" version of the Oculus Rift would be given as a reward to backers who pledged $300 or more on Kickstarter, with an expected shipping date set of December 2012 (though they did not actually ship until March 2013).
There was also a limited run of 100 unassembled Rift prototype kits for pledges over $275 that would ship a month earlier. Both versions were intended to include Steam or the Oculus store.US$250,000,
Although Oculus only released a development prototype of its headset, on March 25, 2014, Mark Zuckerberg announced that Facebook, Inc. would be acquiring Oculus for US$2 billion, pending regulatory approval. The deal included $400 million in cash and 23.1 million common shares of Facebook, valued at $1.6 billion, as well as an additional $300 million assuming Facebook reaches certain milestones.
Many Kickstarter backers and game industry figures, such as Markus Persson, criticized the sale of Oculus to Facebook.Michael Abrash joined the company as Chief Scientist.Irvine, California to Menlo Park, where Facebook"s headquarters are also located. Oculus has stated that this move is for their employees to be closer to Silicon Valley.
News reported that Oculus and Surreal Vision could create "mixed reality" technology in Oculus" products, similar to the upcoming HMD, Microsoft HoloLens.telepresence possible.
On March 28, 2016, the first consumer version of Oculus Rift, Oculus Rift "CV1", was released.Oculus Go in partnership with Chinese electronics manufacturer Xiaomi.The Eye Tribe.division of a new structural entity within Facebook known as Facebook Technologies, LLC.Burlingame, California, then under construction.
In February 2019, Facebook released Oculus Quest, a high-end standalone headset.Oculus Rift S, an updated revision of the original Rift PC headset in partnership with Chinese electronics manufacturer Lenovo, which featured updated hardware and features carried over from the Go and Quest.
On August 13, 2019, Nate Mitchell, Oculus co-founder and VP of product announced his departure from the company.John Carmack wrote in a Facebook post that he would step down as CTO of Oculus to focus on developing artificial general intelligence. He stated he would remain involved with the company as a "Consulting CTO".
Upon the acquisition of Oculus by Facebook, Inc., Luckey "guaranteed" that "you won"t need to log into your Facebook account every time you wanna use the Oculus Rift."Facebook Video and social games.Oculus from Facebook.
In September 2016, support for optional Facebook integration was added to the Oculus Rift software, automatically populating the friends list with Facebook friends who have also linked their accounts (displaying them to each other under their real names, but still displaying screen names to anyone else).
In 2018, Oculus VR became a division of Facebook Technologies, LLC, to create "a single legal entity that can support multiple Facebook technology and hardware products" (such as Facebook Portal).
On August 18, 2020, Facebook announced that all "decisions around use, processing, retention, and sharing of [user] data" on its platforms will be delegated to the Facebook social network moving forward. Users became subject to the unified Facebook privacy policy, code of conduct, and community guidelines, and all users will be required to have a Facebook account to access Oculus products and services.
Users and media criticized Facebook for the move. targeted advertising.Facebook requires the use of a person"s real name.General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which prohibits making use of a service contingent on consenting to the collection of personally identifiable information, and the requirement that existing users also link to a Facebook account to use Oculus hardware and services.
On August 25, 2020, Facebook announced the formation of Facebook Reality Labs, a new unit that would encompass all of Facebook"s virtual and augmented reality (AR) hardware and software, including Oculus, Portal, and Facebook Spark AR. The Oculus Connect conference was also renamed Facebook Connect.
In June 2021, Facebook announced it would do a test launch of targeted advertisements in applications for Oculus Quest. The company claims that movement data, voice recordings and raw images from the headset will not be used in targeting. Instead, the ads will rely on information from the user"s Facebook profile and all user activity related to Oculus, including apps used or installed. The company has not stated whether ads will appear only in applications or in the Oculus Home experience as well.
On October 25, 2021 during Connect, Facebook announced that it would invest $10 billion over the next year into Reality Labs, and that it would begin to report its revenue separately from the Facebook "Family of Apps"—which includes Facebook, Messenger, Instagram and WhatsApp.Meta (legally Meta Platforms, Inc.), as part of the company"s long-term focus on metaverses and related technologies.mixed reality headset codenamed "Project Cambria".Meta Quest Pro.
As a result, CTO Andrew Bosworth announced that the Oculus brand would be phased out in 2022; all Facebook hardware products will be marketed under the Meta name, and Oculus Store would be renamed Quest Store. Likewise, immersive social platforms associated with Oculus will be brought under the Horizon brand (such as Horizon Worlds). He also stated that "as we’ve heard feedback from the VR community more broadly, we’re working on new ways to log into Quest that won’t require a Facebook account, landing sometime next year. This is one of our highest priority areas of work internally".
In January 2022, the Oculus social media accounts were renamed "Meta Quest" in reference to its current VR product line. Concurrently, Meta began to retroactively refer to the Quest 2 as the "Meta Quest 2"
The initial Oculus headsets, produced under the "Oculus Rift" brand, are traditional VR headsets that require a PC to operate.Oculus Quest—a standalone headset which contains integrated mobile computing hardware and does not require a PC to operate, but can optionally be used with Oculus Rift-compatible VR software by connecting it to a PC over USB-C.
In 2018, Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg stated that the original Oculus Rift "CV1", Oculus Go (a lower-end standalone headset released in 2017),Oculus Rift S — a follow-up to the original model manufactured by Lenovo that incorporates elements of the Go and Quest.Oculus Quest 2 was unveiled as an updated iteration of the first-generation Quest,
On September 26, 2018, Facebook unveiled Oculus Quest. It is a standalone headset which is not dependent on a PC for operation; the Quest contains embedded mobile hardware running an operating system based on Android source code, including a Snapdragon 835 system-on-chip, and 64 or 128 GB of internal storage. It contains two OLED displays with a resolution of 1600x1440 per-eye and running at 72 Hz. It supports included Oculus Touch controllers via an "inside-out" motion tracking system known as "Oculus insight", which consists of a series of cameras embedded in the headset. The controllers were redesigned to properly function with Insight.
In November 2019, Facebook released a beta for a new feature known as Oculus Link, which allows Oculus Rift-compatible software to be streamed from a PC to a Quest headset over USB.USB 2.0 cables, such as the charging cable supplied with the headset. Support for controller-free hand tracking was also launched that month.
In September 2020, Facebook unveiled an updated version of the Quest, Oculus Quest 2. It is similar to the original Quest, but with the Snapdragon XR2 system-on-chip and additional RAM, an all plastic exterior, new cloth head straps, updated Oculus Touch controllers with improved ergonomics and battery life, and a 1832x1920 display running at 90 Hz,inter-pupillary distance options than the original Quest, with the ability to physically move the lenses to adjust for 3 common measurements. The Quest 2"s models were both priced US$100 cheaper than their first-generation equivalents at launch,
In October 2022, Meta unveiled Meta Quest Pro, a mixed reality headset aimed primarily at the professional market. The headset uses quantum dot displays, with thinner optics for a more visor-like form factor, and has upgraded cameras designed to facilitate mixed reality applications. Its hardware is upgraded from the Quest 2, with the Snapdragon XR2+ system-on-chip, increased RAM, and updated controllers with built-in tracking.
The Oculus Rift CV1, also known as simply the Oculus Rift, was the first consumer model of the Oculus Rift headset. It was released on March 28, 2016, in 20 countries, at a starting price of US$599.Oculus Touch.
In 2014, Samsung partnered with Oculus to develop the Gear VR, a VR headset accessory for Samsung Galaxy smartphones. It relies on the phone"s display, which is viewed through lenses inside the headset.Galaxy S6 and Galaxy S7 product lines, as well as the Galaxy Note 5.
On October 11, 2017, Oculus unveiled the Oculus Go, a mobile VR headset manufactured by Xiaomi (the device was released in the Chinese market as the Xiaomi Mi VR). Unlike the Oculus Rift, the Go is a standalone headset which is not dependent on a PC for operation. Unlike VR systems such as Cardboard, Daydream, and the Oculus co-developed Samsung Gear VR (where VR software is run on a smartphone inserted into a physical enclosure, and its screen is viewed through lenses), it contains its own dedicated display and mobile computing hardware. The headset includes a 5.5-inch 1440p fast-switching LCD display, integrated speakers with spatial audio and a headphone jack for external audio, a Qualcomm Snapdragon 821 system-on-chip, and 32 or 64 GB of internal storage. It runs an Android-based operating system with access to VR software via the Oculus Home user experience and app store, including games and multimedia apps. The Go includes a handheld controller reminiscent of one designed for the Gear VR, which uses relative motion tracking. The Oculus Go does not use positional tracking.
While official sales numbers have not been released, according to IDC the Oculus Go and Xiaomi Mi VR had sold nearly a quarter million units combined during the third quarter 2018,retention rate was as high as the Rift"s, something that nobody at the company had predicted.
On March 20, 2019, at the Game Developers Conference, Facebook announced the Oculus Rift S, a successor to the original Oculus Rift headset.Lenovo, and launched at a price of US$399. The Rift S contains hardware features from the Oculus Go and Oculus Quest, including Oculus Insight, integrated speakers, and a new "halo" strap. The Rift S uses the same 1440p fast-switching LCD display and lenses as the Oculus Go (a higher resolution in comparison to the original model, but lower in comparison to Oculus Quest), running at 80 Hz, and is backwards compatible with all existing Oculus Rift games and software. Unlike the original Oculus Rift, it does not have hardware control for inter-pupillary distance.
Oculus Studios was initially a division of Meta that focused on funding, publishing and giving technical advice to third & second party studios to create games and experiences for Oculus Rift. Meta pledged to invest more than US$500 million on Oculus Studios to make games and content.Insomniac Games, Twisted Pixel Games, Turtle Rock Studios, and Gunfire Games.
Starting in 2020, Meta purchased both Beat GamesSanzaru GamesReady at Dawn, a game studio composed of former members of Naughty Dog and Blizzard Entertainment (and had also developed the Oculus Rift exclusive
In 2021, Meta began a deliberate effort of buying up studios that had made strong sales on their Quest 2 platform. In April 2021, Downpour Interactive, the developer of the virtual reality FPS multiplayer game, Onward, were purchased. The team would migrate over to Oculus Studios, although the game would continue to receive updates on all supported VR platforms. Crayta, a free-to-play platform that allows players to create and share their games via Facebook Gaming.Twisted Pixel Games. The developer had been a successful second-party studio for Meta since 2017, and had produced the VR games B-Team, Defector, and Path of the Warrior, all exclusively for Oculus platforms.
Additionally, in October 2021, Meta announced they were purchasing Within, the studio behind the successful VR fitness app, Supernatural. It was stated they would continue to operate independently as part of Reality Labs. FTC conducted a probe into the 400 million dollar deal.Supernatural, they would unfairly corner the VR fitness market. This legal action has blocked the purchase indefinitely.
Following Facebook"s acquisition of Oculus VR, ZeniMax Media, the parent company of id Software and John Carmack"s previous employer, sought legal action against Oculus, accusing the company of theft of intellectual property relating to the Oculus Rift due to Carmack"s transition from id Software to Oculus. The case, ZeniMax v. Oculus, was heard in a jury trial in the United States District Court for the Northern District of Texas, and their verdict was reached in February 2017, finding that Carmack had taken code from ZeniMax and used it in developing the Oculus Rift"s software, violating his non-disclosure agreement with ZeniMax, and Oculus" use of the code was considered copyright infringement. ZeniMax was awarded $500 million in the verdict, and both ZeniMax and Oculus are seeking further court actions.
In May 2022, Immersion Corporation sued Meta Platforms for patent infringement relating to the use of vibration functions in their gaming controllers.
Gilbert, Ben. "Oculus Rift hires Doom co-creator John Carmack as Chief Technology Officer". engadget.com. Archived from the original on August 10, 2013. Retrieved August 7, 2013.
"Update on Developer Kit Technology, Shipping Details". Oculus VR. November 28, 2012. Archived from the original on March 20, 2014. Retrieved March 20, 2014.
Matulef, Jeffrey (August 1, 2012). "John Carmack"s snazzy VR headset takes to Kickstarter with the Oculus Rift". Archived from the original on October 5, 2013. Retrieved February 2, 2017.
Welch, Chris (March 25, 2014). "Facebook buying Oculus VR for $2 billion". Archived from the original on September 24, 2017. Retrieved February 2, 2017.
Gleasure, R., & Feller, J. (2016). A Rift in the Ground: Theorizing the Evolution of Anchor Values in Crowdfunding Communities through the Oculus Rift Case Study. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 17(10), 708-36.
Etherington, Darrell (May 26, 2015). "Oculus Acquires Surreal Vision To Bring The Real World to VR". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on March 15, 2016. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
Day, Matt (January 6, 2016). "CES 2016: Rewind from Day 2 of the Consumer Electronics Show". Seattle Times. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
Robertson, Adi (October 11, 2017). "Oculus announces new $199 self-contained VR headset called Oculus Go, shipping in 2018". The Verge. Archived from the original on August 12, 2020. Retrieved November 27, 2019.
"Cushman & Wakefield Arranges $515 Million Financing for New Bay Area Office Campus" (Press release). Cushman & Wakefield San Francisco. April 23, 2019. Archived from the original on July 30, 2019. Retrieved July 30, 2019.
Statt, Nick (March 20, 2019). "Oculus unveils the Rift S, a higher-resolution VR headset with built-in tracking". The Verge. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved March 20, 2019.
Machkovech, Sam (August 20, 2020). "Why the Facebookening of Oculus VR is bad for users, devs, competition". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on August 21, 2020. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
"Oculus becomes a division of "Facebook Technologies"". MCV/DEVELOP. November 20, 2018. Archived from the original on November 26, 2020. Retrieved August 22, 2020.
Healey, Nic. "You can now connect Facebook to Gear VR and play games with friends". CNET. Archived from the original on November 30, 2020. Retrieved September 4, 2020.
Jagneaux, David (April 12, 2017). "New Gear VR Sign-Up Process Highlights Facebook Over Oculus". UploadVR. Archived from the original on August 24, 2020. Retrieved August 21, 2020.
Sam Machkovech. "The Facebookening of Oculus VR becomes more pronounced starting in October". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on August 18, 2020. Retrieved August 19, 2020.
Hayden, Scott (September 2, 2020). "Facebook Halts Sale of Rift & Quest in Germany Amid Regulatory Concerns". Road to VR. Archived from the original on October 29, 2021. Retrieved October 29, 2021.
Piper, Daniel (February 3, 2022). "Meta"s Oculus Quest rebrand is off to a disastrous start". Creative Bloq. Archived from the original on February 14, 2022. Retrieved February 14, 2022.
Khan, Imad (January 27, 2022). "Oculus Quest 2 just officially renamed Meta Quest — and it"s not going well". Tom"s Guide. Archived from the original on February 14, 2022. Retrieved February 14, 2022.
"Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg: "Oculus Quest Completes Company"s First-Gen Lineup"". RoadtoVR.com. October 15, 2018. Archived from the original on October 17, 2018. Retrieved October 18, 2018.
Lang, Ben (May 14, 2020). "Oculus Quest Can Now Tether to PC with Its Included USB 2.0 Cable". Road to VR. Archived from the original on August 13, 2020. Retrieved June 23, 2020.
Robertson, Adi (September 24, 2015). "The new Gear VR will work with any new Samsung phone and cost $99". The Verge. Archived from the original on October 29, 2021. Retrieved October 28, 2021.
Robertson, Adi (May 1, 2018). "The Oculus Go improves mobile VR, but there"s still a long way to go". The Verge. Archived from the original on September 6, 2018. Retrieved September 6, 2018.
Machkovech, Sam (May 1, 2018). "Oculus Go review: The wireless-VR future begins today for only $199". Ars Technica. Archived from the original on May 1, 2018. Retrieved November 27, 2019.
Carmack, John (September 27, 2018). "Oculus Connect 5 | Keynote Day 02". YouTube. Oculus VR, LLC. 3 minutes 46 seconds. Archived from the original on May 28, 2019. Retrieved May 20, 2019. Now, I was probably the most optimistic inside Oculus about how well Go would do, but it turned out that it exceeded even my expectations. A remarkable point is, Go is retaining as well as Rift. And that"s pretty shocking. Nobody predicted that.
Carmack, John (September 27, 2018). "Oculus Connect 5 | Keynote Day 02". YouTube. Oculus VR, LLC. 6 minutes 23 seconds. Archived from the original on May 28, 2019. Retrieved May 20, 2019. The one shock was how well we"ve done in Japan. … we are not catering to the Japanese market. We don"t have great internationalisation for Japanese and different areas, but something about Go has really struck a nerve in the Japanese market consciousness.
Statt, Nick (March 20, 2019). "Oculus unveils the Rift S, a higher-resolution VR headset with built-in tracking". The Verge. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved November 27, 2019.
Constine, Josh (January 26, 2015). "Oculus" Pixar Exec-Led Story Studio Will Release VR Cinema Examples". TechCrunch. Archived from the original on July 7, 2017. Retrieved November 14, 2016.




 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey 
 Ms.Josey
Ms.Josey